Page 4277 of 5135
A82347
S6
Suction Control Valve
E13 2
PCV+
21
LG LG−R
PCV−
E13 1
EDU
1PRDECM
E13 32
1
EA1 PRDR−L
E54
W
PRVE58
B
COM3
E472 P3
Pressure Discharge Valve
W
B 2
EA1
(Shielded) (Shielded)
BR
BR
BR
EIJ12 D
J12 E
J13 D J13 E J/C
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−323
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data usingthe hand−held tester.Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air−fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data
from the time the malfunction occurred.
Page 4286 of 5135
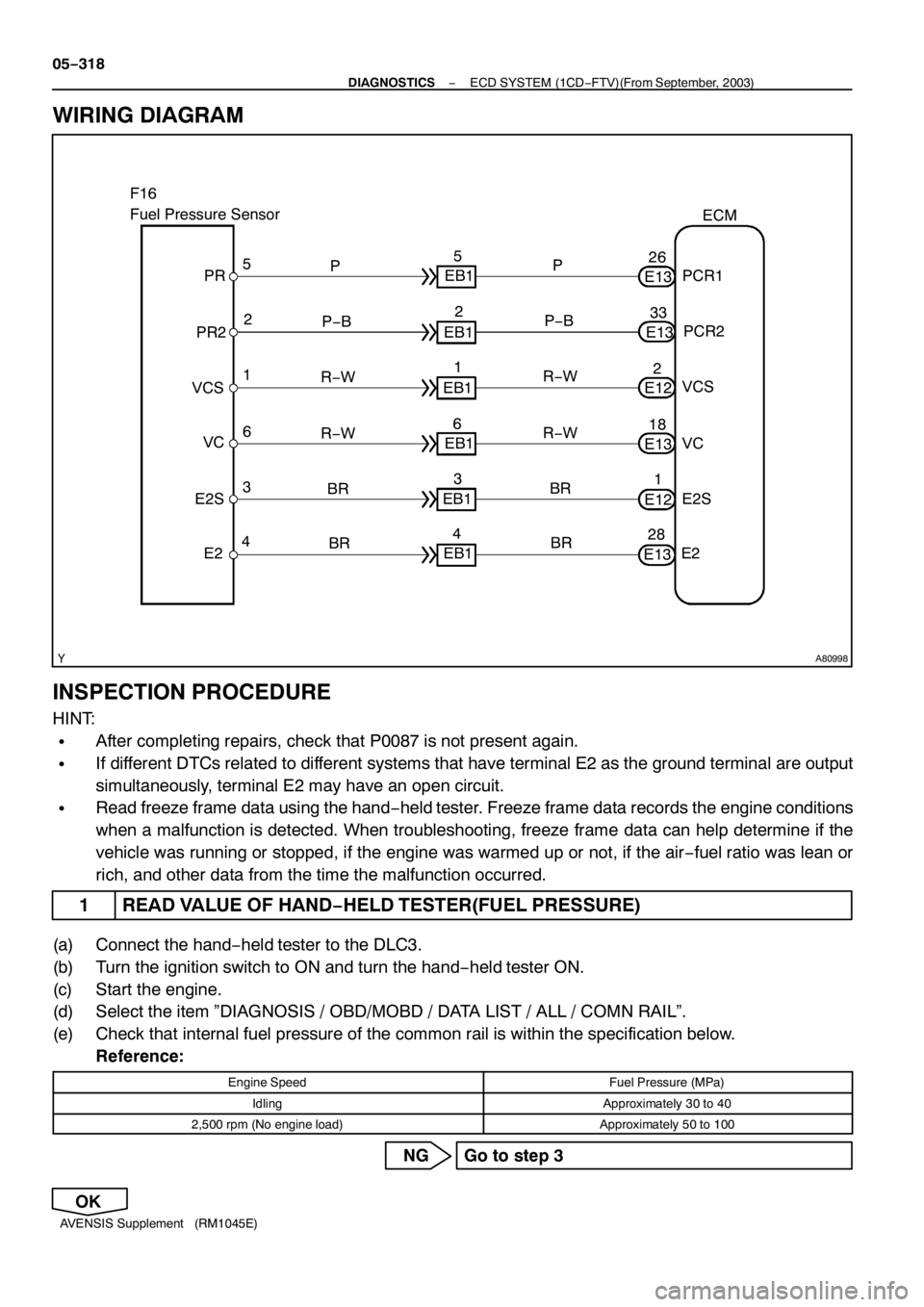
A80998
F16
Fuel Pressure Sensor
5
P
PCR1 ECM
E13 26 5
EB1
2
P−B
PCR2
E13 33 2
EB1
1
R−W
VCS
E12 2 1
EB1
6
R−W
VC
E13 18 6
EB1
3
BR
E2S
E12 1 3
EB1
4
BR
E2
E13 28 4
EB1 PR
PR2P
P−B
R−W
R−W
BR
BR VC
E2S VCS
E2
05−318
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
SAfter completing repairs, check that P0087 is not present again.
