2007 TOYOTA SIENNA brake
[x] Cancel search: brakePage 1 of 3000

INTRODUCTION – REPAIR INSTRUCTIONIN–25
IN
VEHICLE LIFT AND SUPPORT
LOCATIONS
1. NOTICE ABOUT VEHICLE CONDITION WHEN
JACKING UP VEHICLE
(a) The vehicle must be unloaded before jacking up/
lifting up the vehicle. Never jack up/lift up a heavily
loaded vehicle.
(b) When removing heavy parts such as the engine and
transmission, the center of gravity of the vehicle
may shift. To stabilize the vehicle, place a balance
weight in a location where it will not roll or shift, or
use a transmission jack to hold the jacking support.
2. NOTICE FOR USING 4 POST LIFT
(a) Follow the safety procedures outlined in the lift
instruction manual.
(b) Use precautionary measures to prevent the free
wheel beam from damaging tires or wheels.
(c) Use wheel chocks to secure the vehicle.
3. NOTICE FOR USING JACK AND SAFETY STAND
(a) Work on a level surface. Use wheel chocks at all
times.
(b) Set the jack and rigid racks to the specified
locations of the vehicle accurately.
(c) When jacking up the vehicle, first release the
parking brake and move the shift lever to N.
(d) When jacking up the entire vehicle:
(1) When jacking up the front wheels first, make
sure wheel chocks are behind the rear wheels.
(2) When jacking up the rear wheels first, make sure
wheel chocks are in front of the front wheels.
(e) When jacking up only the front or rear wheels of the
vehicle:
(1) Before jacking up the front wheels, place wheel
chocks on both sides of the rear wheels.
(2) Before jacking up the rear wheels, place wheel
chocks on both sides of the front wheels.
(f) When lowering a vehicle that only has its front or
rear wheels jacked up:
(1) Before lowering the front wheels, make sure
wheel chocks are in front of the rear wheels.
(2) Before lowering the rear wheels, make sure
wheel chocks are behind the front wheels.
Page 11 of 3000

PREPARATION – BRAKE CONTROLPP–55
PP
EQUIPMENT
Torque wrench
Oscilloscope
Page 12 of 3000

PP–56PREPARATION – BRAKE CONTROL
PP
LUBRICANT
Item Capacity Classification
Brake fluid - SAE J1703 or FMVSS No. 116 DOT3
Page 16 of 3000

SS–30SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS – U151E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
SS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
Part Tightened N*m kgf*cm ft*lbf
Park/neutral position switch Nut 6.9 70 61 in.*lbf
Bolt 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
Control shaft lever x Control shaft 13 130 9
Shift control cable x Control shaft lever 13 130 9
Transaxle housing x Engine block A bolt 64 653 47
B bolt 46 470 34
C bolt 43 439 32
Torque converter clutch x Drive plate 41 413 35
Flywheel housing under cover x Automatic transaxle 7.8 80 69 in.*lbf
Engine mounting bracket FR x Transaxle 64 653 47
Oil filler tube x Transaxle5.5 56 49 in.*lbf
Control cable bracket No. 1 x Transaxle 12 122 9
Control cable bracket No. 2 x Transaxle 12 122 9
Oil cooler tube clamp x Control cable bracket 5.5 56 49 in.*lbf
Oil cooler inlet tube x Transaxle27 275 20
Oil cooler outlet tube x Transaxle 27 275 20
Starter x Transaxle37 377 27
Starter wire x Starter9.8 100 87 in.*lbf
Wire harness x Transaxle13 133 10
Wire harness clamp x Transaxle8.4 86 74 in.*lbf
Speed sensor (NC) x Transaxle11 11 5 8
Speed sensor (NT) x Transaxle11 11 2 8
Air cleaner x Air cleaner hose5.0 51 44 in.*lbf
Drain plug x Oil pan49 500 36
Transmission wire x Transaxle5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
ATF temperature sensor x Valve body 6.6 67 58 in.*lbf
Oil pan x Transaxle7.8 80 69 in.*lbf
Solenoid valve x Valve body A B bolt 11 110 8
C D bolt 6.6 67 58 in.*lbf
Valve body x Transaxle11 11 0 8
Oil strainer x Valve body11 11 0 8
Floor shift assembly x Body21 214 15
Control cable x Body12 122 9
Engine mount bracket RR x Transfer stiffener plate RH 34 350 25
Oil cooler assembly x Body Nut
7.0 71 62 in.*lbf
bolt
Differential gear lube apply tube x Transaxle housing 9.8 100 87 in.*lbf
Front planetary gear lock nut
210 to 3502,141 to
3,569155 to 258
Brake apply tube clamp x Transaxle case 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
Transaxle case No. 1 plug x Transaxle rear cover 7.4 75 65 in.*lbf
Transaxle rear cover x Transaxle case Bolt A 19 190 14
Other bolt 25 250 18
Pawl shaft clamp x Transaxle case 9.8 100 87 in.*lbf
Oil pump assembly x Transaxle case 22 226 16
Page 50 of 3000

