Page 9 of 219

Safe driving
● Adjust the seat so that there is a distance
of at least 25 cm between the steering wheel
and your chest ››› Fig. 1 and so that you can
ho l
d the steering wheel with both hands on
the outside of the ring at the 9 o'clock and 3
o'clock positions with your arms slightly
bent.
● The adjusted steering wheel must face your
chest and not your face.
● Adjust the driver seat forwards or back-
wards so that you are able to press the accel-
erator, brake and clutch pedals to the floor
with your knees slightly angled and the dis-
tance between your knees and the dash pan-
el is at least 10 cm ››› Fig. 1
.
● Adjust the height of the driver seat so that
you can easily reach the top of the steering
wheel.
● Keep both feet in the footwell so that you
have the vehicle under control at all times.
● Adjust and fasten your seat belt correctly
››› page 11.
Va
lid for the passenger:
● Adjust the seat backrest to an upright posi-
tion so that your back rests completely
against it.
● Move the front passenger seat back as far
as possible for optimum protection should
the airbag deploy.
● Always keep your feet in the footwell while
the vehicle is in motion. ●
Adjust and fasten your seat belt correctly
››› page 11.
Va
lid for the passengers in the rear section:
● Adjust the head restraint so that its upper
edge is at the same level as the top of your
head, or as close as possible to the same lev-
el as the top of your head and under no cir-
cumstances below eye level. Keep the back
of your neck as close as possible to the head
restraint ››› Fig. 1 and ››› Fig. 2
.
● Short people must lower the head restraint
to the first anchorage position, even if your
head is below its upper edge.
● Tall people must raise the head restraint
completely.
● Always keep your feet in the footwell while
the vehicle is in motion.
● Adjust and fasten your seat belt correctly
››› page 11
. Adjusting the steering wheel position Fig. 3
Mechanical steering wheel adjustment Adjust the steering wheel before your trip
and only when the vehicle is stationary.
●
Push the lever ››› Fig. 3 1 downwards.
● Adjust the steering wheel so that you can
hold onto the steering wheel with both hands
on the outside of the ring at the 9 o'clock and
3 o'clock positions and your arms slightly
bent.
● Push the lever firmly upwards until it is
flush to the steering column ››› .
Adjust the correct distance between the driv-
er and the steering wheel ››› Fig. 1 using the
c ontr
ols on the driver seat ››› page 63.
»
7
Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 10 of 219

Safety
WARNING
Incorrect use of the steering wheel adjust-
ment function and an incorrect adjustment of
the steering wheel can result in severe or fa-
tal injury.
● After adjusting the steering column, push
the lever ››› Fig. 3 1 firmly upwards to en-
sure the steering wheel does not accidentally
change position while driving.
● Never adjust the steering wheel while the
vehicle is in motion. If you need to adjust the
steering wheel while the vehicle is in motion,
stop safely and make the proper adjustment.
● The adjusted steering wheel should be fac-
ing your chest and not your face so as not to
hinder the driver's front airbag protection in
the event of an accident.
● When driving, always hold the steering
wheel with both hands on the outside of the
ring at the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock positions
to reduce injuries when the driver's front air-
bag deploys.
● Never hold the steering wheel at the 12
o'clock position or in any other manner (e.g.
in the centre of the steering wheel). In such
cases, if the driver's airbag deploys, you may
sustain injuries to your arms, hands and
head. Danger of injuries due to an incorrect
sitting position
Number of seats
The vehicle has a total of
4 seats: 2 front
se ats
and 2 rear seats. Each seat is equipped
with a seat belt.
If the seat belts are worn incorrectly or not at
all, the risk of severe injuries increases. Seat
belts can provide optimal protection only if
the belt web is properly worn. Being seated
in an incorrect position means the seat belt
cannot offer its full protection. This could re-
sult in severe and even fatal injuries. The risk
of severe or fatal injuries is especially height-
ened when a deploying airbag strikes a vehi-
cle occupant who has assumed an incorrect
sitting position. The driver is responsible for
all passengers in the vehicle, particularly
children.
The following list shows just some examples
of incorrect sitting positions which can be
dangerous to all vehicle occupants.
When the vehicle is in motion:
● Never stand in the vehicle.
