2007 TOYOTA SIENNA spark plugs
[x] Cancel search: spark plugsPage 80 of 3000

IG–62GR-FE IGNITION – IGNITION COIL AND SPARK PLUG
IG
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
NOTICE:
In this section, the terms "cold" and "hot" refer to the
temperature of the coils. "Cold" means approximately -
10
C (14F) to 50C (122F). "Hot" means approximately
50
C (122F) to 100C (212F).
1. INSPECT IGNITION COIL ASSEMBLY
(a) Check for DTCs.
NOTICE:
If any DTC is present, perform troubleshooting
in accordance with the procedures for that DTC.
(b) Remove the ignition coil assembly and spark plug.
(See page IG-8).
(c) Check that sparks occur.
(1) Disconnect the 6 fuel injector connectors.
(2) Install the spark plugs to each ignition coil, and
connect the ignition coil connectors.
(3) Ground the spark plugs.
(4) Check if a spark occurs at each spark plug
while the engine is being cranked.
NOTICE:
• Be sure to ground the spark plugs when
checking.
• Replace the ignition coil if it receives an
impact.
• Do not crank the engine for more than 2
seconds.
(d) Perform the spark test according to the flowchart
below.
(1) Check that the ignition coil connector is
securely connected.
Result
(2) Perform a spark test on each ignition coil.
1. Replace the ignition coil with a normal one.
2. Perform the spark test again.
Result
A133895
A133897
Result Proceed to
NG Connect securely
OK Go to next step
Result Proceed to
NG Go to next step
OK Replace ignition coil
Page 81 of 3000

2GR-FE IGNITION – IGNITION COIL AND SPARK PLUGIG–7
IG
(3) Check the spark plug (See page EM-1).
Result
(4) Check the power supply to the ignition coil.
1. Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
2. Check that there is battery voltage at the
ignition coil positive (+) terminal.
Result
(5) Measure the resistance of the crankshaft
position sensor (See page ES-514).
Result
(6) Check the IGT signal from the ECM (See page
ES-233)
Result
(e) Using a 16 mm (0.63 in.) plug wrench, install the
spark plugs.
Torque: 18 N*m (184 kgf*cm, 13 ft.*lbf)
(f) Connect the 6 fuel injector connectors.
(g) Install the ignition coil assembly (See page IG-10).
2. INSPECT SPARK PLUG
NOTICE:
• Never use a wire brush for cleaning.
• Never attempt to adjust the electrode gap on a
used spark plug.
(a) Check the electrode.
(1) Using a megohmmeter, measure the insulation
resistance.
Standard insulation resistance:
10 M
or higher
HINT:
• If the result is 10 M
or less, clean the plug
and measure the resistance again.
• If a megohmmeter is not available, perform
the following simple inspection instead.
(b) Alternative inspection method:
(1) Quickly accelerate the engine to 4000 rpm 5
times.
Result Proceed to
NG Replace spark plug
OK Go to next step
Result Proceed to
NGCheck wiring between ignition
switch and ignition coil
OK Go to next step
Result Proceed to
NG Replace crankshaft position sensor
OK Go to next step
Result Proceed to
NG Check ECM
OKRepair wiring between ignition coil
and ECM
I039522E10
Page 82 of 3000

IG–82GR-FE IGNITION – IGNITION COIL AND SPARK PLUG
IG
(2) Remove the spark plugs.
(3) Visually check the spark plug.
If the electrode is dry, the spark plug is
functioning properly. If the electrode is damp,
proceed to the next step.
(c) Check the spark plug for any damage to its threads
and insulator. If there is damage, replace the spark
plug.
Recommended spark plug
NOTICE:
Use only the listed spark plug or equivalent to
ensure engine performance and smooth
driveability.
(d) Check the spark plug electrode gap.
Maximum electrode gap for used spark plug:
1.4 mm (0.055 in.)
If the gap is greater than the maximum, replace the
spark plug.
Electrode gap for new spark plug:
1.0 to 1.1 mm (0.039 to 0.043 in.)
(e) Clean the spark plugs.
If the electrode has traces of wet carbon, clean the
electrode with a spark plug cleaner and then dry it.
