1900 MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: oil pressurePage 168 of 408
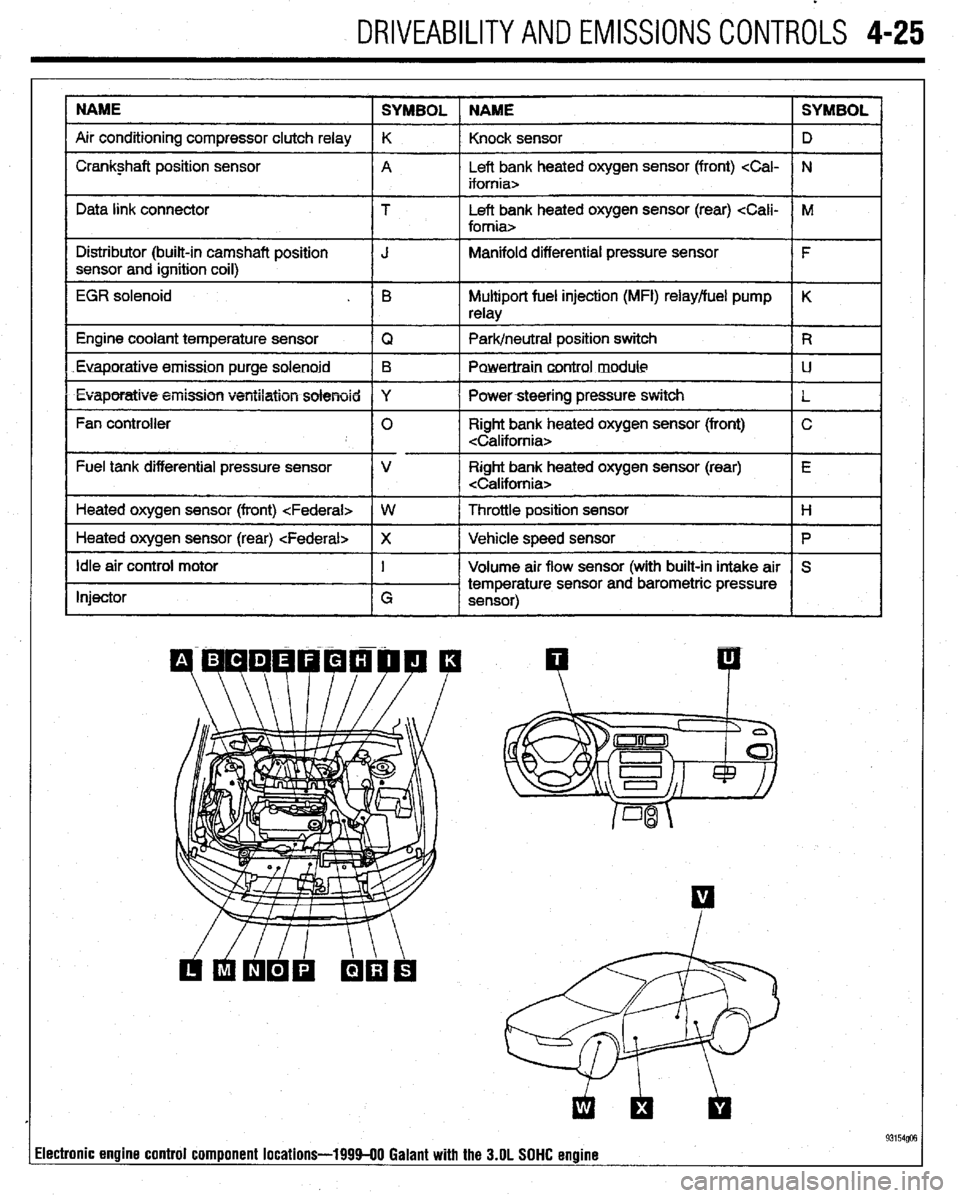
DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS 4-25
NAME
SYMBOL NAME SYMBOL
Air conditioning compressor clutch relay K
Knock sensor D
I Crankshaft position sensor
A Left bank heated oxygen sensor (front)
I I
Data link connector T Left bank heated oxygen sensor (rear)
I Distributor (built-in camshaft position
I J Manifold differential pressure sensor
I F
sensor and ignition coil)
I
EGR solenoid . B Multiport fuel injection (MFI) relay/fuel pump K
relay
1 Engine coolant temperature sensor
IQ 1 Park/neutral position switch IR
Euaporatiue.emission purge solenoid B
Powertraincontrol module LJ
l Evaporatiw5+eiiission ventilation solenoid Y
I Powersteering pressure switch
L
Fan controller 0 Right bank heated oxygen sensor (front) C
Fuel tank differential pressure sensor V Right bank heated oxygen sensor (rear) E
Heated oxygen sensor (front)
I
1 Heated oxygen sensor (rear)
Ip I
Idle air control motor
Injector I
G Volume air flow sensor (with built-in intake air S
temperature sensor and barometric pressure
sensor)
I I
93154@3 lectronic engine control component locations-199940 Galant with the 3.OL SOHC engine
Page 170 of 408

DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS 4-27
WITHOUTASCANTOOL
8 See Figure 87. 1. Remove the under dash cover, if equipped.
2. Attach an analoa voltmeter between the on-
board diagnostic outpit terminal of the data link con-
nector and the ground terminal
3. Turn the ignition switch ON.
4. Read the on-board diagnostic output pattern
from the voltmeter and record.
5. Diagnose and repair the faulty components as
required.
OBD OUTPUT
[TERMINAL
tic (OBO) output and ground terminal loca-
tions on the data link connector
6. Erase the trouble code.
7. Turn the ignition swatch ON, and read the di-
agnostic trouble codes, checking that a normal code
is output.
*To erase diagnostic trouble codes with a
scan tool, follow the directions given by the
tools manufacturer.
1. Turn the ignition switch OFF. 2. Disconnect the negative battery cable from the
battery for 1 minute or more, then reattach it.
3. Turn ON the ignition switch and read the diag-
nostic trouble codes checking that a normal code is
output.
