1982 CHEVROLET CAMARO steering wheel
[x] Cancel search: steering wheelPage 48 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 48
BRAKES
BASIC OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Hydraulic systems are used to actuate t he brakes of all modern automobiles.
The system transports the power required to force the frictional surfaces of the
braking system together from the pedal to the individual brake units at each
wheel. A hydraulic system is used for two reasons.
First, fluid under pressure can be carried to all parts of an automobile by small
pipes and flexible hoses without taking up a significant amount of room or
posing routing problems.
Second, a great mechanical advantage can be given to the brake pedal end of
the system, and the foot pressure requi red to actuate the brakes can be
reduced by making the surface area of t he master cylinder pistons smaller than
that of any of the pistons in t he wheel cylinders or calipers.
The master cylinder consists of a flui d reservoir along with a double cylinder
and piston assembly. Double type master cylinders are designed to separate
the front and rear braking systems hydraulic ally in case of a leak. The master
cylinder coverts mechanical motion from t he pedal into hydraulic pressure within
the lines. This pressure is translated back into mechanical motion at th\
e wheels
by either the wheel cylinder (drum brak es) or the caliper (disc brakes).
Steel lines carry the brake fluid to a po int on the vehicle's frame near each of
the vehicle's wheels. The fluid is then ca rried to the calipers and wheel cylinders
by flexible tubes in order to allow for suspension and steering movements.
In drum brake systems, each wheel cylinde r contains two pistons, one at either
end, which push outward in opposite direct ions and force the brake shoe into
contact with the drum.
In disc brake systems, the cylinders ar e part of the calipers. At least one
cylinder in each caliper is used to fo rce the brake pads against the disc.
All pistons employ some type of seal, us ually made of rubber, to minimize fluid
leakage. A rubber dust boot seals the outer end of the cylinder against dust and
dirt. The boot fits around the outer end of the piston on disc brake calipers, and
around the brake actuating rod on wheel cylinders.
The hydraulic system operates as follows : When at rest, the entire system, from
the piston(s) in the master cylinder to t hose in the wheel cylinders or calipers, is
full of brake fluid. Upon app lication of the brake pedal, fluid trapped in front of
the master cylinder piston(s) is forced through the lines to the wheel cylinders.
Here, it forces the pistons outward, in the case of drum brakes, and inward
toward the disc, in the case of disc brakes. The motion of the pistons is
opposed by return springs mounted outside the cylinders in drum brakes, and
by spring seals, in disc brakes.
Page 73 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 73
To install:
9. Install the new line or hose, starti
ng with the end farthest from the master
cylinder. Connect the other end, then confirm that both fittings are correctly
threaded and turn smoothly using finger pressure. Make sure the new line
will not rub against any ot her part. Brake lines must be at least 1/2 in.
(13mm) from the steering column and other moving parts. Any protective
shielding or insulators must be rein stalled in the original location.
WARNING - Make sure the hose is NO T kinked or touching any part of the
frame or suspension after installation. These conditions may cause the hose to
fail prematurely.
10. Using two wrenches as bef ore, tighten each fitting.
11. Install any retaining clips or brackets on the lines.
12. If removed, install the wheel and tire assemblies, then carefully lower the
vehicle to the ground.
13. Refill the brake master cylinder re servoir with clean, fresh brake fluid,
meeting DOT 3 specifications. Pr operly bleed the brake system.
