Page 383 of 962
![SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 1987 Service Repair Manual Fig. 18-43 @ Tire tread wear indicator
@ Wear indicating platform
[ Inflation of tires]
l Tire inflation pressures are listed on the
Tire Placard at driver’s side of instrument
panel.
l Tire inflati SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 1987 Service Repair Manual Fig. 18-43 @ Tire tread wear indicator
@ Wear indicating platform
[ Inflation of tires]
l Tire inflation pressures are listed on the
Tire Placard at driver’s side of instrument
panel.
l Tire inflati](/manual-img/20/57437/w960_57437-382.png)
Fig. 18-43 @ Tire tread wear indicator
@ Wear indicating platform
[ Inflation of tires]
l Tire inflation pressures are listed on the
Tire Placard at driver’s side of instrument
panel.
l Tire inflation pressures should be checked
(including spare tire) at least monthly and
when significantly changing the load in the
car.
l Always check tire inflation pressures when
tires are “cold”.
l Always use tire pressure gauge when checking
inflation pressure.
l Be sure to reinstall tire inflation valve caps to
prevent dirt and moisture from getting into
valve core, as they may cause air leakage.
l If air loss occurs while driving, do not drive
on the deflated tire more than is needed to
stop safety. Driving even a short distance on a
deflated tire can damage a tire and wheel
beyond repair.
NOTE:
Before installing wheels, remove any build-up of
corrosion on the wheel mounting surface and
brake drum or disc mounting surface by scraping
and wire brushing. Installing wheels without
good metal-to-metal contact at the mounting
surfaces can cause wheel nuts to loosen, which
can later allow a wheel to come off while the
car is moving.
RADIAL TIRES
.i II
9T
\
I
4-wheels
Fig. 18-44
fT
u
[I
5-wheels
[Wheels]
Wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented,
have excessive lateral or radial runout, leak air
through welds, have elongated bolt holes, if
lug nuts won’t stay tight, or if they are heavily
rusted. Wheels with greater runout than shown
in below figure may cause objectional vibrations.
Replacement wheels must be equivalent to the
original equipment wheels in load capacity,
diameter,rim width, offset and mounting
configuration. A wheel of improper size or type
may affect wheel and bearing life, brake cooling,
speedometer/odometer calibration, car ground
clearance and tire clearance to the body and
chassis.
[Tire rotation]
“Rotate” tires at the regular intervals in order to