● Never stand on the seats.
● Never kneel on the seats.
● Never tilt your seat backrest too far to the
rear.
● Never lean against the dash panel. ●
Never lie on the rear seats.
● Never sit on the front edge of a seat.
● Never sit sideways.
● Never lean out of a window.
● Never put your feet out of a window.
● Never put your feet on the dash panel.
● Never put your feet on the surface of a seat
or seat backrest.
● Never travel in a footwell.
● Never travel on a seat without wearing the
seat belt.
● Never carry any person in the luggage com-
partment. WARNING
An incorrect sitting position in the vehicle
can lead to severe injuries or death in the
event of sudden braking or manoeuvres, colli-
sion or accidents or if the airbag deploys.
● Before the vehicle moves, assume the prop-
er sitting position and maintain it throughout
the trip. This also includes fastening the seat
belt.
● Never transport more people than there are
seats with a seat belt available in the vehicle.
● Children must always be protected with an
approved child restraint system suited to
their height and weight ››› page 25,
››› page 17.8
Page 11 of 219

Safe driving
●
Always keep your feet in the footwell while
the vehicle is in motion. Never, for example,
put your feet on the surface of a seat or on
the dash panel and never put them out of a
window. Otherwise the airbag and seat belt
offer insufficient protection and the risk of in-
jury in the event of an accident is increased. WARNING
Before every trip, adjust the seat, the seat
belt and the head restraints and instruct your
passengers to fasten their seat belts proper-
ly.
● Move the front passenger seat back as far
as possible.
● Adjust the driver seat so that there is at
least 25 cm distance between your chest and
the hub of the steering wheel. Adjust the
driver seat so that you are able to press the
accelerator, brake and clutch pedals to the
floor with your knees slightly angled and that
the distance between your knees and the
dash panel is at least 10 cm. If your physical
constitution prevents you from meeting these
requirements, contact a specialised work-
shop to make any modifications required.
● Never drive with the seat backrest tilted far
back. The further the seat backrests are tilted
to the rear, the greater the risk of injury due
to incorrect positioning of the belt web or to
the incorrect sitting position!
● Never drive with the seat backrest tilted
forwards. Should a front airbag deploy, it could throw the seat backrest backwards and
injure the passengers of the rear seats.
●
Sit as far away as possible from the steer-
ing wheel and the dash panel.
● Keep your back straight and resting com-
pletely against the seat backrest and the
front seats correctly adjusted. Never place
any part of your body in the area of the airbag
or very close to it.
● If passengers on the rear seats are not sit-
ting in an upright position, the risk of severe
injury due to incorrect positioning of the belt
web increases. WARNING
Incorrect seat adjustment may lead to acci-
dents and severe injuries.
● Only adjust the seats when the vehicle is
stationary, as the seats could move unex-
pectedly while the vehicle is in motion and
you could lose control of the vehicle. Further-
more, an incorrect position is adopted when
adjusting the seat.
● Only adjust the height, seat backrest and
forwards or backwards position of the seat
when there is nobody in the seat adjustment
area.
● There must be no objects blocking the front
seat adjustment area. Adjust the rear head restraints
Fig. 4
Adjusting the rear head restraints All seats are equipped with a head restraint.
The front seat head restraints are integrated
in the backrests and adjusting them is not
possible.
Adjusting height
● Push the head restraint up or down in the
direction of the arrow with the button press-
ed ››› Fig. 4 1
››› .
● The head restraint must engage securely in
position.
Correct adjustment of head restraints
Adjust the head restraint so that its upper
edge is at the same level as the top of your
head, or as close as possible to the same lev-
el as the top of your head and under no cir-
cumstances below eye level. Keep the back »
9Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 12 of 219

Safety
of your neck as close as possible to the head
restraint.
Adjusting the head restraint for short people
Set the head restraint in the first anchorage
position, even if your head is below its upper
edge. When the head restraint is at its low-
est, it is possible that a small gap remains
between it and the seat backrest.
Adjusting the head restraint for tall people
Raise the head restraint completely. WARNING
Travelling with the head restraints removed
or improperly adjusted increases the risk of
severe or fatal injuries in the event of acci-
dents and sudden braking or manoeuvres.
