1982 CHEVROLET CAMARO cooling
[x] Cancel search: coolingPage 50 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 50
DISC BRAKES
Instead of the traditional ex
panding brakes that press out ward against a circular
drum, disc brake systems utilize a disc (rotor) with brake pads positioned on
either side of it. An easily-seen analog y is the hand brake arrangement on a
bicycle. The pads squeeze onto the rim of the bike wheel, slowing its motion.
Automobile disc brakes use the identical principle but apply the braking effort to
a separate disc instead of the wheel.
The disc (rotor) is a casting, usually eq uipped with cooling fins between the two
braking surfaces. This enables air to ci rculate between the braking surfaces
making them less sensitive to heat bui ldup and more resistant to fade. Dirt and
water do not drastically affect braking ac tion since contaminants are thrown off
by the centrifugal action of the rotor or scraped off the by the pads. Also, the
equal clamping action of the two brake pad s tends to ensure uniform, straight
line stops. Disc brakes are inherently se lf-adjusting. There are three general
types of disc brake:
1. A fixed caliper.
2. A floating caliper.
3. A sliding caliper.
The fixed caliper design uses two pistons mounted on either side of the rotor (in
each side of the caliper). The caliper is mounted rigidly and does not move.
The sliding and floating designs are quite similar. In fact, these two types are
often lumped together. In both designs, the pad on the inside of the rotor is
moved into contact with the rotor by hy draulic force. The caliper, which is not
held in a fixed position, moves slightly, bringing the outside pad into contact with
the rotor. There are various methods of attaching floating calipers. Some pivot
at the bottom or top, and some slide on mounting bolts. In any event, the end
result is the same.
DRUM BRAKES
Drum brakes employ two brake shoes mounted on a st ationary backing plate.
These shoes are positioned inside a circul ar drum which rotates with the wheel
assembly. The shoes are held in place by springs. This allows them to slide
toward the drums (when they are applied) while keeping the linings and drums
in alignment. The shoes are actuated by a wheel cylinder which is mounted at
the top of the backing plat e. When the brakes are app lied, hydraulic pressure
forces the wheel cylinder's actuating links outward. Since these links bear
directly against the top of the brake s hoes, the tops of the shoes are then forced
against the inner side of the drum. This action forces the bottoms of the two
shoes to contact the brake drum by rotati ng the entire assembly slightly (known
as servo action). When pressure within the wheel cylinder is relaxed, return
springs pull the shoes back away from the drum.
Most modern drum brakes are designed to self-adjust themselves during
application when the vehicle is moving in reverse. This motion causes both
Page 151 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 151
ARMING THE SYSTEM
1. Turn the ignition key to the LO CK position and remove the key.
2. On vehicles with a passenger side ai r bag, reconnect the yellow two-way
connector assembly located near the yellow 24-way DERM harness
connector. Install the glov e box door assembly.
3. Connect the yellow two-way connector assembly at the base of the
steering column.
Always be sure to reinstall the Connec tor Position Assurance (CPA) device.
4. Install the left side trim panel and rein stall the fuse in the fuse block.
5. Turn the ignition key to the RUN posit ion and verify that the warning lamp
flashes seven to nine times and then turn s OFF. If it does not operate as
described, have the system repair ed by a qualified technician.
HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
BLOWER MOTOR
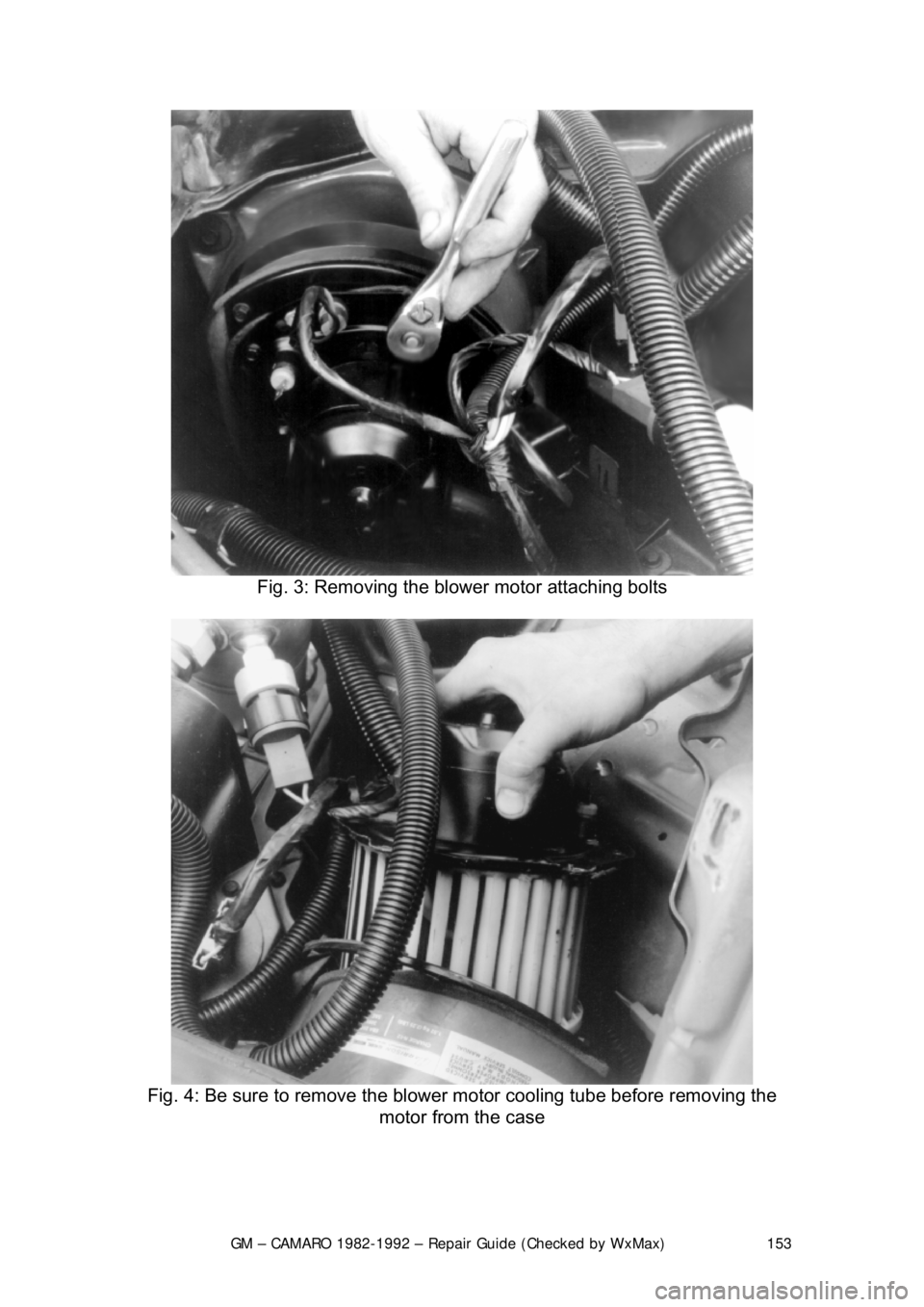
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable. If necessary, remove the diagonal
fender brace at the right rear corner of the engine compartment to gain
access to the blower motor.
2. Disconnect the electrical wiring fr om the blower motor. If equipped with
air conditioning, remove the blower relay and bracket as an assembly
and swing them aside.
3. Remove the blower motor cooling tube.
4. Remove the blower mo tor retaining screws.
5. Remove the blower motor and fan as an assembly from the case.
To install: 6. Position the blower motor into pl ace and install the retaining screws.
7. Install the blower motor cooling tube.
8. Connect all the electrical connections.
9. Connect the negative battery cable.
Page 153 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 153
Fig. 3: Removing the blower motor attaching bolts
Fig. 4: Be sure to remove the blow er motor cooling tube before removing the
motor from the case
Page 154 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 154
HEATER CORE
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
CAUTION - When draining the coolant, keep in mind that cats and dogs are
attracted by the ethylene gl ycol antifreeze, and are quite likely to drink any that
is left in an uncovered container or in puddles on the ground. This will prove
fatal in sufficient quantity. Always drai n the coolant into a sealable container.
Coolant should be reused unless it is contaminated or several years old.
1. Drain the cooling system.
2. Remove both heater hoses.
3. Remove the lower right hush panel.
4. Remove the lower right instru ment panel and the ESC module if
necessary.
5. Remove the lower right in strument panel-to-cowl screw.
6. Remove the heater case screws.
The upper left screw may be reached with a long socket extension. Carefully lift
the lower right corner of the instrument panel to align the extension.
7. Remove the case cover.
8. Remove the support plate and baffle screws.
9. Remove the heater core and ba ffle plate from the housing.
To install: 10. Position the heater core and baffle plate into the housing.
