2006 MERCEDES-BENZ SPRINTER engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 2169 of 2305

3.2.5 TRANSMISSION OPERATION AND
SHIFT SCHEDULING
The transmission covered in this manual has
unique shift schedules depending on the tempera-
ture of the transmission oil. The transmission oil
temperature has a decisive effect on the shift qual-
ity of the transmission. The shift schedule is modi-
fied to extend the life of the transmission while
operating under extreme conditions and to improve
driver comfort by modifying shift schedules.
The transmission oil temperature is measured
with a Temperature Sensor on the NAG1 transmis-
sion. The Temperature Sensor is an integral com-
ponent of the Transmission Solenoid assembly. If
the Temperature Sensor is causing a problem, a
DTC will be set in the TCM.
The Transmission Temperature Sensor is wired in
series with the Park /Neutral (P/N) switch. The P/N
switch is also located in the transmission. The trans-
mission temperature is only read by the TCM when
the P/N switch closes while in the R, D position.
When the shifter lever is in the park or neutral
position, the P/N switch opens and the temperature
being displayed is Engine temperature.
AutoStick Feature (If equipped)
This feature allows the driver to manually shift the
transaxle when the shift lever is moved sideways to
the (+ / -) in position D to adjust the shift range.
3.2.6 TRANSMISSION ADAPTIVES -
INITIALIZE AND STORE
Initialize Adaptive -This TCM function should be
used when a new transmission has been placed in
the vehicle. This command will reset the TCM
adaptive to the factory setting.
Store Adaptive -This command should be used
after the vehicle has been test driven by the tech-
nician to store any learned adaptive changes that
occurred during the test drive. During normal op-
eration adaptive are updated every 10 minutes.
Using this command the latest adaptive will be
written to the TCM immediately.
3.3 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTC's) are codes stored
by the Transmission Control Module (TCM) and the
Shift Lever Assembly Module (SLA) to help diag-
nose Transmission and Shifter problems. They are
viewed using the DRBIIItscan tool.
Always begin by performing a visual inspection of
the wiring, connectors, cooler lines and the trans-
mission. Any obvious wiring problems or leaks
should be repaired prior to performing any diagnos-
tic test procedures. Some engine driveability prob-lems can be misinterpreted as a transmission prob-
lem. Ensure that the engine is running properly
and that no ECM DTC's are present that could
cause a transmission complaint.
If there is a communication K-ABS,Shifter or
K-TCM circuit problem, trouble codes will not be
accessible until the problem is fixed. The DRBIIIt
will display an appropriate message. The following
is a possible list of causes for a bus problem:
± open or short to ground/battery in K line
circuit.
± internal failure of any module or component
connected to the K line circuit
Each diagnostic trouble code is diagnosed by
following a specific testing sequence. The diagnostic
test procedures contain step-by-step instructions
for determining the cause of a transmission diag-
nostic trouble code. Possible sources of the code are
checked and eliminated one by one. It is not neces-
sary to perform all of the tests in this book to
diagnose an individual code. These tests are based
on the problem being present at the time that the
test is run.
If the TCM records a DTC that will adversely
affect the vehicles transmission, it will request (via
the communication bus) that the ECM illuminate
the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL). All trans-
mission DTC's will be stored in the TCM.
3.3.1 ACTIVE (HARD) CODE
Any Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) that is set
whenever the system or component is monitored is
an Active code. This means that the problem is
there every time the TCM checks that system or
component. Some codes will set immediately at
start up and others will require a road test under
specific conditions to set the DTC. It must be
determined if a code is Active (repeatable) or Stored
(Intermittent) before attempting diagnosis.
3.3.2 STORED (INTERMITTENT) CODE
A diagnostic trouble code that is not there every
time the TCM checks the circuit or function is a
Stored (Intermittent) code. Problems that come and
go like this are the most difficult to diagnose, they
must be looked for under the specific conditions
that cause them. If the DTC is reset (after an
ignition cycle) the DTC will be set to Stored (Inter-
mittent) status. A DTC status can be9Active9or
9Stored9(Intermittent). Active is when the DTC is
present in the controller and the transmission is in
the particular mode of operation for that DTC.