Code 11 Oxygen sensor Code 12 Air flow sensor Code 13 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Code 14 Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Code 15 SC Motor Position Sensor (MPS)
Code 21 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Code 22 Crank angle sensor Code 23 No. 1 cylinder TDC (camshaft position)
Sensor
Code 24 Vehicle speed sensor Code 25 Barometric pressure sensor Code 31 Knock sensor (KS) Code 32 Manifold pressure sensor Code 36 Ignition timmg adjustment signal Code 39 Oxygen sensor (rear - turbocharged) Code 41 Injector Code 42 Fuel pump Code 43 EGR-California Code 44 Ignition Coil; power transistor unit (No.
1 and No. 4 cvlinders) on 3.OL
Code 62 ignition Coil; power transistor unit (No.
2 and No. 5 cvlinders) on 3.OL
Code 53 ignition Coil; power transistor unit (No.
3 and No. 6 cylinders) on 3.OL
Code 55 AC valve position sensor Code 59 Heated oxygen sensor Code 61 Transaxle control unit cable (automatic
transmission)
Code 62 Warm-up control valve position sensor
(non-turbo)
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is given
responsibrlity for the operation of the emission con-
trol devices, cooling fans, ignition and advance and
in some cases, automatic transaxle functions. Be-
cause the PCM oversees both the ignition timing and
the fuel injection operation, a precise air/fuel ratio
will be maintained under all operating conditions,
The PCM is a microprocessor, or small computer,
which receives electrical inputs from several sensors,
switches and relays on and around the engine.
Based on combinations of these inputs, the PCM
controls outputs to various devices concerned with
engine operation and emissions. The control module
relies on the signals to form a correct picture of cur-
rent vehicle operation. If any of the input signals is
incorrect, the PCM reacts to whatever picture is
painted for it. For example, if the coolant temperature
sensor is inaccurate and reads too low, the PCM may
see a picture of the engine never warming up. Conse-
quently, the engine settings will be maintained as if
the engine were cold. Because so many inputs can
affect one output, correct diagnostic procedures are
essential on these systems,
One part of the PCM is devoted to monitoring
both input and output functions within the system.
This ability forms the core of the self-diagnostic sys-
tem. If a problem is detected within a circuit, the con-
trol module will recognize the fault, assign it a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC), and store the code in
memory. The stored code(s) may be retrieved during
diagnosis. While the OBD-II system is capable of recognizing
many internal faults, certain faults WIII not be recog-
nized. Because the control module sees only electri-
cal signals, it cannot sense or react to mechanical or
vacuum faults affecting engine operation. Some of
these faults may affect another component which will
set a code. For example, the PCM monitors the out-
put signal to the fuel injectors, but cannot detect a
partially clogged injector. As long as the output dri-
ver responds correctly, the computer will read the
system as functioning correctly. However, the im-
proper flow of fuel may result in a lean mixture. This
would, in turn, be detected by the oxygen sensor and
noticed as a constantly lean signal by the PCM. Once
the signal falls outside the pre-programmed limits,
the control module would notice the fault and set a
trouble code.
Additionally, the OBD-II system employs adaptive
fuel logic. This process is used to compensate for
normal wear and variability within the fuel system.
Once the engine enters steady-state operation, the
control module watches the oxygen sensor signal for
a bias or tendency to run slightly rich or lean. If such
a bias is detected, the adaptive logic corrects the fuel
delivery to bring the air/fuel mixture towards a cen-
tered or 14.7:1 ratio. This compensating shift is
stored In a non-volatile memory which is retained by
battery power even with the ignition switched
OFF. The correction factor is then available the next time
the vehicle is operated.
WITHASCANTOOL
8 See Figures 88, 89, 90, and 91
The Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC), under the
left-hand side of the instrument panel, must be lo-
cated to retrieve any OTC’s
Reading the control module memory is on of the
first steps in OBD II system diagnostics. This step
should be initially performed to determine the general
nature of the fault. Subsequent readings will deter-
mine if the fault has been cleared.
Reading codes can be performed by any of the
methods below:
l Read the control module memory with the
Generic Scan Tool (GST)
l Read the control module memory with the ve-
hicle manufacturers specific tester
To read the fault codes, connect the scan tool or
tester according to the manufacturers instructions.
Follow the manufacturers specified procedure for
reading the codes.
WITHOUTASCANTOOL
8 See Figure 92
The Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC), under the
left-hand side of the instrument panel, must be lo-
cated to retrieve any DTC’s.
Page 172 of 408

DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS 4-29
PO108 Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric
Pressure Circuit High Input
PO109 Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric
Pressure Circuit Intermittent
PO110 intake Air Temperature Circuit Malfunction
PO111 Intake Air Temperature Circuit Range/Per-
formance Problem
PO112 Intake Air Temperature Circuit Low Input
PO113 Intake Air Temoerature Circuit Hiah lnout
PO114 Intake Air Temberature Circuit lnt&miitent
PO115 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Mal-
function -
PO116 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit
Range/Performance Problem
PO117 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Low
Input
PO118 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High
Input
PO119 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Inter-
mittent
PO120 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “A” Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO121 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “A” Cir-
cuit Range/Performance Problem
PO122 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “A” Cir-
cuit Low Input
PO123 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “A” Cir-
cuit High Input
PO124 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “A” Cir-
cuit Intermittent
PO125 Insufficient Coolant Temperature For
Closed Loop Fuel Control
PO126 Insufficient Coolant Temperature For Sta-
ble Operation
PO130 02 Circuit Malfunction (Bank no. 1 Sen-
sor no. 1)
PO131 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank no.
1 Sensor no. 1)
PO132 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank no.
1 Sensor no. 1)
PO133 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank
no. 1 Sensor no. 1)
PO134 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected
(Bank no. 1 Sensor no. 1)
PO135 02 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction
(Bank no. 1 Sensor no. 1)
PO136 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank no.
1 Sensor no. 2)
PO137 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank no.
1 Sensor no. 2)
PO138 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank no.
