1900 MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: oil pressurePage 333 of 408
SUSPENSION AND STEERING 8-37
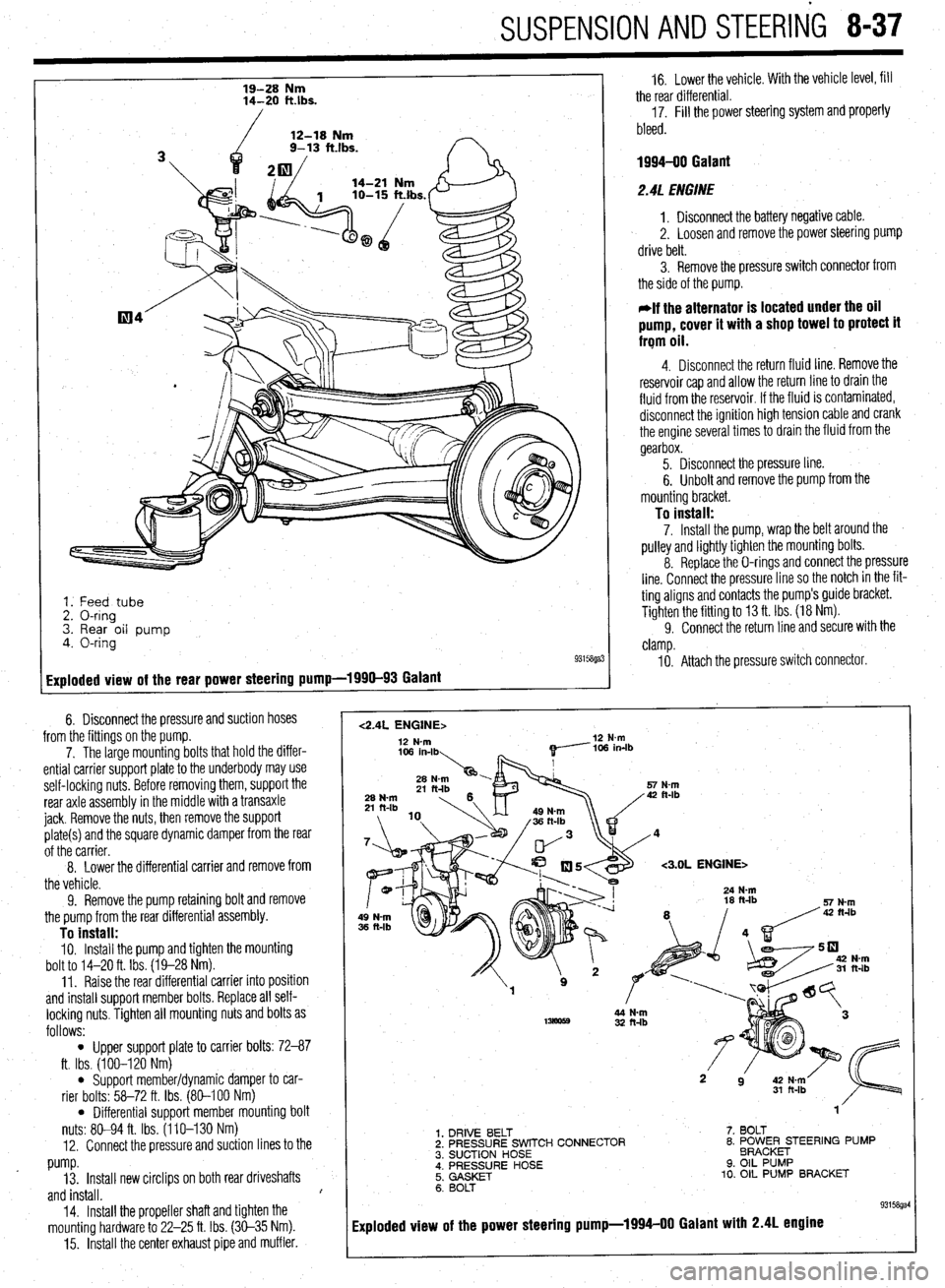
19-28 Nm
14-20 klbs.
/
12-18 Nm
9- 13 ft.lbs.
2rd
,
1. Feed tube
2. O-ring
3. Rear oil pump
4. O-ring
93158ga:
Exploded view of the rear power steering pump-1990-93 Galant
6. Disconnect the pressure and suction hoses
from the fittings on the pump.
7. The large mounting bolts that hold the differ-
ential carrier support plate to the underbody may use
self-locking nuts. Before removing them, support the
rear axle assembly in the middle with a transaxle
jack. Remove the nuts, then remove the support
plate(s) and the square dynamic damper from the rear
of the carrier.
8. Lower the differential carrier
and remove from
the vehicle.
9. Remove the pump retaining bolt and remove
the pump from the rear differential assembly.
To install: IO. Install the pump and tighten the mounting
bolt to 14-20 ft. Ibs. (19-28 Nm).
11. Raise the rear differential carrier into position
and install support member bolts. Replace all self-
locking nuts. Tighten all mounting nuts and bolts as
follows:
l Upper support plate to carrier bolts: 72-87
ft. Ibs. (100-120 Nm)
l Support member/dynamic damper to car-
rier bolts: 58-72 ft. Ibs. (80-100 Nm)
l Differential support member mounting bolt
nuts: 80-94 ft. Ibs. (110-130 Nm)
12. Connect the pressure and suction lines to the
pump.
13. Install new circlips on both rear driveshafts
and install. I
14.
Install the propeller shaft and tighten the
mounting hardware to 22-25 ft. Ibs. (30-35 Nm).
15. Install the center exhaust pipe and muffler.
1
16. Lower the vehicle. With the vehicle level, fill
the rear differential.
17. Fill the power steering system and properly
bleed.
1994-00 Galant
2.4L ENGINE
1. Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2. Loosen and remove the power steering pump
drive belt.
3. Remove the pressure switch connector from
the side of the pump.
*If the alternator is located under the oil
pump, cover it with a shop towel to protect it
frqm oil.
4. Disconnect the return fluid line. Remove the
reservoir cap and allow the return line to drain the
fluid from the reservoir. If the fluid is contaminated,
disconnect the ignition high tension cable and crank
the engine several times to drain the fluid from the
gearbox.
5. Disconnect the pressure line.
6. Unbolt and remove the pump from the
mounting bracket.
To install: 7. Install the pump, wrap the belt around the
pulley and lightly tighten the mounting bolts.