Stored means that the DTC occurred at some point,
but is not currently present, or the conditions have
not been right to check for the presence of the
problem, when a DTC is classified as Stored (Inter-
mittent), no TCM reaction is required.
4
GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 2170 of 2305

Emergency running function
If DTCs occur, safe-driving conditions must be re-
tained but full functionality of the transmission will
be limited to avoid damaging the automatic trans-
mission. In the event of certain DTCs the TCM
switches to emergency running. The TCM will store
the appropriate DTC codes and solenoids will be
de-energized (turned off)
The transmission effects will be:
²The last gear shifted remains in that position
²The modulating pressure and shift pressure in-
crease to maximum value
²The torque converter clutch is disengaged
(turned off)
Shifting manually after a DTC detection
NOTE: The vehicle can still be shifted
manually to 2nd or reverse gear.
To accomplish these shifts you must
Stop the vehicle
Turn the ignition off
Start the engine
Place the selector lever into D for 2nd gear
Place the selector lever into R for reverse gear
The emergency running function is retained until
the DTC is eliminated or the stored DTC code is
erased.
Stored (Intermittent) DTCs can be reset by cy-
cling the ignition switch
3.3.3 TROUBLE CODE ERASURE
Diagnostic Trouble Codes can be erased in two
ways. The first is to erase the DTC with the DRBIII
or scan tool. The second is if the DTC is no longer
present, the DTC is reset by the TCM (after an
ignition cycle), which will place the DTC in an
intermittent status (Stored DTC).
When there are no diagnostic trouble codes
stored in memory, the DRBIIItwill display
(NO DTC's DETECTED(
3.4 USING THE DRBIIIT
Refer to the DRBIIItuser's guide for instructions
and assistance with reading trouble codes, erasing
trouble codes, and other DRBIIItfunctions.
3.5 DRBIIITERROR MESSAGES
Under normal operation, the DRBIIItwill display
one of only two error messages:
± User-Requested WARM Boot
± User-Requested COLD Boot
If the DRBIIItshould display any other error
message, record the entire display and call the
S.T.A.R. Center.
3.5.1 DRBIIITDOES NOT POWER UP
(BLANK SCREEN)
If the LED's do not light or no sound is emitted at
start up, check for loose cable connections or a bad
cable. Check the vehicle battery voltage. A mini-
mum of 11 volts is required to adequately power the
DRBIIIt.
If all connections are proper between the DRBI-
IItand the vehicle or other devices, and the vehicle
battery is fully charged, an inoperative DRBIIIt
may be the result of faulty cable or vehicle wiring.
For a blank screen, refer to the appropriate Body
Diagnostic manual.
3.5.2 DISPLAY IS NOT VISIBLE
Low temperatures will affect the visibility of the
display. Adjust the contrast to compensate for this
condition.
4.0 DISCLAIMERS, SAFETY,
AND WARNINGS
4.1 DISCLAIMERS
All information, illustrations, and specifications
contained in this manual are based on the latest
5
GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 2171 of 2305

information available at the time of publication.
The right is reserved to make changes at any time
without notice.
4.2 SAFETY
4.2.1 TECHNICIAN SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: ENGINES PRODUCE CARBON
MONOXIDE THAT IS ODORLESS, CAUSES
SLOWER REACTION TIME, AND CAN LEAD
TO SERIOUS INJURY. WHEN THE ENGINE IS
OPERATING KEEP SERVICE AREAS WELL
VENTILATED OR ATTACH THE VEHICLE
EXHAUST SYSTEM TO THE SHOP EXHAUST
REMOVAL SYSTEM.