1 Sensor no. 2)
PO139 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank
no. 1 Sensor no. 2)
PO140 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected
(Bank no. 1 Sensor no. 2)
PO141 02 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction
(Bank no. 1 Sensor no. 2)
PO142 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank no.
1 Sensor no. 3)
PO143 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank no.
1 Sensor no. 3)
PO144 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank no.
1 Sensor no. 3)
PO145 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank
no. 1 Sensor no. 3)
PO146 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected
(Bank no. 1 Sensor no. 3)
PO147 02 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction
(Bank no. 1 Sensor no. 3)
PO150 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank no.
2 Sensor no. 1) PO151 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank no.
2 Sensor no. 1)
PO152 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank no.
2 Sensor no. 1)
PO153 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank
no. 2 Sensor no. 1)
PO154 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected
(Bank no. 2 Sensor no. 1)
PO155 02 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction
(Bank no. 2 Sensor no. 1)
PO156 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank no.
2 Sensor no. 2)
PO157 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank no.
2 Sensor no. 2)
PO158 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank no.
2 Sensor no. 2)
PO159 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank
no. 2 Sensor no. 2)
PO160 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected
(Bank no. 2 Sensor no. 2)
PO161 02 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction
(Bank no. 2 Sensor no. 2)
PO162 02 Sensor CircuitMalfunction(8ank
no.2 Sensorno.3)
PO16302 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
(Bankno. Sensorno.3)
PO16402 Sensor Circuit HighVoltage
(Bankno. Sensorno.3)
PO16502 Sensor Circuit Slow Response
(Bankno. Sensorno.3)
PO166 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity De-
tected(Bankno.2 Sensorno.3)
PO16702 SensorHeaterCircuitMalfunc-
tion(Bank no.2 Sensorno.3)
PO170 Fuel Trim Malfunction (Bank no. 1 )
PO171 System Too Lean (Bank no. 1 )
PO172 Svstem Too Rich (Bank no 1 )
PO173 F;el Trim Malfundtion (Bank io. 2 )
PO174 System Too Lean (Bank no 2 )
PO175 System Too Rich (Bank no. 2 )
PO176 Fuel Composition Sensor Circuit Mal-
function
PO177 Fuel Composition Sensor Circuit
Range/Performance
PO178 Fuel Composition Sensor Circuit Low In-
put
PO179 Fuel Composition Sensor Circuit High In-
put
PO180 Fuel Temperature Sensor “A” Circuit Mal-
function
PO181 Fuel Temperature Sensor “A” Circuit
Range/Performance
PO182 Fuel Temperature Sensor “A” Circuit Low
Input
PO183 Fuel Temperature Sensor “A” Circuit High
Input
PO184 Fuel Temperature Sensor “A” Circuit Inter-
mittent
PO185 Fuel Temperature Sensor “B” Circuit Mal-
function
PO186 Fuel Temperature Sensor “B” Circuit
Range/Performance
PO187 Fuel Temperature Sensor “B” Circuit Low
Input
PO188 Fuel Temperature Sensor “B” Circuit High
Input
PO189 Fuel Temperature Sensor “B” Circuit Inter-
mittent
PO190 Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit Mal-
funchon
PO191 Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit
Range/Performance PO192 Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit Low In-
put
PO193 Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit High In-
put
PO194 Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit Intermit-
tent
PO195 Engine Oil Tempetature Sensor Malfunc-
tion
PO198 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor
Range/Performance
PO197 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor Low
PO198 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor High
W199 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor Intermit-
tent
PO200 Injector Circuit Malfunction
PO201 Injector Circuit Malfunction-Cylinder
no. 1
PO202 Injector Circuit Malfunction-Cylinder
no. 2
PO203 Injector Circuit Malfunction-Cylinder
no. 3
PO204 Injector Circuit Malfunction-Cylinder
no. 4
PO205 Injector Circuit Malfunction-Cylinder
no. 5
PO206 Injector Circuit Malfunction-Cylinder
no. 6
PO214 Cold Start Injector no. 2 Malfunction
PO215 Engine Shutoff Solenoid Malfunction
PO218 Injection Timing Control Circuit Malfunc-
tion
PO217 Engine Over Temperature Condition
PO218 Transmission Over Temperature Condition
PO219 Engine Over Speed Condition
PO220 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch ‘9” Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO221 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “B” Cir-
cuit Range/Performance Problem
PO222 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “B” Cir-
cuit Low Input
PO223 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “B” Cir-
cuit High Input
PO224 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “B” Cir-
cuit Intermittent
PO225 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “C” Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO226 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “C” Cir-
cuit Range/Performance Problem
PO227 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “c” Cir-
cuit Low Input
PO228 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “C” Cir-
cuit High Input
PO229 Throttle Position Sensor/Switch “C” Cir-
cuit Intermittent
PO230 Fuel Pump Primary Circuit Malfunction
PO231 Fuel Pump Secondary Circuit Low
PO232 Fuel Pump Secondary Circuit High
PO233 Fuel Pump Secondary Circuit Intermittent
PO261 Cylinder no. 1 Injector Circuit Low
PO262 Cylinder no. 1 Injector Circuit High
PO263 Cylinder no. 1 Contribution/Balance Fault
PO264 Cvlinder no. 2 lniector Circuit Low
PO265 Cylinder no. 2 Injector Circuit High
PO266 Cylinder no. 2 Contribution/Balance Fault
PO267 Cylinder no. 3 Injector Circuit Low
PO268 Cylinder no. 3 Injector Circuit High
PO269 Cylinder no. 3 Contribution/Balance Fault
PO270 Cylinder no. 4 Injector Circuit Low
PO271 Cvlinder no. 4 lniector Circuit Hiah
PO272 Cylinder no. 4 CbntributionlBalaice Fault
PO273 Cylinder no. 5 Injector Circuit Low
PO274 Cylinder no. 5 Injector Circuit High
Page 173 of 408
.
