2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 5047 of 5267

With the scan tool in HVAC, select System Tests and then select Cooldown test. Allow the test to run to completion.
Does the scan tool display a status message that indicates a fault has occurred?
Yes, Conditions Too Cold - Test Not Run
If running, turn the A/C compressor off. Verify that the work area ambient temperature is above 15.6°C
(60°F). If not, move the vehicle to a warmer work area. Verify that the evaporator temperature is above
13°C (55°F). If not, set the blower to high speed and allow the blower to run for five minutes. Then, run
the Cooldown Test again.
Yes, Blowers Not On High - Test Not Run
Set the blower speed to high speed and then run the Cooldown Test again.
Yes, No Results Stored/Test Not Complete
Verify that power is not interrupted while rerunning the Cooldown Test.
Yes, Refrigerant Temperature Sensor Error
For Dual-Zone HVAC systems, refer to B10B2–A/C COOL DOWN TEST PERFORMANCEfor the diag-
nostic test procedure. For Single-Zone HVAC systems, refer to B1079–CLIMATE CONTROL COOL
DOWN TEST EXCESSIVE TIME for the diagnostic test procedure.
Yes, DTC Set During Routine - Test Not Passed
For Dual-Zone HVAC systems, refer to B10B2–A/C COOL DOWN TEST PERFORMANCEfor the diag-
nostic test procedure. For Single-Zone HVAC systems, refer to B1079–CLIMATE CONTROL COOL
DOWN TEST EXCESSIVE TIME for the diagnostic test procedure.
No>>
Asnecessary,eitherGoTo3,4,or5,or Perform BODY VERIFICATION TEST - VER1. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
3.MODE SWITCH & DOOR ACTUATOR CIRCUIT TEST
NOTE: If at anytime a DTC becomes active during this test, proceed to the conclusion question.
NOTE: If multiple DTCs are active, diagnose those that relate to a short circuit first.
NOTE: Dual-Zone A/C Heater Controls do not set DTCs for stuck mode switches. Therefore, verify that the
A/C Heater Control is not damaged and that the mode switches and status indicators function properly and
repair as necessary before proceeding.
If not done so previously, start the engine.
Turn the Blower control to the low speed position.
Set the Blend control (single-zone) or Driver Blend control (dual-zone) to the full cold position.
If equipped, set the Passenger Blend control to the full cold position.
Monitor the scan tool for active HVAC DTCs while performing the following test steps.
If equipped, press the A/C mode switch on, wait 30 seconds, and then press itoff.
On Dual-Zone systems, press the Recirc mode switch on, wait 30 seconds, andthen press it off.
If equipped, press the EBL mode switch on, wait 30 seconds, and then press itoff.
Move the Blend control (single-zone) or Driver Blend control (dual-zone)from full cold to full hot, wait 30 seconds,
and then move it back to full cold.
If equipped, move the Passenger Blend control from full cold to full hot, wait 30 seconds, and then moved it back
to full cold.
Turn the Mode select control to the defrost position, wait 30 seconds, and then turn it to the panel position (dual-
zone) or panel / recirc position (single-zone). Wait 30 seconds before proceeding.
Does the scan tool display any active DTCs?
Ye s>>
Diagnose and repair the DTC(s). Refer to the Table of Contents in this Section for a complete list of
HVAC related symptoms.
No>>
If you are here due to a stored DTC, it is possible that a technician may not have erased the DTC
following a repair. If possible, verify if the vehicle was recently in for this type of service. Otherwise,
either Go To 4 or 5, or visually inspect the related wiring harness for chafed, pierced, pinched, and
partially broken wires and the wiring harness connectors for broken, bent, pushed out, and corroded
terminals, and repair as necessary.
Perform BODY VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Page 5050 of 5267

HVAC - SERVICE INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
A manually controlled single zone type heating-air conditioning system or a manually controlleddualzonetypeheat-
ing-air conditioning system is available on this model.
To maintain the performance level of the heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system, the engine cooling
system must be properly maintained. The use of a bug screen is not recommended. Any obstructions in front of the
radiator or A/C condenser will reduce the performance of the A/C and enginecooling systems.
