2000 DODGE NEON sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 239 of 1285

The PCM sends approximately 8 volts to the Hall-
effect sensor. This voltage is required to operate the
Hall-effect chip and the electronics inside the sensor.
A ground for the sensor is provided through the sen-
sor return circuit. The input to the PCM occurs on a
5 volt output reference circuit.
The notches generate pulses from high to low in
the crankshaft position sensor output voltage. When
a metal portion of the counterweight aligns with the
crankshaft position sensor, the sensor output voltage
goes low (less than 0.5 volts). When a notch aligns
with the sensor, voltage goes high (5.0 volts). As a
group of notches pass under the sensor, the output
voltage switches from low (metal) to high (notch)
then back to low.
If available, an oscilloscope can display the square
wave patterns of each voltage pulses. From the width
of the output voltage pulses, the PCM calculates
engine speed. The width of the pulses represent the
amount of time the output voltage stays high before
switching back to low. The period of time the sensor
output voltage stays high before switching back to
low is referred to as pulse width. The faster the
engine is operating, the smaller the pulse width on
the oscilloscope.
By counting the pulses and referencing the pulse
from the 60 degree signature notch, the PCM calcu-
lates crankshaft angle (position). In each group of
timing reference notches, the first notch represents
69 degrees before top dead center (BTDC). The sec-
ond notch represents 49 degrees BTDC. The third
notch represents 29 degrees. The last notch in each
set represents 9 degrees before top dead center
(TDC).
The timing reference notches are machined at 20É
increments. From the voltage pulse width the PCM
tells the difference between the timing reference
notches and the 60 degree signature notch. The 60
degree signature notch produces a longer pulse width
than the smaller timing reference notches. If the
camshaft position sensor input switches from high to
low when the 60 degree signature notch passes under
the crankshaft position sensor, the PCM knows cylin-
der number one is the next cylinder at TDC.CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The camshaft position sensor attaches to the rear
of the cylinder head. The PCM determines fuel injec-
tion synchronization and cylinder identification from
inputs provided by the camshaft position sensor (Fig.
