2007 TOYOTA SIENNA door lock
[x] Cancel search: door lockPage 51 of 3000
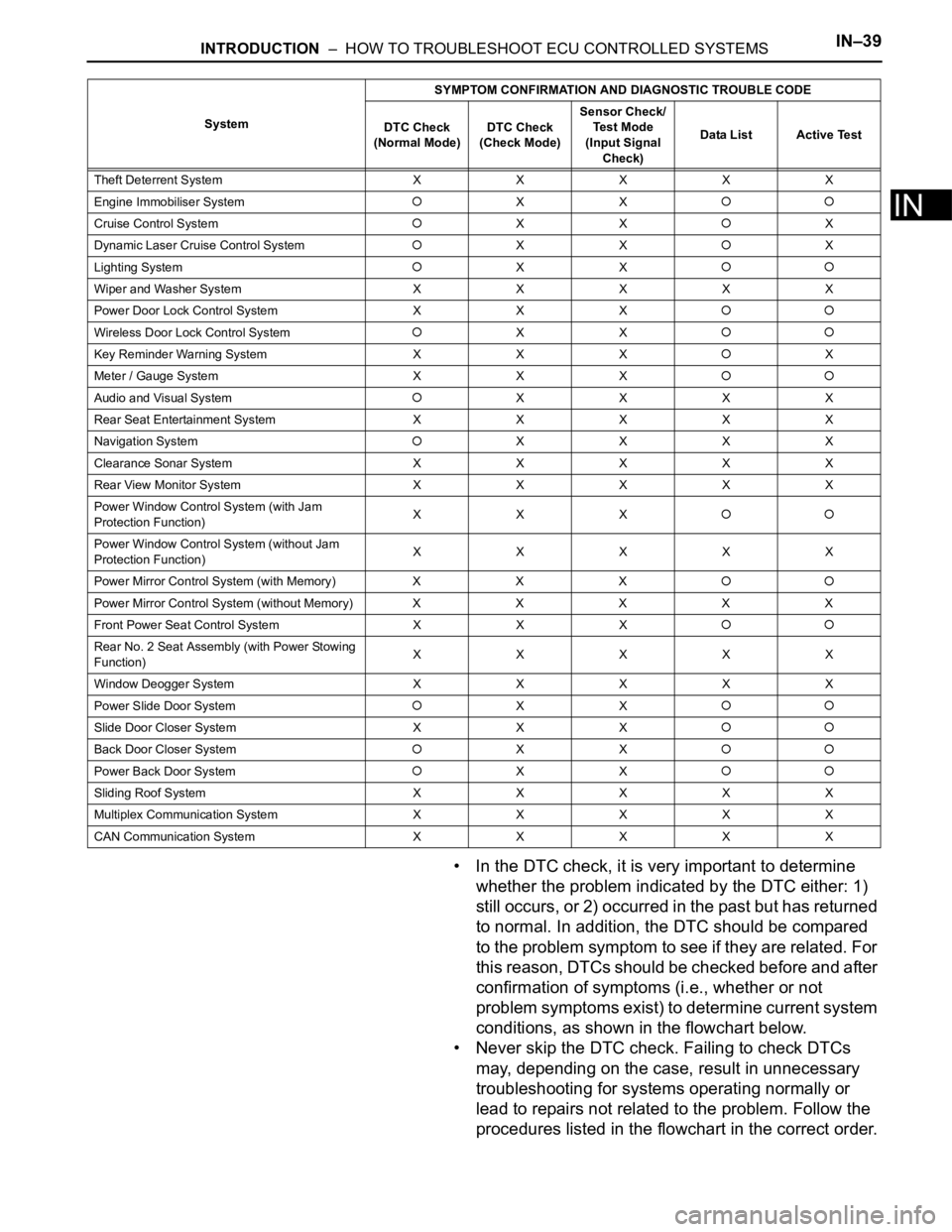

INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMSIN–39
IN
• In the DTC check, it is very important to determine
whether the problem indicated by the DTC either: 1)
still occurs, or 2) occurred in the past but has returned
to normal. In addition, the DTC should be compared
to the problem symptom to see if they are related. For
this reason, DTCs should be checked before and after
confirmation of symptoms (i.e., whether or not
problem symptoms exist) to determine current system
conditions, as shown in the flowchart below.
