1988 PONTIAC FIERO engine coolant
[x] Cancel search: engine coolantPage 898 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) 6E3-C2-11
3. Separate left hand fuel rail and plug assembly
(200) from right hand fuel rail and plug assembly
(220).
4. Bracket-to-rail
attaching screw assembly (256),
two bracket-to-base attaching screw assemblies
(258) and pressure regulator and base assembly
bracket
(255).
5. Screw
assembly (235), which attaches fuel outlet
tube to right hand rail (220).
6. Base to right hand rail screw assembly (275).
7. Pressure regulator and base assembly (240) from
right hand rail assembly (220).
8. Rotate regulator and base assembly to remove
from fuel outlet tube.
9. Base to rail connector (250).
10. O-ring seals and discard:
@ Connector (252).
@ Fuel outlet tube (224).
@ Rear crossover tube (267).
@ Front crossover tube (232).
Important
When removing O-ring seals, note locations and
sizes, to assure correct replacement and re-
assembly.
Inspect
@ O-rings and sealing surfaces, for damage that
could prevent proper sealing.
- Replace any damaged O-ring seals.
n Install or Connect
1. Lubricate with engine oil, and install O-ring seals:
@ Connector (252).
@ Fuel outlet tube (224).
@ Rear crossover tube (267).
@ Front crossover tube (232).
Base-to-rail connector (250) in pressure regulator
and base assembly (240).
Regulator and base assembly on fuel outlet tube.
Rotate the regulator and base assembly to install
base to rail connector
(250) into right hand rail
assembly
(220).
Base to right hand rail screw assembly (275).
Pressure regulator and base assembly bracket
(2551, two brackets to base attaching screw
assembly (258) and bracket to rail attaching screw
assembly (256).
Rear bracket attaching screw assembly
(235).
Left hand rail and plug assembly (2001, with front
and rear crossover tubes (230) and
265), to right
hand rail and tube assembly
(220).
Rear crossover tube retainer (270) and retainer to
base screw assembly
(273).
240PRESSUREREGUbATORAND
BASE ASSEMBLY
Figure C2-13 Fuel Pressure Regulator
10. Front crossover tube retainer (234) and retainer
attaching screw assembly
(235).
Tighten
@ Above mentioned seven assemblies to 5 N-m
(44 in. lbs.).
COLD START FUEL INJECTION SWITCH
Remove or Disconnect
1. Air inlet duct.
2. Alternator bracket.
3. Electrical connector
4. Switch.
Install or Connect
1. Coat threads with pipe sealant.
2. Reverse
removal procedure to reinstall.
THROTTLE BODY
Remove or Disconnect
I. Air inlet duct.
2. IAC and 'I'PS connectors.
3. Vacuum lines.
4. Coolant hoses (2).
5. 'I'hrottle, 'L'V, and cruise control cables.
6. Throttle body retaining bolts.
a Install or Connect
1, Reverse procedure to reinstall.
2. Refill
radiator with lost coolant. Refer to Figure
C2-14 for torque specifications.
Page 899 of 1825

6E3-C2-12 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
UNIT REPAIR PROCEDURES
Figure C2-14 Throttle Body Removal
THROTTLE BODY SERVICE
IDENTIFICATION
An eight digit identification number is stamped
on the throttle body casting, next to the coolant cover,
as shown in Figure C2-15. Refer to this model
identification number if servicing or part replacement
is required.
Names of component parts will be found on the
numbered list that accompanies the exploded view
(Figure
C2-18). Numbers used to identify parts in the
exploded views also are used to identify the same parts
in other illustrations of this manual.
IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
Figure C2-15 Throttle Body Identification
TPS Adjustment
Refer to Section "C-1" for TPS replacement or
adjustment. The unit repair procedures cover component
replacement with the unit on the vehicle. However,
throttle body replacement requires that the complete
unit be removed from the engine. If removed, it may
be placed on a holding fixture, such as
5-9789-118, BT-
3553, or equivalent, to prevent damage to the throttle
valve.
Cleaning and a Inspection
Throttle body parts, except as noted below, may be
cleaned in a cold-immersion-type cleaner such
a; AC
Delco X-55 or equivalent.
NOTICE: The throttle position sensor (TPS), idle air
control
(IAC) valve, throttle body with
cover and seals or gaskets in place, should
NOT be soaked in liquid solvent or
cleaner, as they may be damaged. If TPS
or IAC valve is still mounted in the
throttle body, do not immerse throttle
body.
