1988 PONTIAC FIERO ignition
[x] Cancel search: ignitionPage 749 of 1825
6E3-CZ-14 2.8L (VIN S) DRlVEABlLlTV AND EMISSIONS
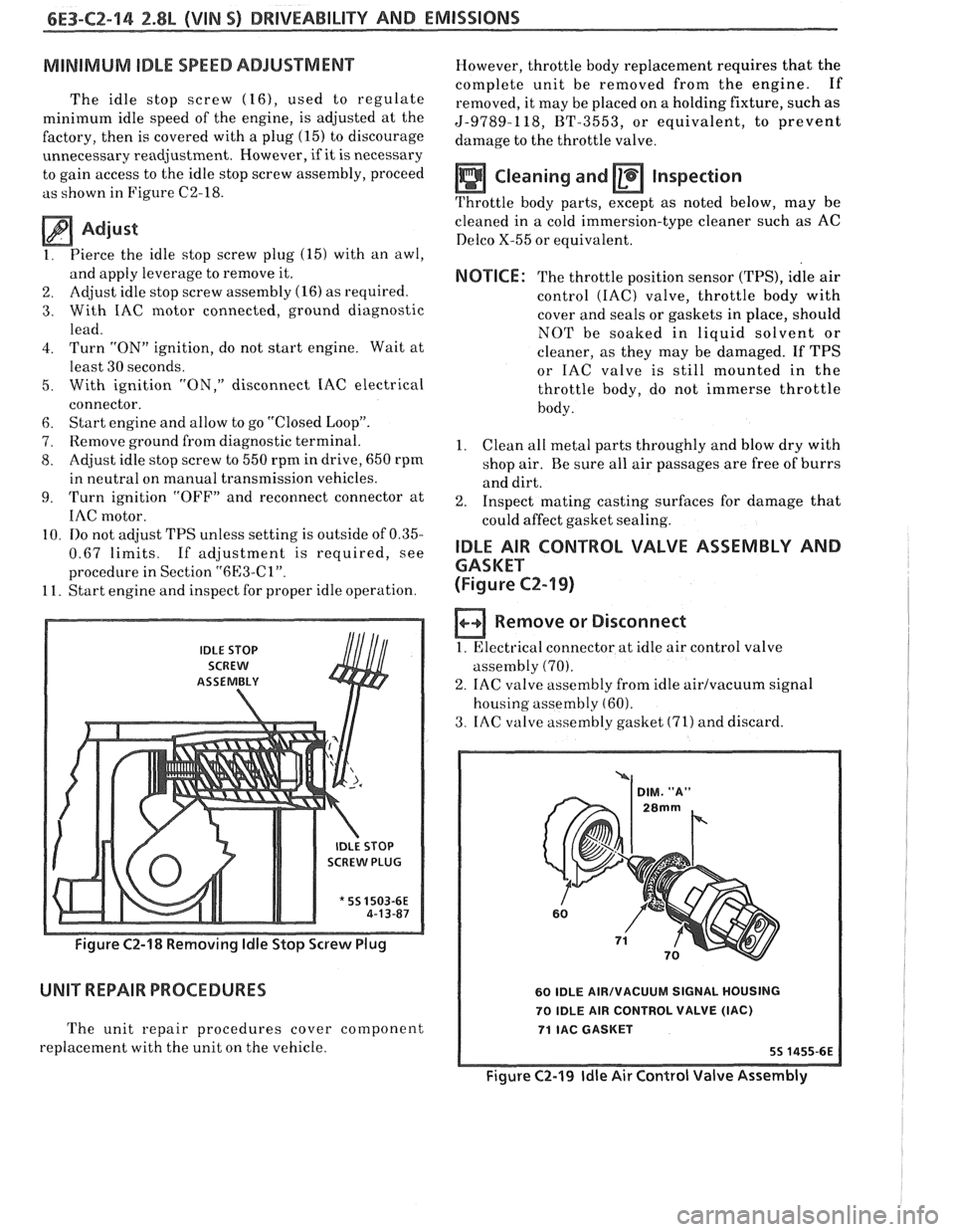
MINIMUM IDLE SPEED ADJUSTMENT
The idle stop screw (16), used to regulate
minimum idle speed of the engine, is adjusted at the
factory, then is covered with a plug
(15) to discourage
unnecessary readjustment. However,
if it is necessary
to gain access to the idle stop screw assembly, proceed
as shown in Figure C2-18.
Adjust
1. Pierce
the idle stop screw plug (15) with an awl,
and apply leverage to remove it.
2. Adjust idle
stop screw assembly (16) as required.
3. With IAC motor connected, ground diagnostic
lead.
4. Turn "ON" ignition, do not start engine. Wait at
least 30 seconds.
5. With ignition "ON," disconnect IAC electrical
connector.
6. Start engine and allow to go "Closed Loop".
7. Remove ground from diagnostic terminal.
8. Adjust idle stop screw to 550 rpm in drive, 650 rpm
in neutral on manual transmission vehicles.
9. Turn ignition "OFF7' and reconnect connector at
IAC motor.
10.
110 not adjust TPS unless setting is outside of 0.35-
0.67 limits. If adjustment is required, see
procedure in Section
"6l33-Cl".
