2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 1788 of 4284

ENGINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLANT
DESCRIPTION...........................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................15
COOLANT CONCENTRATION TESTING......15
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................15
COOLANT SERVICE.....................15
ADDING ADDITIONAL COOLANT...........15
COOLANT LEVEL CHECK................16
REFILLING COOLING SYSTEM............16
DRAINING COOLING SYSTEM.............16
COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS CONTAINER
DESCRIPTION...........................17
OPERATION.............................17
REMOVAL..............................18
INSTALLATION...........................18
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................19
OPERATION.............................19
REMOVAL..............................19
INSTALLATION...........................19
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT
DESCRIPTION...........................19
OPERATION.............................19
REMOVAL..............................19
INSTALLATION...........................20
RADIATOR
DESCRIPTION...........................20
OPERATION.............................20
REMOVAL..............................20
INSTALLATION...........................21
RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
REMOVAL..............................22INSTALLATION...........................22
WATER PUMP
DESCRIPTION...........................22
OPERATION.............................22
REMOVAL..............................22
CLEANING..............................23
INSTALLATION...........................23
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
DESCRIPTION...........................24
OPERATION.............................24
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................25
COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP........25
PRESSURE RELIEF TEST................25
CLEANING..............................25
INSPECTION............................26
RADIATOR FAN
DESCRIPTION...........................26
OPERATION.............................26
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................26
RADIATOR FAN MOTOR.................26
REMOVAL..............................27
INSTALLATION...........................27
HOSE CLAMPS
DESCRIPTION...........................27
OPERATION.............................28
RADIATOR FAN RELAY
DESCRIPTION...........................28
OPERATION.............................28
COOLANT SYSTEM HOSES
REMOVAL..............................28
INSTALLATION...........................29
COOLANT
DESCRIPTION
Coolant flows through the engine water jackets
and cylinder heads absorbing heat produced by the
engine during operation. The coolant carries heat to
the radiator and heater core. Here it is transferred to
ambient air passing through the radiator and heater
core fins.
The required ethylene-glycol (antifreeze) and water
mixture depends upon the climate and vehicle oper-
ating conditions. The recommended mixture of 50/50
ethylene-glycol and water will provide protectionagainst freezing to -37 deg. C (-35 deg. F). The anti-
freeze concentrationmust alwaysbe a minimum of
44 percent, year-round in all climates.If percentage
is lower than 44 percent, engine parts may be
eroded by cavitation, and cooling system com-
ponents may be severely damaged by corrosion.
Maximum protection against freezing is provided
with a 68 percent antifreeze concentration, which
prevents freezing down to -67.7 deg. C (-90 deg. F). A
higher percentage will freeze at a warmer tempera-
ture. Also, a higher percentage of antifreeze can
cause the engine to overheat because the specific
heat of antifreeze is lower than that of water.
7a - 14 ENGINERG
Page 1789 of 4284

100 Percent Ethylene-GlycolÐShould Not Be Used in
Chrysler Vehicles
Use of 100 percent ethylene-glycol will cause for-
mation of additive deposits in the system, as the cor-
rosion inhibitive additives in ethylene-glycol require
the presence of water to dissolve. The deposits act as
insulation, causing temperatures to rise to as high as
149 deg. C (300 deg. F). This temperature is hot
enough to melt plastic and soften solder. The
increased temperature can result in engine detona-
tion. In addition, 100 percent ethylene-glycol freezes
at -22 deg. C (-8 deg. F ).
Propylene-glycol FormulationsÐShould Not Be Used in
Chrysler Vehicles
Propylene-glycol formulations do not meet
Chrysler coolant specifications.It's overall effec-
tive temperature range is smaller than that of ethyl-
ene-glycol. The freeze point of 50/50 propylene-glycol
and water is -32 deg. C (-26 deg. F). 5 deg. C higher
than ethylene-glycol's freeze point. The boiling point
(protection against summer boil-over) of propylene-
glycol is 125 deg. C (257 deg.F)at96.5 kPa (14 psi),
compared to 128 deg. C (263 deg. F) for ethylene-gly-
col. Use of propylene-glycol can result in boil-over or
freeze-up in Chrysler vehicles, which are designed for
ethylene-glycol. Propylene glycol also has poorer heat
transfer characteristics than ethylene glycol. This
can increase cylinder head temperatures under cer-
tain conditions.
