2004 SUBARU FORESTER height
[x] Cancel search: heightPage 773 of 2870

PM-36
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE SERVICE
Suspension
22.Suspension
A: INSPECTION
1. SUSPENSION BALL JOINT
1) Jack-up the vehicle until front wheels are off
ground.
2) Grasp the bottom of tire and move it in and out.
If relative movement (B) is observed between the
brake disc cover (A) and end of transverse link (D),
ball joint (C) may be excessively worn.
3) Grasp the end of transverse link (C) and move it
up and down. Relative movement (A) between the
housing (D) and transverse link boss indicates ball
joint (B) may be excessively worn.
4) If relative movement is observed in the immedi-
ately preceding two steps, remove and inspect the
ball joint. If free play exceeds standard, replace the
ball joint.
5) Damage of dust seal
Visually inspect the ball joint dust seal. If it is dam-
aged, remove the transverse link.
ball joint.
(1) When looseness exceeds standard value,
replace the ball joint.
(2) If the dust seal is damaged, replace with the
new ball joint.
NOTE:
When the transverse link ball joint has been re-
moved or replaced, check the toe-in of front wheel. If the front wheel toe-in is not at specified value, ad-
just the toe-in.
2. TRANSVERSE LINK’S REAR BUSHING
Check oil leaks at around liquid-filled bushing. If oil
leaks, replace the bushing.
3. WHEEL ARCH HEIGHT
1) Unload cargoes and set the vehicle in curb
weight (empty) condition.
2) Then, check the wheel arch height of front and
rear suspensions to ensure that they are within
specified values.
3) When the wheel arch height is out of standard,
visually inspect the following components and re-
place deformed parts.
Suspension components [Front strut assembly
and rear strut assembly]
