2009 SUBARU TRIBECA ac 25 procedure
[x] Cancel search: ac 25 procedurePage 1952 of 2453
ME(H6DO)-86
Engine Trouble in General
MECHANICAL
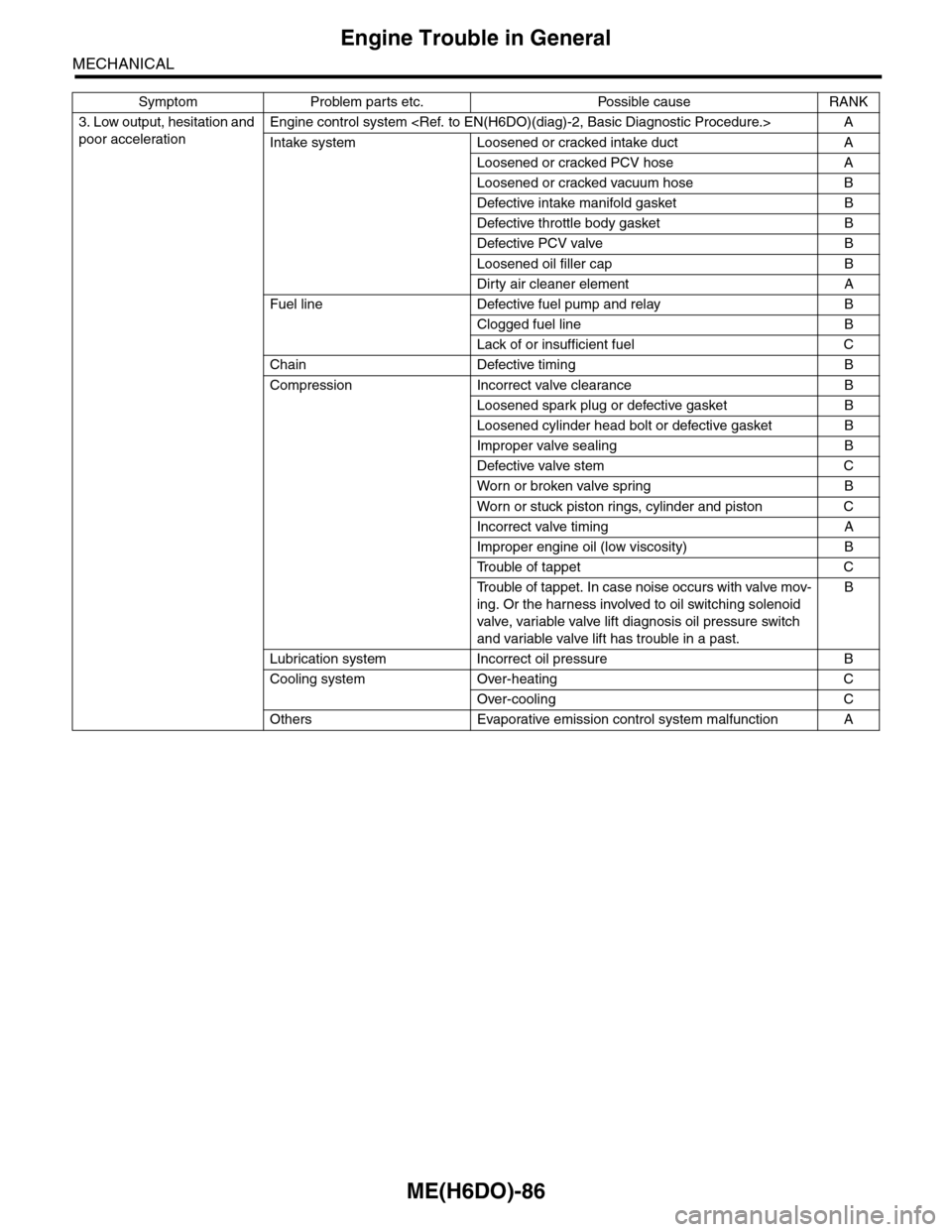
3. Low output, hesitation and
poor acceleration
Engine control system
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct A
Loosened or cracked PCV hose A
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose B
Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Defective PCV valve B
Loosened oil filler cap B
Dirty air cleaner element A
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay B
Clogged fuel line B
Lack of or insufficient fuel C
Chain Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plug or defective gasket B
Loosened cylinder head bolt or defective gasket B
Improper valve sealing B
Defective valve stem C
Wor n or broken valve spr ing B
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing A
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
Lubrication system Incorrect oil pressure B
Cooling system Over-heating C
Over-cooling C
