Page 17 of 219

Seat belts
How to properly adjust your
seatbelt Fastening and unfastening the seat
belt Fig. 10
Positioning and removing the seat
belt buckle. Fig. 11
Position of seat belt during pregnan-
cy. Properly worn seat belts hold the vehicle oc-
cupants in the position that most protects
them in the event of an accident or sudden
braking
››› .
Fastening the seat belt
Fasten your seat belt before each trip.
● Correctly adjust the front seat ›››
page 6.
● Engage the seat backrest in the upright po-
sition and correctly adjust the hear restraint
››› .
● Pull the latch plate and place the belt web-
bing evenly across your chest and lap. Do not
twist the seat belt when doing so ››› .
● Engage the latch plate in the buckle of the
corresponding seat ›››
Fig. 10
A. ●
Pull the belt to ensure that the latch plate is
securely engaged in the buckle.
Unfastening the seat belt
The seat belt must not be unfastened until
the vehicle has come to a standstill ››› .
● Press the red button on the buckle
››› Fig. 10
B
. The latch plate is released from
the buckle.
● Guide the belt back by hand so that it rolls
up easily and the trim will not be damaged.
Correct seat belt position
Seat belts offer their maximum protection in
the event of an accident and reduce the risk
of sustaining severe or fatal injuries only
when they are properly positioned. Further-
more, if the webbing is correctly positioned,
the seat belt will hold the vehicle occupants
in the optimum position to ensure the airbag
provides the maximum protection. The seat
belt must therefore always be worn and the
webbing correctly positioned.
Incorrectly worn seat belts can cause severe
or even fatal injuries ››› page 6, Correct sit-
ting position for vehicle occupants .
● The shoulder part of the seat belt must lie
on the centre of the shoulder, never across
the neck or the arm, under the arm or behind
the shoulder. »
15
Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 18 of 219

Safety
● The lap part of the seat belt must lie across
the pelvis, never across the stomach.
● The seat belt must lie flat and fit comforta-
bly. Pull the belt tight if necessary to take up
any slack.
In the case of pregnant women , the seat belt
must lie evenly across the chest and as low
as possible over the pelvis, never across the
stomach and must be worn properly at all
times during the pregnancy ››› Fig. 11 .
Ad aptin
g the position of the belt webbing to
your size
The seat belt can be adapted using the fol-
lowing equipment:
● Front seat height adjustment. WARNING
An incorrectly worn seat belt web can cause
severe or fatal injuries in the event of an acci-
dent.
● The seat belt cannot offer its full protection
unless the seat backrest is in an upright posi-
tion and the seat belt is worn correctly, ac-
cording to your size.
● Unbuckling your seat belt while the vehicle
is in motion can cause severe or fatal injuries
in the event of an accident or sudden braking.
● The seat belt itself or a loose seat belt can
cause severe injuries if the belt moves from hard areas of the body to soft areas (e.g. the
stomach).
●
The shoulder part of the seat belt must lie
on the centre of the shoulder, never across
the neck or the arm.
● The seat belt must lie flat and fit comforta-
bly on the torso
● The lap part of the seat belt must lie across
the pelvis, never across the stomach. The
seat belt must lie flat and fit comfortably on
the pelvis Pull the belt tight if necessary to
take up any slack.
● For pregnant women, the lap part of the
seat belt must lie as low as possible over the
pelvis and always lie flat, “surrounding” the
stomach.
● Do not twist the seat belt while it is fas-
tened.
● Never pull the seat belt away from your
body using your hand.
● Do not lie the seat belt across rigid or frag-
ile objects, e.g. glasses, pens or keys.
● Never use seat belt clips, retaining rings or
similar instruments to alter the position of
the belt webbing. Note
If your physical constitution prevents you
from maintaining the correct position of the
belt webbing, contact a specialised workshop
for help with any special devices to ensure
the optimum protection of the seat belt and airbag. SEAT recommends taking your car in
for technical service.