11. Start engine and inspect for proper idle operation.
IDLE STOP
SCREW
ASSEtVIBLY
SCREW PLUG
* 55 1503-6E
Figure C2-18 Removing ldle Stop Screw Plug
UNIT REPAIR PROCEDURES
The unit repair procedures cover component
replacement with the unit on the vehicle. However,
throttle body replacement requires that the
complete unit be removed from the engine. If
removed, it may be placed on a holding fixture, such as
5-9789-118, BT-3553, or equivalent, to prevent
damage to the throttle valve.
Cleaning and Inspection
Throttle body parts, except as noted below, may be
cleaned in
a cold immersion-type cleaner such as AC
Delco X-55 or equivalent.
NOTICE: The throttle position sensor (TPS), idle air
control
(IAC) valve, throttle body with
cover and seals or gaskets in place, should
NOT be soaked in liquid solvent or
cleaner, as they may be damaged. If TPS
or IAC valve is still mounted in the
throttle body, do not immerse throttle
body.
1. Clean
all metal parts throughly and blow dry with
shop air. Be sure all air passages are free of burrs
and dirt.
2. Inspect mating casting surfaces for damage that
could affect gasket sealing.
IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE ASSEMBLY AND
GASKET
(Figure
CZ-19)
Remove or Disconnect
1. Electrical connector at idle air control valve
assembly
(70).
2. IAC valve assembly from idle airlvacuum signal
housing assembly
(60).
3. IAC valve assembly gasket (71) and discard.
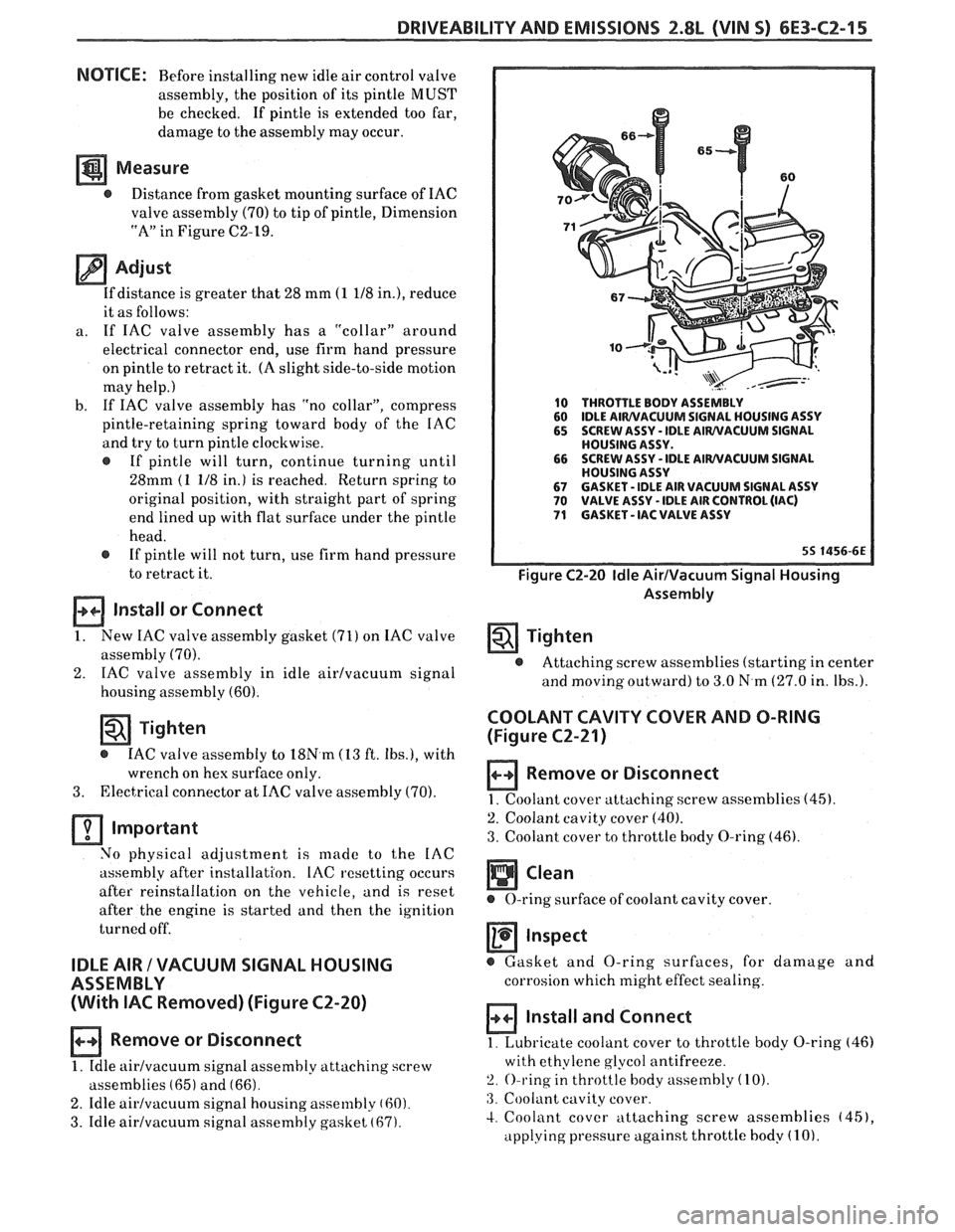
60 IDLE AIRIVACUUM SIGNAL HOUSING
70 IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE
(IAC)
71 IAC GASKET
Figure C2-19 ldle Air Control Valve Assembly
Page 750 of 1825
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 2.8L (VIN S) 6E3-CZ-15
NOTICE: Before instal ling new idle air control valve
assembly, the position of its pintle
MUST
be checked. If pintle is extended too far,
damage to the assembly may occur.
