1982 CHEVROLET CAMARO cooling
[x] Cancel search: coolingPage 449 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 449
1. Remove the intake manifold, valve
cover and pushrod cover (4-cylinder).
Disassemble the rocker arms and remove the pushrods.
2. Remove the lifters. If they are coat ed with varnish, clean with carburetor
cleaning solvent.
3. If installing new lifters or you have disassembled the lifters, they must be
primed before installation. Submer ge the lifters in SAE 10 oil and
carefully push down on the plunger with a
1/8 in. (3mm) drift. Hold the
plunger down (DO NOT pum p), then release the plunger slowly. The lifter
is now primed.
4. Coat the bottoms of the lifters wit h Molykote® before installation. Install
the lifters and pushrods into the e ngine in their original position.
5. Install the rocker arms and adjust the valves. Complete the installation by
reversing the removal procedure.
FREEZE PLUGS
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
CAUTION - When draining the coolant, keep in mind that cats and dogs are
attracted by the ethylene gl ycol antifreeze, and are quite likely to drink any that
is left in an uncovered container or in puddles on the ground. This will prove
fatal in sufficient quantity. Always drai n the coolant into a sealable container.
Coolant should be reused unless it is contaminated or several years old.
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Drain the cooling system.
3. Raise and support the vehicle safely.
4. Remove the coolant drain plug on t he side of the block, if equipped. If not
you can use a punch to put a small ho le in the center of the freeze plug
that is being replaced.
5. Remove all components in order to gain access to the freeze plug(s).
6. Using a punch, tap the bottom corner of the freeze plug to cock it in the
bore. Remove the plug using pliers.
7. Clean the freeze plug hole and c oat the new plug with sealer.
8. Using a suitable tool, install the freeze plug into the block.
9. Connect the negative battery cable, fill the cooling system, start the
engine and check for leaks.
REAR MAIN OIL SEAL
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
CAUTION - The EPA warns that prol onged contact with used engine oil may
cause a number of skin disorders, incl uding cancer! You should make every
effort to minimize your exposure to used engine oil. Pr otective gloves should be
worn when changing the oil. Wash y our hands and any other exposed skin
areas as soon as possible after exposure to used engine oil. Soap and water, or
waterless hand cleaner should be used.
1-PIECE NEOPRENE SEAL
Page 465 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 465
Fig. 12: Muffler hanger attachment
ENGINE RECONDITIONING DETE RMINING ENGINE CONDITION
Anything that generates heat and/or friction will eventually burn or wear out (i.e.
a light bulb generates heat, therefore its life span is limited). With this in mind, a
running engine generates trem endous amounts of both; friction is encountered
by the moving and rotating parts inside the engine and heat is created b\
y
friction and combustion of the fuel. Ho wever, the engine has systems designed
to help reduce the effects of heat and fr iction and provide added longevity. The
oiling system reduces the amount of fr iction encountered by the moving parts
inside the engine, while the cooling system reduces heat created by friction and
combustion. If either system is not main tained, a break-down will be inevitable.
Therefore, you can see how regular main tenance can affect the service life of
your vehicle. If you do not drain, flush and refill your cooling system at the
proper intervals, deposits will begin to accumulate in the radiator, thereby
reducing the amount of heat it can extrac t from the coolant. The same applies to
your oil and filter; if it is not changed often enoug h it becomes laden with
contaminates and is unable to properly lubricate the engine. This increases
friction and wear.
There are a number of methods for evaluat ing the condition of your engine. A
compression test can reveal the condition of your pistons, piston rings, cylinder
bores, head gasket(s), valves and valve seat s. An oil pressure test can warn
you of possible engine bearing, or oil pump failures. Excessive oil consumption,
evidence of oil in the engine air intake area and/or bluish smoke from the tail
pipe may indicate worn piston rings, worn valve guides and/or valve seals. As a
general rule, an engine that uses no more than one quart of oil every 1000
miles is in good condi tion. Engines that use one quart of oil or more in less than
1000 miles should first be checked for oil leaks. If any oil leaks are present,
have them fixed before dete rmining how much oil is consumed by the engine,
especially if blue smoke is not visible at the tail pipe.
COMPRESSION TEST
A noticeable lack of engine power, excessive oil consumption and/or poor fuel
mileage measured over an extended period are all indicators of internal engine
Page 467 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 467
8. According to the tool manufacture
r's instructions, connect a remote
starting switch to the starting circuit.