Propylene-glycol/Ethylene-glycol MixturesÐShould Not Be
Used in Chrysler Vehicles
Propylene-glycol/ethylene-glycol Mixtures can
cause the destabilization of various corrosion inhibi-
tors, causing damage to the various cooling system
components. Also, once ethylene-glycol and propy-
lene-glycol based coolants are mixed in the vehicle,
conventional methods of determining freeze point will
not be accurate. Both the refractive index and spe-
cific gravity differ between ethylene glycol and propy-
lene glycol.
CAUTION: Richer antifreeze mixtures cannot be
measured with normal field equipment and can
cause problems associated with 100 percent ethyl-
ene-glycol.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLANT
CONCENTRATION TESTING
Coolant concentration should be checked when any
additional coolant was added to system or after a
coolant drain, flush and refill. The coolant mixture
offers optimum engine cooling and protection against
corrosion when mixed to a freeze point of -37ÉC
(-34ÉF) to -59ÉC (-50ÉF). The use of a hydrometer or a
refractometer can be used to test coolant concentra-
tion.
A hydrometer will test the amount of glycol in a
mixture by measuring the specific gravity of the mix-
ture. The higher the concentration of ethylene glycol,
the larger the number of balls that will float, and
higher the freeze protection (up to a maximum of
60% by volume glycol).
A refractometer will test the amount of glycol in a
coolant mixture by measuring the amount a beam of
light bends as it passes through the fluid.
Some coolant manufactures use other types of gly-
cols into their coolant formulations. Propylene glycol
is the most common new coolant. However, propylene
glycol based coolants do not provide the same freez-
ing protection and corrosion protection and is not rec-
ommended.
CAUTION: Do not mix types of coolantÐcorrosion
protection will be severely reduced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT SERVICE
For engine coolant recommended service schedule,
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAIN-
TENANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ADDING
ADDITIONAL COOLANT
The pressure/vent cap should not be removed
from the coolant recovery pressure container.
When additional coolant is needed to maintain this
level, it should be added to the coolant recovery pres-
sure container (Fig. 1). Use only 50/50 mix of ethyl-
ene glycol type antifreeze and distilled water. For the
recommeded antifreeze/coolant type (Refer to LUBRI-
CATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
CAUTION: Do not use well water, or suspect water
supply in cooling system. A 50/50 ethylene glycol
and distilled water mix is recommended. For the
recommeded antifreeze/coolant type (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
RGENGINE7a-15
COOLANT (Continued)
Page 1790 of 4284

STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT LEVEL
CHECK
NOTE: Do not remove pressure/vent cap for routine
coolant level inspections.
The coolant reserve system provides a quick visual
method for determining the coolant level without
removing the pressure/vent cap.With the engine
cold and not running,simply observe the level of
the coolant in the coolant recovery pressure container
(Fig. 2). The coolant level should be between the MIN
and MAX marks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFILLING
COOLING SYSTEM
Remove pressure/vent cap (Fig. 1) and fill system,
using a 50/50 mix of MopartAntifreeze/Coolant, 5
Year/100,000 Mile Formula and distilled water.
Continue filling system until full.Be careful not
to spill coolant on drive belts or the generator.
Fill coolant recovery pressure container (Fig. 1) to
at least the MAX mark with 50/50 solution. It may
be necessary to add coolant to the coolant recovery
pressure container after three or four warm up/cool
down cycles to maintain coolant level between the
MAX and MIN mark. This will allow trapped air to
be removed from the system.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING COOLING
SYSTEM
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE OR LOOSEN THE
COOLANT PRESSURE/VENT CAP, CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS, OR THE DRAINCOCK WHEN
THE SYSTEM IS HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
(1)Without removing pressure/vent cap and
with system not under pressure, open the drain-
cock. The draincock is located on the lower right side
of radiator (Fig. 3).