I. Clean all metal parts throughly and blow dry with
shop air. Be sure all air passages are free of burrs
and dirt.
2. Inspect mating casting surfaces for damage that
could affect gasket sealing.
MINIMUM IDLE SPEED CHECK
The idle stop screw (161, used to regulate
minimum idle speed of the engine, is adjusted at the.
factory, then is covered with a plug (15) to discourage
unnecessary readjustment. However, if it is necessary
to gain access to the idle stop screw assembly, proceed
as shown in Figure C2-16.
Before checking minimum idle speed, be sure
ignition timing is correct and, before making any idle
speed adjustments, be sure throttle body is clean
around the throttle plates.
Adjust
1. Pierce
the idle stop screw plug (15) with an awl,
and apply leverage to remove it.
2. Adjust idle stop screw assembly
(16) as required.
Page 900 of 1825
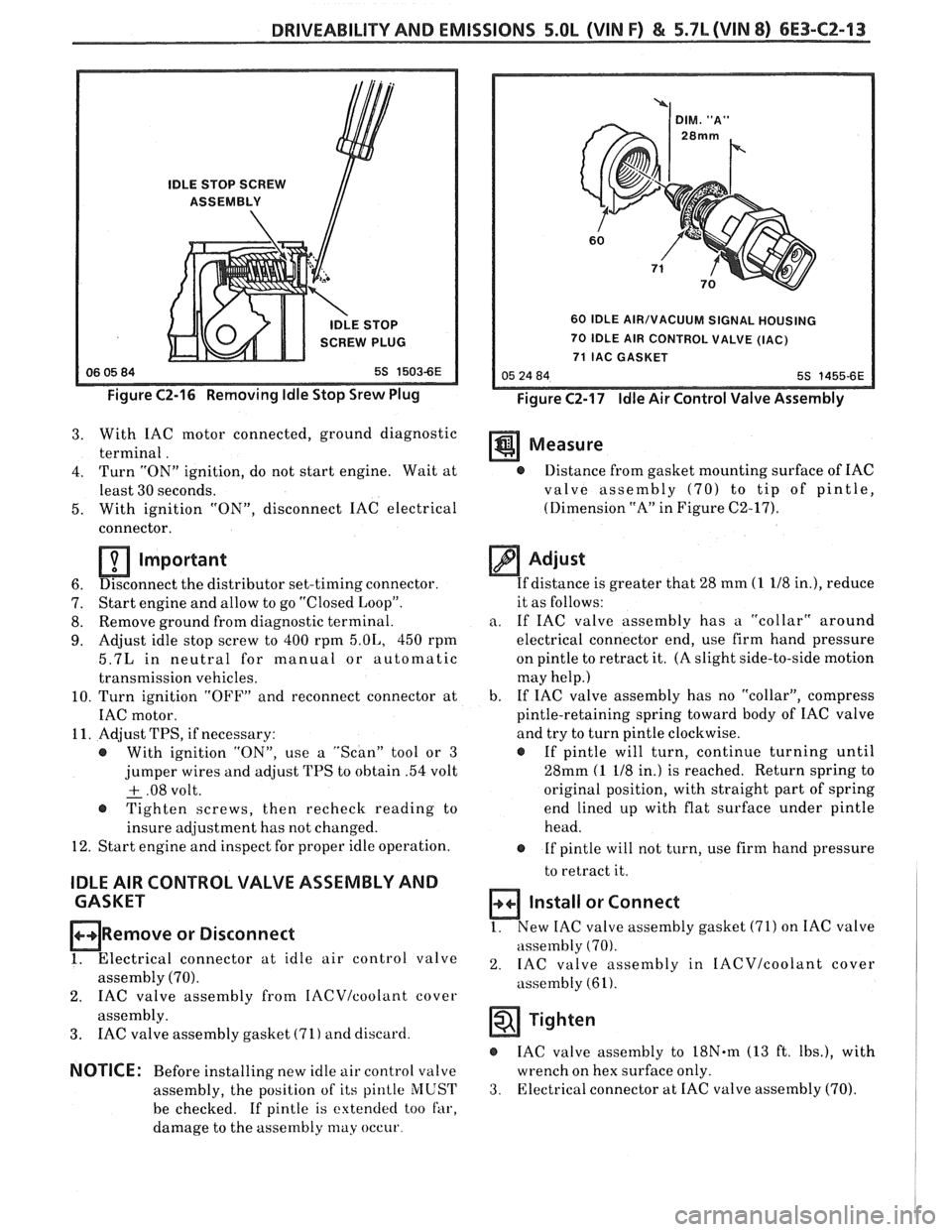
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7b (VIN 8) 6E3-CZ-13
IDLE STOP SCREW
ASSEMBLY
IDLE STOP
SCREW PLUG
Figure C2-16 Removing Idle Stop Srew Plug
60 IDLE AIR/VACUUM SIGNAL HOUSING
70 IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE (IAC)
71 IAC GASKET
Figure C2-17 Idle Air Control Valve Assembly
3. With IAC motor connected, ground diagnostic
terminal. Measure
4. Turn "ON" ignition, do not start engine. Wait at @ Distance from gasket mounting surface of IAC
least 30 seconds. valve assembly
(70) to tip of pintle,
5. With ignition
"ON", disconnect IAC electrical (Dimension
"A" in Figure C2-17).