Others Evaporative emission control system malfunction A
Symptom Problem parts etc. Possible cause RANK
Page 1953 of 2453
ME(H6DO)-87
Engine Trouble in General
MECHANICAL
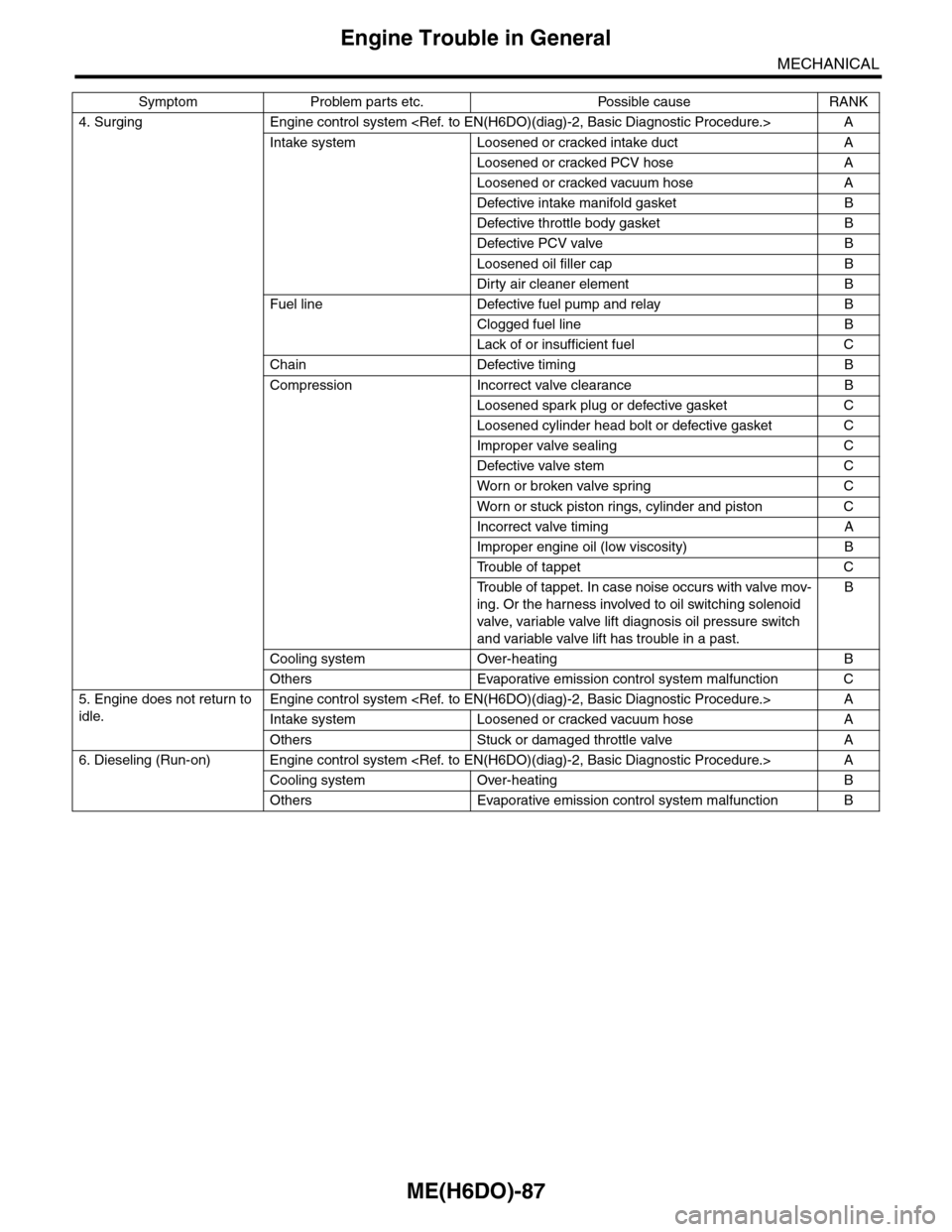
4. Surging Engine control system
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct A
Loosened or cracked PCV hose A
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose A
Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Defective PCV valve B
Loosened oil filler cap B
Dirty air cleaner element B
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay B
Clogged fuel line B
Lack of or insufficient fuel C
Chain Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plug or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolt or defective gasket C
Improper valve sealing C
Defective valve stem C
Wor n or broken valve spr ing C
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing A
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
Cooling system Over-heating B
Others Evaporative emission control system malfunction C
5. Engine does not return to
idle.