(2) After the coolant recovery pressure container is
empty, then remove coolant pressure/vent cap.
Fig. 1 UNDERHOOD FLUID FILL LOCATIONS
1 - COOLANT PRESSURE/VENT CAP
2 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
3 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE
4 - BATTERY
5 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER6 - OIL DIPSTICK
7 - WINDSHIELD SOLVENT RESEVOIR
8 - AIR FILTER HOUSING
9 - ENGINE OIL FILL CAP
7a - 16 ENGINERG
COOLANT (Continued)
Page 1791 of 4284
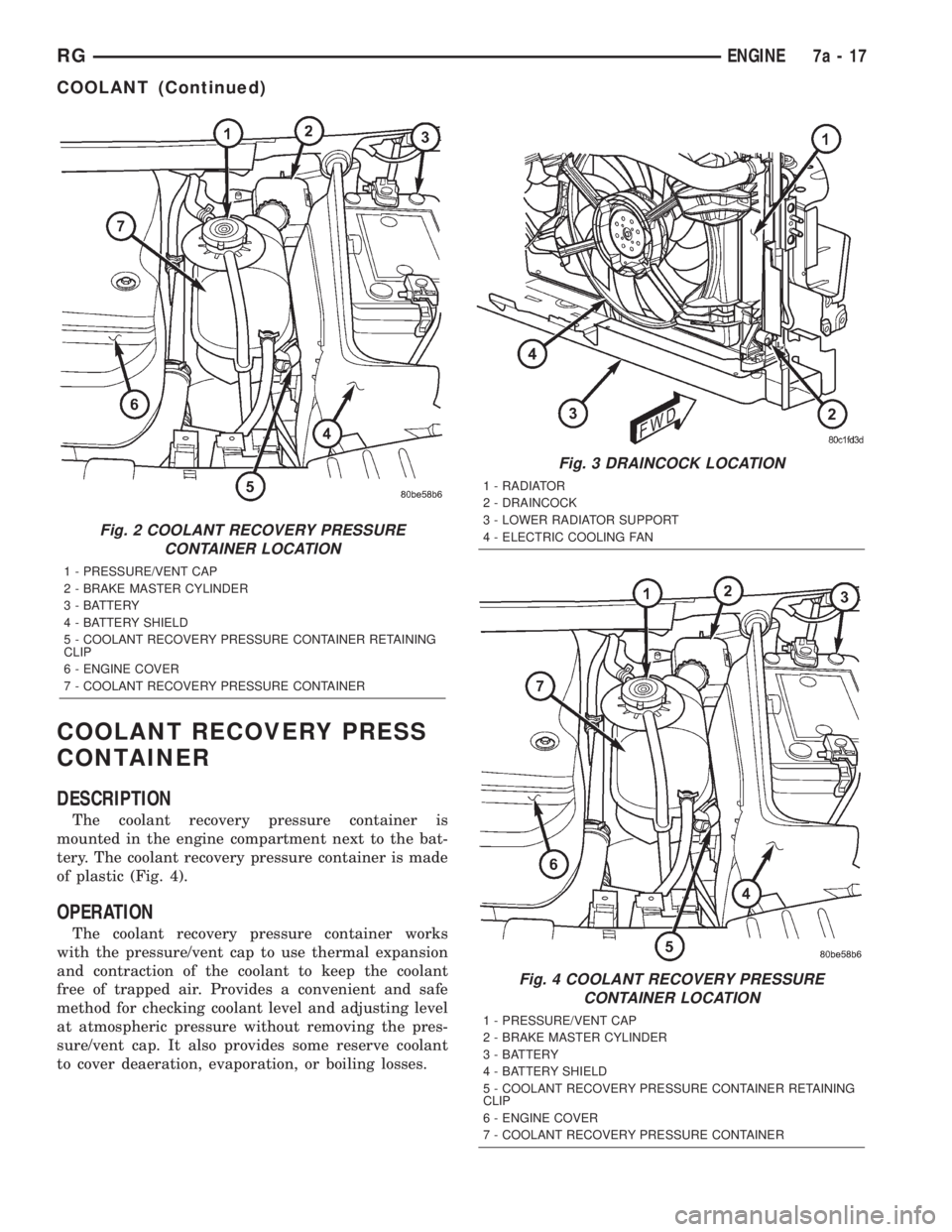
COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS
CONTAINER
DESCRIPTION
The coolant recovery pressure container is
mounted in the engine compartment next to the bat-
tery. The coolant recovery pressure container is made
of plastic (Fig. 4).