IN–38INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
HINT:
• In troubleshooting, confirm that the problem symptoms
have been accurately identified. Preconceptions should be
discarded in order to make an accurate judgment. To
clearly understand what the problem symptoms are, it is
extremely important to ask the customer about the
problem and the conditions at the time the malfunction
occurred.
• Gather as much information as possible for reference.
Past problems that seem unrelated may also help in some
cases.
• The following 5 items are important points in the problem
analysis:
3. SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION AND DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE CODE
HINT:
The diagnostic system in the SIENNA has various
functions.
• The first function is the Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) check. A DTC is a code stored in the ECU
memory whenever a malfunction in the signal circuits
to the ECU occurs. In a DTC check, a previous
malfunction's DTC can be checked by a technician
during troubleshooting.
• Another function is the Input Signal Check, which
checks if the signals from various switches are sent to
the ECU correctly.
By using these functions, the problem areas can be
narrowed down and troubleshooting is more effective.
Diagnostic functions are incorporated in the following
system in the SIENNA.
What Vehicle model, system name
When Date, time, occurrence frequency
Where Road conditions
Under what conditions? Running conditions, driving conditions, weather conditions
How did it happen? Problem symptoms
SystemSYMPTOM CONFIRMATION AND DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
DTC Check
(Normal Mode)DTC Check
(Check Mode)Sensor Check/
Test Mode
(Input Signal
Check)Data List Active Test
2GR-FE SFI System
X
U151E Automatic Transaxle SystemX
U151F Automatic Transaxle SystemX
Tire pressure warning systemXX
Anti-lock Brake System
X
Vehicle Stability Control SystemX
Air Conditioning System (for Manual Air
Conditioning System)XXXXX
Air Conditioning System (for Automatic Air
Conditioning System)
XX
Airbag SystemXX
Occupant Classification System
XXX
Page 68 of 3000

