Page 4129 of 5135
A76882
Battery FL MAINIGN
B−G11
E9
2 6
Engine
Room
J/B No.4Engine Room
R/B No.1
AM2
1 2
B−G4
18Driver
Side J/B
B−W B−R
WECM
DH
DA B−R
B−R 1
1A 1
1
4A
1 4B(LHD) (RHD)IP1 IE41
1
I13
Ignition Switch
AM2
IG2
(LHD)J8C
(RHD)J26A
(LHD)J8C
(RHD)J26AB−WCheck
Engine
Warning
LightW
C11
Combination Meter
229
J/C Engine Room
J/B No.1
− DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
05−251
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
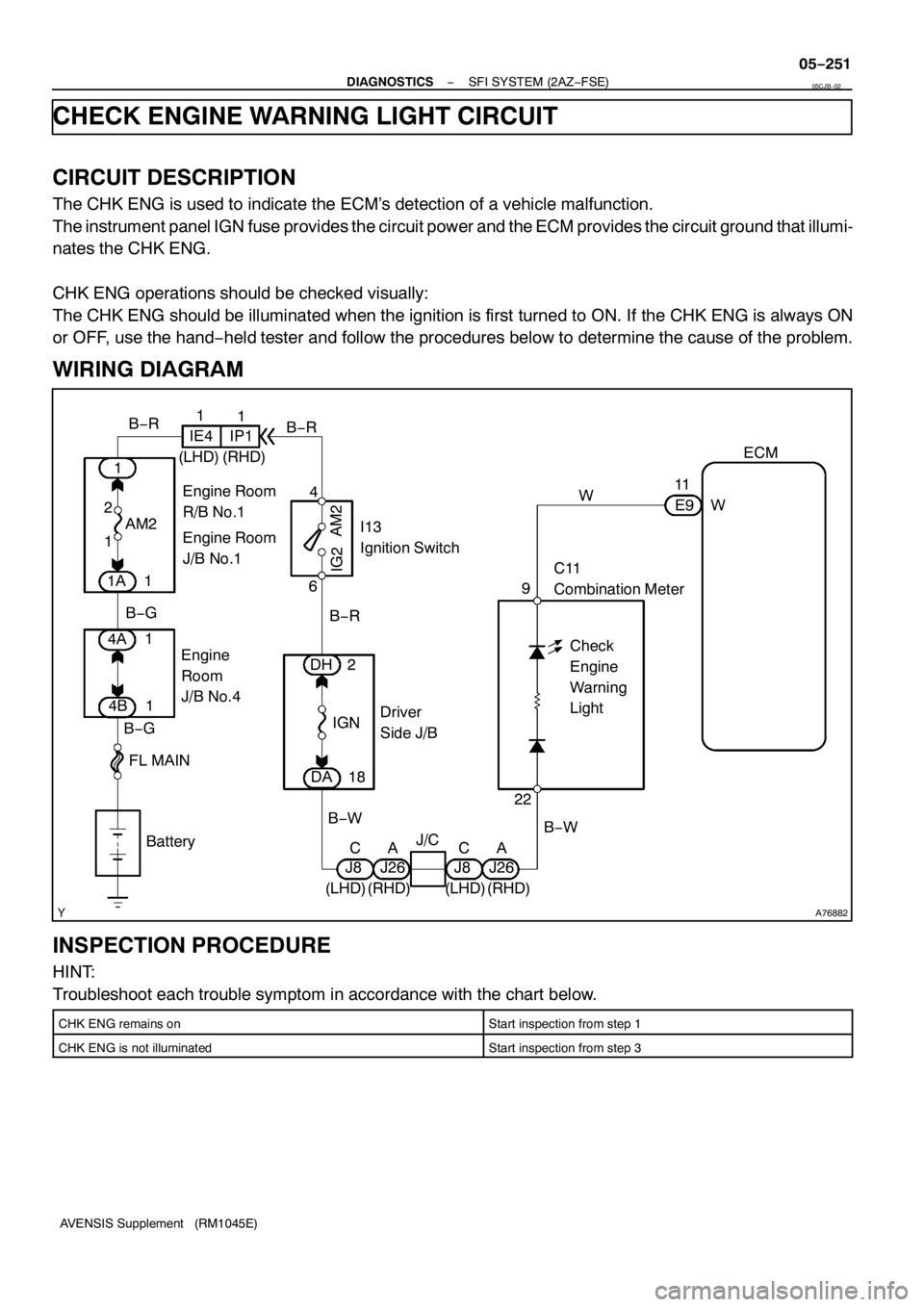
CHECK ENGINE WARNING LIGHT CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The CHK ENG is used to indicate the ECM’s detection of a vehicle malfunction.
