1982 CHEVROLET CAMARO tow
[x] Cancel search: towPage 6 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 6
HOOD
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
Fig. 1: Front end sheet metal
Fig. 2: Hood removal
1. Open the hood and mark the position of the hood hinge assembly-to-hood
by a scribe, chalk or paint.
2. Remove the hood attaching bolts that are towards the front of the hood.
3. Slowly loosen the remaining hood attaching bolts.
4. With the aid of a helper, remove the bolts and remove the hood. Place the
hood on a protected surface.
Page 40 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 40
INSIDE REAR VIEW MIRROR
INSTALLATION
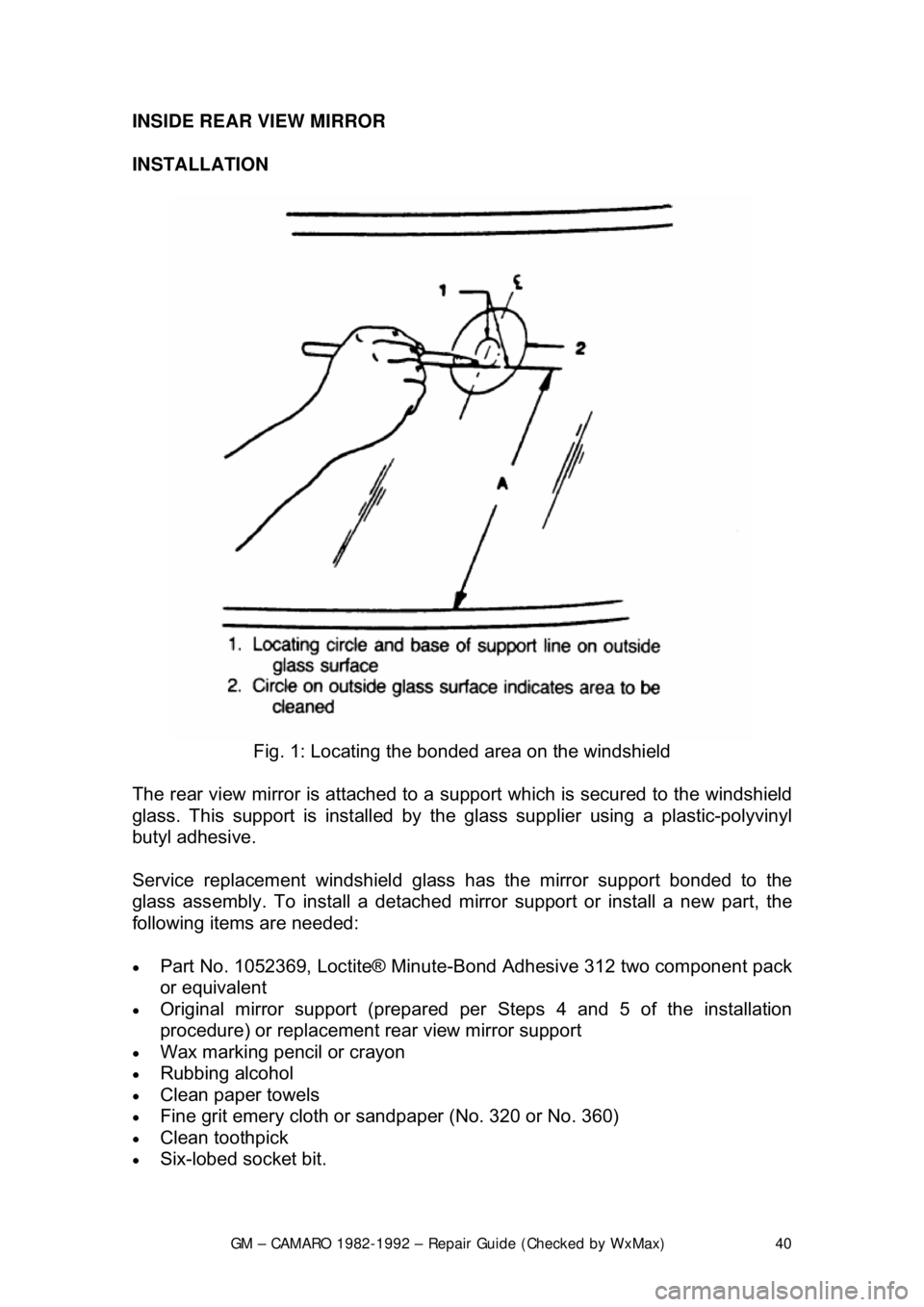
Fig. 1: Locating the bonded area on the windshield
The rear view mirror is attached to a s upport which is secured to the windshield
glass. This support is inst alled by the glass supplier using a plastic-polyvinyl
butyl adhesive.
