Page 2174 of 4592
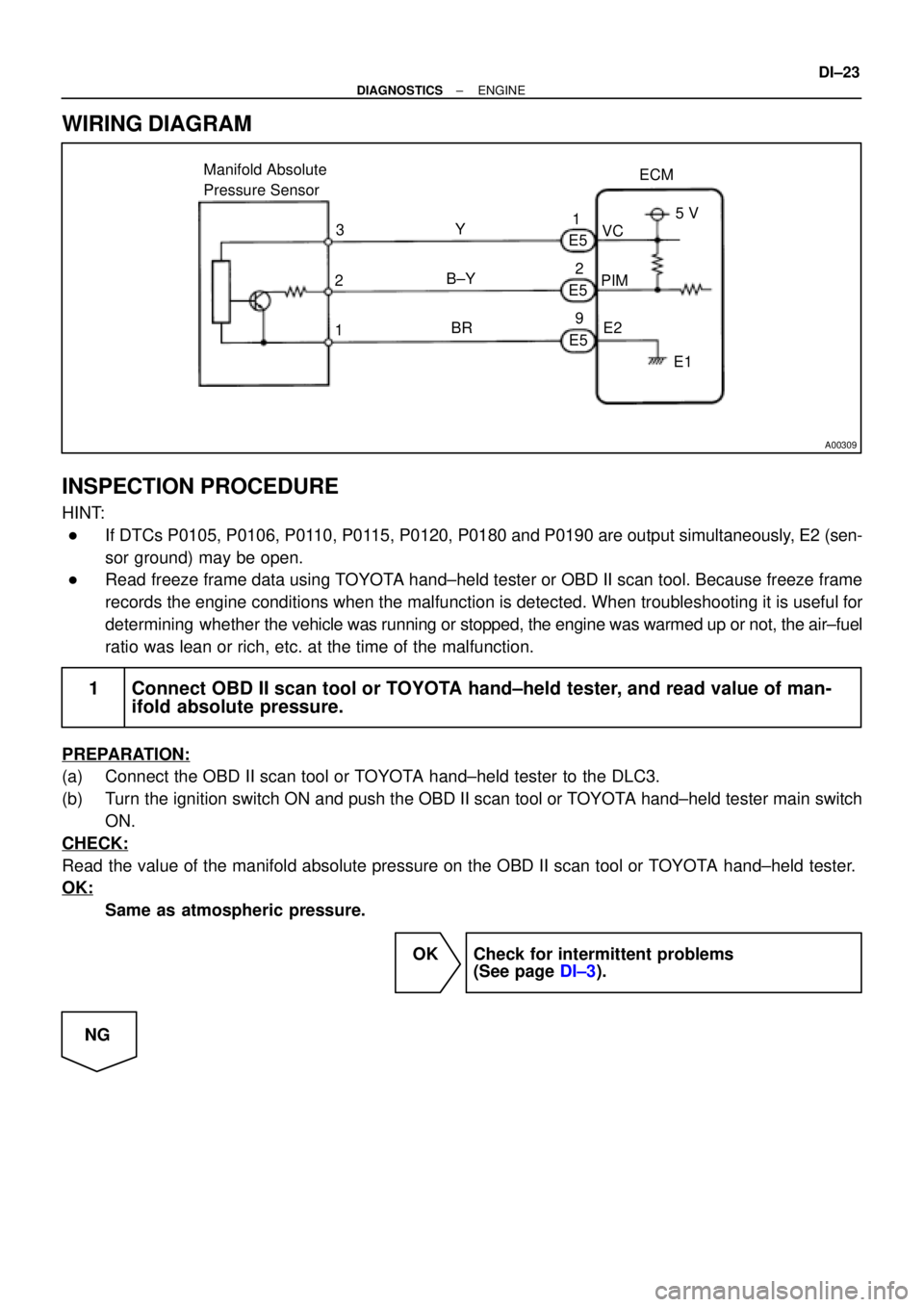
A00309
ECM Manifold Absolute
Pressure Sensor
1PIMVC
E2 Y
B±Y
BRE5
E5
E5 3
25 V
E1 1
2
9
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI±23
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
�If DTCs P0105, P0106, P0110, P0115, P0120, P0180 and P0190 are output simultaneously, E2 (sen-
sor ground) may be open.
�Read freeze frame data using TOYOTA hand±held tester or OBD II scan tool. Because freeze frame
records the engine conditions when the malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting it is useful for
determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the air±fuel
ratio was lean or rich, etc. at the time of the malfunction.
1 Connect OBD II scan tool or TOYOTA hand±held tester, and read value of man-
ifold absolute pressure.