SIf different DTCs related to different systems that have terminal E2 as the ground terminal are output
simultaneously, terminal E2 may have an open circuit.
SRead freeze frame data using the hand−held tester. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions
when a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the
vehicle was running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air−fuel ratio was lean or
rich, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
1READ VALUE OF HAND−HELD TESTER(FUEL PRESSURE)
(a) Connect the hand−held tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the hand−held tester ON.
(c) Start the engine.
(d) Select the item ”DIAGNOSIS / OBD/MOBD / DATA LIST / ALL / COMN RAIL”.
(e) Check that internal fuel pressure of the common rail is within the specification below.
Reference:
Engine SpeedFuel Pressure (MPa)
IdlingApproximately 30 to 40
2,500 rpm (No engine load)Approximately 50 to100
NG Go to step 3
OK
Page 4289 of 5135
A66060
E13
ECM ConnectorE12
VN(+) E1(
−)
A82974
VRV Signal Waveforms
GND
20V/
Division
1 msec./ Division
05 −312
−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
DTC P0045 TURBO/SUPER CHARGER BOOST CONTROL SOLENOID CIRCUIT / OPEN
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC No.DTC Detection ConditionTrouble Area
P0045Open or short in VRV circuit for 0.5 second or more
(1 trip detection logic)S VRV
S Open or short in VRV circuit
S ECM
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0234 on page 05 −376.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
1 INSPECT VACUUM REGULATING VALVE ASSY (See page 13− 8)
NG REPLACE VACUUM REGULATING VALVE ASSY
OK
2 INSPECT ECM(VN VOLTAGE)
(a) Inspect using the oscilloscope.
(b) During idling, check the waveform between terminals E12 and E13 of the ECM connectors.
Standard:
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
VN (E13 −10) − E1 (E12 −7)Correct waveform is as shown
OK REPLACE ECM (See page 10− 29)
NG
05CPC −03
Page 4293 of 5135
A91217
MREL
W
GRE9
IE5
B
Battery FL MAINAF2+ 8
1 126
Engine Room
