Page 4970 of 5135

A64984Camshaft Position Sensor Component Side:
– DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (1ZZ–FE/3ZZ–FE)(From February, 2004)
05–141
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL SUPPLEMENT
(RM1098E)
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester II. Freeze frame data record the engine condition when
malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air–fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data
from the time the malfunction occurred.
1 INSPECT CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR(RESISTANCE)
(a) Disconnect the C1 camshaft position sensor connector.
(b) Measure the resistance between the terminals of the
camshaft position sensor.
Standard:
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
1 – 2835 to 1,400 Ω at cold
1 – 21,060 to 1,645 Ω at hot
NOTICE:
Terms ”cold” and ”hot” refer to the temperature of the
coils. ”Cold” means approximately –10� to 50�C (14� to
122�F). ”Hot” means approximately 50� to 100�C (122� to
212�F).
(c) Reconnect the camshaft position sensor connector.
NG REPLACE CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
(See page 18–5 of Pub. No. RM1018E AVENSIS)
OK
Page 4971 of 5135
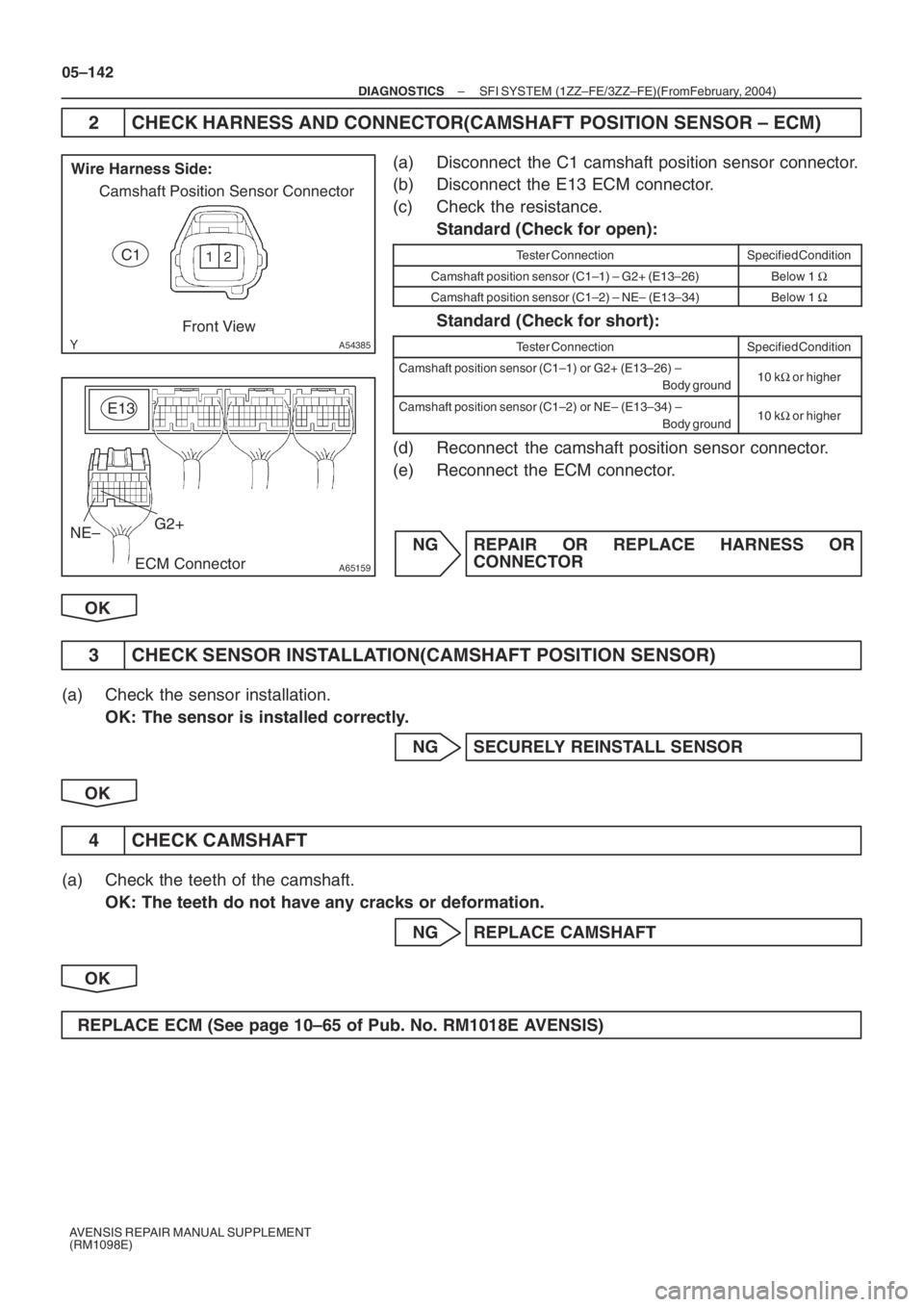
A54385
Wire Harness Side:
Camshaft Position Sensor Connector
C1
Front View
A65159ECM ConnectorG2+ E13
NE–
05–142
– DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (1ZZ–FE/3ZZ–FE)(From February, 2004)
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL SUPPLEMENT
(RM1098E)
2 CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR(CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR – ECM)
(a) Disconnect the C1 camshaft position sensor connector.
