2005 TOYOTA AVENSIS code
[x] Cancel search: codePage 4108 of 5135
05HI0−01
FI2547
A76859
Hand −Held Tester
DLC3
−
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
05 −1 5
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
1. DESCRIPTION for EURO −OBD (European spec.)
S When troubleshooting Euro −OBD vehicles, the only dif-
ference from the usual troubleshooting procedure is that
you c onnect an O BD scan t ool com plying wit h I SO
1 503 1− 4 or a hand −held tester to the vehicle, and read
the various data output from the vehicle’s ECM.
S Eur o −O BD r egulat ions r equir e t hat t he v ehicle’s on −
board computer illuminates the check engine warning
light (CHK ENG) on the instrument panel when the com-
puter detects a malfunction in: 1) the emission control
system / components, or 2) the powertrain control compo-
nents (which affect vehicle emissions), or 3) the comput-
er. In addition, the applicable Diagnostic Trouble Codes
(DTCs) prescribed by ISO 1503 1− 4 are recorded in the
ECM memory (see page 05 −31).
If the malfunction does not reoccur in 3 consecutive trips, the
CHK ENG goes off automatically but the DTCs remain recorded
in the ECM memory.
S To check the DTCs, connect the OBD scan tool or hand −
held tester to Data Link Connector 3 (DLC3) on the ve-
hicle. The OBD scan tool or hand −held tester also en-
ables you to erase the DTCs and check the freeze frame
data and various forms of engine data. (See the instruc-
tion manual for the OBD scan tool or the hand −held tes-
ter).
S DTCs include ISO controlled codes and manufacturer
controlled codes. ISO controlled codes must be set ac-
cording to the ISO, while manufacturer controlled codes
can be set by a manufacturer within certain restrictions
(see the DTC chart on page 05 −31).
S The diagnosis system operates in normal mode during
normal vehicle use. In ”normal mode”, 2 trip detection log-
ic* is used to ensure accurate detection of malfunctions.
A ”check mode”, is also available to technicians as an op-
tion. In ”check mode”, 1 trip detection logic is used for sim-
ulating malfunction symptoms and increasing the sys-
tem’s ability to detect malfunctions, including intermittent
malfunctions (hand −held tester only)
(see page 05 −1 9) .
S*2 trip detection logic:
When a malfunction is first detected, the malfunction is
temporarily stored in the ECM memory ( 1st trip). If the
ignition switch is turned OFF and then ON again, and the
same malfunction is detected again, the CHK ENG will il-
luminate (2nd trip).
Page 4109 of 5135

FI2547
A76859
Hand−Held Tester
DLC3
05 −1 6
−
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
S Freeze frame data:
The freeze frame data records the engine conditions (fuel
system, calculated load, engine coolant temperature, fuel
trim, engine speed, vehicle speed, etc.) when a malfunc-
tion is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data
can help determine if the vehicle was running or stopped,
if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air −fuel ratio
was lean or rich, and other data from the time the malfunc-
tion occurred.
Priorities for troubleshooting:
When multiple DTCs occur, find out the order in which the DTCs
should be inspected by checking the component’s DTC chart.
If no instructions are written in the DTC chart, check DTCs in the
following order of priority:
(a) DTCs ot her t han f uel t r im m alf unct ion DTCs ( P0 1 71 ,
P0 172, P0 174 and P0 175) and misfire DTCs (P0300 to
P0304).
(b) Fuel trim malfunction DTCs (P0 171,P0 172, P0 174 and
P0 175).
(c) Misfire DTCs (P0300 to P0304).
2. DESCRIPTION for M −OBD (Except European spec.)
S When troubleshoot Multiplex OBD (M −OBD) vehicles, the
only difference from the usual troubleshooting procedure
is that you connect the hand −held tester to the vehicle,
and read the various data output from the vehicle’s ECM.
S The vehicle’s on −board computer illuminates the check
engine warning lamp (CHK ENG) on the instrument panel
when the computer detects a malfunction in the computer
itself or in drive system components. In addition, the appli-
cable Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are recorded in
the ECM memory (see page 05 −31).
If the malfunction does not recur, the CHK ENG goes off be dis-
appeared by turning the ignition switch to OFF, but the recorded
DTCs remain in the ECM memory.