Service replacement windshield glass has the mirror support bonded to the
glass assembly. To install a detached mi rror support or install a new part, the
following items are needed:
• Part No. 1052369, Loctite® Minute-B ond Adhesive 312 two component pack
or equivalent
• Original mirror support (prepared per Steps 4 and 5 of the installation
procedure) or replacement rear view mirror support
• Wax marking pencil or crayon
• Rubbing alcohol
• Clean paper towels
• Fine grit emery cloth or sandpap er (No. 320 or No. 360)
• Clean toothpick
• Six-lobed socket bit.
Page 41 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 41
1. Determine the rear view mirror suppor
t position on the windshield. Support is
to be located at the center of the glass 271/8 in. (69cm) from the base of the
glass to the base of the support.
2. Mark the location on the outside of the glass with wax pencil or crayon.
Make a larger diameter circle around t he mirror support circle on the outside
of the glass surface.
3. On the inside of the glass surface, clean the large circle with a paper towel
and domestic scouring cleanser, gla ss cleaning solution or polishing
compound. Rub until the area is comple tely clean and dry. When dry, clean
the area with an alcohol saturated paper towel to remove any traces of
scouring powder or cleaning solution from this area.
4. With a piece of fine grit (No. 320 or No. 360) emery cloth or sandpaper, sand
the bonding surface of the new rear view mirror support or factory installed
support. If original rear view mirror support is to be reused, all traces of the
factory installed adhesive must be re moved prior to reinstallation.
5. Wipe the sanded mirror support with a clean paper towel saturated with alcohol and allow it to dry.
6. Follow the directions on the manufac turer's kit to prepare the rear view
mirror support prior to inst allation on the glass.
7. Properly position the support to it s premarked location, with rounded end
pointed upward, press the support agai nst the glass for 30-60 seconds,
exerting steady pressure against the gla ss. After five minutes, any excess
adhesive may be removed with an alcohol moistened paper towel or glass
cleaning solution.
8. Install the mirror.
SEATS
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
1. Operate the seat to the full-forwar d position. If a six-way power seat is
operable, operate the seat to the full-forward and up positions. Where
necessary to gain access to the adjuste r-to-floor pan attaching nuts, remove
the adjuster rear foot covers and/or carpet retainers.
2. Remove the track covers where nec essary; then remove the adjuster-to-
floor pan rear attaching nuts. Operate t he seat to the full-rearward position.
Remove the adjuster front foot covers ; then remove the adjuster-to-floor pan
front attaching nuts.
3. Remove the seat assembly from the car.
4. Check that both seat adjusters ar e parallel and in phase with each other.
5. Install the adjuster-to- floor pan attaching nuts by moving the seat forward
and rearward and torque nuts to 15-21 ft. lbs. (20-28 Nm).
6. Check the operation of the seat a ssembly to full limits of travel.
Page 48 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 48
BRAKES
BASIC OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Hydraulic systems are used to actuate t he brakes of all modern automobiles.
The system transports the power required to force the frictional surfaces of the
braking system together from the pedal to the individual brake units at each
wheel. A hydraulic system is used for two reasons.
First, fluid under pressure can be carried to all parts of an automobile by small
pipes and flexible hoses without taking up a significant amount of room or
posing routing problems.
Second, a great mechanical advantage can be given to the brake pedal end of
the system, and the foot pressure requi red to actuate the brakes can be
reduced by making the surface area of t he master cylinder pistons smaller than
that of any of the pistons in t he wheel cylinders or calipers.
The master cylinder consists of a flui d reservoir along with a double cylinder
and piston assembly. Double type master cylinders are designed to separate
the front and rear braking systems hydraulic ally in case of a leak. The master
cylinder coverts mechanical motion from t he pedal into hydraulic pressure within
the lines. This pressure is translated back into mechanical motion at th\
e wheels
by either the wheel cylinder (drum brak es) or the caliper (disc brakes).