14. Connect the negative battery cable.
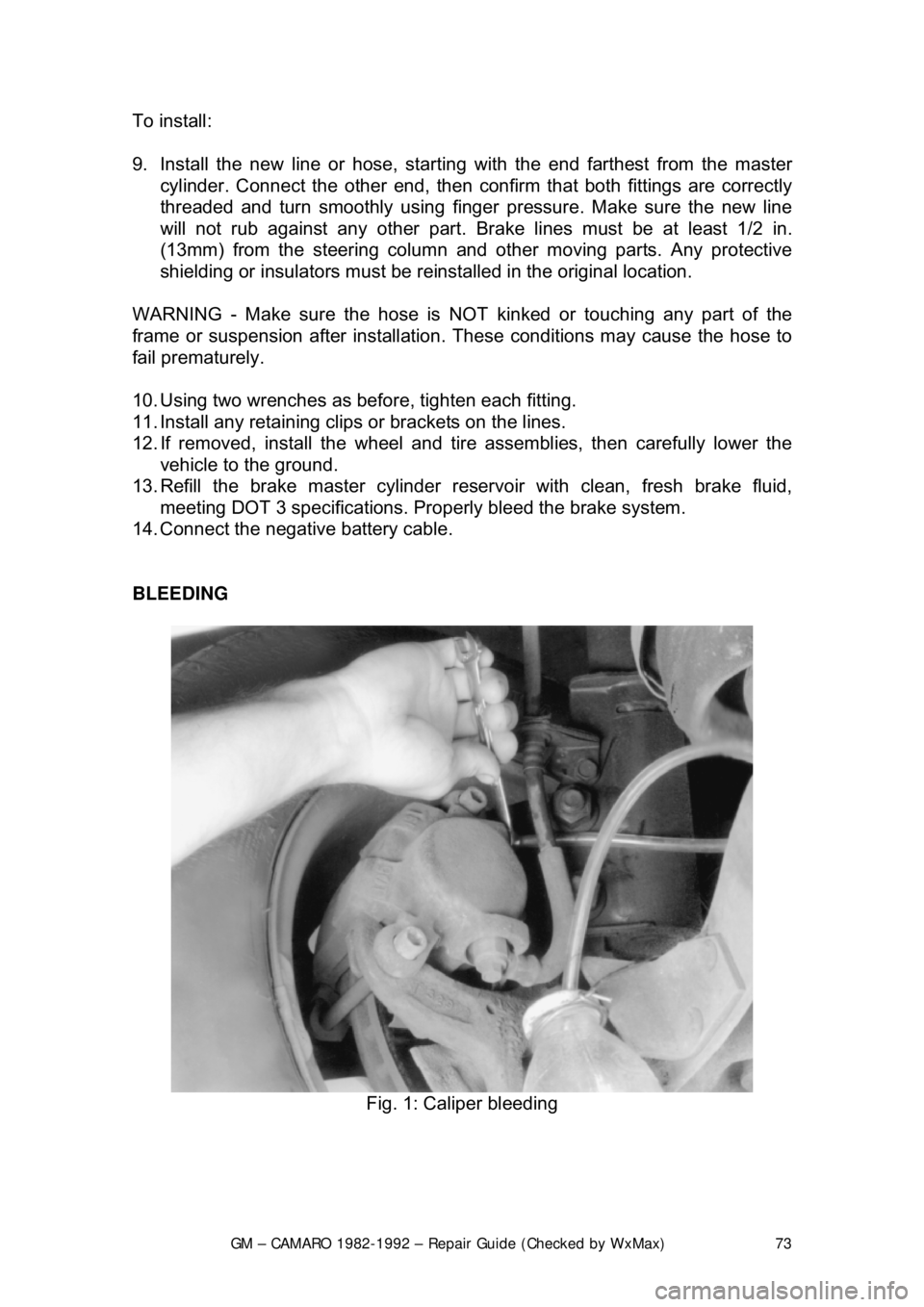
BLEEDING
Fig. 1: Caliper bleeding
Page 80 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 80
4. Remove the mounting bo
lts, if equipped with single piston caliper or the
circlip and pin, if equipped with dual piston ca liper. Inspect the bolts for
corrosion and replace as necessary.
5. Remove the caliper fr om the steering knuckle an d suspend it from the body
of the car with a length of wire. Do not allow the caliper to hang by its hose.
6. Remove the pad retaining springs and remove the pads from the caliper.
7. Remove the plastic sleeves and the rubber bushings from the mounting bolt
holes.
8. Obtain a pad replacem ent kit. Lubricate and install the new sleeves and
bushings with a light coat of silicone grease.
9. Install the retainer spring on the i nboard pad, if equipped with single piston
caliper.
A new spring should be included in the pad replacement kit.
10. Install the new inboard pad into the caliper with the wear sensor at the
leading end of the shoe duri ng forward wheel rotation.
11. Install the outboard pad into the caliper.
12. Use a large pair of slip joint plie rs to bend the outer pad ears down over the
caliper, if equipped with t he single piston caliper.
13. Install the calip er onto the steering knuckle. Tighten the mounting bolts to
21-35 ft. lbs. (28-47 Nm), if equipped. In stall the wheel and lower the car. Fill
the master cylinder to its proper le vel with a good quality brake fluid.
14. Pump the brake pedal slowly a nd firmly 3 times with the engine running
before attempting to move the vehicle; bleed the brakes as required.
BRAKE CALIPER
CAUTION - Some brake pads contain asbest os, which has been determined to
be a cancer causing agent. Never clean the brake surfaces with compressed
air! Avoid inhaling any dust from any brake surface! When cleaning brake
surfaces, use a commercially available brake cleaning fluid.
REMOVAL & INSTALATION
Page 91 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 91
Avoid inhaling any dust from
any brake surface! When cleaning brake surfaces,
use a commercially available brake cleaning fluid.