Parts connecting between suspension and body.
4) When no components are deformed, adjust the
wheel arch height by replacing coil spring in the
suspension which wheel arch height is out of stan-
dard.
PM-00057
(A)
(B)
(C) (D)
PM-00058
(A)
(B) (C)(D)
(A) Dust seal
(A) Rear bushing
(B) Transverse link
PM-00059
(A)
PM-00060
(A)
(B)
Page 871 of 2870
ME(H4SO)-2
MECHANICAL
General Description
1. General Description
A: SPECIFICATION
NOTE:
STD: Standard I.D.: Inner Diameter O.D.: Outer Diameter US: Undersize OS: Oversize
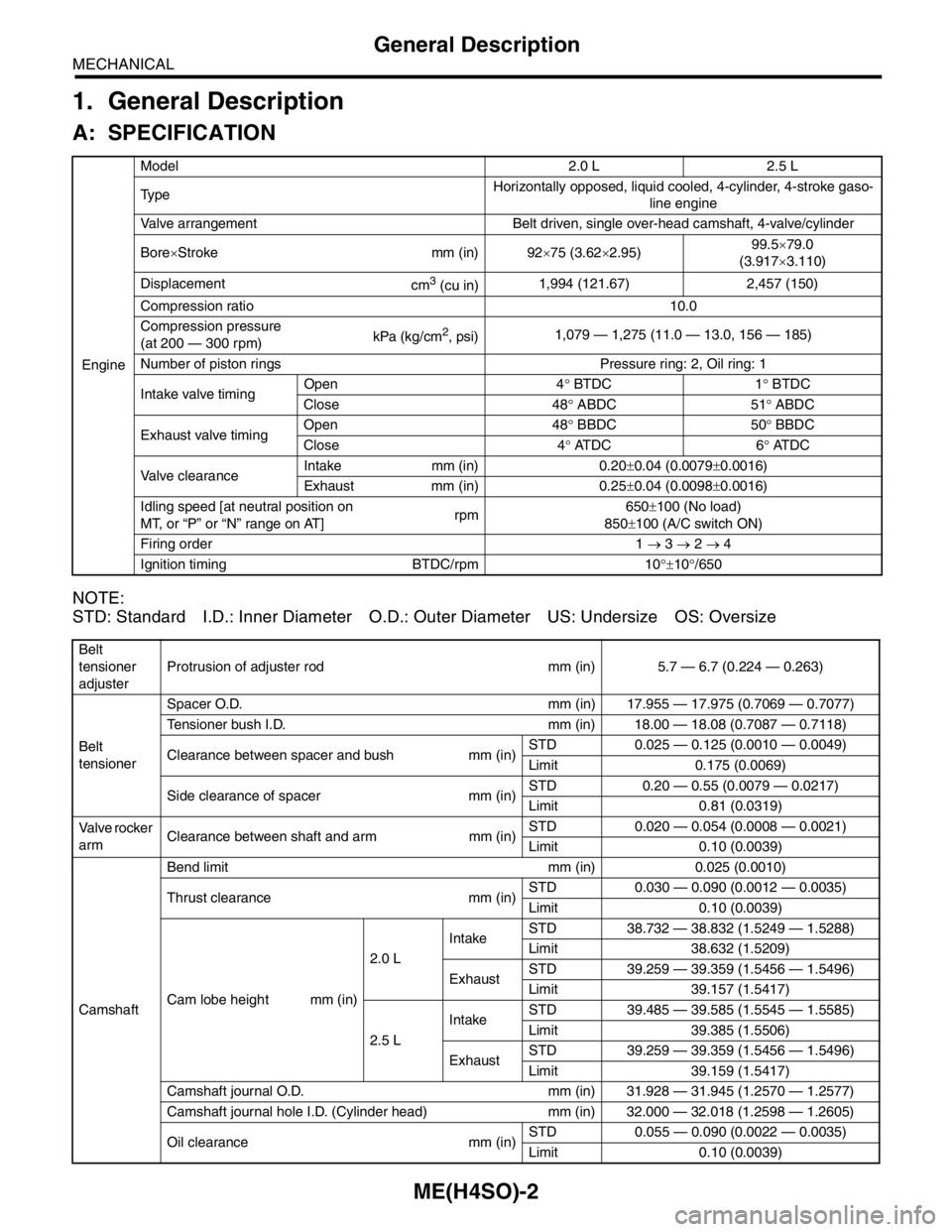
EngineModel 2.0 L 2.5 L
Ty p eHorizontally opposed, liquid cooled, 4-cylinder, 4-stroke gaso-
line engine
Valve arrangement Belt driven, single over-head camshaft, 4-valve/cylinder
Bore×Stroke mm (in) 92×75 (3.62×2.95)99.5×79.0
(3.917×3.110)
Displacement
cm
3 (cu in)1,994 (121.67) 2,457 (150)
Compression ratio 10.0
Compression pressure
(at 200 — 300 rpm)kPa (kg/cm
2, psi)1,079 — 1,275 (11.0 — 13.0, 156 — 185)
Number of piston rings Pressure ring: 2, Oil ring: 1
Intake valve timingOpen 4° BTDC 1° BTDC
Close 48° ABDC 51° ABDC
Exhaust valve timingOpen 48° BBDC 50° BBDC
Close 4° AT D C 6° AT D C
Valve clearance Intake mm (in) 0.20±0.04 (0.0079±0.0016)
Exhaust mm (in) 0.25±0.04 (0.0098±0.0016)
Idling speed [at neutral position on
MT, or “P” or “N” range on AT]rpm650±100 (No load)
850±100 (A/C switch ON)
Firing order 1 → 3 → 2 → 4
Ignition timing BTDC/rpm 10°±10°/650
Belt
tensioner
adjusterProtrusion of adjuster rod mm (in) 5.7 — 6.7 (0.224 — 0.263)
Belt
tensionerSpacer O.D. mm (in) 17.955 — 17.975 (0.7069 — 0.7077)
Tensioner bush I.D. mm (in) 18.00 — 18.08 (0.7087 — 0.7118)
Clearance between spacer and bush mm (in)STD 0.025 — 0.125 (0.0010 — 0.0049)
Limit 0.175 (0.0069)
