Page 4342 of 5135
A81480
Plunger A: Pumping End
Plunger B: Suction EndPlunger A: Suction Start
Plunger B: Pumping Start Check Valve
Eccentric Cam
Ring Cam
Plunger B
Plunger A
Plunger A: Pumping Start
Plunger B: Suction StartPlunger A: Suction End
Plunger B: Pumping End Supply Pump Operation Diagram:
From
Feed Pump
To Common Rail Suction
Control
Valve
05−264
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
5. SUPPLY PUMP OPERATION SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The rotation of the eccentric cam causes the ring cam pushes plunger A upward as illustrated below. The
spring force pulls plunger B (located on the opposite of plunger A) upward. As a result, plunger B draws the
fuel in, and plunger A pumps the fuel at the same time.
Page 4367 of 5135
A81015
Engine
Room
R/B No. 1W
9ECM
W
E912
1 2
B
B−W22 1
3
Battery4
2 DH 6
B−R B−R
C11
Combination
Meter Assy
Check
Engine
Warning
Light AM2
IG2
AM2
Driver
Side
J/B
FL MAINEngine
Room
R/B
No. 3
3B 1A 1B−R
IE41
(LHD)IP11
(RHD)
18 DA
J8C
(LHD)J26A
(RHD)J8C
(LHD)J26A
(RHD) J/CB−W IGNI13
Ignition
Switch
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−497
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
CHECK ENGINE WARNING LIGHT CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
If the ECM detects a trouble, the CHK ENG is illuminated. At this time, the ECM records the DTC in its
memory.
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Troubleshoot each trouble symptom in accordance with the chart below .
Reference:
ResultProceed to
CHK ENG remains onStart inspection from step 1
CHK ENG is not illuminatedStart inspection from step 3
05B62−07
Page 4369 of 5135
A81016
ECM
STA
E97
B−Y
IJW−BJ12
B B
J13
J/C W−B 1 5
32 1AM2 2
B
B−R1
S51
S4
Starter
Battery7IK1
FL MAIN 3 3
Engine Room
R/B No. 3
B B 55
55 1
11A
BB−R
IE41
(LHD)IP11
(RHD)B−R
Engine
Room
R/B No. 1
Driver
Side R/B ST
Relay
2
DJ
9
DADriver
Side J/B B−R
B−RI13
Ignition Switch
4
5
AM2 ST2B−Y
B−Y
6
2ST 1
6 Fuse
Block
B−WB−YB−Y B−Y
J12
A C
J13C
J13 05−494
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
STARTER SIGNAL CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
HINT:
While the engine is being cranked, current flows from terminal ST2 of the ignition switch to the ST relay coil
and also current flows to terminal STA of the ECM (STA signal).
WIRING DIAGRAM
05I7V−01
Page 4372 of 5135
A81013
ECM
+BMREL IGSW J27
9
B−W I13
Ignition Switch
6IGNB−W E
E1
EE110BR
W−B 1Driver Side J/B
2 2
1E9
E9
E98
1
7
E12 J26A
B−W
C C B−W
J8
J/C DA 18
DH2
4
EFI5
1
32 EFI
MAIN
Relay
B−W Engine Room R/B No. 1IK1
6J/C
IE12
BR B−R
Battery AM2B−W
EC
EI
AM2 IG2
GR
B B
33
Engine Room R/B No. 3
FL MAIN1 1
1 1A1 1
1 1 B−R B−R
IE4 1(LHD)
IP1 1(RHD)B−W (RHD) (RHD)
(LHD)
(LHD)
GR B−Y (RHD) B−R (LHD)
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−489
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
ECM POWER SOURCE CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When the ignition switch is turned to ON, the positive battery voltage is applied to terminal IGSW of the ECM
and the EFI MAIN relay control circuit in the ECM sends a signal to terminal MREL of the ECM switching
on the EFI MAIN relay.
This signal causes current to flow to the coil, closing the contacts of the EFI MAIN relay and supplying power
to terminal +B of the ECM.