6) and crankshaft position sensor. From the two
inputs, the PCM determines crankshaft position.
OPERATION
The PCM sends approximately 8 volts to the hall
affect sensor. This voltage is required to operate the
hall effect chip and the electronics inside the sensor.
A ground for the sensor is provided through the sen-
sor return circuit. The input to the PCM occurs on a
5 volt output reference circuit.
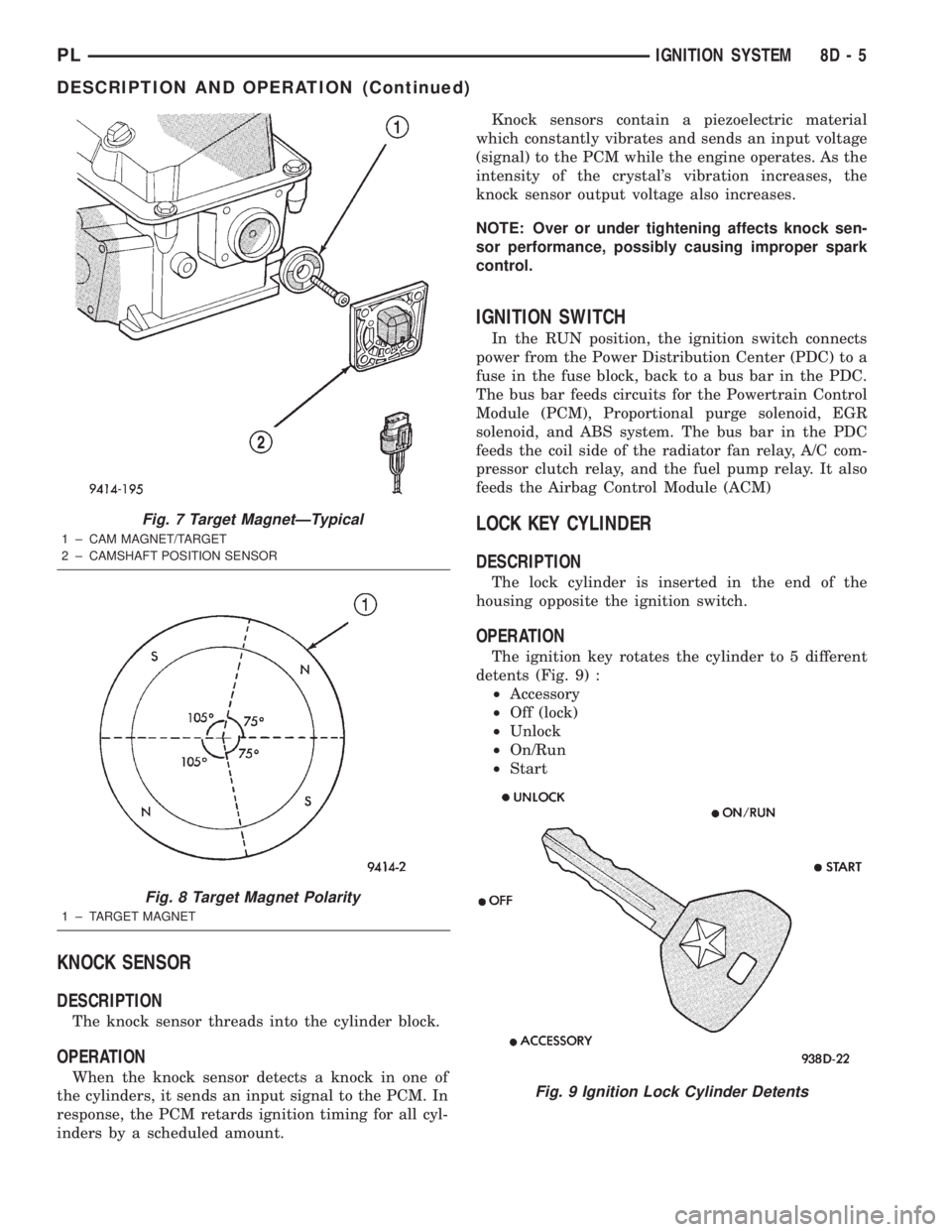
A target magnet attaches to the rear of the cam-
shaft and indexes to the correct position. The target
magnet has four different poles arranged in an asym-
metrical pattern (Fig. 7). As the target magnet
rotates, the camshaft position sensor senses the
change in polarity (Fig. 8). The sensor output switch
switches from high (5.0 volts) to low (0.5 volts) as the
target magnet rotates. When the north pole of the
target magnet passes under the sensor, the output
switches high. The sensor output switches low when
the south pole of the target magnet passes under-
neath.
The sensor also acts as a thrust plate to control
camshaft endplay.
Fig. 6 Camshaft Position SensorÐSOHC
8D - 4 IGNITION SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 240 of 1285
KNOCK SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The knock sensor threads into the cylinder block.
OPERATION
When the knock sensor detects a knock in one of
the cylinders, it sends an input signal to the PCM. In
response, the PCM retards ignition timing for all cyl-
inders by a scheduled amount.Knock sensors contain a piezoelectric material
which constantly vibrates and sends an input voltage
(signal) to the PCM while the engine operates. As the
intensity of the crystal's vibration increases, the
knock sensor output voltage also increases.
NOTE: Over or under tightening affects knock sen-
sor performance, possibly causing improper spark
control.
IGNITION SWITCH
In the RUN position, the ignition switch connects
power from the Power Distribution Center (PDC) to a
fuse in the fuse block, back to a bus bar in the PDC.
The bus bar feeds circuits for the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM), Proportional purge solenoid, EGR
solenoid, and ABS system. The bus bar in the PDC
feeds the coil side of the radiator fan relay, A/C com-
pressor clutch relay, and the fuel pump relay. It also
feeds the Airbag Control Module (ACM)
LOCK KEY CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION
The lock cylinder is inserted in the end of the
housing opposite the ignition switch.