Engine control system
Intake system Loosened or cracked vacuum hose A
Others Stuck or damaged throttle valve A
6. Dieseling (Run-on) Engine control system
Cooling system Over-heating B
Others Evaporative emission control system malfunction B
Symptom Problem parts etc. Possible cause RANK
Page 1954 of 2453
ME(H6DO)-88
Engine Trouble in General
MECHANICAL
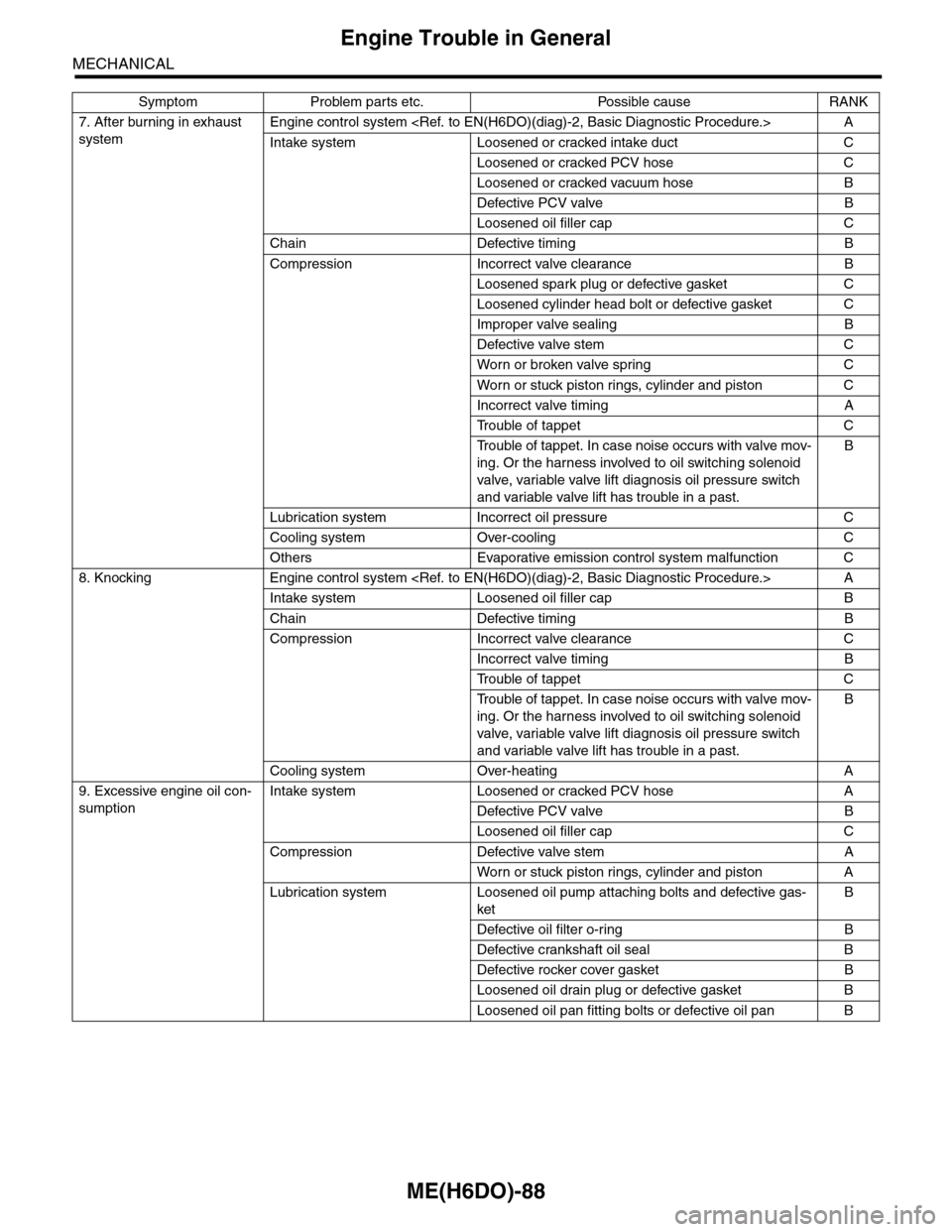
7. After burning in exhaust
system
Engine control system
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct C
Loosened or cracked PCV hose C
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose B
Defective PCV valve B
Loosened oil filler cap C
Chain Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plug or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolt or defective gasket C
Improper valve sealing B
Defective valve stem C
Wor n or broken valve spr ing C
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing A
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
Lubrication system Incorrect oil pressure C
Cooling system Over-cooling C
Others Evaporative emission control system malfunction C
8. Knocking Engine control system
Intake system Loosened oil filler cap B
Chain Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance C
Incorrect valve timing B
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
Cooling system Over-heating A
9. Excessive engine oil con-
sumption
