1985 FORD GRANADA lug pattern
[x] Cancel search: lug patternPage 8 of 255

to release any pressure. When pressure has
been released, carry on unscrewing the cap
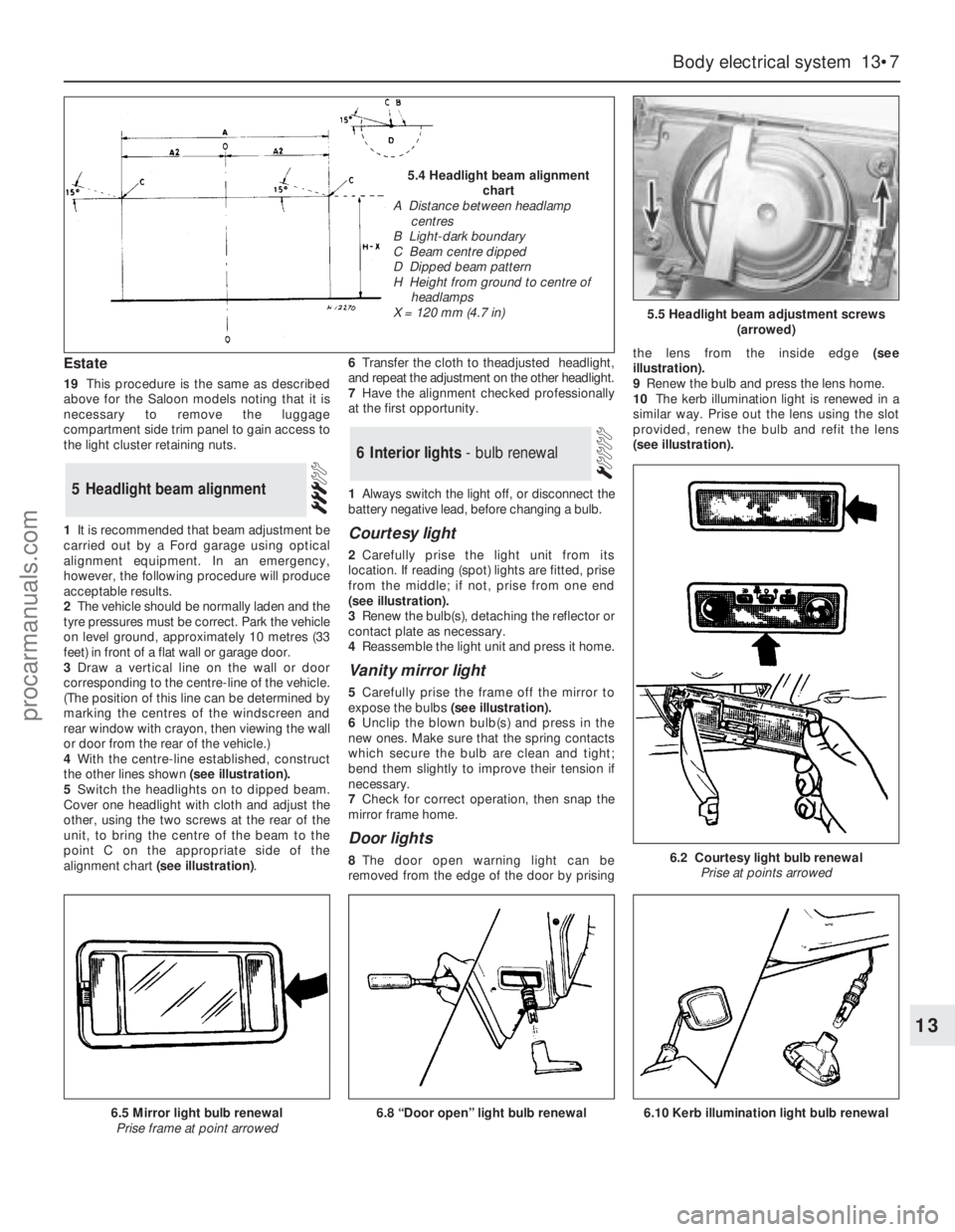
and remove it.
9Top-up to the MAX mark with the specified
coolant (see illustration).In an emergency
plain water is better than nothing, but
remember that it is diluting the proper coolant.
Do not add cold water to an overheated
engine whilst it is still hot.
10Refit the expansion tank cap securely
when the level is correct. With a sealed type
cooling system like this, the addition of
coolant should only be necessary at very
infrequent intervals. If frequent topping-up is
required, it is likely there is a leak in the
system. Check the radiator, all hoses and joint
faces for any sign of staining or actual
wetness, and rectify as necessary. If no leaks
can be found, it is advisable to have the
pressure cap and the entire system pressure-
tested by a dealer or suitably-equipped
garage, as this will often show up a small leak
not previously apparent.
Brake fluid
Be sure to use only the specified brake
hydraulic fluid, since mixing different types of
fluid can cause damage to the system. See
“Lubricants, fluids and capacities”at the
beginning of this Chapter. When adding fluid,
it is a good idea to inspect the reservoir for
contamination. The system should be drained
and refilled if deposits, dirt particles or
contamination are seen in the fluid.