equalize tire wear and thereby make full use of
each tire. Refer to below figure for the scheme
of rotation. Adherence to this scheme prolongs
tire life.
18-20
Page 384 of 962
/I
d-
Limitl.Mmm(0.047 in)
1.20 mm(0.047 in 1
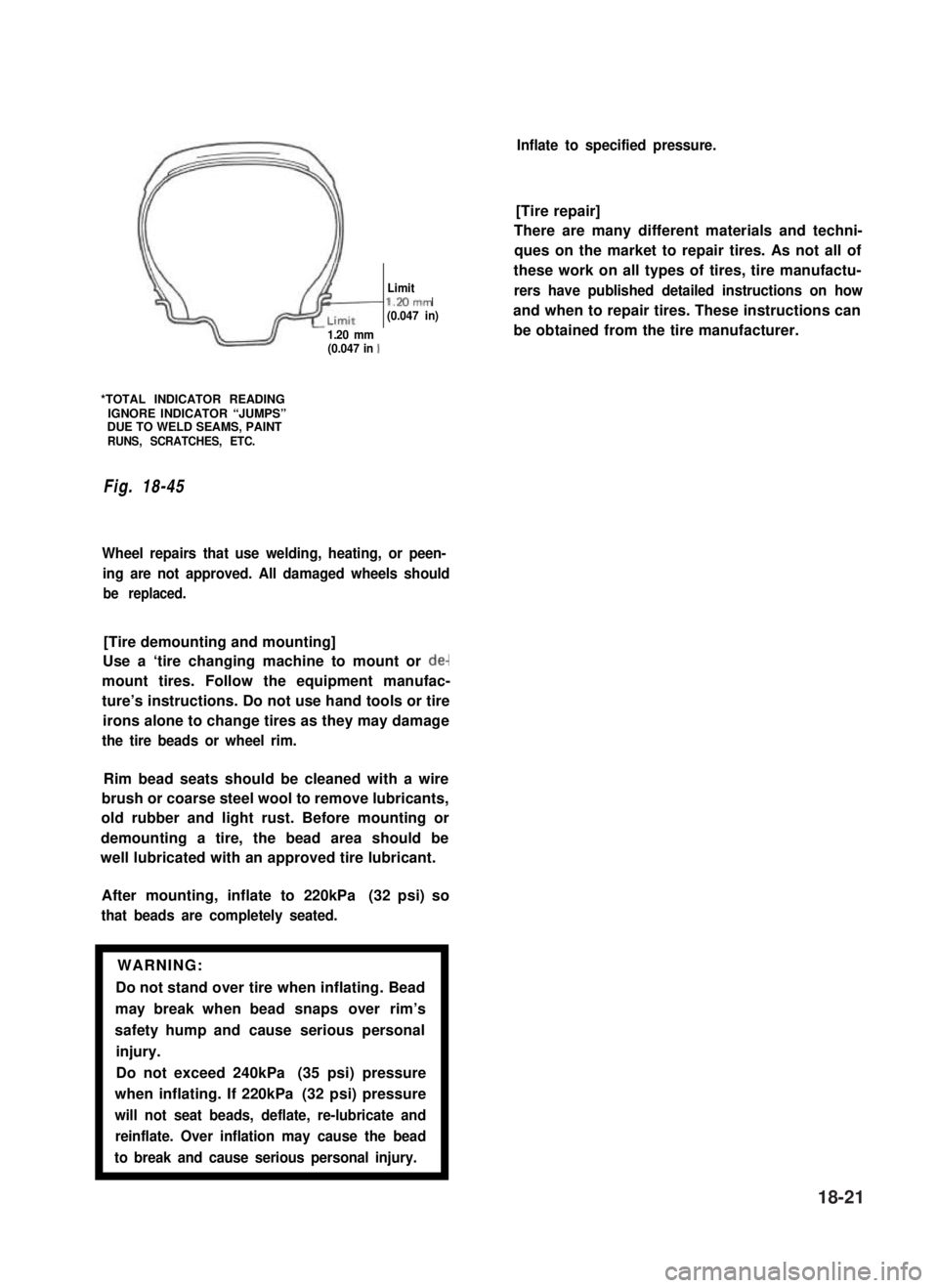
*TOTAL INDICATOR READINGIGNORE INDICATOR “JUMPS”DUE TO WELD SEAMS, PAINTRUNS, SCRATCHES, ETC.
Fig. 18-45
Wheel repairs that use welding, heating, or peen-
ing are not approved. All damaged wheels should
be replaced.
[Tire demounting and mounting]
Use a ‘tire changing machine to mount or de-
mount tires. Follow the equipment manufac-
ture’s instructions. Do not use hand tools or tire
irons alone to change tires as they may damage
the tire beads or wheel rim.
Rim bead seats should be cleaned with a wire
brush or coarse steel wool to remove lubricants,
old rubber and light rust. Before mounting or
demounting a tire, the bead area should be
well lubricated with an approved tire lubricant.
After mounting, inflate to 220kPa (32 psi) so
that beads are completely seated.
WARNING:
Do not stand over tire when inflating. Bead
may break when bead snaps over rim’s
safety hump and cause serious personal
injury.
Do not exceed 240kPa (35 psi) pressure
when inflating. If 220kPa (32 psi) pressure
will not seat beads, deflate, re-lubricate and
reinflate. Over inflation may cause the bead
to break and cause serious personal injury.1
Inflate to specified pressure.
[Tire repair]
There are many different materials and techni-
ques on the market to repair tires. As not all of
these work on all types of tires, tire manufactu-
rers have published detailed instructions on how
and when to repair tires. These instructions can
be obtained from the tire manufacturer.
18-21
Page 405 of 962
Inspection for Front Brake After installing
Mount tires and make certain that they rotate
smoothly, with a force of less than 3.0 kg (6.6
lb).
NOTE:
For the above check, the following must be
observed.
1) Jack up front wheels, both right and left,
off the ground.
2) Set free wheeling hubs of both right and left
wheels to “LOCK”, if equipped.
3) Shift transfer shift lever to 2H (rear wheel)
position.
4) The below figure shows outer periphery of
tire.
5) Be careful not to depress brake pedal when
checking tire for rotation.
tire rotation is heavy, check the following:
Wheel bearings for breakage.
Wheel bearing starting preload for proper
adjustment.
Disc for flatness (Improper flatness brings
disc into contact with lining during rotation
and makes rotation heavy).
To check this, measure disc deflection.