(b) Disconnect the E13 ECM connector.
(c) Check the resistance.
Standard (Check for open):
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
Camshaft position sensor (C1–1) – G2+ (E13–26)Below 1 Ω
Camshaft position sensor (C1–2) – NE– (E13–34)Below 1 Ω
Standard (Check for short):
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
Camshaft position sensor (C1–1) or G2+ (E13–26) –
Body ground10 kΩ or higher
Camshaft position sensor (C1–2) or NE– (E13–34) –
Body ground10 kΩ or higher
(d) Reconnect the camshaft position sensor connector.
(e) Reconnect the ECM connector.
NG REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR
CONNECTOR
OK
3 CHECK SENSOR INSTALLATION(CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR)
(a) Check the sensor installation.
OK: The sensor is installed correctly.
NG SECURELY REINSTALL SENSOR
OK
4 CHECK CAMSHAFT
(a) Check the teeth of the camshaft.
OK: The teeth do not have any cracks or deformation.
NG REPLACE CAMSHAFT
OK
REPLACE ECM (See page 10–65 of Pub. No. RM1018E AVENSIS)
Page 4972 of 5135

A85286
GND KNK1 Signal Waveform 05–132
– DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (1ZZ–FE/3ZZ–FE)(From February, 2004)
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL SUPPLEMENT
(RM1098E)
DTC P0325 KNOCK SENSOR 1 CIRCUIT (BANK 1 OR
SINGLE SENSOR)
DTC P0327 KNOCK SENSOR 1 CIRCUIT LOW INPUT
(BANK 1 OR SINGLE SENSOR)
DTC P0328 KNOCK SENSOR 1 CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT
(BANK 1 OR SINGLE SENSOR)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The flat type knock sensor (non–resonant type) has a structure that can detect vibration in a wider band of
frequency, from about 6 kHz to 15 kHz and has the following features:
�The knock sensor is fitted on the cylinder block to detect engine knocking.
�The sensor contains a piezoelectric element which generates voltage when it becomes deformed. This
occurs when the cylinder block vibrates due to knocking. If engine knocking occurs, the ignition timing
is retarded to suppress it.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0325Knock sensor signal level remains at low for more than 10
seconds�Open or short in knock sensor circuit
�Knock sensor (under–torqued or looseness)
�ECM
P0327Output voltage of the knock sensor is 0.5 V or less
�Short in knock sensor circuit
�Knock sensor
�ECM
P0328Output voltage of the knock sensor is 4.5 V or more
�Open in knock sensor circuit
�Knock sensor
�ECM
HINT:
If the ECM detects DTC P0325, P0327 and/or P0328, it enters fail–safe mode in which the corrective re-
tarded angle value is set to the maximum value.
Reference: Inspection by using the oscilloscope.
The correct waveform is as shown.