IN–38INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
HINT:
• In troubleshooting, confirm that the problem symptoms
have been accurately identified. Preconceptions should be
discarded in order to make an accurate judgment. To
clearly understand what the problem symptoms are, it is
extremely important to ask the customer about the
problem and the conditions at the time the malfunction
occurred.
• Gather as much information as possible for reference.
Past problems that seem unrelated may also help in some
cases.
• The following 5 items are important points in the problem
analysis:
3. SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION AND DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE CODE
HINT:
The diagnostic system in the SIENNA has various
functions.
• The first function is the Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) check. A DTC is a code stored in the ECU
memory whenever a malfunction in the signal circuits
to the ECU occurs. In a DTC check, a previous
malfunction's DTC can be checked by a technician
during troubleshooting.
• Another function is the Input Signal Check, which
checks if the signals from various switches are sent to
the ECU correctly.
By using these functions, the problem areas can be
narrowed down and troubleshooting is more effective.
Diagnostic functions are incorporated in the following
system in the SIENNA.
What Vehicle model, system name
When Date, time, occurrence frequency
Where Road conditions
Under what conditions? Running conditions, driving conditions, weather conditions
How did it happen? Problem symptoms
SystemSYMPTOM CONFIRMATION AND DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
DTC Check
(Normal Mode)DTC Check
(Check Mode)Sensor Check/
Test Mode
(Input Signal
Check)Data List Active Test
2GR-FE SFI System
X
U151E Automatic Transaxle SystemX
U151F Automatic Transaxle SystemX
Tire pressure warning systemXX
Anti-lock Brake System
X
Vehicle Stability Control SystemX
Air Conditioning System (for Manual Air
Conditioning System)XXXXX
Air Conditioning System (for Automatic Air
Conditioning System)
XX
Airbag SystemXX
Occupant Classification System
XXX
Page 110 of 3000