9. With the ignition switch in the OFF position, use the remote starting
switch to crank the engine through at least five compression strokes
(approximately 5 seconds of cranking) and record the highest reading on
the gauge.
10. Repeat the test on each cylinder, cranking the engine approximately the
same number of compression stroke s and/or time as the first.
11. Compare the highest readi ngs from each cylinder to that of the others.
The indicated compression pre ssures are considered within
specifications if the lo west reading cylinder is within 75 percent of the
pressure recorded for the highest readi ng cylinder. For example, if your
highest reading cylinder pressure was 150 psi (1034 kPa), then 75
percent of that would be 113 psi (779 kPa). So the lowest reading
cylinder should be no less than 113 psi (779 kPa).
12. If a cylinder exhibits an unusually low compression reading, pour a
tablespoon of clean engine oil into the cylinder through the spark plug
hole and repeat the compression tes t. If the compression rises after
adding oil, it means that the cylinder's piston rings and/or cylinder bore
are damaged or worn. If the pressure re mains low, the valves may not be
seating properly (a valve job is needed), or the head gasket may be
blown near that cylinder. If compressi on in any two adjacent cylinders is
low, and if the addition of oil doesn' t help raise compression, there is
leakage past the head gasket. Oil and coolant in the combustion
chamber, combined with blue or const ant white smoke from the tail pipe,
are symptoms of this pr oblem. However, don't be alarmed by the normal
white smoke emitted from the tail pipe during engine warm-up or from
cold weather driving. There may be evidence of water droplets on the
engine dipstick and/or oil droplets in the cooling system if a head gasket
is blown.
OIL PRESSURE TEST
Check for proper oil pressu re at the sending unit passage with an externally
mounted mechanical oil pressure gauge (a s opposed to relying on a factory
installed dash-mounted gauge). A tachom eter may also be needed, as some
specifications may require running the engine at a specific rpm.
1. With the engine cold, locate and remo ve the oil pressure sending unit.
2. Following the manufacturer's inst ructions, connect a mechanical oil
pressure gauge and, if necessary, a tachometer to the engine.
3. Start the engine and allow it to idle.
4. Check the oil pressure reading when cold and record the number. You
may need to run the engine at a specified rpm, so check the
specifications chart located earlier in this section.
5. Run the engine until normal operati ng temperature is reached (upper
radiator hose will feel warm).
6. Check the oil pressure reading agai n with the engine hot and record the
number. Turn the engine OFF.
Page 512 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 512
5. Make sure the ring gaps are pr
operly spaced around the circumference
of the piston. Fit a piston ring co mpressor around the piston and slide the
piston and connecting rod assembly do wn into the cylinder bore, pushing
it in with the wooden hammer handle. Pu sh the piston down until it is only
slightly below the top of the cylinder bore. Guide the connecting rod onto
the crankshaft bearing journal carefully, to avoid damaging the
crankshaft.
6. Check the bearing clearance of all the rod bearings, fitting them to the
crankshaft bearing journals. Follow the procedure in the crankshaft
installation above.
7. After the bearings have been fitted, apply a light coating of assembly oil
to the journals and bearings.
8. Turn the crankshaft until the appropria te bearing journal is at the bottom
of its stroke, then push the piston a ssembly all the way down until the
connecting rod bearing seat s on the crankshaft journal. Be careful not to
allow the bearing cap screws to stri ke the crankshaft bearing journals
and damage them.
9. After the piston and connecting rod assemblies have been installed, check the connecting rod side clearance on each crankshaft journal.
10. Prime and install t he oil pump and the oil pump intake tube.
CAMSHAFT, LIFTERS AND TIMING ASSEMBLY 1. Install the camshaft.
2. Install the lifters/followers into their bores.
3. Install the timing gears/chain assembly.
CYLINDER HEAD(S) 1. Install the cylinder head(s) using new gaskets.
2. Assemble the rest of the valve tr ain (pushrods and rocker arms and/or
shafts).
ENGINE COVERS AND COMPONENTS
Install the timing cover(s) and oil pan. Re fer to your notes and drawings made
prior to disassembly and install all of the components that were removed. Install
the engine into the vehicle.
ENGINE START-UP AND BREAK-IN
STARTING THE ENGINE
Now that the engine is inst alled and every wire and hose is properly connected,
go back and double check that all cool ant and vacuum hoses are connected.
Check that you oil drain plug is instal led and properly tightened. If not already
done, install a new oil filt er onto the engine. Fill the crankcase with the proper
amount and grade of engine oil. Fill the cooling system with a 50/50 mixture of
coolant/water.