Spring measure
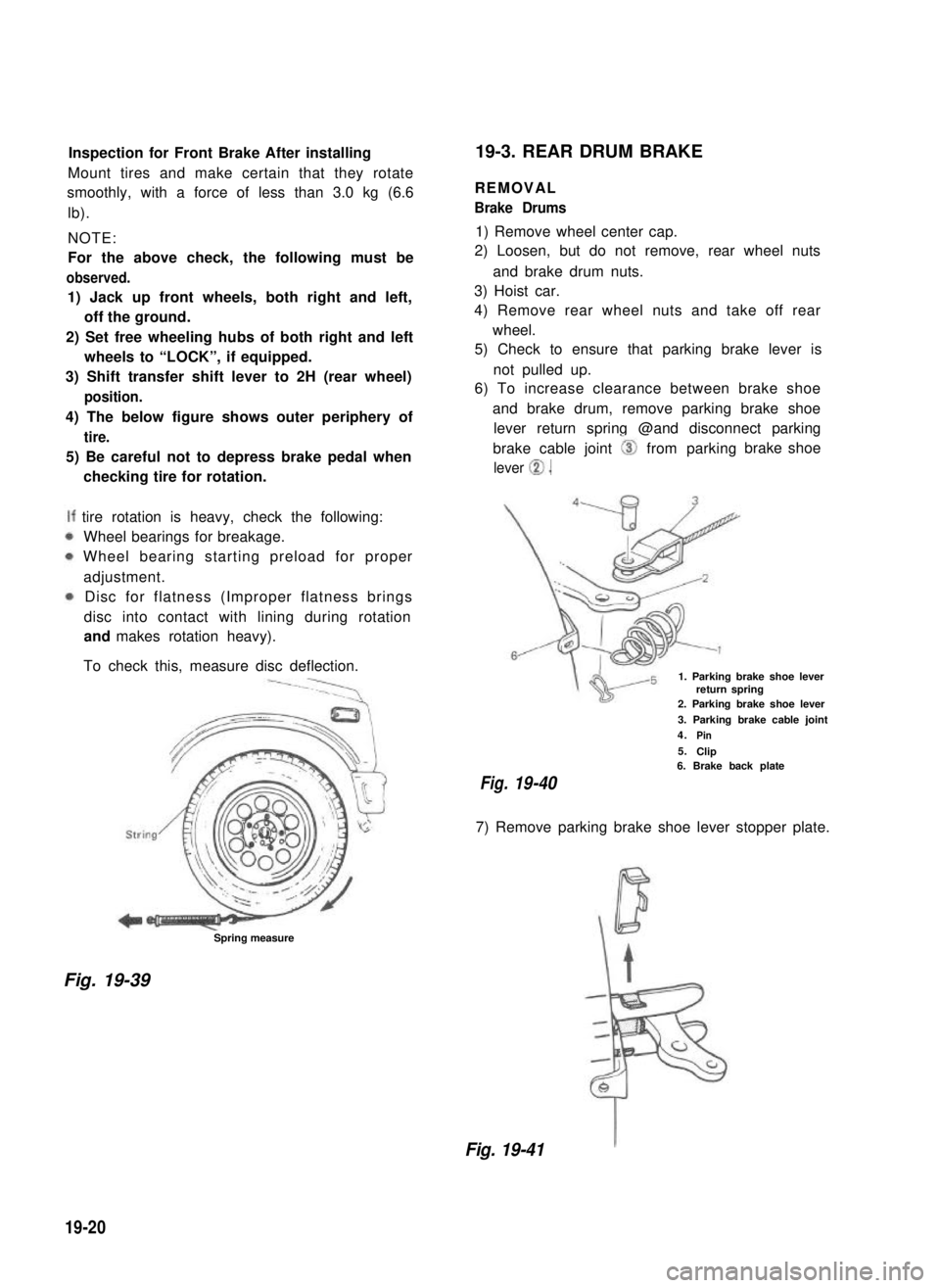
19-3. REAR DRUM BRAKE
REMOVAL
Brake Drums
1) Remove wheel center cap.
2) Loosen, but do not remove, rear wheel nuts
and brake drum nuts.
3) Hoist car.
4) Remove rear wheel nuts and take off rear
wheel.
5) Check to ensure that parking brake lever is
not pulled up.
6) To increase clearance between brake shoe
and brake drum, remove parking brake shoe
lever return spring @and disconnect parking
brake cable joint 0 from parking
lever 0.
brake shoe
1. Parking brake shoe leverreturn spring2. Parking brake shoe lever
3. Parking brake cable joint
4.Pin
5.Clip6. Brake back plate
Fig.19-40
7) Remove parking brake shoe lever stopper plate.
Fig. 19-39
Fig. 19-41
19-20
Page 452 of 962
HEADLIGHT INSPECTION
1.Lighting (Low beam, High beam, Passing)
2. Mounting
3.Dirt and cracks on lenses
4.Main beam axis direction and brightness
HEADLIGHT BEAM SETTING (STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Before setting the headlight beams, adjust air pressures of four tires to a specified value respectively. Move
the vehicle up and down by hand to settle its attitude. Then move it over a flat surface. There are available
a variety of headlight beams setting methods (e.g., the screen method using a focusing tester, etc.). How-
ever, the method described here does not use such tester.