OPERATION
The coolant recovery pressure container works
with the pressure/vent cap to use thermal expansion
and contraction of the coolant to keep the coolant
free of trapped air. Provides a convenient and safe
method for checking coolant level and adjusting level
at atmospheric pressure without removing the pres-
sure/vent cap. It also provides some reserve coolant
to cover deaeration, evaporation, or boiling losses.
Fig. 2 COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE
CONTAINER LOCATION
1 - PRESSURE/VENT CAP
2 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
3 - BATTERY
4 - BATTERY SHIELD
5 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER RETAINING
CLIP
6 - ENGINE COVER
7 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER
Fig. 3 DRAINCOCK LOCATION
1 - RADIATOR
2 - DRAINCOCK
3 - LOWER RADIATOR SUPPORT
4 - ELECTRIC COOLING FAN
Fig. 4 COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE
CONTAINER LOCATION
1 - PRESSURE/VENT CAP
2 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
3 - BATTERY
4 - BATTERY SHIELD
5 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER RETAINING
CLIP
6 - ENGINE COVER
7 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER
RGENGINE7a-17
COOLANT (Continued)
Page 1799 of 4284

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
PRESSURE CAP
Dip the pressure cap in water. Clean any deposits
off the vent valve or its seat and apply cap to end of
the Pressure Cap Test Adaptor that is included with
the Cooling System Tester 7700. Working the
plunger, bring the pressure to 104 kPa (15 psi) on the
gauge. If the pressure cap fails to hold pressure of at
least 97 kPa (14 psi), replace the pressure cap.
CAUTION: The Cooling System Tester Tool is very
sensitive to small air leaks that will not cause cool-
ing system problems. A pressure cap that does not
have a history of coolant loss should not be
replaced just because it leaks slowly when tested
with this tool. Add water to the tool. Turn tool
upside down and recheck pressure cap to confirm
that cap is bad.
If the pressure cap tests properly while positioned
on Cooling System Tester (Fig. 20), but will not hold
pressure or vacuum when positioned on the filler
neck. Inspect the filler neck and cap top gasket for
irregularities that may prevent the cap from sealing
properly.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRESSURE
RELIEF TEST
The pressure cap upper gasket (seal) pressure
relief can be checked by removing the overflow hose
at the radiator filler neck nipple (Fig. 21). Attach the
Radiator Pressure Tool to the filler neck nipple and
pump air into the radiator. Pressure cap upper gas-
ket should relieve at 69-124 kPa (10-18 psi) and hold
pressure at 55 kPa (8 psi) minimum.WARNING: THE WARNING WORDS ªDO NOT OPEN
HOTº ON THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP IS A
SAFETY PRECAUTION. WHEN HOT, PRESSURE
BUILDS UP IN COOLING SYSTEM. TO PREVENT
SCALDING OR INJURY, THE RADIATOR CAP
SHOULD NOT BE REMOVED WHILE THE SYSTEM
IS HOT OR UNDER PRESSURE.
There is no need to remove the radiator cap at any
timeexceptfor the following purposes:
(1) Check and adjust coolant freeze point.
(2) Refill system with new coolant.
(3) Conducting service procedures.
(4) Checking for vacuum leaks.