ItemContents
TerminalKNK1 – EKNK
Equipment Setting0.01 to 10 V/Division,
0.01 to 10 msec./Division
ConditionAfter warming up the engine,
keep the engine speed at 4,000 rpm
05JOG–03
Page 4973 of 5135
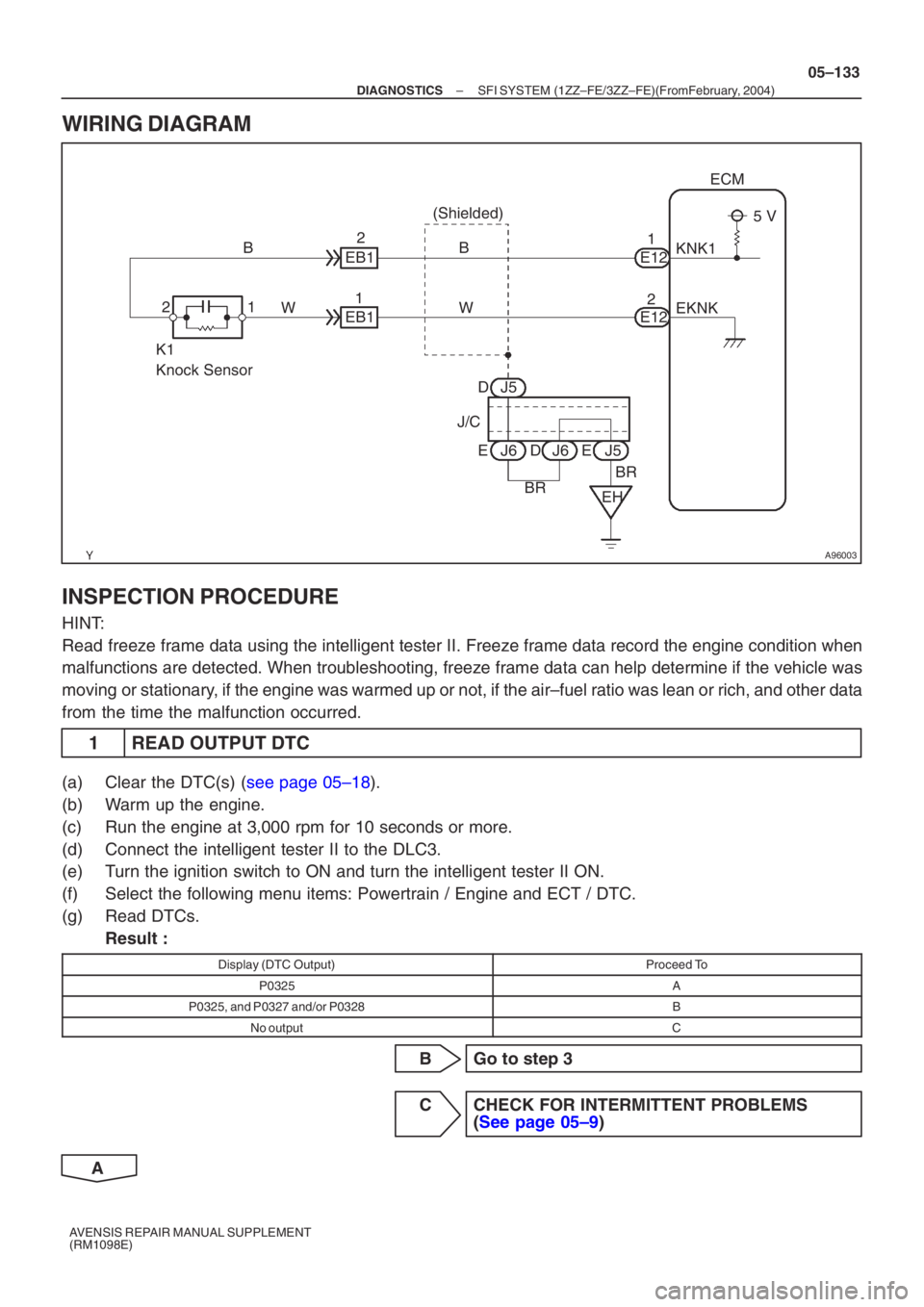
A96003
K1
Knock Sensor1 (Shielded)
J/C J5
J51
E12 ECM
KNK1
EH
2
E122
EKNK
BB
J65 V
W
J6
EE D
EB1
EB1
2
1
D
BR BR
W
–
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM (1ZZ–FE/3ZZ–FE)(From February, 2004)
05–133
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL SUPPLEMENT
(RM1098E)
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester II. Freeze frame data record the engine condition\
when
malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can h\
elp determine if the vehicle was
moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air–fuel ratio was lean \
or rich, and other data
from the time the malfunction occurred.
1 READ OUTPUT DTC
(a) Clear the DTC(s) ( see page 05–18).
(b) Warm up the engine.
(c) Run the engine at 3,000 rpm for 10 seconds or more.
(d) Connect the intelligent tester II to the DLC3.
(e) Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the intelligent tester II ON.