The instrument panel IGN fuse provides the circuit power and the ECM provides the circuit ground that illumi-
nates the CHK ENG.
CHK ENG operations should be checked visually:
The CHK ENG should be illuminated when the ignition is first turned to ON. If the CHK ENG is always ON
or OFF, use the hand−held tester and follow the procedures below to determine the cause of the problem.
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Troubleshoot each trouble symptom in accordance with the chart below.
CHK ENG remains onStart inspection from step1
CHK ENG is not illuminatedStart inspection from step 3
05CJB−02
Page 4131 of 5135

−
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
05 −249
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
STARTER SIGNAL CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When the engine is cranked, the intake air flow is slow, so fuel vaporization is poor. A rich mixture is therefore
necessary in order to achieve good startability. While the engine is being cranked, the battery voltage is ap-
plied to terminal STA of the ECM. The starter signal is mainly used to increase the fuel injection volume for
the starting injection control and after −start injection control.
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P06 17 on page 05 −203.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
This diagnostic troubleshooting procedure is on the premise that the engine is being cranked under normal
conditions. If the engine does not crank, proceed to the problem symptoms table on page 05 −1 0.
1 READ VALUE OF HAND −HELD TESTER(STARTER SIGNAL)
(a) Connect the hand −held tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the hand −held tester ON.
(c) On the hand −held tester, select the item: DIAGNOSIS / OBD/MOBD / DATA LIST / ALL / STARTER
SIG. Read the values.
Result:
Ignition Switch PositionONSTART
STA SignalOFFON
OK PROCEED TO NEXT CIRCUIT INSPECTION SHOWN IN PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
(See page 05 −1 0)
NG
05CJC −02
Page 4133 of 5135

1
2
3
4
A93906
−
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
05 −24 1
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
FUEL PUMP CONTROL CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P0230 on page 05 −141.
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0230 on page 05 −141.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
1 CHECK FUEL PUMP OPERATION (See page 11− 4)
(a) Check if there is pressure in the fuel inlet hose.
HINT:
If there is fuel pressure, you will hear the sound of fuel flowing.
OK Go to step 9
NG
2 PERFORM ACTIVE TEST BY HAND −HELD TESTER(OPERATION OF CIRCUIT
OPENING RELAY)
(a) Connect the hand −held tester to the DLC3.
(b) Start the engine and warm it up.
(c) Turn the ignition switch to ON.
(d) Select the item: DIAGNOSIS / OBD/MOBD / ACTIVE TEST / FUEL PUMP/SPD.
(e) Check the relay operation when it is operated by the hand −held tester.
Standard: Operating sound can be heard from the relay.
OK Go to step 4
NG
3 INSPECT RADIATOR FAN RELAY
(a) Remove the R21 radiator fan relay.
(b) Check for continuity in the radiator fan relay relay. Standard:
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
1−2Continuity
3−4Continuity
1−2No Continuity
(Apply battery voltage to terminals 3 and 4)
(c) Reinstall the radiator fan relay relay.