S To check the DTCs, connect the hand −held tester to the
Data Link Connector 3 (DLC3) on the vehicle or connect
terminals TC and CG on the DLC3(DTCs will be displayd
on the multi −information display).
S The diagnosis system operates in normal mode during
normal vehicle use. In ”normal mode”, 2 trip detection log-
ic* is used to ensure accurate detection of malfunctions.
A ”check mode”, is also available to technicians as an op-
tion. In ”check mode”, 1 trip detection logic is used for sim-
ulating malfunction symptoms and increasing the sys-
tem’s ability to detect malfunctions, including intermittent
malfunctions (hand −held tester only)
(see page 05 −20).
Page 4115 of 5135

05CDX−02
05 −1 0
−
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
When the malfunction is not confirmed in the diagnostic trouble code check and the problem still can not be
confirmed in the basic inspection, proceed to this matrix chart and troubleshoot according to the numbered
order given below.
SymptomSuspected AreaSee page
Engine does not crank (Does not start)
1. Starter
2. Starter relay
3. Park/neutral position switch19 −1
1 9 −1
* 1
No initial combustion (Does not start)
1 . ECM power source circuit
2. Ignition coil assy
3. Fuel pump control circuit
4. Injector circuit05 −236
05 −1 67
05 −24 1
05 −1 36
No complete combustion (Does not start)
1. Ignition coil assy
2. Fuel pump control circuit
3. Injector circuit05 −1 67
05 −24 1
05 −1 36
Difficult to start (Engine cranks normally)
1. Starter signal circuit
2. Ignition coil assy
3. Spark plug
4. Compression
5. Injector circuit
6. Fuel pump control circuit05 −249
05 −1 67
1 8 − 3
1 4 −1