8. Replace the O-rings and connect the pressure
line. Connect the pressure line so the notch in the fit-
ting aligns and contacts the pump’s guide bracket.
Tighten the fitting to 13 ft. Ibs. (18 Nm).
9. Connect the return line and secure with the
clamp.
IO. Attach the pressure switch connector.
<2.4L ENGINE> 12 N-m 12 N-m
<3.OL ENGINE>
32 ft-lb
1. DRIVE BELT
2. PRESSURE SWITCH CONNECTOR
3. SUCTION HOSE
; i’;;‘;;RE HOSE 7. BOLT
8. ~O~~~E;TEER’NG PUMP
9. OIL PUMP
10. OIL PUMP BRACKET
6. BOLT
93158gal
Exploded view of the power steering pump-1994-00 Galant with 2.4L engine
Page 334 of 408
- 8-38 SUSPENSION AND STEERING
11. Adjust the power steering belt for proper ten-
sion and tighten the adjusting bolts.
12. Reconnect the negative battery cable.
13. Refill the reservoir and bleed the system.
3. Of EIJGINE
1. Disconnect the battery negative cable. 2. Disconnect the return fluid line. Remove the
reservoir cap and allow the return line to drain the
fluid from the reservoir. If the fluid is contaminated,
disconnect the ignition high tension cable and crank
the engine several times to drain the fluid from the
gear box.
3. Remove the power steering pump drive belt.
4. Remove the pressure switch connector from
the side of the pump.
5. If the alternator is located under the oil pump,
cover it with a shop towel to protect it from oil.
6. Disconnect the high pressure hose and the
return hose from the pump.
7. Remove the pump drive belt and unbolt the
pump from its bracket and remove the pump.
To install: 8. Install the pump, *rap the belt around the
pulley and tighten the bolts that secure the pump to
17 ft. Ibs. (24 Nm).
9. Replace the O-rings and connect the high
pressure hose. Connect the pressure line so the
notch in the fitting aligns and contacts the pump’s
guide bracket. Tighten the mounting nut with lock-
washer to 17 ft. Ibs. (24 Nm).
IO. Using a new hose clamp, connect the return
line.
11. Attach the pressure switch connector.
12. Adjust the belt tension and tighten the
adjust- ing bolts.
13. Refill the reservoir and bleed the system.
Diamante *
FRONT
. 1. Disconnect the battery negative cable. 2. Disconnect the return fluid line. Remove the
reservoir cap and allow the return line to drain the
fluid from the reservoir. If the fluid is contaminated,
disconnect the ignition high tension cable and crank
the engine several times to drain the fluid from the
gearbox.
3. Remove the power steering pump drive belt.
4. Remove the pressure switch connector from
the side of the pump.
5. If the alternator is located under the oil pump,
cover it with a shop towel to protect it from oil.
6. Disconnect the high pressure hose and the
return hose from the pump.
7. Remove the pump drive belt and unbolt the
pump from its bracket and remove the pump.
To install: 8. Install the pump, wrap the belt around the
pulley and tighten the bolts that secure the pump to
17 ft. Ibs. (24 Nm).
9. Replace the O-rings and connect the high
pressure hose. Connect the pressure line so the
notch in the fitting aligns and contacts the pump’s
guide bracket. Tighten the mounting nut with lock-
washer to 17 ft. Ibs. (24 Nm).
10. Using a new hose clamp, connect the return
line.
Il. Attach the pressure switch connector.
12. Adjust the belt tension and tighten the adjust-
ing bolts.
13. Refill the reservoir and bleed the system.
REAR
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Drain the power steering fluid.
3. Remove the rear power steering pump heat
protector, located on the engine side of the differen-
tial on the transaxle.
4. Disconnect the pressure line from the pump.
5. Disconnect the suction hose from the pump.
6. Remove the mounting bolts and remove the
pump from the transaxle.