Intake system Loosened or cracked PCV hose A
Defective PCV valve B
Loosened oil filler cap C
Compression Defective valve stem A
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston A
Lubrication system Loosened oil pump attaching bolts and defective gas-
ket
B
Defective oil filter o-ring B
Defective crankshaft oil seal B
Defective rocker cover gasket B
Loosened oil drain plug or defective gasket B
Loosened oil pan fitting bolts or defective oil pan B
Symptom Problem parts etc. Possible cause RANK
Page 1955 of 2453
ME(H6DO)-89
Engine Trouble in General
MECHANICAL
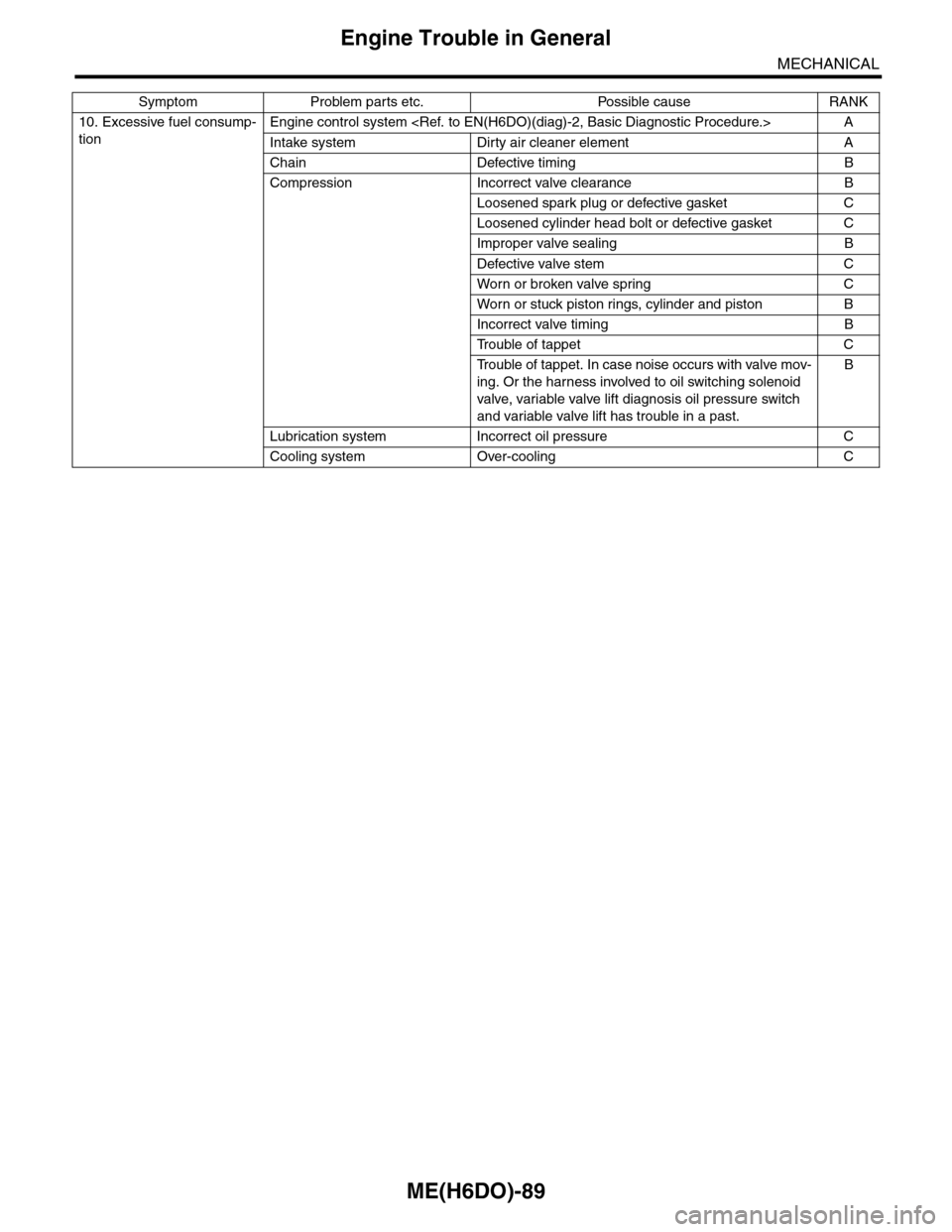
10. Excessive fuel consump-
tion
Engine control system
Intake system Dirty air cleaner element A
Chain Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plug or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolt or defective gasket C
Improper valve sealing B
Defective valve stem C
Wor n or broken valve spr ing C
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston B
Incorrect valve timing B
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
Lubrication system Incorrect oil pressure C
Cooling system Over-cooling C
Symptom Problem parts etc. Possible cause RANK
Page 1956 of 2453
ME(H6DO)-90
Engine Noise
MECHANICAL
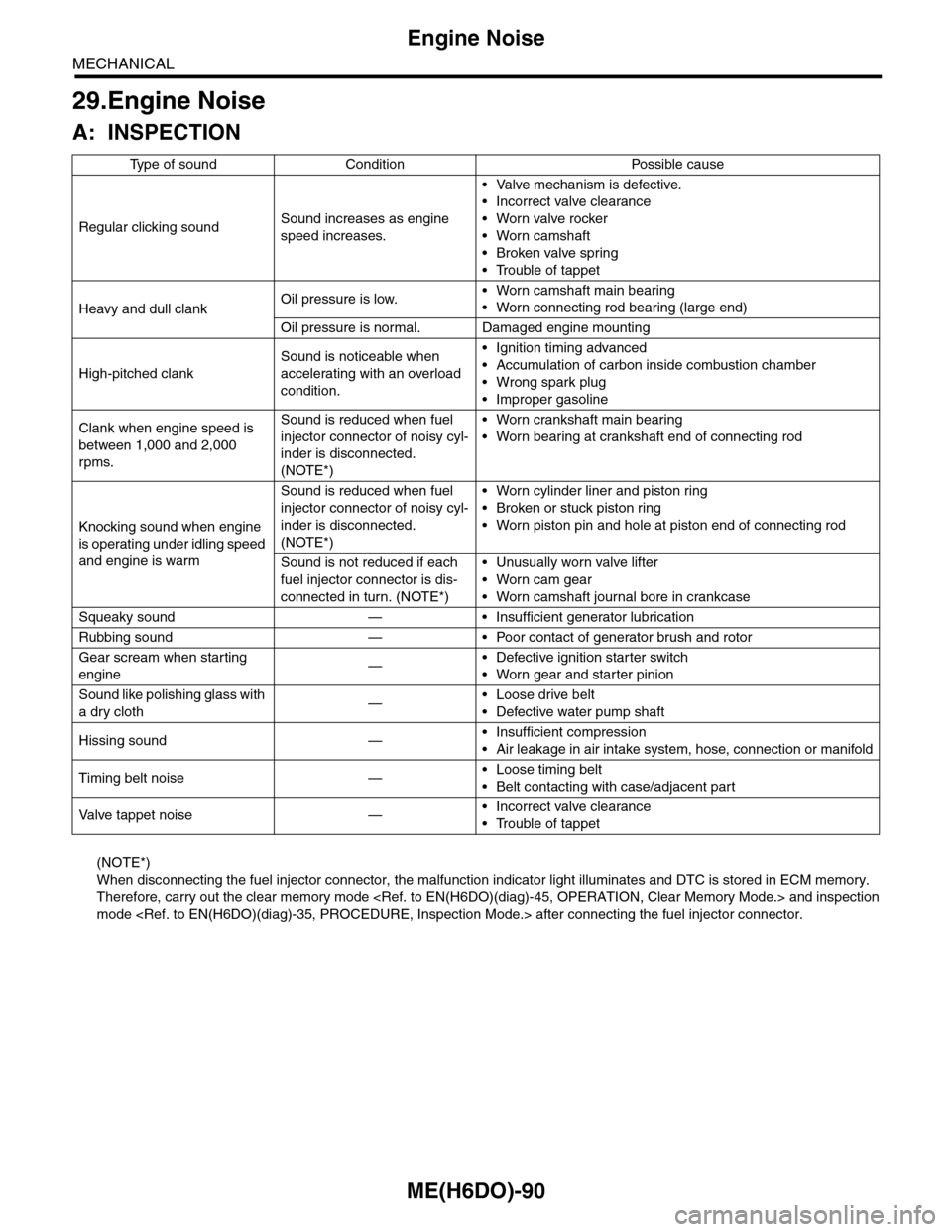
29.Engine Noise
A: INSPECTION
(NOTE*)
When disconnecting the fuel injector connector, the malfunction indicator light illuminates and DTC is stored in ECM memory.