NG REPLACE FUEL PUMP RELAY
OK
05HIS −01
Page 4141 of 5135
A76879
IP1I13
Ignition Switch
IGN Driver Side J/B
E9
E11ECM
Battery FL MAINEFI
No. 1
2
B−G2
118
9
18 4DH
2
E9E9
1 12 31 5
EFI
Relay
D
EEBR GR B−W
DA
J/C 1A
J28IGSW
+B2 MREL
E1
Engine Room
J/B No. 41 4A
4BEngine Room
R/B No. 1 1EFI
AM2
1 211
1 2
B−G6
(RHD) IE4 1 (LHD)
B−R B−RB−R
4 4
4
4
4
4Engine Room
R/B No. 4
Engine
Room
R/B No. 4B−Y
B−W
B−R
ECW−B
B−RB−R B−R
(RHD) (LHD)
D J14D J28 (RHD)(LHD)
D J14
D
J28 D J141
E9 +B (RHD)
(LHD)B−W
B−W (RHD)
(LHD)B−W
J26A
J27E
J8
J/CJ/C
CC
IE12
GR
(LHD)(RHD)IP1 IE42
3
AM2 IG2
Engine Room
J/B No. 1 05−236
− DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
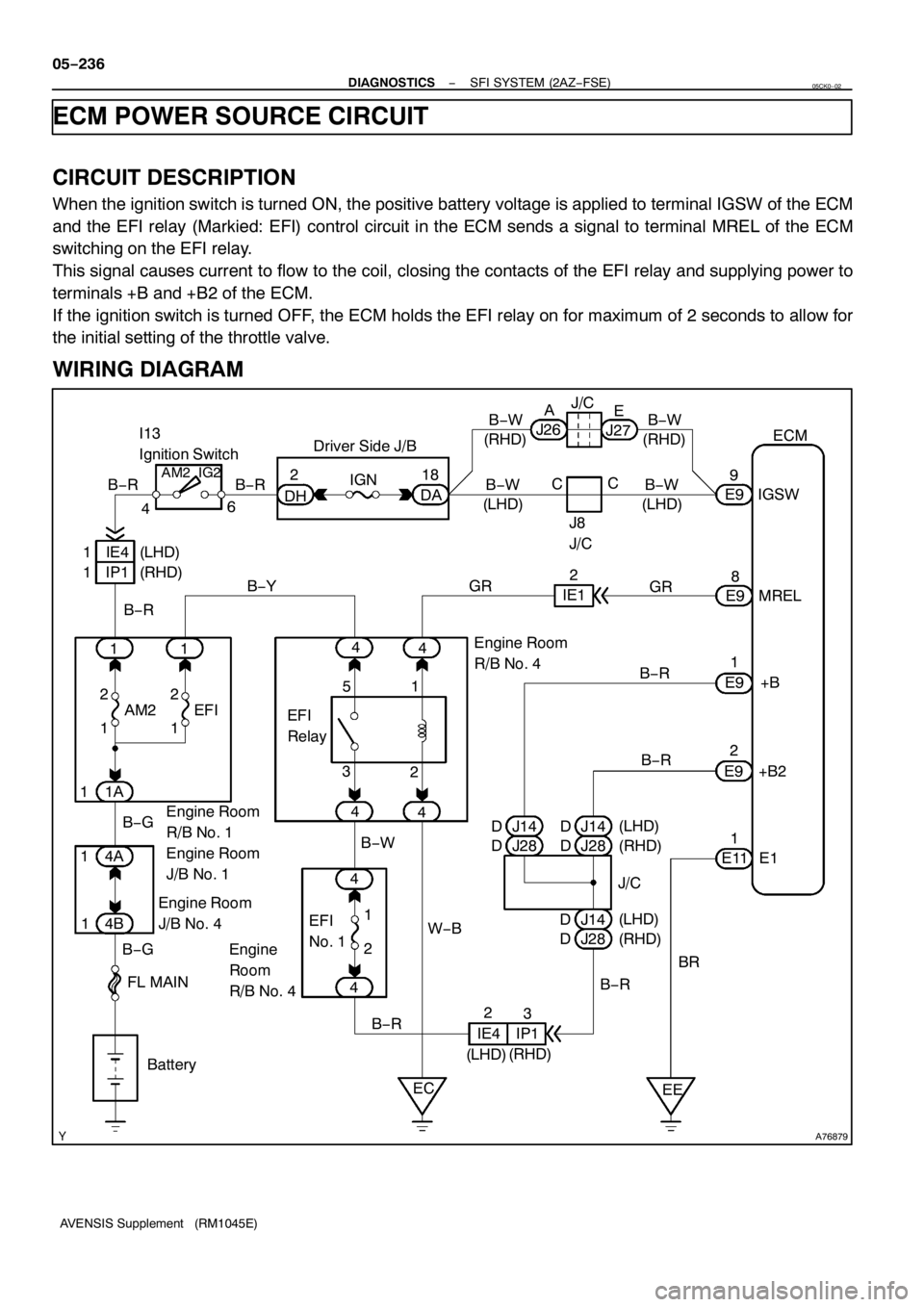
ECM POWER SOURCE CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When the ignition switch is turned ON, the positive battery voltage is applied to terminal IGSW of the ECM
and the EFI relay (Markied: EFI) control circuit in the ECM sends a signal to terminal MREL of the ECM
switching on the EFI relay.
This signal causes current to flow to the coil, closing the contacts of the EFI relay and supplying power to
terminals +B and +B2 of the ECM.