connector.
Important
6. Disconnect
the distributor set-timing connector.
7. Start
engine and allow to go "Closed Loop".
8. Remove
ground from diagnostic terminal.
9. Adjust idle stop screw to 400 rpm 5.01,, 450 rpm
5.7L in neutral for manual or automatic
transmission vehicles.
10. Turn ignition "OFF" and reconnect connector at
IAC motor.
11. Adjust TPS, if necessary:
@ With ignition "ON", use a "Scan" tool or 3
jumper wires and adjust TPS to obtain .54 volt
+ .08 volt. - @ Tighten screws, then recheck reading to
insure adjustment has not changed.
12. Start engine and inspect for proper idle operation.
IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE ASSEMBLY AND
CASKET
ORemove or Disconnect
1. Electrical connector at idle air control valve
assembly (70).
2. IAC valve assembly from IACVIcoolant cover
assembly.
3. IAC valve assembly gasket (71) and discard.
NOTICE: Before installing new idle air control valve
assembly, the position of its
pinlle MUST
be checked. If pintle is extended too far,
damage to the assembly
may occur
Adjust
If distance is greater that 28 mm (1 118 in.), reduce
it as follows:
a. If IAC valve assembly has a "collar" around
electrical connector end, use firm hand pressure
on pintle to retract it. (A slight side-to-side motion
may help.)
b. If
IAC valve assembly has no "collar", compress
pintle-retaining spring toward body of IAC valve
and try to turn pintle clockwise.
@ If pintle will turn, continue turning until
28mm
(1 118 in.) is reached. Return spring to
original position, with straight part of spring
end lined up with flat surface under pintle
head.
@ If pintle will not turn, use firm hand pressure
to retract it.
Install or Connect
1. New IAC valve assembly gasket (71) on IAC valve
assembly
(70).
2. IAC valve assembly in IACVIcoolant cover
assembly (61).
Tighten
IAC valve assembly to 18N.m (13 ft. Ibs.), with
wrench on hex surface only.
3. Electrical connector at IAC valve assembly (70).
Page 902 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (WIN F) & 5.7L (WIN 8) 6E3-C2-15
Important
No physical adjustment is made to the IAC
assembly after installation. IAC
valve resetting
occurs after reinstallation on the vehicle, and is
reset after the engine is started and then the
ignition turned "OFF".
THROTTLE BODY
PARTS INFORMATION
FIGURE CZ-18
PART NAME PART #
. Gasket Flange ......................... 1
Throttle Body Assembly .................. 10
Plug . Idle Stop Screw .................... 15
Screw Assembly - Idle Stop. ................ 16
Spring
- Idle Stop Screw ................... 17
Sensor - Throttle Position (TPS) ............. 20
Screw Assembly
- TPS Attaching ............ 21
Retainer
- TPS Attaching Screw ............. 22
Cover-CleanAir........................ 41
Screw Assembly
- Clean Air Cover
Attaching...
.......................... 42
Gasket
- Clean Air Cover .................. 43
IACVICoolant Cover Assembly ............. 61
Screw Assembly
- IACV Cover
Assembly to Throttle Body
................ 62
Gasket
- IACVICoolant Cover to
Throttle Body..
........................ 63
Valve Assembly
- ldle Air Control
(IAC) ................................ 70
Gasket
- IAC Valve Assembly .............. 71
CLEAN AIR COVER AND GASKET
ORemove or Disconnect
1. Clean
air cover attaching screw assemblies (42)
2. Clean air cover (41).
3. Clean air cover gasket (43).
@ Cover mounting surface to ensure a good seal.
Install and Connect
1. New clean air cover gasket (43) on throttle body
assembly
(10).