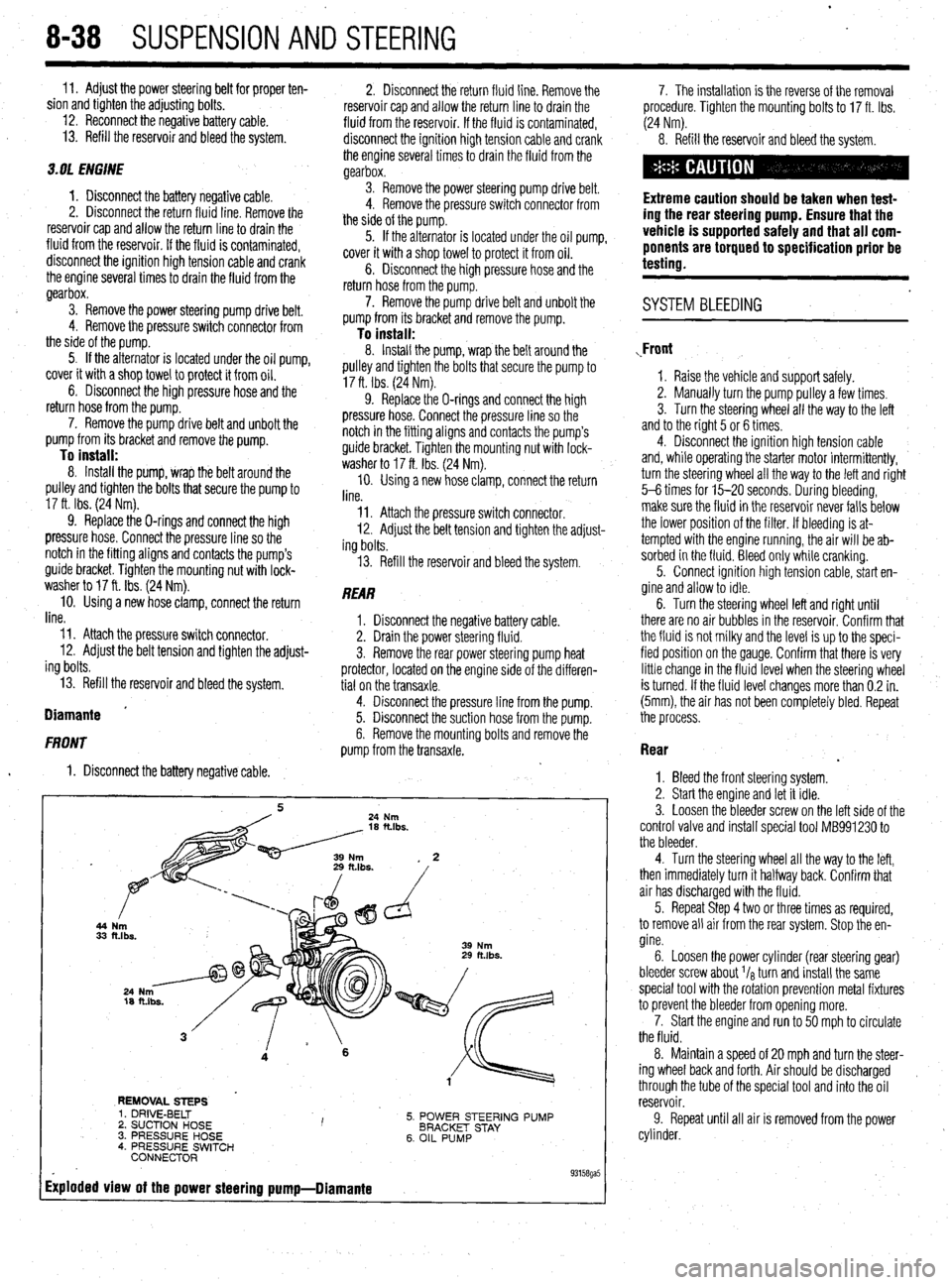
44
33
REMOVAL STEPS
5. POWER STEERING PUMP
BRACKET STAY
6. OIL PUMP 1. DRIVE-BELT
2. SUCTION HOSE I ’ 3. PRESSURE HOSE
4. PRESSURE SWITCH
CONNECTOR
Exploded view of the power steering pump-Diamante
. 93158ga5
7. The installation is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Tighten the mounting bolts to 17 ft. Ibs.
(24 Nm).
8. Refill the reservoir and bleed the system.
Extreme caution should be taken when test-
ing the rear steering pump. Ensure that the
vehicle is supported safely and that all com-
ponents are torqued to specification prior be
testing.
. SYSTEM BLEEDING
,Front
1. Raise the vehicle and support safely.
2. Manually turn the pump pulley a few times.
3. Turn the steering wheel all the way to the left
and to the right 5 or 6 times.
4. Disconnect the ignition high tension cable
and, while operating the starter motor intermittently,
turn the steering wheel all the way to the letI and right
5-6 times for 15-20 seconds. During bleeding,
make sure the fluid in the reservoir never falls below
the lower position of the filter. If bleeding is at-
tempted with the engine running, the air will be ab-
sorbed in the fluid. Bleed only while cranking.
5. Connect ignition high tension cable, start en-
gine and allow to idle.
6. Turn the steering wheel left and right until
there are no air bubbles in the reservoir. Confirm that
the fluid is not milky and the level is up to the speci-
fied position on the gauge. Confirm that there is very
little change in the fluid level when the steering wheel
is turned. If the fluid level changes more than 0.2 in.
(5mm), the air has not been completely bled. Repeat
the process.
Rear
.
1. Bleed the front steering system.
2. Start the engine and let it idle.
3. Loosen the bleeder screw on the left side of the
control valve and install special tool MB991230 to
the bleeder.
4. Turn the steering wheel all the way to the left,
then immediately turn it halfway back. Confirm that
air has discharged with the fluid.
5. Repeat Step 4 two or three times as required,
to remove all air from the rear system. Stop the en-
gine.
6. Loosen the power cylinder (rear steering gear)
bleeder screw about I/* turn and install the same
special tool with the rotation prevention metal fixtures
to prevent the bleeder from opening more.
7. Start the engine and run to 50 mph to circulate
the fluid.
8. Maintain a speed of 20 mph and turn the steer-
ing wheel back and forth. Air should be discharged ,
through the tube of the special tool and into the oil
reservoir.
9. Repeat until all air is removed from the power
cylinder.
Page 360 of 408

9-24 BRAKES
Shoe-to-anchor spring (rear)
e Forward
69579946 Fig. 114 Shoe-to-anchor spring installation
*When servicing drum
brakes, only dissem-
ble and assemble one side at a time, leaving
the remaining side intact for reference.
4. Remove the front and rear shoe-to-anchor
springs.
5. Remove the adjusting wheel spring and the
adjuster.
6. Remove the strut and the strut return spring.
7. Remove the shoe hold-down cup, spring and
pin.
8. Remove the shoe and lining assembly.
9. Unfasten the clips and the retaining bolts,
then remove the parking brake cable(s).
To install: 10. Installation is the reverse of the removal pro-
cedure.
11. Install the adjuster so the shoe adjusting bolt
of the left hand wheel is attached toward the front of the vehicle and the shoe adjusting bolt of the right
hand wheel is toward the rear of the vehicle. -
12. The load on the respective shoe-to-anchor
springs is different, so the spring in the figure has
hen painteb, a> shm in the a~~0mparrying figure.
1997-00 Diamante
‘) See Figure 115
1. Raise and safely support the vehicle securely
on jackstands.
2. Remove the caliper assembly.
3. Remove the rear brake rotor.
*When servicing drum brakes, only dissem-
ble and assemble one side at a time, leaving
the remaining side intact for reference.
4. Remove the shoe hold-down spring retaining
screw.
5. Remove the shoe hold-down spring.
6. Remove the shoe assembly from the backing
plate.
7. The installation is the reverse of removal.
ADJUSTMENT
1. Remove the floor console, release the lever
and back off the cable adjuster locknut at the base of
the lever.
2. Raise the vehicle, support safely and remove
the wheel. 3. Remove the hole plug in the brake rotor.
4. Remove the brake caliper and hang out of the
way with wire. Do not disconnect the fluid line.
5. Use a suitable prybar to pry up on the self-ad-
juskr V&I&I unti tie T&IT wi\ not tirn.
6. Return the adjuster 5 notches in the opposite
direction. Make sure the rotor turns freely with a
slight drag.
7. Install the caliper and check operation.
9. Shoe 93159go3 Fig. 115 Exploded view of the parking brake
shoes and related components-l 997-00
Diamante
The 4-Wheel Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) is an
electronically operated, all wheel brake control sys-
tem. Major components include the vacuum power
brake booster, master cylinder, the wheel speed sen-
sors, the Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU), Anti-lock
control unit, a relay, and on the AWD Galant, a G sen-
sor.