PREPARATION:
(a) Connect the OBD II scan tool or TOYOTA hand±held tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON and push the OBD II scan tool or TOYOTA hand±held tester main switch
ON.
CHECK:
Read the value of the manifold absolute pressure on the OBD II scan tool or TOYOTA hand±held tester.
OK:
Same as atmospheric pressure.
OK Check for intermittent problems
(See page DI±3).
NG
Page 2175 of 4592
BE6653A03008A09254
E2 VC
ON
(±) (+)
A03009BE6653A09255
PIME2
(±) (+)
DI±24
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
2 Check voltage between terminals VC and E2 of ECM connector.
PREPARATION:
(a) Remove the glove compartment (See Pub. No. RM654U,
page SF±64).
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON.
CHECK:
Measure the voltage between terminals VC and E2 of the ECM
connector.
OK:
Voltage: 4.5 ± 5.5 V
NG Check and replace ECM (See page IN±29).
OK
3 Check voltage between terminals PIM and E2 of ECM connector.
PREPARATION:
(a) Remove the glove compartment.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON.
CHECK:
Measure the voltage between terminals PIM and E2 of the ECM
connector.
OK:
Voltage: 3.3 ± 3.9 V
OK Check and replace ECM (See page IN±29).
NG
4 Check for open and short in harness and connector between manifold absolute
pressure sensor and ECM (See page IN±29).
NG Repair or replace harness or connector.
OK
Replace manifold absolute pressure sensor
(See Pub. No. RM654U, page SF±52).
Page 2176 of 4592

± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI±25
DTC P0106 Manifold Absolute Pressure Circuit Range/
Performance Problem
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P0105 on page DI±22.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0106
After engine is warmed up, conditions (a) and (b) continue with
engine speed 400 ± 1,000 rpm: (2 trip detection logic)
(a) Throttle valve fully closed
(b) Manifold absolute pressure sensor output > 3.0 V
�Vacuum lineP0106Conditions (c) and (d) continue with engine speed 2,500 rpm or
less: (2 trip detection logic)
(c) VTA > 1.85
(d) Manifold absolute pressure sensor output < 1.0 V
�Vacuum line
�Manifold absolute pressure sensor
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
�If DTCs P0105, P0106, P0110, P0115, P0120 and P0180 are output simultaneously, manifold abso-
lute pressure sensor circuit may be open. Perform troubleshooting of DTC P0105 first.
�If DTCs P0105, P0106, P0110, P0115, P0120, P0180 and P0190 are output simultaneously, E2 (sen-
sor ground) may be open.
�Read freeze frame data using TOYOTA hand±held tester or OBD II scan tool. Because freeze frame
records the engine conditions when the malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting it is useful for
determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the air±fuel
ratio was lean or rich, etc. at the time of the malfunction.
1 Are there any other codes (besides DTC P0106) being output?
YES Go to relevant DTC chart.
NO
2 Check manifold absolute pressure sensor operation (See Pub. No. RM654U,
page SF±53).
OK Check vacuum line between intake air chamber
and manifold absolute pressure sensor.
NG
Replace manifold absolute pressure sensor.
DI00N±06
Page 2200 of 4592
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI±49
DTC P0171 System too Lean (Fuel Trim)
DTC P0172 System too Rich (Fuel Trim)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Fuel trim refers to the feedback compensation value compared to the basic injection time. Fuel trim includes
short±term fuel trim and long±term fuel trim.
Short±term fuel trim is the short±term fuel compensation used to maintain the air±fuel ratio at its ideal
theoretical value.
The signal from the A/F sensor is approximately proportional to the existing air±fuel ratio, and ECM compar-
ing it with the ideal theoretical value, the ECM reduces fuel volume immediately if the air±fuel ratio is rich
and increases fuel volume if it is lean.
Long±term fuel trim compensates for the deviation from the central value of the short±term fuel trim stored
up by each engine tolerance, and the deviation from the central value due to the passage of time and
changes of environment.
If both the short±term fuel trim and long±term fuel trim exceed a certain value, it is detected as a malfunction
and the MIL lights up.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0171
When air±fuel ratio feedback is stable after engine warming up,
fuel trim is considerably in error on RICH side
(2 trip detection logic)
�Air induction system
�Injector blockage
�Manifold absolute pressure sensor
�Engine coolant temp. sensor
�Fuel shutoff valve for delivery pipe
�Gas leakage on exhaust system
�Air induction system
�Open or short in A/F sensor (bank 1 sensor 1) circuit
�A/F sensor (bank 1 sensor 1)
�ECM
P0172
When air±fuel ratio feedback is stable after engine warming up,
fuel trim is considerably in error on LEAN side
(2 trip detection logic)
�Injector leak, blockage
�Manifold absolute pressure sensor
�Engine coolant temp. sensor
�Ignition system
�Fuel shutoff valve for delivery pipe
�Gas leakage on exhaust system
�Open or short in A/F sensor (bank 1 sensor 1) circuit
�A/F sensor (bank 1 sensor 1)
�ECM
HINT:
�When the DTC P0171 is recorded, the actual air±fuel ratio is on the LEAN side. When DTC P0172 is
recorded, the actual air±fuel ratio is on the RICH side.