The engine cooling system includes the radiator, thermostat, radiator hoses and the engine coolant pump. Refer to
7 - Cooling for more information before opening or attempting any service to the engine cooling system.
All vehicles are equipped with a common heater, ven-
tilation and air conditioning (HVAC) housing (1). The
system combines air conditioning, heating, and venti-
lating capabilities in a single unit housing mounted
within the passenger compartment under the instru-
ment panel. The HVAC housing includes:
Blend-air door(s) and actuator(s) (2)
Recirculation-air door and actuator (3)
A/C evaporator (4)
Blower motor (5)
Blower motor resistor (6)
Evaporator temperature sensor (7)
Heater core (8)
Mode-air doors and actuators (9)
Based upon the system and mode selected, conditioned air can exit the HVAC housing through one or a combi-
nation of the three main housing outlets: defrost, panel or floor. The defrost and the panel outlets are located on the
top of the housing and, the floor outlet is located on the bottom of the housing. Once the conditioned air exits the
HVAC housing, it is further directed through molded plastic ducts to the various outlets within the vehicle interior.
These outlets and their locations are as follows:
Defroster Outlet- A single large defroster outlet is located in the center of the instrumentpanel top cover,
near the base of the windshield.
Side Window Demister Outlets- There are two side window demister outlets, one is located at each out-
board end of the instrument panel top cover, near the belt line at the A-pillars.
Panel Outlets- There are four panel outlets in the instrument panel, one located near each outboard end of
the instrument panel facing the rear of the vehicle and two located near thetop of the instrument panel center
bezel.
Front Floor Outlets- There are two front floor outlets, one located above each side of the floorpanel center
tunnel near the dash panel.
Rear Outlets- On Mega Cab models there are two outlets located at the rear of the center front seat.
OPERATION
Both the manual temperature control (MTC) single zone and dual zone heating-A/C system are blend-air type sys-
tems. In a blend-air heating-A/C, a blend-air door controls the amount of conditioned air that is allowed to flow
through, or around, the heater core.In the available dual zone system, twoblend-air doors are used to provide
completely independent side-to-side temperature control of the discharge air. The temperature control(s) determines
the discharge air temperature(s) by operating the blend door actuator(s), which move the blend-air door(s). This
design allows almost immediate control of output air temperature(s).
Page 5051 of 5267

The heating-A/C systems pulls outside (ambient) air
through the cowl opening at the base of the wind-
shield, then into the air inlet housing above the heat-
ing, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) housing.
On models equipped with A/C, the air passes through
the A/C evaporator (3). Air flow can be directed either
through or around the heater core (1). This is done by
adjusting the blend-air door(s) (2) with the temperature
control(s) located on the A/C-heater control in the
instrument panel. The air flow can then be directed
from the panel, floor and defrost outlets in various
combinations using the mode control located on the A/C-heater control. Air flow velocity can be adjusted with the
blower speed control located on the A/C-heater control.
On all models, the outside air intake can be shut off by selecting the Recirculation Mode with the mode control. This
will operate a electrically actuated recirculation-air door (4) that closes off the fresh air intake and recirculates the air
that is already inside the vehicle.
On models with A/C, the A/C compressor can be engaged in any mode by pressingthe snowflake, A/C on/off but-
ton. It can also be engaged by placing the mode control in the mix to defrost positions. This will remove heat and
humidity from the air before it is directed through or around the heater core. The mode control on the A/C-heater
control is used to also direct the conditioned air to the selected system outlets. The mode control uses electric
actuators to control the mode-air doors (5 and 6).
The defroster outlet receives airflow from the HVAC housing through the molded plastic defroster duct, which con-
nects to the HVAC housing defroster outlet. The airflow from the defrosteroutlets is directed by fixed vanes in the
defroster outlet grilles and cannot be adjusted. The defroster outlet grilles are integral to the instrument panel top
cover.