05 −1 36
05 −24 1
Difficult to start with cold engine
1. Starter signal circuit
2. Injector circuit
3. Ignition coil assy
4. Spark plug
5. Fuel pump control circuit05 −249
05 −1 36
05 −1 67
1 8 − 3
05 −24 1
Difficult to start with hot engine
1. Starter signal circuit
2. Injector circuit
3. Ignition coil assy
4. Spark plug
5. Fuel pump control circuit05 −249
05 −1 36
05 −1 67
1 8 − 3
05 −24 1
High engine idle speed (Poor idling)
1. ECM power source circuit
2. Park/neutral position switch
3. Back up power source circuit05 −236
* 1
05 −1 99
Low engine idle speed (Poor idling)
1. Park/neutral position switch
2. Injector circuit
3. Back up power source circuit
4. Fuel pump control circuit* 1
05 −1 36
05 −1 99
05 −24 1
Rough idling (Poor idling)
1. Mass air flow meter circuit
2. Vacuum sensor circuit
3. Injector circuit
4. Fuel pump control circuit
5. Ignition coil assy
6. Compression
7. Back up power source circuit05 −55
05 −61
05 −1 36
05 −24 1
05 −1 67
1 4 −1
05 −1 99
Hunting (Poor idling)
1. Mass air flow meter circuit
2. Vacuum sensor circuit
3. ECM power source circuit05 −55
05 −61
05 −236
Hesitation/Poor acceleration (Poor driveability)
1. Mass air flow meter circuit
2. Vacuum sensor circuit
3. Injector circuit
4. Ignition coil assy
5. Fuel pump control circuit05 −55
05 −61
05 −1 36
05 −1 67
05 −24 1
Muffler explosion after fire (Poor driveability)
1. Ignition coil assy
2. Spark plug
3. Injector circuit05 −1 67
1 8 − 3
05 −1 36
Page 4120 of 5135
05CDT−02
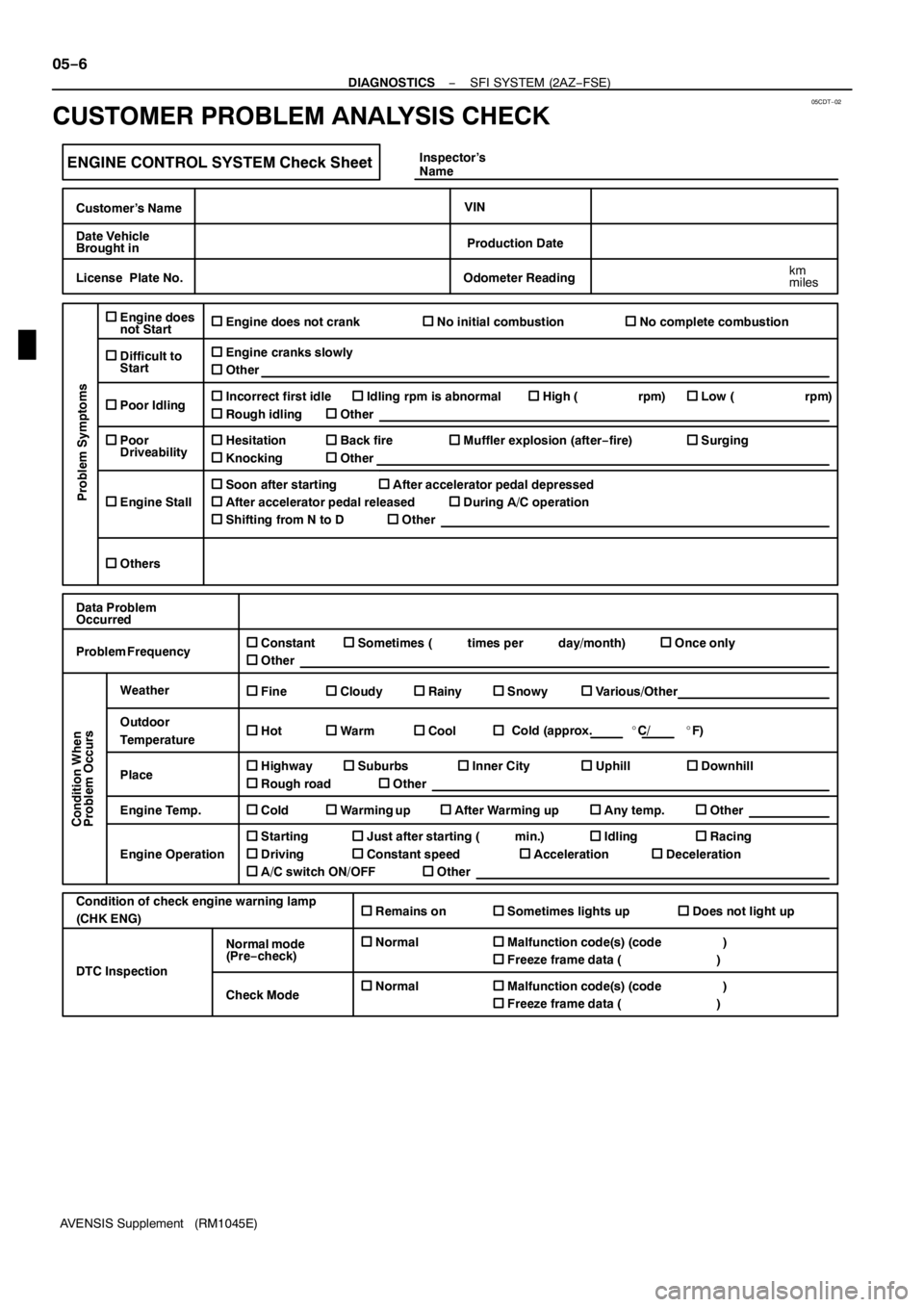
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM Check Sheet
Customer’s Name
Date Vehicle
Brought in
License Plate No.
