Page 408 of 4770
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT: If diagnostic trouble codes ª22º (engine coolant temperature sensor circuit), ª24º (intake air
temperature sensor circuit), ª31º (manifold absolute pressure sensor circuit) and ª41 ª (throttle
position sensor circuit) are output simultaneously, E2 (sensor ground) may be open,
(1) Remove glove compartment
(See page EG1±234)
(2) Turn ignition switch on.
Measure voltage between terminals THW and E2 of engine
control module connector.
Check voltage between terminals THW and E2 of engine control
module connector.
Check for momentary interruption
(See page EG1±309)
Engine Coolant Temp. �C (�F)
20 (68)
( Engine is cool )
80 (176)
(Engine is hot)0.2 ~1.0 v 0.5 ~ 3.4 V Voltage
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±358
Page 425 of 4770
Check for open and short in harness and connector between engine
control module and manifold absolute pressure sensor
(See page IN±31).
Turn ignition switch on
Check voltage between terminals PIM and E2 of engine control
module connector.
Check and replace manifold absolute pressure
sensor.When diagnostic trouble code 31 is dis-
played, check and replace engine control
module.
Repair or replace harness or connector. Voltage: 13 ± 3.9 V Measure voltage between terminals PI M
and E2 of engine control module connector.
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±375
Page 428 of 4770

INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT: If diagnostic trouble code ª22º (engine coolant temperature sensor circuit), ª24º (intake air
temperature sensor circuit), ª31º (manifold absolute pressure sensor circuit) and ª41 ª (throttle
position sensor circuit) are output simultaneously, E2 (sensor ground) may be open.
(1) Remove glove compartment.
(See page EG1±234).
(2) Disconnect the vacuum hose from the throt±
tle body, then apply vacuum to the throttle
opener (See page EG1±204).
(3) Turn ignition switch ON.
Measure voltage between terminals VTA, IDL and
E2 of engine control module connector when the
throttle valve is opened gradually from the closed
condition.
Check voltage between terminals VTA, IDL and E2 of engine
control module connector.
The voltage should increase steadily in propor±
tion to the throttle valve opening angle.
Check for momentary interruption
(See page EG1±309).
Throttle Valve
Fully Closed
Fully OpenVTA ± E2 Terminal
IDL ± E2
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±378
Page 474 of 4770
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
VSV Circuit for Fuel Pressure Control (Only for California
spec.)
Check for open and short in harness and
connector between EFI main relay and ECM.Proceed to next circuit inspection
shown on matrix chart
(See page EG1±327).
Repair or replace harness or connector. Check voltage of VSV power source. Check VSV for fuel pressure control.
Check and replace ECM.Replace VSV.
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
The ECM turns on a VSV (Vacuum Switching
Valve) to draw the air into the diaphragm chamber
of the pressure regulator if it detects that the tem-
perature of the engine coolant is too high during
engine starting. The air drawn into the chamber
increases the fuel pressure to prevent fuel vapor
