1988 PONTIAC FIERO radiator
[x] Cancel search: radiatorPage 22 of 1825

MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION OB-5
Throttle linkage inspection -- Inspect for inter-
ference, binding, damaged or missing parts.
Engine drive belts inspection - Inspect all
belts for cracks, fraying and wear. Adjust or replace as
needed.
Rear axle service (if equipped) - Check gear
lubricant level and add if needed. For cars equipped with a
limited slip rear axle, fluid does not require changing
(except Caprice and Corvette
- change fluid and required
additive at first
7,500 miles (12 500 km). See your
Owner's Manual or "Recommended Fluids
& Lubricants
Chart" in this section.
IF YOU USE YOUR GAR TO PULL A TRAILER,
CHANGE GEAR LUBRICANT EVERY 7,500 MILES
(12 500 KM).
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Power antenna - Clean and then lubricate power
antenna mast. The proper lubricant as shown in Figure
OB-2 should be used.
AT LEAST ONCE A YEAR
Lap and shoulder belts condition and opera-
tion
- Inspect belt system, including webbing, buckles,
latch plates, retractors, guide loops and anchors.
Moveable head restraint operation - On cars
with moveable restraints, make sure restraints stay in the
desired position. (See adjustment instructions in your
Owner's Manual.)
Seatback latch and recliner operation on
cars equipped
with recliner seat --- Be sure seat-
backs latch on those cars with folding seats using mechan-
ical latches. Make sure the recliner is holding by pushing
and pulling on the top of the
seatback while it is reclined.
See your Owner's Manual for seat operating information.
Spare tire and jack storage- Be alert to rattles
in rear of car. Make sure the space tire, all jacking equip-
ment, any tire inflator and any covers or doors are securely
stowed at all times. Oil jack ratchet or screw mechanism
after each use.
Key lock service - Lubricate key lock cylinder at
least annually.
Body lubrication service - Lubricate all body
door hinges including the tailgate or hatchback lid (if
equipped). Also lubricate the body hood, fuel door and
rear compartment hinges and latches including interior
glove box and counsel doors, and any folding seat
hardware.
"Fansmissionltransaxle neutral or clutch
starl switch operation
CAUnON: Before pedorming the follow-
ing safety switch check, be sure to have
enough room around the car. Then, firmly
apply both the parking brake (see your
Owner's Manual for procedure) and the
regular brakes. Do not use the accelerator pedal.
If the engine
starls, be ready to turn
off the ignition promptly. Take these pre-
cautions because the car could move
without warning and possibly cause per-
sonal injury or properly damage. On auto-
matic transmissionltransaxle cars, try to
starl the engine in each gear. The starler
should crank only in "Park" or "Neutral."
On manual transmissionltransaxle cars,
place the
shiR lever in "Neutral," push the
clutch halfway and try to starl. The starler
should crank only when the clutch is fully
depressed.
Steering column lock operation
- While
parked, try to turn key to "Lock" in each gear range. The
key should turn to "Lock" only when gear is in "Park" on
automatic or "Reverse" on manual
transmissionltransax-
le. On cars with key release lever, try to turn key toULock"
without depressing the lever. The key should turn to
"Lock" only with the key lever depressed. On all vehicles,
the key should come out only in "Lock."
Parking brake and transmissionltransaxle
"Park" mechanism operation
CAUT1ON:Before checking the holding
ability of the parking brake and automatic
transmissionltransaxle "Park" mecha-
nism, park on a fairly steep hill with
enough room for movement in the down-
hill direction. To reduce the risk of person-
al injury or property damage, be prepared
to apply the regular brakes promptly if the
car begins to move.
To check the parking brake, with the engine running and
transmission/transaxle in "Neutral." slowly remove foot
pressure from the regular brake pedal (until the car is held
by only the parking brake).
To check the automatic transmissionltransaxle "Park"
mechanism holding ability, release all brakes after shift-
ing the transmissionltransaxle to "Park."
ljnderbody flushing - At least every spring,
tlush from the underbody with plain water any corrosive
materials used for ice and snow removal and dust control.
Take care to thoroughly clean any areas where mud and
other debris can collect.
Sediment packed in closed areas
of the vehicle should be loosened before being flushed.
Engine cooling system service - Inspect
coolant and freeze protection. If dirty or rusty, drain, flush
and refill with new coolant. Keep coolant
at the proper
mixture as specified in your Owner's Manual. This pro-
vides proper freeze protection. corrosion inhibitor level
and engine operating temperature. Inspect hoses and re-
place if cracked. swollen or deteriorated. Tighten hose
clamps. Clean outside of radiator and air conditioning
condensor. Wash radiator filler cap and neck.
To help
ensure proper operation. a pressure test of both the cooling
system and cap is also recommended. (See maintenance
schedule charts in Figure
OB-l for the recommended
coolant change interval.)