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN RECENTLY,
WAIT 15 MINUTES BEFORE REMOVING CAP. THEN
PLACE A SHOP TOWEL OVER THE CAP AND WITH-
OUT PUSHING DOWN ROTATE COUNTERCLOCK-
WISE TO THE FIRST STOP. ALLOW FLUIDS TO
ESCAPE THROUGH THE OVERFLOW TUBE AND
WHEN THE SYSTEM STOPS PUSHING COOLANT
AND STEAM INTO THE CRS TANK AND PRESSURE
DROPS PUSH DOWN AND REMOVE THE CAP COM-
PLETELY. SQUEEZING THE RADIATOR INLET HOSE
WITH A SHOP TOWEL (TO CHECK PRESSURE)
BEFORE AND AFTER TURNING TO THE FIRST
STOP IS RECOMMENDED.
CLEANING
Use only a mild soap to clean the pressure cap.
Fig. 20 Testing Cooling System Pressure Cap
1 - PRESSURE CAP
2 - PRESSURE TESTER
Fig. 21 Radiator Pressure Cap Filler Neck
1 - OVERFLOW NIPPLE
2 - MAIN SPRING
3 - GASKET RETAINER
4 - STAINLESS-STEEL SWIVEL TOP
5 - RUBBER SEALS
6 - VENT VALVE
7 - PRESSURE BOTTLE
8 - FILLER NECK
RGENGINE7a-25
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP (Continued)
Page 1801 of 4284
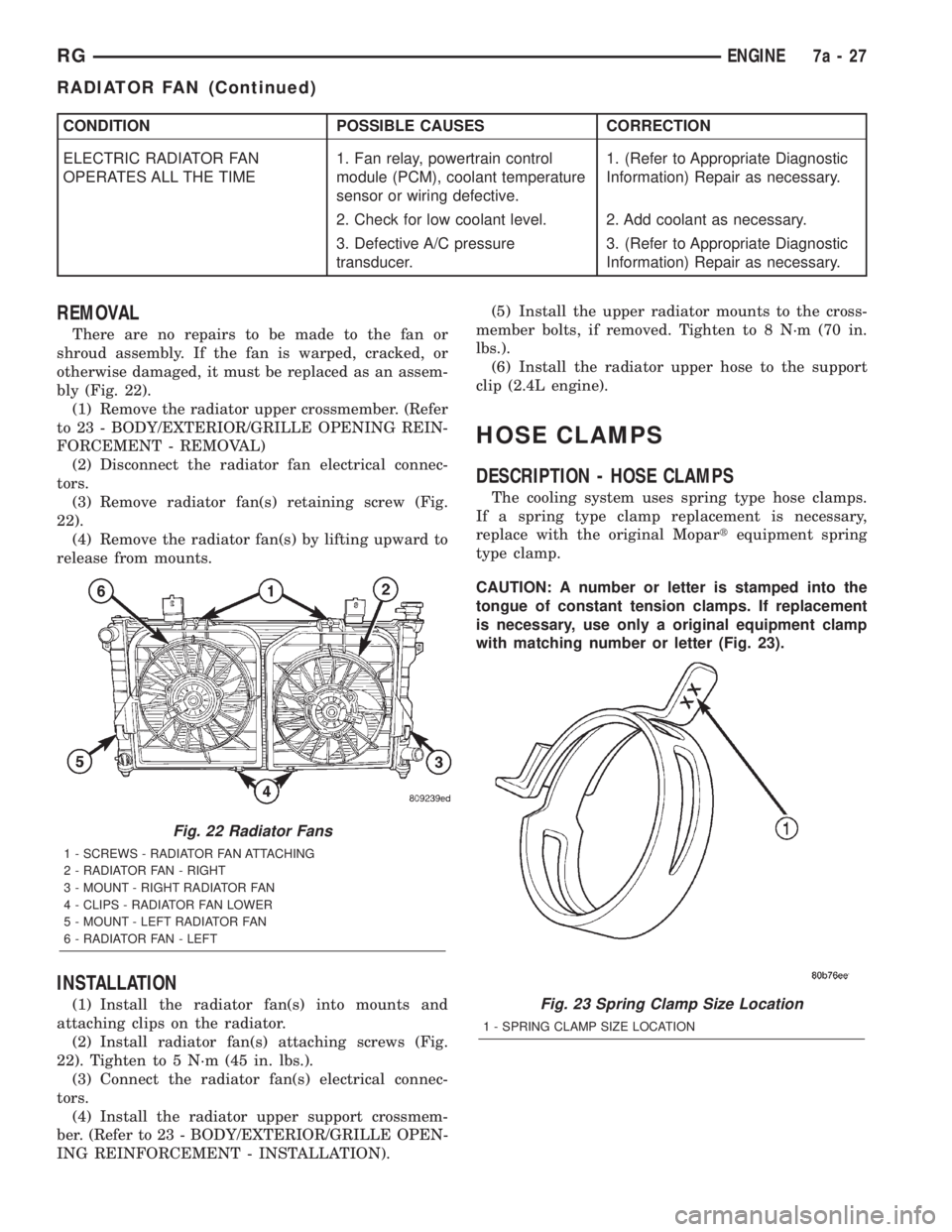
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
ELECTRIC RADIATOR FAN
OPERATES ALL THE TIME1. Fan relay, powertrain control
module (PCM), coolant temperature
sensor or wiring defective.1. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
2. Check for low coolant level. 2. Add coolant as necessary.
3. Defective A/C pressure
transducer.3. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
REMOVAL
There are no repairs to be made to the fan or
shroud assembly. If the fan is warped, cracked, or
otherwise damaged, it must be replaced as an assem-
bly (Fig. 22).
(1) Remove the radiator upper crossmember. (Refer
to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE OPENING REIN-
FORCEMENT - REMOVAL)
(2) Disconnect the radiator fan electrical connec-
tors.
(3) Remove radiator fan(s) retaining screw (Fig.
22).
(4) Remove the radiator fan(s) by lifting upward to
release from mounts.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the radiator fan(s) into mounts and
attaching clips on the radiator.
(2) Install radiator fan(s) attaching screws (Fig.
22). Tighten to 5 N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the radiator fan(s) electrical connec-
tors.
(4) Install the radiator upper support crossmem-