• Never skip the DTC check. Failing to check DTCs
may, depending on the case, result in unnecessary
troubleshooting for systems operating normally or
lead to repairs not related to the problem. Follow the
procedures listed in the flowchart in the correct order.
Theft Deterrent System XXXXX
Engine Immobiliser System
XX
Cruise Control SystemXXX
Dynamic Laser Cruise Control System
XXX
Lighting System
XX
Wiper and Washer SystemXXXXX
Power Door Lock Control System X X X
Wireless Door Lock Control SystemXX
Key Reminder Warning System X X XX
Meter / Gauge System X X X
Audio and Visual SystemXXXX
Rear Seat Entertainment System XXXXX
Navigation System
XXXX
Clearance Sonar SystemXXXXX
Rear View Monitor System XXXXX
Power Window Control System (with Jam
Protection Function)XXX
Power Window Control System (without Jam
Protection Function)XXXXX
Power Mirror Control System (with Memory) X X X
Power Mirror Control System (without Memory)XXXXX
Front Power Seat Control System X X X
Rear No. 2 Seat Assembly (with Power Stowing
Function)XXXXX
Window Deogger SystemXXXXX
Power Slide Door System
XX
Slide Door Closer System X X X
Back Door Closer SystemXX
Power Back Door SystemXX
Sliding Roof System XXXXX
Multiplex Communication System XXXXX
CAN Communication System XXXXXSystemSYMPTOM CONFIRMATION AND DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
DTC Check
(Normal Mode)DTC Check
(Check Mode)Sensor Check/
Test Mode
(Input Signal
Check)Data List Active Test
Page 69 of 3000