OPERATION
The ignition key rotates the cylinder to 5 different
detents (Fig. 9) :
²Accessory
²Off (lock)
²Unlock
²On/Run
²Start
Fig. 7 Target MagnetÐTypical
1 ± CAM MAGNET/TARGET
2 ± CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Fig. 8 Target Magnet Polarity
1 ± TARGET MAGNET
Fig. 9 Ignition Lock Cylinder Detents
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 241 of 1285

IGNITION INTERLOCK
OPERATION
All vehicles equipped with automatic transaxles
have an interlock system. The system prevents shift-
ing the vehicle out of Park unless the ignition lock
cylinder is in the Off, Run or Start position. In addi-
tion, the operator cannot rotate the key to the lock
position unless the shifter is in the park position. On
vehicles equipped with floor shift refer to the - Tran-
saxle for Automatic Transmission Shifter/Ignition
Interlock.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SPARK PLUG SERVICE
Failure to route the cables properly could cause the
radio to reproduce ignition noise, cross ignition of the
spark plugs or short circuit the cables to ground.
REMOVAL
REMOVE CABLES FROM COIL FIRST.
Always remove the spark plug cable by grasping
the top of the spark plug insulator, turning the boot
1/2 turn and pulling straight up in a steady motion.
(1) Remove the spark plug using a quality socket
with a rubber or foam insert.
(2) Inspect the spark plug condition.
INSTALLATION
(1) To avoid cross threading, start the spark plug
into the cylinder head by hand.
(2) Tighten spark plugs to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Install spark plug insulators over spark plugs.
Ensure the top of the spark plug insulator covers the
upper end of the spark plug tube.
Reconnect to coil.
SPARK PLUG CABLE SERVICE
Failure to route the cables properly could cause the
radio to reproduce ignition noise, cross ignition of the
spark plugs or short circuit the cables to ground.
REMOVAL
Remove spark plug cable from coil first.
Always remove the spark plug cable by grasping
the top of the spark plug insulator, turning the boot
1/2 turn and pulling straight up in a steady motion.
INSTALLATION
Install spark plug insulators over spark plugs.
Ensure the top of the spark plug insulator covers the
upper end of the spark plug tube. The connect theother end to coil pack. Be sure that dual plastic clip
holds the cables off of the valve cover.
IGNITION COIL
The electronic ignition coil pack attaches directly
to the valve cover (Fig. 11).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from coil pack
(Fig. 10).
(2) Remove coil pack mounting bolts.
(3) Remove coil pack.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install coil pack on valve cover.
(2) Transfer spark plug cables to new coil pack.
The coil pack towers are numbered with the cylinder
identification. Be sure the ignition cables snap onto
the towers.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY
The relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) (Fig. 12). The PDC is located next to the
battery in the engine compartment. For the location
of the relay within the PDC, refer to the PDC cover
for location. Check electrical terminals for corrosion
and repair as necessary.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The camshaft position sensor is mounted to the
rear of the cylinder head (Fig. 13).
Fig. 10 Electronic Ignition Coil Connector
1 ± COIL
2 ± LOCKING TAB
8D - 6 IGNITION SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 242 of 1285

REMOVAL
(1) Remove brake booster hose and electrical con-
nector from holders on end of cylinder head cover
and reposition.
(2) Disconnect electrical connectors from camshaft
position sensor.
(3) Remove camshaft position sensor mounting
screws. Remove sensor.
(4) Loosen screw attaching target magnet to rear
of camshaft (Fig. 14).
INSTALLATION
The target magnet has two locating dowels that fit
into machined locating holes in end of the camshaft.
(1) Install target magnet in end of camshaft.
Tighten mounting screw to 3.4 N´m (30 in. lbs.)
torque.
(2) Install camshaft position sensor. Tighten sensor
mounting screws to 9 N´m (80 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Place brake booster hose and electrical harness
in holders on end of valve cover.
(4) Attach electrical connectors to camshaft posi-
tion sensor.