Seat belt tensioners
Automatic belt retainer, belt
tensioner, belt tension limiter Seat belts are part of the vehicle safety con-
cept
››› page 17 and consist of the follow-
in g impor
tant functions:
Automatic belt retainer
Every seat belt is equipped with an automatic
belt retainer on the shoulder belt. If the belt
is pulled slowly or during normal driving, the
system allows for total freedom of movement
on the shoulder belt. However, during sud-
den braking, during travel in mountains or
bends and during acceleration, the automat-
ic belt retainer on the seat belt is locked is
pulled quickly.
Belt tensioners
The seat belts for the occupants in the front
seats are equipped with belt tensioners.
Sensors trigger the belt tensioners during se-
vere head-on, lateral and rear collisions and
retract and tighten the seat belts. If the seat
belt is loose, it is retracted to reduce the for-
wards movement of occupants or movement
16
Page 19 of 219

Airbag system
in the direction of the collision. The belt ten-
sioner works in combination with the airbag
system. The belt tensioner will not be trig-
gered in the event of the vehicle overturning
if the side airbags are not deployed.
If the belt tensioner is triggered, a fine dust is
produced. This is normal and it is not an indi-
cation of fire in the vehicle.
Belt tension limiter
The belt tension limiter reduces the force of
the seat belt on the body in the event of an
accident. Note
The relevant safety requirements must be ob-
served when the vehicle is dismantled or sys-
tem components are removed. These require-
ments are known to specialised workshops
››› page 17. Service and disposal of belt
tensioners
If you work on the belt tensioners or remove
and install other parts of the vehicle when
performing other repair work, the seat belt
may be damaged. The consequence may be
that, in the event of an accident, the belt ten-
sioners function incorrectly or not at all. So that the effectiveness of the belt tensioner
is not reduced and that removed parts do not
cause any injuries or environmental pollu-
tion, regulations must be observed. These re-
quirements are known to specialised work-
shops.
WARNING
Improper handling and homemade repairs of
seat belts, automatic belt retainers and ten-
sion devices increase the risk of sustaining
severe or fatal injuries. The belt tensioner
may fail to trigger or may trigger in the wrong
circumstances.
● Never attempt to repair, adjust or remove or
install parts of the belt tensioners or seat
belts. Any work must be performed by a spe-
cialised workshop only ››› page 118.
● Belt tensioners and automatic belt retain-
ers cannot be repaired and must be replaced. For the sake of the environment
Airbag modules and belt tensioners may con-
tain perchlorate. Observe the legal require-
ments for their disposal. Airbag system
Brief introduction Introduction Front airbags have been installed for both
driver and passenger. The front airbags can
also protect the chest and head of driver and
passenger if the seats, seat belts head re-
straints and, for the driver, the steering
wheel are correctly adjusted and used. Air-
bags are considered as additional safety
equipment. An airbag cannot replace the
seat belt, which must be worn at all times,
even in front seats where front airbags have
been installed.
The airbag can protect vehicle occupants in
the event of an accidents, cushioning the
movement of the occupants in the direction
of the collision in frontal and side accidents.
Deployed airbags fill with a propellant gas.
This causes the airbag covers to break and
the airbags to deploy extremely quickly in
their entire deployment space within frac-
tions of a second. When an occupant with the
seat belt properly fastened puts pressure on
the inflated airbag, the propellant gas es-
capes to absorb the force of the impact and
slow the movement. This reduces the risk of
severe or fatal injuries. Airbag deployment
does not mean that other types of injury such
»
17Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 20 of 219

Safety
as swelling, bruising and skin injuries can be
ruled out. Upon deployment of the airbag,
friction can cause the generation of heat.
Airbags do not protect the arms or the lower
part of the body.
The most important factors for triggering the
airbag are the type of accident, the angle of
impact, the vehicle speed and the character-
istics of the object the vehicle hits. Therefore,
airbags are not triggered every time the vehi-
cle is visibly damaged.
The activation of the airbag system depends
on the magnitude of the deceleration of the
vehicle caused by a collision, which registers
through an electronic control unit. If the de-
celeration magnitude value is below the ref-
erence value programmed in the control unit,
the airbags will not deploy even though seri-
ous damage might be caused to the vehicle
as the result of an accident. Damage suffered
by the vehicle, reparation costs or absence of
damage suffered from the accident are not
indications of whether an airbag should have
been deployed. Due to the varying nature of
collision situations, it is impossible to define
a speed range of the vehicle and reference
values. For this reason, it is not possible to
cover all types of collisions and collision an-
gles resulting in the deployment of the air-
bag. Factors necessary for the airbag to be
deployed can be, the characteristics of the
object (hard or soft) against which the vehi- cle collides, the collision angle and the vehi-
cle speed.