11Check the brake fluid level as follows.
12With the vehicle parked on level ground
and the ignition switched off, pump the brake
pedal at least 20 times or until the pedal feels
hard.
13Open the bonnet. Switch on the ignition:
the hydraulic unit pump will be heard running.
Wait until the pump stops, then switch off the
ignition.
14The fluid level in the reservoir should now
be between the MAX and MIN marks. If
topping-up is necessary, unplug the electrical
connectors from the cap, then unscrew and
remove it (see illustration).Catch the
hydraulic fluid which will drip off the level
sensor with a piece of rag.
15Top-up with fresh brake fluid of the
specified type (see illustration).Do not
overfill. Refit and reconnect the reservoir cap
immediately.16The fluid level in the reservoir will drop
slightly as the brake pads wear down during
normal operation. If the reservoir requires
repeated replenishment to maintain the proper
level, this is an indication of a hydraulic leak
somewhere in the system, which should be
investigated immediately.
Washer fluid
17When topping-up the windscreen or rear
screen washer fluid reservoir, a screenwash
additive should be added in the quantities
recommended on the bottle.
1On later models tyres may have tread wear
safety bands, which will appear when the
tread depth reaches approximately 1.6 mm.
Otherwise, tread wear can be monitored with a
simple, inexpensive device known as a tread
depth indicator gauge (see illustration).
2Wheels and tyres should give no real
problems in use, provided that a close eye is
kept on them with regard to excessive wear or
damage. To this end, the following points
should be noted.
3Ensure that the tyre pressures are checked
regularly and maintained correctly (see
illustration). Checking should be carried out
with the tyres cold, not immediately after the
vehicle has been in use. If the pressures are
checked with the tyres hot, an apparently-high
reading will be obtained, owing to heat
expansion. Under no circumstancesshould
an attempt be made to reduce the pressures
to the quoted cold reading in this instance, or
effective under-inflation will result.
4Note any abnormal tread wear (see
illustration). Tread pattern irregularities such
as feathering, flat spots, and more wear on
one side than the other, are indications of front
wheel alignment and/or balance problems. If
any of these conditions are noted, they should
be rectified as soon as possible.
5Under-inflation will cause overheating of the
tyre, owing to excessive flexing of the casing,
and the tread will not sit correctly on the road
surface. This will cause excessive wear, not to
mention the danger of sudden tyre failure due
to heat build-up.
4Tyre checks
1•7
1
Weekly checks
3.14 Removing the brake fluid reservoir cap3.15 Topping up the brake fluid reservoir
4.1 Checking the tyre tread depth4.3 Checking tyre pressure
3.9 Topping up the cooling system
Warning: Brake hydraulic fluid
can harm your eyes and damage
painted surfaces, so use extreme
caution when handling and
pouring it. Do not use fluid that has been
standing open for some time, as it absorbs
moisture from the air. Excess moisture can
cause a dangerous loss of braking
effectiveness.If any brake fluid gets onto
paintwork, wash it off
immediately with clean water.
procarmanuals.com
Page 29 of 255

14Take the weight of the engine and remove
the two engine bearer-to-mounting nuts.
15Lift the engine/transmission, at the same
time lowering the trolley jack. Draw the unit
forwards and lift it out of the engine bay.
16Temporarily refit the anti-roll bar if the
vehicle is to be moved.
1With the engine and gearbox on the bench,
remove the starter motor.
2Remove the bolt from the engine adapter plate.
3Remove the bracing strap and the
remaining engine-to-bellhousing bolts.
4With the aid of an assistant draw the
gearbox off the engine. Do not allow the weight
of the gearbox to hang on the input shaft.
1It is best to mount the engine on a
dismantling stand, but if this is not available,
stand the engine on a strong bench at a
comfortable working height. Failing this, it will
have to be stripped down on the floor.
2Cleanliness is most important, and if the
engine is dirty, it should be cleaned with
paraffin while keeping it in an upright position.
3Avoid working with the engine on a concrete
floor, as grit can be a real source of trouble.
4As parts are removed, clean them in paraffin.
However, do not immerse parts with internal
oilways in paraffin as it is difficult to remove,
usually requiring a high pressure hose.
5It is advisable to have suitable containers to
hold small items according to their use, as this
will help when reassembling the engine and
also prevent possible losses.
6Always obtain complete sets of gaskets
when the engine is being dismantled, but
retain the old gaskets with a view of using
them as a pattern to make a replacement if a
new one is not available.7When possible, refit nuts, bolts and washers
in their location after being removed, as this
helps protect the threads and will also be
helpful when reassembling the engine.
8Retain unserviceable components in order
to compare them with the new parts supplied.
9A Torx key, size T55, will be needed for
dealing with the cylinder head bolts. A 12-
spline key (to fit bolt size M8) will be needed
for the oil pump bolts. Other Torx and 12-
spline bolts may be encountered; sets of the
keys required to deal with them are available
from most motor accessory shops and tool
factors.