Set the parking brake and block the wheels before
testing or repairing the vehicle. If is especially
important to block the wheels on front-wheel drive
vehicles: the parking brake does not hold the drive
wheels.
Some operations in this manual require that
hydraulic tubes, hoses, and fittings, disconnected
for inspection or testing purposes. These systems,
when fully charged, contain fluid at high pressure.
Before disconnecting any hydraulic tubes, hoses,
and fittings, be sure that the system is fully depres-
surized.
When servicing a vehicle, always wear eye pro-
tection, and remove any metal jewelry such as
watchbands or bracelets that might make an inad-
vertent electrical contact.
When diagnosing a Transmission system prob-
lem, it is important to follow approved procedures
where applicable. These procedures can be found in
the service information. Following these procedures
is very important to the safety of individuals per-
forming diagnostic tests.
4.2.2 VEHICLE PREPARATION FOR
TESTING
Make sure the vehicle being tested has a fully
charged battery. If it does not, false diagnostic
DTC's or error messages may occur. It is extremely
important that accurate shift lever position data is
available to the TCM. The accuracy of any DTC
found in memory is doubtful unless the Shift Lever
Test, performed on the DRBIIItScan Tool, passes
without failure.
4.2.3 SERVICING SUB-ASSEMBLIES
Some components of the Transmission system are
intended to be serviced in assembly only. Attempt-
ing to remove or repair certain system sub-
components may result in personal injury and/orimproper system operation. Only those components
with approved repair and installation procedures in
the service information should be serviced.
4.2.4 DRBIIITSAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: EXCEEDING THE LIMITS OF THE
DRBIIITMULTIMETER IS DANGEROUS. IT
CAN EXPOSE YOU TO SERIOUS OR
POSSIBLY FATAL INJURY. CAREFULLY
READ AND UNDERSTAND THE CAUTIONS
AND THE SPECIFICATION LIMITS.
²Follow the vehicle manufacturer's service speci-
fications at all times.
²Do not use the DRBIIItif it has been damaged.
²Do not use the test leads if the insulation is
damaged or if metal is exposed.
²To avoid electrical shock, do not touch the test
leads, tips or the circuit being tested.
²Choose the proper range and function for the
measurement. Do not try voltage or current mea-
surements that may exceed the rated capacity.
²Do not exceed the limits shown in the table.
FUNCTION INPUT LIMIT
Volts 0-500 volts peak AC
0-500 volts DC
Ohms (resistance)* 0-1.12 megohms
Frequency measured
Frequency generated0-10 khz
Temperature -58-1100ÉF
-50-600C
*Ohms cannot be measured if voltage is present.
Ohms can be measured only in a non-powered
circuit.
²Voltage between any terminal and ground must
not exceed 500v DC or 500v peak AC.
²Use caution when measured voltage above 25v
DC or 25v AC.
²The circuit being tested must be protected by a
10A fuse or circuit breaker.
²Use the low current shunt to measure circuits up
to 10A. Use the high current clamp to measure
circuits exceeding 10A.
²When testing for the presence of voltage or cur-
rent, make sure the meter is functioning cor-
rectly. Take a reading of a known voltage or
current before accepting a zero reading.
²When measuring current, connect the meter in
series with the load.
6
GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 2172 of 2305

²Disconnect the live test lead before disconnecting
the common test lead.
²When using the meter function, keep the
DRBIIItaway from spark plug or coil wires to
avoid measuring error from outside interference.
4.3 WARNINGS
4.3.1 VEHICLE DAMAGE WARNINGS
Before disconnecting any control module, make
sure the ignition is9lock9position. Failure to do so
could damage the module.
When testing voltage or continuity at any control
module, use the terminal side (not the wire end) of
the connector. Do not probe a wire through the
insulation: this will damage the wire and eventu-
ally cause the wire to fail because of corrosion.
Be careful when performing electrical tests so as
to prevent accidental shorting of terminals. Such
mistakes can damage fuses or components. Also, a
second DTC could be set, making diagnosis of the
original problem more difficult.