Page 28 of 1825
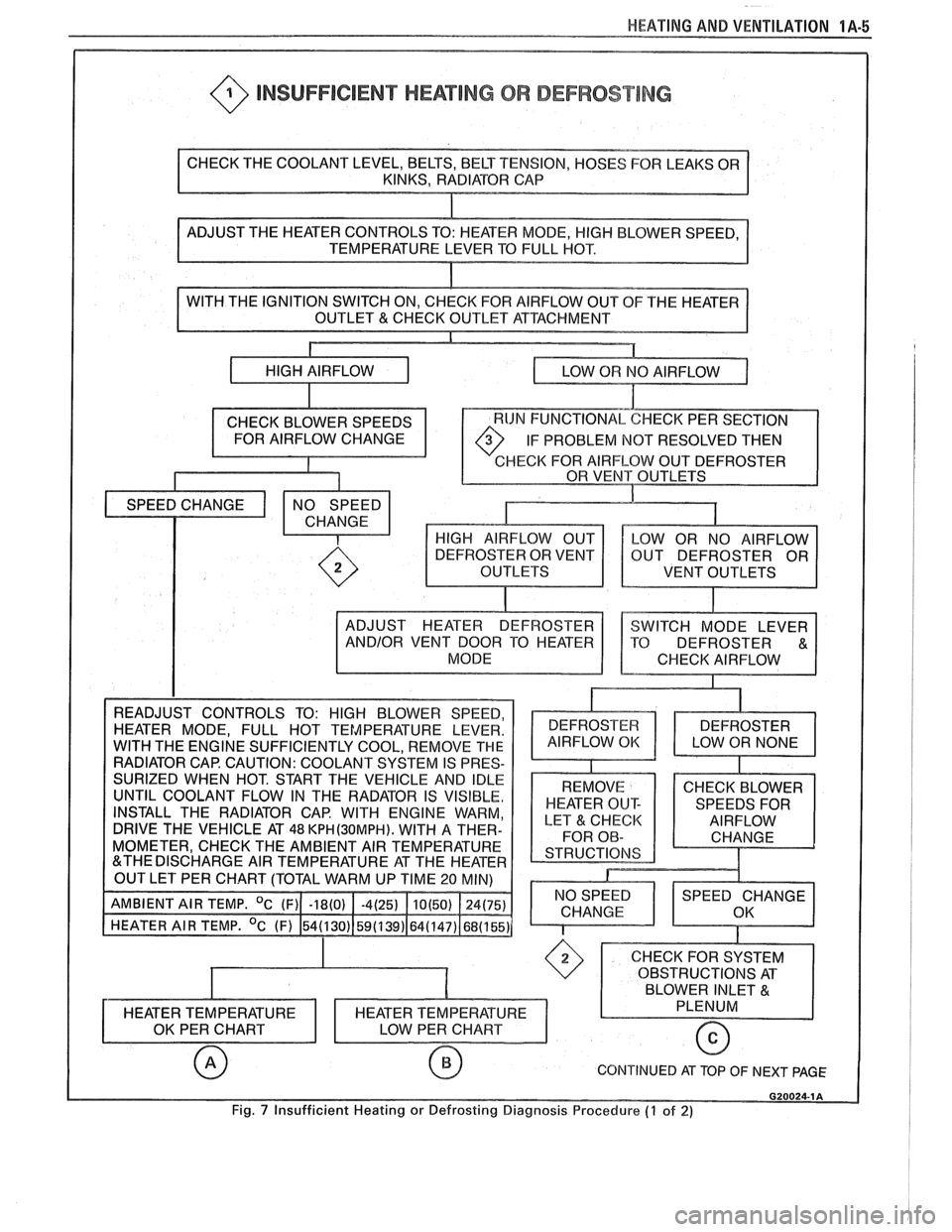
HEATING AND VENTILATION 1A-5
@ INSUFFICIENT HEATING OR DEFROST lNG
OF THE HEATER
IF PROBLEM
NOT RESOLVED THEN
HECK FOR AIRFLOW OUT DEFROSTER
VENT OUTLETS
INSTALL THE RADIATOR CAP. WITH ENGINE WARM,
DRIVE THE VEHICLE AT
48 KPH(3OMPH). WITH A THER-
MOMETER, CHECK THE AMBIENT AIR TEMPERATURE
CONTINUED AT TOP OF NEXT PAGE
Fig. 7 Insufficient Heating or Defrosting Diagnosis Procedure (7 of 2)
Page 45 of 1825
18-2 AIR CONDITIONING
SYSTEM GONIPONENE - FFUNCnIONAL
Compressor
All compressors are belt driven from the engine
crankshaft through the compressor clutch pulley. The
compressor pulley rotates without driving the com-
pressor shaft until an electromagnetic clutch coil is
energized. When voltage is applied to energize the
clutch coil, the clutch plate and hub assembly is
drawn rearward toward the pulley. The magnetic
force locks the clutch plate and pulley together as one
unit to drive the compressor shaft.
As the compressor shaft is driven, it compresses
the low-pressure refrigerant vapor from the evaporator
into a high-pressure, high-temperature vapor. Carried
with the refrigerant is the refrigerant oil which is used
to lubricate the compressor. Complete compressor
overhaul procedures can be found in Section
ID of the
General Service Manual.
Pressure Relief Valve
The compressor is equipped with a pressure
relief valve which is placed in the system as a safety
factor. Under certain conditions, the refrigerant on the
discharge side may exceed the designed operating
pressure. To prevent system damage, the valve is
designed to open automatically at approximately
3036
kPa (440 psi). Conditions that might cause this valve
to open (defective high pressure cut-off switch, inop-
erative electric cooling fan, etc.) should be corrected,
and the refrigerant oil and refrigerant should be
replaced as necessary.