If the ignition switch is turned OFF, the ECM holds the EFI relay on for maximum of 2 seconds to allow for
the initial setting of the throttle valve.
WIRING DIAGRAM
05CK0−02
Page 4149 of 5135
A76878
A20
Accelerator pedal
Position Sensor
VCP16 (LHD)
E926ECM
VCPA B
4 (RHD)
(LHD)B
(LHD) 5
IG2
B
(RHD)
VPA15 (LHD)
E922
VPA G
5 (RHD)
(LHD)G
(LHD) 6
IG2
G
(RHD)
EP13 (LHD)
E928
EPA Y
1(RHD)
(LHD)Y
(LHD) 1
IG2
Y
(RHD)
VCP24 (LHD)
E927
VCP2 B
6 (RHD)
(LHD)B
(LHD) 7
IG2
B
(RHD)
VPA22 (LHD)
E923
VPA2 W
2 (RHD)
(LHD)W
(LHD) 2
IG2
W
(RHD)
EP21(LHD)
E929
EPA2 Y
3 (RHD)
(LHD)Y
(LHD) 3
IG2
Y
(RHD)
− DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
05−227
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data usingthe hand−held tester. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air−fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data
from the time the malfunction occurred.
Page 4155 of 5135
A76877
ECM
+BM
FL MAINTHROTTLE Engine Room J/B No.1
Engine Room R/B No.1
E10
IE2 1A 4B15
2 Engine Room J/B No. 4
6
B−G
Battery4A1
B−G
1 1
1G−RG−Y
A82233
THROTTLE Fuse Engine Room R/B No.1:
A67446
+BM (+) E1(−)
E10E11
ECM Connector
05−220
− DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
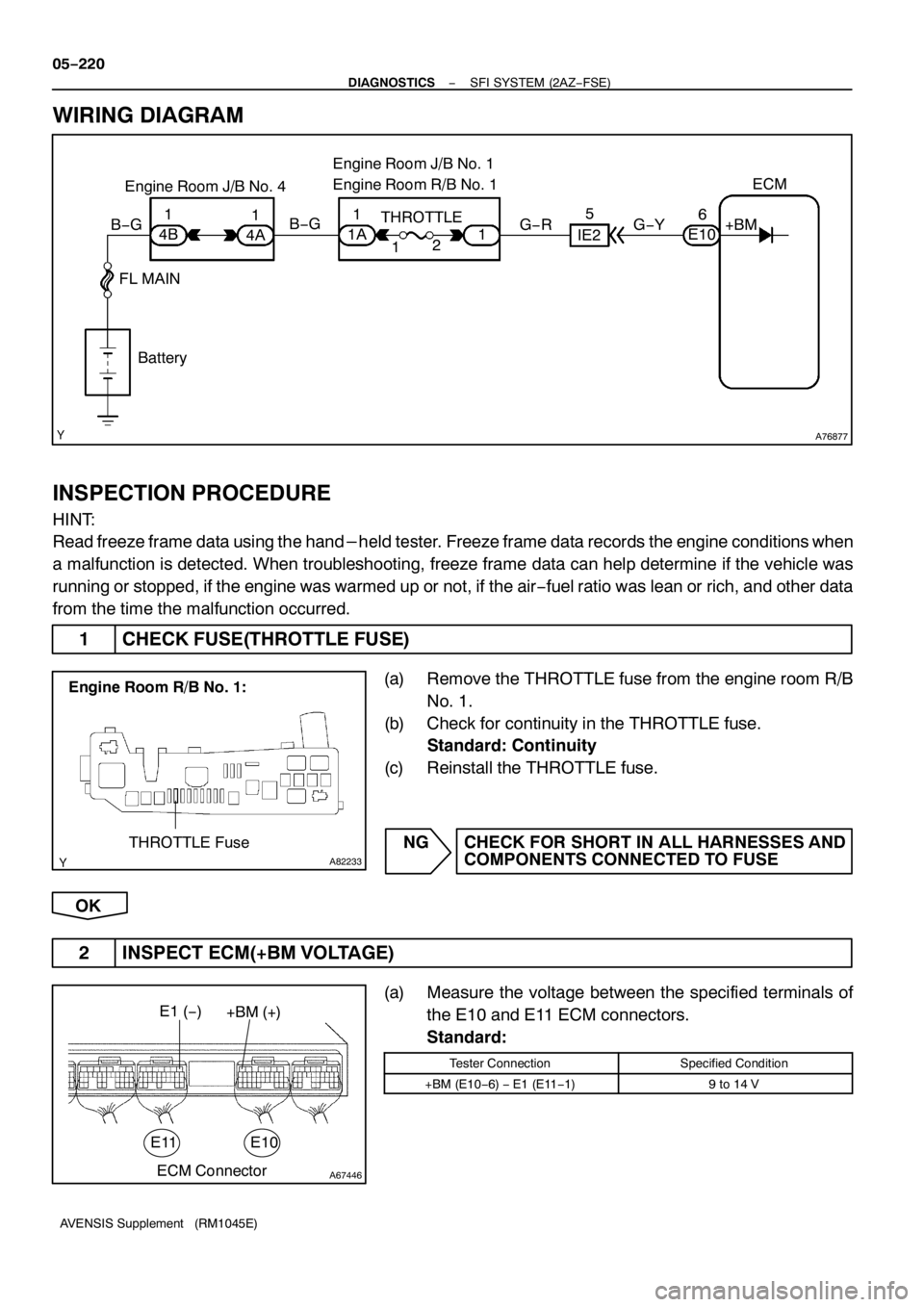
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data usingthe hand−held tester. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air−fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data
from the time the malfunction occurred.