4-30 DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONS CONTROLS
PO275 Cvlinder no. 5 Contribution/Balance Fault
PO276 Cylinder no. 6 Injector Circuit Low
PO277 Cylinder no. 6 lniector Circuit High
PO278 Cylinder no. 6 Contribution/Balance Fault
PO300 Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire De-
tected
PO301 Cylinder no. l-Misfire Detected
PO302 Cvlinder no 2-Misfire Detected
PO303 Cylinder no. 3-Misfire Detected
PO304 Cylinder no. 4-Misfire Detected
PO305 Cylinder no. +-Misfire Detected
PO306 Cylinder no. &-Misfire Detected
PO320 Ignition/Distributor Engine Speed Input
Circuit Malfunction
PO321 Ignition/Distributor Engine Speed Input
Circuit Range/Performance
PO322 Ignibon/Distributor Engine Speed Input
Circuit No Signal
PO323 Ignition/Distributor Engine Speed Input
Circuit Intermittent
PO325 Knock Sensor no. l-Circuit Malfunction
(Bank no. 1 or Single Sensor)
PO326 Knock Sensor no. l-Circuit Range/Per-
formance (Bank no. 1 or Srngle Sensor)
PO327 Knock Sensor no. l-Circuit Low Input
(Bank no. 1 or Single Sensor)
PO328 Knock Sensor no. l-Circuit High Input
(Bank no. 1 or Single Sensor)
PO329 Knock Sensor no. l-Circuit Input Inter-
mittent (Bank no. 1 or Smgle Sensor)
PO330 Knock Sensor no. 2-Circuit Malfunction
(Bank no. 2 )
PO331 Knock Sensor no. 2-Circuit Range/Per-
formance (Bank no. 2 )
PO332 Knock Sensor no. 2-Circuit Low Input
(Bank no. 2 )
PO333 Knock Sensor no. 2-Circuit High Input
(Bank no. 2 )
PO334 Knock Sensor no. 2-Circuit Input Inter-
mittent (Bank no. 2)
PO335 Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit
Malfunction
PO336 Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit
Range/Performance
PO337 Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit
Low Input
PO338 Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit
High Input
PO339 Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit In-
termittent
PO340 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Mal-
function
PO341 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
Range/Performance
PO342 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Low In-
put
PO343 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit High In-
put
PO344 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Inter-
mittent
PO350 Ignition Coil Primary/Secondary Circuit
Malfunction
PO351 Ignition Coil “A” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO352 Ignition Coil “B” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO353 Ignition Coil “C” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO354 Ignition Coil “D” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO355 Ignition Coil “E” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction PO356 Ignition Coil “F” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO357 Ignition Coil “G” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO358 Ignition Coil ‘Y-l” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunctron
PO359 Ignition Coil “I” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO360 Ignition Coil “J” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO361 Ignition Coil “K” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO362 Ignition Coil “L” Primary/Secondary Cir-
cuit Malfunction
PO370 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“A” Malfunction
PO371 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“A” Too Many Pulses
PO372 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“A” Too Few Pulses
PO373 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“A” Intermittent/Erratic Pulses
PO374 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“A” No Pulses
PO375 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“B” Malfunction
PO376 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“B” Too Many Pulses
PO377 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
9” Too Few Pulses
PO378 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“B” Intermittent/Erratic Pulses
PO379 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal
“B” No Pulses
PO385 Crankshaft Position Sensor 9” Circuit
Malfunction
PO386 Crankshaft Position Sensor “B” Circuit
Range/Performance
PO387 Crankshaft Position Sensor ‘9” Circuit
Low Input
PO388 Crankshaft Position Sensor “B” Circuit
High Input
PO389 Crankshaft Position Sensor “B” Circuit In-
termittent
PO400 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Malfunc-
tion
PO401 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insuffi-
cient Detected
PO402 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Excessive
Detected
PO403 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Circuit Mal-
function
PO404 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Circuit
Range/Performance
PO405 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor “A” Cir-
cuit Low
PO406 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor “A” Cir-
cuit High
PO407 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor “B” Cir-
cuit Low
PO408 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor “B” Cir-
cuit High
PO410 Secondary Air Injection System Malfunc-
tion
PO411 Secondary Air Injection System Incorrect
Flow Detected
PO412 Secondary Air Injection System Switching
Valve “A” Circuit Malfunction
PO413 Secondary Air Injection System Switching