Steel lines carry the brake fluid to a po int on the vehicle's frame near each of
the vehicle's wheels. The fluid is then ca rried to the calipers and wheel cylinders
by flexible tubes in order to allow for suspension and steering movements.
In drum brake systems, each wheel cylinde r contains two pistons, one at either
end, which push outward in opposite direct ions and force the brake shoe into
contact with the drum.
In disc brake systems, the cylinders ar e part of the calipers. At least one
cylinder in each caliper is used to fo rce the brake pads against the disc.
All pistons employ some type of seal, us ually made of rubber, to minimize fluid
leakage. A rubber dust boot seals the outer end of the cylinder against dust and
dirt. The boot fits around the outer end of the piston on disc brake calipers, and
around the brake actuating rod on wheel cylinders.
The hydraulic system operates as follows : When at rest, the entire system, from
the piston(s) in the master cylinder to t hose in the wheel cylinders or calipers, is
full of brake fluid. Upon app lication of the brake pedal, fluid trapped in front of
the master cylinder piston(s) is forced through the lines to the wheel cylinders.
Here, it forces the pistons outward, in the case of drum brakes, and inward
toward the disc, in the case of disc brakes. The motion of the pistons is
opposed by return springs mounted outside the cylinders in drum brakes, and
by spring seals, in disc brakes.
Page 50 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 50
DISC BRAKES
Instead of the traditional ex
panding brakes that press out ward against a circular
drum, disc brake systems utilize a disc (rotor) with brake pads positioned on
either side of it. An easily-seen analog y is the hand brake arrangement on a
bicycle. The pads squeeze onto the rim of the bike wheel, slowing its motion.
Automobile disc brakes use the identical principle but apply the braking effort to
a separate disc instead of the wheel.
The disc (rotor) is a casting, usually eq uipped with cooling fins between the two
braking surfaces. This enables air to ci rculate between the braking surfaces
making them less sensitive to heat bui ldup and more resistant to fade. Dirt and
water do not drastically affect braking ac tion since contaminants are thrown off
by the centrifugal action of the rotor or scraped off the by the pads. Also, the
equal clamping action of the two brake pad s tends to ensure uniform, straight
line stops. Disc brakes are inherently se lf-adjusting. There are three general
types of disc brake:
1. A fixed caliper.
2. A floating caliper.
3. A sliding caliper.
The fixed caliper design uses two pistons mounted on either side of the rotor (in
each side of the caliper). The caliper is mounted rigidly and does not move.
The sliding and floating designs are quite similar. In fact, these two types are
often lumped together. In both designs, the pad on the inside of the rotor is
moved into contact with the rotor by hy draulic force. The caliper, which is not
held in a fixed position, moves slightly, bringing the outside pad into contact with
the rotor. There are various methods of attaching floating calipers. Some pivot
at the bottom or top, and some slide on mounting bolts. In any event, the end
result is the same.
DRUM BRAKES
Drum brakes employ two brake shoes mounted on a st ationary backing plate.
These shoes are positioned inside a circul ar drum which rotates with the wheel
assembly. The shoes are held in place by springs. This allows them to slide
toward the drums (when they are applied) while keeping the linings and drums
in alignment. The shoes are actuated by a wheel cylinder which is mounted at
the top of the backing plat e. When the brakes are app lied, hydraulic pressure
forces the wheel cylinder's actuating links outward. Since these links bear
directly against the top of the brake s hoes, the tops of the shoes are then forced
against the inner side of the drum. This action forces the bottoms of the two
shoes to contact the brake drum by rotati ng the entire assembly slightly (known
as servo action). When pressure within the wheel cylinder is relaxed, return
springs pull the shoes back away from the drum.
Most modern drum brakes are designed to self-adjust themselves during
application when the vehicle is moving in reverse. This motion causes both
Page 51 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 51
shoes to rotate very slightly with the
drum, rocking an adjusting lever, thereby
causing rotation of the adjusting scr ew. Some drum brake systems are
designed to self-adjust duri ng application whenever the br akes are applied. This
on-board adjustment system reduces the need for maintenance adjustments
and keeps both the brake function and pedal feel satisfactory.