(f) Select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
(g) Read DTCs. Result :
Display (DTC Output)Proceed To
P0325A
P0325, and P0327 and/or P0328B
No outputC
B Go to step 3
C CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS (See page 05–9 )
A
Page 4974 of 5135
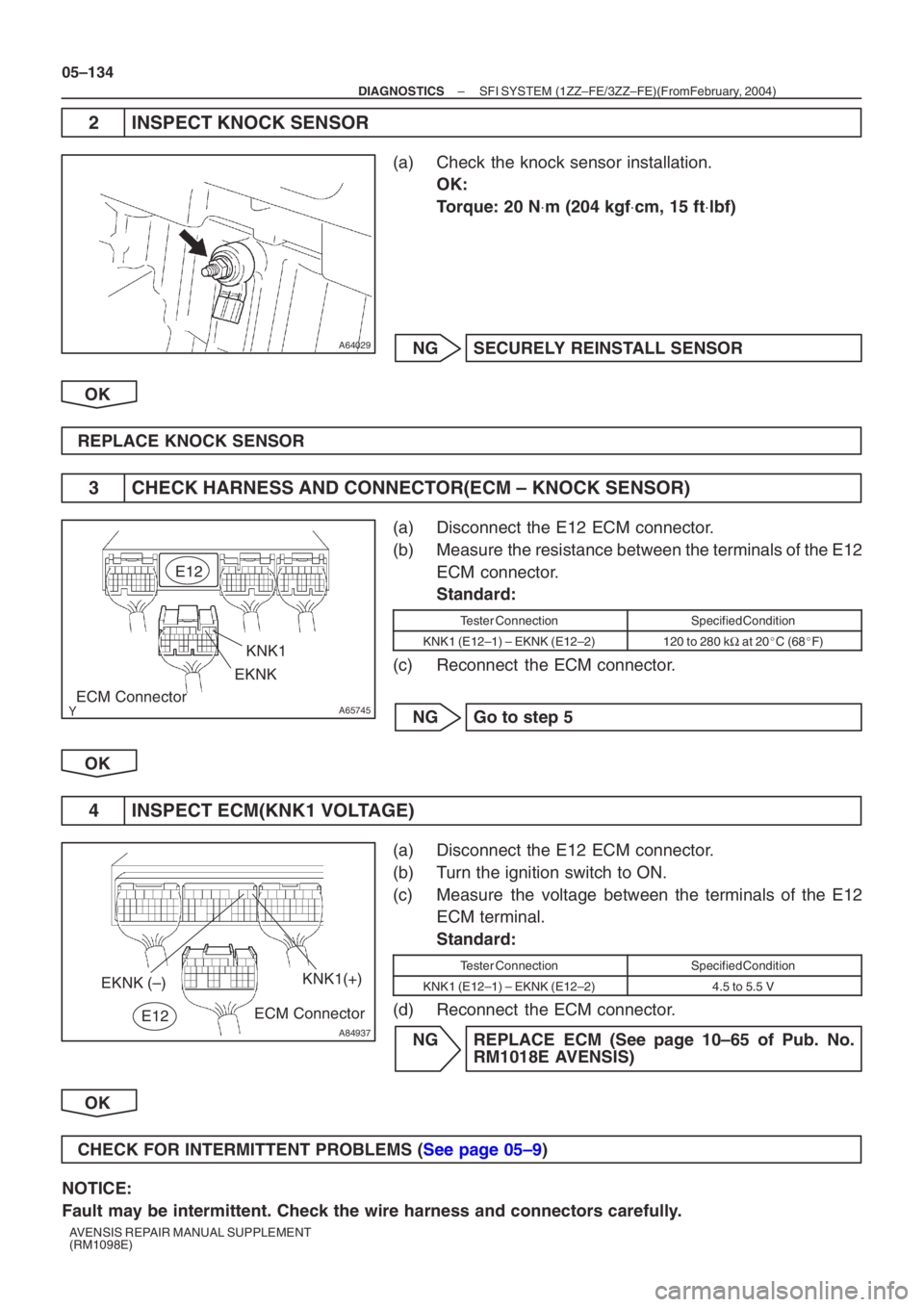
A64029
A65745
E12KNK1
EKNK
ECM Connector
A84937
ECM Connector KNK1(+)
EKNK (–)E12
05–134
–
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM (1ZZ–FE/3ZZ–FE)(From February, 2004)
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL SUPPLEMENT
(RM1098E)
2 INSPECT KNOCK SENSOR
(a) Check the knock sensor installation. OK:
Torque: 20 N ⋅m (204 kgf ⋅cm, 15 ft ⋅lbf)
NG SECURELY REINSTALL SENSOR
OK
REPLACE KNOCK SENSOR
3 CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR(ECM – KNOCK SENSOR)
(a) Disconnect the E12 ECM connector.