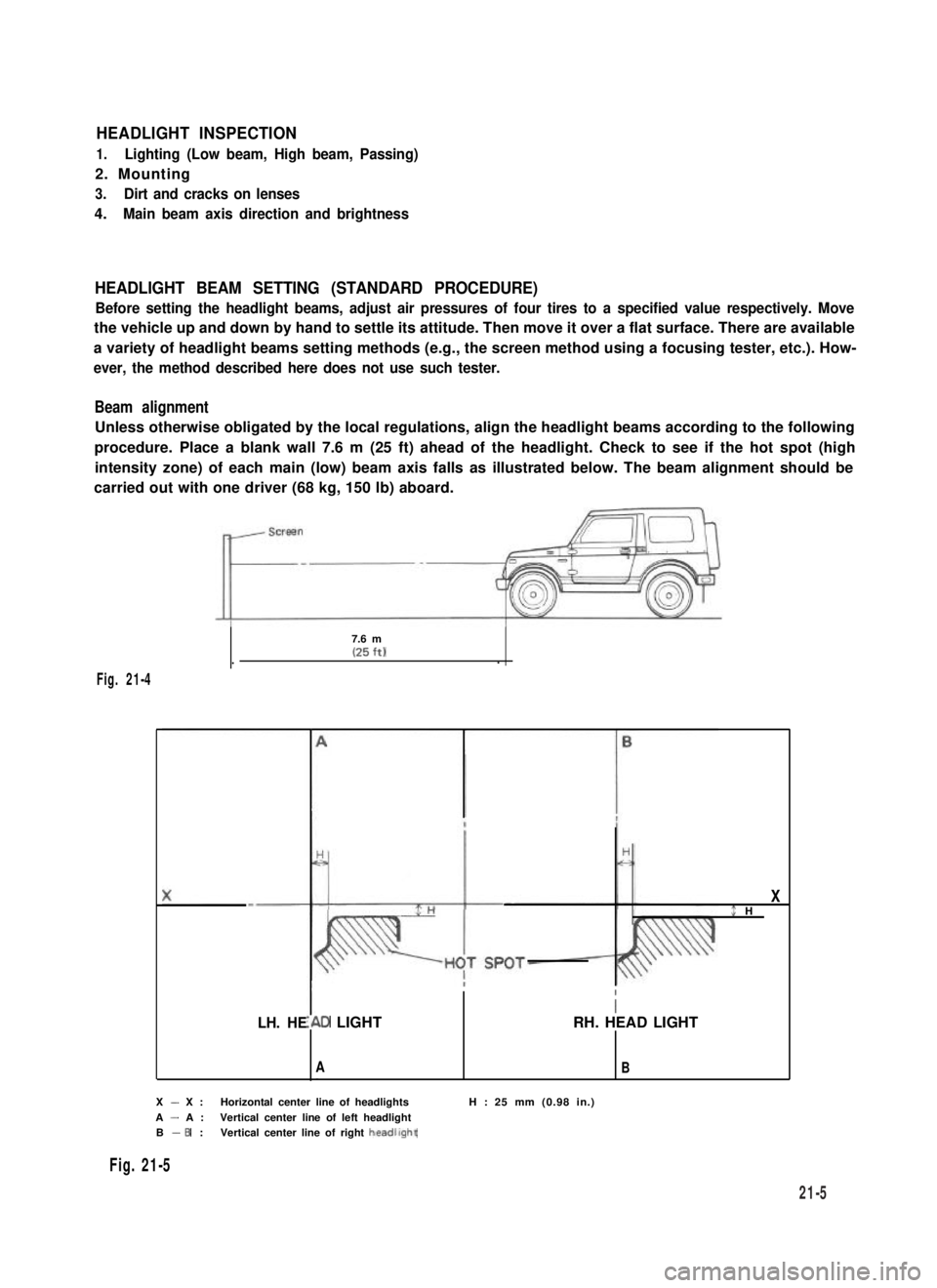
Beam alignment
Unless otherwise obligated by the local regulations, align the headlight beams according to the following
procedure. Place a blank wall 7.6 m (25 ft) ahead of the headlight. Check to see if the hot spot (high
intensity zone) of each main (low) beam axis falls as illustrated below. The beam alignment should be
carried out with one driver (68 kg, 150 lb) aboard.
7.6 m(25 ft)..
Fig. 21-4
LH. HE
X$ H
I
I\D LIGHTRH. HEAD LIGHT
AB
X - X :Horizontal center line of headlightsH : 25 mm (0.98 in.)
A - A :Vertical center line of left headlightB - 6 :Vertical center line of right headllght
Fig. 21-5
21-5