Standard air pressure:
588 kPa (6 kgf*cm
2, 85 psi)
Standard duration:
20 seconds or less
HINT:
Only use the spark plug cleaner when the electrode
is free of oil. If the electrode has traces of oil, use
gasoline to clean off the oil before using the spark
plug cleaner.
(f) Install the ignition coil assembly and spark plug.
(See page IG-10).
Manufacturer Spark Plug Type
DENSO FK20HR11
A163282E01
B062019
Page 501 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–195
ES
Between 7.4 g/s and 18.9 g/s (shift position: N, A/
C: OFF).
NG
OK
(a) Check the fuel pressure (See page FU-7).
NG
OK
OK:
No gas leakage.
NG
OK
(a) Check for sparks and ignition (See page ES-217).
HINT:
If the spark plugs or ignition system malfunctions, engine
misfire may occur. The misfire count can be read using
the intelligent tester. Select the following menu items:
DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / DATA LIST /
PRIMARY / CYL #1 (to CYL #6).
NG
OK
(a) Inspect the fuel injector assembly (See page FU-16).
HINT:
If the injectors malfunction, engine misfire may occur.
The misfire count can be read using the intelligent tester.
Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DATA LIST / PRIMARY / CYL #1
(to CYL #6).
NG
OKREPLACE MASS AIR FLOW METER (See
page ES-504)
7CHECK FUEL PRESSURE
REPAIR OR REPLACE FUEL SYSTEM
8INSPECT FOR EXHAUST GAS LEAK
REPAIR OR REPLACE EXHAUST SYSTEM
9CHECK FOR SPARKS AND IGNITION
REPAIR OR REPLACE IGNITION SYSTEM
10INSPECT FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY (INJECTION AND VOLUME)
REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY (See
page FU-13)
Page 514 of 3000

ES–2082GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
7. Drive the vehicle several times with the conditions, such as engine rpm and engine load, shown in
MISFIRE RPM and MISFIRE LOAD in the Data List.
HINT:
• In order to store misfire DTCs, it is necessary to operate the vehicle for the period of time shown in
the table below, using the MISFIRE RPM and MISFIRE LOAD in the Data List.
8. Check whether misfires have occurred by checking DTCs and freeze frame data.
HINT:
Do not turn the ignition switch off until the stored DTC(s) and freeze frame data have been recorded.
When the ECM returns to normal mode (default), the stored DTC(s), freeze frame data and other data
will be erased.
9. Record the DTC(s), freeze frame data and misfire counts.
10.Turn the ignition switch OFF and wait for at least 5 seconds.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
• If any DTCs other than misfire DTCs are output, troubleshoot those DTCs first.
• Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester or Techstream. Freeze frame data records the
engine condition when malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help
determine if the vehicle was moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel
ratio was lean or rich, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
• If the misfire does not recur when the vehicle is brought to the workshop, reproduce the conditions
stored in the ECM as freeze frame data.
• If the misfire still cannot be reproduced even though the conditions stored in the ECM as freeze frame
data have been reproduced, one of the following factors is considered to be a possible cause of the
problem:
(a) There was insufficient fuel volume in the tank.
(b) Improper fuel is used.
(c) The spark plugs have been contaminated.
• After finishing repairs, check the misfire counts of the cylinders (CYL #1, #2, #3, #4, #5, #6).
• Be sure to confirm that no misfiring cylinder DTCs are set again by conducting the confirmation driving
pattern after finishing repairs.
• For 6 and 8 cylinder engines, the ECM intentionally does not set the specific misfiring cylinder DTCs at
high engine RPM. If misfires occur only in high engine RPM areas, only DTC P0300 is set.
In the event of DTC P0300 being present, perform the following operations:
(a) Clear the DTC (See page ES-39).
(b) Start the engine and conduct the confirmation driving pattern.
(c) Read the misfiring rates of each cylinder or DTC(s) using the tester.
(d) Repair the cylinder(s) that has a high misfiring rate or is indicated by the DTC.
(e) After finishing repairs, conduct the confirmation driving pattern again, in order to verify that DTC
P0300 is not set.