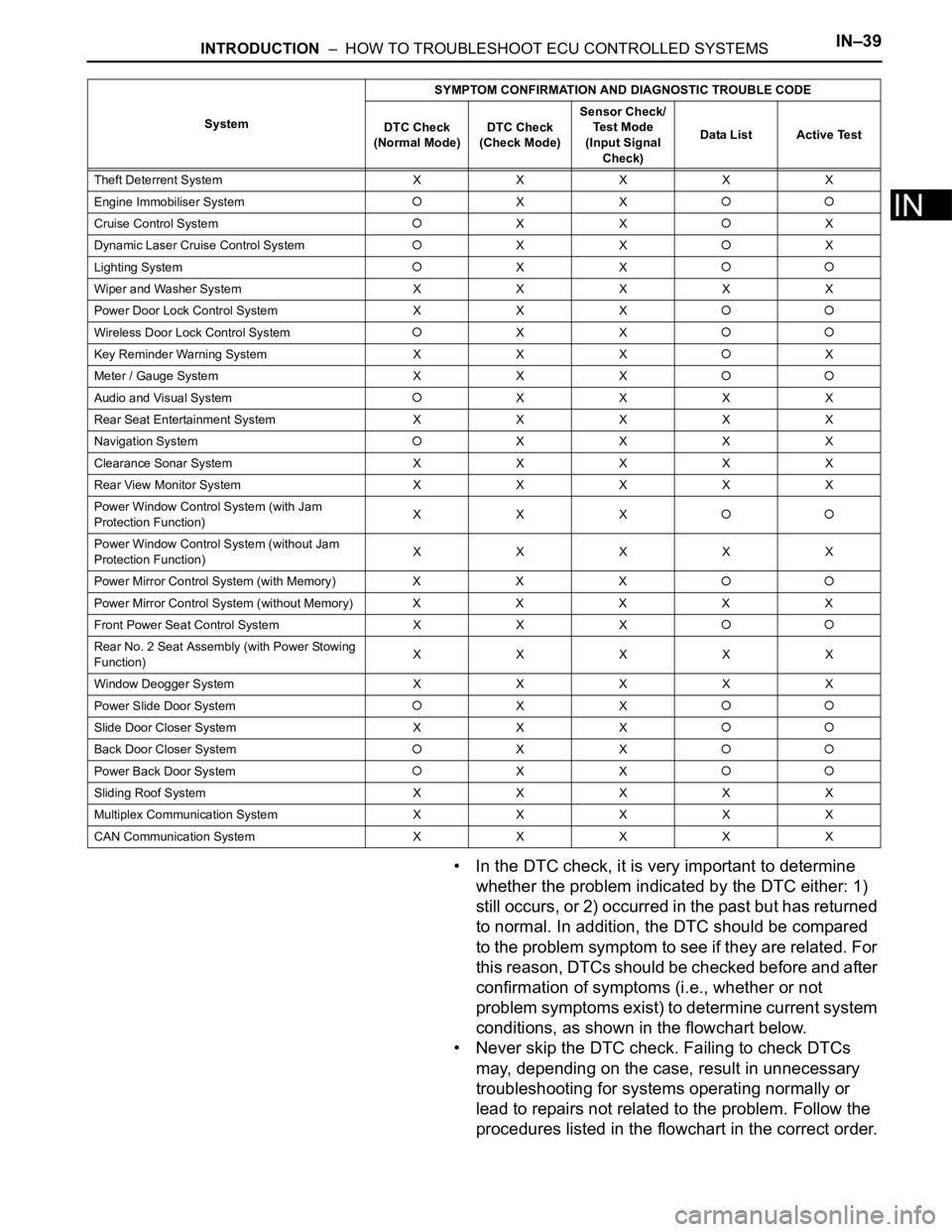

INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMSIN–39
IN
• In the DTC check, it is very important to determine
whether the problem indicated by the DTC either: 1)
still occurs, or 2) occurred in the past but has returned
to normal. In addition, the DTC should be compared
to the problem symptom to see if they are related. For
this reason, DTCs should be checked before and after
confirmation of symptoms (i.e., whether or not
problem symptoms exist) to determine current system
conditions, as shown in the flowchart below.
• Never skip the DTC check. Failing to check DTCs
may, depending on the case, result in unnecessary
troubleshooting for systems operating normally or
lead to repairs not related to the problem. Follow the
procedures listed in the flowchart in the correct order.
Theft Deterrent System XXXXX
Engine Immobiliser System
XX
Cruise Control SystemXXX
Dynamic Laser Cruise Control System
XXX
Lighting System
XX
Wiper and Washer SystemXXXXX
Power Door Lock Control System X X X
Wireless Door Lock Control SystemXX
Key Reminder Warning System X X XX
Meter / Gauge System X X X
Audio and Visual SystemXXXX
Rear Seat Entertainment System XXXXX
Navigation System
XXXX
Clearance Sonar SystemXXXXX
Rear View Monitor System XXXXX
Power Window Control System (with Jam
Protection Function)XXX
Power Window Control System (without Jam
Protection Function)XXXXX
Power Mirror Control System (with Memory) X X X