Fig. 11 Electronic Ignition Coil Pack
1 ± IGNITION COILS
2 ± SPARK PLUG CABLE
3 ± SPARK PLUG INSULATOR
Fig. 12 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
Fig. 13 Camshaft Position Sensor Location
Fig. 14 Target Magnet Removal/Installation
1 ± TARGET MAGNET
2 ± MOUNTING BOLT
3 ± REAR OF CYLINDER HEAD
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 243 of 1285
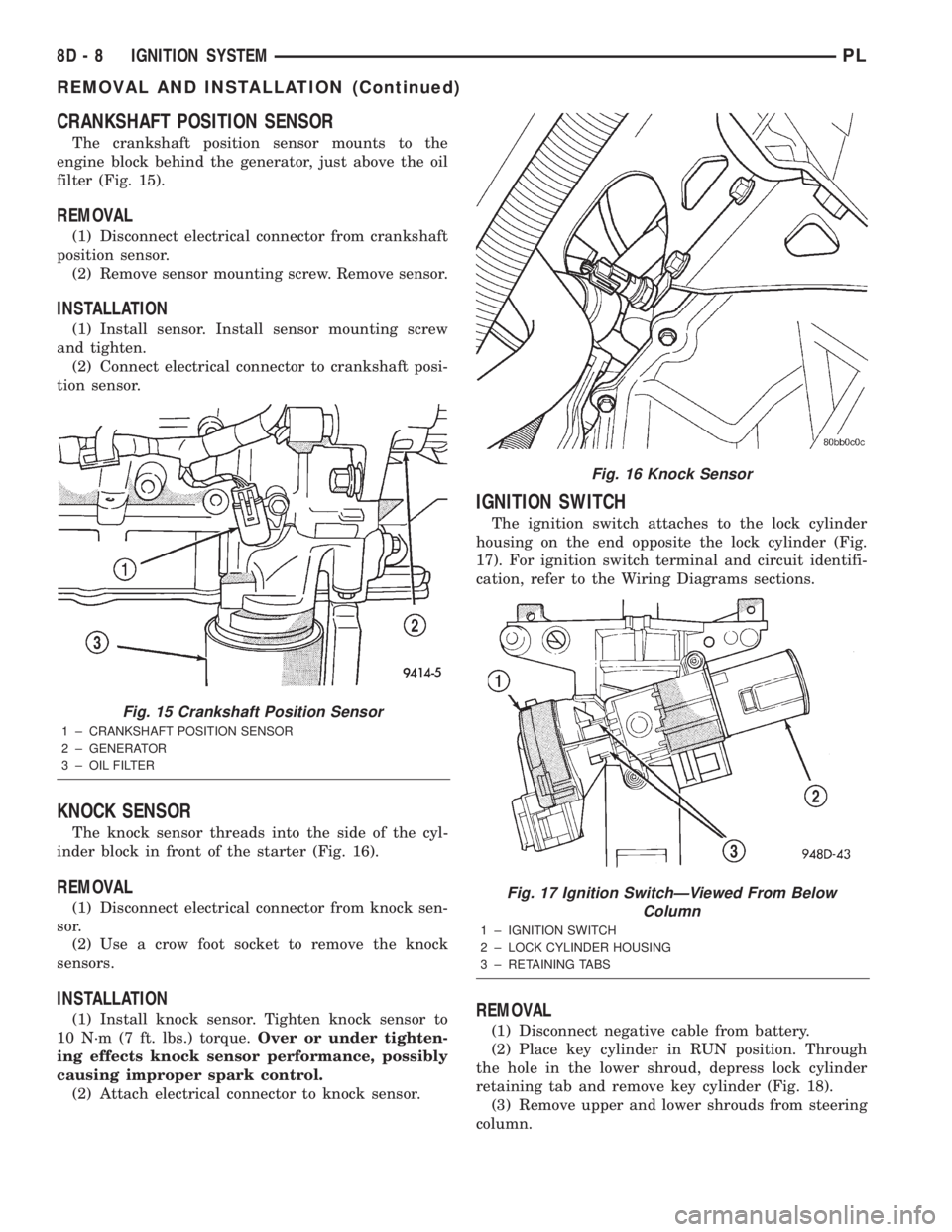
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The crankshaft position sensor mounts to the
engine block behind the generator, just above the oil
filter (Fig. 15).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from crankshaft
position sensor.