The system is designed to retard wheel lockup
during periods of high wheel slip when braking. Re-
tarding wheel lockup is accomplished by modulating
fluid pressure to the wheel brake units. When the
control unit detects a variation in voltage across the
wheel speed sensors, the ABS is activated. The con-
trol unit opens and closes various valves located in-
side the HCU. These valves, called dump and isola-
tion valves, modulate the hydraulic pressure to the
wheels by applying and venting the pressure to the
brake fluid circuits.
PRECAUTIONS
l Certain components within the Anti-Lock Brake
System (ABS) are not intended to be serviced or re-
paired individually. Only those components with re- !
moval and installation procedures should be ser-
viced.
0 Do not use rubber hoses or other parts not
specifically specified for an ABS system. When using
repair kits, replace all parts included in the kit. Partial
or incorrect repair may lead to functional problems
and require the replacement of components.
l Lubricate rubber parts with clean, fresh brake
fluid to ease assembly. Do not use lubricated shop air
to clean parts; damage to rubber components may re-
sult.
l Use only specified brake fluid from an un-
opened container.
l If any hydraulic component or line is removed
or replaced, it may be necessary to bleed the entire
system.
l A clean repair area is essential. Always clean
the reservoir and cap thoroughly before removing the
cap. The slightest amount of dirt in the fluid may plug
an orifice and impair the system function. Perform re-
pairs after components have been thoroughly
cleaned; use only denatured alcohol to clean compo-
nents. Do not allow ABS components to come into
contact with any substance containing mineral oil;
this includes used shop rags.
l The Anti-Lock control unit is a microprocessor
similar to other computer units in the vehicle. Ensure
that the ignition switch is
OFF before removing or in-
stalling controller harnesses. Avoid static electricity
discharge at or near the controller.
l If any arc welding is to be done on the vehicle,
the control unit should be unplugged before welding
operations begin.
) See Figures 116 thru 123
The diagnosis of the ABS system is rather complex
and requires quite a few special tools including scan tools, special test harnesses and other special and
expensive tools. Alternative methods and common
sense can be substituted, however, We at Chilton feel
that it is beyond the scope of the average do-it-your-
selfer. If you experience the amber ANTI LOCK light
on in the instrument cluster of your vehicle, check the
fluid level in the master cylinder first. Low fluid level
will usually illuminate the red BRAKE lamp in the in-
strument cluster as well as, but not always, the amber
ANTI LOCK lamp in the instrument cluster. The low
fluid level could indicate a leak, but sometimes just
indicates low, worn brake linings that have caused the
caliper pistons and wheel cylinders to extend further,
and thus using more fluid to exert force on them. In-
spect the brake system for hydraulic fluid leaks and
also inspect the brake linings for excessive wear.
89579956 Fig. 116 You can connect a scan tool to the
data link connector to retrieve ABS trouble
codes
Page 383 of 408

TROUBLESHOOTING INDEX 11-2
SECTION 1: ENGINE 11-2
SECTION 2: DRIVE TRAIN
11-3
SECTION 3:BRAKESYSTEM 11-3
SECTION 4:WHEELS,TIRES, STEERING,
AND SUSPENSION II-4
SECTION 5: ELECTRICAL
ACCESSORIES II-4
SECTION 6:lNSTRUMENTSAND
GAUGES II-5
SECTION 7:CLlMATE CONTROL II-5
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES II-6
SECTION 1: ENGINE II-6
ENGINE STARTING PROBLEMS II-6
ENGINE RUNNING CONDITIONS II-7
ENGINE NOISES,ODORSAND
VIBRATIONS II-8
ENGINE ELECTRICALSYSTEM 11-8
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM II-8
ENGINE EXHAUSTSYSTEM II-9
SECTION 2: DRIVE TRAIN
II-9
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION II-9
MANUALTRANSMISSION II-10
CLUTCH II-10
DIFFERENTIAL AND FINAL
DRIVE II-10
TRANSFER ASSEMBLY II-10
DRIVESHAFT II-10
AXLES II-II
OTHER DRIVE TRAIN
CONDITIONS II-II
SECTION 3:BRAKE SYSTEM II-II
BRAKESYSTEM
TROUBLESHOOTING II-II
SECTION 4:WHEELS, TIRES, STEERING
AND SUSPENSION II-12
WHEELSAND WHEEL
BEARINGS II-12
TIRES II-12
STEERING II-12
SUSPENSION II-12
DRIVING NOISES AND
VIBRATIONS II-13
SECTION 5:ELECTRlCAL
ACCESSORIES II-13 -
HEADLIGHTS II-13
TAIL, RUNNING AND SIDE MARKER
LIGHTS II-13
INTERIOR LIGHTS II-14
BRAKE LIGHTS II-14
WARNING LIGHTS II-14
TURN SlGNALAND4-WAYHAZARD
LIGHTS II-15
WINDSHIELD WIPERS II-15
SECTION 6:lNSTRUMENTSAND
GAUGUES II-15
I
SPEEDOMETER(CABLE
OPERATED) II-15
SPEEDOMETER(ELECTRONICALLY
OPERATED) II-16
FUEL,TEMPERATUREAkJD OIL
PRESSURE GAUGES II-16 SECTION 7:CLlMATECON
AIR CONDITIONER ll-
HEATER II-16 TR(
-16 IL II-16
Page 387 of 408

.