Power Mirror Control System (without Memory)XXXXX
Front Power Seat Control System X X X
Rear No. 2 Seat Assembly (with Power Stowing
Function)XXXXX
Window Deogger SystemXXXXX
Power Slide Door System
XX
Slide Door Closer System X X X
Back Door Closer SystemXX
Power Back Door SystemXX
Sliding Roof System XXXXX
Multiplex Communication System XXXXX
CAN Communication System XXXXXSystemSYMPTOM CONFIRMATION AND DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
DTC Check
(Normal Mode)DTC Check
(Check Mode)Sensor Check/
Test Mode
(Input Signal
Check)Data List Active Test
Page 187 of 3000
PARKING BRAKE – PARKING BRAKE PEDALPB–5
PB
REMOVAL
1. DISCONNECT BATTERY NEGATIVE TERMINAL
2. REMOVE FRONT DOOR SCUFF PLATE LH
3. REMOVE COWL SIDE TRIM BOARD LH
4. REMOVE INSTRUMENT PANEL FINISH PANEL SUB-
ASSEMBLY LOWER LH (See page IP-6)
5. REMOVE REAR DOOR SCUFF PLATE RH
6. REMOVE REAR DOOR SCUFF PLATE LH
7. REMOVE FRONT SEAT ASSEMBLY LH
HINT:
• Manual Seat Type (See page SE-48)
• Power Seat Type (See page SE-58)
• Fold Flat Type (See page SE-40)
8. REMOVE REAR SEAT NO.1 ASSEMBLY
HINT:
• Captain Seat Type (See page SE-68)
• Center Seat Type (See page SE-77)
9. REMOVE REAR FLOOR SEAT LOCK COVER
10. REMOVE REAR FLOOR SEAT LOCK COVER
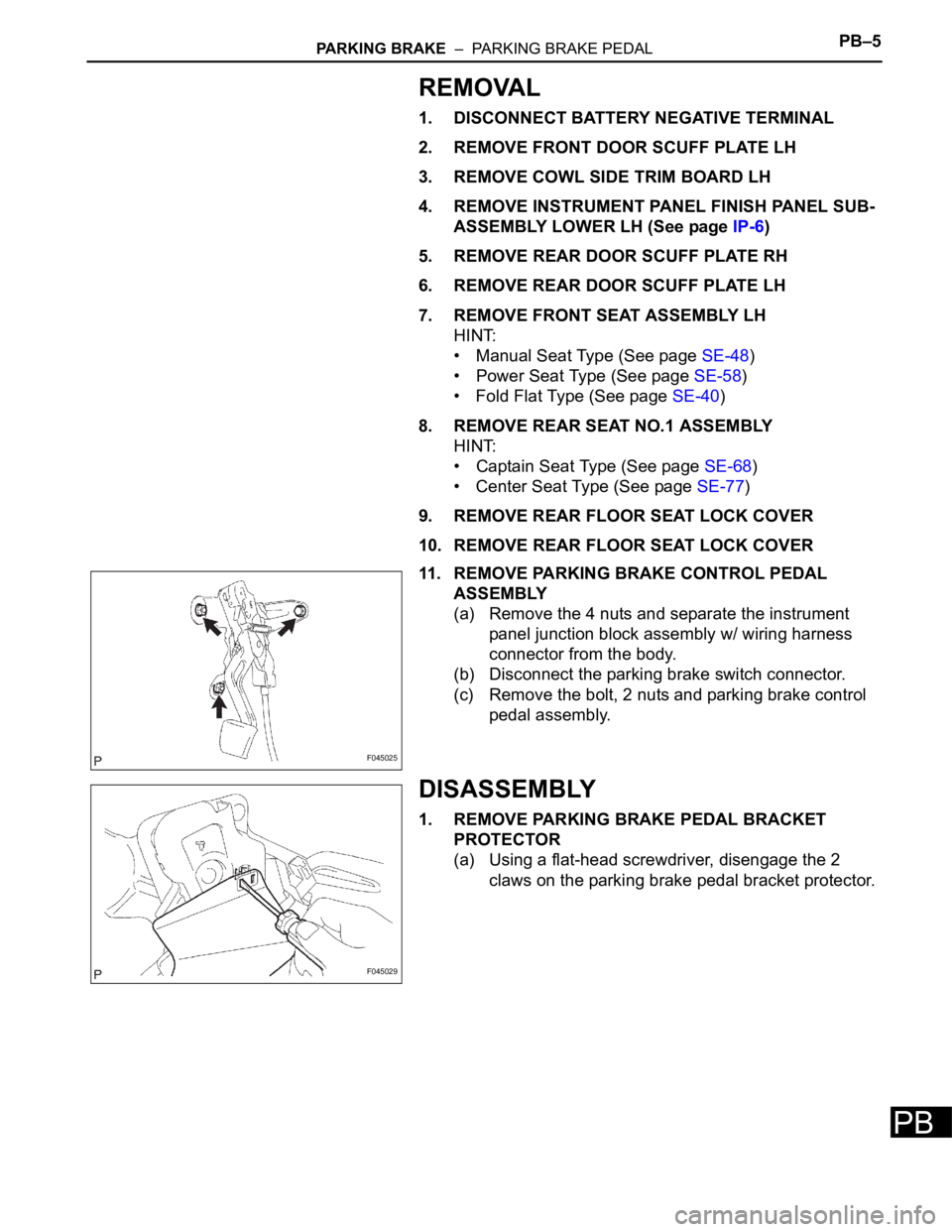
11. REMOVE PARKING BRAKE CONTROL PEDAL
ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the 4 nuts and separate the instrument
panel junction block assembly w/ wiring harness
connector from the body.