POWER BOOSTERS
Virtually all modern vehicles use a va cuum assisted power brake system to
multiply the braking force and reduce pedal effort. Since vacuum is always
available when the en gine is operating, the system is simple and efficient. A
vacuum diaphragm is located on the front of the master cylinder and assists the
driver in applying the brakes, reducing both the effort and travel he must put into
moving the brake pedal.
The vacuum diaphragm housing is normally connected to the intake manifold by
a vacuum hose. A check valve is placed at the point where the hose enters the
diaphragm housing, so that during periods of low manifold vacuum brakes
assist will not be lost.
Depressing the brake pedal closes o ff the vacuum source and allows
atmospheric pressure to enter on one side of the diaphragm. This causes the
master cylinder pistons to move and app ly the brakes. When the brake pedal is
released, vacuum is applied to both si des of the diaphragm and springs return
the diaphragm and master cylinder pist ons to the released position.
If the vacuum supply fails, the brake pedal rod will contact the end of the master
cylinder actuator rod and the system will apply the br akes without any power
assistance. The driver will notice that much higher pedal effort is needed to stop
the car and that the pedal f eels harder than usual.
VACUUM LEAK TEST
1. Operate the engine at idle without t ouching the brake pedal for at least one
minute.
2. Turn off the engine and wait one minute.
3. Test for the presence of assist va cuum by depressing the brake pedal and
releasing it several times. If vac uum is present in the system, light
application will produce less and less pedal travel. If there is no vacuum, air
is leaking into the system.
SYSTEM OPERATION TEST
1. With the engine OFF, pump the brake p edal until the supply vacuum is
entirely gone.
2. Put light, steady pressu re on the brake pedal.
3. Start the engine and let it idle. If the system is operating correctly, the brake
pedal should fall toward the floor if t he constant pressure is maintained.
Page 55 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 55
BRAKE LIGHT SWITCH
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
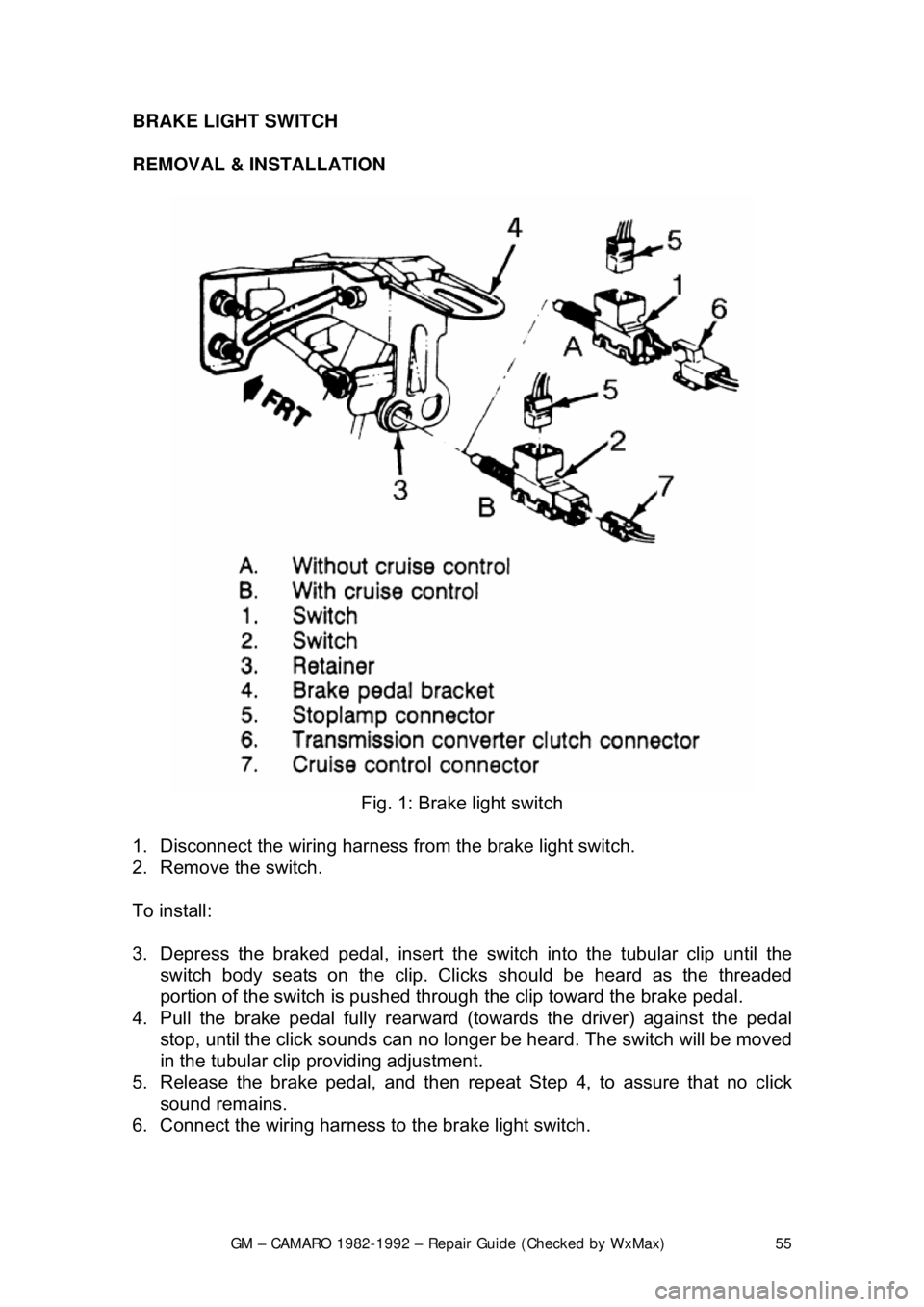
Fig. 1: Brake light switch
1. Disconnect the wiring harness fr om the brake light switch.
2. Remove the switch.
To install:
3. Depress the braked pedal, insert the switch into the tubular clip until the
switch body seats on the clip. Cli cks should be heard as the threaded