• When one of SHORT FT #1, LONG FT #1, SHORT FT #2 or LONG FT #2 in the freeze frame data is
outside the range of +/-20%, the air-fuel ratio may be Rich (-20% or less) or Lean (+20% or more).
• When the COOLANT TEMP in the freeze frame data is less than 75
C (167F), the misfire have
occurred only while warming up the engine.
Engine RPM Duration
Idling 3.5 minutes or more
1000 3 minutes or more
2000 1.5 minutes or more
3000 1 minute or more
Page 547 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–241
ES
HINT:
• These DTCs indicate malfunctions relating to the primary circuit.
• If DTC P0351 is set, check the No. 1 ignition coil with igniter circuit.
• If DTC P0352 is set, check the No. 2 ignition coil with igniter circuit.
• If DTC P0353 is set, check the No. 3 ignition coil with igniter circuit.
• If DTC P0354 is set, check the No. 4 ignition coil with igniter circuit.
• If DTC P0355 is set, check the No. 5 ignition coil with igniter circuit.
• If DTC P0356 is set, check the No. 6 ignition coil with igniter circuit.
DESCRIPTION
A Direct Ignition System (DIS) is used on this vehicle.
The DIS is a 1-cylinder ignition system in which each cylinder is ignited by one ignition coil and one spark
plug is connected to the end of each secondary wiring. High-voltage is generated in the secondary wiring
and then applied directly to each spark plug. The sparks of the spark plugs pass from the center
electrodes to the ground electrodes.
The ECM determines the ignition timing and transmits the ignition (IGT) signals to each cylinder. Using the
IGT signal, the ECM turns the power transistor inside the igniter on and off. The power transistor, in turn,
switches on and off the current to the primary coil. When the current to the primary coil is cut off, high-
voltage is generated in the secondary coil. This voltage is applied to the spark plugs, causing them to
spark inside the cylinders. As the ECM cuts the current to the primary coil off, the igniter sends back an
ignition confirmation (IGF) signal to the ECM, for each cylinder ignition.
DTC P0351 Ignition Coil "A" Primary / Secondary Circuit
DTC P0352 Ignition Coil "B" Primary / Secondary Circuit
DTC P0353 Ignition Coil "C" Primary / Secondary Circuit
DTC P0354 Ignition Coil "D" Primary / Secondary Circuit
DTC P0355 Ignition Coil "E" Primary / Secondary Circuit