10Another tool which is useful, though by no
means essential, is a valve spring compressor
of the type which hooks under the camshaft
(see illustration). As a Ford tool this bears the
number 21-005-A; proprietary versions may
also be available.
Before dismantling the engine into its main
components, the following ancillary
components can be removed. The actual
items removed, and the sequence of removal,
will depend on the work to be done:
Inlet manifold and associated items
Exhaust manifold
Fuel pump (mechanical type) and pushrod
Alternator
Distributor, HT leads and spark plugs
Fan, water pump and thermostat
Oil pressure switch
(see illustration)
Temperature gauge senderOil filter and dipstick
Engine bearer arms (see illustration)
Crankcase ventilation components
Clutch
Alternator mounting bracket (see
illustration)
1If the engine is still in the vehicle, carry out
the following preliminary operations:
a)Disconnect the battery negative lead
b)Drain the cooling system
c)Remove the inlet and exhaust manifolds
d)Disconnect the radiator top hose from the
thermostat housing, and the spur from the
expansion tank
e)Disconnect the wiring from the
temperature gauge sender
f)Remove the distributor cap, HT leads and
spark plugs
2Unscrew the bolts and withdraw the timing
cover (see illustration). Note the location of
the cover in the special bolt.
3Using a socket on the crankshaft pulley bolt.
turn the engine clockwise until the TDC (top
dead centre) notch on the pulley is aligned
with the pointer on the crankshaft front oil seal
housing, and the pointer on the camshaft
sprocket is aligned with the indentation on the
cylinder head (see illustrations).Note the
position of the distributor rotor arm, and mark
its contact end in relation to the rim of the
distributor body.
4Slacken the timing belt tensioner bolts. Pivot
10Cylinder head - removal
9Ancillary components - removal
8Engine dismantling - general
information
7Engine - separation from
manual gearbox
2A•6SOHCengines
9.1a Engine oil pressure switch (arrowed)
9.1b Removing an engine bearer arm9.1c Removing the alternator bracket
8.10 This valve spring compressor is used
by hooking it under the camshaft
Clean oilways with nylon pipe
cleaners.
10.2 Removing the timing cover
procarmanuals.com
Page 184 of 255
Estate
19This procedure is the same as described
above for the Saloon models noting that it is
necessary to remove the luggage
compartment side trim panel to gain access to
the light cluster retaining nuts.
1It is recommended that beam adjustment be
carried out by a Ford garage using optical
alignment equipment. In an emergency,
however, the following procedure will produce
acceptable results.
2The vehicle should be normally laden and the
tyre pressures must be correct. Park the vehicle
on level ground, approximately 10 metres (33
feet) in front of a flat wall or garage door.
3Draw a vertical line on the wall or door
corresponding to the centre-line of the vehicle.
(The position of this line can be determined by
marking the centres of the windscreen and
rear window with crayon, then viewing the wall
or door from the rear of the vehicle.)
4With the centre-line established, construct
the other lines shown (see illustration).
5Switch the headlights on to dipped beam.
Cover one headlight with cloth and adjust the
other, using the two screws at the rear of the
unit, to bring the centre of the beam to the
point C on the appropriate side of the
alignment chart (see illustration).6Transfer the cloth to theadjusted headlight,
and repeat the adjustment on the other headlight.
7Have the alignment checked professionally
at the first opportunity.
1Always switch the light off, or disconnect the
battery negative lead, before changing a bulb.
Courtesy light
2Carefully prise the light unit from its
location. If reading (spot) lights are fitted, prise
from the middle; if not, prise from one end
(seeillustration).
3Renew the bulb(s), detaching the reflector or
contact plate as necessary.
4Reassemble the light unit and press it home.
Vanity mirror light
5Carefully prise the frame off the mirror to
expose the bulbs(see illustration).
6Unclip the blown bulb(s) and press in the
new ones. Make sure that the spring contacts
which secure the bulb are clean and tight;
bend them slightly to improve their tension if
necessary.
7Check for correct operation, then snap the
mirror frame home.
Door lights
8The door open warning light can be
removed from the edge of the door by prisingthe lens from the inside edge (see
illustration).
9Renew the bulb and press the lens home.
10The kerb illumination light is renewed in a
similar way. Prise out the lens using the slot
provided, renew the bulb and refit the lens
(seeillustration).
6Interior lights - bulb renewal
5Headlight beam alignment
Body electrical system 13•7
13
5.5 Headlight beam adjustment screws
(arrowed)
6.2 Courtesy light bulb renewal
Prise at points arrowed
6.8 “Door open” light bulb renewal6.5 Mirror light bulb renewal
Prise frame at point arrowed
5.4 Headlight beam alignment
chart
A Distance between headlamp
centres
B Light-dark boundary
C Beam centre dipped
D Dipped beam pattern
H Height from ground to centre of
headlamps
X = 120 mm (4.7 in)
6.10 Kerb illumination light bulb renewal
procarmanuals.com