ber. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE OPEN-
ING REINFORCEMENT - INSTALLATION).(5) Install the upper radiator mounts to the cross-
member bolts, if removed. Tighten to 8 N´m (70 in.
lbs.).
(6) Install the radiator upper hose to the support
clip (2.4L engine).
HOSE CLAMPS
DESCRIPTION - HOSE CLAMPS
The cooling system uses spring type hose clamps.
If a spring type clamp replacement is necessary,
replace with the original Mopartequipment spring
type clamp.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only a original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter (Fig. 23).
Fig. 22 Radiator Fans
1 - SCREWS - RADIATOR FAN ATTACHING
2 - RADIATOR FAN - RIGHT
3 - MOUNT - RIGHT RADIATOR FAN
4 - CLIPS - RADIATOR FAN LOWER
5 - MOUNT - LEFT RADIATOR FAN
6 - RADIATOR FAN - LEFT
Fig. 23 Spring Clamp Size Location
1 - SPRING CLAMP SIZE LOCATION
RGENGINE7a-27
RADIATOR FAN (Continued)
Page 1813 of 4284

OK, repair the open circuit to the battery as
required.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
Check for battery voltage at the fuse in the junction
block. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the ignition switch as required.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the OFF position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Remove the radio, but do not unplug the wire har-
ness connectors. Check for continuity between the
radio chassis and a good ground. There should be
continuity. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the
open radio chassis ground circuit as required.
(5) Connect the battery negative cable. Turn the
ignition switch to the ON position. Check for battery
voltage at the fused ignition switch output circuit
cavity of the left (gray) radio wire harness connector.
If OK, go to Step 6. If not OK, repair the open circuit
as required.
(6) Turn the ignition switch to the OFF position.
Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) circuit
cavity of the left (gray) radio wire harness connector.
If OK, replace the faulty radio. If not OK, repair the
open circuit to the Ignition-Off Draw (IOD) fuse as
required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove cup holder.