VIN
Production Date
Odometer Reading
km
miles
Problem Symptoms
Engine does
not Start
Difficult to
Start
Poor Idling
Poor
Driveability
Engine Stall
Others
Engine does not crankNo initial combustionNo complete combustion
Engine cranks slowly
Other
Incorrect first idleIdling rpm is abnormalHigh ( rpm)Low ( rpm)
Rough idling
Other
HesitationBack fireMuffler explosion (after−fire)Surging
Knocking
Other
Soon after startingAfter accelerator pedal depressed
After accelerator pedal released
During A/C operation
Shifting from N to D
Other
Data Problem
Occurred
Problem Frequency
Condition When
Problem Occurs
Weather
Engine Operation
Engine Temp. Place Outdoor
TemperatureConstant
Sometimes ( times per day/month)Once only
Other
Fine
CloudyRainySnowyVarious/Other
Hot
Warm Cool
HighwaySuburbsInner CityUphillDownhill
Rough road
Other
Cold
Warming upAfter Warming upAny temp.Other
Starting
Just after starting ( min.)IdlingRacing
Driving
Constant speedAccelerationDeceleration
A/C switch ON/OFF
Other
Condition of check engine warning lamp
(CHK ENG)Remains on Sometimes lights up Does not light up
Normal Malfunction code(s) (code )
Freeze frame data ( )
Normal Malfunction code(s) (code )
Freeze frame data ( )
Normal mode
(Pre−check)
Check Mode DTC InspectionInspector’s
Name
Cold (approx._C/_F)
05−6
− DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
CUSTOMER PROBLEM ANALYSIS CHECK
Page 4122 of 5135
05−4
−
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
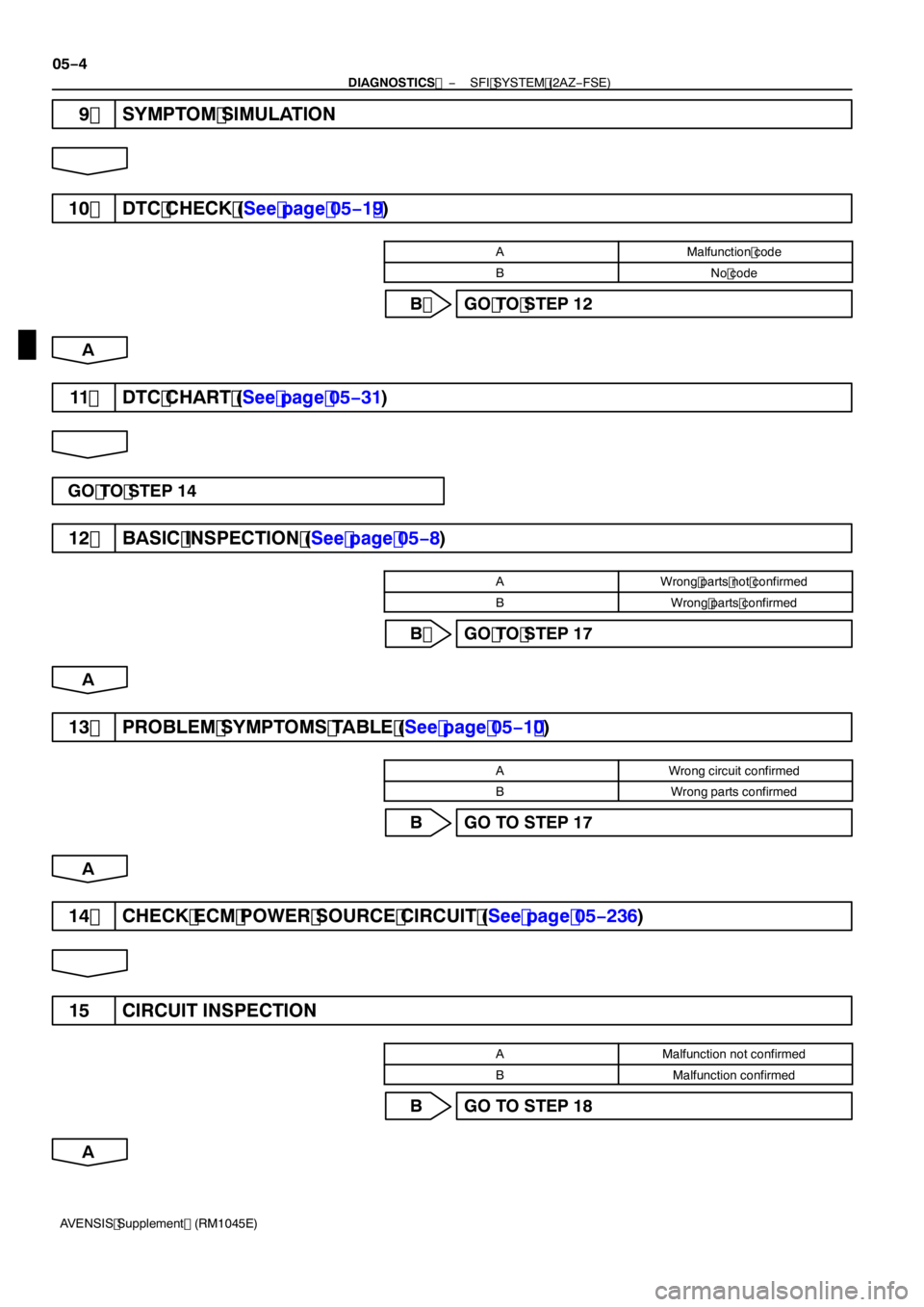
9 SYMPTOM SIMULATION
1 0 DTC CHECK (See page 05 −1 9)
AMalfunction code
BNo code
B GO TO STEP 12
A
11 DTC CHART (See page 05 −31)
GO TO STEP 14
12 BASIC INSPECTION (See page 05 −8)
AWrong parts not confirmed
BWrong parts confirmed
B GO TO STEP 17
A
1 3 PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE (See page 05 −1 0)
AWrong circuit confirmed
BWrong parts confirmed
B GO TO STEP 17
A