TROUBLESHOOTING II-5
Condition Section/Item Number
One brake light inoperative
Both brake lights inoperative
One or both brake lights very dim 5-D, 1
5-D, 2
5-D, 3
Ignition, Battery and Alternator Warning Lights, Check Engine
Light, Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) Light, Brake Warning
Light, Oil Pressure Warning Light, and Parking Brake Warning
Light
Warning light(s) remains on after the engine is started
Warning light(s) flickers on and off when driving
Warning light(s) inoperative with ignition on, and engine not started 5-E, 1
5-E, 2
5-E, 3
Turn signals or hazard lights come on, but do not flash
Turn signals or hazard lights do not function on either side
Turn signals or hazard lights only work on one side
One signal light does not work
Turn signals flash too slowly
Turn signals flash too fast
Four-way hazard flasher indicator light inoperative
Turn signal indicator light(s) do not work in either direction
One turn signal indicator light does not work 5-F, 1
5-F, 2
5-F, 3
5-F, 4
5-F, 5
5-F, 6
5-F, 7
5-F, 8
5-F, 9
Horn does not operate
Horn has an unusual tone 5-G, 1
5-G, 2
Windshield wipers do not operate
Windshield wiper motor makes a humming noise, gets hot or blows fuses
Windshield wiper motor operates but one or both wipers fail to move
Windshield wipers will not park 5-H, 1
5-H, 2
5-H, 3
5-H, 4
Speedometer does not work
Speedometer needle fluctuates when driving at steady speeds
Speedometer works intermittently 6-A, 1
6-A, 2
6-A, 3
Speedometer does not work
Speedometer works intermittently 6-B, 1
6-B, 2
Gauge does not register 6-C 1
Gauge operates erratically 6-C 2
’
Gauge operates fully pegged 6-C 3
No air coming from air conditioner vents 7-A, 1
Air conditioner blows warm air ’ 7-A, 2
Water collects on the interior floor when the air conditioner is used
Air conditioner has a moldy odor when used 7-A, 3
7-A, 4
Blower motor does not operate
Heater blows cool air
Heater steams the windshield when used 7-B, 1
7-B, 2
7-B, 3
Page 388 of 408

II-6 TROUBLESHOOTING
DIAGhUSTIC PROCEDURES
Gasoline Engines
1. Engine turns over, but wilt not start
a. Check fuel level in fuel tank, add fuel if empty.
b. Check battery condition and state of charge. If voltage and load test below specifica-
tion, charge or replace battery.
c. Check battery terminal and cable condition and tightness. Clean terminals and replace
damaged, worn or corroded cables.
d. Check fuel delivery system. If fuel is not reaching the fuel injectors, check for a loose
electrical connector or defective fuse, relay or fuel pump and replace as necessary.
e. Engine may have excessive wear or mechanical damage such as low cylinder cranking
pressure, a broken camshaft drive system, insufficient valve clearance or bent valves.
f. Check for fuel contamination such as water in the fuel. During winter months, the wa-
ter may freeze and cause a fuel restriction. Adding a fuel additive may help, however
the fuel system may require draining and purging with fresh fuel.
g. Check for ignition system failure. Check for loose or shorted wires or damaged igni-
tion system components. Check the spark plugs for excessive wear or incorrect elec-
trode gap. If the problem is worse in wet weather, check for shorts between the spark
plugs and the ignition coils.
h. Check the engine management system for a failed sensor or control module.
2. Engine does not turn over when attempting to start
a. Check the battery state of charge and condition. If the dash lights are not visible or
very dim when turning the ignition key on, the battery has either failed internally or
discharged, the battery cables are loose, excessively corroded or damaged, or the al-
ternator has failed or internally shorted, discharging the battery. Charge or replacethe
battery, clean or replace the battery cables, and check the alternator output.
b. Check the operation of the neutral safety switch. On automatic transmission vehicles,
try starting the vehicle in both Park and Neutral. On manual transmission vehicles, de-
press the clutch pedal and attempt to start. On some vehicles, these switches can be
adjusted. Make sure the switches or wire connectors are not loose or damaged. Re-
place or adjust the switches as necessary.
c. Check the starter motor, starter solenoid or relay, and starter motor cables and wires.
Check the ground from the engine to the chassis. Make sure the wires are not loose,
damaged, or corroded. If battery voltage is present at the starter relay, try using a re-
mote starter to start the vehicle for test purposes only. Replace any damaged or cor-
roded cables, in addition to replacing any failed components.
d. Check the engine for seizure. If the engine has not been started for a long period of
time, internal parts such as the rings may have rusted to the cylinder walls. The engine
may have suffered internal damage, or could be hydro-locked from ingesting water.
Remove the spark plugs and carefully attempt to rotate the engine using a suitable
breaker bar and socket on the crankshaft pulley. If the engine is resistant to moving, or
moves slightly and then binds, do not force the engine any further before determining
the problem.
3. Enpine stalls immediately when started
a. Check the ignition switch condition and operation. The electrical contacts in the run
position may be worn or damaged. Try restarting the engine with all electrical acces-
sories in the off position. Sometimes turning the key on an off will help in emergency
situations, however once the switch has shown signs of failure, it should be replaced
as soon as possible.
b. Check for loose, corroded, damaged or shorted wires for the ignition system and re-
pair or replace.
c. Check for manifold vacuum leaks or vacuum hose leakage and repair or replace parts
as necessary.
d. Measure the fuel pump delivery volume and pressure. Low fuel pump pressure can
also be noticed as a lack of power when accelerating. Make sure the fuel pump lines
are not restricted. The fuel pump output is not adjustable and requires fuel pump re-
placement to repair.
e. Check the engine fuel and ignition management system. Inspect the sensor wiring and
electrical connectors. A dirty, loose or damaged sensor or control module wire can
simulate a failed component.
f. Check the exhaust system for internal restrictions.
4. Starter motor spins, but does not engage
a. Check the starter motor for a seized or binding pinion gear.
b. Remove the flywheel inspection plate and check for a damaged ring gear.
5. Engine is difficult to start when Gold
a. Check the battery condition, battery state of charge and starter motor current draw. Re-
place the battery if marginal and the starter motor if the current draw is beyond specifi-
cation. b. Check the battery cable condition. Clean the battery terminals and replace corroded or
damaged cables.
c. Check the fuel system for proper operation. A fuel pump with insufficient fuel pressure
or clogged injectors should be replaced.
d. Check the engine’s tune-up status. Note the tune-up specifications and check for items
such as severely worn spark plugs; adjust or replace as needed. On vehicles with
manually adjusted valve clearances, check for tight valves and adjust to specification.
e. Check for a failed coolant temperature sensor, and replace if out of specification.
f. Check the operation of the engine management systems for fuel and ignition; repair or
replace failed components as necessary.
6. En#ine is ditticutt to start when hot
a. Check the air filter and air intake system. Replace the air filter if it is dirty or contami-
nated. Check the fresh air intake system for restrictions or blockage.
b. Check for loose or deteriorated engine grounds and clean, tighten or replace as
needed.
c. Check for needed maintenance. Inspect tune-up and service related items such as
spark plugs and engine oil condition, and check the operation of the engine fuel and
ignition management system.