Side clearance of spacer mm (in)STD 0.20 — 0.55 (0.0079 — 0.0217)
Limit 0.81 (0.0319)
Valve rocker
armClearance between shaft and arm mm (in)STD 0.020 — 0.054 (0.0008 — 0.0021)
Limit 0.10 (0.0039)
CamshaftBend limit mm (in) 0.025 (0.0010)
Thrust clearance mm (in)STD 0.030 — 0.090 (0.0012 — 0.0035)
Limit 0.10 (0.0039)
Cam lobe height mm (in)2.0 LIntakeSTD 38.732 — 38.832 (1.5249 — 1.5288)
Limit 38.632 (1.5209)
ExhaustSTD 39.259 — 39.359 (1.5456 — 1.5496)
Limit 39.157 (1.5417)
2.5 LIntakeSTD 39.485 — 39.585 (1.5545 — 1.5585)
Limit 39.385 (1.5506)
ExhaustSTD 39.259 — 39.359 (1.5456 — 1.5496)
Limit 39.159 (1.5417)
Camshaft journal O.D. mm (in) 31.928 — 31.945 (1.2570 — 1.2577)
Camshaft journal hole I.D. (Cylinder head) mm (in) 32.000 — 32.018 (1.2598 — 1.2605)
Oil clearance mm (in)STD 0.055 — 0.090 (0.0022 — 0.0035)
Limit 0.10 (0.0039)
Page 872 of 2870
ME(H4SO)-3
MECHANICAL
General Description
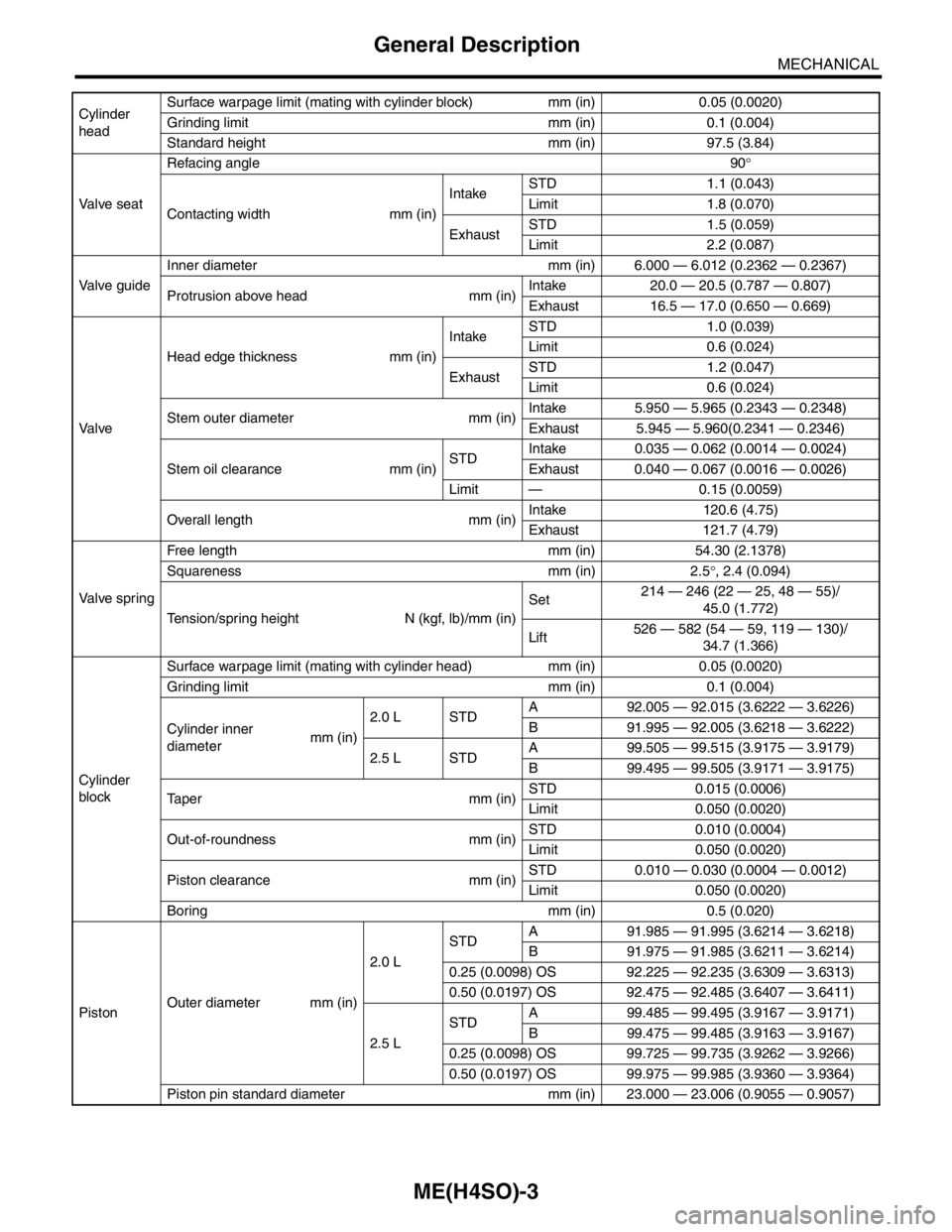
Cylinder
headSurface warpage limit (mating with cylinder block) mm (in) 0.05 (0.0020)
Grinding limit mm (in) 0.1 (0.004)
Standard height mm (in) 97.5 (3.84)
Va l ve s e a tRefacing angle90°
Contacting width mm (in)IntakeSTD 1.1 (0.043)
Limit 1.8 (0.070)
ExhaustSTD 1.5 (0.059)
Limit 2.2 (0.087)
Valve guideInner diameter mm (in) 6.000 — 6.012 (0.2362 — 0.2367)
Protrusion above head mm (in)Intake 20.0 — 20.5 (0.787 — 0.807)
Exhaust 16.5 — 17.0 (0.650 — 0.669)
Va l veHead edge thickness mm (in)IntakeSTD 1.0 (0.039)
Limit 0.6 (0.024)
ExhaustSTD 1.2 (0.047)
Limit 0.6 (0.024)
Stem outer diameter mm (in)Intake 5.950 — 5.965 (0.2343 — 0.2348)
Exhaust 5.945 — 5.960(0.2341 — 0.2346)
Stem oil clearance mm (in)STDIntake 0.035 — 0.062 (0.0014 — 0.0024)
Exhaust 0.040 — 0.067 (0.0016 — 0.0026)
Limit — 0.15 (0.0059)