WIRING DIAGRAM
05B5V−05
Page 4377 of 5135

05−484
−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
DTC P2237 OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR PUMPING
CURRENT CIRCUIT/OPEN (FOR A/F
SENSOR)(BANK1 SENSOR 1)
DTC P2238 OXYGEN (A/F)SENSOR PUMPING CURRENT CIRCUIT LOW (FOR A/F SENSOR)(BANK 1
SENSOR 1)
DTC P2239 OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR PUMPING CURRENT CIRCUIT HIGH (FOR A/F
SENSOR)(BANK1 SENSOR 1)
HINT:
S For more information on the A/F sensor and TOYOTA D −CAT (* 1) system, see page 05 −255.
S If P2237, P2238 and/or P2239 is present, refer to the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) table for TOYO-
TA D −CAT system on page 05 −255.
S These DTCs are recorded when A/F sensor has malfunction, although the caption is the oxygen sen-
sor.
* 1 : Diesel Clean Advanced Technology.
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P003 1 on page 05 −305.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P2237ECM internal error ( 10 seconds)
( 1 trip detection logic)S ECM
P2238
S A/F sensor circuit low (bank 1 sensor 1)
AF+ is less than 04 V for 50 seconds or more
Main trouble area: Open in A/F sensor circuit
S Open or short in A/F sensor circuit
S A/F sensor
S A/F sensor heaterP2238AF+ is less than 0.4 V for 5.0 seconds or more
( 1 trip detection logic)S A/F sensor heater
S A/F sensor heater relay
S A/F sensor heater and relay circuit
S ECM
P2239
S A/F sensor circuit high (bank 1 sensor 1)
AF+ is more than 44 V for 50 seconds or more
Main trouble area: Short in A/F sensor circuit
S Open or short in A/F sensor circuit
S A/F sensor
S A/F sensor heaterP2239AF+ is more than 4.4 V for 5.0 seconds or more
( 1 trip detection logic)S A/F sensor heater
S A/F sensor heater relay
S A/F sensor heater and relay circuit
S ECM
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The A/F sensor has a characteristic that it varies its voltage output in proportion to the air −fuel ratio. If imped-
ance (alternating current resistance) or voltage output of the sensor extraordinarily deviates from the stan-
dard range, the ECM interprets this as an open or short malfunction of the A/F sensor circuit.
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P003 1 on page 05 −305.
05I7U −01
Page 4383 of 5135

−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
05 −479
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
DTC P2 121 THROTTLE/PEDAL POSITION SENSOR/
SWITCH ”D” CIRCUIT RANGE/
PERFORMANCE
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P2 120 on page 05 −473.
DTC No.DTC Detection ConditionTrouble Area
P2 121
Conditions (a) and (b) continue for 0.5 second:
(a) Difference between VPA and VPA2 exceeds the threshold
(b) IDL is OFFS Accelerator pedal position sensor circuit
S Accelerator pedal position sensor
S ECM
HINT:
After confirming DTC P2 121, check the accelerator pedal position sensor output voltage using the hand −
held tester. Reference:
Accelerator Pedal Position (Voltage Output)
Trouble AreaAccelerator Pedal ReleasedAccelerator Pedal DepressedTrouble Area
ACCEL POS # 1ACCEL POS #2ACCEL POS #1ACCEL POS #2
Normal condition0.5 to1.1 V1.2 to 2.0 V2.6 to 4.5 V3.4 to 5.3 V
VCP circuit open0 to 0.2 V0 to 0.2 V0 to 0.2 V0 to 0.2 V
VPA circuit open or ground short0 to 0.2 V1.2 to 2.0 V0 to 0.2 V3.4 to 5.3 V
VPA2 circuit open or ground short0.5 to 1.1 V0 to 0.2 V2.6 to 4.5 V0 to 0.2 V
EP circuit open4.5 to 5.5 V4.5 to 5.5 V4.5 to 5.5 V4.5 to 5.5 V
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P2 120 on page 05 −473.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the hand−held tester. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air −fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data
from the time the malfunction occurred.