�If the vehicle runs out of fuel, the air±fuel ratio is lean and DTC P0171 is recorded. The MIL then comes
on.
�If the total of the short±term fuel trim value and long±term fuel trim value is within +38 %, the system
is functioning normally.
�The A/F sensor output voltage and the short±term fuel trim value can be read using the OBD II scan
tool or TOYOTA hand±held tester.
DI1JW±04
Page 2201 of 4592

DI±50
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
�The ECM controls the voltage of AF+ and AF± terminals of ECM to the fixed voltage. Therefore, it is
impossible to confirm the A/F sensor output voltage without OBD II scan tool or TOYOTA hand±held
tester.
�OBD II scan tool (excluding TOYOTA hand±held tester) displays the one fifth of the A/F sensor output
voltage which is displayed on the TOYOTA hand±held tester.
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0125 on page DI±40.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using TOYOTA hand±held tester or OBD II scan tool. Because freeze frame records
the engine conditions when the malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting it is useful for determining
whether the vehicle was running or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the airÅfuel ratio was lean
or rich, etc. at the time of the malfunction.
1 Check air induction system (See Pub. No. RM654U, page SF±1).
NG Repair or replace.
OK
2 Check injector injection (See Pub. No. RM654U, page SF-23).
NG Replace injector.
OK
3 Check manifold absolute pressure sensor (See Pub. No. RM654U, page SF±53)
and engine coolant temperature sensor (See Pub. No. RM654U, page SF±49).
NG Repair or replace.
OK
4 Check for spark and ignition (See page IG±1).
NG Repair or replace.
Page 2207 of 4592
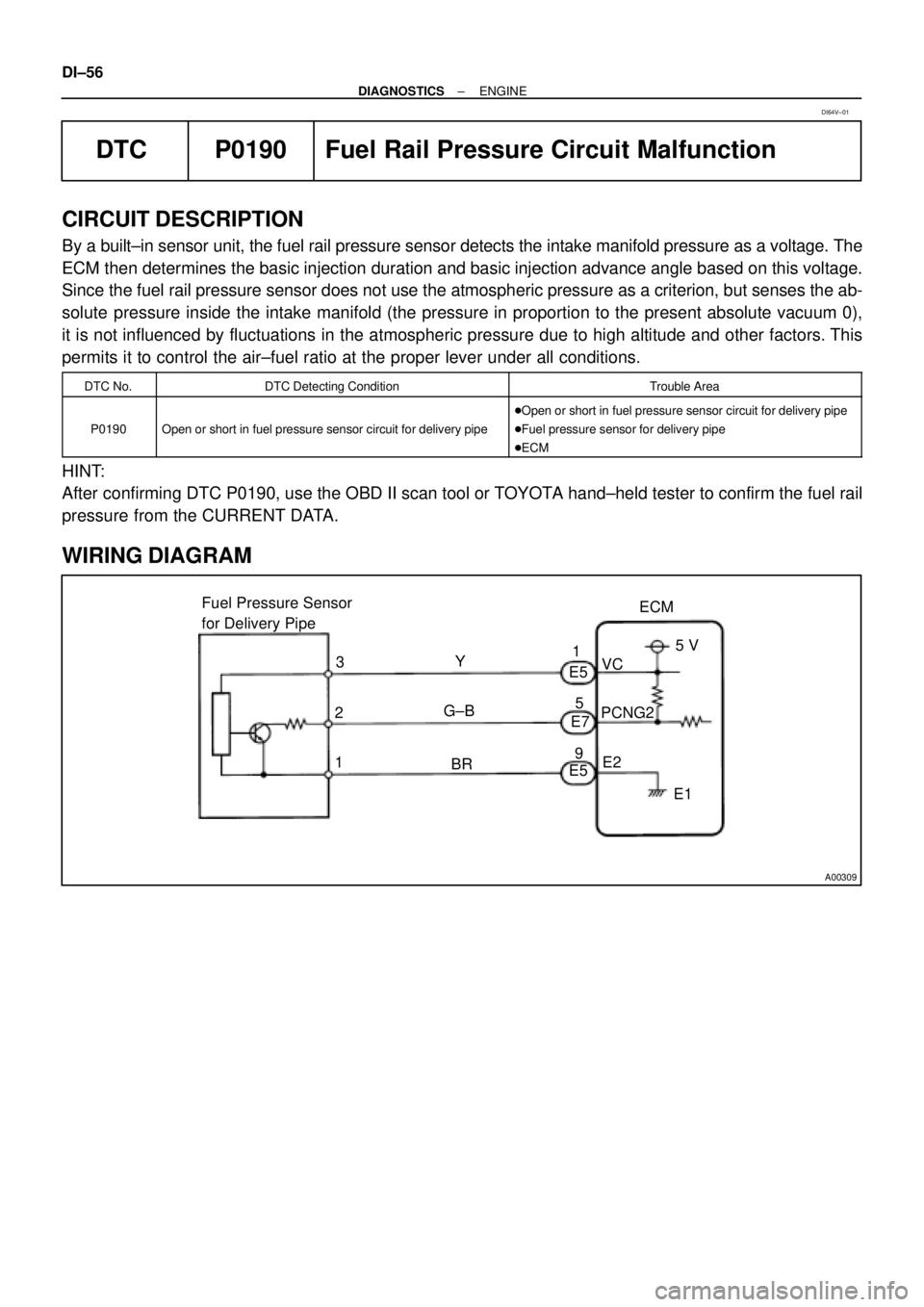
A00309
ECM Fuel Pressure Sensor
for Delivery Pipe
1PCNG2VC
E2 Y
G±BE5
E7
E5 3
25 V
E1 1
5
9
BR DI±56
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DTC P0190 Fuel Rail Pressure Circuit Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
By a built±in sensor unit, the fuel rail pressure sensor detects the intake manifold pressure as a voltage. The
ECM then determines the basic injection duration and basic injection advance angle based on this voltage.
Since the fuel rail pressure sensor does not use the atmospheric pressure as a criterion, but senses the ab-
solute pressure inside the intake manifold (the pressure in proportion to the present absolute vacuum 0),
it is not influenced by fluctuations in the atmospheric pressure due to high altitude and other factors. This