Measure
@ Distance from gasket mounting surface of IAC
valve assembly
(70) to tip of pintle, Dimension
"A" in Figure
C2-19.
Adjust
If distance is greater that 28 mm (1 118 in.), reduce -
it as follows:
a. If
IAC valve assembly has
a "collar" around
electrical connector end, use firm hand pressure
on pintle to retract it. (A slight side-to-side motion
may help.)
b. If IAC valve assembly has "no collar", compress
pintle-retaining spring toward body of the IAC
and try to turn pintle clockwise.
@ If pintle will turn, continue turning until
28mm
(1 118 in.) is reached. Return spring to
original position, with straight part of spring
end lined up with flat surface under the pintle
head.
@ If pintle will not turn, use firm hand pressure
to retract it.
Install or Connect
1. New IAC valve assembly gasket (71) on IAC valve
assembly
(70).
2. IAC valve assembly in idle airlvacuum signal
housing assembly
(60).
Tighten
IAC valve assembly to 18N.m (13 ft. Ibs.), with
wrench on hex surface only.
3. Electrical connector at IAC valve assembly (70).
Important
No physical adjustment is made to the IAC
assembly after installation.
IAC resetting occurs
after reinstallation on the vehicle, and is reset
after the engine is started and then the ignition
turned off.
IDLE AIR / VACUUM SIGNAL HOUSING
ASSEMBLY
(With
IAC Removed) (Figure C2-20)
Remove or Disconnect
1. Idle airlvacuurn signal assembly attaching screw
assemblies
(65) and (66).
2. Idle airlvacuum signal housing assembly (60).
3. Idle airlvacuum signal assembly gasket (67).
10 THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY
60 IDLE AIWVACUUM SIGNAL
HOUSING ASSY
65 SCREW ASSY - IDLE AIWVACUUM SIGNAL
HOUSING ASSY.
66 SCREW
ASSY
- IDLE AIWVACUUM SIGNAL
HOUSING ASSY
67 GASKET - IDLE AIR VACUUM SIGNAL ASSY 70 VALVE ASSY - IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) 71 GASKET - IAC VALVE ASSY
Figure C2-20 Idle AirIVacuum Signal Housing
Assembly
Tighten
@ Attaching screw assemblies (starting in center
and
moving outward) to 3.0 N.m (27.0 in. Ibs.).
COOLANT CAVITY COVER AND O-RING
(Figure
C2-21)
Remove or Disconnect
1. Coolant cover attaching. screw assemblies (45).
2. Coolant cavity cover (40).
3. Coolant cover to throttle body O-ring (46).
Inspect
@ Gasket and O-ring surfaces, for damage and
corrosion which might effect sealing.
Install and Connect
1. Lubricate coolant cover to throttle body O-ring (46)
with ethylene glycol antifreeze.
2. O-ring in throttle body assembly (10).
:3. Coolant cavity cover.
4. Coolant cover attaching screw assemblies (451,
applying pressure against throttle body (1 0).
Page 753 of 1825

6E3-C2-18 2.8L (VIN S) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CHART C-2A
INJECTOR BALANCE TEST
The injector balance tester is a tool used to turn the injector on for a precise
amount of time, thus spraying a measured amount of fuel into the manifold.
This causes a drop in fuel rail pressure that we can record and compare between
each injector. All injectors should have the same amount of pressure drop
( k 10
kpa). Any injector with a pressure drop that is 10 kpa (or more) greater or less
than the average drop of the other injectors should be considered faulty and
replaced.
Engine "cool down" period
(10 minutes) is necessary to avoid irregular
readings due to "Hot Soak" fuel boiling. With ignition
"OFF" connect fuel gauge
5347301 or equivalent to fuel pressure tap. Wrap a shop towel around fitting
while connecting gage to avoid fuel spillage.
Disconnect harness connectors at all injectors, and connect injector tester
J-
34730-3, or equivalent, to one injector. On Turbo equipped engines, use adaptor
harness furnished with injector tester to energize injectors that are not
accessible. Follow manufacturers instructions for use of adaptor harness.
Ignition must be
"OFF" at least 10 seconds to complete ECM shutdown cycle.
Fuel pump should run about
2 seconds after ignition is turned "ON". At this
point, insert clear tubing attached to vent valve into a suitable container and
bleed air from gauge and hose to insure accurate gauge operation. Repeat this
step until all air is bled from gauge.
STEP 2
Turn ignition "OFF" for 10 seconds and then "ON" again to get fuel pressure
to its maximum. Record this initial pressure reading. Energize tester one time
and note pressure drop at its lowest point (Disregard any slight pressure
increase after drop hits low point.). By subtracting this second pressure reading
from the initial pressure, we have the actual amount of injector pressure drop.