2. Clean air cover (41).
3. Clean air cover attaching screw assemblies (42).
61 IACVICOOLANT COVER ASSV 62 SCREW ASSY . IACV COVER ASSY TO THROrRE BODV 63 GASKET. IACV COOLANT COVER TO THROTTLE BODY 70 VALVE ASSV -IDLE AIR CONTROL 71 GASKET - IDLE AIR COHTROLVALVE
Figure C2-19 ldle Air Control/Coolant Cover
Assembly
IDLE AIR CONTRBLICOOLANT COVER
ASSEMBLY (Figure
CZ-19)
(With Throttle Body Removed From Engine)
a Remove or Disconnect
1. Idle
air control (IAC) valve assembly (70) from
IACVIcoolant cover assembly. (See "Idle Air
Control Valve and Gasket" instructions.)
2. IACV
cover assembly to throttle body screw
assemblies
(62).
3. Cover assembly (61).
4. Cover
assembly to throttle body gasket (63) and
discard.
alnstall or Connect
Clean
e Throttle body gasket mounting surface to
ensure a good seal.
e Sealing surface for damage that could prevent
sealing properly or
cause coolant leak.
a Install and Connect
1. New IACVIcoolant cover
assembly to throttle body
gasket
(63).
2. IACV/coolant cover assembly (61).
3. IACV
cover assembly to throttle body screw
assemblies
(62).
Page 907 of 1825
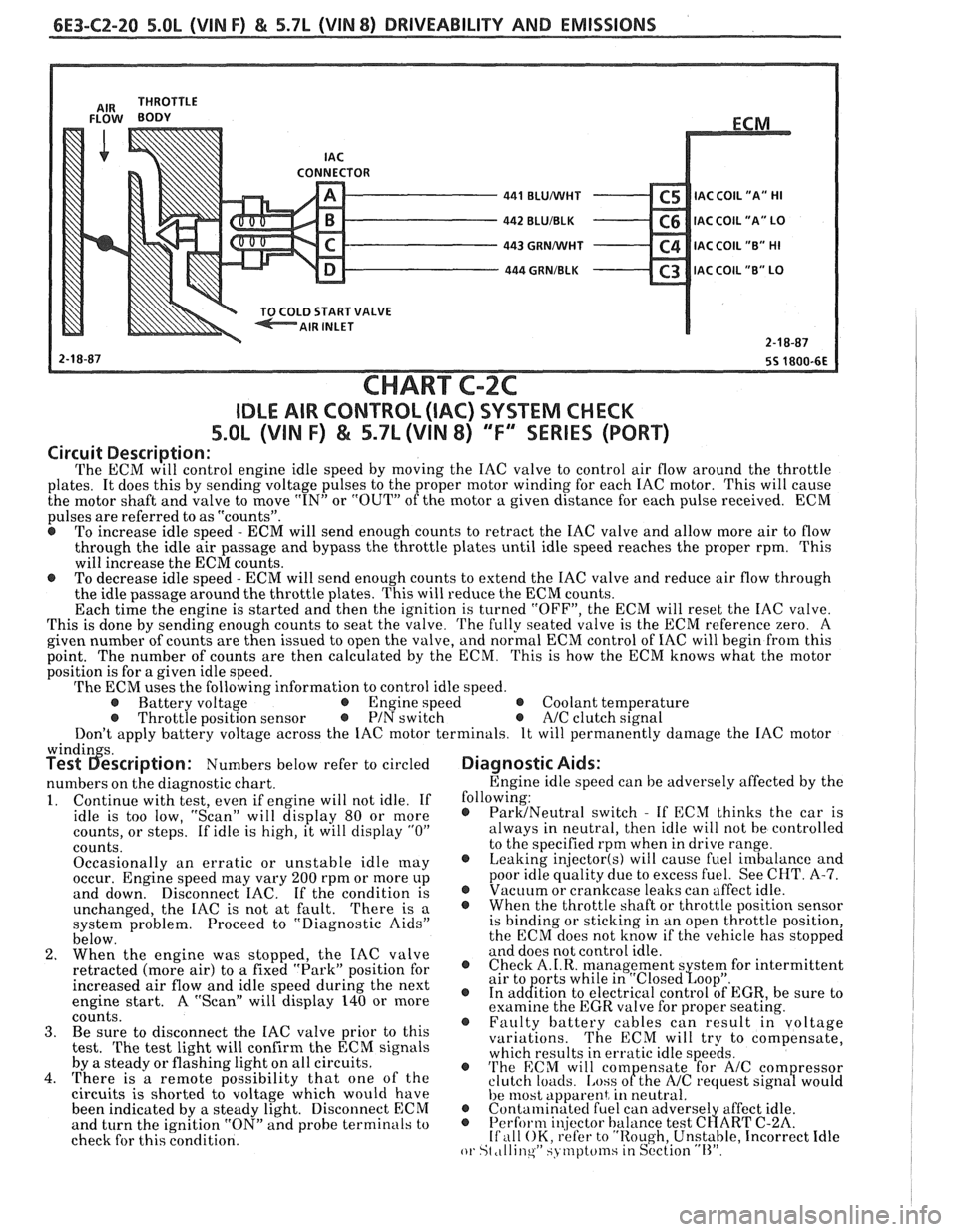
6E3-C2-20 5.0L (VIN F) & 5.7L (WIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CONNECTOR - 441 BLUMlHT C5 IAC C0lL1'A" HI - 442 BLUIBLK C6 IAC COIL "A" LO - 443 GRNMlHT C4 IAC COIL "B" HI - 444 GRNIBLK C3 lAC COIL "B" LO v
START VALVE
CHART C-2C
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) SYSTEM CHECK
S.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) "F'" SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The ECM will control engine idle speed by moving the IAC valve to control air flow around the throttle
plates. It does this by sending voltage pulses to the proper motor winding for each IAC motor. This will cause
the motor shaft and valve to move
"IN" or "OUT" of the motor a given distance for each pulse received. ECM
pulses are referred to as "counts".
@ To increase idle speed - ECM will send enough counts to retract the IAC valve and allow more air to flow
through the idle air passage and bypass the throttle plates until idle speed reaches the proper rpm. This
will increase the ECM counts.
e To decrease idle speed - ECM will send enough counts to extend the IAC valve and reduce air flow through
the idle passage around the throttle plates. This will reduce the ECM counts.
Each time the engine is started and then the ignition is turned "OFF", the ECM will reset the IAC valve.
This is done by sending enough counts to seat the valve.
The fully seated valve is the ECM reference zero. A
given number of counts are then issued to open the valve, and normal ECM control of IAC will begin from this