permits it to control the air±fuel ratio at the proper lever under all conditions.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0190Open or short in fuel pressure sensor circuit for delivery pipe
�Open or short in fuel pressure sensor circuit for delivery pipe
�Fuel pressure sensor for delivery pipe
�ECM
HINT:
After confirming DTC P0190, use the OBD II scan tool or TOYOTA hand±held tester to confirm the fuel rail
pressure from the CURRENT DATA.
WIRING DIAGRAM
DI64V±01
Page 2214 of 4592

P25430
ECM
Throttle Body
EGR
Vacuum
Modulator EGR Valve
VSV
Exhaust Gas Throttle
Valve
u
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI±63
DTC P0400 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The EGR system recirculates exhaust gas, which is controlled to the proper quantity to suit the driving condi-
tions, into the intake air mixture to slow down combustion, reduce the combustion temperature and reduce
NOx emissions. The amount of EGR is regulated by the EGR vacuum modulator according to the engine
load.
If even one of the following conditions is fulfilled, the VSV is
turned ON by a signal from the ECM.
This results in atmospheric air acting on the EGR valve, closing
the EGR valve and shutting off the exhaust gas (EGR cut±off).
Under the following conditions, EGR is cut to maintain driveabil-
ity.
�Before engine is warmed up.
�During deceleration (throttle valve closed).
�Light engine load (amount of intake air very small).
�Engine idling.
�Engine speed over 4,400 rpm.
�High engine load (amount of intake air very large).
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0400
After engine is warmed up, intake manifold absolute pressure
is larger than value calculated by ECM while EGR system is
ON (2 trip detection logic)
�Vacuum or EGR hose is connected to wrong post
�Open or short in VSV circuit for EGR
�VSV for EGR
�EGR system
�EGR vacuum modulator
�EGR valve
�Manifold absolute pressure sensor
�ECM
DI64W±01
Page 2217 of 4592
DI±66
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
NG Replace VSV for EGR.
OK
Check for open and short in harness and con-
nector between engine room J/B No.2 and
ECM (See page IN±29).
4 Check EGR system (See Pub. No. RM654U, page EC±12).
NG Repair or replace.
OK
5 Check EGR vacuum modulator (See Pub. No. RM654U, page EC±12).
NG Repair or replace.
OK
6 Check EGR valve (See Pub. No. RM654U, page EC±12).
NG Repair or replace.
OK
7 Check manifold absolute pressure sensor (See Pub. No. RM654U, page SF±53).
NG Repair or replace.
OK