1CHECK FUSE(THROTTLE FUSE)
(a) Remove the THROTTLE fuse from the engine room R/B
No.1.
(b) Check for continuity in the THROTTLE fuse.
Standard: Continuity
(c) Reinstall the THROTTLE fuse.
NG CHECK FOR SHORT IN ALL HARNESSES AND
COMPONENTS CONNECTED TO FUSE
OK
2 INSPECT ECM(+BM VOLTAGE)
(a) Measure the voltage between the specified terminals of
the E10 and E11ECM connectors.
Standard:
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
+BM (E10−6)−E1(E11−1)9to14V
Page 4157 of 5135

−
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
05 −217
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
DTC P2 111 THROTTLE ACTUATOR CONTROL SYSTEM
− STUCK OPEN
DTC P2 11 2 THROTTLE ACTUATOR CONTROL SYSTEM
− STUCK CLOSED
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The throttle motor is operated by the ECM and it opens and closes the throttle valve using gears. The open-
ing angle of the throttle valve is detected by the throttle position sensor, which is mounted on the throttle body.
The throttle position sensor provides feedback to the ECM to control the throttle motor and set the throttle
valve angle in response to driver input.
HINT:
This Electrical Throttle Control System (ETCS) does not use a throttle cable.
DTC No.DTC Detection ConditionTrouble Area
P2 111Throttle valve opening angle is stuck during ECM orders to
close ( 1 trip detection logic)
S Throttle control motor circuit
S Throttle control motor
S Throttle body
S Throttle valve
P2 11 2Throttle valve opening angle is stuck during ECM orders to
open ( 1 trip detection logic)
SThrottle control motor circuit
S Throttle control motor
S Throttle body
S Throttle valve
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P2 102 on page 05 −214.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the hand−held tester . Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air −fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data
from the time the malfunction occurred.
1 INSPECT THROTTLE BODY ASSY(VISUALLY CHECK THROTTLE VALVE)
(a) Check if a foreign object has been caught between the throttle valve and the housing.