1. Remove the caliper by following instru ctions of caliper removal procedure.
2. Remove dust cap, cotter pin, castle nut, thrust washer and outside wheel
bearing. Pull the disc/hub assembly from the steering knuckle.
To install:
3. Position the disc/hub assembly to t he spindle/steering knuckle. Install the
outside wheel bearing, thru st washer and castle nut. Tighten the castle nut
until the bearing is s nug. Back off the nut
1/4 turn. Refer to Suspension &
Steering for details on wheel bearing remo val, installation, and adjustment.
Install a new cotter pin and dust cap.
4. Install the brake caliper.
INSPECTION
Fig. 6: Checking disc runout
Page 146 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 146
SUPPLEMENTAL INFLATABLE RESTRAINT SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
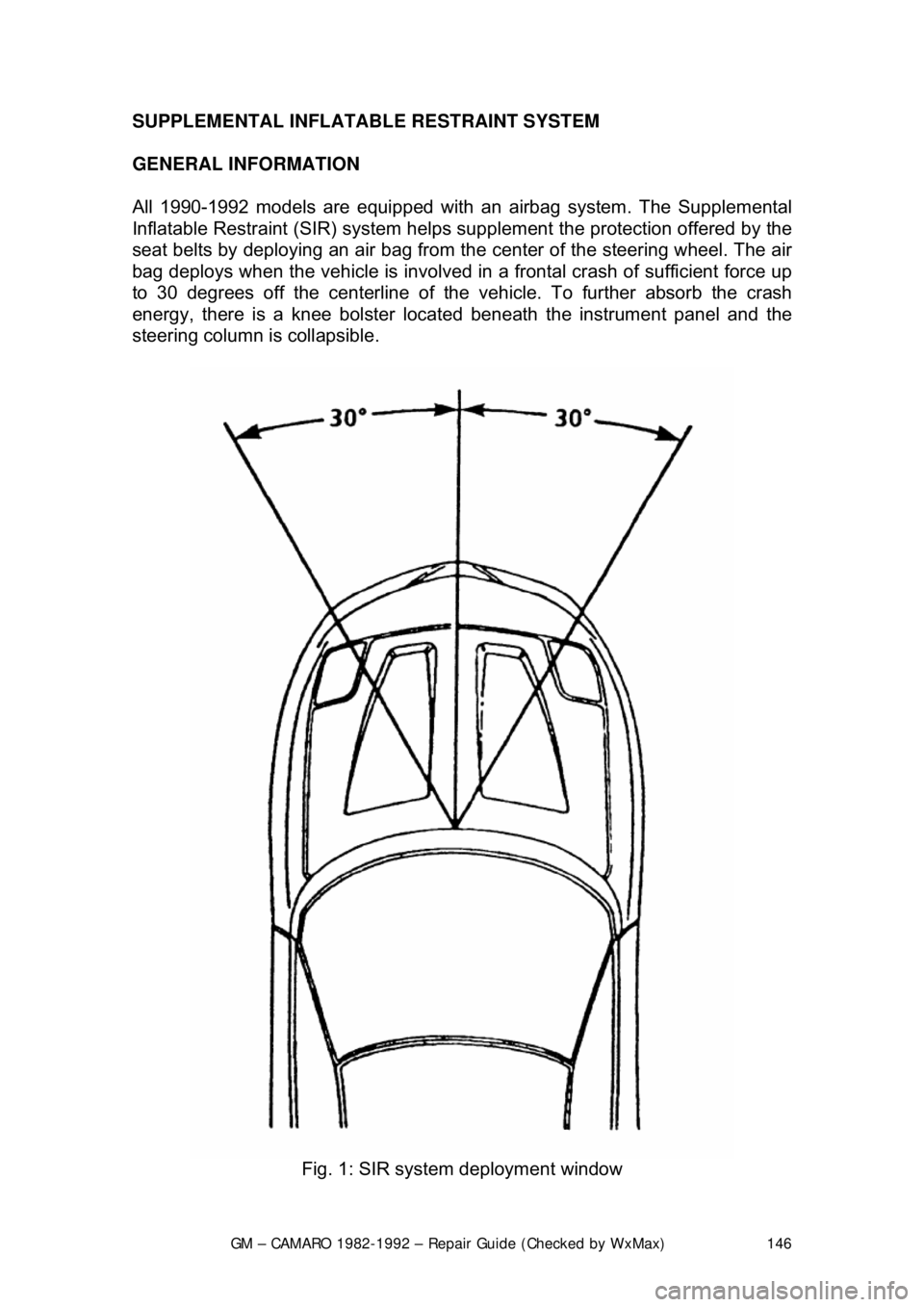
All 1990-1992 models are equi
pped with an airbag system. The Supplemental
Inflatable Restraint (SIR) syst em helps supplement the protection offered by the
seat belts by deploying an ai r bag from the center of the steering wheel. The air
bag deploys when the vehicle is involved in a frontal crash of sufficient force up
to 30 degrees off the center line of the vehicle. To further absorb the crash
energy, there is a knee bolster located beneath the instrument panel and the
steering column is collapsible.