When replacing a blown fuse, it is important to
use only a fuse having the correct amperage rating.
The use of a fuse with a rating other than indicated
may result in a dangerous electrical system over-
load. If a properly rated fuse continues to blow, it
indicates a problem in the circuit that must be
corrected.
4.3.2 ROAD TESTING A COMPLAINT
VEHICLE
Some complaints will require a test drive as part
of the repair verification procedure. The purpose of
the test drive is to try to duplicate the diagnostic
DTC or symptom condition.
CAUTION: Before road testing a vehicle, be
sure that all components are reassembled.
During the test drive, do not try to read
DRBIIITscreen while in motion. Do not hang
the DRBIIITfrom the rear view mirror or
operate it yourself. Have an assistant
available to operate the DRBIIIT.
Road testing is an essential step in the diagnostic
process that must not be overlooked. Along with the
diagnostic information obtained from the DRBIIIt
Scan Tool and the original customer concern, the
road test helps verify the problem was current and
any repairs performed, fixed the vehicle correctly.
Always operate and observe the vehicle under ac-
tual driving conditions.
Just as important as the road test is, there are
preliminary inspections that should be performed
prior to the road test. Always check the fluid leveland condition before taking the vehicle on a road
test. Determine if the incorrect fluid is being used,
improper fluid will result in erratic transmission
operation.
Some of the conditions of incorrect fluid level are as
follows:
²Delayed engagement
²Poor shifting or erratic shifting
²Excessive noise
²Overheating
The next step is to verify that the shift linkage is
correctly adjusted. If the shift linkage is incorrectly
adjusted, a number of complaints can result.
The TCM monitors the Shift Lever Position (SLP)
continuously. If the linkage is incorrectly adjusted,
the TCM will sense a shift lever position that is not
correct for the gear chosen by the driver. This may
cause a DTC to be set.
The following complaints may also be the result of
an incorrectly adjusted or worn linkage:
²Delayed clutch engagement
²Erratic shifts
²Vehicle will drive in neutral
²Engine will not crank in park or neutral
²Gear shift linkage will be able to be shifted
without the key in the ignition
²Not able to remove the ignition key in park
²Parking pawl will not engage properly
The shift linkage should also be adjusted when
replacing the Transmission, repairing the valve
body, or when repairing any component between the
shift lever and the Transmission.
Some questions to ask yourself when performing
the road test are as follows:
²Is the complaint or concern what you think the
problem is, based on the drivers description of the
problem?
²Is the Transmission operating normally, or is
there a real problem?
²When does the problem occur?
²Is the problem only in one gear range?
²What temperature does the problem occur?
²Does the vehicle have to sit over night for the
problem to occur?
²Does the transmission go into Limp-in mode?
4.4.4 BULLETINS AND RECALLS
Always perform all Safety Recalls and Technical
Service Bulletins that are applicable to the prob-
lem.
7
GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 2173 of 2305

5.0 REQUIRED TOOLS AND
EQUIPMENT
> DRBIIIt(diagnostic read-out box) - DRBIIIt
must use the latest release level.
> Jumper wires
> Test Light
> Ohmmeter
> Voltmeter
6.0 GLOSSARY OF TERMS
6.1 ACRONYMS
ABSAntilock Braking system
A/CAir conditioner
A/DAnalog to Digital conversion
APPAccelerator Pedal Position
CANController Area Network (Vehicle
Bus System)
CKTCircuit
DLCData Link Connector
DRBIIItDiagnostic Readout Box
DTCDiagnostic Trouble Code
ECMDiesel Engine Controller
EMCCElectronically Modulated Converter
Clutch
IODIgnition off-draw
ISSInput Speed Sensor (N2 and N3)
KK line communication bus
LEDLight Emitting Diode
MILMalfunction Indicator LampOSSOutput Speed Sensor (derived from
the ABS controller)
PEMCCPartial Electronically Modulated
Converter Clutch
PWMPulse width modulated
SKREEMSentry Key Remote Entry Module
SLAShift Lever Assembly
SWSwitch
TCCTorque Converter Clutch
TCMTransmission Control Module
TPThrottle Position
TRDTorque Reduction
TTSTransmission Temperature Sensor
1-2/4-5
solenoidcontrols the shift into and out of
2nd gear or 5th gear.