(b) Disconnect the parking brake switch connector.
(c) Remove the bolt, 2 nuts and parking brake control
pedal assembly.
DISASSEMBLY
1. REMOVE PARKING BRAKE PEDAL BRACKET
PROTECTOR
(a) Using a flat-head screwdriver, disengage the 2
claws on the parking brake pedal bracket protector.
F045025
F045029
Page 236 of 3000

THEFT DETERRENT – THEFT DETERRENT SYSTEMTD–3
TD
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
1. OUTLINE OF THEFT DETERRENT SYSTEM
(a) When the theft deterrent system detects that the
vehicle is being tampered with, the system sets off
the alarm, causing the horns to sound and the lights
to light up or blink in order to alert people around the
vehicle to the theft.
(b) The theft deterrent system has 2 modes; one is the
active arming mode (see ACTIVE ARMING MODE)
and the other is passive arming mode (see
PASSIVE ARMING MODE). The passive arming
mode can be switched ON/OFF using the specified
method.
(c) Each mode has 4 states; a disarmed state, an
arming preparation state, an armed state and an
alarm sounding state.
(1) Disarmed state:
• The alarm function is not operating.
• The theft deterrent system is not operating.
(2) Arming preparation state:
• The time until the system goes into the armed
state.
• The theft deterrent system is not operating.
(3) Armed state:
• The theft deterrent system is operating.
(4) Alarm sounding state:
• Alarm function is operating.
Alarm time:
Approx. 60 sec.
Refer to table below for alarm method and time:
HINT:
If any of the doors are unlocked with no key in
the ignition key cylinder during the armed state,
a forced door lock signal will be output (see
FORCED DOOR LOCK CONTROL).
2. ACTIVE ARMING MODE
HINT:
• Active arming mode starts the alarm control
immediately after the doors are locked.
• This system activates as described in the diagram
below when one of items for each condition is met.
Alarm MethodHeadlight Blinking (approx. 0.4 second cycles)
Taillight Blinking (approx. 0.4 second cycles)
Hazard Warning Light Blinking (cycles of flasher relay)
Interior Light Illuminating
Vehicle HornSounding
(approx. 0.4 second cycles)
Security HornSounding
(approx. 0.4 second cycles)
Alarm Time Approx. 60 sec.