STEP 3
Repeat step 2 on each injector and compare the amount of drop. Usually, good
injectors will have virtually the same drop. Retest any injector that has
a
pressure difference of lOkPa, either more or less than the average of the other
injectors on the engine. Replace any injector that also fails the retest. If the
pressure drop of all injectors is within
lOkPa of this average, the injectors
appear to be flowing properly. Reconnect
them and review "Symptoms," Section
"B".
NOTE: The entire test should not be repeated more than once without
running the engine to prevent flooding. (This includes any retest on
fa ulty injectors).
Page 755 of 1825
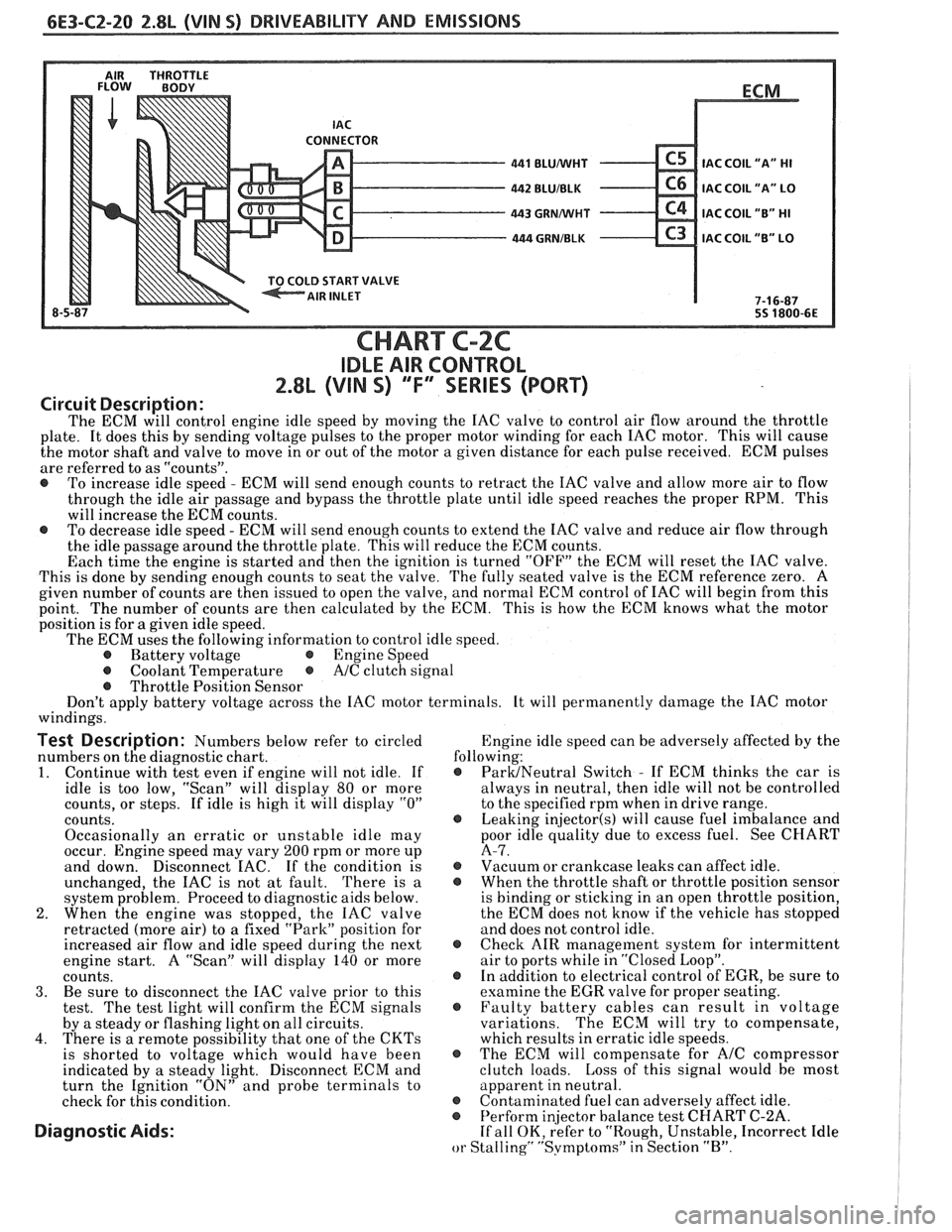
6E3-C2-20 2.8L (VIN S) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
AIR THROTTLE FLOW BODY
LD START VALVE
8-5 BLUNVHT
BLUIBLK
GRMNVHT
. GRNIBLK
ECM
.
IAC COIL
"A" HI
IAC COIL "A" LO
IAC COIL "B" HI
C3 IAC COIL "B" LO
7-1 6-87
55 1800-6E
CHART C-2C
IDLE AIR CONTROL
2.8L (VIN S) ""F-SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The ECM will control engine idle speed by moving the IAC valve to control air flow around the throttle
plate. It does this by sending voltage pulses to the proper motor winding for each IAC motor. This will cause
the motor shaft and valve to move in or out of the motor a given distance for each pulse received. ECM pulses
are referred to as "counts".
@ To increase idle speed - ECM will send enough counts to retract the IAC valve and allow more air to flow
through the idle air passage and bypass the throttle plate until idle speed reaches the proper RPM. This
will increase the ECM counts.
@ To decrease idle speed - ECM will send enough counts to extend the IAC valve and reduce air flow through
the idle passage around the throttle plate. This will reduce the ECM counts.