Therefore, carry out the clear memory mode
mode
Ty p e o f s o u n d C o n d i t i o n P o s s i b l e c a u s e
Regular clicking soundSound increases as engine
speed increases.
•Valve mechanism is defective.
•Incorrect valve clearance
•Worn valve rocker
•Worn camshaft
•Broken valve spring
•Trouble of tappet
Heavy and dull clankOil pressure is low.•Worn camshaft main bearing
•Worn connecting rod bearing (large end)
Oil pressure is normal. Damaged engine mounting
High-pitched clank
Sound is noticeable when
accelerating with an overload
condition.
•Ignition timing advanced
•Accumulation of carbon inside combustion chamber
•Wrong spark plug
•Improper gasoline
Clank when engine speed is
between 1,000 and 2,000
rpms.
Sound is reduced when fuel
injector connector of noisy cyl-
inder is disconnected.
(NOTE*)
•Worn crankshaft main bearing
•Worn bearing at crankshaft end of connecting rod
Knocking sound when engine
is operating under idling speed
and engine is warm
Sound is reduced when fuel
injector connector of noisy cyl-
inder is disconnected.
(NOTE*)
•Worn cylinder liner and piston ring
•Broken or stuck piston ring
•Worn piston pin and hole at piston end of connecting rod
Sound is not reduced if each
fuel injector connector is dis-
connected in turn. (NOTE*)
•Unusually worn valve lifter
•Worn cam gear
•Worn camshaft journal bore in crankcase
Squeaky sound — • Insufficient generator lubrication