Valve “A” Circuit Open
PO414 Secondary Air Injection System Switching
Valve “A” Circuit Shorted PO415 Secondary Air Injection System Switching
Valve “B” Circuit Malfunction
PO416 Secondary Air Injection System Switching
Valve “B” Circuit Open
PO417 Secondary Air Injection System Switching
Valve “B” Circuit Shorted
PO418 Secondary Air Injection System Relay “A
Circuit Malfunction
PO419 Secondary Air Injection System Relay “B”
Circuit Malfunction
PO420 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Thresh-
old (Bank no. 1 )
PO421 Warm Up Catalyst Efficiency Below
Threshold (Bank no. 1 )
PO422 Main Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold
(Bank no. 1 )
PO423 Heated Catalyst Efficiency Below Thresh-
old (Bank no. 1 )
PO424 Heated Catalyst Temperature Below
Threshold (Bank no. 1)
PO430 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Thresh-
old (Bank no. 2 )
PO431 Warm Up Catalyst Efficiency Below
Threshold (Bank no. 2 )
PO432 Main Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold
(Bank no. 2)
PO433 Heated Catalyst Efficiency Below Thresh-
old (Bank no. 2 )
PO434 Heated Catalvst Temoerature Below
Threshold (Bank no. 2
j ’
PO440 Evaporative Emission Control System
Malfunction
PO441 Evaporative Emission Control System In-
correct Purge Flow
PO442 Evaporative Emission Control System
Leak Detected (Small Leak)
PO443 Evaporative Emission Control System
Purge Control Valve Circuit Malfunction
PO444 Evaporative Emission Control System
Purge Control Valve Circuit Open
PO445 Evaporative Emission Control System
Purge Control Valve Circuit Shorted
PO446 Evaporative Emission Control System
Vent Control Circuit Malfunction
PO447 Evaporative Emission Control System
Vent Control Circuit Open
PO448 Evaporative Emission Control System
Vent Control Circuit Shorted
PO449 Evaporative Emission Control System
Vent Valve/Solenoid Circuit Malfunction
PO450 Evaporative Emission Control System
Pressure Sensor Malfunction
PO451 Evaporative Emission Control System
Pressure Sensor Range/Performance
PO452 Evaporative Emission Control System
Pressure Sensor Low Input
PO453 Evaporative Emission Control System
Pressure Sensor High Input
PO454 Evaporative Emission Control System
Pressure Sensor Intermittent
PO455 Evaporative Emission Control System
Leak Detected (Gross Leak)
PO460 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Malfunction
PO461 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Range/Perfor-
mance
PO462 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Low Input
PO463 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit High Input
PO464 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Intermittent
PO465 Purge Flow Sensor Circuit Malfunction
PO466 Purge Flow Sensor Circuit Range/Perfor-
mance
PO467 Purge Flow Sensor Circuit Low Input
Page 174 of 408
DRIVEABILITYAND EMISSIONSCONTROL-S 4-31
PO466 Purge Flow Sensor Circuit High Input
PO469 Purqe Flow Sensor Circuit Intermittent
PO470 Exhaust Pressure Sensor Malfunction
PO471 Exhaust Pressure Sensor Range/Perfor-
mance
PO472 Exhaust Pressure Sensor Low
PO473 Exhaust Pressure Sensor Hiah
PO474 Exhaust Pressure Sensor lnirmittent
PO475 Exhaust Pressure Control Valve Malfunc-
tion
PO476 Exhaust Pressure Control Valve
Range/Performance
PO477 Exhaust Pressure Control Valve Low
PO476 Exhaust Pressure Control Valve High
PO479 Exhaust Pressure Control Valve Intermit-
tent
PO460 Cooling Fan no 1 Control Circuit Mal-
function
PO461 Cooling Fan no. 2 Control Circuit Mal-
function
PO462 Cooling Fan no. 3 Control Circuit Mal-
function
PO463 Cooling Fan Rationality Check Malfunc-
tion
PO464 Cooling Fan Circuit Over Current
PO465 Cooling Fan Power/Ground Circuit Mal-
function
PO500 Vehicle Speed Sensor Malfunction
PO501 Vehicle Speed Sensor Range/Performance
PO502 Vehicle Speed Sensor Circuit Low Input
PO503 Vehicle Speed Sensor Intermittent/Er-
ratic/High
PO505 Idle Control System Malfunction
PO506 Idle Control System RPM Lower Than Ex-
pected
PO507 Idle Control System RPM Higher Than Ex-
pected
PO510 Closed Throttle Position Switch Malfunc-
tion
PO520 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor/Switch Circuit
Malfunction
PO521 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor/Switch
Range/Performance
PO522 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor/Switch Low
Voltage
PO523 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor/Switch High
Voltage
PO530 A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor Circuit
Malfunction
PO531 A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor Circuit
Range/Performance
PO532 A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor Circuit
Low Input
PO533 A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor Circuit
High Input
PO534 A/C Refrigerant Charge Loss
PO550 Power Steering Pressure Sensor Circuit
Malfunction
PO551 Power Steering Pressure Sensor Circuit
Range/Performance
PO552 Power Steering Pressure Sensor Circuit
Low Input
PO553 Power Steering Pressure Sensor Circuit
High Input
PO554 Power Steering Pressure Sensor Circiit
Intermittent
PO560 System Voltage Malfunction
PO561 System Voltage Unstable
PO562 System Voltage Low
PO563 Svstem Voltaoe Hlah
PO565 Ciuise Control On%ignal Malfunction