Page 237 of 3000
TD–4THEFT DETERRENT – THEFT DETERRENT SYSTEM
TD
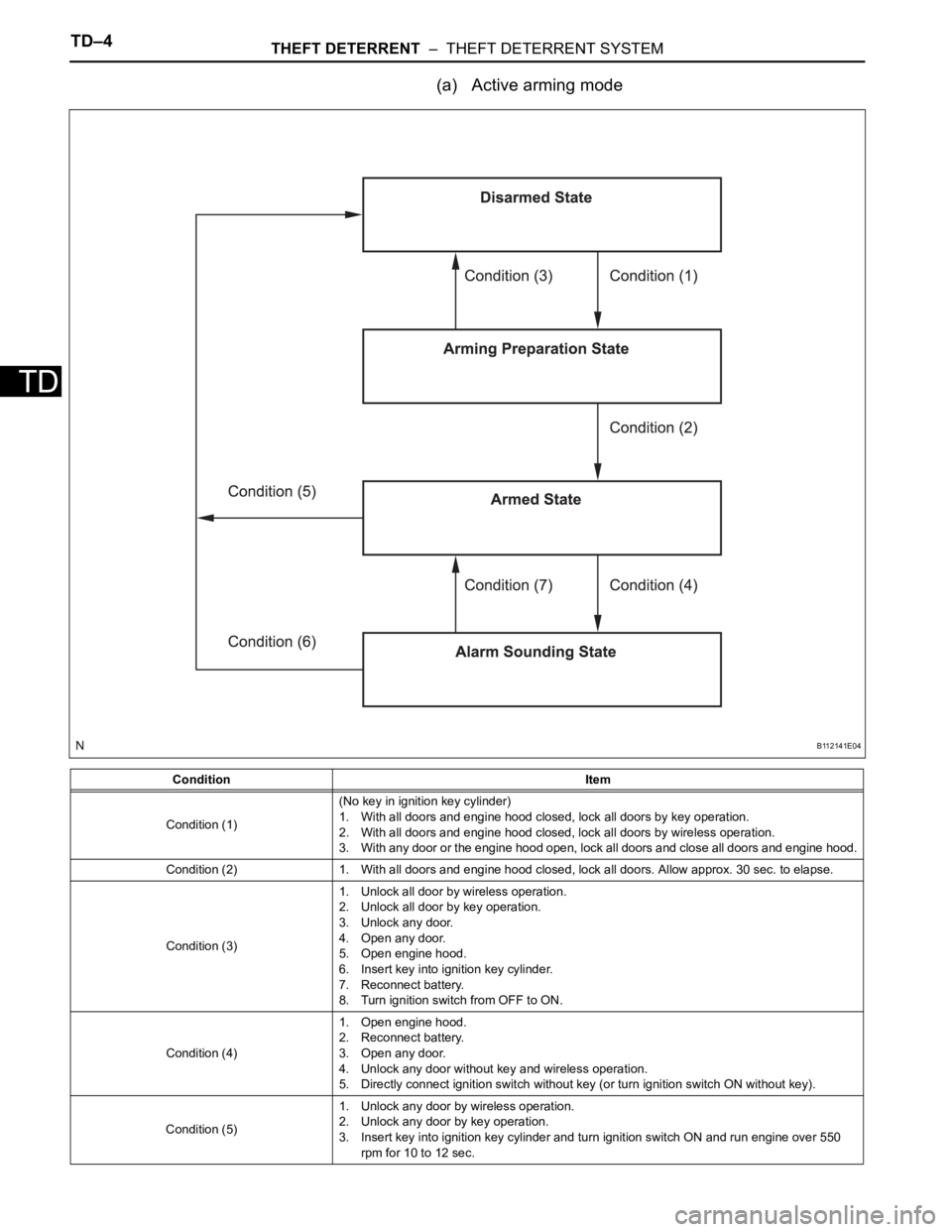
(a) Active arming mode
Condition Item
Condition (1)(No key in ignition key cylinder)
1. With all doors and engine hood closed, lock all doors by key operation.
2. With all doors and engine hood closed, lock all doors by wireless operation.
3. With any door or the engine hood open, lock all doors and close all doors and engine hood.
Condition (2) 1. With all doors and engine hood closed, lock all doors. Allow approx. 30 sec. to elapse.
Condition (3)1. Unlock all door by wireless operation.
2. Unlock all door by key operation.
3. Unlock any door.
4. Open any door.
5. Open engine hood.
6. Insert key into ignition key cylinder.
7. Reconnect battery.
8. Turn ignition switch from OFF to ON.
Condition (4)1. Open engine hood.
2. Reconnect battery.
3. Open any door.
4. Unlock any door without key and wireless operation.
5. Directly connect ignition switch without key (or turn ignition switch ON without key).
Condition (5)1. Unlock any door by wireless operation.
2. Unlock any door by key operation.
3. Insert key into ignition key cylinder and turn ignition switch ON and run engine over 550
rpm for 10 to 12 sec.
B112141E04
Page 238 of 3000

THEFT DETERRENT – THEFT DETERRENT SYSTEMTD–5
TD
3. PASSIVE ARMING MODE
HINT:
• Passive arming mode starts the alarm control after
the key is removed from the ignition key cylinder and
doors are closed.