Airbags act in conjunction with the three-
point seat belts in certain accident situa-
tions, when the vehicle deceleration rate is
severe enough to trigger the airbags. Airbags
only deploy once and only under certain cir-
cumstances. Seat belts remain present to of-
fer protection in situations where airbags are
not triggered or where they have already de-
ployed. For example, when a vehicle hits an-
other after an initial collision or is hit by an-
other vehicle.
The airbag system is an integral part of the
car's passive safety system. The airbag sys-
tem can only work effectively when the vehi-
cle occupants are wearing their seat belts
correctly and have adjusted the head re-
straints properly
››› page 6. WARNING
Never exclusively trust the airbag system as a
means of protection.
● Even when triggered, airbag protection is
only auxiliary.
● The airbags provide the best protection
when the seat belts are properly fastened,
thus reducing the risk of sustaining injuries
››› page 11, Using seat belts .
● Before each trip, every occupant must sit
properly, correctly fasten the seat belt be-
longing to his or her seat and keeping it fas- tened throughout the trip. This rule is valid
for all vehicle occupants.
WARNING
Occupants sitting in the front of the vehicle
must never carry any objects in the deploy-
ment space between them and the airbags,
as this increases the risk of sustaining inju-
ries if the airbag is triggered. This modifies
the airbag deployment space or the objects
may fly uncontrollably and hit your body.
● Never carry objects in your hand or on your
lap while the vehicle is in motion.
● Never transport objects on the front pas-
senger seat. In the event of sudden braking
and manoeuvres, the objects may end up in
the airbag deployment space and fly uncon-
trollably around the interior if the airbag is
activated.
● Occupants of the front and rear seats must
never carry any other people, pets or objects
in the deployment space between them and
the airbags. Make sure children and other
passengers also respect this recommenda-
tion. WARNING
The airbag system provides protection for
one accident only. If they have been de-
ployed, they must be replaced. 18
Page 21 of 219

Airbag system
●
Ensure deployed airbags and the system
components involved are immediately re-
placed with new, SEAT-approved components
for the vehicle.
● Have any repairs or modifications carried
out at a specialised workshop. Specialised
workshops have the necessary tools, diag-
nostics equipment, repair information and
qualified personnel.
● Never fit recycled or reused airbag compo-
nents in your vehicle.
● Never modify the airbag system compo-
nents. WARNING
If the airbags are triggered, a fine dust is pro-
duced. This is normal and it is not an indica-
tion of fire in the vehicle.
● This fine dust may irritate the skin and eyes
and cause breathing difficulties, particularly
in people suffering from or who have suffered
from asthma or other illnesses of the respira-
tory tract. To reduce breathing difficulties,
get out of the vehicle and open and doors and
windows to breath in fresh air.
● Should you touch the dust, wash your
hands and face using a mild soap and water
before you eat.
● Prevent the dust from affecting the eyes or
open wounds.
● Rinse your eyes with water if you have dust
in them. WARNING
Solvents cause the surfaces of the airbag
modules to become porous. If an airbag is ac-
cidentally triggered, the detachment of plas-
tic parts could cause serious injury.
● Never clean the dash panel and the surfa-
ces of the airbag modules with cleaners con-
taining solvents. Description of airbag system
Vehicle safety components
The following safety equipment makes up the
vehicle safety design to reduce the risk of se-
vere and fatal injuries. Depending on the ve-
hicle equipment, some equipment may not
be fitted in the vehicle or may not be availa-
ble in some markets.
●
Optimised seat belts for all seats.
● Seat belt tension devices for driver and
passenger.
● Seat belt force limiters for driver and pas-
senger.
● Seat belt warning lamp
● Front airbags for driver and passenger.
● Side airbags for driver and passenger.
● Airbag control lamp .
● Control units and sensors. ●
Head restraints optimised for rear-end colli-
sion.