point. The
number of counts are then calculated by the ECM. This is how the ECM knows what the motor
position is for a given idle speed.
The ECM uses the following information to control idle speed.
@ Battery voltage @ Engine speed @ Coolant temperature @ Throttle position sensor @ PIN switch e A/C clutch signal
Don't apply battery voltage across the IAC motor terminals. It will permanently damage the IAC motor
windin s. Test 6escription: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Continue with test, even if engine will not idle. If
idle is too low, "Scan" will display 80 or more
counts, or steps. If idle is high, it will display
"0"
counts.
Occasionally an erratic or unstable idle
[nay occur. Engine speed may vary 200 rpm or more up
and down. Disconnect IAC. If the condition is
unchanged, the IAC is not at fault.
There is a
system problem. Proceed to "Diagnostic Aids"
below.
2. When the engine was stopped, the IAC valve
retracted (more air) to
a fixed "Park" position for
increased air flow and idle speed during the next
engine start. A "Scan" will display 140 or more
coiints. 3. Be sure to disconnect the IAC valve prior to this
test.
The test light will confirm the ECM signals
by a steady or flashing light on all circuits.
4. There is a remote possibility that one of the
circuits is shorted to voltage which would have
been indicated by a steady light. Disconnect ECM
and turn the ignition "ON" and probe terminals to
check for this condition.
Diagnostic Aids:
Engine idle speed can be adversely affected by the
following:
@ ParMNeutral switch - If ECM thinks the car is
always in neutral, then idle will not be controlled
to the specified rpm when in drive range.
@ Leaking injector(s) will cause fuel imbalance and
poor idle quality due to excess fuel. See CHT.
A-7. @ Vacuum or crankcase leaks can affect idle. @ Whenthethrottleshaftorthrottlepositionsensor
is binding or sticking in an open throttle position,
the ECM does not know if the vehicle has stopped
and does not control idle.
@ Check A.I.R. management s stem for intermittent
air to orts while in "~losed~oo~". @ In ad&tion to electrical control of EGR, be sure to
examine the EGR valve for proper seating.
@ Faulty battery cables can result in voltage
variations. The ECM will try to compensate,
which results in erratic idle speeds.
@ 'I'he ECM will com ensate for A/C com ressor
clutch loacls. [.ass ofthe NC request sign8 would
he 11lost apparent, in neutral. @ Contalninatecl fuel can adverse1 affect idle. @ Perform i~!jector balance test C~ART C-2A. If ,111 OK, refer to "Rough, Unstable, Incorrect Idle or St ,tllinqW SJ tnptcfinsiin S~'ction "11''.