Diesel Engines
1. Engine turns over but won’t start
a. Check engine starting procedure and restart engine.
b. Check the glow plug operation and repair or replace as necessary.
c. Check for air in the fuel system or fuel filter and bleed the air as necessary.
d. Check the fuel delivery system and repair or replace as necessary.
e. Check fuel level and add fuel as needed.
f. Check fuel quality. If the fuel is contaminated, drain and flush the fuel tank.
g. Check engine compression. If compression is below specification, the engine may
need to be renewed or replaced.
h. Check the injection pump timing and set to specification.
i. Check the injection pump condition and replace as necessary.
j. Check the fuel nozzle operation and condition or replace as necessary.
2. Engine does
hot turn over when attempting to start
a. Check the battery state of charge and condition. If the dash lights are not visible or
very dim when turning the ignition key on, the battery has either failed internally or
discharged, the battery cables are loose, excessively corroded or damaged, or the al-
ternator has failed or internally shorted, discharging the battery. Charge or replace the
battery, clean or replace the battery cables, and check the alternator output.
b. Check the operation of the neutral safety switch. On automatic transmission vehicles,
try starting the vehicle in both Park and Neutral. On manual transmission vehicles, de-
press the clutch pedal and attempt to start. On some vehicles, these switches can be
adjusted. Make sure the switches or wire connectors are not loose or damaged. Re-
place or adjust the switches as necessary.
c. Check the starter motor, starter solenoid or relay, and starter motor cables and wires.
Check the ground from the engine to the chassis. Make sure the wires are not loose,
damaged, or corroded. If battery voltage is present at the starter relay, try using a re-
mote starter to start the vehicle for test purposes only. Replace any damaged or cor-
roded cables, in addition to replacing any failed components.
d. Check the engine for seizure. If the engine has not been started for a long period of
time, internal parts such as the rings may have rusted to the cylinder walls. The engine
may have suffered internal damage, or could be hydro-locked from ingesting water.
Remove the injectors and carefully attempt to rotate the engine using a suitable
breaker bar and socket on the crankshaft pulley. If the engine is resistant to moving, or
moves slightly and then binds, do not force the engine any further before determining
the cause of the problem.
3. Engine stalls afier starting
a. Check for a restriction in the fuel return line or the return line check valve and repair as
necessary.
b. Check the glow plug operation for turning the glow plugs off too soon and repair as
necessary.
c. Check for incorrect injection pump timing and reset to specification.
d. Test the engine fuel pump and replace if the output is below specification.
e. Check for contaminated or incorrect fuel. Completely flush the fuel system and replace
with fresh fuel.
f. Test the engine’s compression for low compression. If below specification, mechanical
repairs are necessary to repair.
g. Check for air in the fuel. Check fuel tank fuel and fill as needed.
h. Check for a failed injection pump. Replace the pump, making sure to properly set the
pump timing.
Page 389 of 408

TROUBLESHOOiNG 11-7
4. Starter motor spins, but does not engage
a. Check the starter motor for a seized or binding pinion gear.
b. Remove the flywheel inspection plate and check for a damaged ring gear.
Gasoline Engines
1. Engine runs poor/y, hesiiates
a. Check the engine ignition system operation and adjust if possible, or replace defective
parts.
b. Check for restricted fuel injectors and replace as necessary.
c. Check the fuel pump output and delivery. Inspect fuel lines for restrictions. If the fuel
pump pressure is below specification, replace the fuel pump.
d. Check the operation of the engine management system and repair as necessary.
2. Enfline lacks power
a. Check the engine’s tune-up status. Note the tune-up specifications and check for items
such as severely worn spark plugs; adjust or replace as needed. On vehicles with
manually adjusted valve clearances, check for tight valves and adjust to specification.
b. Check the air filter and air intake system. Replace the air filter if it is dirty or contami-
nated. Check the fresh air intake system for restrictions or blockage.
c. Check the operation of the engine fuel and ignition management systems. Check the
sensor operation and wiring. Check for low fuel pump pressure and repair or replace
components as necessary.
d. Check the throttle linkage adjustments. Check to make sure the linkage is fully open-
ing the throttle. Replace any worn or defective bushings or linkages.
e. Check for a restricted exhaust system. Check for bent or crimped exhaust pipes, or in-
ternally restricted mufflers or catalytic converters. Compare inlet and outlet tempera-
tures for the converter or muffler. If the inlet is hot, but outlet cold, the component is
restricted.
f. Check for a loose or defective knock sensor. A loose, improperly torqued or defective
knock sensor will decrease spark advance and reduce power. Replace defective knock
sensors and install using the recommended torque specification.
g. Check for engine mechanical conditions such as low compression, worn piston rings,
worn valves, worn camshafts and related parts. An engine which has severe mechani-
cal wear, or has suffered internal mechanical damage must be rebuilt or replaced to re-
store lost power.
h. Check the engine oil level for being overfilled. Adjust the engine’s oil level, or change
the engine oil and filter, and top off to the correct level.
i. Check for an intake manifold or vacuum hose leak. Replace leaking gaskets or worn
vacuum hoses.
j. Check for dragging brakes and replace or repair as necessary.
k. Check tire air pressure and tire wear. Adjust the pressure to the recommended set-
tings. Check the tire wear for possible alignment problems causing increased rolling
resistance, decreased acceleration and increased fuel usage.
I. Check the octane rating of the fuel used during refilling, and use a higher octane rated
fuel.
3. Poor fuel economy
a. Inspect the air filter and check for any air restrictions going into the air filter housing.
Replace the air filter if it is dirty or contaminated.
b. Check the engine for tune-up and related adjustments. Replace worn ignition parts,
check the engine ignition timing and fuel mixture, and set to specifications if possible.
c. Check the tire size, tire wear, alignment and tire pressure. Large tires create more
rolling resistance, smaller tires require more engine speed to maintain a vehicle’s road
speed. Excessive tire wear can be caused by incorrect tire pressure, incorrect wheel
alignment or a suspension problem. All of these conditions create increased rolling
resistance, causing the engine to work harder to accelerate and maintain a vehicle’s
speed.
d. Inspect the brakes for binding or excessive drag. A sticking brake caliper, overly ad-
justed brake shoe, broken brake shoe return spring, or binding parking brake cable or
linkage can create a significant drag, brake wear and loss of fuel economy. Check the
brake system operation and repair as necessary.
4. Engine runs on (diesels) when turned off
a. Check for idle speed set too high and readjust to specification.
b. Check the operation of the idle control valve, and replace if defective.
c. Check the ignition timing and adjust to recommended settings.