Overall length mm (in)Intake 120.6 (4.75)
Exhaust 121.7 (4.79)
Valve springFree length mm (in) 54.30 (2.1378)
Squareness mm (in) 2.5°, 2.4 (0.094)
Tension/spring height N (kgf, lb)/mm (in)Set214 — 246 (22 — 25, 48 — 55)/
45.0 (1.772)
Lift526 — 582 (54 — 59, 119 — 130)/
34.7 (1.366)
Cylinder
blockSurface warpage limit (mating with cylinder head) mm (in) 0.05 (0.0020)
Grinding limit mm (in) 0.1 (0.004)
Cylinder inner
diametermm (in)2.0 L STDA 92.005 — 92.015 (3.6222 — 3.6226)
B 91.995 — 92.005 (3.6218 — 3.6222)
2.5 L STDA 99.505 — 99.515 (3.9175 — 3.9179)
B 99.495 — 99.505 (3.9171 — 3.9175)
Ta p e r m m ( i n )STD 0.015 (0.0006)
Limit 0.050 (0.0020)
Out-of-roundness mm (in)STD 0.010 (0.0004)
Limit 0.050 (0.0020)
Piston clearance mm (in)STD 0.010 — 0.030 (0.0004 — 0.0012)
Limit 0.050 (0.0020)
Boring mm (in) 0.5 (0.020)
PistonOuter diameter mm (in)2.0 LSTDA 91.985 — 91.995 (3.6214 — 3.6218)
B 91.975 — 91.985 (3.6211 — 3.6214)
0.25 (0.0098) OS 92.225 — 92.235 (3.6309 — 3.6313)
0.50 (0.0197) OS 92.475 — 92.485 (3.6407 — 3.6411)
2.5 LSTDA 99.485 — 99.495 (3.9167 — 3.9171)
B 99.475 — 99.485 (3.9163 — 3.9167)
0.25 (0.0098) OS 99.725 — 99.735 (3.9262 — 3.9266)
0.50 (0.0197) OS 99.975 — 99.985 (3.9360 — 3.9364)
Piston pin standard diameter mm (in) 23.000 — 23.006 (0.9055 — 0.9057)
Page 932 of 2870

ME(H4SO)-61
MECHANICAL
Camshaft
C: INSPECTION
1. CAMSHAFT
1) Measure the bend, and repair or replace if nec-
essary.
Limit:
0.025 mm (0.0010 in)
2) Check the journal for damage and wear. Re-
place if faulty.
3) Measure the outside diameter of camshaft jour-
nal and inside diameter of cylinder head journal,
and determine the difference between two (= oil
clearance). If the oil clearance exceeds specifica-
tions, replace the camshaft or cylinder head as
necessary.