The side window demister outlets receive airflow from the HVAC housing through the molded plastic defroster duct
and two molded plastic demister ducts. The airflow from the side window demister outlets is directed by fixed vanes
in the demister outlet grilles and cannot be adjusted. The side window demister outlet grilles are integral to the
instrument panel. The demisters direct air from the HVAC housing through the outlets located on the top corners of
the instrument panel. The demisters operate when the mode control knob is positioned in the floor-defrost and
defrost-only settings. Some air may be noticeable from the demister outlets when the mode control is in the bi-level
to floor positions.
The panel outlets receive airflow from the HVAC housing through a molded plastic main panel duct, center panel
duct and two end panel ducts. The two end panel ducts direct airflow to the left and right instrument panel outlets,
while the center panel duct directs airflow to the two center panel outlets. Each of these outlets can be individually
adjusted to direct the flow of air.
The floor outlets receive airflow from the HVAC housing through the floor distribution duct. The front floor outlets are
integral to the molded plastic floor distribution duct, which is secured to the bottom of the housing. The floor outlets
cannot be adjusted.
NOTE: It is important to keep the air intake opening clear of debris. Leaf particles and other debris that is
small enough to pass through the cowl opening screen can accumulate withinthe HVAC housing. The
closed, warm, damp and dark environment created within the housing is ideal for the growth of certain
molds, mildews and other fungi. Any accumulation of decaying plant matterprovides an additional food
source for fungal spores, which enter the housing with the fresh intake-air. Excess debris, as well as objec-
tionable odors created by decaying plant matter and growing fungi can be discharged into the passenger
compartment during heater-A/C operation if the air intake opening is not kept clear of debris.
The A/C system on models so equipped is designed for the use of non-CFC, R-134a refrigerant and uses an A/C
fixedorificetubelocatedintheliquidlinetometertheflowofrefrigerant to the A/C evaporator. The A/C evaporator
cools and dehumidifies the incoming air prior to blending it with the heated air. To maintain minimum evaporator
temperature and prevent evaporator freezing, an evaporator temperaturesensor is used to supply evaporator tem-
perature input to the A/C-heater control. The powertrain control module (PCM) cycles the A/C compressor clutch off
and on as necessary to protect the A/C system from evaporator freezing and optimize A/C system performance.
Page 5052 of 5267

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
HEATING-A/C SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS
CAUTION: Do not exchange A/C Heater Controls from vehicle to vehicle. Software versions differ between
models and model years. Installing an A/C Heater Control with software that is incompatible for a given
vehicle can result in either improper or failed HVAC system operation.
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
The A/C-heater control communicates on the controller area network (CAN)B bus and is fully addressable with a
scan tool.
The A/C-heater control’s primary means of fault detection is through active and stored diagnostic trouble codes
(DTCs). Active DTCs are those which currently exist in the system. The condition causing the fault must be repaired
in order to clear this type of DTC. Stored DTCs are those which occurred in the system since the A/C-heater control
received the last clear diagnostic info message. DTCs must be read with a scan tool. Refer to 24 - HVAC - Elec-
trical Diagnostics for HVAC DTC diagnostic test procedures.
The A/C-heater control’s secondary means of fault detection is through system tests. These tests include the HVAC
System Test, the A/C Cooldown Test, Actuator Calibration, and Actuator DTC Detection. Refer to System Tests in
this Section for a detailed description of each test.
SYSTEM TESTS
HVAC System Test
The HVAC System Test, found in 24 - HVAC - Electrical Diagnostics, providesa starting point in the diagnostic
process by identifying the appropriate diagnostic procedure or system test to perform when diagnosing a given
symptom, condition, or DTC. It also provides a means for testing the entireHVAC system by utilizing the A/C-heater
control’s On-Board System Tests. The On-Board System Tests can also assistindiagnosingstoredDTCs.
A/CCOOLDOWNTEST
The A/C Cooldown Test:
is actuated with a scan tool.
tests A/C system performance based on evaporator temperature sensor input.
will fail if evaporator temperature isbelow 13°C (55°F) when initiating the test.
will pass if the evaporator temperature drops 11°C (20°F).
indicates an outcome by displaying one or more test status messages on the scan tool. These test status
messages will clear after paging back out of this test function. Therefore, is it important to note all of the mes-
sages before doing so.
will cause the A/C status indicator to flash while the test is running.