(b) Measure the resistance between the terminals of the E12 ECM connector.
Standard:
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
KNK1 (E12–1) – EKNK (E12–2)120 to 280 k Ω at 20 �C (68 �F)
(c) Reconnect the ECM connector.
NG Go to step 5
OK
4 INSPECT ECM(KNK1 VOLTAGE)
(a) Disconnect the E12 ECM connector.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to ON.
(c) Measure the voltage between the terminals of the E12 ECM terminal.
Standard:
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
KNK1 (E12–1) – EKNK (E12–2)4.5 to 5.5 V
(d) Reconnect the ECM connector.
NG REPLACE ECM (See page 10–65 of Pub. No. RM1018E AVENSIS)
OK
CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS ( See page 05–9)
NOTICE:
Fault may be intermittent. Check the wire harness and connectors careful\
ly.
Page 4975 of 5135
A65174
Ohmmeter
– DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (1ZZ–FE/3ZZ–FE)(From February, 2004)
05–135
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL SUPPLEMENT
(RM1098E)
5 INSPECT KNOCK SENSOR
(a) Remove the knock sensor.
(b) Measure the resistance between the terminals.
Standard:
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
KNK1 (K1–1) – EKNK (K1–2)120 to 280 kΩ at 20�C (68�F)
(c) Reinstall the knock sensor.
NG REPLACE KNOCK SENSOR
OK
REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR
Page 4976 of 5135

05–118
– DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (1ZZ–FE/3ZZ–FE)(From February, 2004)
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL SUPPLEMENT
(RM1098E)
DTC P0300 RANDOM/MULTIPLE CYLINDER MISFIRE
DETECTED
DTC P0301 CYLINDER 1 MISFIRE DETECTED
DTC P0302 CYLINDER 2 MISFIRE DETECTED
DTC P0303 CYLINDER 3 MISFIRE DETECTED
DTC P0304 CYLINDER 4 MISFIRE DETECTED
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When a misfire occurs in the engine, hydrocarbons (HC) enter the exhaust gas in high concentrations. If this
HC concentration is high enough, there could be an increase in exhaust emission levels. High concentra-
tions of HC can also cause temperature of the catalyst to increase, possibly damaging the catalyst. To pre-
vent this increase in emissions and limit the possibility of thermal damage, the ECM monitors the misfire rate.
When the temperature of the catalyst reaches a point of thermal degradation, the ECM will blink the MIL.
For monitoring misfire, the ECM uses both the camshaft position sensor and the crankshaft position sensor.
The camshaft position sensor is used to identify misfiring cylinders and the crankshaft position sensor is used
to measure variations in the crankshaft rotation speed. The misfire counter increments when crankshaft rota-
tion speed variations exceed threshold values.
If the misfiring rate exceeds the threshold and could cause emission deterioration, the ECM illuminates the
MIL.
HINT:
�For any particular 200 revolutions of the engine, misfiring which could result in overheating of the cata-
lyst is detected. This will cause the MIL to blink (1 trip detection logic).
�For any particular 1,000 revolutions of the engine, misfiring which could result in emission deterioration
is detected. This will cause the MIL to illuminate (2 trip detection logic).