Page 580 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 580
4. Spray a commercial solvent onto the sensor threads and allow it to soak
in for at least five minutes.
5. Carefully remove the sensor wit h a special oxygen sensor socket.
To install: 6. First coat the new sensor's th reads with GM anti-seize compound No.
5613695 or the equivalent. This is not a conventional anti-seize paste.
The use of a regular compound may el ectrically insulate the sensor,
rendering it inoperative. Y ou must coat the threads with an electrically
conductive anti-seize compound. Installati on torque is 30 ft. lbs. (41 Nm).
Do not overtighten.
7. Reconnect the electric al wiring. Be careful not to damage the electrical
pigtail. Check the sensor boot fo r proper fit and installation.
8. Reconnect the negative battery cable.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
OPERATION
Most engine functions are affected by the coolant temperature. Determining
whether the engine is hot or cold is largely dependent on the temperature of the
coolant. An accurate temperature signal to the ECM is supplied by the coolant
temperature sensor. The coolant temperatur e sensor is a thermistor mounted in
the engine coolant stream. A thermistor is an electrical device that varies its
resistance in relation to changes in temperature. Low coolant temperature
produces a high resistance and high coolant temperature produces low
resistance. The ECM supplies a signal of 5 volts to the coolant temperature
sensor through a resistor in the ECM and measures the voltage. The voltage
will be high when the engine is cold and low when the engine is hot.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Drain the cooling system to an appropr iate and clean container for reuse.
3. Disconnect the electrical wiring fr om the coolant temperature sensor.
4. Remove the coolant temperature sensor.
To install: 5. Install the coolant temperature sensor.
6. Connect the electrical wiring.
7. Fill the cooling system.
8. Connect the negative battery cable.
9. Start the engine and check for leaks.
Page 593 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 593
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Drain the engine coolant.
3. Raise and properly support the vehicle.
4. Disconnect the knock sensor wiring harness.
5. Remove the knock sensor from the engine block.
CAUTION - The knock sensor is mounted in the engine block cooling passage.
Engine coolant in the block will dr ain when the sensor is removed.
6. Installation is the reverse of remova l. Tighten the sensor to 14 ft. lbs (19
Nm).
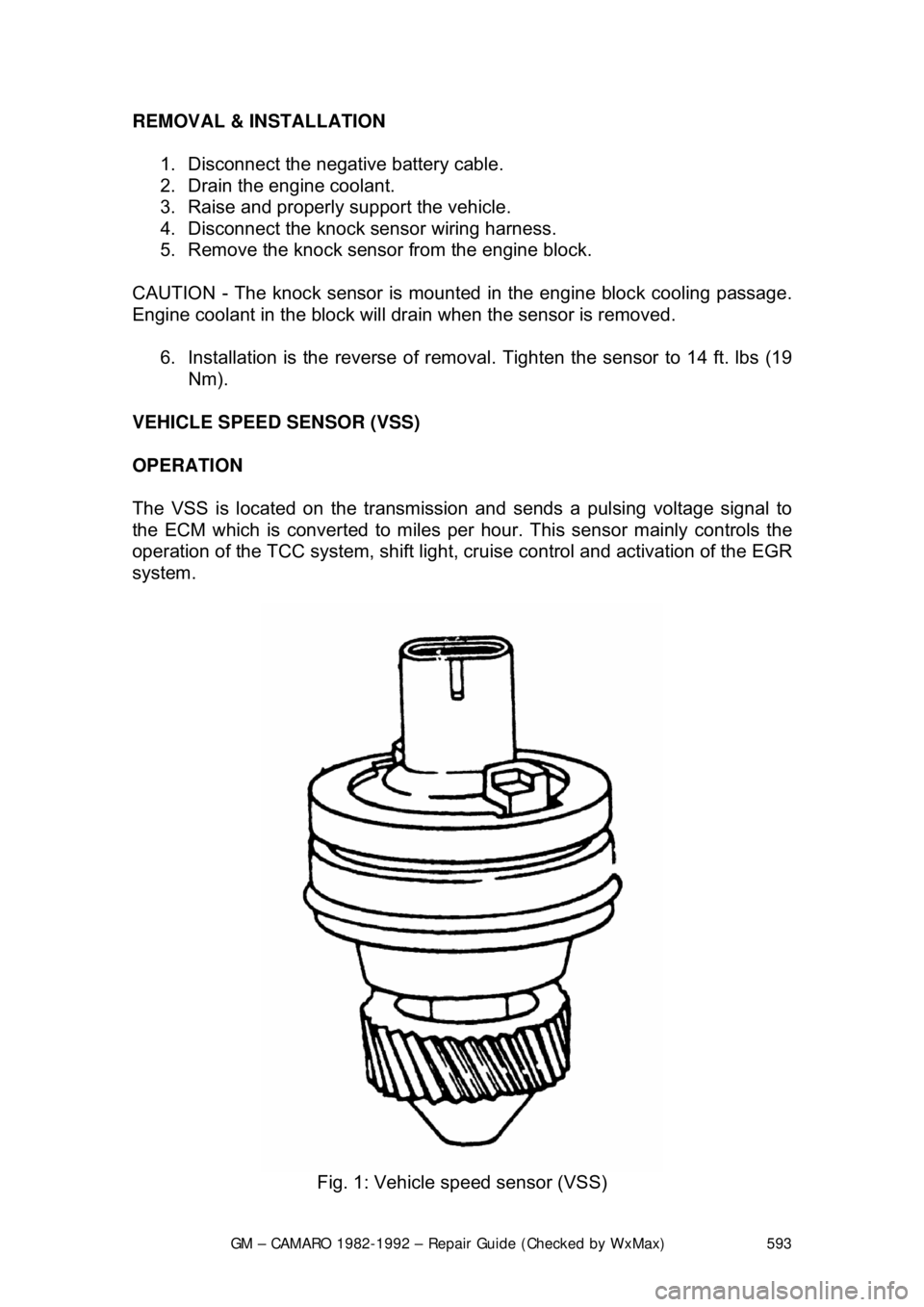
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (VSS)
OPERATION
The VSS is located on the transmission and sends a pulsing voltage signal to
the ECM which is converted to miles per hour. This sensor mainly controls the
operation of the TCC system, shift light, cr uise control and activation of the EGR
system.