PO566 Cruise Control Off Signal Malfunction PO567 Cruise Control Resume Signal Malfunc-
tion
PO566 Cruise Control Set Signal Malfunction
PO569 Cruise Control Coast Signal Malfunction
PO570 Cruise Control Accel Signal Malfunction
PO571 Cruise Control/Brake Switch “A” Circuit
Malfunction
PO572 Cruise Control/Brake Switch “A” Circuit
Low
PO573 Cruise Control/Brake Switch “A” Circuit
High
P0574Through PO560 Reserved for Cruise
Codes
PO600 Serial Communication Link Malfunction
PO601 Internal Control Module Memory Check
Sum Error
PO602 Control Module Programming Error
PO603 Internal Control Module Keep Alive Mem-
ory (KAM) Error
PO604 Internal Control Module Random Access
Memory (RAM) Error
PO605 Internal Control Module Read Only Mem-
ory (ROM) Error
PO606 PCM Processor Fault
PO606 Control Module VSS Output “A” Malfunc-
tion
PO609 Control Module VSS Output “6” Malfunc-
tion
PO620 Generator Control Circuit Malfunction
PO621 Generator Lamp “L” Control Circuit Mal-
function
PO622 Generator Field “F” Control Circuit Mal-
function
PO650 Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Control
Circuit Malfunctron
PO654 Engine RPM Output Circuit Malfunction
PO655 Engine Hot Lamp Output Control Circuit
Malfunction
PO656 Fuel Level Output Circuit Malfunction
PO700 Transmission Control System Malfunction
PO701 Transmission Control System Range/Per-
formance
PO702 Transmission Control System Electrical
PO703 Torque Converter/Brake Switch “B” Circuit
Malfunction
PO704 Clutch Switch Input Circuit Malfunction
PO705 Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Mal-
function (PRNDL Input)
PO706 Transmission Range Sensor Circuit
Range/Performance
PO707 Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Low
Input
PO706 Transmission Range Sensor Circuit High
Input
PO709 Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Inter-
mittent
PO710 Transmission FluId Temperature Sensor
Circuit Malfunction
PO711 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor
Circuit Range/Performance
PO712 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor
Circuit Low Input
PO713 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor
Circuit High Input
PO714 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor
Circuit Intermittent
PO715 Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Mal-
function
PO716 Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit
Range/Performance
PO717 InpWurbine Speed Sensor Circuit No
Signal PO716 Inputflurbine Speed Sensor Circuit Inter-
mittent
PO719 Torque Converter/Brake Switch “B” Circuit
Low
PO720 Output Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction
PO721 Output Speed Sensor Circuit Range/Per-
formance
PO722 Output Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal
PO723 Output Speed Sensor Circuit Intermittent
PO724 Toraue Converter/Brake Switch “B” Circuit
High
PO725 Engine Speed Input Circuit Malfunction
PO726 Engine Speed Input Circuit Range/Perfor-
PO727 Engine Speed Input Circuit No Signal
PO726 Engine Speed Input Circuit Intermittent
PO730 Incorrect Gear Ratio
PO731 Gear no. 1 Incorrect Ratio
PO732 Gear no. 2 Incorrect Ratio
PO733 Gear no. 3 Incorrect Ratio
PO734 Gear no 4 Incorrect Ratio
PO735 Gear no. 5 Incorrect Ratio
PO736 Reverse Incorrect Ratio
PO740 Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Malfunc-
tion
PO741 Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Perfor-
mance or Stuck Off
PO742 Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Stuck On
PO743 Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Electrical
PO744 Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Intermit-
tent
PO745 Pressure Control Solenoid Malfunction
PO746 Pressure Control Solenoid Performance or
Stuck Off
PO747 Pressure Control Solenoid Stuck On
PO746 Pressure Control Solenoid Electrical
PO749 Pressure Control Solenoid Intermittent
PO750 Shift Solenoid “A” Malfunction
PO751 Shift Solenoid “A” Performance or Stuck
Off
PO752 Shift Solenoid “A” Stuck On
PO753 Shift Solenoid “A” Electrical
PO754 Shift Solenoid “A” Intermittent
PO755 Shift Solenoid “8 Malfunction
PO756 Shift Solenoid “B” Performance or Stuck
Oft
PO757 Shift Solenoid “B” Stuck On
PO756 Shift Solenoid “6” Electrical
PO759 Shift Solenoid “8” Intermittent
PO760 Shift Solenoid “C” Malfunction
PO761 Shift Solenoid “C” Performance Or Stuck
Oft
PO762 Shift Solenoid “C” Stuck On
PO763 Shift Solenoid “C” Electrical
PO764 Shift Solenoid “C” Intermittent
PO765 Shift Solenoid “D” Malfunction
PO766 Shift Solenoid “D” Performance Or Stuck
Oft
PO767 Shift Solenoid “D” Stuck On
PO766 Shift Solenoid “D” Electrical
PO769 Shift Solenoid “D” Intermittent
PO770 Shift Solenoid “E” Malfunction
PO771 Shift Solenoid “E” Performance Or Stuck
Off
PO772 Shift Solenoid “E” Stuck On
PO773 Shift Solenoid “E” Electrical
PO774 Shift Solenoid “E” Intermittent
PO760 Shift Malfunction
PO761 l-2 Shift Malfunction
PO762 2-3 Shift Malfunction
PO763 3-4 Shift Malfunction
PO764 4-5 Shift Malfunction
Page 192 of 408
FUEL SYSTEM 5-5,
21. Connect the negative battery cable. Refill the
cooling system.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
1.5L, 1.8L, And 2.OL SOHC Engines
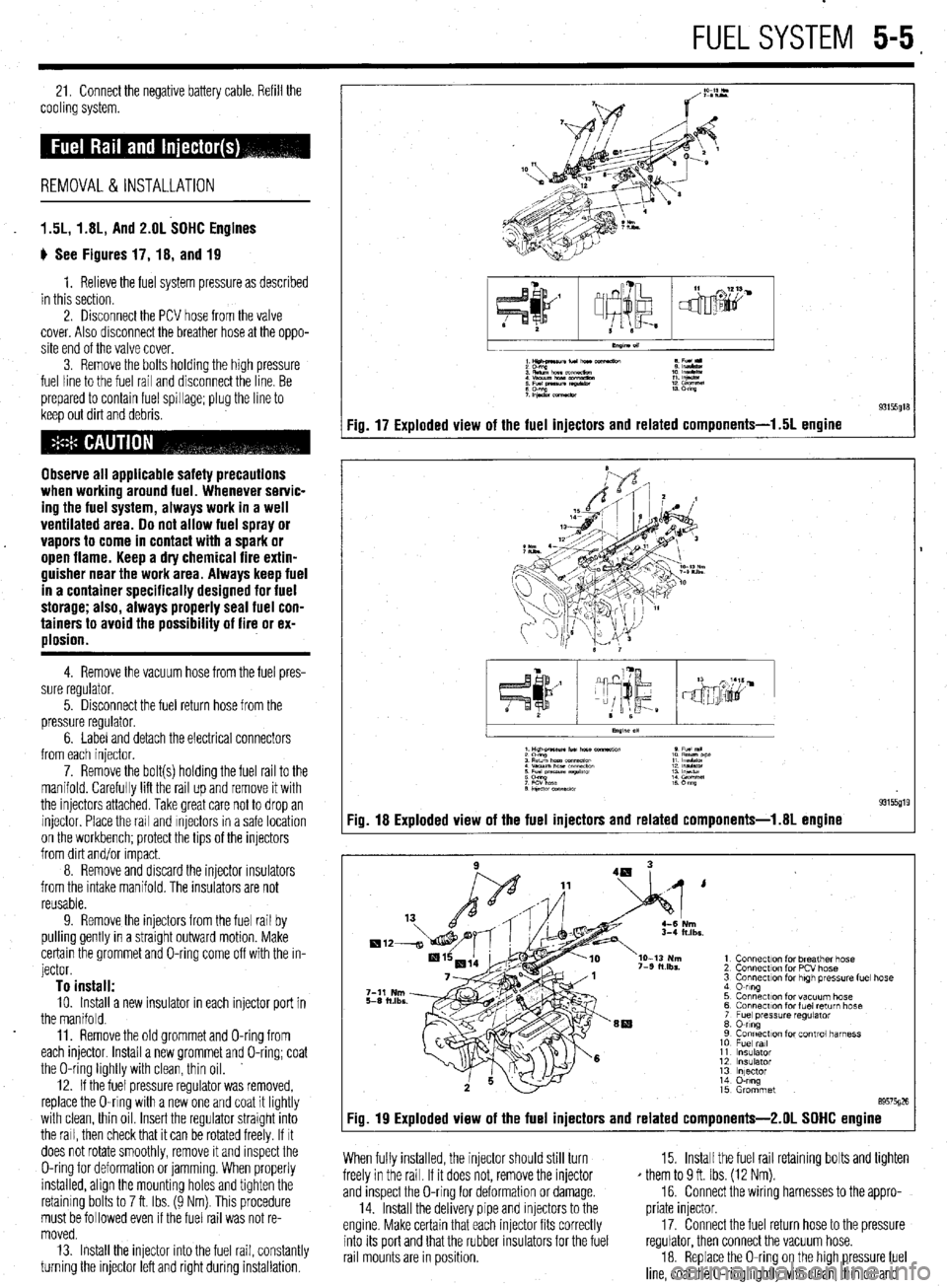
ti See Figures 17, 18, and 19
1. Relieve the fuel system pressure as described
in this section.