R/B No. 1ECM
6AGR
3AF2−
HAF2
E1 E1035
E1034 1
IP1 (RHD)(LHD) 1
2
W
1
2
1
11B
W
2
1
325
3
W−B
A
A
A
W−B(RHD)
(LHD)W−B
A
IP IKEI J17
J/C
J15
J/C B−R
Fuse Block
A/F AM1 No. 1 140A ALT
A35
A/F Sensor
Relay B−R
W
(*1)W
(*2)
IH2 1
B−W
(*1)A34A34 A34 A34A34
A34
A34
A34 2
2 11 3
44
3
+B AF+
AF−
HT B
(*1)
(*2)
(*1)
(*2) (*2)
B(*1)
(*3)W(*1)
W
(*2) IH2 3
IH2 4
B
(*1)BR
(*1)
A34
A/F sensor BR
E12
E127 5
IK1 3
L−RL−R
(*2)
L−R
(*1) IH2
2R
(*1)
BR J/C J13
J12 D
E
BR
*1: w/ Headlight Beam Level Control
*2: w/o Headlight Beam Level Control
*3: Shielded
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−307
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
WIRING DIAGRAM
Page 4333 of 5135
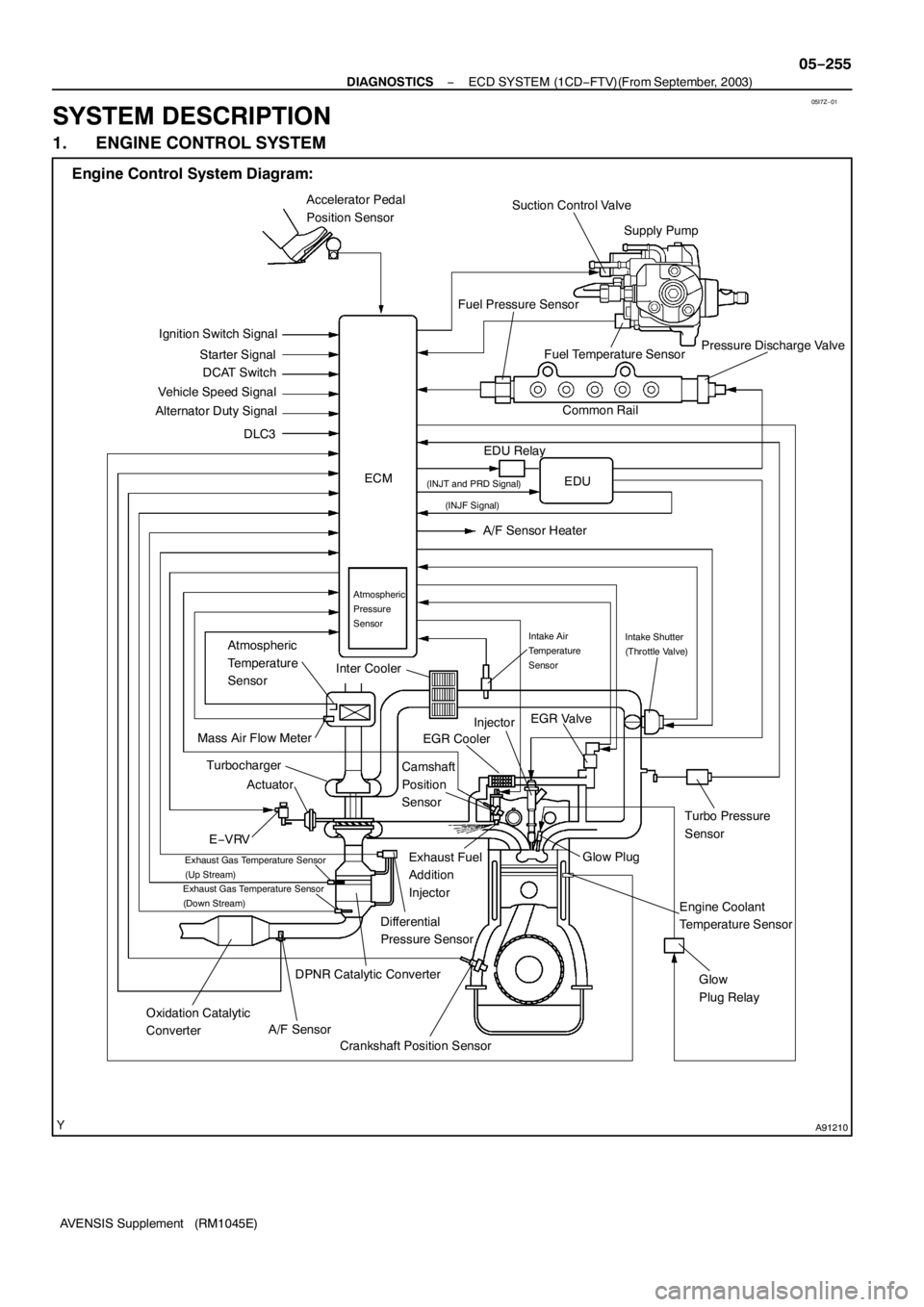
05I7Z−01
A91210
Engine Control System Diagram:
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Ignition Switch Signal
Starter Signal
Vehicle Speed Signal
DLC3Supply Pump
Pressure Discharge Valve Fuel Pressure Sensor
EDU Relay
EDU
Atmospheric
Temperature
Sensor
Glow
Plug Relay
Crankshaft Position SensorCamshaft
Position
SensorCommon Rail Suction Control Valve
Alternator Duty SignalDCAT Switch
ECM
Atmospheric
Pressure
Sensor
A/F Sensor Heater
Mass Air Flow Meter
Differential
Pressure Sensor
A/F Sensor Actuator
E−VRV
Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor
(Up Stream)
Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor
(Down Stream)Glow Plug EGR Valve
Injector
Turbo Pressure
Sensor
Engine Coolant
Temperature Sensor
Intake Air
Temperature
Sensor
Fuel Temperature Sensor
EGR Cooler Inter Cooler
Exhaust Fuel
Addition
Injector
DPNR Catalytic Converter
Turbocharger
(INJT and PRD Signal)
(INJF Signal)
Intake Shutter
(Throttle Valve)
Oxidation Catalytic
Converter
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−255
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
1. ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
Page 4334 of 5135
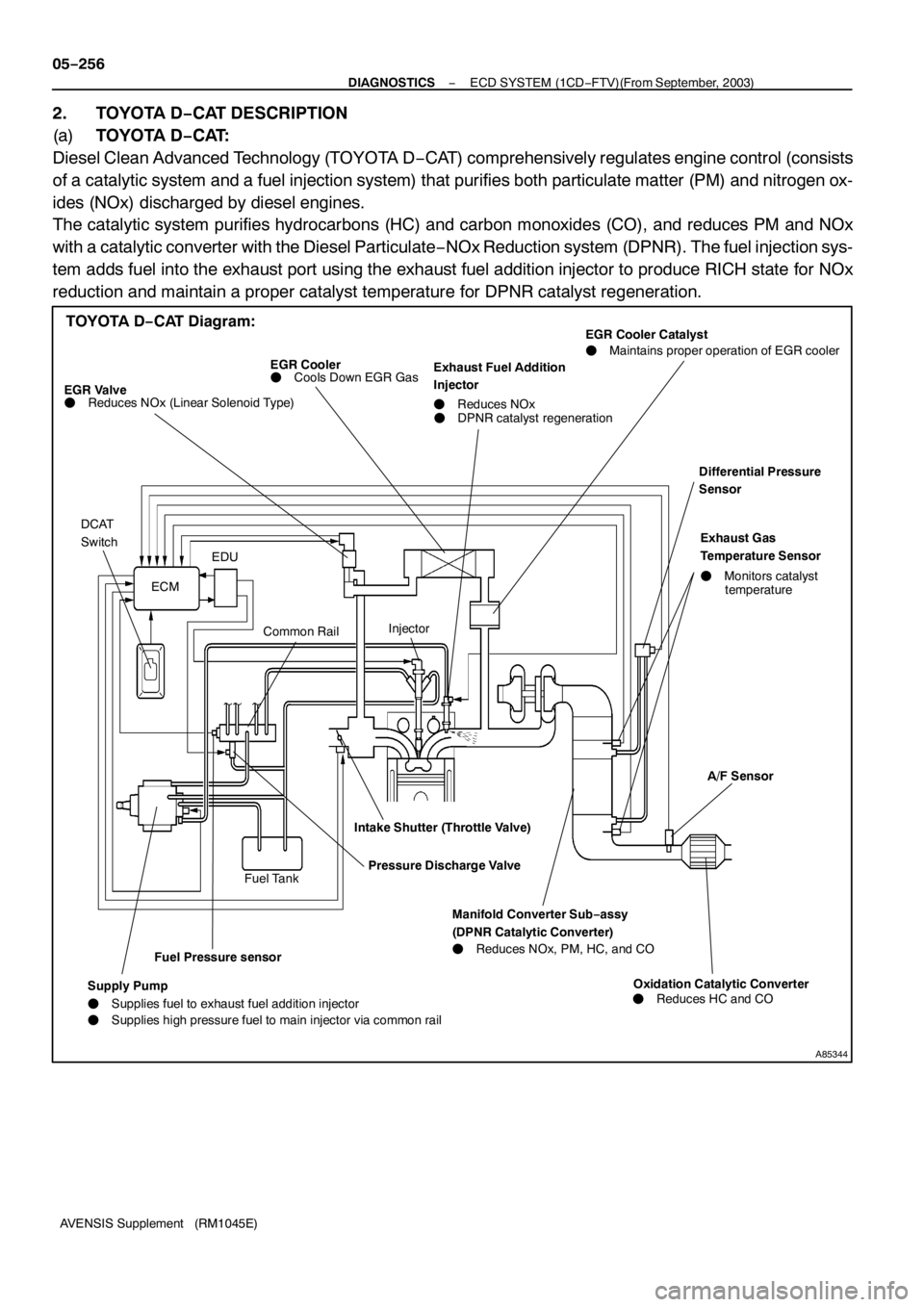
A85344
TOYOTA D−CAT Diagram:
DCAT
Switch
EDU
ECM
Common RailInjector
Fuel Tank EGR Valve