11. Install the support plate and baffle screws.
12. Install the case cover.
13. Install the heater case screws.
14. Install the lower right in strument panel-to-cowl screw.
15. Install the lower right instrument panel and the ESC module if necessary.
16. Install the lower right hush panel.
17. Install both heater hoses.
18. Fill the cooling system and check for leaks.
Fig. 1: Heater module assembly
Page 158 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 158
HOT WATER VALVE
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
Not all model years and engine applic
ations use hot water valves.
1. Drain the coolant.
2. Disconnect the vacuum hose at the hot water valve by sliding the tab of
the connector past the L-shaped bend in the ac tuator vacuum tube.
Then, slide the hose connector off the tube while continuing to hold the
tab back against the connector end.
3. Disconnect the heater hos es from the valve.
To install: 4. Install the valve with the vacuum actuator faci ng up. The heater hoses
will hold the valve in position.
5. Install the vacuum hose to the actuator.
6. Refill the cooling system. R un the engine long enough to purge any
trapped air, then add more coolant if necessary.
7. Check for leaks.
Fig. 1: Hot water valve loca tion on carbureted V8 engines
Page 304 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 304
Never release a depressed clutch pedal
with the bleeder screw open or air will
be drawn into the system.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
UNDERSTANDING AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS
The automatic transmission allows eng ine torque and power to be transmitted
to the rear wheels within a narrow range of engine operating speeds. It will
allow the engine to turn fast enough to produce plenty of power and torque at
very low speeds, while keeping it at a s ensible rpm at high vehicle speeds (and
it does this job without driv er assistance). The transmission uses a light fluid as
the medium for the transmission of power. This fluid also works in the operation
of various hydraulic control circui ts and as a lubricant. Because the
transmission fluid performs all of thes e functions, trouble within the unit can
easily travel from one part to another. For this reason, and because of the
complexity and unusual oper ating principles of the transmission, a very sound
understanding of the basic principles of operation will simplify troubleshooting.
TORQUE CONVERTER
The torque converter replaces the convent ional clutch. It has three functions:
1. It allows the engine to idle with t he vehicle at a standstill, even with the
transmission in gear.
2. It allows the transmission to shi ft from range-to-range smoothly, without
requiring that the driver close the throttle during the shift.
3. It multiplies engine torque to an incr easing extent as vehicle speed drops
and throttle opening is increased. This has the effect of making the
transmission more responsive and redu ces the amount of shifting
required.
The torque converter is a metal case which is shaped like a sphere that
has been flattened on opposite sides. It is bolted to the rear end of the
engine's crankshaft. Generally, the ent ire metal case rotates at engine
speed and serves as the engine's flywheel.
The case contains three sets of bl ades. One set is attached directly to
the case. This set forms the torus or pump. Another set is directly
connected to the output shaft, and forms the turbine. The third set is
mounted on a hub which, in turn, is mounted on a stationary shaft
through a one-way clutch. This third set is known as the stator.
A pump, which is driven by the conv erter hub at engine speed, keeps the
torque converter full of transmission fluid at all times. Fluid flows
continuously through the unit to provide cooling.
Under low speed acceleration, the tor que converter functions as follows:
Page 347 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 347
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
1. Disconnect the wires from the cap.
2. Remove the distributor cap.
3. Remove the two module attaching screws and capacitor attaching screw.
Lift module, capacitor and harnes s assembly from base.
4. Disconnect wiring harness.
To install: 5. Apply silicone grease underneath the module. This grease is necessary
for ignition module cooling.
6. Connect the wiring harness.
7. Install the module and attaching screws.
8. Install the distributor cap and wires.
DISTRIBUTOR
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
Fig. 1: Matchmarking the rotor
Page 365 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 365
31. Connect the bulkhead harness connec
tor, wires and hoses. Reroute the
ECM harness in its original location. Install the hush panel and fenderwell
splash panel.
32. Install the radiator, fan and fan sh roud. Connect the radiator and heater
hoses, along with the transmission cooler lines.
33. Connect the vacuum brake booster li ne, the throttle linkage and cruise
control cable. Install the distributor cap.
34. Fill the cooling system with the proper type and amount of coolant and
the crankcase with the proper type of oil to the correct level.
35. Install the water pump drive bel t, the air cleaner duct and the hood.
36. Connect the negative battery cable, st art the engine and check for leaks.
2.8L AND 3.1L ENGINES
Fig. 2: Engine mountin g points for the V6
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the air cleaner duct.
3. Mark the hood location on the hood supports and remove the hood.
4. Remove the water pump drive belt.
5. Drain the radiator and remove t he radiator hoses. Disconnect the heater
hoses and the transmission cooler lines.
6. Remove the fan shroud, fan and radiator.
7. Disconnect the throttle linkage, includi ng the cruise control detent cable.