(2) Remove sensor mounting screw. Remove sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install sensor. Install sensor mounting screw
and tighten.
(2) Connect electrical connector to crankshaft posi-
tion sensor.
KNOCK SENSOR
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in front of the starter (Fig. 16).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from knock sen-
sor.
(2) Use a crow foot socket to remove the knock
sensors.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install knock sensor. Tighten knock sensor to
10 N´m (7 ft. lbs.) torque.Over or under tighten-
ing effects knock sensor performance, possibly
causing improper spark control.
(2) Attach electrical connector to knock sensor.
IGNITION SWITCH
The ignition switch attaches to the lock cylinder
housing on the end opposite the lock cylinder (Fig.
17). For ignition switch terminal and circuit identifi-
cation, refer to the Wiring Diagrams sections.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Place key cylinder in RUN position. Through
the hole in the lower shroud, depress lock cylinder
retaining tab and remove key cylinder (Fig. 18).
(3) Remove upper and lower shrouds from steering
column.
Fig. 15 Crankshaft Position Sensor
1 ± CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 ± GENERATOR
3 ± OIL FILTER
Fig. 16 Knock Sensor
Fig. 17 Ignition SwitchÐViewed From Below
Column
1 ± IGNITION SWITCH
2 ± LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
3 ± RETAINING TABS
8D - 8 IGNITION SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 246 of 1285
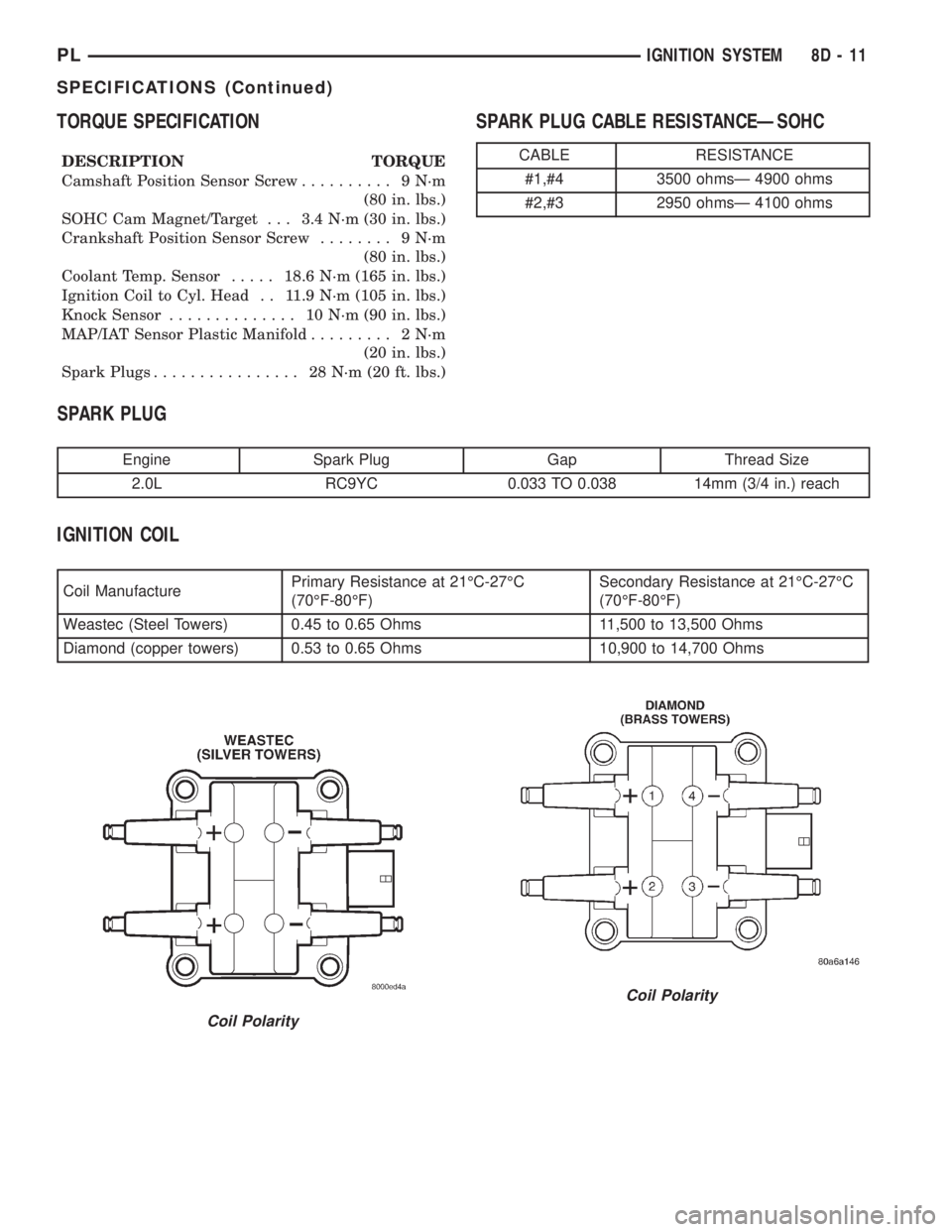
TORQUE SPECIFICATION
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Camshaft Position Sensor Screw.......... 9N´m
(80 in. lbs.)
SOHC Cam Magnet/Target . . . 3.4 N´m (30 in. lbs.)
Crankshaft Position Sensor Screw........ 9N´m
(80 in. lbs.)
Coolant Temp. Sensor.....18.6 N´m (165 in. lbs.)
Ignition Coil to Cyl. Head . . 11.9 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
Knock Sensor.............. 10N´m(90in.lbs.)
MAP/IAT Sensor Plastic Manifold......... 2N´m
(20 in. lbs.)
Spark Plugs................ 28N´m(20ft.lbs.)
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCEÐSOHC
SPARK PLUG
Engine Spark Plug Gap Thread Size
2.0L RC9YC 0.033 TO 0.038 14mm (3/4 in.) reach