FReduces NOx (Linear Solenoid Type)EGR Cooler
FCools Down EGR GasExhaust Fuel Addition
Injector
FReduces NOxEGR Cooler Catalyst
FMaintains proper operation of EGR cooler
Differential Pressure
Sensor
Exhaust Gas
Temperature Sensor
FMonitors catalyst
A/F Sensor
Oxidation Catalytic Converter
FReduces HC and CO Manifold Converter Sub−assy
(DPNR Catalytic Converter)
FReduces NOx, PM, HC, and CO Intake Shutter (Throttle Valve)
Supply Pump
FSupplies fuel to exhaust fuel addition injector
temperature FDPNR catalyst regeneration
FSupplies high pressure fuel to main injector via common rail
Pressure Discharge Valve
Fuel Pressure sensor
05−256
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
2. TOYOTA D−CAT DESCRIPTION
(a)TOYOTA D−CAT:
Diesel Clean Advanced Technology (TOYOTA D−CAT) comprehensively regulates engine control (consists
of a catalytic system and a fuel injection system) that purifies both particulate matter (PM) and nitrogen ox-
ides (NOx) discharged by diesel engines.
The catalytic system purifies hydrocarbons (HC) and carbon monoxides (CO), and reduces PM and NOx
with a catalytic converter with the Diesel Particulate−NOx Reduction system (DPNR). The fuel injection sys-
tem adds fuel into the exhaust port using the exhaust fuel addition injector to produce RICH state for NOx
reduction and maintain a proper catalyst temperature for DPNR catalyst regeneration.
Page 4338 of 5135

A91221
Common Rail System Diagram (1CD−FTV Fuel System):
Sensors ECM EDU
Common Rail
Fuel Pressure SensorPressure Discharge
Valve
Supply Pump Assy
Suction Control Valve
Fuel TankMain
Injector
Fuel Filter
: High−pressurized Area
Exhaust Fuel
Addition Injector
Exhaust Port
To DPNR
Catalytic
Converter 05−260
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
3. COMMON RAIL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
(a)COMMON RAIL SYSTEM:
The common rail system stores high−pressurized fuel supplied from the supply pump in the common rail and
injects it using the injectors. Fuel injection timing and fuel injection volume are regulated by the ECM; it pro-