ACTUATOR CALIBRATION FUNCTION
The Actuator Calibration function:
is actuated with a scan tool.
clears all actuator related DTCs when the test is actuated.
homes and repositions door actuators.
monitors for door span faults. Door span faults (XXX Door Travel Range Too Large or XXX Door Travel Range
Too Small) will only display after calibration.
will cause the electric backlight (EBL) status indicator (if equipped) toflash while the test is running.
Page 5055 of 5267
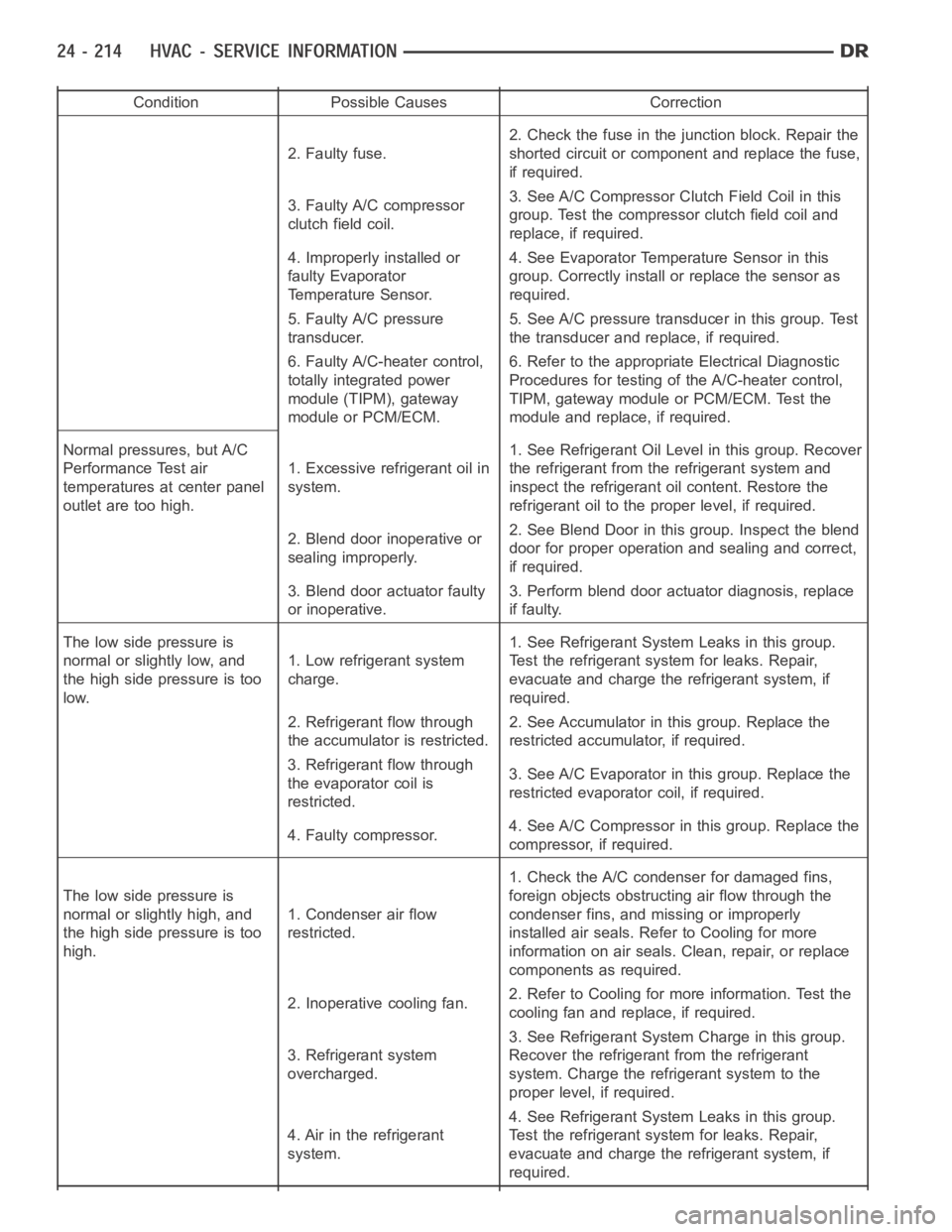
Condition Possible Causes Correction
2. Faulty fuse.2. Check the fuse in the junction block. Repair the
shorted circuit or component and replace the fuse,
if required.