● Always fit and adjust the head restraint
properly whenever a person is occupying a
seat.
● All vehicle occupants must correctly adjust
the head restraint according to their height to
reduce the risk of back injuries in the event of
an accident. The upper edge of the head re-
straint must be as close as possible to the
same level as the top of your head and under
no circumstances below eye level. Keep the
back of your neck as close as possible to the
head restraint.
● Never adjust the head restraint while the
vehicle is in motion. Pedal area
Pedals Do not allow floor mats or other objects to
obstruct the free passage of the pedals.
Floor mats should leave the pedal area free
and unobstructed and be correctly secured in
the footwell zone.
In the event of failure of a brake circuit, the
brake pedal must be pressed harder than
normal to brake the vehicle.
WARNING
Objects falling into the driver's footwell could
prevent use of the pedals. This could lead the
driver to lose control of the vehicle, increas-
ing the risk of a serious accident.
● Make sure the pedals can be used at all
times, with no objects rolling underneath
them.
● Always secure the mat in the footwell.
● Never place other mats or rugs on top of
the original mat supplied by the factory.
● Ensure that no objects can fall into the driv-
er's footwell while the vehicle is in motion. CAUTION
The pedals must always have free and unob-
structed passage to the floor. For example, in
case of a fault in the brake circuit, the brake pedal will need to be pressed further to stop
the vehicle. To press the brake pedal down
further will require more force than usual.
10
Page 13 of 219

Seat belts
Seat belts
Using seat belts Introduction Check the condition of all the seat belts at
regular intervals. If you notice that the belt
webbing, fittings, retractor mechanism or
buckle of any of the belts is damaged, the
belt must be replaced immediately by a spe-
cialised workshop
››› . The specialised
workshop must use the appropriate spare
parts corresponding to the vehicle, the
equipment and the model year. SEAT recom-
mends taking your car in for technical serv-
ice. WARNING
Unbuckled or badly buckled seat belts in-
crease the risk of severe or even fatal inju-
ries. The seat belt cannot offer its full protec-
tion if it is not fastened and used correctly.
● Seat belts are the most effective way of re-
ducing the risk of sustaining severe or fatal
injuries in the event of an accident. Seat belts
must be correctly fastened when the vehicle
is in motion to protect the driver and all vehi-
cle occupants.
● Before each trip, every occupant in the ve-
hicle occupants must sit properly, correctly
fasten the seat belt belonging to his or her
seat and keep it fastened throughout the trip. This also applies to other vehicle occupants
when driving in town.
●
When travelling, children must be secured
in the vehicle with a child restraint system
suitable for their weight and height and with
the seat belts correctly fastened
››› page 25.
● Ins
truct your passengers to fasten their
seat belts properly before driving off.
● Insert the latch plate into the buckle for the
appropriate seat and ensure it is engaged.
Using the latch plate in the buckle of another
seat will not protect you properly and may
cause severe injuries.
● Do not allow liquids or foreign bodies to en-
ter the buckle fastenings. This could damage
the buckles and seat belts.
● Never unbuckle your seat belt when the ve-
hicle is moving.
● Never allow more than one passenger to
share the same seat belt.
● Never hold children or babies on your lap
sharing the same seat belt.
● Loose, bulky clothing (such as a jacket) im-
pairs the proper fit and function of the seat
belt. WARNING
It is extremely dangerous to drive using dam-
aged seat belts and could result in serious in-
jury or loss of life. ●
Avoid damaging the seat belt by jamming it
in the door or the seat mechanism.
● If the fabric or other parts of the seat belt
are damaged, the seat belts could break in
the event of an accident or sudden braking.
● Always have damaged seatbelts replaced
immediately by seat belts approved for the
vehicle in question by SEAT. Seat belts which
have been worn in an accident and stretched
must be replaced by a specialised workshop.
Renewal may be necessary even if there is no
apparent damage. The belt anchorage should
also be checked.
● Never attempt to repair, modify or remove a
seat belt yourself. All repairs to seat belts, re-
tractors and buckles must be carried out by a
specialised workshop. 11Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 14 of 219

Safety
Warning lamp Fig. 5
Warning lamp on the instrument panel Fig. 6
Indication of seat belt status in the rear
seats on the instrument panel displayLights
up or
flashesPossible causeSolution
On the instrument panel:
Driver's seat belt not fas-
tened or front passenger
seat belt not fastened if
the front passenger seat
is occupied.