vides an electric current to the solenoid valve of the injector with the EDU to regulate them.
By storing high−pressurized fuel produced in the supply pump in the common rail, this system can always
offer stable fuel injection pressure regardless of the engine speed and engine load, even if a driving speed
is low. In addition, this system uses the injector that opens and closes its fuel passage with the Two−Wa y
Valve (TWV) therefore both the fuel injection time and volume are precisely regulated by the ECM.
The ECM monitors internal fuel pressure of the common rail with the fuel pressure sensor and commands
the supply pump to supply fuel to obtain a target internal pressure, approximately 30 to180 MPa (306 to
1,835 kgf/cm
2, 4,351to 26,106 psi). The ECM opens and closes the pressure discharge valve to improve
controllability for the common rail internal fuel pressure.
This system has two split fuel injections. It performs ”pilot−injection” as subsidiary fuel injection prior to the
main fuel injection to make combustion soft, and this helps to reduce engine vibration and noise.
Page 4341 of 5135
A81479
Injection Control Diagram:
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Camshaft Position Sensor
Crankshaft Position Sensor
(NE Signal)
Other Sensors
Fuel TankFeed
Pump
Eccentric
CamPlungerCheck Valve Fuel Pressure SensorCommon Rail EDU
TWV
Orifice
Orifice
Nozzle
NeedleControl
Chamber
Piston
Injector ECM
Suction
Control
ValveSolenoid
Valve
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−263
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
4. INJECTION CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The ECM controls the fuel injection system by using the injectors and supply pump. The ECM determines
the fuel injection volume and timing by controlling both duration and timing of energization to the solenoid
valve in the injector, and determines the injection pressure by controlling the suction control valve located
on the supply pump.
The feed pump is used to pump fuel from the fuel tank into the supply pump.