3. Faulty A/C compressor
clutch field coil.3. See A/C Compressor Clutch Field Coil in this
group. Test the compressor clutch field coil and
replace, if required.
4. Improperly installed or
faulty Evaporator
Temperature Sensor.4. See Evaporator Temperature Sensor in this
group. Correctly install or replace the sensor as
required.
5. Faulty A/C pressure
transducer.5. See A/C pressure transducer in this group. Test
the transducer and replace, if required.
6. Faulty A/C-heater control,
totally integrated power
module (TIPM), gateway
module or PCM/ECM.6. Refer to the appropriate Electrical Diagnostic
Procedures for testing of the A/C-heater control,
TIPM, gateway module or PCM/ECM. Test the
module and replace, if required.
Normal pressures, but A/C
Performance Test air
temperatures at center panel
outlet are too high.1. Excessive refrigerant oil in
system.1. See Refrigerant Oil Level in this group. Recover
the refrigerant from the refrigerant system and
inspect the refrigerant oil content. Restore the
refrigerant oil to the proper level, if required.
2. Blend door inoperative or
sealing improperly.2. See Blend Door in this group. Inspect the blend
door for proper operation and sealing and correct,
if required.
3. Blend door actuator faulty
or inoperative.3. Perform blend door actuator diagnosis, replace
if faulty.
The low side pressure is
normal or slightly low, and
the high side pressure is too
low.1. Low refrigerant system
charge.1. See Refrigerant System Leaks in this group.
Test the refrigerant system for leaks. Repair,
evacuate and charge the refrigerant system, if
required.
2. Refrigerant flow through
the accumulator is restricted.2. See Accumulator in this group. Replace the
restricted accumulator, if required.
3. Refrigerant flow through
the evaporator coil is
restricted.3. See A/C Evaporator in this group. Replace the
restricted evaporator coil, if required.
4. Faulty compressor.4. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace the
compressor, if required.
The low side pressure is
normal or slightly high, and
the high side pressure is too
high.1. Condenser air flow
restricted.1. Check the A/C condenser for damaged fins,
foreign objects obstructing air flow through the
condenser fins, and missing or improperly
installed air seals. Refer to Cooling for more
information on air seals. Clean, repair, or replace
components as required.
2. Inoperative cooling fan.2. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling fan and replace, if required.
3. Refrigerant system
overcharged.3. See Refrigerant System Charge in this group.
Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system. Charge the refrigerant system to the
proper level, if required.
4. Air in the refrigerant
system.4. See Refrigerant System Leaks in this group.
Test the refrigerant system for leaks. Repair,
evacuate and charge the refrigerant system, if
required.
Page 5057 of 5267

Improper heater hose routing.
Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports at the cooling system connections.
Plugged heater core.
If proper coolant flow through the cooling system is verified, and heater outlet air temperature is low, a mechanical
problem may exist.
MECHANICAL PROBLEMS
Possible locations or causes of insufficient heat due to mechanical problems are as follows:
Obstructed cowl air intake.
Obstructed heater system outlets.
Blend-air door(s) or actuator(s) not functioning properly.
Faulty blower motor system
Faulty A/C-heater control
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If the heater outlet air temperature cannot be adjusted with the temperature control on the A/C-heater control, the
following could require service:
Faulty A/C-heater control.
Faulty blend door actuator(s).
Faulty, obstructed or improperly installed blend-air door.
Faulty related wiring harness or connectors.
Improper engine coolant temperature.