Rubbing sound — • Poor contact of generator brush and rotor
Gear scream when starting
engine—•Defective ignition starter switch
•Worn gear and starter pinion
Sound like polishing glass with
a dry cloth—•Loose drive belt
•Defective water pump shaft
Hissing sound —•Insufficient compression
•Air leakage in air intake system, hose, connection or manifold
Timing belt noise —•Loose timing belt
•Belt contacting with case/adjacent part
Va l ve t a p p e t n o i s e —•Incorrect valve clearance
•Trouble of tappet
Page 1997 of 2453

PM-14
Engine Coolant
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE SERVICES
10.Engine Coolant
A: REPLACEMENT
1. REPLACEMENT OF ENGINE COOLANT
WARNING:
The radiator is of the pressurized type. Do not
attempt to open the radiator cap immediately
after the engine has been stopped.
1) Lift-up the vehicle.
2) Remove the under cover.
3) Place a container under drain pipe.
4) Remove the drain cock to drain engine coolant
into container.
5) For quick draining, open the radiator cap.
NOTE:
Be careful not to spill coolant on the floor.
6) Drain the coolant from reservoir tank.
7) Tighten the radiator drain cock securely after
draining coolant.
8) Pour cooling system conditioner through the fill-
er neck.
Cooling system protective agent:
Cooling system conditioner (Part number:
SOA345001)
9) Fill engine coolant into the reservoir tank up to
“FULL” level.