Fasten seat
belts!
On the instrument panel:
Objects on the front pas-
senger seat.
Remove any
objects from
the front pas-
senger seat
and store them
safely.
Instrument panel dis-
play: a passenger in the
rear seats has not fas-
tened their seat belt, if
the seat is occupied.*
Fasten seat
belts!
On the instrument panel
display: a passenger in
the rear seats has fas-
tened their seat belt, if
the seat is occupied.*
Several warning and control lamps light up
for a few seconds when the ignition is switch-
ed on, signalling that the function is being
verified. They will switch off after a few sec-
onds.
An audible warning will be heard if the seat
belts are not fastened as the vehicle drives
off and reaches a speed of more then25 km/h (15 mph) or if the seat belts are un-
fastened while the vehicle is in motion. The
seat belt warning lamp
will also flash.
The w arnin
g lamp does not switch off until
the driv
er and front passenger fasten their
seat belts while the ignition is switched on.
Seat belt status display for rear seats
The seat belt status display on the instru-
ment panel informs the driver, when the igni-
tion is switched on, whether any passengers
in the rear seats have fastened their seat
belts. The symbol indicates that the pas-
senger in this seat has fastened “his or her”
seat belt ››› Fig. 6.
The seat
belt status is displayed for around
30 seconds when a seat belt in the rear seats
is fastened or unfastened. You can switch off
this display by pressing the 0.0 / SET button.
The seat belt status flashes for a maximum of
30 seconds when a seat belt in the rear seats
is unfastened while the vehicle is in motion.
An audible warning will also be heard if the
vehicle is travelling at over 25 km/h
(15 mph).
12
Page 15 of 219

Seat belts
Seat belt protection Fig. 7
Drivers with properly worn seat belts
will not be thrown forward in the event of sud-
den braking Properly worn seat belts hold the occupants
in the proper position. They also help prevent
uncontrolled movements that may result in
serious injury and reduce the risk of being
thrown out of the vehicle in case of an acci-
dent.
Vehicle occupants wearing their seat belts
correctly benefit greatly from the ability of the
belts to absorb kinetic energy. In addition,
the front part of your vehicle and other pas-
sive safety features (such as the airbag sys-
tem) are designed to absorb the kinetic ener-
gy released in a collision. Taken together, all
these features reduce the releasing kinetic
energy and consequently, the risk of injury.
This is why it is so important to fasten seat
belts before every trip, even when "just driv-
ing around the corner". Ensure that your passengers wear their seat
belts as well. Accident statistics have shown
that wearing seat belts is an effective means
of substantially reducing the risk of injury
and improving the chances of survival when
involved in a serious accident. Furthermore,
properly worn seat belts improve the protec-
tion provided by airbags in the event of an
accident. For this reason, wearing a seat belt
is required by law in most countries.
Although your vehicle is equipped with air-
bags, the seat belts must be fastened and
worn. The front airbags, for example, are only
triggered in some cases of head-on collision.
The front airbags will not be triggered during
minor frontal or side collisions, rear-end colli-
sions, rollovers or accidents in which the air-
bag trigger threshold value in the control unit
is not exceeded.
Therefore, you should always wear your seat
belt and ensure that all vehicle occupants
have fastened their seat belts properly before
you drive off!
Using seat belts Twisted seat belt
If it is difficult to remove the seat belt from
the guide, the seat belt may have become
twisted inside the side trim after being
wound too quickly on unfastening:●
Pull out the seat belt completely, carefully
pulling on the latch plate.
● Untwist the belt and guide it back, assist-
ing it by hand.
The seat belt must be fastened even if it is
impossible to untwist it. In this case, the
twisted area must not be in an area in direct
contact with your body. Have the seat belt
untwisted urgently by a specialised work-
shop. WARNING
An improperly handled seat belt increases
the risk of sustaining severe or fatal injuries.
● Regularly check that the seat belts and
their components are in perfect condition.
● Always keep your seat belt clean.
● Do not jam or damage the seat belt or rub it
with sharp edges.