Page 913 of 1825
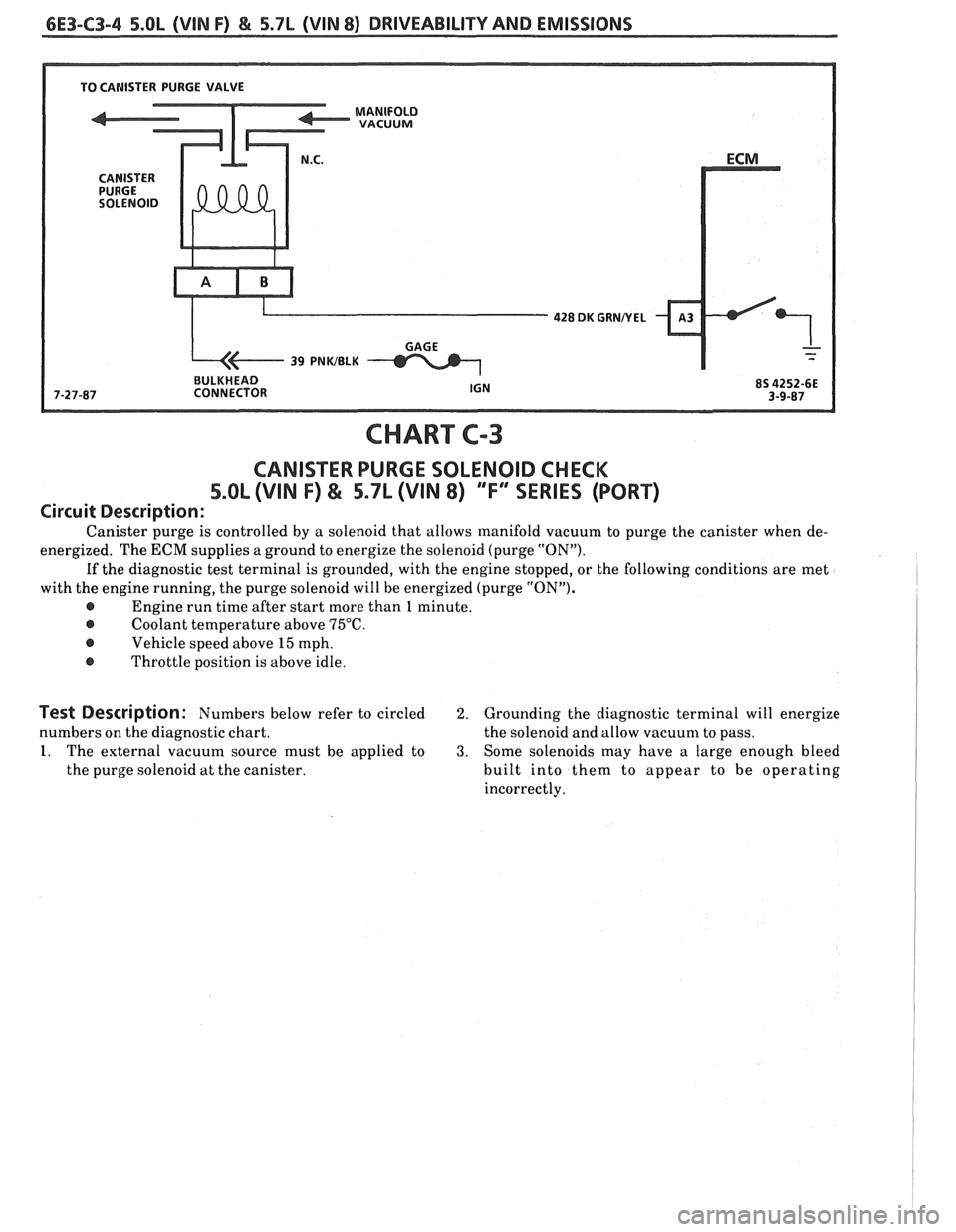
6E3-C3-4 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
428 DK GUNNEL
BULKHEAD
CHART
CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID CHECK
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) ""FYSERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
Canister purge is controlled by a solenoid that allows manifold vacuum to purge the canister when de-
energized. The
ECM supplies a ground to energize the solenoid (purge "ON").
If the diagnostic test terminal is grounded, with the engine stopped, or the following conditions are met
with the engine running, the purge solenoid will be energized (purge "ON").