Each time the engine is started and then the ignition is turned "OFF" the ECM will reset the IAC valve.
This is done by sending enough counts to seat the valve. The fully seated valve is the ECM reference zero. A
given number of counts are then issued to open the valve, and normal ECM control of IAC will begin from this
point. The
number of counts are then calculated by the ECM. This is how the ECM knows what the motor
position is for
a given idle speed.
The ECM uses the following information to control idle speed.
@ Battery voltage @ Engine Speed
@ Coolant Temperature @ A/C clutch signal
@ Throttle Position Sensor
Don't apply battery voltage across the IAC motor terminals. It will permanently damage the IAC motor
windings.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled Engine
idle speed can be adversely affected by the
numbers on the diagnostic chart. following:
1. Continue
with test even if engine will not idle. If @ ParUNeutral Switch - If ECM thinks the car is
idle is too low, "Scan" will display
80 or more always
in neutral, then idle will not be controlled
counts, or steps. If idle is high it will display
"0" to the specified rpm when in drive range.
counts.
@ Leaking injector(s) will cause fuel imbalance and
Occasionally an erratic or unstable idle may poor
idle quality due to excess fuel. See CHART
occur. Engine speed may vary
200 rpm or more up A-7.
and down. Disconnect
EAC. If the condition is @ Vacuum or crankcase leaks can affect idle.
unchanged, the IAC is not at fault. There is
a @ When the throttle shaft or throttle position sensor
system problem. Proceed to diagnostic aids below. is
binding or sticking in an open throttle position,
2. When the engine was stopped, the IAC valve the
ECM does not know if the vehicle has stopped
retracted (more air) to a fixed "Park" position for and does not control idle.
increased air flow and idle speed during the next
@ Check AIR management system for intermittent
engine start. A "Scan" will display
140 or more air
to ports while in "Closed Loop".
counts. @ In addition to electrical control of EGR, be sure to
3. Be sure to disconnect the IAC valve prior to this examine the
EGR valve for proper seating.