05I7T −01
Page 4388 of 5135
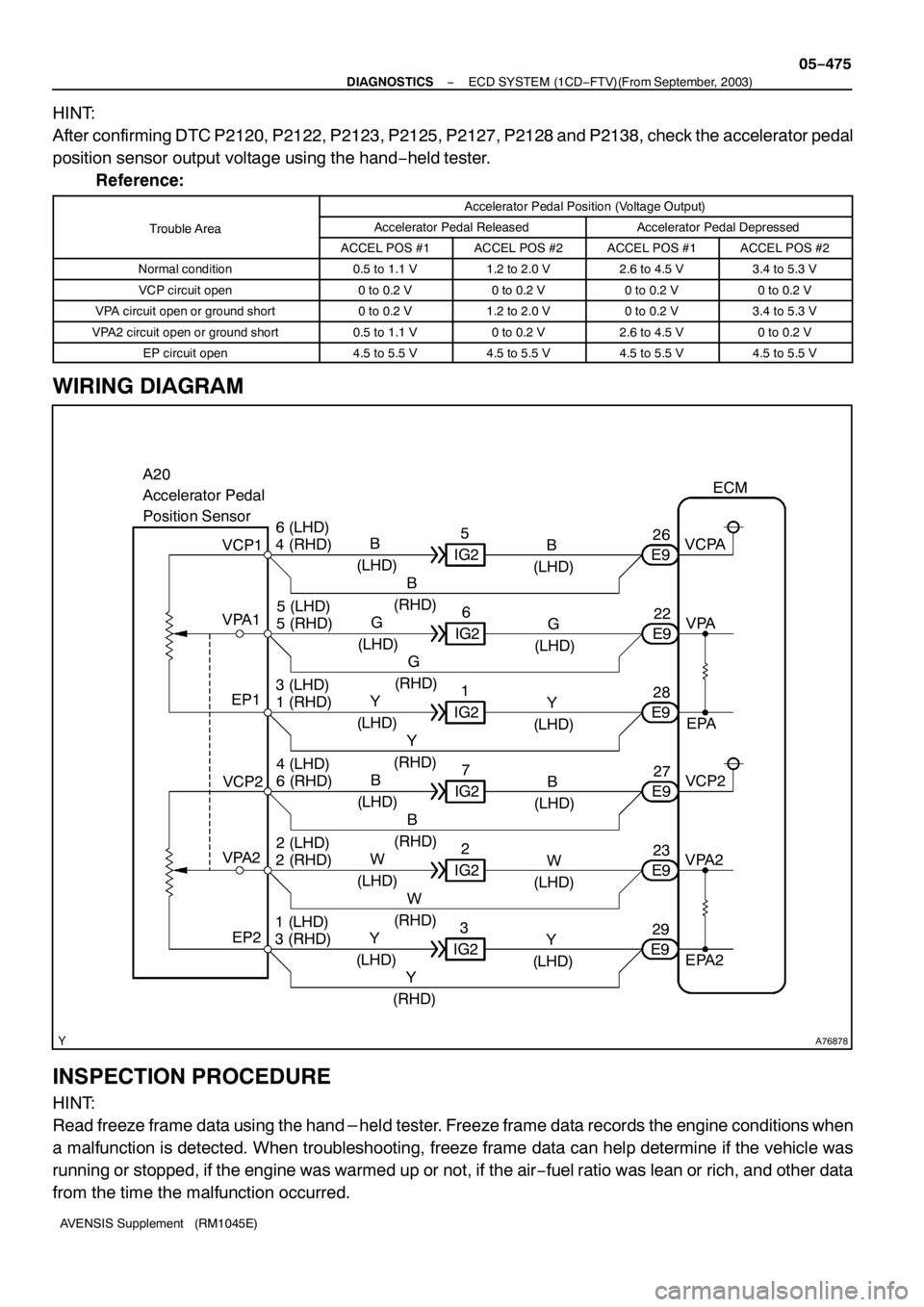
A76878
A20
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
VCP16 (LHD)
E926ECM
VCPA B
4 (RHD)
(LHD)B
(LHD) 5
IG2
B
(RHD)
VPA15 (LHD)
E922
VPA G
5 (RHD)
(LHD)G
(LHD) 6
IG2
G
(RHD)
EP13 (LHD)
E928
EPA Y
1(RHD)
(LHD)Y
(LHD) 1
IG2
Y
(RHD)
VCP24 (LHD)
E927
VCP2 B
6 (RHD)
(LHD)B
(LHD) 7
IG2
B
(RHD)
VPA22 (LHD)
E923
VPA2 W
2 (RHD)
(LHD)W
(LHD) 2
IG2
W
(RHD)
EP21(LHD)
E929
EPA2 Y
3 (RHD)
(LHD)Y
(LHD) 3
IG2
Y
(RHD)
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−475
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
HINT:
After confirming DTC P2120, P2122, P2123, P2125, P2127, P2128 and P2138, check the accelerator pedal
position sensor output voltage using the hand−held tester.