IGNITION COIL
Coil ManufacturePrimary Resistance at 21ÉC-27ÉC
(70ÉF-80ÉF)Secondary Resistance at 21ÉC-27ÉC
(70ÉF-80ÉF)
Weastec (Steel Towers) 0.45 to 0.65 Ohms 11,500 to 13,500 Ohms
Diamond (copper towers) 0.53 to 0.65 Ohms 10,900 to 14,700 Ohms
CABLE RESISTANCE
#1,#4 3500 ohmsÐ 4900 ohms
#2,#3 2950 ohmsÐ 4100 ohms
Coil Polarity
Coil Polarity
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 11
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 248 of 1285

INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION..........................1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
HEADLAMP SWITCH......................2
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER....................2
WARNING AND INDICATOR LAMPS..........2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
AIRBAG WARNING SYSTEM................2
BRAKE SYSTEM WARNING LAMP TEST.......2
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER LAMPS.............2
LOW OIL PRESSURE WARNING LAMP TEST...3
MULTIPLE/INDIVIDUAL GAUGES
INOPERATIVE..........................4
SERVICE PROCEDURES
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTICS...4
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ACCESSORY SWITCH/POWER OUTLET
BEZEL................................4CENTER CONSOLE FLOOD LAMP............5
CIGAR LIGHTER / POWER OUTLET
ASSEMBLY.............................5
GLOVE BOX DOOR/BIN....................6
GLOVE BOX DOOR/BIN....................6
GLOVE BOX SWITCH/LAMP.................6
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER....................6
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER BEZEL..............6
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER LAMPS.............7
INSTRUMENT PANEL ASSEMBLY............7
INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL........10
INSTRUMENT PANEL END CAPS............10
INSTRUMENT PANEL TOP COVER...........10
LOWER INSTRUMENT PANEL COVER........10
LOWER STORAGE BIN....................10
STEERING COLUMN SHROUDS.............11
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
The purpose of the dash gauges and indicator
lamps is to keep the driver informed about the oper-
ating condition of the vehicle. If an abnormal condi-
tion occurs, the driver is informed by indicator lamp.