Check for defective
sensors or related components and replace if defective.
d. Check for a vacuum leak at the intake manifold or vacuum hose
and replace defective
gaskets or hoses.
e. Check the engine for excessive carbon build-up in the combustion chamber. Use a
recommended decarbonizing fuel additive or disassemble the cylinder head to remove
the carbon.
f. Check the operation of the engine fuel management system and replace defective sen-
sors or control units.
g. Check the engine operating temperature for overheating and repair as necessary. 5. Engine knocks and pinfls during heavy accele/ation, and on steep hills
a. Check the octane rating of the fuel used during refilling, and use a higher octane rated
fuel.
b. Check the ignition timing and adjust to recommended settings. Check for defective
sensors or related components and replace if defective.
c. Check the engine for excessive carbon build-up in the combustion chamber. Use a
recommended decarbonizing fuel additive or disassemble the cylinder head to remove
the carbon.
d. Check the spark plugs for the correct type, electrode gap and heat range. Replace worn
or damaged spark plugs. For severe or continuous high speed use, install a spark plug
that is one heat range colder.
e. Check the operation of the engine fuel management system and replace defective sen-
sors or control units.
f. Check for a restricted exhaust system. Check for bent or crimped exhaust pipes, or in-
ternally restricted mufflers or catalytic converters. Compare inlet and outlet tempera-
tures for the converter or muffler. If the inlet is hot, but outlet cold, the component is
restricted.
6. Engine atxelerates, but vehicle does not gain speed
a. On manual transmission vehicles, check for causes of a slipping clutch. Refer to the
clutch troubleshooting section for additional information.
b. On automatic transmission vehicles, check for a slipping transmission” Check the
transmission fluid level and condition. If the fluid level is too high, adjust to the cor-
rect level. If the fluid level is low, top off using the recommended fluid type. If the fluid
exhibits a burning odor, the transmission has been slipping internally. Changing the
fluid and filter may help temporarily, however in this situation a transmission may re-
quire overhauling to ensure long-term reliability.
Diesel Engines
1. Engine runs pOOr!y a. Check the injection pump timing and adjust to specification.
b. Check for air in the fuel lines or leaks, and bleed the air from the fuel system.
c. Check the fuel filter, fuel feed and return lines for a restriction and repair as necessary.
d. Check the fuel for contamination, drain and flush the fuel tank and replenish with fresh
fuel.
2. Enfline lacks power
a. Inspect the air intake system and air filter for restrictions and, if necessary, replace the
air filter.
b. Verify the injection pump timing and reset if out of specification.
c. Check the exhaust for an internal restriction and replace failed parts.
d. Check for a restricted fuel filter and, if restricted, replace the filter.
e. Inspect the fuel filler cap vent. When removing the filler cap, listen for excessive hiss-
ing noises indicating a blockage in the fuel filler cap vents, If the filler cap vents are
blocked, replace the cap.
f. Check the fuel system for restrictions and repair as necessary.
g. Check for low engine compression and inspect for external leakage at the glow plugs
or nozzles. If no external leakage is noted, repair or replace the engine.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS When troubleshooting an engine running or performance condition, the mechanical
condition of the engine should be determined before lengthy troubleshooting procedures
are performed.
The engine fuel management systems in fuel injected vehicles rely on electronic sen-
sors to provide information to the engine control unit for precise fuel metering. Unlike
carburetors, which use the incoming air speed to draw fuel through the fuel metering jets
in order to provide a proper fuel-to-air ratio, a fuel injection system provides a specific
amount of fuel which is introduced by the fuel injectors into the intake manifold or intake
port, based on the information provided by electronic sensors.
The sensors monitor the engine’s operating temperature, ambient temperature and the
amount of air entering the engine, engine speed and throttle position to provide informa-
tion to the engine control unit, which, in turn, operates the fuel injectors by electrical
pulses. The sensors provide information to the engine control unit using low voltage
electrical signals. As a result, an unplugged sensor or a poor electrical contact could
cause a poor running condition similar to a failed sensor.
When troubleshooting a fuel related engine condition on fuel injected vehicles, care-
fully inspect the wiring and electrical connectors to the related components. Make sure
the electrical connectors are fully connected, clean and not physically damaged. If neces-
sary, clean the electrical contacts using electrical contact cleaner. The use of cleaning
agents not specifically designed for electrical contacts should not be used, as they could
leave a surface film or damage the insulation of the wiring.
The engine electrical system provides the necessary electrical power to operate the ve-
hicle’s electrical accessories, electronic control units and sensors. Because engine man-
agement systems are sensitive to voltage changes, an alternator which over or under-
charges could cause engine running problems or component failure. Most alternators
utilize internal voltage regulators which cannot be adjusted and must be replaced indi-
vidually or as a unit with the alternator.
Page 390 of 408

11-8 TROUBLESHOOTING
Ignition systems may be controlled by, or linked to, the engine fuel management sys-
tem. Similar to the fuel injection system, these ignition systems rely on electronic sen-
sors for information to determine the optimum ignition timing for a given engine speed
and load. Some ignition systems no longer allow the ignition timing to be adjusted.
Feedback from low voltage electrical sensors provide information to the control unit to
determine the amount of ignition advance. On these systems, if a failure occurs the failed
component must be replaced. Before replacing suspected failed electrical components,
carefully inspect the wiring and electrical connectors to the related components. Make
sure the electrical connectors are fully connected, clean and not physically damaged. If
necessary, clean the electrical contacts using electrical contact cleaner. The use of clean-
ing agents not specifically designed for electrical contacts should be avoided, as they
could leave a surface film or damage the insulation of the wiring.
1. Engine makes a knocking or pinging noise when accelerating
a. Check the octane rating of the fuel being used. Depending on the type of driving or
driving conditions, it may be necessary to use a higher octane fuel.
b. Verify the ignition system settings and operation. Improperly adjusted ignition timing
or a failed component, such as a knock sensor, may cause the ignition timing to ad-
vance excessively or prematurely. Check the ignition system operation and adjust, or
replace components as needed.
c. Check the spark plug gap, heat range and condition. If the vehicle is operated in se-
vere operating conditions or at continuous high speeds, use a colder heat range spark
plug. Adjust the spark plug gap to the manufacturer’s recommended specification and
replace worn or damaged spark plugs.
2. Sfarter motor grinds when used
a. Examine the starter pinion gear and the engine ring gear for damage, and replace dam-
aged parts.
b. Check the starter mounting bolts and housing. If the housing is cracked or damaged
replace the starter motor and check the mounting bolts for tightness.