test. The test light will confirm the ECM signals @ Faulty battery cables can result in voltage
by a steady or flashing light on all circuits. variations. The
ECM will try to compensate,
4. There is a remote possibility that one of the CKTs which results in erratic idle speeds.
is shorted to voltage which would have been @ The ECM will compensate for A/C compressor
indicated by a steady light. Disconnect ECM and clutch
loads. Loss of this signal would be most
turn the Ignition "ON" and probe terminals to apparent
in neutral.
check for this condition.
@ Contaminated fuel can adversely affect idle. @ Perform in
or Stalling" "Svmptoms" in Section "B".
Page 761 of 1825
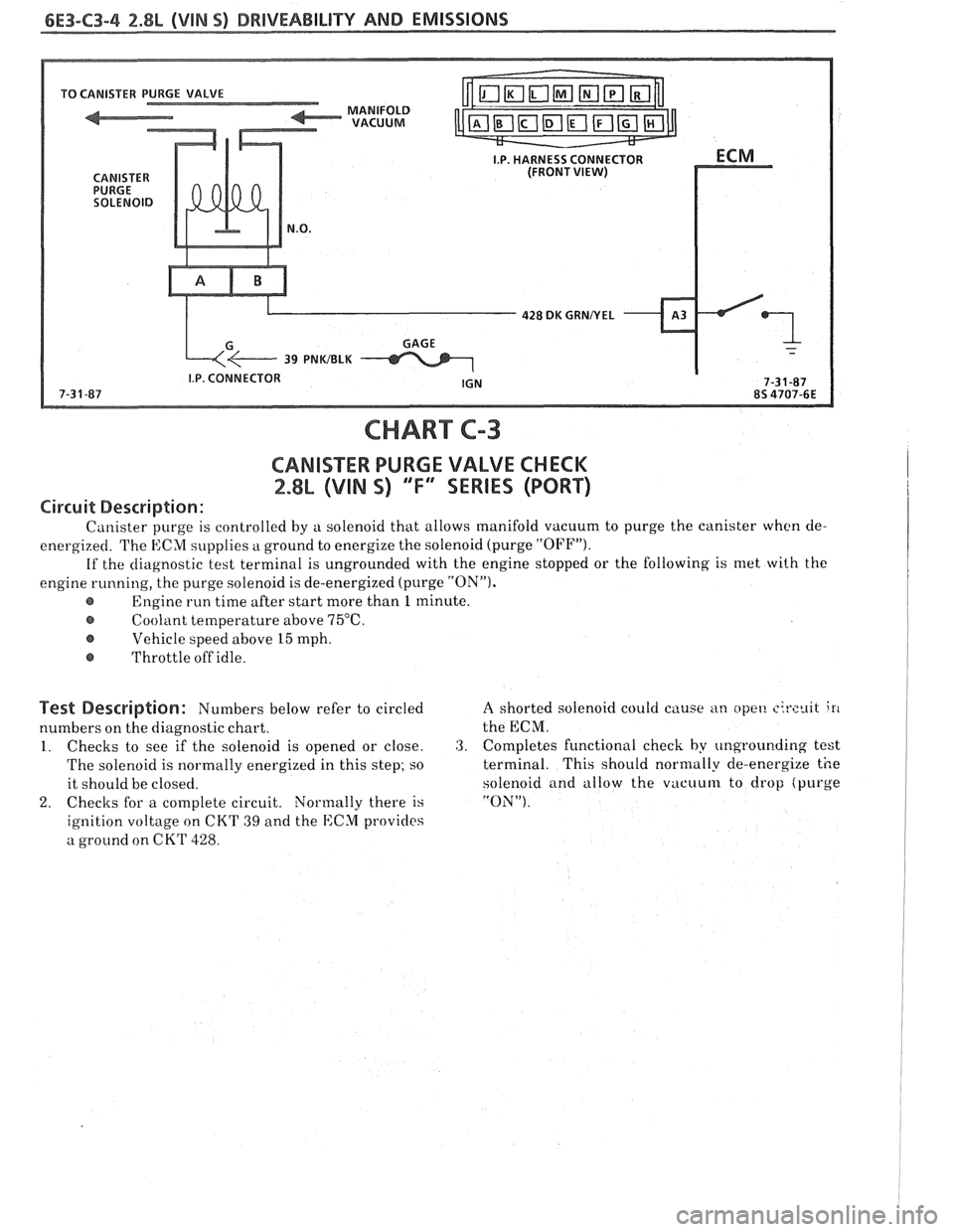
6E3-C3-4 2.8L (VIN S) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
TO CANISTER
I.P. HARNESS CONNECTOR (FRONT VIEW)
428 DK GRNNEL
CHART C-3
CARIISXE PURGE VALVE CHECK
2.88 (VIN S) ""F4 SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
Canister purge is controlled by a solenoid that allows manifold vacuum to purge the canister when cle-
energized. The ECM supplies
a ground to energize the solenoid (purge "OFFJ').
If the diagnostic test terminal is ungrounded with the engine stopped or the following is met with the
engine running, the purge solenoid is de-energized (purge
"ON").
Engine run time after start more than 1 minute.
@ Coolant temperature above 75°C.
Vehicle speed above 15 mph.
@ Throttle off idle.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Checks to see if the solenoid is opened or close.
The solenoid is normally energized in this step;
so
it should be closed.
2. Checks for a complete circuit. Normally there is
ignition voltage on CKT
39 and the ECM provicles
a ground on CKT
428.
A shorted solenoid could cause an opet! circuit i11
the ECM.
3. Completes functional check by ungrounding test
terminal. This should normally de-energize the
solenoid
and allow the vacuum to drop (purge
"ON").
Page 762 of 1825
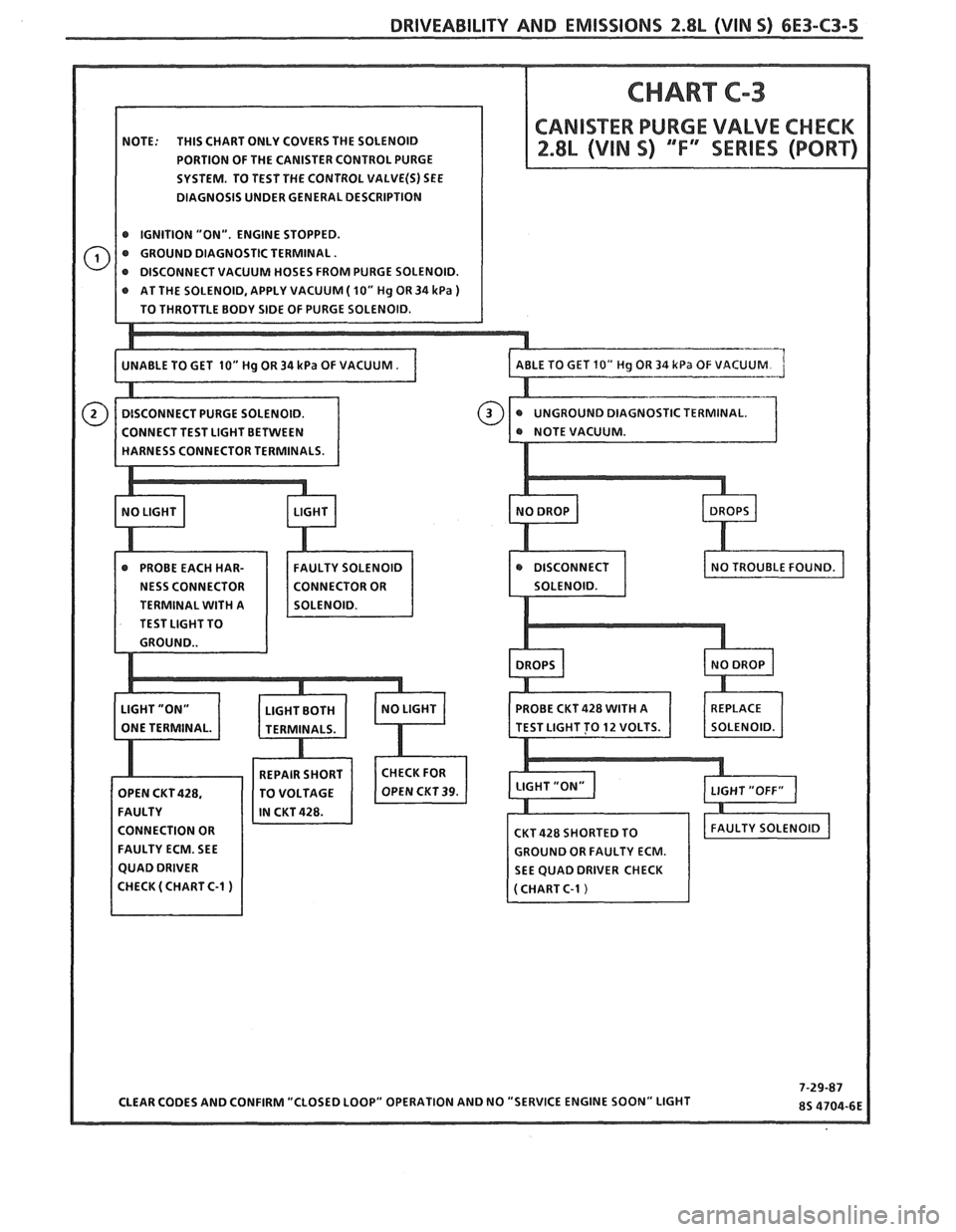
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS f.8L (VIN 5) 6E3-C3-5
NOTE: THIS CHART ONLY COVERS THE SOLENOID
PORTION OF THE CANISTER CONTROL PURGE
SYSTEM. TO TEST THE CONTROL
VALVE(S) SEE
DIAGNOSIS UNDER GENERAL DESCRIPTION
@ IGNITION "ON". ENGINE STOPPED.