● Make sure there are no liquids or foreign
bodies on the latch plate and in the buckle. 13Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 16 of 219

Safety
Head-on collisions and the laws of
physics Fig. 8
A driver not wearing a seat belt is
thrown forward violently Fig. 9
The unbelted passenger in the rear
seat is thrown forward violently, hitting the
driver who is wearing a seat belt. It is easy to explain how the laws of physics
work in the case of a head-on collision: when
a vehicle starts moving, a type of energy called “kinetic energy” is created both in the
passengers and inside the vehicle.
The amount of “kinetic energy” depends on
the speed of the vehicle and the weight of
the vehicle and its passengers. The higher
the speed and the greater the weight, the
more energy there is to be “absorbed” in an
accident.
The most significant factor, however, is the
speed of the vehicle. If the speed doubles
from 25 km/h (15 mph) to 50 km/h
(30 mph), for example, the corresponding ki-
netic energy is multiplied by four.
Because the vehicle occupants in our exam-
ple are not restrained by seat belts, in the
event of crashing against a wall, all of the oc-
cupants' kinetic energy will be absorbed
solely by said impact.
Even at speeds of 30 km/h (19 mph) to
50 km/h (30 mph), the forces acting on bod-
ies in a collision can easily exceed one tonne
(1000 kg). At greater speed these forces are
even higher.
Vehicle occupants not wearing seat belts are
not “attached” to the vehicle. In a head-on
collision, they will move forward at the same
speed their vehicle was travelling just before
the impact. This example applies not only to
head-on collisions, but to all accidents and
collisions.
Even at low speeds the forces acting on the
body in a collision are so great that it is not
possible to brace oneself with one's hands.
In a frontal collision, unbelted passengers
are thrown forward and will make violent con-
tact with the steering wheel, dash panel,
windscreen or whatever else is in the way
››› Fig. 8 .
It i
s also important for rear passengers to
wear seat belts properly, as they could other-
wise be thrown forward violently through the
vehicle interior in an accident. Passengers in
the rear seats who do not use seat belts en-
danger not only themselves but also the front
occupants ››› Fig. 9.
14
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13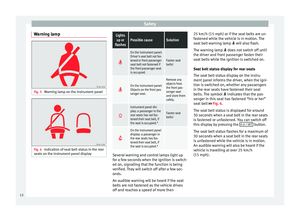 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60 61
61 62
62 63
63 64
64 65
65 66
66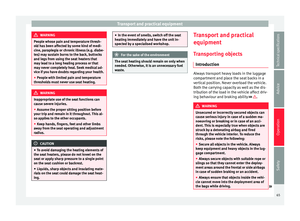 67
67 68
68 69
69 70
70 71
71 72
72 73
73 74
74 75
75 76
76 77
77 78
78 79
79 80
80 81
81 82
82 83
83 84
84 85
85 86
86 87
87 88
88 89
89 90
90 91
91 92
92 93
93 94
94 95
95 96
96 97
97 98
98 99
99 100
100 101
101 102
102 103
103 104
104 105
105 106
106 107
107 108
108 109
109 110
110 111
111 112
112 113
113 114
114 115
115 116
116 117
117 118
118 119
119 120
120 121
121 122
122 123
123 124
124 125
125 126
126 127
127 128
128 129
129 130
130 131
131 132
132 133
133 134
134 135
135 136
136 137
137 138
138 139
139 140
140 141
141 142
142 143
143 144
144 145
145 146
146 147
147 148
148 149
149 150
150 151
151 152
152 153
153 154
154 155
155 156
156 157
157 158
158 159
159 160
160 161
161 162
162 163
163 164
164 165
165 166
166 167
167 168
168 169
169 170
170 171
171 172
172 173
173 174
174 175
175 176
176 177
177 178
178 179
179 180
180 181
181 182
182 183
183 184
184 185
185 186
186 187
187 188
188 189
189 190
190 191
191 192
192 193
193 194
194 195
195 196
196 197
197 198
198 199
199 200
200 201
201 202
202 203
203 204
204 205
205 206
206 207
207 208
208 209
209 210
210 211
211 212
212 213
213 214
214 215
215 216
216 217
217 218
218