3. Engine makes a screeching noise
a. Check the accessory drive belts for looseness and adjust as necessary.
b. Check the accessory drive belt tensioners for seizing or excessive bearing noises and
replace if loose, binding, or excessively noisy.
c. Check for a seizing water pump. The pump may not be leaking; however, the bearing
may be faulty or the impeller loose and jammed. Replace the water pump.
4. Engine makes a growling noise
a. Check for a loose or failing water pump. Replace the pump and engine coolant.
b. Check the accessory drive belt tensioners for excessive bearing noises and replace if
loose or excessively noisy.
5. Engine makes a ticking or tapping noise
a. On vehicles with hydraulic lash adjusters, check for low or dirty engine oil and top off
or replace the engine oil and filter.
b. On vehicles with hydraulic lash adjusters, check for collapsed lifters and replace failed
components.
c. On vehicles with hydraulic lash adjusters, check for low oil pressure caused by a re-
stricted oil filter, worn engine oil pump, or oil pressure relief valve.
d. On vehicles with manually adjusted valves, check for excessive valve clearance or
worn valve train parts. Adjust the valves to specification or replace worn and defective
parts.
e. Check for a loose or improperly tensioned timing belt or timing chain and adjust or re-
place parts as necessary.
f. Check for a bent or sticking exhaust or intake valve. Remove the engine cylinder head
to access and replace.
6. Engine makes a heavy knocking noise
a. Check for a loose crankshaft pulley or flywheel; replace and torque the mounting
bolt(s) to specification.
b. Check for a bent connecting rod caused by a hydro-lock condition. Engine disassem-
bly is necessary to inspect for damaged and needed replacement parts.
c. Check for excessive engine rod bearing wear or damage. This condition is also asso-
ciated with low engine oil pressure and will require engine disassembly to inspect for
damaged and needed replacement parts,
7. Vehicle has a fuel odor when driven ’ a. Check the fuel gauge level. If the fuel gauge registers full, it is possible that the odor is
caused by being filled beyond capacity, or some spillage occurred during refueling.
The odor should clear after driving an hour, or twenty miles, allowing the vapor canis-
ter to purge.
b. Check the fuel filler cap for looseness or seepage. Check the cap tightness and, if
loose, properly secure. If seepage is noted, replace the filler cap.
c. Check for loose hose clamps, cracked or damaged fuel delivery and return lines, or
leaking components or seals, and replace or repair as necessary. d. Check the vehicle’s fuel economy. If fuel consumption has increased due to a failed
component, or if the fuel is not properly ignited due to an ignition related failure, the
catalytic converter may become contaminated. This condition may also trigger the
check engine warning light. Check the spark plugs for a dark, rich condition or verify
the condition by testing the vehicle’s emissions. Replace fuel fouled spark plugs, and
test and replace failed components as necessary.
5. Vehicle has a rotten egg odor when driven
a. Check for a leaking intake gasket or vacuum leak causing a lean running condition. A
lean mixture may result in increased exhaust temperatures, causing the catalytic con-
verter to run hotter than normal. This condition may also trigger the check engine
warning light. Check and repair the vacuum leaks as necessary.
b. Check the vehicle’s alternator and battery condition. If the alternator is overcharging,
the battery electrolyte can be boiled from the battery, and the battery casing may begin
to crack, swell or bulge, damaging or shorting the battery internally. If this has oc-
curred, neutralize the battery mounting area with a suitable baking soda and water
mixture or equivalent, and replace the alternator or voltage regulator. Inspect, service,
and load test the battery, and replace if necessary.
9. Vehicle has a sweet odor when driven
a. Check for an engine coolant leak caused by a seeping radiator cap, loose hose clamp,
weeping cooling system seal, gasket or cooling system hose and replace or repair as
needed.
b. Check for a coolant leak from the radiator, coolant reservoir, heater control valve or
under the dashboard from the heater core, and replace the failed part as necessary.
c. Check the engine’s exhaust for white smoke in addition to a sweet odor. The presence
of white, steamy smoke with a sweet odor indicates coolant leaking into the combus-
tion chamber. Possible causes include a failed head gasket, cracked engine block or
cylinder head. Other symptoms of this condition include a white paste build-up on the
inside of the oil filler cap, and softened, deformed or bulging radiator hoses.
19. Engine vibraies when idling
a. Check for loose, collapsed, or damaged engine or transmission mounts and repair or
replace as necessary.
b. Check for loose or damaged engine covers or shields and secure or replace as neces-
sary.
11. Engine vibrates during acceleration
a. Check for missing, loose or damaged exhaust system hangers and mounts; replace or
repair as necessary.
b. Check the exhaust system routing and fit for adequate clearance or potential rubbing;
repair or adjust as necessary.
7. Battery goes dead while driving
a. Check the battery condition. Replace the battery if the battery will not hold a charge or
fails a battery load test. If the battery loses fluid while driving, check for an overcharg-
ing condition. If the alternator is overcharging, replace the alternator or voltage regula-
tor. (A voltage regulator is typically built into the alternator, necessitating alternator re-
placement or overhaul.)
b. Check the battery cable condition. Clean or replace corroded cables and clean the bat-
tery terminals.
c. Check the alternator and voltage regulator operation. If the charging system is over or
undercharging, replace the alternator or voltage regulator, or both.
d. Inspect the wiring and wire connectors at the alternator for looseness, a missing .
ground or defective terminal, and repair as necessary.
e. Inspect the alternator drive belt tension, tensioners and condition. Properly tension the
drive belt, replace weak or broken tensioners, and replace the drive belt if worn or
cracked.
2. Battery goes dead overnight
a. Check the battery condition. Replace the battery if the battery will not hold a charge or
fails a battery load test.
b. Check for a voltage draw, such as a trunk light, interior light or glove box light staying
on. Check light switch position and operation, and replace if defective.
c. Check the alternator for an internally failed diode, and replace the alternator if defec-
tive.
1. Engine overheats
a. Check the coolant level. Set the heater temperature to full hot and check for internal air
pockets, bleed the cooling system and inspect for leakage. Top off the cooling system
with the correct coolant mixture.
b. Pressure test the cooling system and radiator cap for leaks. Check for seepage caused
by loose hose clamps, failed coolant hoses, and cooling system components such as
the heater control valve, heater core, radiator, radiator cap, and water pump. Replace
defective parts and fill the cooling system with the recommended coolant mixture.