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C SYSTEM
Item Description Notes
A/C Compressor Denso 10S17 (3.7L/4.7L/5.7L/8.3L
engines)ND-8 PAG oil
Visteon HS-18 (5.9L engine) VC-46 PAG oil
Freeze–up Control Evaporator Temperature Sensor A/C evaporator mounted
High psi Control A/C pressure transducer A/C discharge line mounted
Refrigerant Charge Capacity Refer to the A/C Underhood
Specification Label located in the
engine compartment.R134a refrigerant
A/C Clutch Field Coil Draw 3.2 - 3.3 amps @ 12V ± 0.5V @
21° C (70° F)3.7L/4.7L/5.7L/8.3L engines
3.1 - 4 amps @ 12V ± 0.5V @ 21°
C(70°F)5.9L engine
A/C Clutch Air Gap 0.35 - 0.60 mm (0.014 - 0.024 in.) 3.7L/4.7L/5.7L/8.3L engines
0.35 - 0.75 mm (0.014 - 0.030 in.) 5.9L engine
TORQUE
Page 5060 of 5267

page page
ACTUATOR-BLEND DOOR
DESCRIPTION ............................... 220
OPERATION ................................. 220
REMOVAL ................................... 221
INSTALLATION .............................. 222
ACTUATOR-MODE DOOR
DESCRIPTION ............................... 225
OPERATION ................................. 225
REMOVAL ................................... 226
INSTALLATION .............................. 227
ACTUATOR-RECIRCULATION DOOR
DESCRIPTION ............................... 229
OPERATION ................................. 229
REMOVAL ................................... 230
INSTALLATION .............................. 230
CLUTCH-A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION ............................... 232
OPERATION ................................. 232
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH COIL.......... 232
STANDARD PROCEDURE
A/C CLUTCH PLATE INSPECTION.......... 233
A/C CLUTCH BREAK-IN.................... 233
REMOVAL
DENSO A/C COMPRESSOR ................ 234
VISTEON A/C COMPRESSOR .............. 235INSTALLATION
DENSO A/C COMPRESSOR................ 238
VISTEON A/C COMPRESSOR.............. 240
CONTROL-A/C HEATER
DESCRIPTION
MANUAL SINGLE ZONE .................... 243
MANUAL DUAL ZONE ...................... 243
REMOVAL ................................... 244
INSTALLATION .............................. 244
RESISTOR-BLOWER MOTOR
DESCRIPTION ............................... 245
OPERATION ................................. 245
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR ............... 245
REMOVAL ................................... 246
INSTALLATION .............................. 247
SENSOR-EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE
DESCRIPTION ............................... 248
OPERATION ................................. 248
REMOVAL ................................... 249
INSTALLATION .............................. 250
TRANSDUCER-A/C PRESSURE
DESCRIPTION ............................... 251
OPERATION ................................. 251
REMOVAL ................................... 251
INSTALLATION .............................. 252
Page 5089 of 5267

SENSOR-EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE
DESCRIPTION
The evaporator temperature sensor is a two-wire tem-
perature sensing element located at the coldest point
on the face of the A/C evaporator. The probe (1) for
evaporator temperature sensor is attached to the
evaporator coil fins. The wire lead (2) for evaporator
temperature sensor is routed through an opening at
the back of the HVAC housing and the connector (3)
is attached to the HVAC wire harness.
OPERATION
The evaporator temperature sensor monitors the surface temperature of A/C evaporator and supplies an input signal
to the A/C-heater control. The A/C-heater control uses the evaporator temperature sensor input signal to optimize
A/C system performance and to protect the A/C system from evaporator freezing. The evaporator temperature sen-
sor will change its internal resistance in response to the temperatures itmonitors and is connected to the A/C-heater
control through sensor ground circuit and a 5-volt reference signal circuit. As the temperature of the A/C evaporator
decreases, the internal resistance of the evaporator temperature sensordecreases.
The A/C-heater control uses the monitored voltage reading as an indication of evaporator temperature. The A/C-
heater control is programmed to respond to this input by requesting the powertrain control module (PCM) or the
engine control module (ECM) (depending on engine application) to cycle the A/C compressor clutch as necessary to
optimize A/C system performance and to protect the A/C system from evaporatorfreezing(Referto24-HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/COIL-A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH - OPERATION formore information).
The evaporator temperature sensor is diagnosed using a scan tool (Refer to24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING and to 24 - HVAC Electrical Diagnostics for more information).
The evaporator temperature sensor cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.