@ Engine run time after start more than 1 minute.
@ Coolant temperature above 75°C.
@ Vehicle speed above 15 mph.
@ Throttle position is above idle.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled 2. Grounding the diagnostic terminal will energize
numbers on the diagnostic chart. the solenoid and allow vacuum to pass.
1. The external vacuum source must be applied to 3. Some solenoids may have a large enough bleed
the purge solenoid at the canister. built into them to appear to be operating
incorrectly.
Page 916 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) 6E3-C4-1
SECTION C4
IGNIION SYSTEM 1 EST
..................... GENERAL DESCRIPTION ................ C4-1 ON-CAR SERVICE C4-2
.................. PURPOSE ......................... C4-1 SETTING TIMING.. C4-2
OPERATION ....................... C4-1 HOW CODE 42 IS DETERMINED.. ....... C4-2
................. RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION .... C4-1 PARTS INFORMATION C4-2
DIAGNOSIS ......................... C4-1
CODE12.......................... C4-1
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
PURPOSE
The high energy ignition (HEI) system controls
fuel combustion by providing a spark to ignite the
compressed
airlfuel mixture at the correct time. To
provide improved engine performance, fuel economy,
and control of exhaust emissions, the
ECM controls
distributor spark advance (timing) with the electronic
spark timing (EST) system.
Only the electronic spark timing (EST) system
will be described here. Additional information on the
FIE1 system is found in Section "6D".
To properly control ignitionlcombustion timing
the ECM needs to know:
e Crankshaft position
e Engine speed (rpm)
@ Mass Air Flow
@ Engine temperature
OPERATION
The EST system consists of the distributor
module, ECM, and connecting wires. The connector
terminals are lettered as shown in CHART C-4.
These circuits perform the following functions:
@ Distributor reference (CKT 430).
This provides the ECM with rpm and crankshaft
position information.
If the wire becomes open or
grounded the engine will not run, because the ECM
will not operate the injectors.
If the engine cranks hut
won't run, see CHART
A-3.
e Reference ground (CKT 453).
This wire is grounded in the distributor and
makes sure the ground circuit has no voltage drop
which could affect performance. If it is open, it may
cause poor performance.
@ Bvpass (CKT 424).
At about 400 rpm, the ECM applies
5 volts to this
circuit to switch spark timing control from the
I-IEI
module to the ECM. The wire goes through a
connector between the 4 wire connector and the ECM.
This is disconnected to the set hase timing. An
open or grounded bypass circuit will set a Code
42 and the engine will run at base timing, plus a small
amount of advance built into the
HE1 module.
@ EST (CKT 423). - This circuit triggers the HE1 module after the
engine is started and no Code 42 detected. The ECM
does not know what the actual timing is, but it does
know when it gets the reference signal. It then
advances or retards the spark from that point.
Therefore, if the base timing is set incorrectly, the
entire spark curve will be incorrect.
RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION
An open or ground in the EST circuit will set u
Code 42 and cause the engine to run on the HE1
module timing. This will cause reduced performance
and poor fuel economy.
The ECM uses information from the
MAE' and
coolant sensors in addition to rpm to calculate spark
advance as follows:
e Cold engine = more spark advance.
r Engine under minimum load based on rpm
and low amount of air flow- more spark
advance. Hot engine
= less spark advance.
@ Engine under heavy load based on rpm and
high amount
of air flow- less spark advance.
DIAGNOSIS
The description, operation, and repair procedures
of the
HE1 system are found in Section "6D" of this
manual. For an ignition system check, refer to
CHART C-4 at the end of this section.
CODE 12
Code 12 is used during the diagnostic circuit check
procedure to test the code display ability of the
ECM
This code indicates that the ECM is not receiving the
engine rpm (REFERENCE) signal.
'Phis occurs with
the ignition key
"ON", and the engine not running.