V2-3 so-
lenoidcontrols the shift into and out of 3rd
gear
V3-4 so-
lenoidcontrols the shift into and out of 4th
gear
VTCC
solenoidis pulse width modulated and con-
trols the TCC clutch
Shift
Pressure
Solenoidis a pulse width modulated solenoid
and controls the hydraulic pressure
to the shift elements.
Modula-
tion
pressure
solenoidis a pulse width modulated solenoid
and controls the hydraulic system
pressure
6.2 DEFINITIONS
Driving cycle counter) -The starts since first set
counter indicates the number of driving cycles since
the first occurrence of an error.
8
GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 2180 of 2305

Symptom:
BACKUP LAMP CKT SHORT TO VOLTAGE OR OPEN
POSSIBLE CAUSES
BACKUP LAMP CIRCUIT OPEN
BACKUP LAMP CIRCUIT SHORT TO VOLTAGE
SHIFT LEVER ASSEMBLY
TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
1 Start the engine.
While back probing, measure the voltage of the Backup Lamp circuit.
Is the voltage above 0.5 volts?All
Ye s!Go To 2
No!Go To 3
2 Turn the ignition off to the lock position.
Disconnect the Shift Lever Assembly harness connector.
Start the engine.
Measure the voltage of the Backup Lamp circuit in the Shift Lever Assembly harness
connector.
Is the voltage above 0.5 volts?All
Ye s!Repair the Backup Lamp circuit for a short to voltage.
No!Replace the Shift Lever Assembly per the Service Information.
3 Turn the ignition off to the lock position.