1 4 CHECK ECM POWER SOURCE CIRCUIT (See page 05 −236)
1 5 CIRCUIT INSPECTION
AMalfunction not confirmed
BMalfunction confirmed
B GO TO STEP 18
A
Page 4128 of 5135
05DVP−02
A8570 1
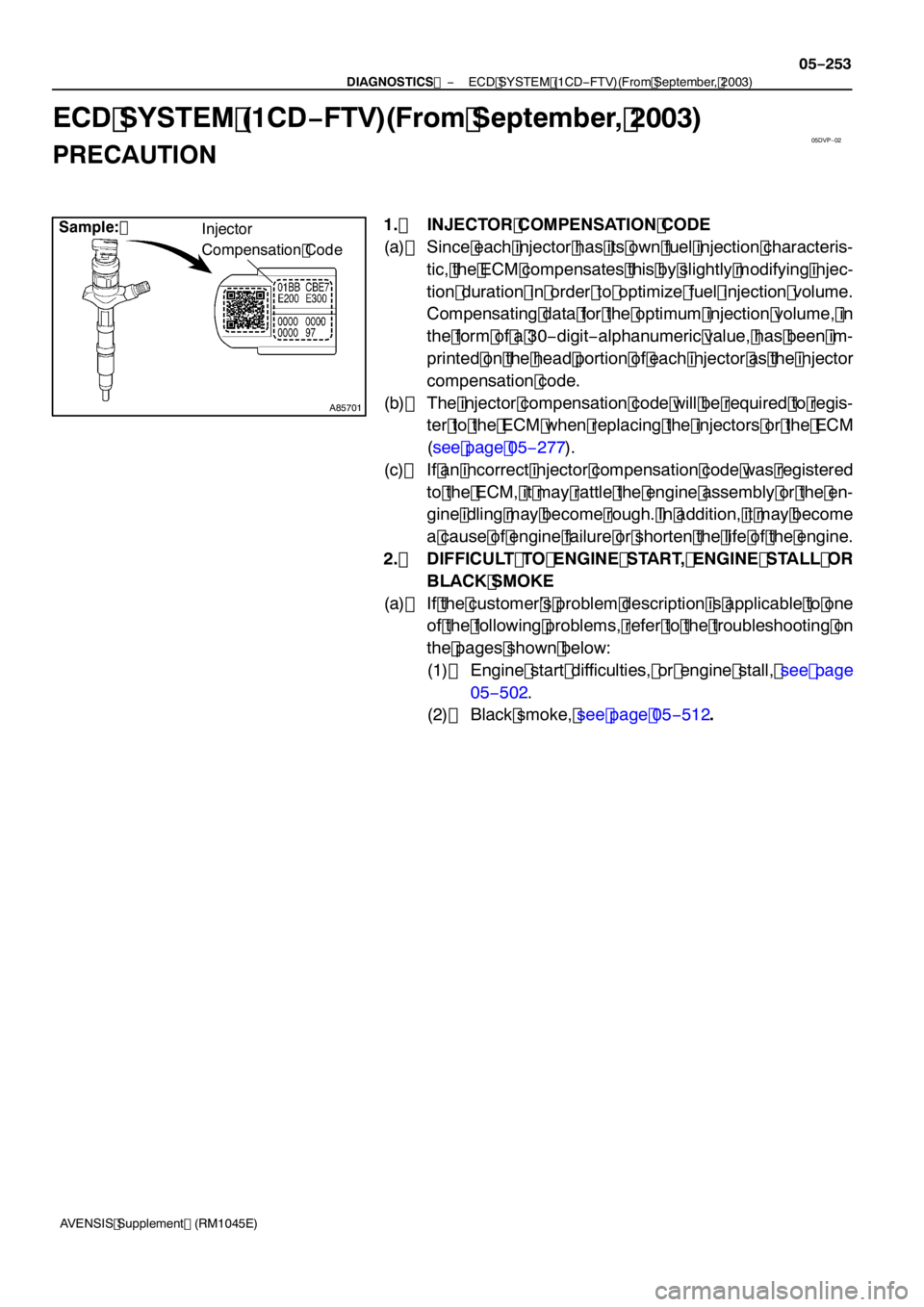
Sample:
Injector
Compensation Code
−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
05 −253
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
ECD SYSTEM ( 1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
PRECAUTION
1. INJECTOR COMPENSATION CODE
(a) Since each injector has its own fuel injection characteris- tic, the ECM compensates this by slightly modifying injec-
tion duration in order to optimize fuel injection volume.
Compensating data for the optimum injection volume, in
the form of a 30 −digit −alphanumeric value, has been im-
printed on the head portion of each injector as the injector
compensation code.
(b) The injector compensation code will be required to regis- ter to the ECM when replacing the injectors or the ECM
(see page 05 −277).
(c) If an incorrect injector compensation code was registered
to the ECM, it may rattle the engine assembly or the en-
gine idling may become rough. In addition, it may become
a cause of engine failure or shorten the life of the engine.
2. DIFFICULT TO ENGINE START, ENGINE STALL OR BLACK SMOKE
(a) If the customer ’s problem description is applicable to one of the following problems, refer to the troubleshooting on
the pages shown below:
(1 ) Engine start difficulties, or engine stall, see page
05−502.
(2) Black smoke, see page 05 −512.
Page 4172 of 5135

05−206
−
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
6 CHECK IF DTC OUTPUT REOCCURS
(a) Connect the hand −held tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the hand −held tester ON.
(c) Erease DTC, enter the following menus: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO / CLEAR
CODE; and press YES.
(d) Drive the vehicle more than 25 mph (40 km/h) for 20 seconds or more.
