2007 TOYOTA SIENNA ECU
[x] Cancel search: ECUPage 54 of 3000
IN–42INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
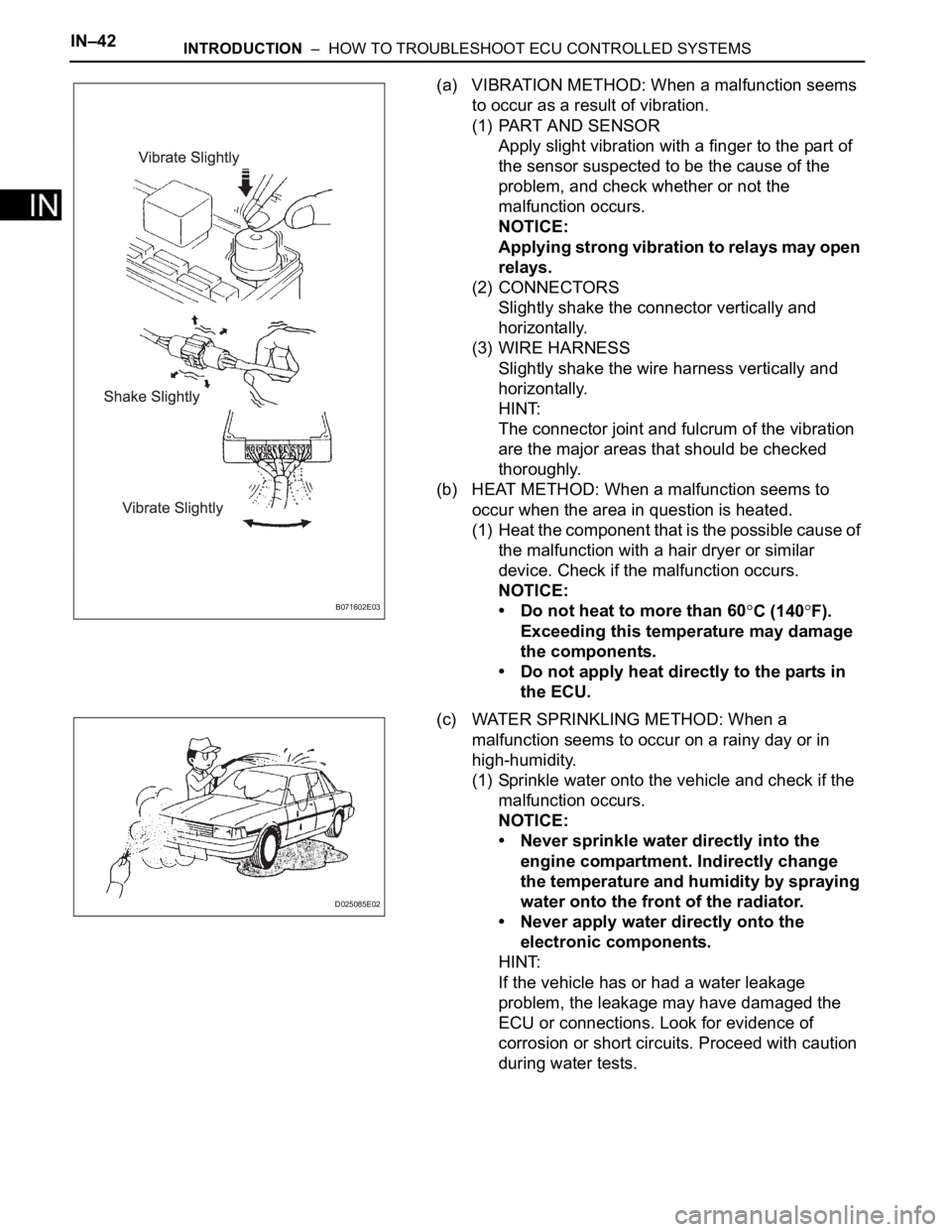
(a) VIBRATION METHOD: When a malfunction seems
to occur as a result of vibration.
(1) PART AND SENSOR
Apply slight vibration with a finger to the part of
the sensor suspected to be the cause of the
problem, and check whether or not the
malfunction occurs.