DTC P0356 Ignition Coil "F" Primary / Secondary Circuit
Page 881 of 3000
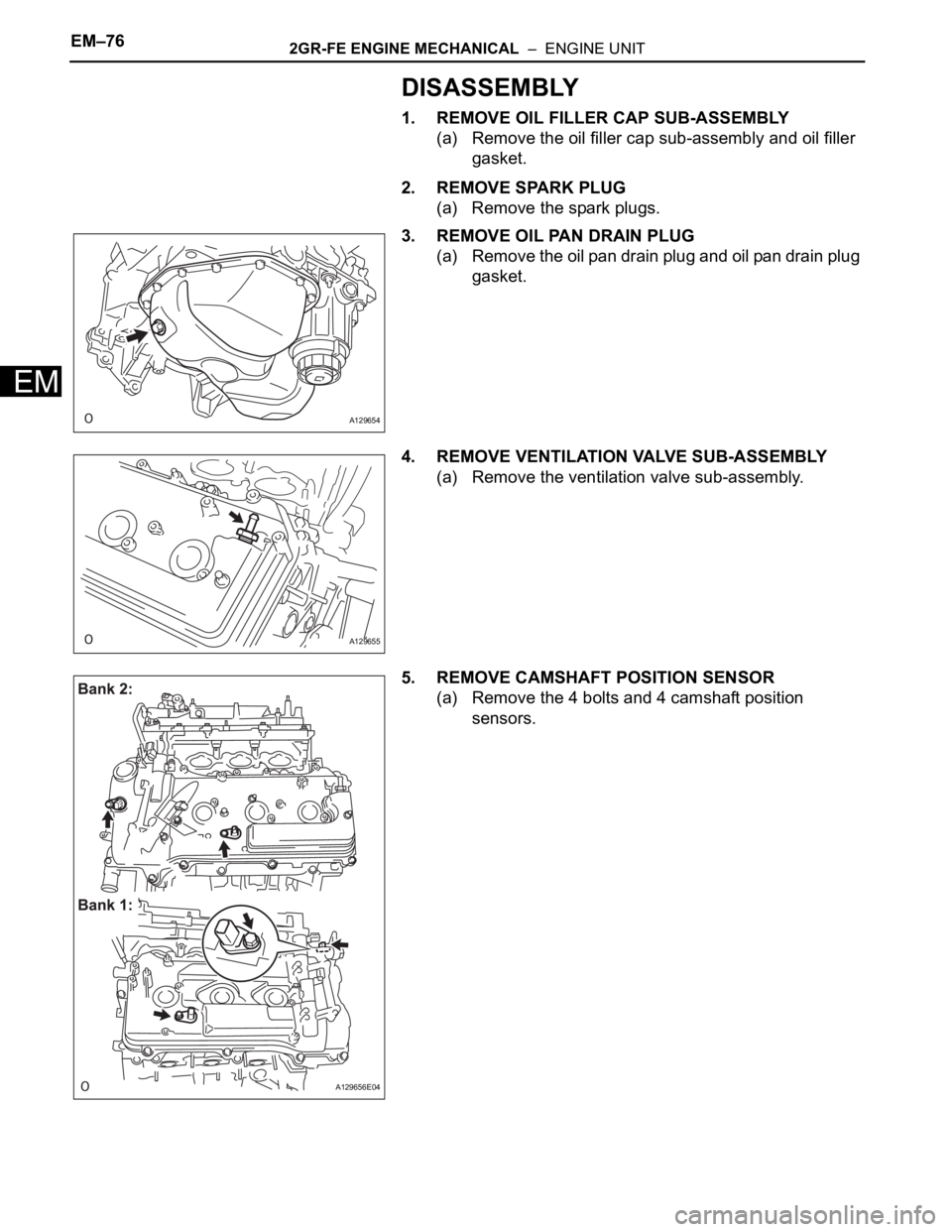
EM–762GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNIT
EM
DISASSEMBLY
1. REMOVE OIL FILLER CAP SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the oil filler cap sub-assembly and oil filler
gasket.
2. REMOVE SPARK PLUG
(a) Remove the spark plugs.
3. REMOVE OIL PAN DRAIN PLUG
(a) Remove the oil pan drain plug and oil pan drain plug
gasket.
4. REMOVE VENTILATION VALVE SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the ventilation valve sub-assembly.
5. REMOVE CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
(a) Remove the 4 bolts and 4 camshaft position
sensors.
A129654
A129655
A129656E04
Page 931 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINEEM–1
EM
ENGINE
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
1. INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT
(a) Inspect the engine coolant (See page CO-1).
2. INSPECT ENGINE OIL
(a) Inspect the engine oil (See page LU-1).
3. INSPECT BATTERY
(a) Inspect the battery (See page CH-5).
4. INSPECT AIR CLEANER FILTER ELEMENT SUB-
ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the air cleaner filter element sub-assembly.
(b) Visually check that there is no dirt, blockage, and/or
damage to the air cleaner filter element.
HINT:
• If there is any dirt or a blockage in the air cleaner
filter element, clean it with compressed air.
• If any dirt or a blockage remains even after
cleaning the air cleaner filter element with
compressed air, replace it.
5. INSPECT SPARK PLUG
(a) Inspect the spark plugs (See page IG-5).
6. INSPECT VALVE LASH ADJUSTER NOISE
(a) Rev up the engine several times. Check that the
engine does not emit unusual noises.
If unusual noises occur, warm up the engine and
idle it for over 30 minutes. Then repeat this
procedure.
HINT:
If any defects or problems are found during the
inspection above, perform lash adjuster inspection
(See page EM-100).
7. INSPECT IGNITION TIMING
(a) Warm up the engine.
(b) When using the intelligent tester:
Check the ignition timing.
(1) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(2) Enter DATA LIST mode with the intelligent
tester.
Ignition timing:
8 to 12
BTDC at idle
HINT:
Refer to the intelligent tester operator's manual
for help when selecting the DATA LIST.
C110200E02