NG REMOVE FOREIGN OBJECT AND CLEANTHROTTLE BODY
OK
05CKQ −02
Page 4159 of 5135
A54292
T1
Throttle Control Motor
(Built in Throttle Body)
2
1B
WECM
3
2
17M+
M−
E11
(Shielded)
E11
E11
GE01 05−214
− DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
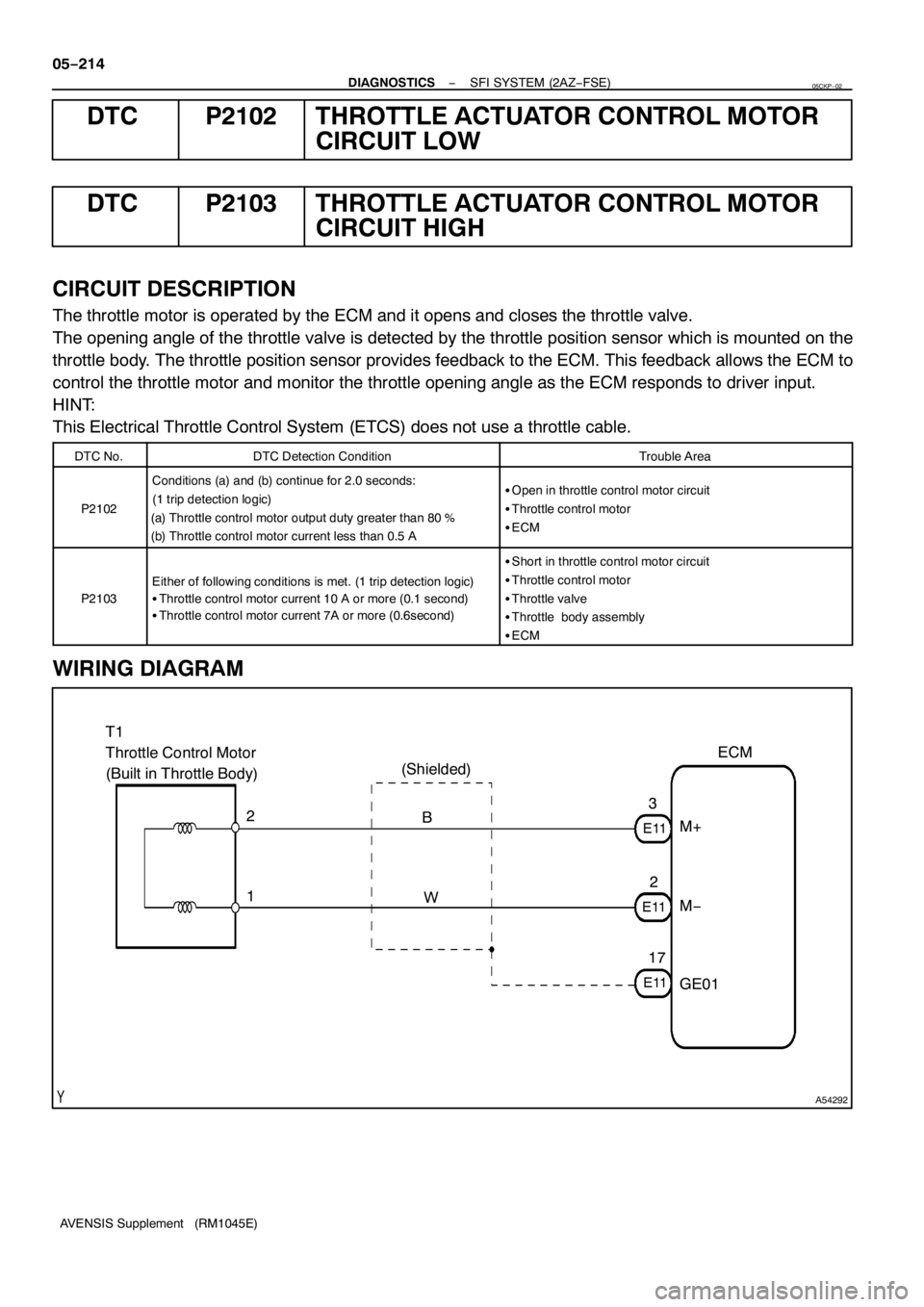
DTC P2102 THROTTLE ACTUATOR CONTROL MOTOR
CIRCUIT LOW
DTC P2103 THROTTLE ACTUATOR CONTROL MOTOR
CIRCUIT HIGH
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The throttle motor is operated by the ECM and it opens and closes the throttle valve.
The opening angle of the throttle valve is detected by the throttle position sensor which is mounted on the
throttle body. The throttle position sensor provides feedback to the ECM. This feedback allows the ECM to
control the throttle motor and monitor the throttle opening angle as the ECM responds to driver input.
HINT:
This Electrical Throttle Control System (ETCS) does not use a throttle cable.
DTC No.DTC Detection ConditionTrouble Area
P2102
Conditions (a) and (b) continue for 2.0 seconds:
(1 trip detection logic)
(a) Throttle control motor output duty greater than 80 %
(b) Throttle control motor current less than 0.5 ASOpen in throttle control motor circuit
SThrottle control motor
SECM
P2103
Either of following conditions is met. (1 trip detection logic)
SThrottle control motor current 10 A or more (0.1 second)
SThrottle control motor current 7A or more (0.6second)
SShort in throttle control motor circuit
SThrottle control motor
SThrottle valve
SThrottle body assembly
SECM
WIRING DIAGRAM
05CKP−02