● Adjustable steering column.
● If necessary, anchor points for child seats
for the rear seats.
● Where applicable, mountings for the child
seat upper retaining strap.
Situations in which the front and side
airbags do not deploy:
● If the ignition is switched off during the col-
lision.
● In frontal collisions, when the deceleration
measured by the control unit is too low.
● In minor side collisions.
● In rear collisions.
● In the event of the vehicle overturning.
● When the impact speed is lower than the
reference value set in the control unit.
There is a fault in the system if the control
lamp :
● does not light up when the ignition is
switched on,
● turns off after 4 seconds after the ignition
is switched on
● turns off and then lights up again after the
ignition is switched on
● illuminates or flashes while the vehicle is
moving. »
19Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 22 of 219

Safety
WARNING
● The seat belts and airbags can only provide
maximum protection if the occupants are
seated correctly ››› page 6.
● If a f
ault has occurred in the airbag system,
have the system checked immediately by a
specialised workshop. Otherwise, during a
frontal collision the system might not trigger
correctly or may fail to trigger at all. Airbag activation
The airbags deploy extremely rapidly, within
thousandths of a second, to provide addi-
tional protection in the event of an accident.
A fine dust may develop when the airbag de-
ploys. This is normal and it is not an indica-
tion of fire in the vehicle.
The airbag system is only ready to function
when the ignition is on.
In special accidents instances, several air-
bags may activate at the same time.
In the event of minor head-on and side colli-
sions, rear-end collisions, overturning or roll-
over of the vehicle, airbags
do not activate.
Activation factors
The conditions that lead to the airbag system
activating in each situation cannot be gener-
alised. Some factors play an important role,
such as the properties of the object the vehi- cle hits (hard/soft), angle of impact, vehicle
speed, etc.
Deceleration trajectory is key for airbag acti-
vation.
The control unit analyses the collision trajec-
tory and activates the respective restraint
system.
If the deceleration rate is below the prede-
fined reference value in the control unit the
airbags will not be triggered, even though
the accident may cause extensive damage to
the car.
The following airbags are triggered in
serious head-on collisions
● Driver airbag.
● Front passenger front airbag
The following airbags are triggered in
serious side-on collisions
● Front side airbag on the side of the acci-
dent.
● Rear side airbag on the side of the acci-
dent.
In an accident with airbag activation:
● the interior lights switch on (if the interior
light switch is in the courtesy light position);
● the hazard warning lights switch on;
● all doors are unlocked; ●
the fuel supply to the engine is cut.
20
Page 23 of 219

Airbag system
General overview of the airbag Front airbags Fig. 12
Location and deployment area of the
front airbag for the driver. Fig. 13
Location and deployment area of the
front airbag for the passenger. In conjunction with the seat belts, the front
airbag system gives the driver and the front
passenger additional protection for the head
and chest in the event of a severe frontal col-
lision. Always remain as far away as possible
from the front airbag
››› page 6. This way, in
the event of an accident, the front airbags can deploy fully when triggered, providing
maximum protection.
The front airbag for the driver is located in
the steering wheel
››› Fig. 12 and the airbag
f or the fr
ont passenger is located in the dash
panel ››› Fig. 13. Airbags are identified by the
wor
d “AIRBAG”.
When the front airbags are triggered they fill
the zones marked in red ››› Fig. 12
and
››› Fig. 13 (radius of action). Therefore, ob-
jects
should never be placed or mounted in
these areas ››› , Factory-fitted accessories
are outside the range of the front airbag for
the driver and the front passenger, e.g. the
baseplate for the mobile phone support.
The airbag covers fold out of the steering
wheel ››› Fig. 12 or dash panel
›
›
› Fig. 13
when the driver and front passenger airbags
are triggered. The airbag covers remain con-
nected to the steering wheel or the dash pan-
el. WARNING
The airbag is deployed at high speed in frac-
tions of a second.
● Always keep the deployment areas of the
front airbags vacant.
● Never secure objects to the covers or in the
deployment area of the airbag modules, e.g.
drink holders or phone supports.
● The deployment space between the front
passengers and the airbags must not in any » 21
Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 24 of 219

Safety
case be occupied by other passenger, pets
and objects.