The driver can seek service before damage occurs.
Indicator lamps use ON/OFF switch functions for
operation, while gauges use a sending unit or sensor.
The Instrument Panel can be removed as an
assembly after a few part are removed to allow
access to the retaining bolts. There is one self-align-
ing bulkhead connector on the left underside of the
instrument panel replacing most of the main harness
connectors. Once removed, the instrument panel can
be serviced for replacement. Most of the parts of the
instrument panel can be replaced individually with-
out removing the complete instrument panel assem-
bly.
Fig. 1 Instrument Panel
1 ± DEMISTER OUTLET
2 ± INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
3 ± CENTER AIR OUTLET
4 ± INSTRUMENT PANEL SPEAKERS
5 ± GLOVE BOX
6 ± HVAC CONTROL HEAD
7 ± RADIO
8 ± CIGAR LIGHTER/AUXILIARY POWER OUTLET
9 ± TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH
10 ± REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER SWITCH
PLINSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEMS 8E - 1
Page 251 of 1285
MULTIPLE/INDIVIDUAL GAUGES INOPERATIVE
Test speedometer, tachometer and other gauges for
malfunction:
(1) Remove the cluster. Refer to Cluster Removal
and Installation.
(2) Check for ignition voltage at Pin 15 of the clus-
ter wire harness connector (Fig. 5). Check for battery
voltage at Pin 21 of the connector. If no voltage,
repair as necessary.
(3) Check Pin 10 of the connector for continuity to
ground. If no ground, repair as necessary.
(4) If the voltage and ground are OK, and the pins
or the connectors are not distorted, replace the
instrument cluster.
(5) Install cluster. Refer to Instrument Cluster
Removal and Installation in this section.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTICS
To put the cluster in self-diagnostics mode press
the trip reset button down and then turn the ignition
to the RUN position simultaneously, then release the
button. The gauges will increment to selected stoops
and all indicators will light with the exception of the
turn signals, high beam, and fog lamp indicators.
The oil lamp will come on when the ignition is
turned ON and the engine is OFF.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ACCESSORY SWITCH/POWER OUTLET BEZEL
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable (Fig. 6).
(2) Remove the instrument panel center bezel.
Refer to Instrument Panel Center Bezel Removal and
Installation in this section.
(3) Remove four screws retaining accessory switch/
power outlet bezel (Fig. 7).(4) Disconnect the harness connectors to the fol-
lowing:
²Rear Window Defogger Switch (if equipped)
²Traction Control Switch (if equipped)
²Cigar Lighter/Power Outlet
Fig. 5 Cluster Wire Harness Connector
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER CONNECTOR PIN
CALL-OUT
PIN DESCRIPTION PIN DESCRIPTION
1 REAR FOG
LAMP FEED14 PARK LAMP
SWITCH
OUTPUT
2 PCI BUS 15 FUSED IGNITION
SWITCH
OUTPUT
(RUN-START)
3 COURTESY
LAMPS DRIVER16 DAYTIME
RUNNING
LAMPS
4 FOG LAMP
SWITCH
OUTPUT17 DAYTIME
RUNNING
LAMPS
5 VTSS
INDICATOR
DRIVER18 LEFT TURN
SIGNAL
6 PANEL LAMPS
DIMMER
SIGNAL19 RIGHT TURN
SIGNAL
7 FUEL LEVEL
SENSOR
SIGNAL20 DIMMER
SWITCH LOW
BEAM OUTPUT
8 NOT USED 21 FUSED B+
9 NOT USED 22 RED BRAKE
WARNING
INDICATOR
DRIVER
10 GROUND 23 KEY-IN IGNITION
SWITCH SENSE
11 NOT USED 24 DRIVER DOOR
AJAR SWITCH
SENSE
12 PANEL LAMPS
DRIVER25 SEAT BELT
SWITCH SENSE
13 KEYLESS
ENTRY SIGNAL26 DIMMER
SWITCH HIGH
BEAM OUTPUT
Fig. 4 Oil Pressure Switch
8E - 4 INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEMSPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)