A muffler is used on some refrigerant systems to
reduce compressor noises from high or low pressure
vibrations.
Condenser Gore
The condenser assembly in front of the radiator
is made up of coils which carry the refrigerant TO
cooling fins to provide rapid transfer of heat. The air
passing through the condenser cools the high-pressure
refrigerant vapor causing it to condense to a liquid.
Expansion (Orifice) Tube
The plastic expansion tube, with its mesh screen
and orifice, is located in the evaporator inlet pipe at
the liquid line connection. It provides a restriction to
the high-pressure liquid refrigerant in the liquid line,
metering the flow of refrigerant to the evaporator as a
low-pressure liquid. The expansion tube and orifice
are protected from contamination by filter screens on
both inlet and outlet sides. The tube is serviced only
as a replacement assembly.
When the engine is turned "OFF" with the
A/C
system operating, the refrigerant in the system will
flow from the high-pressure side of the expansion tube (orifice) to the low-pressure side until the pressure
is
equalized. This may be detected as a faint sound of
liquid flowing (hissing) for 30 to
60 seconds and is a
normal condition.
Evaporator Gore
The evaporator is a device which cools and
dehumidifies the air before it enters the car. High-
pressure liquid refrigerant flows through the expan-
sion tube (orifice) into the low-pressure area of the
evaporator. The heat in the air passing through the
evaporator core is transferred to the cooler surface of
the core, thereby cooling the air. As the process of
heat transfer from the air to the evaporator core sur-
face is taking place, any moisture (humidity) in the air
condenses on the outside surface of the evaporator
core and is drained off as water.
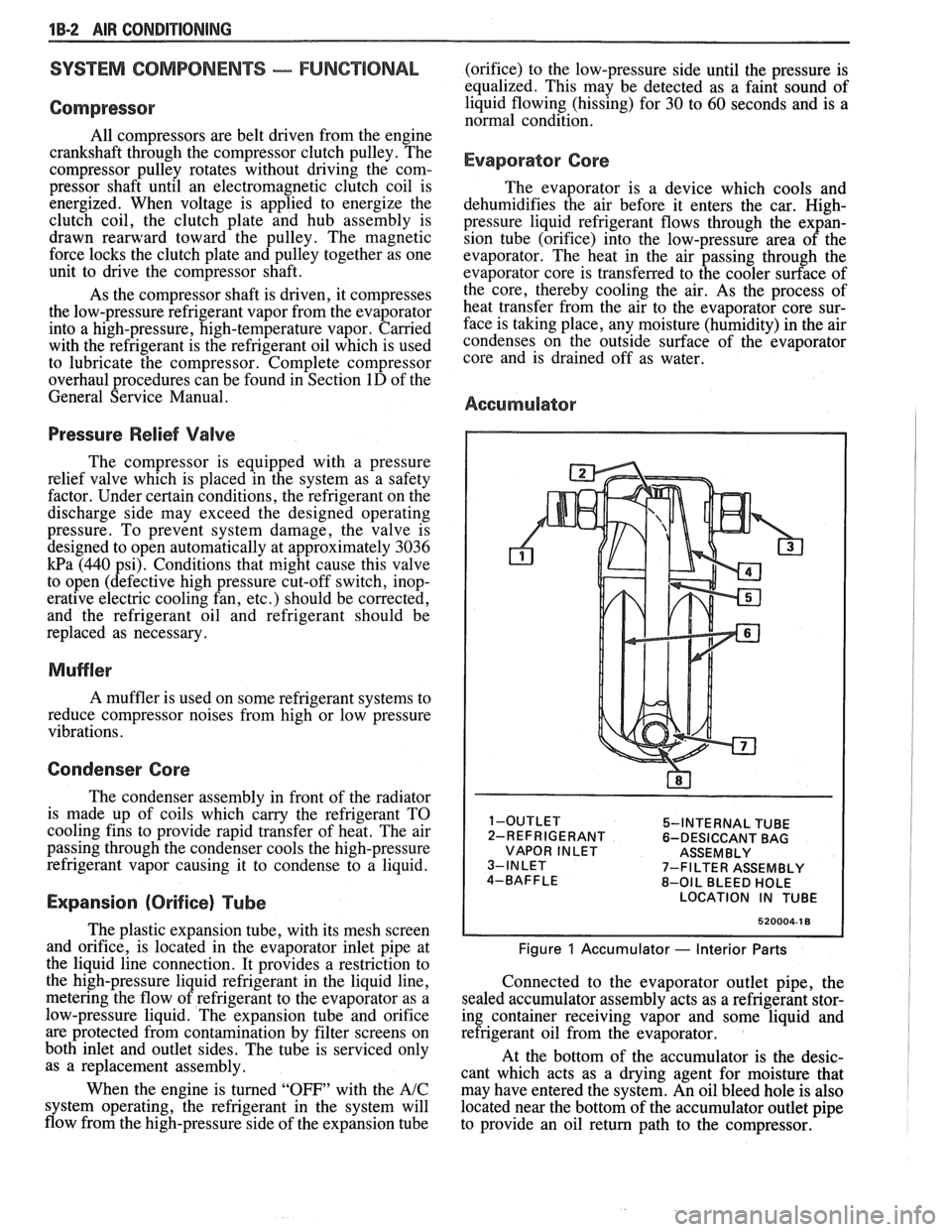
Accumulator
5-INTERNAL TUBE
2-REFRIGERANT 6-DESICCANT BAG
VAPOR INLET ASSEMBLY
7-FILTER ASSEMBLY
8-OIL BLEED HOLE
LOCATION IN TUBE
520004-1 8
Figure 1 Accumulator - Interior Parts
Connected to the evaporator outlet pipe, the
sealed accumulator assembly acts as a refrigerant stor-
ing container receiving vapor and some liquid and
refrigerant oil from the evaporator.