(e) Check DTC reoccur. Result:
Display (DTC output)Proceed to
P0617A
No outputB
B CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS (See page 05 −7)
A
REPLACE ECM (See page 10− 65 of Pub. No. RM 1018E AVENSIS)
Page 4177 of 5135

−
DIAGNOSTICS SFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
05 −1 89
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
DTC P0505 IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The idle speed is controlled by the Electric Throttle Control System (ETCS).
ETCS is composed of the throttle motor which operates the throttle valve, the throttle position sensor which
detects the opening angle of the throttle valve, the accelerator pedal position sensor which detects the accel-
erator pedal position,and the one valve type throttle body.
The ECM controls the throttle motor to make the throttle valve opening angle properly for the target idle
speed.
DTC No.DTC Detection ConditionTrouble Area
P0505Idle speed continues to vary greatly from target speed
(2 trip detection logic)S Electric throttle control system
S Air induction system
S PCV hose connection
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the hand−held tester . Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air −fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data
from the time the malfunction occurred.
1 CHECK OTHER DTC OUTPUT(IN ADDITION TO DTC P0505)
(a) Connect the hand −held tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the hand −held tester ON.
(c) Select the item: DIAGNOSIS / OBD/MOBD / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(d) Read the DTCs using the hand −held tester.
Result:
Display (DTC output)Proceed to
P0505A
P0505 and other DTCsB
HINT:
If any other codes besides P0505 are output, perform troubleshoot for those DTCs first.
B GO TO RELEVANT DTC CHART(See page 05 −31)
A
2 CHECK CONNECTION OF PCV HOSE
NG REPAIR OR REPLACE PCV HOSE
OK
05HIN −01