Fig. 1: Vehicle speed sensor (VSS)
Page 628 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 628
SPARK PLUG HEAT RANGE
Spark plug heat range is
the ability of the plug to dissipate heat. The longer the
insulator (or the farther it extends in to the engine), the hotter the plug will
operate; the shorter the insulator (the cl oser the electrode is to the block's
cooling passages) the cooler it will operate. A plug that absorbs little heat and
remains too cool will quickly accumulate deposits of oil and carbon since it is
not hot enough to burn them off. This leads to plug fouling and consequently to
misfiring. A plug that absorbs too much heat will have no deposits but, due to
the excessive heat, the electrodes will burn away quickly and might possibly
lead to preignition or other ignition probl ems. Preignition takes place when plug
tips get so hot that they gl ow sufficiently to ignite the air/fuel mixture before the
actual spark occurs. This early igniti on will usually cause a pinging during low
speeds and heavy loads.
Fig. 3: Spark plug heat range
The general rule of thumb for choosing the correct heat range when picking a
spark plug is: if most of your driving is long distanc e, high speed travel, use a
colder plug; if most of your driving is stop and go, use a hotter plug. Original
equipment plugs are general ly a good compromise between the 2 styles and
most people never have the need to change their plugs from the factory-
recommended heat range.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
A set of spark plugs usually requi res replacement after about 20,000-30,000
miles (32,000-48,000 km), depending on y our style of driving. In normal
operation plug gap increases about 0.001 in. (0.025mm) for every 2500 miles
(4000 km). As the gap increases, the plug' s voltage requirement also increases.
It requires a greater voltage to jump t he wider gap and about two to three times
Page 652 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 652
6. Connect the negative battery cable.
MODULE
It is not necessary to remove t he distributor from the vehicle.
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the distributor cap, rotor and pickup coil.
3. Remove the 2 module attaching screws and lift the module up. Remove
the leads from the module, observi ng the colors on each lead. These
leads can not be interchanged.
If the module is to be reused, do not wi pe the grease from the module or the
distributor base. If a new module is to be installed, a package of silicone grease
will be included with it. Spr ead the grease on the metal face of the module and
on the distributor base wher e the module seats. This grease is necessary for
module cooling.
To install: 4. Install the module, tighten the reta ining screws and connect the wiring.
5. Install the distributor rotor and distributor cap.
6. Connect the negative battery cable.
Fig. 7: Ignition coil module mounting - always coat the base with silicone
dielectric grease.