Disconnect the Shift Lever Assembly harness connector.
Remove the Backup Lamp bulb(s).
Connect a jumper wire between Shift Lever Assembly circuit and B(+).
Using a 12-volt test light connected to 12-volts, check the Backup Lamp circuit in the
Backup Lamp socket(s).
NOTE: The test light must illuminate brightly. Compare the brightness to
that of a direct connection to the battery.
Does the test light illuminate brightly?All
Ye s!Replace the Shift Lever Assembly per the Service Information.
No!Repair the Backup Lamp circuit for an open.
15
SHIFT LEVER ASSEMBLY
Page 2181 of 2305
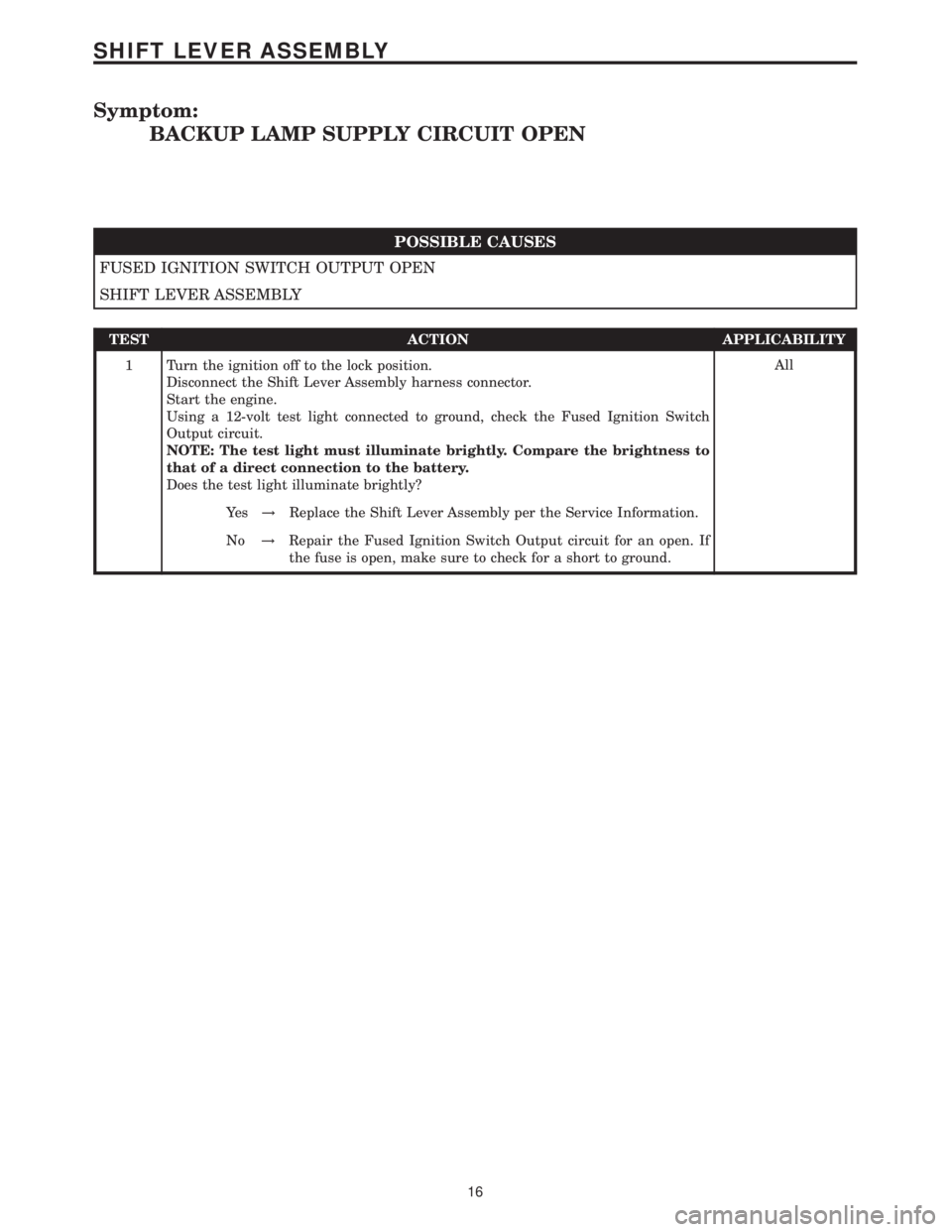
Symptom:
BACKUP LAMP SUPPLY CIRCUIT OPEN
POSSIBLE CAUSES
FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT OPEN
SHIFT LEVER ASSEMBLY
TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
1 Turn the ignition off to the lock position.
Disconnect the Shift Lever Assembly harness connector.
Start the engine.
Using a 12-volt test light connected to ground, check the Fused Ignition Switch
Output circuit.
NOTE: The test light must illuminate brightly. Compare the brightness to
that of a direct connection to the battery.
Does the test light illuminate brightly?All
Ye s!Replace the Shift Lever Assembly per the Service Information.
No!Repair the Fused Ignition Switch Output circuit for an open. If
the fuse is open, make sure to check for a short to ground.