NOTICE:
Applying strong vibration to relays may open
relays.
(2) CONNECTORS
Slightly shake the connector vertically and
horizontally.
(3) WIRE HARNESS
Slightly shake the wire harness vertically and
horizontally.
HINT:
The connector joint and fulcrum of the vibration
are the major areas that should be checked
thoroughly.
(b) HEAT METHOD: When a malfunction seems to
occur when the area in question is heated.
(1) Heat the component that is the possible cause of
the malfunction with a hair dryer or similar
device. Check if the malfunction occurs.
NOTICE:
• Do not heat to more than 60
C (140F).
Exceeding this temperature may damage
the components.
• Do not apply heat directly to the parts in
the ECU.
(c) WATER SPRINKLING METHOD: When a
malfunction seems to occur on a rainy day or in
high-humidity.
(1) Sprinkle water onto the vehicle and check if the
malfunction occurs.
NOTICE:
• Never sprinkle water directly into the
engine compartment. Indirectly change
the temperature and humidity by spraying
water onto the front of the radiator.
• Never apply water directly onto the
electronic components.
HINT:
If the vehicle has or had a water leakage
problem, the leakage may have damaged the
ECU or connections. Look for evidence of
corrosion or short circuits. Proceed with caution
during water tests.B071602E03
D025085E02
Page 55 of 3000

INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMSIN–43
IN
(d) HIGH ELECTRICAL LOAD METHOD: When a
malfunction seems to occur when electrical load is
excessive.
(1) Turn on the heater blower, headlight, rear
window defogger and all other electrical loads.
Check if the malfunction reoccurs.
5. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
Look for output Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) (from the
DTC checks) in the appropriate section's Diagnostic Trouble
Code Chart. Use the chart to determine the trouble area and
the proper inspection procedure. A description of each of the
chart's columns is shown in the table below.
6. PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
When a "Normal" code is output during a DTC check but
the problem still occurs, use the Problem Symptoms
Table. The suspected areas (circuits or parts) for each
problem symptoms are in the table. The suspected areas
are listed in order of probability. A description of each of
the chart's columns is shown in the table below.
HINT:
In some cases, the problem is not detected by the
diagnostic system even though a problem symptom
occurs. It is possible that the problem is occurring
outside the detection range of the diagnostic system, or
that the problem occurs in a completely different system.
7. CIRCUIT INSPECTION
A description of the main areas of each circuit inspection
is shown in the table below.
B107149
Item Description
DTC No. Indicates the diagnostic trouble code
Detection Item Indicates the system or details of the problem
Trouble Area Indicates the suspect areas of the problem
See Page Indicates the page where the inspection procedures for each circuit is
to be found, or gives instruction for checking and repairs.
Item Description
Problem Symptom -
Circuit Inspection, Inspection Order Indicates the order in which the circuits need to be checked
Circuit or Part Name Indicates the circuit or part which needs to be checked
See Page Indicates the page where the flowchart for each circuit is located
Item Description
Circuit Description The major role, operation of the circuit and its component parts are
explained.
Diagnostic Trouble Code No. and Detection item Indicates the diagnostic trouble codes, diagnostic trouble code
settings and suspected areas for a problem
Wiring diagram This shows a wiring diagram of the circuit.
Use this diagram together with ELECTRICAL WIRING DIAGRAM to
thoroughly understand the circuit.
Wire colors are indicated by an alphabetical code. B = Black, L = Blue,
R = Red, BR = Brown, LG = Light Green, V = Violet, G = Green, O =
Orange, W = White, GR = Gray, P = Pink, Y = Yellow, SB = Sky Blue
The first letter indicates the basic wire color and the second letter
indicates the color of the stripe.
Page 56 of 3000

IN–44INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
Inspection Procedures Use the inspection procedures to determine if the circuit is normal or
abnormal. If abnormal, use the inspection procedures to determine
whether the problem is located in the sensors, actuators, wire
harnesses or ECU.
Indicates the condition of the connector of the ECU during the check Connector being checked is connected.
Connections of tester are indicated by (+) or (-) after the terminal
name.
Connector being checked is disconnected.