At the bottom of the accumulator is the desic-
cant which acts as a drying agent for moisture that
may have entered the system. An oil bleed hole is also
located near the bottom of the accumulator outlet pipe
to provide an oil return path to the compressor.
Page 48 of 1825
AIR CONDITIONING 113-5
DIAGNOSIS
TESTING THE REFRIGERANT SYSEEM
If a malfunction in the refrigerant system is sus-
pected, check the following:
1. Check outer surfaces of radiator and condenser
cores to be sure air flow is not blocked by dirt,
leaves or other foreign material. Be sure to
check between the condenser and radiator as
well as the outer surfaces.
2. Restrictions or kinks in the condenser core,
hoses, tubes, etc.
3. Blower fan operation (see Section 8A).
4. Check all air ducts for leaks or restrictions. Low
air flow rate may indicate a restricted evaporator
core.
5. Compressor clutch slippage.
6. Improper drive belt tension.
7. See C.C.O.T. AIC system diagnostic
procedures.
InsufFicient Cooling "Quick-Check"
Procedure
The following "HAND-FEEL" procedure can
be used to approximate whether or not the
AIC system
has the proper charge of Refrigerant- 12 (providing air
temperature is above
2 1°C [70°F])on most models. This check can
be made in a matter of minutes and
may simplify system diagnosis by pinpointing the
problem to the amount of
W- 12 charge in the system or
by eliminating low charge possibility from the overall
checkout.
1. Engine must be
warm(CH0KE OPEN and OFF
FAST IDLE SPEED CAM) and at normal idle
speed.
2. Hood and body doors open.
3. Selector (mode) button set at "NORM."
4. Temperature lever at full COLD.
5. Blower on "HI."
6. "Hand-Feel" temperature of evaporator inlet
pipe after orifice, and accumulator surface, with
compressor engaged.
BOTH SAME TEMPERATURE AND
BOTH SAME DEGREE COOLER
THAN AMBIENT
- Proper condition:
check for other problems; (see Testing the
Refrigerant System).
@ Leak check. If leak found, dis-
charge and repair as required. Evac-
uate and recharge.
e If no leak found, see A/C System
Diagnostic Procedures.
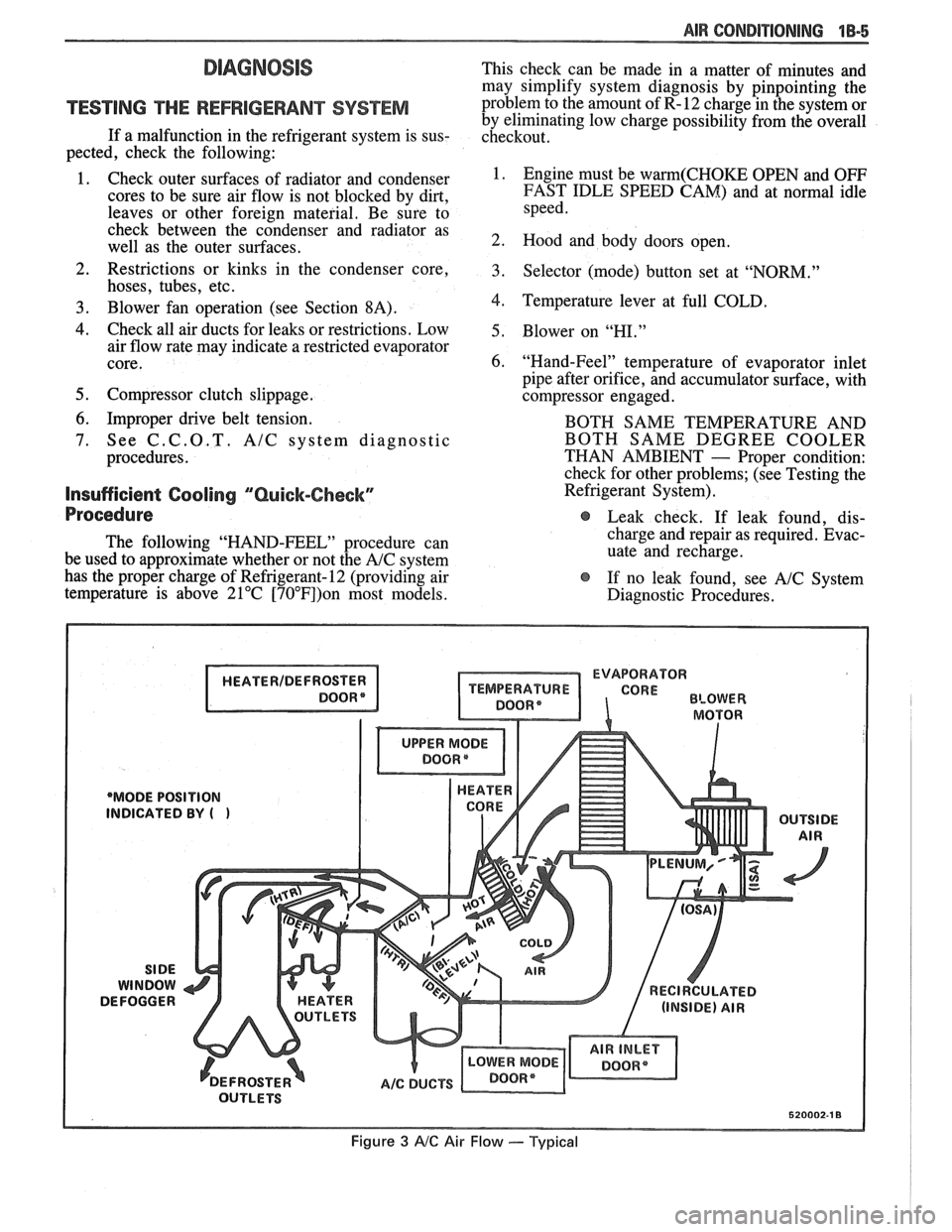
EVAPORATOR
'MODE POSITION
INDICATED
BY (
Figure 3 AIC Air Flow --- Typical
Page 67 of 1825
1B-24 AIR CONDPTIBNING
EVAPORATOR CORE
Remove QP Disconnect