(3) Remove trim panel above cupholder by pulling
straight out.
(4) Remove center instrument panel trim panel.
(5) Remove screws holding radio to instrument
panel.
(6) Pull radio rearward to gain access to the back
of radio (Fig. 10).
(7) Disconnect antenna cable from back of radio.
(8) Remove bolt holding ground strap to the radio.
(9) Disconnect the wire connectors from the back
of the radio.
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect wire harness to back of radio.
(2) Install bolt holding ground strap to the radio.
(3) Connect antenna cable to back of radio.
(4) Position radio into instrument panel.
(5) Install screws holding radio to instrument
panel.
(6) Install center instrument panel trim.
(7) Install trim panel above cupholder.
(8) Install cupholder.
(9) Connect battery negative cable.
RADIO NOISE SUPPRESSION
COMPONENTS
DESCRIPTION
Numerous ground straps are placed throughout the
vehicle for interference elimination (Fig. 11), (Fig.
12), (Fig. 13), (Fig. 14).
OPERATION
If receiving ignition/engine interference noise on
the radio stations, check and clean all engine and
body ground connections. Ensure all ground connec-
tions are without corrosion. Tighten properly after
cleaning.
Fig. 10 RADIO
1 - RADIO
2 - CD-PLAYER
Fig. 11 Motor Mount to Frame Rail Ground
1 - GROUND STRAP
RSAUDIO8A-9
RADIO (Continued)
Page 1819 of 4284

CHIME/BUZZER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHIME/BUZZER
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................1
CHIME SYSTEM.........................1
DOME LAMP ON CHIME..................2
ENGINE TEMPERATURE CRITICAL CHIME....2EXTERIOR LAMPS ON CHIME..............2
KEY-IN IGNITION CHIME..................2
LOW OIL PRESSURE CHIME...............2
SEAT BELT CHIME.......................3
SEAT BELT LAMP.......................3
TURN SIGNAL ON CHIME.................3
WARNING LAMP ANNOUNCEMENT CHIME....3
CHIME/BUZZER
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
The chime/buzzer system provides the driver with
warning chimes for:
²Seat Belt
²Exterior Lamps ON
²Key-In Ignition
²Engine Temperature Critical
²Turn Signals ON
²Dome Lamp ON
²Low Oil Pressure
²High Speed Warning
²Warning Lamp Announcement
²Key-In Accessory
OPERATION
The Chime/Buzzer Warning System is diagnosed
using a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the proper Body
Diagnostic Procedures Manual.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHIME SYSTEM
NO TONE WHEN IGNITION SWITCH IS TURNED ON
AND DRIVER'S SEAT BELT IS NOT BUCKLED.
(1) Using a DRBIIItscan tool, actuate chime
(BCM actuates).
(2) Using a voltmeter, check for voltage:
(a) BCM has two battery feeds at pin 1 and pin
5 of the 6±way connector.
(b) Pin 5 of the (BX2) 32 way connector of the
BCM for ignition feed.
(c) Check voltage (PX2) connector, pin 34 for 12v.
(d) If voltage OK, go to step Step 3
(e) If NO voltage repair as necessary. Refer to
the appropriate wiring information. The wiring
information includes wiring diagrams, proper wire
and connector repair procedures, further details on
wire harness routing and retention, as well as pin-
out and location views for the various wire harness
connectors, splices and grounds.
(3) Check driver's seat belt buckle switch input
(form ORC) for a closed circuit when not buckled. If
input not seen, look for open in wiring or switch. The
switch is grounded when belt is not buckled.
(4) Verify PCI data bus communication between
ORC and BCM.
NO FASTEN SEAT BELT LAMP WHEN IGNITION
SWITCH IS TURNED ON.
(1) Check for burned out lamp.
(2) Using a voltmeter check for voltage at the clus-
ter conncctor:
(a) Pin 2 of the mechanical instrument cluster
for battery feed.
(b) Pin 11 of the mechanical instrument cluster
for ignition voltage.
(3) Repair as necessary.
RSCHIME/BUZZER8B-1