The inspections between a connector and body ground, information
about the body ground is not shown in the illustration. Item Description
Page 57 of 3000

IN–50INTRODUCTION – TERMS
IN
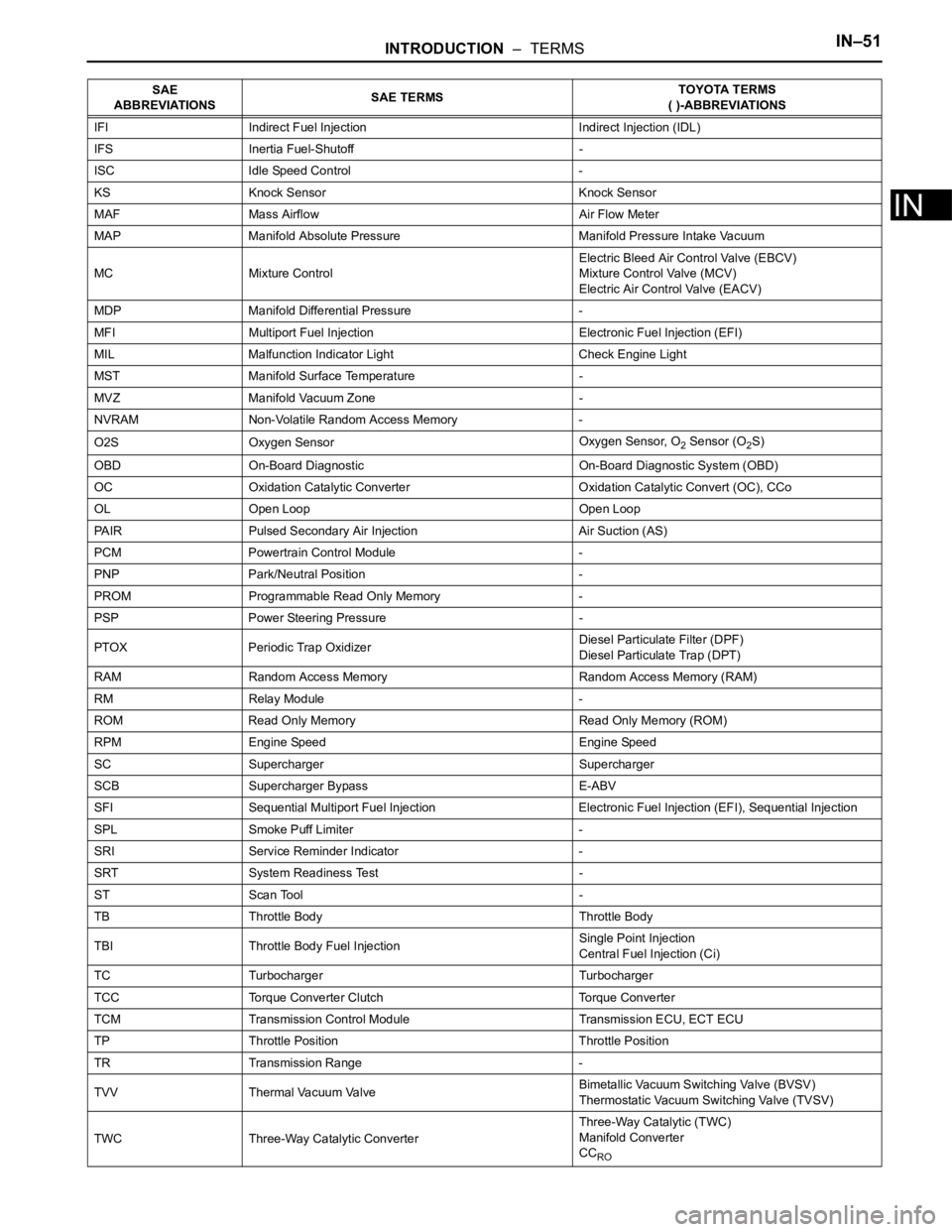
GLOSSARY OF SAE AND TOYOTA
TERMS
This glossary lists all SAE-J1930 terms and abbreviations
used in this manual in compliance with SAE
recommendations, as well as their TOYOTA equivalents.