16
SHIFT LEVER ASSEMBLY
Page 2183 of 2305
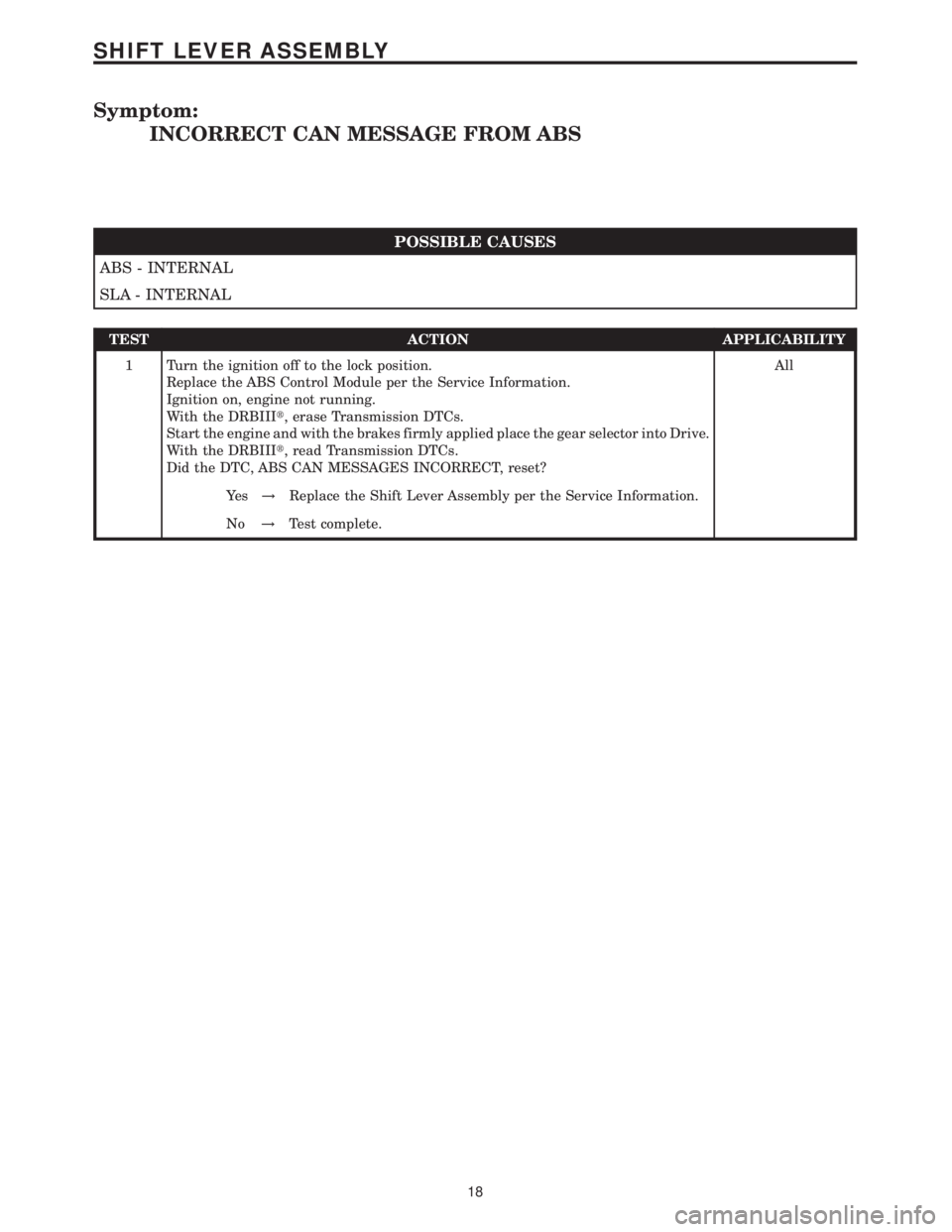
Symptom:
INCORRECT CAN MESSAGE FROM ABS
POSSIBLE CAUSES
ABS - INTERNAL
SLA - INTERNAL
TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
1 Turn the ignition off to the lock position.
Replace the ABS Control Module per the Service Information.
Ignition on, engine not running.
With the DRBIIIt, erase Transmission DTCs.
Start the engine and with the brakes firmly applied place the gear selector into Drive.
With the DRBIIIt, read Transmission DTCs.
Did the DTC, ABS CAN MESSAGES INCORRECT, reset?All
Ye s!Replace the Shift Lever Assembly per the Service Information.
No!Test complete.
18
SHIFT LEVER ASSEMBLY