2. Disconnect the PCV hose from the valve
cover. Also disconnect the breather hose at the oppo-
site end of the valve cover.
3. Remove the bolts holding the high pressure
fuel line to the fuel rail and disconnect the line. Be
prepared to contain fuel spillage; plug the line to
keep out dirt and debris.
Observe all applicable safety precautions
when working around fuel. Whenever servic-
ing the fuel system, always work in a well
ventilated area. 00 not allow fuel spray or
vapors to come in contact with a spark or
open flame. Keep a dry chemical fire extin-
guisher near the work area. Always keep fuel
in a container specifically designed for fuel
storage; also, always properly seal fuel con-
tainers to avoid the possibility of fire or ex-
plosion.
4. Remove the vacuum hose from the fuel pres-
sure regulator.
5. Disconnect the fuel return hose from the
pressure regulator.
6. Label and detach the electrical connectors
from each injector.
7. Remove the bolt(s) holding the fuel rail to the
manifold. Carefully lift the rail up and remove it with
the injectors attached. Take great care not to drop an
injector Place the rail and Injectors in a safe location
on the workbench; protect the tips of the injectors
from dirt and/or Impact.
8. Remove and discard the injector rnsulators
from the intake manifold. The insulators are not
reusable.
9. Remove the injectors from the fuel rail by
pulling gently in a straight outward motion. Make
certain the grommet and O-ring come off with the in-
jector.
To install: 10. Install a new insulator in each injector port in
the manifold.
11. Remove the old grommet and O-ring from
each injector Install a new grommet and O-ring; coat
the O-ring lightly with clean, thin oil.
12. If the fuel pressure regulator was removed,
replace the O-ring with a new one and coat it lightly
with clean, thin oil Insert the regulator straight into
the rail, then check that it can be rotated freely. If It
does not rotate smoothly, remove it and inspect the
O-ring for deformation or jamming. When properly
installed, align the mounting holes and tighten the
retaining bolts to 7 ft. Ibs. (9 Nm). This procedure
must be followed even if the fuel rail was not re-
moved.
13. Install the injector into the fuel rail, constantly
turning the injector left and right during installation.
1Hilt4naunfu(norc e Fu(l
:E%!,,.,.- 1: IEE
: Efgz tz!z? :: %%I
;P&.xmeaw 13 m
Fig. 17 Exploded view of the fuel injectors and related components-l .5L engine
I
.xs.
1 Connection for breather hose
2 Connection for PCV hose
3 Connection for high tm?ss”re fuel hose
4 0-ring
5 Connection for vacuum hose
6 Connecr~on for fuel return hose
7 Fuel pressure regulator
8 0-ring
9 Connection for control harness
10 Fuel ml
11 Insulator
12 insulator
13 lnlector
14 O-ring
15 Grommet
89575026
Fig. 19 Exploded view of the fuel injectors and related components-2.01 SOHC engine
When fully installed, the injector should still turn
freely in the rail. If it does not, remove the injector
and inspect the O-ring for deformation or damage.
14. Install the delivery pipe and injectors to the
engine. Make certain that each injector fits correctly
into its port and that the rubber insulators for the fuel
rail mounts are in position. 15. Install the fuel rail retaining bolts and tighten
* them to 9 ft. Ibs. (12 Nm).
16. Connect the wiring harnesses to the appro-
priate injector.
17. Connect the fuel return hose to the pressure
regulator, then connect the vacuum hose.
18. Replace the O-ring on the high pressure fuel
line, coat the O-ring lightly with clean, thin oil and
Page 193 of 408

install the line to the fuel rail. Tighten the mounting
bolts,
19. Attach the PCV hose and the breather hose if
thev were disconnected.
20. Connect the negative battery cable. Pressur-
ize the fuel system and inspect all connections for
I
leaks.
1.6L and 2.01 DOHC Engines
b See Figure 20
1. Relieve the fuel system pressure as described
in this section.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Wrap the connection with a shop towel and
disconnect the high pressure fuel line at the fuel rail.
Observe all applicable safety precautions
when working around fuel. Whenever servic-
ing the fuel system, always work in a well
ventilated area. Do not allow fuel spray or
vapors to come in contact with a spark or
open flame. Keep a dry chemical fire extin-
guisher near the work area. Always keep fuel
in a container specifically designed for fuel
storage; also, always properly seal fuel con-
* tainers to avoid the possibility of fire or ex-
plosion.
4. Disconnect the fuel return hose and remove
the O-ring.
5. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel
pressure regulator.
6. Disconnect the PCV hose. On 2.OL engine,
remove the center cover.
1 x Connection for PCV hose
2. Connection for high pressure fuel hose
3. O-ring
4. Connection for vacuum hose
5. Connection for fuel return hose
&2 I=, 1c.1 nrncc*.ra regu,ator
lble clamD
7. Label and detach the electrical connectors
from each iniector.