1. Discharge A/C system.
2. Remove accumulator.
3. Remove two (2) screws and remove hi-blower
relay terminal.
4. Remove upper case screws.
5. Relocate wiring harness and remove dipstick.
6. Disconnect liquid line fitting.
7. Remove upper case and lift evaporator core out
of case (retain foam wedge).
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall.
2. Recharge and test system for proper operation.
EVAPBRAWORCASE
Remove or Disconnect
1. Remove accumulator.
2. Remove blower motor.
3. Remove evaporator core.
Remove lower case to cowl screws (three driven from engine compartment, three driven from
interior).
Remove case from cowl.
Install or Connect
Reverse removal procedure to reinstall. Rein-
stall or replace gaskets, seal and sealant
removed during disassembly.
Recharge and test system for proper operation.
NG COMPRESSOR (TYPICAL)
Remove or Disconnect
1. Discharge A/C system.
2. Remove fitting block (coupled hose assembly)
bolt at rear of compressor.
3. Remove mounting bracket bolt(s) .
4. Remove drive belt (route lower loop behind har-
monic balancer to gain additional slack if
required).
5. Remove compressor. If complete compressor is
to be replaced, transfer usable switches, etc. to
new compressor.
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal
procedure to reinstall. Use
new O-rings lubricated with
525 viscosity
refrigerant oil. Refer to Section
6B for drive belt
tension.
2. Evacuate and recharge system.
CONDENSER
a Remove or Disconnect
1. Discharge A/C system.
2. Disconnect coupled hose and liquid line fittings.
3, Remove screws retaining top radiator shield.
4. Remove top condenser retaining screws.
5. Carefully move (tilt) radiator rearward and lift
condenser out of radiator support.
6. Transfer brackets and mounts to new condenser
if replacement is necessary.
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall. Use
new O-rings lubricated with
525 viscosity
refrigerant oil.
2. Recharge and test system for proper operation.
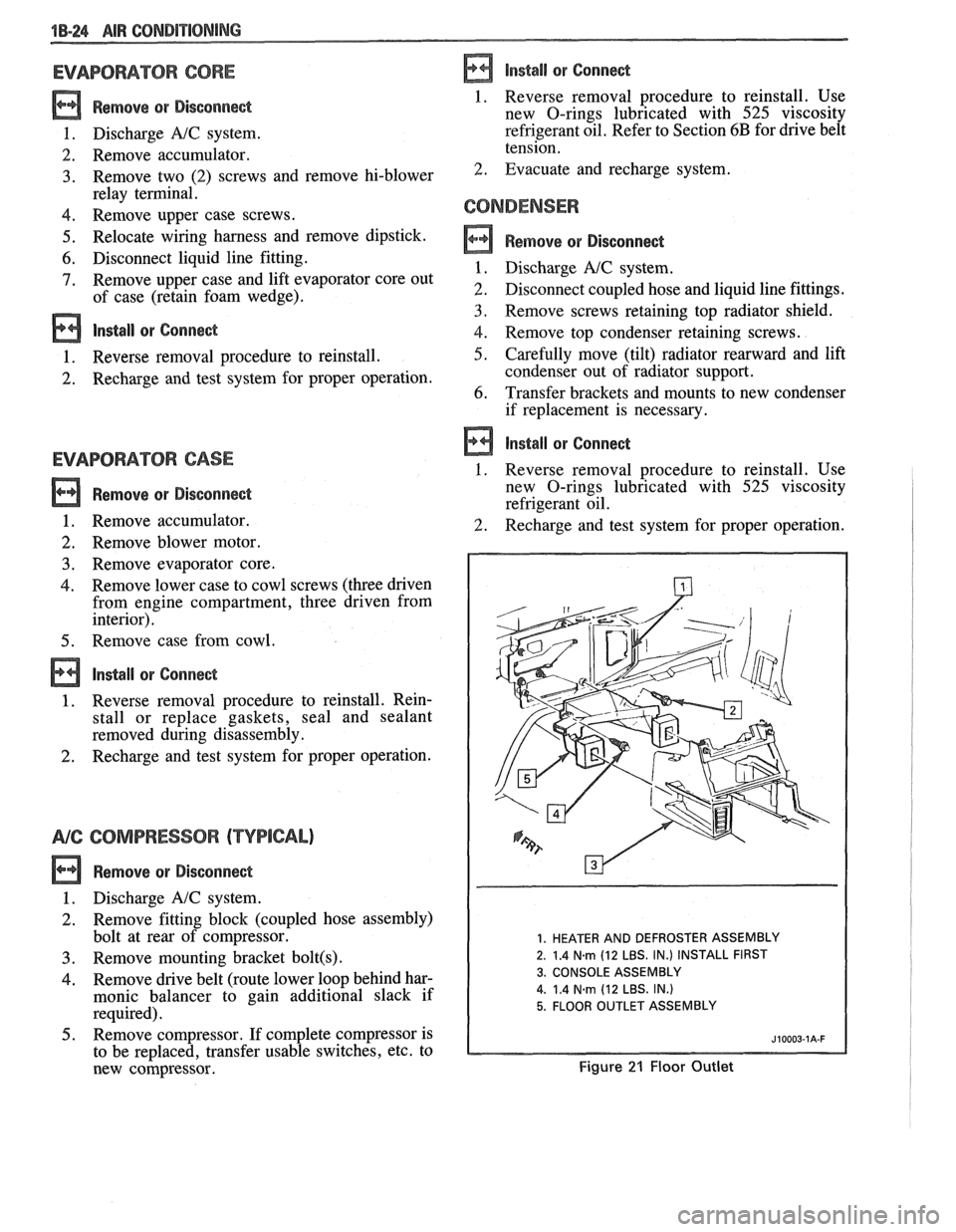
1. HEATER AND DEFROSTER ASSEMBLY
2. 1.4
N.m (12 LBS. IN.) INSTALL FIRST
3. CONSOLE ASSEMBLY
4.
1.4 Narn (12 LBS. IN.)
5. FLOOR OUTLET ASSEMBLY
Figure 21 Floor Outlet
Page 69 of 1825
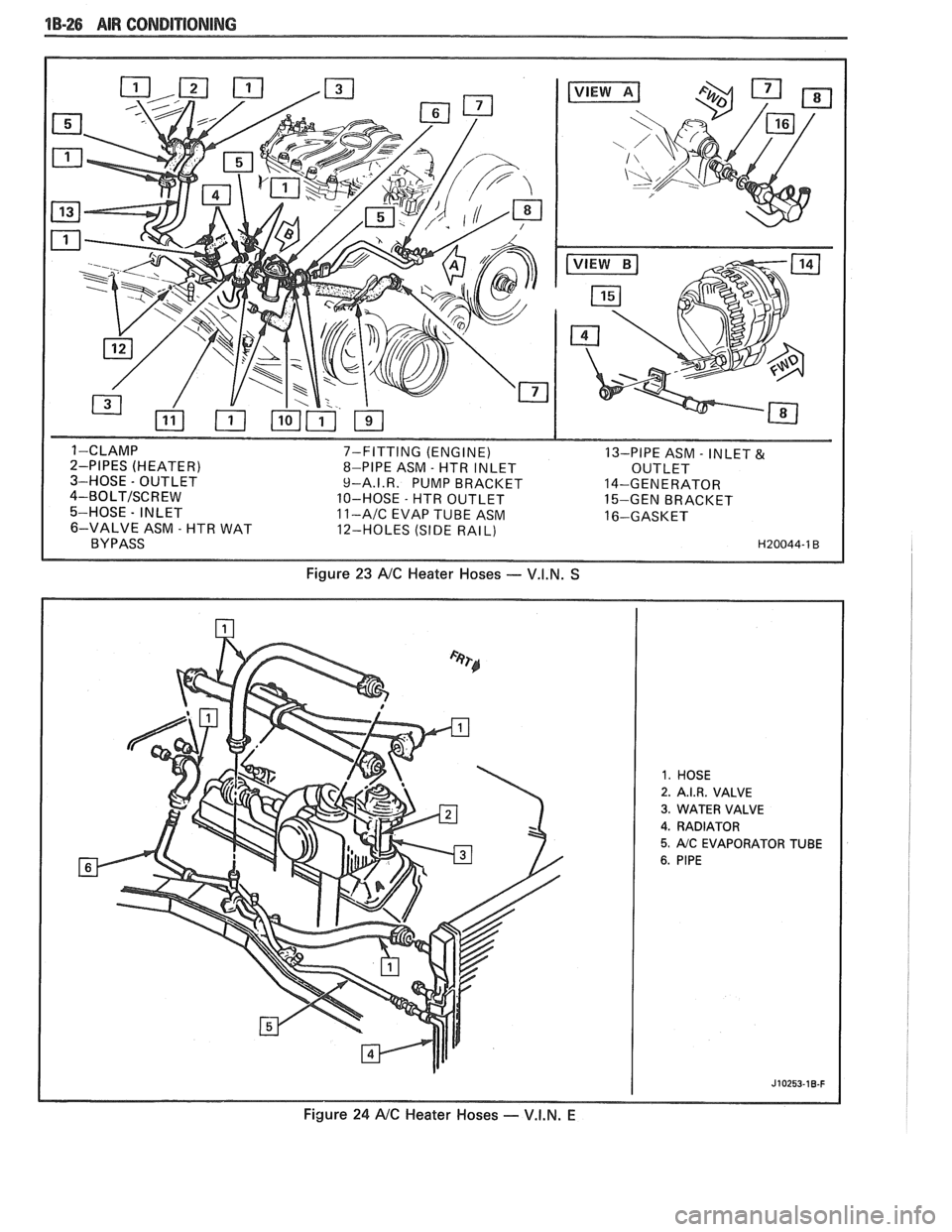
1B-26 AIR CONDITIONING