SAE
ABBREVIATIONSSAE TERMSTOYOTA TERMS
( )-ABBREVIATIONS
A/C Air Conditioning Air Conditioner
ACL Air Cleaner Air Cleaner, A/CL
AIR Secondary Air Injection Air Injection (AI)
AP Accelerator Pedal -
B+ Battery Positive Voltage +B, Battery Voltage
BARO Barometric Pressure HAC
CAC Charge Air Cooler Intercooler
CARB Carburetor Carburetor
CFI Continuous Fuel Injection -
CKP Crankshaft Position Crank Angle
CL Closed Loop Closed Loop
CMP Camshaft Position Cam Angle
CPP Clutch Pedal Position -
CTOX Continuous Trap Oxidizer -
CTP Closed Throttle Position LL ON, Idle ON
DFI Direct Fuel Injection Direct Injection (DI./INJ)
DI Distributor Ignition -
DLC3 Data Link Connector 3 OBD II Diagnostic Connector
DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code Diagnostic Trouble Code
DTM Diagnostic Test Mode -
ECL Engine Coolant Level -
ECM Engine Control Module Engine Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
ECT Engine Coolant Temperature Coolant Temperature, Water Temperature (THW)
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only MemoryElectrically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory (EEPROM), Erasable Programmable Read
Only Memory (EPROM)
EFE Early Fuel Evaporation Cold Mixture Heater (CMH), Heat Control Valve (HCV)
EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
EI Electronic Ignition Distributorless Ignition (DLI)
EM Engine Modification Engine Modification (EM)
EPROM Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM)
EVAP Evaporative Emission Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP)
FC Fan Control -
FEEPROMFlash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory-
FEPROM Flash Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory -
FF Flexible Fuel -
FP Fuel Pump Fuel Pump
GEN Generator Alternator
GND Ground Ground (GND)
HO2S Heated Oxygen SensorHeated Oxygen Sensor (HO
2S)
IAC Idle Air Control Idle Speed Control (ISC)
IAT Intake Air Temperature Intake or Inlet Air Temperature
ICM Ignition Control Module -
Page 58 of 3000

INTRODUCTION – TERMSIN–51
IN
IFI Indirect Fuel Injection Indirect Injection (IDL)
IFS Inertia Fuel-Shutoff -
ISC Idle Speed Control -
KS Knock Sensor Knock Sensor
MAF Mass Airflow Air Flow Meter
MAP Manifold Absolute Pressure Manifold Pressure Intake Vacuum
MC Mixture ControlElectric Bleed Air Control Valve (EBCV)
Mixture Control Valve (MCV)
Electric Air Control Valve (EACV)
MDP Manifold Differential Pressure -
MFI Multiport Fuel Injection Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI)
MIL Malfunction Indicator Light Check Engine Light
MST Manifold Surface Temperature -
MVZ Manifold Vacuum Zone -
NVRAM Non-Volatile Random Access Memory -
O2S Oxygen SensorOxygen Sensor, O
2 Sensor (O2S)
OBD On-Board Diagnostic On-Board Diagnostic System (OBD)
OC Oxidation Catalytic Converter Oxidation Catalytic Convert (OC), CCo
OL Open Loop Open Loop
PAIR Pulsed Secondary Air Injection Air Suction (AS)
PCM Powertrain Control Module -
PNP Park/Neutral Position -
PROM Programmable Read Only Memory -
PSP Power Steering Pressure -
PTOX Periodic Trap OxidizerDiesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
Diesel Particulate Trap (DPT)
RAM Random Access Memory Random Access Memory (RAM)
RM Relay Module -
ROM Read Only Memory Read Only Memory (ROM)
RPM Engine Speed Engine Speed
SC Supercharger Supercharger
SCB Supercharger Bypass E-ABV
SFI Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI), Sequential Injection
SPL Smoke Puff Limiter -
SRI Service Reminder Indicator -
SRT System Readiness Test -
ST Scan Tool -
TB Throttle Body Throttle Body
TBI Throttle Body Fuel InjectionSingle Point Injection
Central Fuel Injection (Ci)
TC Turbocharger Turbocharger
TCC Torque Converter Clutch Torque Converter
TCM Transmission Control Module Transmission ECU, ECT ECU
TP Throttle Position Throttle Position
TR Transmission Range -
TVV Thermal Vacuum ValveBimetallic Vacuum Switching Valve (BVSV)
Thermostatic Vacuum Switching Valve (TVSV)
TWC Three-Way Catalytic ConverterThree-Way Catalytic (TWC)
Manifold Converter
CC
RO
SAE
ABBREVIATIONSSAE TERMSTOYOTA TERMS
( )-ABBREVIATIONS
Page 60 of 3000

IN–30INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU
CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
GENERAL INFORMATION
A large number of ECU controlled systems are used in the
SIENNA. In general, ECU controlled systems are considered
to be very intricate, requiring a high level of technical
knowledge to troubleshoot. However, most problem checking
procedures only involve inspecting the ECU controlled
system's circuits one by one. An adequate understanding of
the system and a basic knowledge of electricity is enough to
perform effective troubleshooting, accurate diagnoses and
necessary repairs.