@ GROUND DIAGNOSTIC TERMINAL.
AT THE SOLENOID, APPLY VACUUM
( 10" Hg OR 34 kPa )
STIC TERMINAL.
TERMINAL
WITH A
TEST LIGHT TO
CONNECTION OR
FAULTY ECM. SEE
GROUND OR FAULTY ECM.
SEE QUAD DRIVER CHECK
Page 764 of 1825
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 2.8L (VIN S) 6E3-C4-1
SECTION C4
IGNI"F0N SYSTEM / EST
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ................ C4-1 ON-CAR SERVICE ..................... C4-2
PURPOSE ......................... C4-1 SETTING TIMING.. .................. C4-2
OPERATION ....................... C4-1 HOW CODE 42 IS DETERMINED.. ....... C4-2
RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION .... C4-2 PARTS INFORMATION ................. C4-2
DIAGNOSIS
......................... C4-2
CODEIZ.......................... C4-2
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
PURPOSE
The High Energy Ignition ([-IEI) system controls
fuel combustion by providing a spark to ignite the
compressed
airlfuel mixture at the correct time. To
provide improved engine performance, fuel economy,
and control of exhaust emissions, the
ECM controls
distributor spark advance (timing) with the Electronic
Spark Timing (EST) system.
Only the Electronic Spark Timing (EST) system
will be described here. Additional information on the
tIEI system is found in Section "6D".
To properly control ignition/combustion timing
the ECM needs to know:
@ Crankshaft position
@ Engine speed (rpm)
@ Mass Air Flow
@ Engine temperature
OPERATION
The EST system consists of the distributor
module, ECM, and connecting wires. The connector
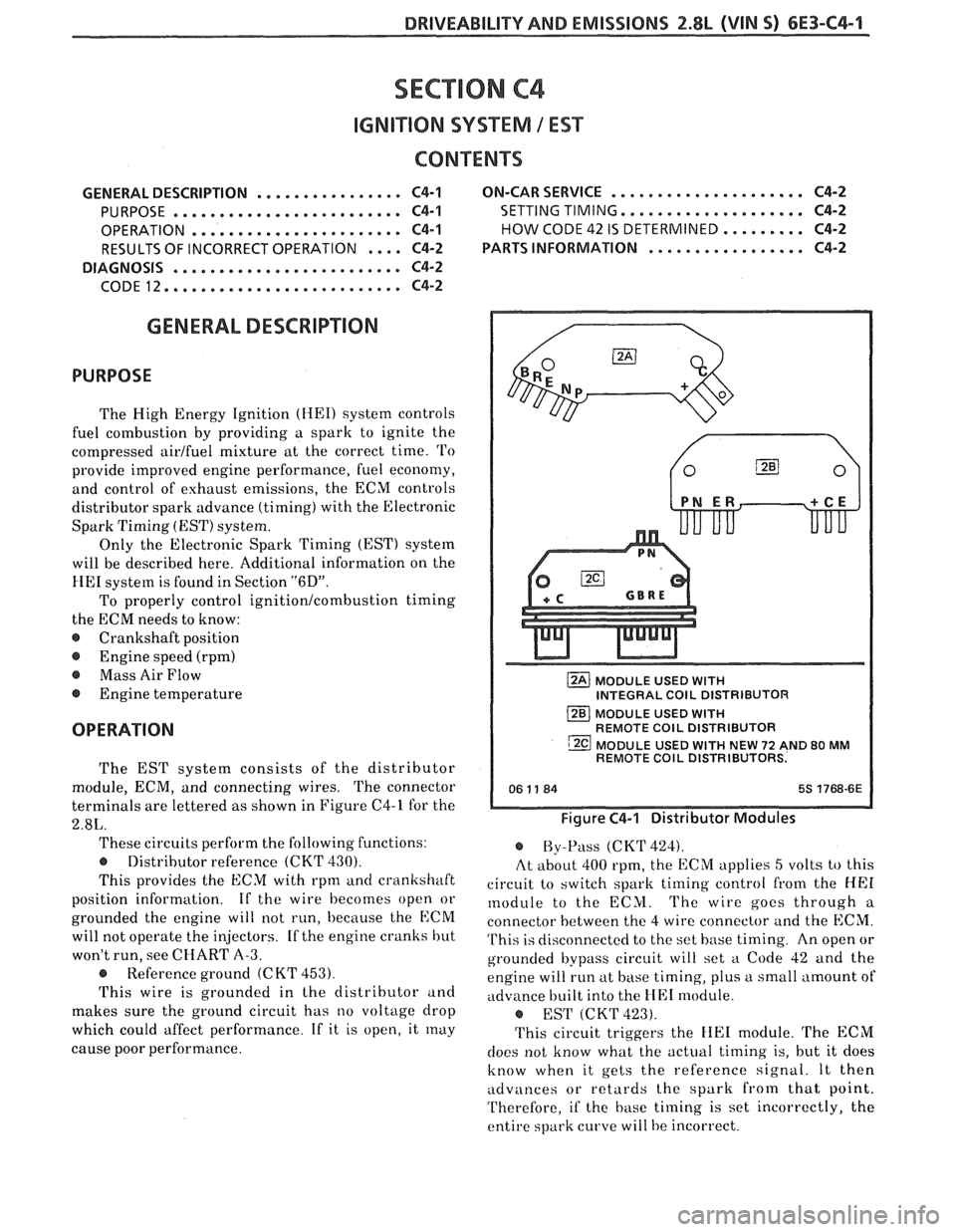
terminals are lettered as shown in Figure C4-1 for the
2.8L.
These circuits perform the following functions:
@ Distributor reference (CKT 430).
This provides the ECM with rpm ancl crankshaft
position information. If
the wire becomes open or
grounded the engine will not run, because the
ECM
will not operate the injectors. If the engine cranks hut
won't run, see CHART A-3.
@ Reference ground (C KT 453).
This wire is grounded in the distributor and
makes sure the ground circuit has no voltage drop
which could affect performance. If it is open, it
rnay
cause poor performance.
MODULE USED WITH INTEGRAL COlL DISTRIBUTOR
MODULE USED
WITH REMOTE COlL DISTRIBUTOR
MODULE USED
WITH NEW 72 AND 80 MM REMOTE COlL DISTRIBUTORS.
Figure C4-1 Distributor Modules
@ By-Pass (CKT 424).
At about 400 rpm, the ECM applies
5 volts to this
circuit to switch spark timing control from the
HE1
module to the ECM. The wire gocs through a
connector between the
4 wire connector and the ECM.
This is disconnectcd to the set base timing. An open or
grounded bypass circuit will set
a Code 42 and the