●
Never fix any object to the windscreen
above the front airbag on the front passenger
side.
● Do not alter, cover or stick anything to the
steering wheel hub or the surface of the air-
bag module on the passenger side of the
dash panel. WARNING
Front airbags are deployed in front of the
steering wheel ››› Fig. 12
and the dash panel
› ›
› Fig. 13.
● When drivin
g, always hold the steering
wheel on the outer edge of the ring with both
hands: 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock position.
● Adjust the driver seat so that there is a dis-
tance of at least 25 cm (10 inches) between
the centre of your chest and the hub of the
steering wheel. If your physical constitution
prevents you from meeting these require-
ments, make sure you contact a specialised
workshop.
● Adjust the front passenger seat so there is
as much distance as possible between the
front passenger and the dash panel. Types of front passenger front airbag
systems
There are two different SEAT front passenger
front airbag systems:
A
Characteristics of the passenger front airbag
without
disabling.
– Control lamp on the instrument panel.*
– Front passenger front airbag on the dash panel.
Description: airbag system
B
Characteristics of the front passenger front airbag that
can be disabled manually ››› page 24.
– Control lamp on the instrument panel.
– Control lamp on the dash panel.
.
– Switch on the dash panel glove compartment, on the
passenger side.
– Front passenger front airbag in the dash panel.
Description: airbag system with front passenger front
airbag disabling. Side airbags
Fig. 14
On the side of the front seat: location
of the side airbag Fig. 15
On the left side of the vehicle: deploy-
ment area of side airbag The side airbags are located in the outer
cushion of the driver and front passenger
seat backrests
››› Fig. 14 . Their position is in-
dic at
ed by the word “AIRBAG”. The area
marked in red ››› Fig. 15
indicates the side
airbag deployment zone.
22
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13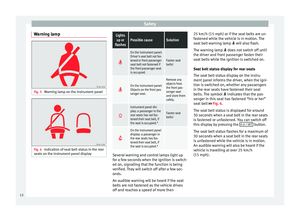 14
14 15
15 16
16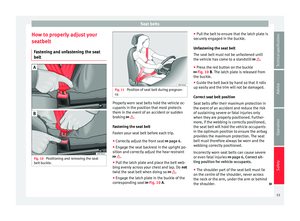 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60 61
61 62
62 63
63 64
64 65
65 66
66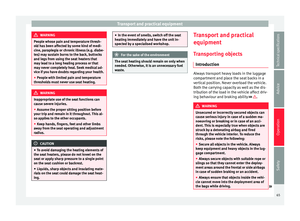 67
67 68
68 69
69 70
70 71
71 72
72 73
73 74
74 75
75 76
76 77
77 78
78 79
79 80
80 81
81 82
82 83
83 84
84 85
85 86
86 87
87 88
88 89
89 90
90 91
91 92
92 93
93 94
94 95
95 96
96 97
97 98
98 99
99 100
100 101
101 102
102 103
103 104
104 105
105 106
106 107
107 108
108 109
109 110
110 111
111 112
112 113
113 114
114 115
115 116
116 117
117 118
118 119
119 120
120 121
121 122
122 123
123 124
124 125
125 126
126 127
127 128
128 129
129 130
130 131
131 132
132 133
133 134
134 135
135 136
136 137
137 138
138 139
139 140
140 141
141 142
142 143
143 144
144 145
145 146
146 147
147 148
148 149
149 150
150 151
151 152
152 153
153 154
154 155
155 156
156 157
157 158
158 159
159 160
160 161
161 162
162 163
163 164
164 165
165 166
166 167
167 168
168 169
169 170
170 171
171 172
172 173
173 174
174 175
175 176
176 177
177 178
178 179
179 180
180 181
181 182
182 183
183 184
184 185
185 186
186 187
187 188
188 189
189 190
190 191
191 192
192 193
193 194
194 195
195 196
196 197
197 198
198 199
199 200
200 201
201 202
202 203
203 204
204 205
205 206
206 207
207 208
208 209
209 210
210 211
211 212
212 213
213 214
214 215
215 216
216 217
217 218
218