FOR USING INTELLIGENT TESTER
– Before using the intelligent tester, read the tester
operator's manual thoroughly.
– If the tester cannot communicate with the ECU controlled
systems when the tester is connected to the DLC3 with the
ignition switch on and the tester turned on, there is a
problem on the vehicle side or tester side.
(1) If communication is normal when the tester is
connected to another vehicle, inspect the diagnosis
data link line (Bus (+) line) or ECU power circuit of the
vehicle.
(2) If communication is still not possible when the tester is
connected to another vehicle, the problem is probably
in the tester itself. Perform the Self Test procedures
outlined in the tester operator's manual.
Page 61 of 3000
INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMSIN–31
IN
ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT INSPECTION
PROCEDURE
1. BASIC INSPECTION
(a) WHEN MEASURING RESISTANCE OF
ELECTRONIC PARTS
(1) Unless otherwise stated, all resistance
measurements should be made at an ambient
temperature of 20
C (68F). Resistance
measurements may be inaccurate if measured
at high temperatures, i.e. immediately after the
vehicle has been running. Measurements should
be made after the engine has cooled down.
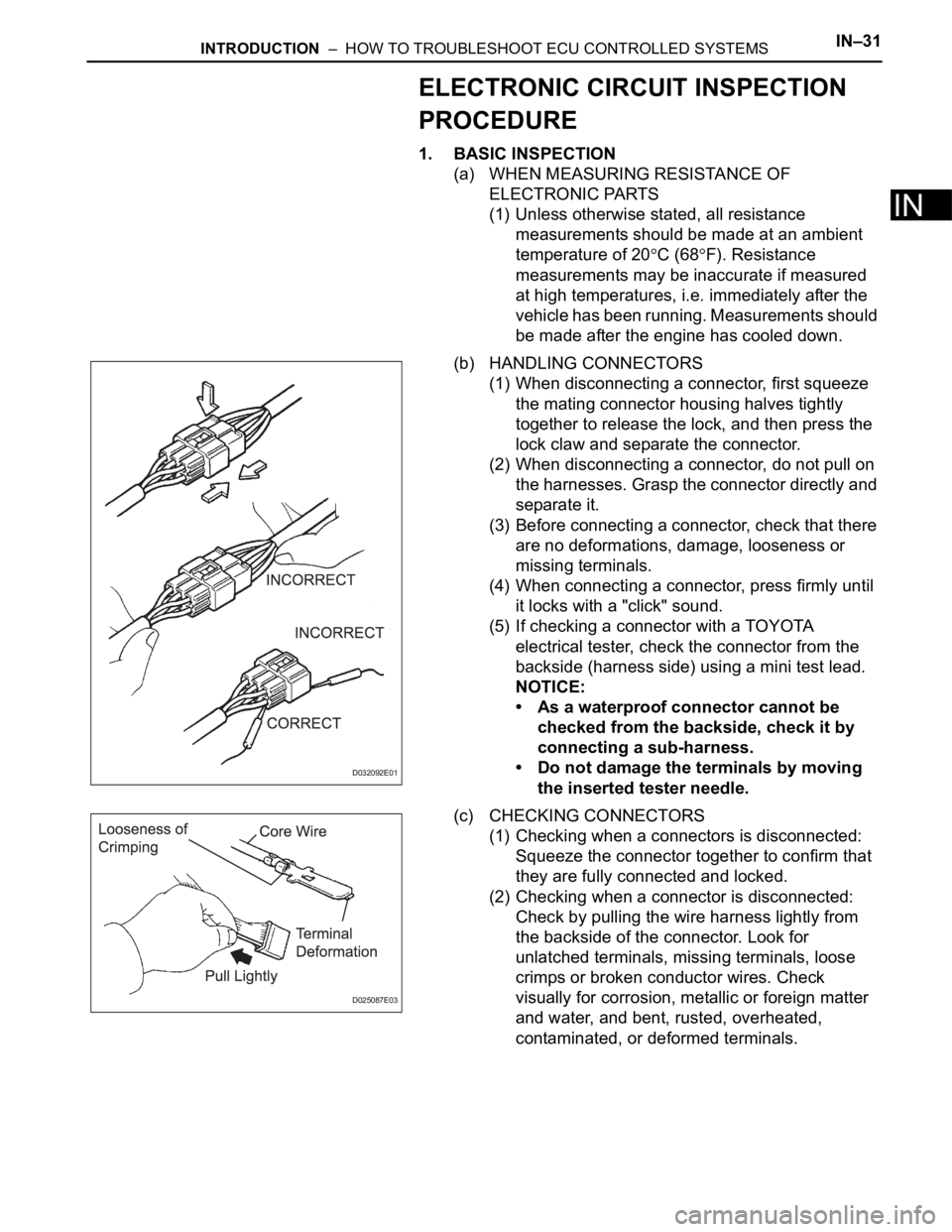
(b) HANDLING CONNECTORS
(1) When disconnecting a connector, first squeeze
the mating connector housing halves tightly
together to release the lock, and then press the
lock claw and separate the connector.