engine will run at hase timing, plus a small amount of
advance built into the
HE1 n~odule.
@ EST (CKT423).
This circuit triggers the FIE1 module. The ECM
does not know what the actual timing is, but it does
know when it gets the reference signal. It then
udva~ces or retards the spark from that point.
Therefore, if the
hase timing is set incorrectly, the
entire spark curve will be incorrect.
Page 765 of 1825

6E3-C4-2 2.8L (WIN S) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION
An open or ground in the EST circuit will set a
Code 42 and cause the engine to run on the HE1
module timing. This will cause reduced performance
and poor fuel economy.
The ECM uses information from the
MAF and
coolant sensors in addition to rpm to calculate spark
~tdvance as follows:
@ Cold engine = more spark advance.
@ Engine under minimum load based on rpm
and low amount of air flow- more spark
advance. Hot engine
= less spark advance.
@ Engine under heavy load based on rprn and
high amount of air flow- less spark advance.
The description, operation, and diagnosis of the
HE1 system are found in Section "GD" of this manual.
CODE 12
Code 12 is used during the Diagnostic Circuit
Check procedure to test the code display ability of the
ECM. This code indicates that the ECM is not
receiving the engine
rpnl (REFERENCE) signal. This
occurs with the ignition key "ON" and the engine not
running.
The "Reference" signal also triggers the fuel
injection system. Without the "Reference" signal the
engine cannot run.
OM-CAR SERVICE
SETTING TIMING
The initial base timing is set by disconnecting the
timing connector, located near the blower motor.
Refer to Emission Control Information Label for
procedure.
This will cause Code 42 to store in the code
memory of the ECM.
The memory must be cleared
after setting timing.
How Code 42 Is Determined
When the system is running on the HE1 module,
that is no voltage on the bypass line, the
HE1 module
grounds the EST signal.
The ECk1 expects to see no
voltage
on the EST line during this condition. If it sees
a voltage, it sets code 42 and will not go into the EST
mode.
When the rpm for EST
is reachecl bout 300 rprn)
the ECM applies 5 volts to the bypass line and the E:SrI'
should no longer be grounded in the tIEI nodule so
the EST voltage should be varying.
If the bypass line is open or grounclecl, the IIEI
tnod~lle will not switch to EST mode so the EST
voltage will be low
and Code 42 will be set. Refer to
Section
"611" for on vehicle service.
PARTS INFORMATION
PART NAME GROUP
Controller, ECM
(Remanufi~ctured) ................ 3.670
.......................... Distributor 2.36 1
Module, Distr ........................ 3.380
........................... Coil, Distr 2.170