lock at high engine temperature in order to help the
engine start when it is warm.
Fuel pressure control ends approx. 90 secs. after
the engine is started.
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±424
Page 511 of 4770
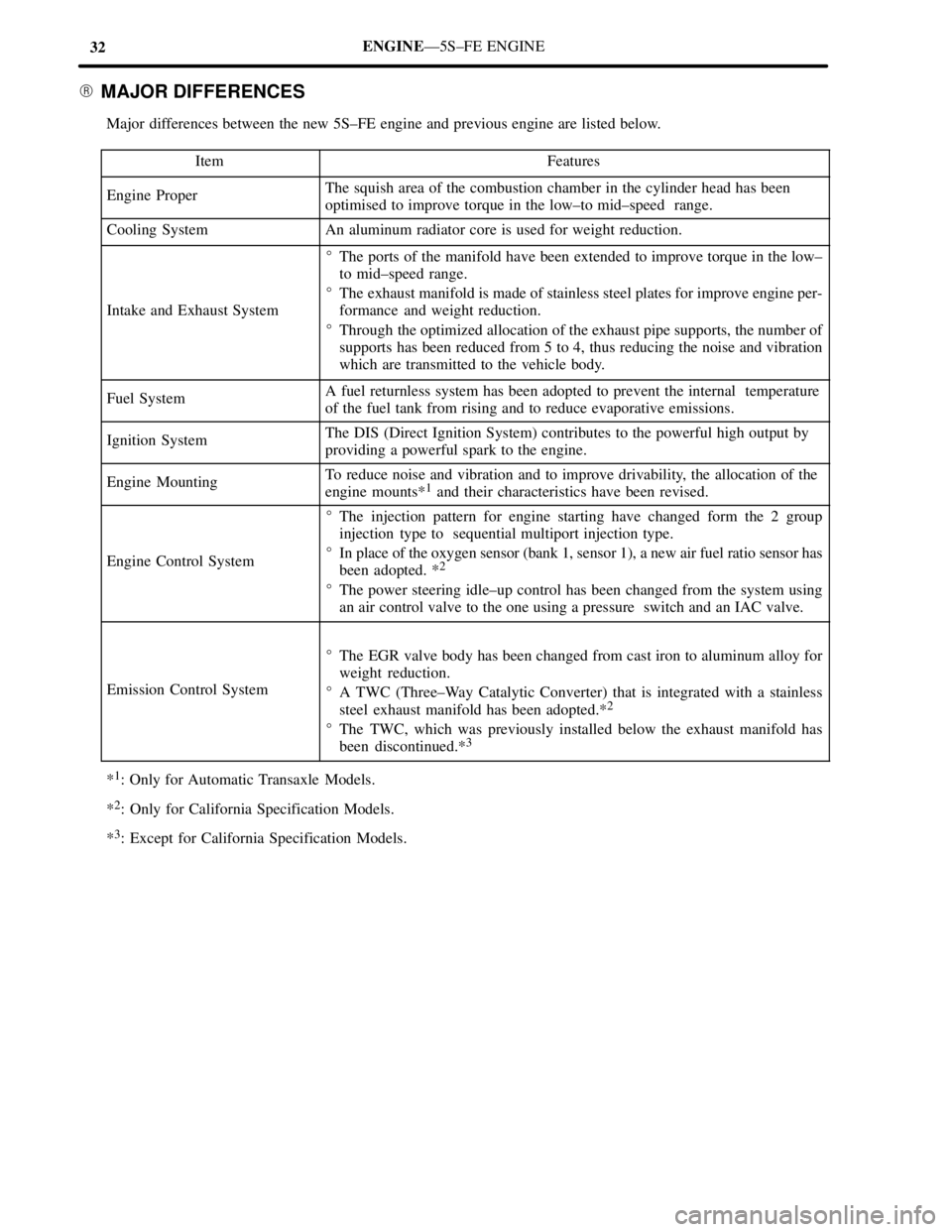
32ENGINEÐ5S±FE ENGINE
� MAJOR DIFFERENCES
Major differences between the new 5S±FE engine and previous engine are listed below.
Item
Features
Engine ProperThe squish area of the combustion chamber in the cylinder head has been
optimised to improve torque in the low±to mid±speed range.
Cooling SystemAn aluminum radiator core is used for weight reduction.
Intake and Exhaust System
�The ports of the manifold have been extended to improve torque in the low±
to mid±speed range.
�The exhaust manifold is made of stainless steel plates for improve engine per-
formance and weight reduction.
�Through the optimized allocation of the exhaust pipe supports, the number of
supports has been reduced from 5 to 4, thus reducing the noise and vibration
which are transmitted to the vehicle body.
Fuel SystemA fuel returnless system has been adopted to prevent the internal temperature
of the fuel tank from rising and to reduce evaporative emissions.
Ignition SystemThe DIS (Direct Ignition System) contributes to the powerful high output by
providing a powerful spark to the engine.
Engine MountingTo reduce noise and vibration and to improve drivability, the allocation of the
engine mounts*1 and their characteristics have been revised.
Engine Control System
�The injection pattern for engine starting have changed form the 2 group
injection type to sequential multiport injection type.
�In place of the oxygen sensor (bank 1, sensor 1), a new air fuel ratio sensor has
been adopted. *
2
�The power steering idle±up control has been changed from the system using
an air control valve to the one using a pressure switch and an IAC valve.
Emission Control System
�The EGR valve body has been changed from cast iron to aluminum alloy for
weight reduction.
�A TWC (Three±Way Catalytic Converter) that is integrated with a stainless
steel exhaust manifold has been adopted.*
2
�The TWC, which was previously installed below the exhaust manifold has
been discontinued.*3
*1: Only for Automatic Transaxle Models.
*
2: Only for California Specification Models.
*
3: Except for California Specification Models.
Page 527 of 4770

48ENGINEÐ1MZ±FE ENGINE
� ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
1. General
The engine control system of the new 1MZ±FE engine is basically the same in construction and operation as that of
the previous 1MZ±FE engine. However, the fuel pressure control has been discontinued and the EGR control system
has been changed.
The engine control system of the new 1MZ±FE engine and previous 1MZ±FE engine are compared below.
System
OutlineNewPrevious
SFI
(SequentialA L±type SFI system directly detects intake air mass with
a hot wire type mass air flow meter.��(q
Multiport Fuel
Injection)The fuel injection system is a sequential multiport fuel
injection system.��
ESA
Ignition Timing is determined by the ECM based on
signals from various sensors. The ECM corrects ignition
timing in response to engine knocking.