Recommended engine coolant:
Refer to “RM” section.
mended Materials.>
Coolant capacity (fill up to “FULL” level):
Approx. 7.4 2 (7.8 US qt, 6.5 Imp qt)
NOTE:
The SUBARU Genuine Coolant containing anti-
freeze and anti-rust agents is especially made for
SUBARU engine, which has an aluminum crank-
case. Always use SUBARU Genuine Coolant,
since other coolant may cause corrosion.
10) Close the radiator cap, and start the engine.
Race 5 to 6 times at 3,000 rpm or less, then stop
the engine. (Complete this operation within 40 sec-
onds.)
11) Wait for one minute after the engine stops, then
open the radiator cap. If the engine coolant level
drops, add engine coolant into radiator up to the fill-
er neck position.
12) Perform the procedures 10) and 11) again.
13) Install the radiator cap and reservoir tank cap
properly.
14) Start the engine and operate the heater at max-
imum hot position and the blower speed setting to
“LO”.
15) Run the engine at 2,000 rpm or less until radia-
tor fan starts and stops.
NOTE:
•Be careful with the engine coolant temperature
gauge to prevent overheating.
•If the radiator hose becomes harden by engine
coolant pressure at this time, air purge seems to be
mostly completed.
16) Stop the engine and wait until the engine cool-
ant temperature lowers to 30°C (86°F).
17) Open the radiator cap. If the engine coolant lev-
el drops, add engine coolant into the coolant filler
tank up to the filler neck position and the reservoir
tank to “FULL” level.
18) Install the radiator cap and reservoir tank cap
properly.
19) Set the heater setting to maximum hot position
and the blower speed setting to “LO” and start the
engine. Perform racing at less than 3,000 rpm. If
the flowing sound is heard from heater core, repeat
the procedures from step 10).
CO-00248
Page 1998 of 2453
PM-15
Engine Coolant
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE SERVICES
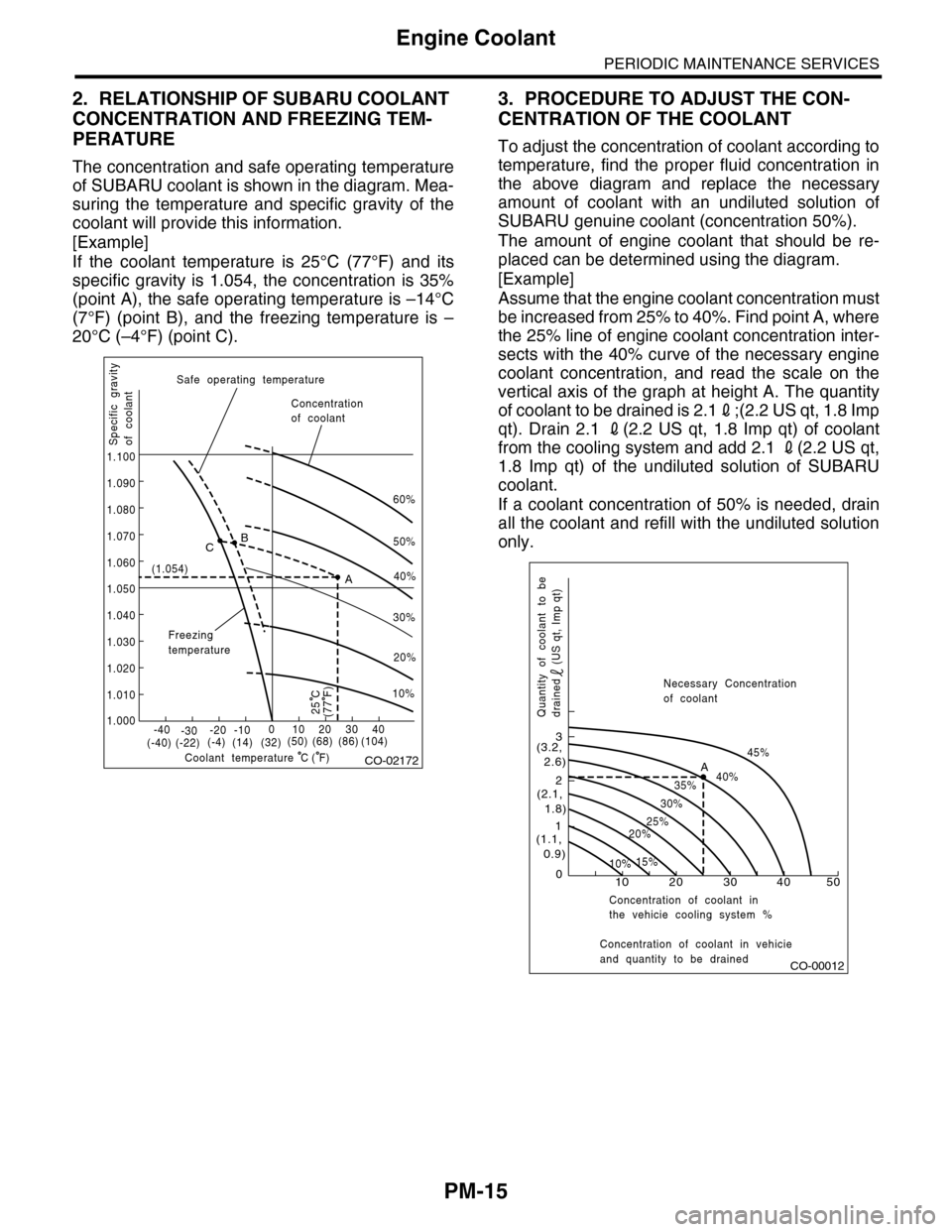
2. RELATIONSHIP OF SUBARU COOLANT
CONCENTRATION AND FREEZING TEM-
PERATURE
The concentration and safe operating temperature
of SUBARU coolant is shown in the diagram. Mea-
suring the temperature and specific gravity of the
coolant will provide this information.
[Example]