4) Check the cam face condition; remove the minor
faults by grinding with oil stone. Measure the cam
height H; replace if the limit has been exceeded.
Cam height: HCam base circle diameter A:
IN: 34.00 mm (1.3386 in)
EX: 34.00 mm (1.3386 in)
2. CAMSHAFT SUPPORT
Measure the thrust clearance of camshaft with dial
gauge. If the clearance exceeds the limit, replace
the camshaft support.
Standard:
0.030 — 0.090 mm (0.0012 — 0.0035 in)
Limit:
0.10 mm (0.0039 in)
Unit: mm (in)
Clear-
ance at
journalStandard 0.055 — 0.090 (0.0022 — 0.0035)
Limit 0.10 (0.0039)
Camshaft journal O.D.31.928 — 31.945 (1.2570 —
1.2577)
Journal hole I.D.32.000 — 32.018 (1.2598 —
1.2605)
Model Item Unit: mm (in)
2.0 LIntakeSTD38.732 — 38.832
(1.5249 — 1.528885)
Limit 38.632 (1.5209)
ExhaustSTD39.259 — 39.359
(1.5456 — 1.5496)
Limit 39.157 (1.5416)
2.5 LIntakeSTD39.485 — 39.585
(1.5545 — 1.5585)
Limit 39.385 (1.5506)
ExhaustSTD39.259 — 39.359
(1.5456 — 1.5496)
Limit 39.157 (1.5416)
ME-00275
ME-00276
H
A
ME-00277
Page 936 of 2870

ME(H4SO)-65
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Head
(5) Compress the valve spring, and then fit the
valve spring retainer key.
(6) After installing, tap the valve spring retainers
lightly with plastic hammer for better seating.
E: INSPECTION
1. VALVE SPRING
1) Check the valve springs for damage, free length,
and tension. Replace the valve spring if it is not
within the standard value presented in the table.
2) To measure the squareness of valve spring,
stand the spring on a surface plate and measure its
deflection at the top using a try square.
2. INTAKE AND EXHAUST VALVE OIL
SEAL
In the following case, pinch and remove the oil seal
from valve using pliers, and then replace it with a
new one.
When the lip is damaged.