(2) When disconnecting a connector, do not pull on
the harnesses. Grasp the connector directly and
separate it.
(3) Before connecting a connector, check that there
are no deformations, damage, looseness or
missing terminals.
(4) When connecting a connector, press firmly until
it locks with a "click" sound.
(5) If checking a connector with a TOYOTA
electrical tester, check the connector from the
backside (harness side) using a mini test lead.
NOTICE:
• As a waterproof connector cannot be
checked from the backside, check it by
connecting a sub-harness.
• Do not damage the terminals by moving
the inserted tester needle.
(c) CHECKING CONNECTORS
(1) Checking when a connectors is disconnected:
Squeeze the connector together to confirm that
they are fully connected and locked.
(2) Checking when a connector is disconnected:
Check by pulling the wire harness lightly from
the backside of the connector. Look for
unlatched terminals, missing terminals, loose
crimps or broken conductor wires. Check
visually for corrosion, metallic or foreign matter
and water, and bent, rusted, overheated,
contaminated, or deformed terminals.
D032092E01
D025087E03
Page 62 of 3000
IN–32INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
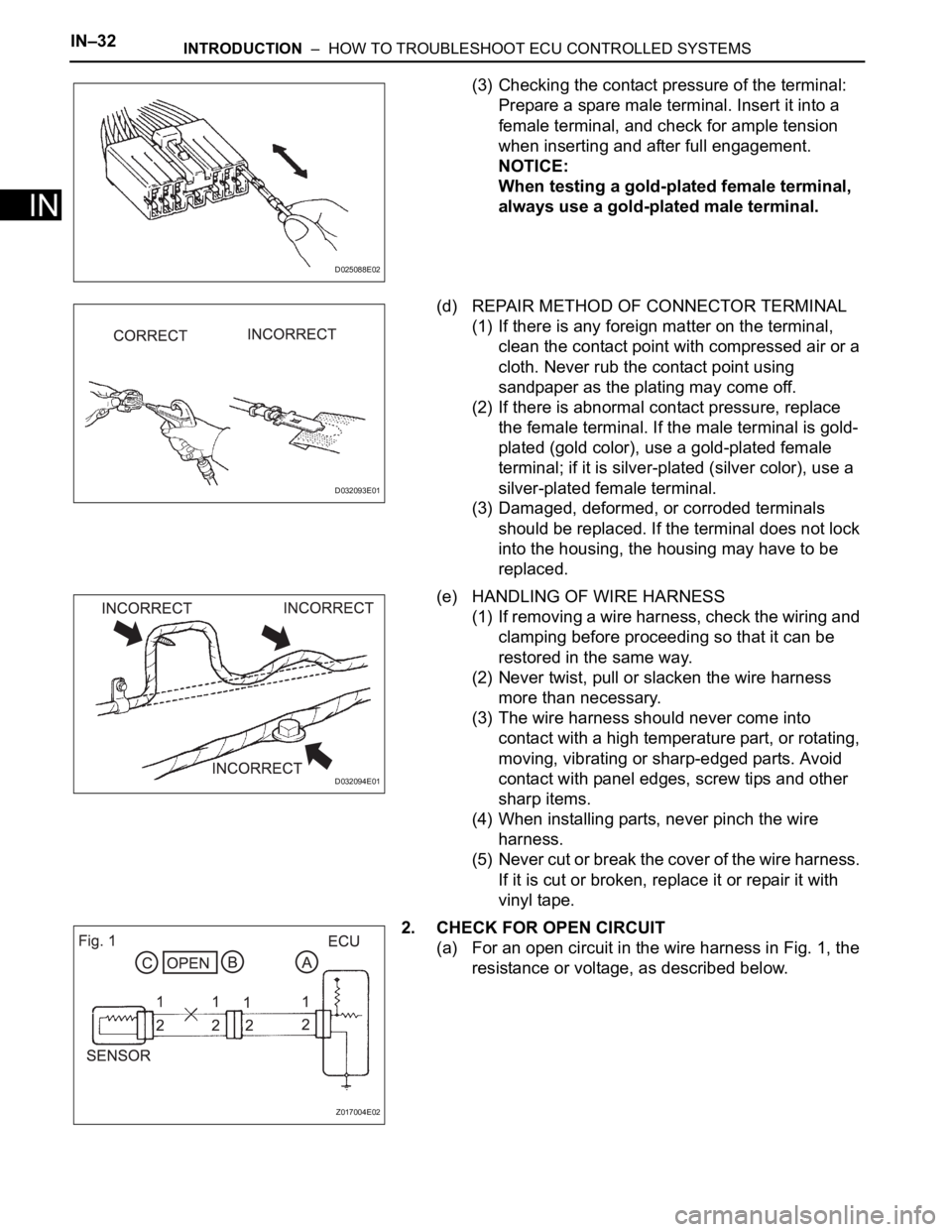
(3) Checking the contact pressure of the terminal:
Prepare a spare male terminal. Insert it into a
female terminal, and check for ample tension
when inserting and after full engagement.
NOTICE:
When testing a gold-plated female terminal,
always use a gold-plated male terminal.
(d) REPAIR METHOD OF CONNECTOR TERMINAL
(1) If there is any foreign matter on the terminal,
clean the contact point with compressed air or a
cloth. Never rub the contact point using
sandpaper as the plating may come off.
(2) If there is abnormal contact pressure, replace
the female terminal. If the male terminal is gold-
plated (gold color), use a gold-plated female
terminal; if it is silver-plated (silver color), use a
silver-plated female terminal.
(3) Damaged, deformed, or corroded terminals
should be replaced. If the terminal does not lock
into the housing, the housing may have to be
replaced.
(e) HANDLING OF WIRE HARNESS
(1) If removing a wire harness, check the wiring and
clamping before proceeding so that it can be
restored in the same way.
(2) Never twist, pull or slacken the wire harness
more than necessary.
(3) The wire harness should never come into
contact with a high temperature part, or rotating,
moving, vibrating or sharp-edged parts. Avoid
contact with panel edges, screw tips and other
sharp items.
(4) When installing parts, never pinch the wire
harness.
(5) Never cut or break the cover of the wire harness.
If it is cut or broken, replace it or repair it with
vinyl tape.
2. CHECK FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
(a) For an open circuit in the wire harness in Fig. 1, the
resistance or voltage, as described below.
D025088E02
D032093E01
D032094E01
Z017004E02