If the coolant temperature is 25°C (77°F) and its
specific gravity is 1.054, the concentration is 35%
(point A), the safe operating temperature is –14°C
(7°F) (point B), and the freezing temperature is –
20°C (–4°F) (point C).
3. PROCEDURE TO ADJUST THE CON-
CENTRATION OF THE COOLANT
To adjust the concentration of coolant according to
temperature, find the proper fluid concentration in
the above diagram and replace the necessary
amount of coolant with an undiluted solution of
SUBARU genuine coolant (concentration 50%).
The amount of engine coolant that should be re-
placed can be determined using the diagram.
[Example]
Assume that the engine coolant concentration must
be increased from 25% to 40%. Find point A, where
the 25% line of engine coolant concentration inter-
sects with the 40% curve of the necessary engine
coolant concentration, and read the scale on the
vertical axis of the graph at height A. The quantity
of coolant to be drained is 2.12;(2.2 US qt, 1.8 Imp
qt). Drain 2.1 2(2.2 US qt, 1.8 Imp qt) of coolant
from the cooling system and add 2.1 2(2.2 US qt,
1.8 Imp qt) of the undiluted solution of SUBARU
coolant.
If a coolant concentration of 50% is needed, drain
all the coolant and refill with the undiluted solution
only.
CO-02172
60%
(1.054)
1.000
1.010
1.020
1.030
1.040
1.050
1.060
1.070
1.080
1.090
1.100
Safe operating temperature
Freezingtemperature
Concentrationof coolant
Specific gravityof coolant
Coolant temperature
B
A
C
-40(-40) (-22)(-4)(14)(32)(50) (68) (86)
( F)
(104)-30-20 -10010203040
(77 F)
50%
40%
30%
20%
25 C
10%
C
CO-00012
100
1
2
3
(1.1, 0.9)
(2.1, 1.8)
(3.2, 2.6)
10%15%
25%20%
30%
35%40%
45%A
20 30 40 50
Concentration of coolant in vehicieand quantity to be drained
Quantity of coolant to bedrained (US qt, Imp qt)
Necessary Concentrationof coolant
Concentration of coolant inthe vehicie cooling system %
Page 2000 of 2453

PM-17
Automatic Transmission Fluid
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE SERVICES
2. ATF FILTER
NOTE:
Basically, the ATF filter is maintenance free, but
when it is rusted or physically damaged or leaking,
the ATF filter needs to be replaced.
For the replacement procedure of ATF filter, refer
to “ATF FILTER”.