Fig. 1: SIR system deployment window
Page 148 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 148
ARMING SENSOR
The arming sensor is a protective switch
located in the power feed side of the
deployment loop. It is calibrated to clos e at low level velocity changes (lower
than the discriminating sens ors). This assures that the inflator module is
connected directly to the 36 volt output of the DERM or battery voltage feed
when either of the discrim inating sensors close.
DISCRIMINATING SENSORS
The discriminating sensors are wired in parallel on the ground side of the
deployment loop. These sensors are calib rated to close with velocity changes
which are severe enough to warrant deployment.
SIR COIL ASSEMBLY
The SIR coil assembly consists of two cu rrent carrying coils. They are attached
to the steering column and allow rotation of the steering wheel while maintaining
continuous contact of the deployment loop to the inflator module.
INFLATOR MODULES
Each inflator module consists of an inflat able bag and an inflator (a canister of
gas generating material with an initiati ng device). When the vehicle is in a
frontal crash of sufficient force, current flows through the deployment loops.
Current flowing through the initiator ignite s the material in the inflator module.
The gas produced from this reaction rapidly inflates the air bag.
Fig. 2: Forward discriminating se nsor location on 1990-1992 models
Page 149 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 149
Fig. 3: Passenger com partment SIR component lo cations on 1990-1992 models
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
The DERM can maintain sufficient volt age to cause a deployment for up to 10
minutes after the ignition switch is tur ned OFF or the battery is disconnected.
Always disable the system when perfo rming service procedures ON OR NEAR
the system and it's components.
CAUTION - The disarming and arming procedures must be followed in the
order listed to temporarily disable the SI R system. Failure to do so could result
in possible air bag deployment, pers onal injury or otherwise unneeded SIR
system repairs.
DISARMING THE SYSTEM
1. Turn the steering wheel so that t he vehicle's wheels are pointing straight
ahead.
2. Turn the ignition switch to the LOCK position.
3. Remove the SIR or AIR BAG fuse from the fuse panel.
4. Remove the left side trim panel, t hen remove the Connector Position
Assurance (CPA) device and disconnec t the yellow two-way SIR harness
connector at the base of the steering column.
5. On vehicles with passenger side air bags, remove the glove box door
then disconnect the yellow two-way c onnector located near the yellow
24-way DERM harness connector.
With the fuse removed and the ignition sw itch ON, the air bag warning lamp will
be on. This is normal and does not indicate a SIR system malfunction.
Page 200 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 200
9. Lubricate the speedometer cable
with an appropriate lubricant, being
sure to cover the lower thirds of the cable.
10. Insert the cable into the casi ng, then connect the cable and casing
assembly to the speedometer.
11. Install the instrument cluster, then install the cluster attaching screws.
12. Install the instrument cluster trim plate.
13. On models without cruise control, connect the speedometer cable strap
at the power brake booste r. On models with cruise control, connect the
speedometer cable at the cr uise control transducer.
14. Connect the negative battery cable at the battery.
WIPER SWITCH
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
The wiper switch is part of the multi-function lever, located on the steering
wheel column.
1. Disconnect the electrical connector of the multi-function lever, located
under the instrument panel.
2. Remove the protective cover from the wire.
3. Grasp the lever firmly, twist and pull (the tang on the lever must align
with the socket) the lever straight out.
4. Pull the wire through the steering column.
To install: 5. Slide a music wire tool through the steering column and connect the
lever wire to the tool wire; pull t he wire through the steering column.
6. Push the control lever into the sp ring loaded socket (be sure to align the
tang).
7. Install the protective cover to the wire.
8. Connect the electrical connector of the multi-function lever.
HEADLIGHT SWITCH
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1. Disconnect the negative batte ry cable at the battery.
2. Remove the four screws from insi de the defroster duct (instrument panel
pad securing screws).
3. Remove the screws which are under the lip of the instrument panel pad.
4. Remove the instrument panel pad.
5. On models equipped with air condition ing, remove the instrument panel
cluster bezel and the cluster.
6. Remove the radio speaker bracket.
7. Pull the headlamp switch knob to the ON position, depress the locking
button for the knob and shaft (locat ed on the switch), and remove the
knob and shaft.
8. Remove the switch bezel (retainer).