Page 939 of 1825
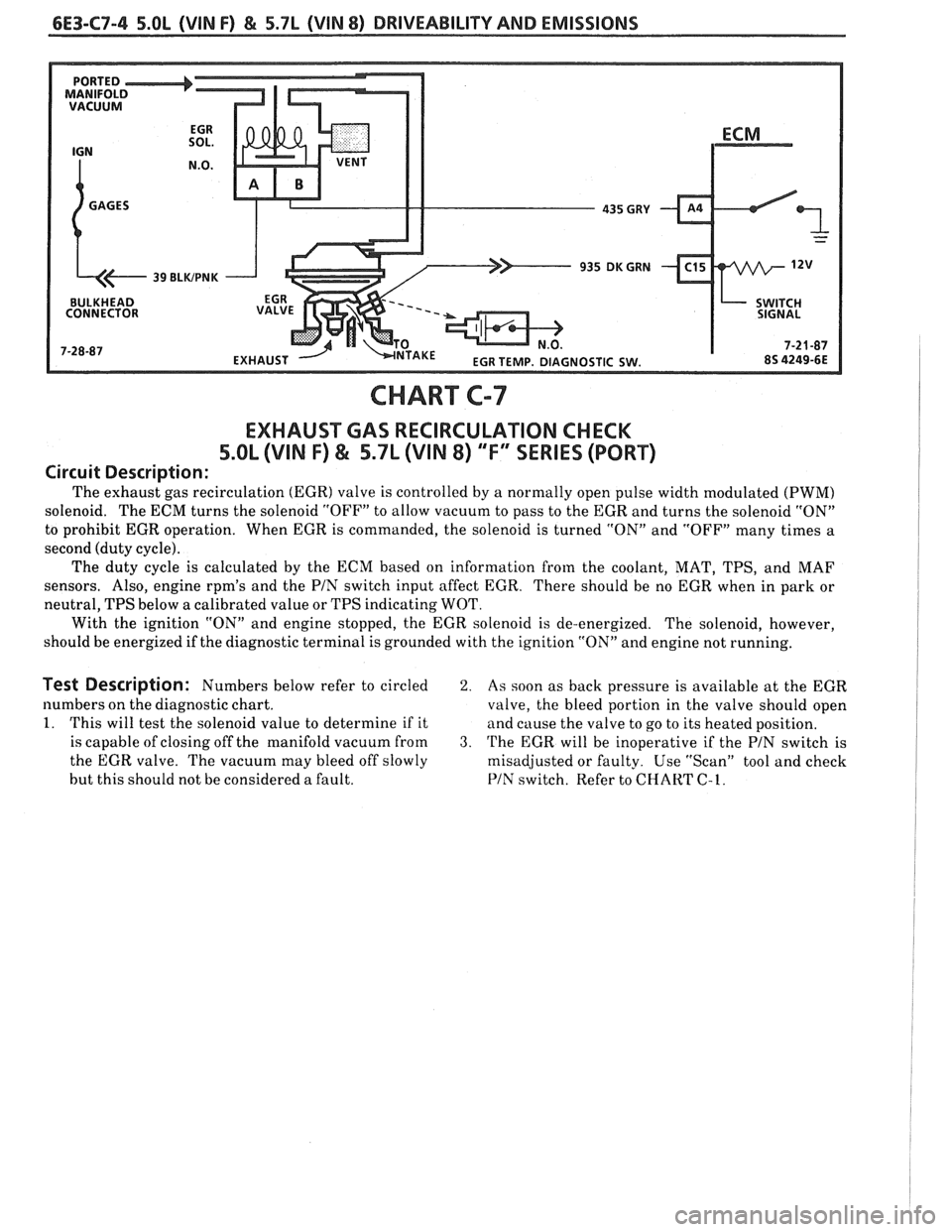
6E3-C7-4 5.OL (VIN F) €4 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CHART C-7
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION CHECK
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) "F" SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve is controlled by a normally open pulse width modulated (PWM)
solenoid. The ECM turns the solenoid "OFF" to allow vacuum to pass to the EGR and turns the solenoid "ON"
to prohibit EGR operation. When EGR is commanded, the solenoid is turned "ON" and "OFF" many times a
second (duty cycle).
The duty cycle is calculated by the ECM based on information from the coolant, MAT, TPS, and MAF
sensors. Also, engine
rpm's and the PIN switch input affect EGR.
There should be no EGR when in park or
neutral, TPS below
a calibrated value or TPS indicating WOT.
With the ignition "ON" and engine stopped, the EGR solenoid is de-energized. The solenoid, however,
should be energized if the diagnostic terminal is grounded with the ignition "ON" and engine not running.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled 2. As soon as back pressure is available at the EGR
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
valve, the bleed portion in the valve should open
1. This will test the solenoid value to determine if it
and cause the valve to go to its heated position.
is capable of closing off the manifold vacuum from
3. 'I'he EGR will be inoperative if the PIN switch is
the EGR valve. The vacuum may bleed off slowly
misadjusted or faulty. Use "Scan" tool and check
but this should not be considered a fault.
PIN switch. Refer to CHART C-1.