Reference:
Accelerator Pedal Position (Voltage Output)
Trouble AreaAccelerator Pedal ReleasedAccelerator Pedal DepressedTroubleArea
ACCEL POS #1ACCEL POS #2ACCEL POS #1ACCEL POS #2
Normal condition0.5 to1.1V1.2 to 2.0 V2.6 to 4.5 V3.4 to 5.3 V
VCP circuit open0 to 0.2 V0 to 0.2 V0 to 0.2 V0 to 0.2 V
VPA circuit open or ground short0 to 0.2 V1.2 to 2.0 V0 to 0.2 V3.4 to 5.3 V
VPA2 circuit open or ground short0.5 to1.1V0 to 0.2 V2.6 to 4.5 V0 to 0.2 V
EP circuit open4.5 to 5.5 V4.5 to 5.5 V4.5 to 5.5 V4.5 to 5.5 V
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data usingthe hand−held tester.Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air−fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data
from the time the malfunction occurred.
Page 4399 of 5135
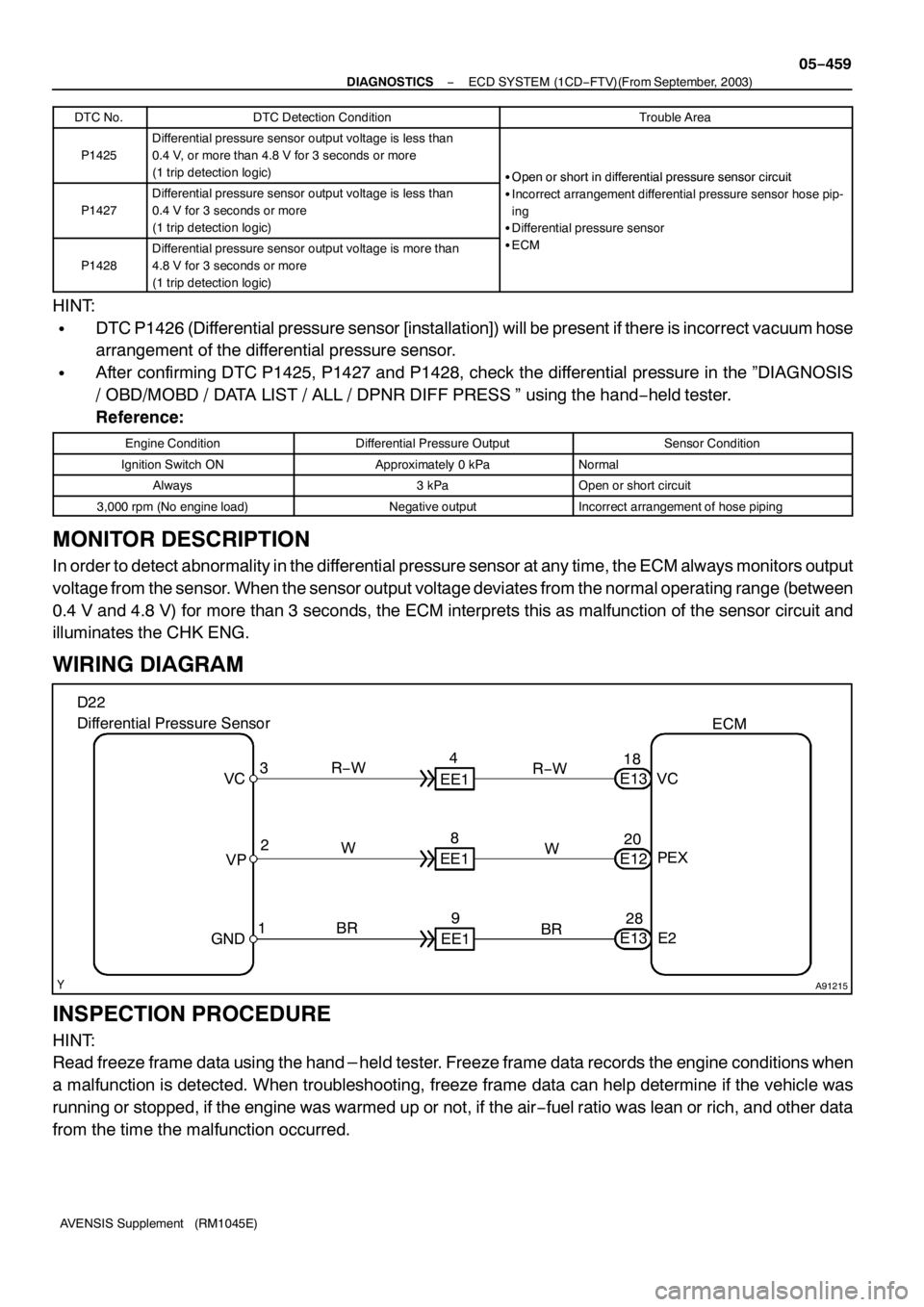
A91215
VCECM
PEX
E2 W R−W
BR D22
Differential Pressure Sensor
13
218
E13
20
E12
28
E13 VC
GNDVPR−W
W
BR EE1
EE1
EE1 4
9 8
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−459
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E) DTC No.
DTC Detection ConditionTrouble Area
P1425
Differential pressure sensor output voltage is less than
0.4 V, or more than 4.8 V for 3 seconds or more
(1trip detection logic)
SOpen or short in differentialpressure sensor circuit
P1427
Differential pressure sensor output voltage is less than
0.4 V for 3 seconds or more
(1trip detection logic)
SOpenorshortindifferentialpressuresensorcircuit
SIncorrect arrangement differential pressure sensor hose pip-
ing
SDifferential pressure sensor
P1428
Differential pressure sensor output voltage is more than
4.8 V for 3 seconds or more
(1trip detection logic)
ee tap essu ese so
SECM
HINT:
SDTC P1426 (Differential pressure sensor [installation]) will be present if there is incorrect vacuum hose
arrangement of the differential pressure sensor.
SAfter confirming DTC P1425, P1427 and P1428, check the differential pressure in the ”DIAGNOSIS
/ OBD/MOBD / DATA LIST / ALL / DPNR DIFF PRESS ” using the hand−held tester.
Reference:
Engine ConditionDifferential Pressure OutputSensor Condition
Ignition Switch ONApproximately 0 kPaNormal
Always3 kPaOpen or short circuit
3,000 rpm (No engine load)Negative outputIncorrect arrangement of hose piping
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
In order to detect abnormality in the differential pressure sensor at any time, the ECM always monitors output
voltage from the sensor. When the sensor output voltage deviates from the normal operating range (between
0.4 V and 4.8 V) for more than 3 seconds, the ECM interprets this as malfunction of the sensor circuit and
illuminates the CHK ENG.
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data usingthe hand−held tester.Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air−fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data
from the time the malfunction occurred.