8. Accelerator ca
9. Center cover . 10. Connection for control harness
11 Fuel rail
12. Insulator
13. Insulator
14. Injector
15. O-ring
16. Grommet
89575g27 Exploded view of the fuel injectors and related
components -1.6L and 2.QL DOHC
5-6 FUELSYSTEM
8. Remove the injector rail retaining bolts, Make
sure the rubber mounting bushings do not get lost.
9. Lift the rail assembly up and away from the
engine.
10. Remove the injectors from the rail by pulling
gently. Discard the lower insulator. Check the resis-
tance through the injector. The specification for 2.OL
turbocharged engine is 2-3 ohms at 70°F (20°C).
The specification for the others is 13-15 ohms at
70°F (20°C). To install:
11. Install a new grommet and O-ring to the in-
jector. Coat the O-ring with light oil.
12. install the injector to the fuel rail.
13. Replace the seats in the intake manifold. In-
stall the fuel rail and injectors to the manifold. Make
sure the rubber bushings are in place before tighten-
ing the mounting bolts.
14. Tighten the retaining bolts to 72 inch lbs. (11
Nm).
Fig. 21 Remove the fuel feed line-to-fuel
rail retaining fitting bolts . . .
15. Attach the connectors to the injectors and in-
stall the center cover. Connect the PCV hose.
16. Connect the fuel pressure regulator vacuum
hose.
17. Connect the fuel return hose.
18. Replace the O-ring, lightly lubricate it and
connect the high pressure fuel line.
19. Connect the negative battery cable and check
the entire system for proper operation and leaks. Fig. 22 . . . then remove the fuel feed line
from the fuel injector rail
2.4L Engine
b See Figures 21 thru 30
Page 194 of 408

FUELSYSTEM 5-7
Fig, 25 Remove the vacuum hose from the Fig. 25 Detach the connectors from all of
pressure regulator the fuel injectors
1 H; :A ..;lt;;aft~rgi,i~;yl the ;F: 1 / . 93155p15 1 Fig 29 Remove the fuel injectors from the
tall by gently rocking them loose Fig. 27 Remove the two fuel rail retaining
bolts . . .
93155ps Fig. 30 Always replace the O-rings on the
injectors before reinstalling them
1. Relieve the fuel system pressure as described
in this section.
2. Label and disconnect the spark plug wires. ’
Position the wires aside.
3. Disconnect the PCV hose from the valve
cover,
4. Remove the bolts holding the high pressure
fuel line to the fuel rail, then disconnect the line. Be
prepared to contain fuel spillage; plug the line to on the workbench; protect the tips of the injectors
from dirt and/or impact.
9. Remove and discard the injector insulators
from the intake manifold. The insulators are not
reusable.
10. Remove the injectors from
pulling gently in a straight outwarc the fuel rail by
I motion. Make cer-
tain the grommet and O-ring come off with the injector. 18. Connect the fuel return hose to the pressure
regulator, then connect the vacuum hose.
19. Replace the O-ring on the high pressure fuel
line, coat the O-ring lightly with clean, thin oil and
install the line to the fuel rail. Tiahten the mountina
To install: -
the fuel system and inspect all connections for leaks. bolts to 4 ft. Ibs. (6 Nm).
20. Connect the PCV hose and spark plug wires.
21. Connect the negative battery cable. Pressurize
1. neneve me rueI system pressure.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable. 3.OL and 3.5L Engines
# See Figures 31 and 32
> - ,. .* , ,
I
I
Work MUST NOT be started until at least 90
seconds after the ignition switch is turned to
the LOCK position and the negative battery
cable is disconnected from the battery. This
will allow time for the air bag system backup
power supply to deplete its stored energy,
preventing accidental air bag deployment
which could result in unnecessary air bag
system repairs and/or personal injury.
3. Drain the cooling system.
4. Disconnect all components from the air in-
take plenum and remove the plenum from the intake
manifold. Refer to Section 3.
5. Wrap the connection with a shop towel and
disconnect the high pressure fuel line at the fuel rail. keep out dirt and debris.
Observe all applicable safety precautions
when working around fuel. Whenever servic-
ing the fuel system, always work in a well
ventilated area. Do not allow fuel spray or
vapors to come in contact with a spark or
open flame. Keep a dry chemical fire extin-
guisher near the work area. Always keep fuel
in a container specifically designed for fuel
storage; also, always properly seal fuel con-
tainers to avoid the possfbility of fire or ex-
plosion.
5. Remove the vacuum hose from the fuel pres-
sure regulator.
6. Disconnect the fuel return hose from the
pressure regulator.
7. Label and detach the electrical connectors
from each injector.
8. Remove the bolt(s) holding the fuel rail to the
manifold. Carefully lift the rail up and remove it with
the injectors attached. Take great care not to drop an
injector. Place the rail and injectors in a safe location 11. Install a new insulator in each injector port in
the manifold.
12. Remove the old grommet and D-ring from
each injector. Install a new grommet and O-ring; coat
the O-ring lightly with clean, thin oil.
13. If the fuel pressure regulator was removed, re-
place the O-ring with a new one and coat it lightly with
clean, thin oil. Insert the regulator straight into the rail,
then check that it can be rotated freely. If it does not ro-
tate smoothly, remove it and inspect the O-ring for de-
formation or jamming. When properly installed, align
the mounting holes and tighten the retaining bolts to 7
ft. Ibs. (9 Nm). This procedure must be followed even if
the fuel rail was not removed.
14. Install the injector into the fuel rail, constantly
turning the injector left and right during installation.
When fully installed, the injector should still turn
freely in the rail. If it does not, remove the injector
and inspect the O-ring for deformation or damage.
15. Install the delivery pipe and injectors to the
engine. Make certain that each injector fits correctly
into its port and that the rubber insulators for the fuel
rail mounts are in position.
16. Install the fuel rail retaining bolts and tighten
them to 9 ff. Ibs. (12 Nm).
17. Connect the wiring harnesses to the appro-
priate injector.