DRIVE SHAFT – FRONT DRIVE SHAFTDS–5
DS
REMOVAL
1. DRAIN AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID
(a) Remove the drain plug, gasket and drain ATF.
(b) Install a new gasket and the drain plug.
Torque: 49 N*m (500 kgf*cm, 36 ft.*lbf)
2. DRAIN TRANSFER OIL (for 4WD)
HINT:
(See page TF-8)
3. REMOVE FRONT WHEEL
4. REMOVE FRONT AXLE HUB LH NUT
(a) Using SST and a hammer, unstake the staked part
of the axle hub LH nut.
SST 09930-00010
NOTICE:
Loosen the staked part of the nut completely,
otherwise the screw of the drive shaft may be
damaged.
(b) While applying the brakes, remove the lock axle hub
LH nut.
5. SEPARATE FRONT STABILIZER LINK ASSEMBLY LH
(a) Remove the nut, and separate the stabilizer link
assembly LH.
HINT:
If the ball joint turns together with the nut, use a
hexagon wrench (6 mm) to hold the stud.
6. SEPARATE SPEED SENSOR FRONT LH
(a) Remove the bolt and clip, and separate the sensor
wire and hose from the shock absorber.
NOTICE:
Be careful not to damage the speed sensor.
(b) Remove the bolt, and separate the speed sensor
from LH from the steering knuckle.
NOTICE:
Prevent foreign matter from adhering to the
speed sensor.
F040146E09
F040136
C083022
F040147
Page 111 of 3000
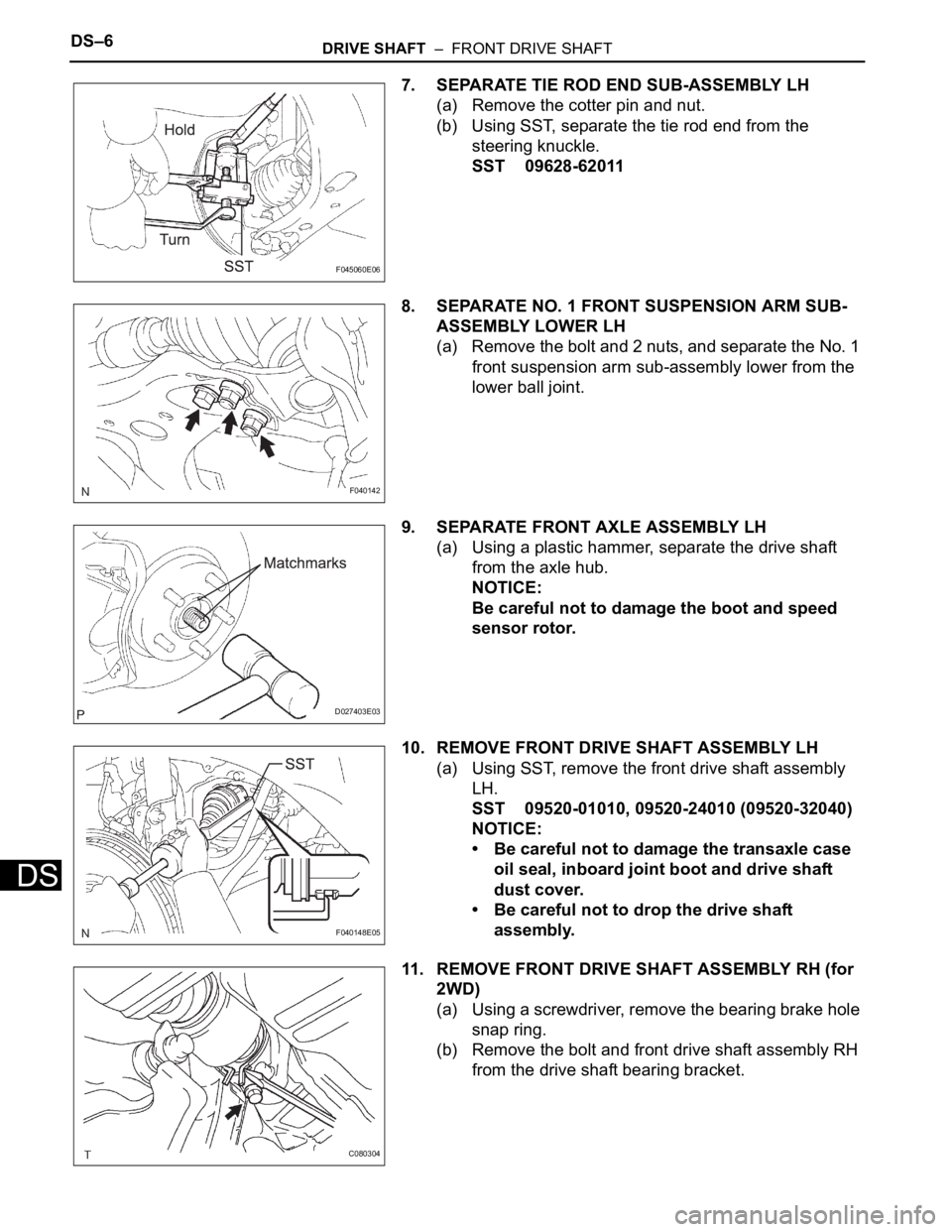
DS–6DRIVE SHAFT – FRONT DRIVE SHAFT
DS
7. SEPARATE TIE ROD END SUB-ASSEMBLY LH
(a) Remove the cotter pin and nut.
(b) Using SST, separate the tie rod end from the
steering knuckle.
SST 09628-62011
8. SEPARATE NO. 1 FRONT SUSPENSION ARM SUB-
ASSEMBLY LOWER LH
(a) Remove the bolt and 2 nuts, and separate the No. 1
front suspension arm sub-assembly lower from the
lower ball joint.
9. SEPARATE FRONT AXLE ASSEMBLY LH
(a) Using a plastic hammer, separate the drive shaft
from the axle hub.
NOTICE:
Be careful not to damage the boot and speed
sensor rotor.
10. REMOVE FRONT DRIVE SHAFT ASSEMBLY LH
(a) Using SST, remove the front drive shaft assembly
LH.
SST 09520-01010, 09520-24010 (09520-32040)
NOTICE:
• Be careful not to damage the transaxle case
oil seal, inboard joint boot and drive shaft
dust cover.
• Be careful not to drop the drive shaft
assembly.
11. REMOVE FRONT DRIVE SHAFT ASSEMBLY RH (for
2WD)
(a) Using a screwdriver, remove the bearing brake hole
snap ring.
(b) Remove the bolt and front drive shaft assembly RH
from the drive shaft bearing bracket.
F045060E06
F040142
D027403E03
F040148E05
C080304