7-FITTING (ENGINE)
13-PIPE ASM - INLET & 8-PIPE ASM - HTR INLET
OUTLET
9-A.I.R. PUMP BRACKET 14-GENERATOR
10-HOSE
- HTR OUTLET
15-GEN BRACKET 11-AIC EVAP TUBE ASM 16-GASKET
12-HOLES (SIDE RAIL)
Figure 23 NC Heater Hoses - V.I.N. S
2. A.I.R. VALVE
3. WATER VALVE
4. RADIATOR
5. AIC EVAPORATOR TUBE
Figure 24 NC Heater Hoses - V.I.N. E
Page 70 of 1825
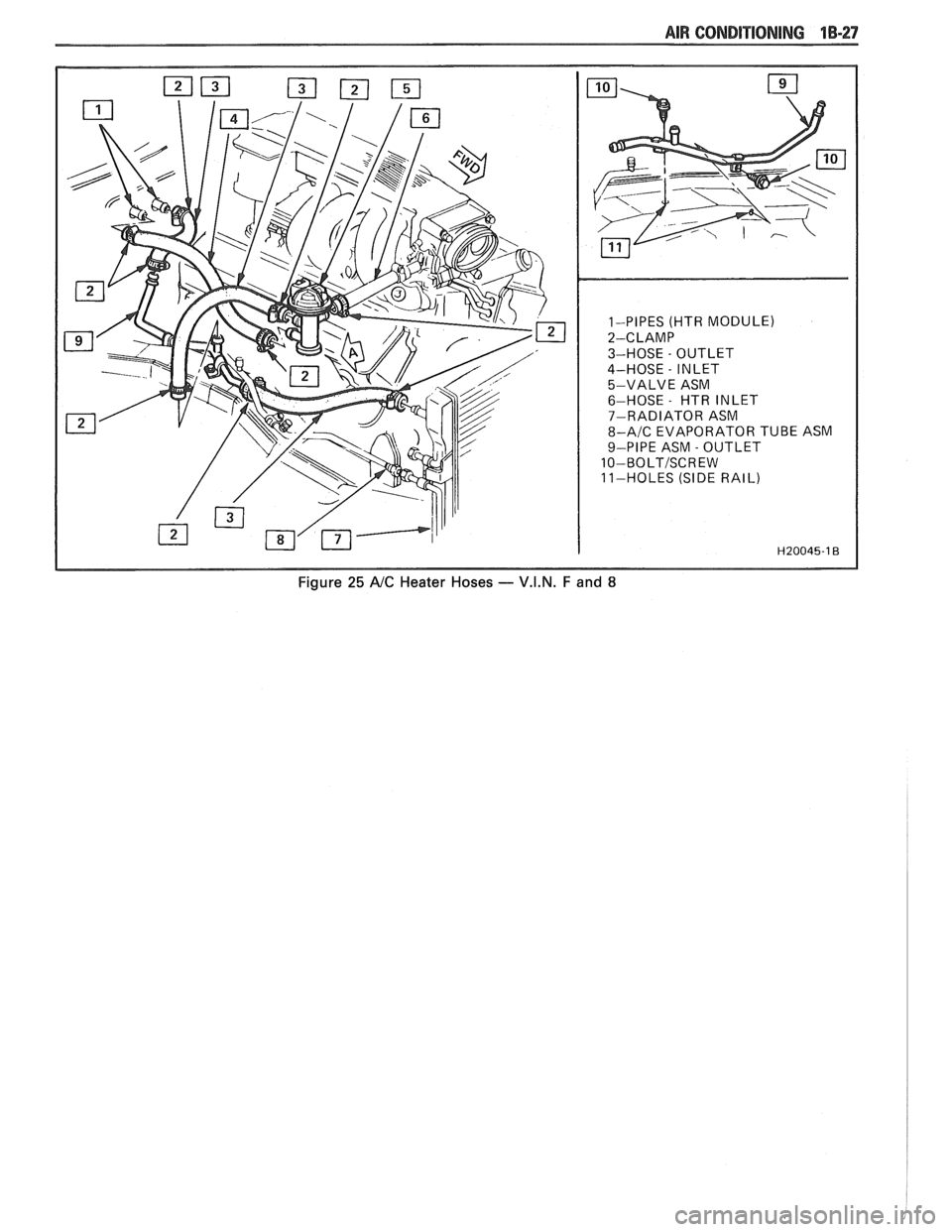
1-PIPES (HTR MODULE)
2-CLAMP
3-HOSE
- OUTLET
4-HOSE
- INLET
5-VALVE ASM
6-HOSE
- HTR INLET
7-RADIATOR ASM
8-A/C EVAPORATOR TUBE ASM
9-PIPE ASM
- OUTLET
10-BOLTISCREW
11-HOLES (SIDE RAIL)
Figure 25 A/C Heater Hoses - V.I.N. F and 8
Page 75 of 1825
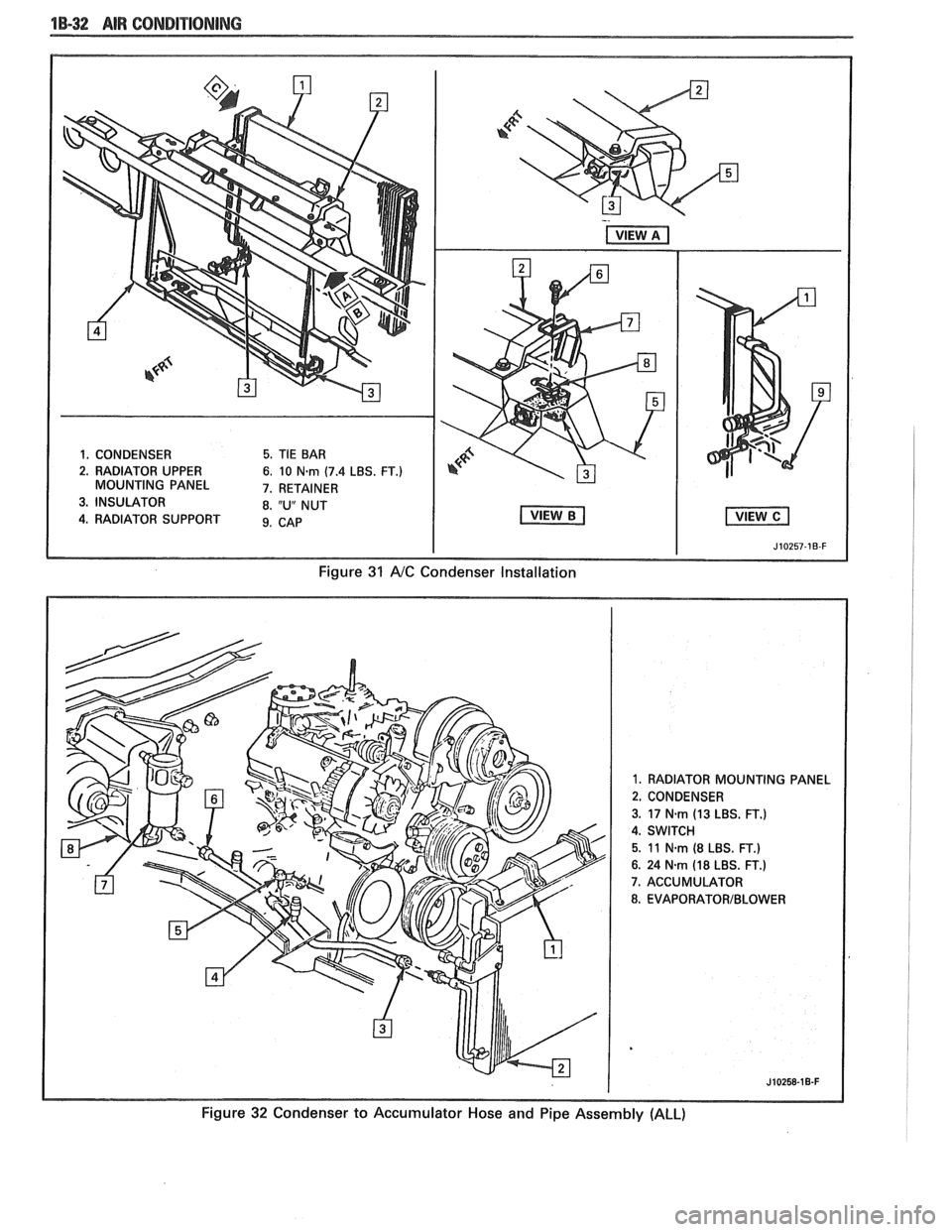
1B-32 AIR CONDITIONING
1. CONDENSER 5. TIE BAR
2. RADIATOR UPPER
6. 10 N-rn (7.4 LBS. FT.) MOUNTING PANEL 7. RETAINER
3. INSULATOR 8. "U" NUT
4. RADIATOR SUPPORT 9. CAB
I I J10257-1B-F
Figure 31 A/C Condenser Installation
1. RADIATOR MOUNTING PANEL
2. CONDENSER
3.
17 N.rn (13 LBS. FT.)
4. SWITCH
5. 11 N-rn (8 LBS. FT.)
6. 24 Nsm (18 LBS. FT.)
7. ACCUMULATOR
8. EVAPORATORIBLOWER
Figure 32 Condenser to Accumulator Hose and Pipe Assembly (ALL)