• Passive arming mode can be switched ON/OFF by
the specified method.
• The alarm is initially set (when shipped from factory)
to active arming mode (not passive arming mode).
• During passive arming mode, the theft deterrent
system goes into the armed state even if the doors
are not locked.
• Detecting that the doors are unlocked does not set off
the alarm during passive arming mode.
• A forced door lock signal is not output during passive
arming mode (see FORCED DOOR LOCK
CONTROL).
• Although the theft deterrent system detects that the
doors are opened during passive arming mode, the
alarm will not go off immediately because an entry
delay time is set.
• If any of the following conditions is met during passive
arming mode, the theft deterrent system will switch to
active arming mode.
– With all doors and engine hood closed, lock all
doors by key operation.
– With all doors and engine hood closed, lock all
doors by wireless operation.
– With any door or the engine hood open, lock all
doors and close all doors and engine hood.
• This system activates as described in the diagram
below when one of items for each condition is met.
Condition (6)1. Unlock any door by wireless operation.
2. Unlock any door by key operation.
3. Insert key into ignition key cylinder and turn ignition switch from OFF to ON.
Condition (7) 1. After approx. 60 sec., alarm stops and system returns to armed state. Condition Item
Page 240 of 3000

THEFT DETERRENT – THEFT DETERRENT SYSTEMTD–7
TDHINT:
*1: When any door is opened while all the doors are
closed during passive arming mode, the entry delay
time starts. If the switch condition (armed state
disarmed state (1) or (2)) is met during the entry
delay time, the theft deterrent system will return to
disarmed state (1) or (2). However, if the switch
condition for disarmed state (1) or (2) is not met, the
theft deterrent system will recognize it as a theft and
set off the alarm.
Entry delay time of 0, 14 or 30 sec. can be selected
by the customizing function.
4. FORCED DOOR LOCK CONTROL
(a) The forced door lock control prevents the vehicle
from being tampered with. Immediately after a door
is unlocked (alarm starts), the door is forced to lock
by a forced door lock signal.
(1) Conditions that force the doors to lock:
No key is in the ignition key cylinder and both of
the following conditions are met.
• The theft deterrent system is in the alarm
sounding state of active arming mode.
• Any door is unlocked.
Condition (3)1. Unlock all door by wireless operation.
2. Insert key into ignition key cylinder.
3. Reconnect battery.
4. Turn ignition switch from OFF to ON.
5. Unlock any door by key operation.
Condition (4) 1. With all doors and engine hood closed, allow approx. 30 sec. to elapse.
Condition (5) 1. Open any door or the engine hood.
Condition (6)1. Open any door and allow entry delay time
*1 to elapse.
2. Open engine hood.
3. Reconnect battery.
4. Directly connect ignition switch without key (or turn ignition switch ON without key).
Condition (7)1. Unlock all door by wireless operation.
2. Unlock all door by key operation.
3. Insert key into ignition key cylinder and turn ignition switch from OFF to ON.
Condition (8) 1. After approx. 60 sec., alarm stops and system returns to armed state. Condition Item
Page 252 of 3000
DOOR LOCK – POWER DOOR LOCK CONTROL SYSTEMDL–3
DL
HOW TO PROCEED WITH
TROUBLESHOOTING
HINT:
• Use these procedures to troubleshoot the power door lock
control system.
• The intelligent tester should be used in steps 3 and 5.
NEXT
(a) Interview the customer to confirm the trouble (See page
IN-35).
NEXT
(a) Use the intelligent tester to check if the Multiplex
Communication System (MPX) is functioning normally.