portion of the switch is pushed through the clip toward the brake pedal.\
4. Pull the brake pe dal fully rearward (towards the driver) against the pedal
stop, until the click sounds can no long er be heard. The switch will be moved
in the tubular clip providing adjustment.
5. Release the brak e pedal, and then repeat Step 4, to assure that no click
sound remains.
6. Connect the wiring harness to the brake light switch.
Page 82 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 82
Avoid inhaling any dust from
any brake surface! When cleaning brake surfaces,
use a commercially available brake cleaning fluid.
1. Remove
2/3 of the brake fluid from the mast er cylinder. Raise the vehicle and
remove the wheel.
2. Place a C-clamp across the caliper, positioned on the brake pads. Tighten it
until the piston is forced into its bore.
3. Remove the C-clamp. Remove the bolt holding the brake hose to the caliper.
4. Remove the Allen head caliper mounting bolts. Inspect them for corrosion
and replace them if necessary. Remove the caliper.
To install:
5. Position the caliper with the brake pad installed and install Allen head caliper
mounting bolts. Mounting bo lt torque is 21-35 ft. lbs. (28-47 Nm.) for the
caliper.
6. Install the bolt holding the brake hos e to the caliper and tighten to 18-30 ft.
lbs. (24-40 Nm.).
7. Fill the master cylinder with brake fluid.
8. Install the wheels and lower the vehicle.
CAUTION - Before moving the vehicle, pump the brakes several times to seat
the brake pad against the rotor
OVERHAUL
Some vehicles may be equipped dual piston calipers. The procedure to
overhaul the caliper is e ssentially the same with t he exception of multiple
pistons, O-rings and dust boots.
1. Remove the caliper from the ve hicle and place on a clean workbench.
CAUTION - NEVER place your finger s in front of the pistons in an attempt to
catch or protect the pistons when applying compressed air. This could result in
personal injury!
Depending upon the vehicle, there are two different ways to remove the piston
from the caliper. Refer to the brake pad replacement procedure to make sure
you have the correct procedure for your vehicle.
2. The first method is as follows: a. Stuff a shop towel or a block of wood into the caliper to catch the piston.
b. Remove the caliper piston using co mpressed air applied into the caliper
inlet hole. Inspect the piston for scor ing, nicks, corrosion and/or worn or
damaged chrome plating. The piston mu st be replaced if any of these
conditions are found.