��
(Electronic Spark2 knock sensors are used to improve knock detection.��(p
Advance)In vehicles equipped with automatic transaxle, torque
control correction during gear shifting has been used to
minimize the shift shock.
��
IACA rotary solenoid type IAC valve controls the fast idle��(Idle Air Control)
A rotary solenoid type IAC valve controls the fast idle
and idle speeds.��
ACIS
(Acoustic Control
The intake air passages are switched according to the en-
gine speed and throttle valve angle to increase perfor��(Acoustic Control
Induction System)
gine speed and throttle valve angle to increase perfor-
mance in all speed ranges.��
Fuel Pressure
ControlIn hot engine conditions, the fuel pressure is increased to
improve restartability.��
Oxygen Sensor
Heater ControlMaintains the temperature of the oxygen sensor at an
approppiate level to increase accuracy of detection of
the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas.
��
EGR Cut±Off
ControlCuts off EGR according to the engine condition to
maintain drivability of the vehicle and durability of
EGR components.
�
EGR Control
Uses the duty control type VSV and EGR valve position
sensor, controlling the EGR volumne in accordance with
engine conditions.
�Ð
Evaporative
Emission ControlThe ECM controls the purge flow of evaporative emis-
sions (HC) in the charcoal canister in accordance with
engine conditions.
��
Diagnosis
When the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM diagnoses
and memorizes the failed section.��
DiagnosisThe diagnosis system includes a function that detects a
malfunction in the evaporative control system.�Ð
Fail SafeWhen the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM stops
or controls the engine according to the data already stored
in memory
��
Page 551 of 4770

72CHASSISÐBRAKES
5. Function of Components
No.ComponentFunction
1Slip Indicator LightBlinks to inform the driver when the TRAC system is operated.
2TRAC OFF Indicator Light
Lights to inform the driver when the TRAC system is turned OFF by
the by the TRAC OFF switch. And, blinks to alert the driver when
the ECU detects the malfunction in the TRAC system.
3ECM
�Sends signals to the ABS & TRAC ECU, such as the throttle
valve opening angle, specific volume of intake air signal, etc.
�Controls the engine output and shift timing in accordance with
the fuel cutoff request and shift timing request that are output by
the ABS & TRAC ECU.
4ABS & TRAC ECU
Judges the vehicle driving condition based on signals from 4 speed
sensors and signals from ECM, and sends fuel cut and shift timing
demand signals to the ECM and brake control signal to the ABS &
TRAC actuator.
5ABS & TRAC Actuator
Controls the brake fluid pressure to each brake wheel cylinder
of the driving wheel (front wheel) by signals from the ABS &
TRAC ECU.
ABS & TRAC
Solenoid RelayDirects electricity to the solenoid valves in the actuator.
6ABS & TRAC
RelayPump Motor
RelayControls the pump motor operation in the actuator.
7Speed Sensors (Front and Rear)Detect the wheel speed of each of four wheels.
8Throttle Position SensorDetects the throttle valve opening angle.
9TRAC OFF SwitchTurns the TRAC system inoperative.
Page 552 of 4770

73 CHASSISÐBRAKES
6. Construction and Operation of Components
TRAC OFF Switch and Indicator Light
1) TRAC OFF Switch
When pressing, this switch turns the TRAC system to be inoperative. Pressing it again changes it to be operative.
When turning the ignition switch from ªOFFº to ªONº, TRAC system always becomes operative.
2) TRAC OFF Indicator Light
This light comes on when the TRAC system is set inoperative by the TRAC OFF switch, and informs the driver
accordingly. And blinks to alert the driver when a malfunction has occurred in the engine and TRAC system.
3) Slip Indicator Light
When the TRAC system is operative, the light blinks and informs the driver accordingly.
ABS & TRAC Actuator
1) Construction
The ABS & TRAC actuator consists of 12 two±position solenoid valves, 1 motor, 2 pumps 2 reservoirs and 2 pressure
regulator valves.
The 12 two±position solenoid valves consists of 2 master cut solenoid valves, 2 reservoirs cut solenoid valves, 4
pressure holding valves, and 4pressure reduction valves.
Pressure regulator valve is assembled into the master cut solenoid valve.
The basic construction and operation of the pump, reservoir, pressure holding valve, and pressure reduction valve
are shared with ABS.
a. Master Cut Solenoid Valve
When the TRAC system is active, a signal from the ABS & TRAC ECU causes the master cut solenoid valve to turn
ON in order to shut off the circuit between the master cylinder and the front brake wheel cylinder.