Result
B
A
Result
B
A
(a) Terminals of ECU
(See page DL-8)
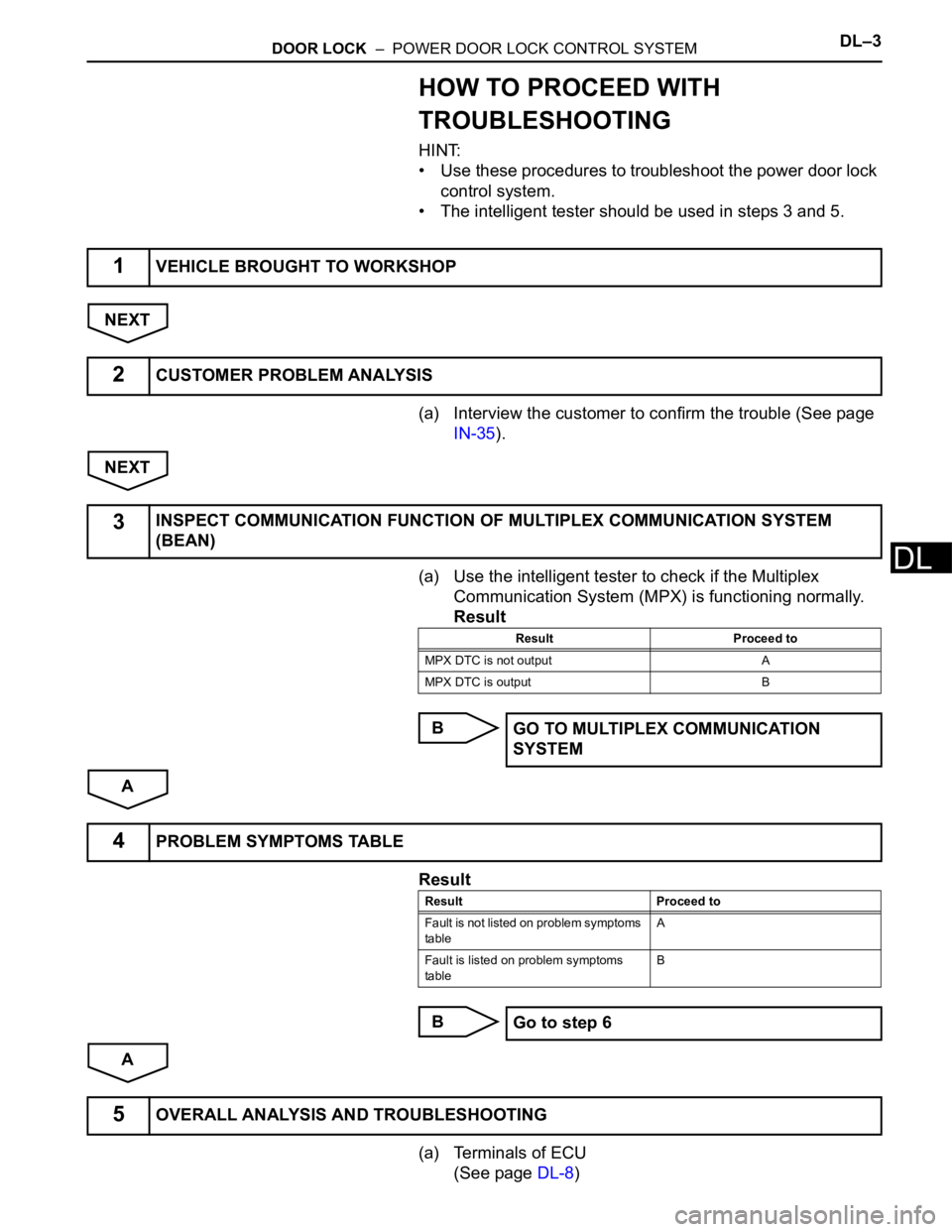
1VEHICLE BROUGHT TO WORKSHOP
2CUSTOMER PROBLEM ANALYSIS
3INSPECT COMMUNICATION FUNCTION OF MULTIPLEX COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
(BEAN)
Result Proceed to
MPX DTC is not output A
MPX DTC is output B
GO TO MULTIPLEX COMMUNICATION
SYSTEM
4PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
Result Proceed to
Fault is not listed on problem symptoms
tableA
Fault is listed on problem symptoms
tableB
Go to step 6
5OVERALL ANALYSIS AND TROUBLESHOOTING