05KOH–02
Page 4977 of 5135
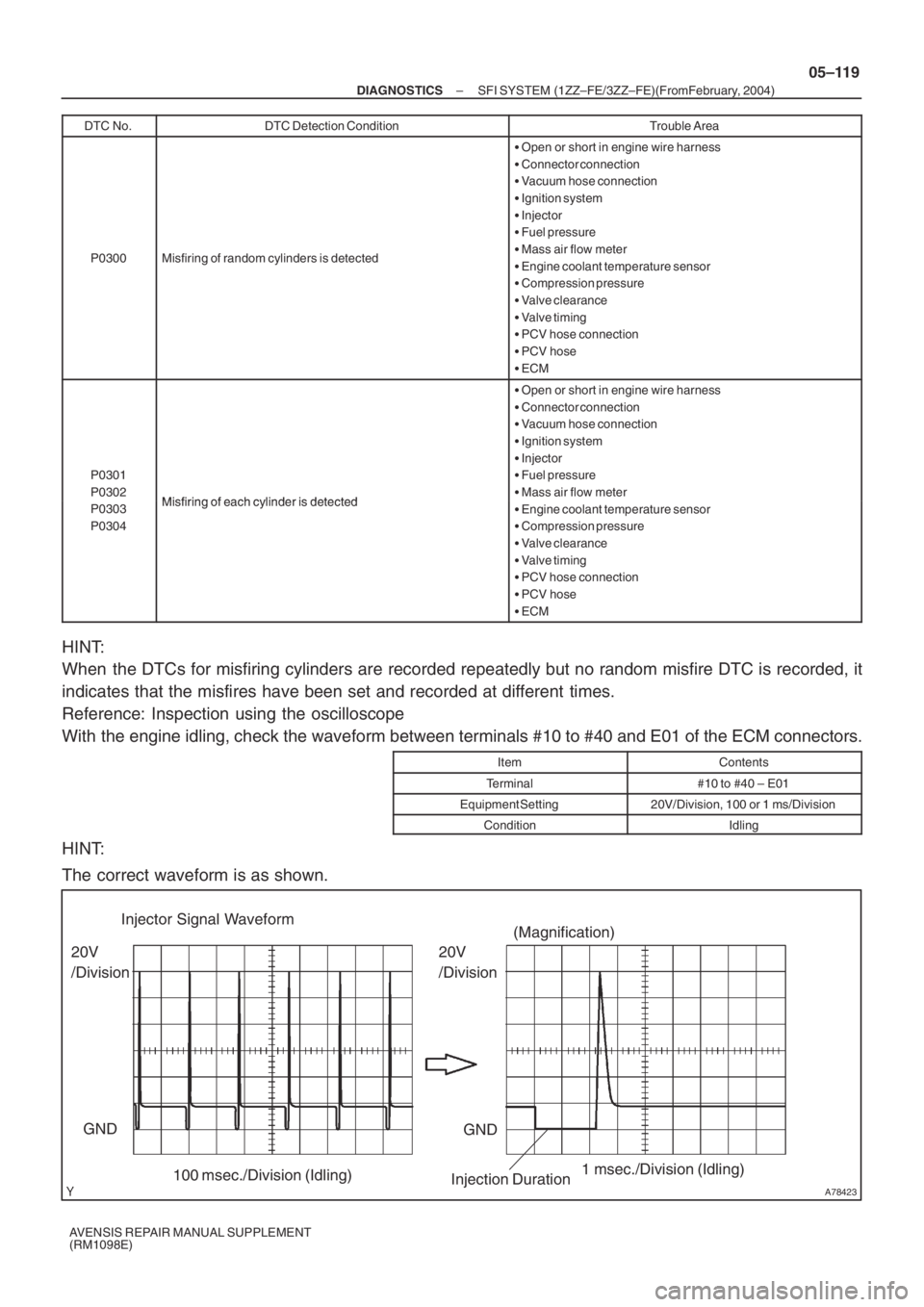
A78423
20V
/Division Injector Signal Waveform
20V
/Division
GND
100 msec./Division (Idling)(Magnification)
GND
1 msec./Division (Idling)
Injection Duration
– DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (1ZZ–FE/3ZZ–FE)(From February, 2004)
05–119
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL SUPPLEMENT
(RM1098E)DTC No.
DTC Detection ConditionTrouble Area
P0300Misfiring of random cylinders is detected
�Open or short in engine wire harness
�Connector connection
�Vacuum hose connection
�Ignition system
�Injector
�Fuel pressure
�Mass air flow meter
�Engine coolant temperature sensor
�Compression pressure
�Valve clearance
�Valve timing
�PCV hose connection
�PCV hose
�ECM
P0301
P0302
Misfiring of each cylinder is detected
�Open or short in engine wire harness
�Connector connection
�Vacuum hose connection
�Ignition system
�Injector
�Fuel pressure
�Mass air flow meter
P0303
P0304Misfiring of each cylinder is detected�Engine coolant temperature sensor
�Compression pressure
�Valve clearance
�Valve timing
�PCV hose connection
�PCV hose
�ECM
HINT:
When the DTCs for misfiring cylinders are recorded repeatedly but no random misfire DTC is recorded, it
indicates that the misfires have been set and recorded at different times.
Reference: Inspection using the oscilloscope
With the engine idling, check the waveform between terminals #10 to #40 and E01 of the ECM connectors.
ItemContents
Terminal#10 to #40 – E01
Equipment Setting20V/Division, 100 or 1 ms/Division
ConditionIdling
HINT:
The correct waveform is as shown.