When the spring is out of the specified position. When readjusting the surfaces of intake valve
and valve sheet.
When replacing the intake valve guide.
1) Place the cylinder head on ST1.
2) Using ST2, press-fit the oil seal.
CAUTION:
Apply engine oil to oil seal before press-fit-
ting.
When press-fitting oil seal, do not use ham-
mer or strike in.
Differentiate between intake valve oil seal
and exhaust valve oil seal by noting their differ-
ence in color.
ST1 498267800 CYLINDER HEAD TABLE
ST2 498857100 VALVE OIL SEAL GUIDE
Color of rubber part:
Intake [Black]
Exhaust [Brown]
Color of spring part:
Intake [Silver]
Exhaust [Silver]
F: ADJUSTMENT
1. CYLINDER HEAD
1) Make sure that no crack or other damage exists.
In addition to visual inspection, inspect important
areas by means of red lead check.
Also make sure that gasket installing surface
shows no trace of gas and water leaks.
2) Place the cylinder head on ST.
ST 498267800 CYLINDER HEAD TABLE
3) Measure the warping of the cylinder head sur-
face that mates with crankcase using a straight
edge and thickness gauge.
If the warping exceeds the limit, regrind the surface
with a surface grinder.
Warping limit:
0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
Grinding limit:
0.1 mm (0.004 in)
Standard height of cylinder head:
97.5 mm (3.839 in)
(A) Retainer
(B) Valve spring
Free length 54.30 mm (2.1378 in)
Squareness 2.5°, 2.4 mm (0.094 in)
Tension/spring
height215 — 246 N
(21.9 — 25.1 kgf, 48.2 — 55.3 lb)/
45.0 mm (1.772 in)
527 — 582 N
(53.7 — 59.3 kgf, 118.1 — 130.8 lb)/
34.7 mm (1.366 in)
ME-00282
(B)(B)
(A)
ME-00283
ME-00284
ST1
ST2
Page 955 of 2870

ME(H4SO)-84
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
E: INSPECTION
1. CYLINDER BLOCK
1) Visually check for cracks and damage. Especial-
ly, inspect the important parts by means of red lead
check.
2) Check the oil passages for clogging.
3) Inspect the crankcase surface that mates with
cylinder head for warping by using a straight edge,
and correct by grinding if necessary.
Warping limit:
0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
Grinding limit:
0.1 mm (0.004 in)
Standard height of cylinder block:
201.0 mm (7.91 in)
2. CYLINDER AND PISTON
1) The cylinder bore size is stamped on cylinder
block’s front upper surface.
NOTE:
Measurement should be performed at a temper-
ature 20°C (68°F).
Standard sized pistons are classified into two
grades, “A” and “B”. These grades should be used
as a guide line in selecting a standard piston.Standard diameter:
2.0 L model
A: 92.005 — 92.015 mm (3.6222 — 3.6226
in)
B: 91.995 — 92.005 mm (3.6218 — 3.6222
in)
2.5 L model
A: 99.505 — 99.515 mm (3.9175 — 3.9179
in)
B: 99.495 — 99.505 mm (3.9171 — 3.9175
in)
2) How to measure the inner diameter of each cyl-
inder
Measure the inner diameter of each cylinder in both
the thrust and piston pin directions at the heights
shown in the figure, using a cylinder bore gauge.
NOTE:
Measurement should be performed at a tempera-
ture 20°C (68°F).
Taper:
Standard
0.015 mm (0.0006 in)
Limit
0.050 mm (0.0020 in)
(A) Main journal size mark
(B) Cylinder block RH-LH combination mark
(C) #1 cylinder bore size mark
(D) #2 cylinder bore size mark
(E) #3 cylinder bore size mark
(F) #4 cylinder bore size mark
ME-00170 #5
#4
#3
#2
#1(A)(B)
(F)
(D)
A BA B
5 45 4
(C) (E)
Page 956 of 2870
ME(H4SO)-85
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
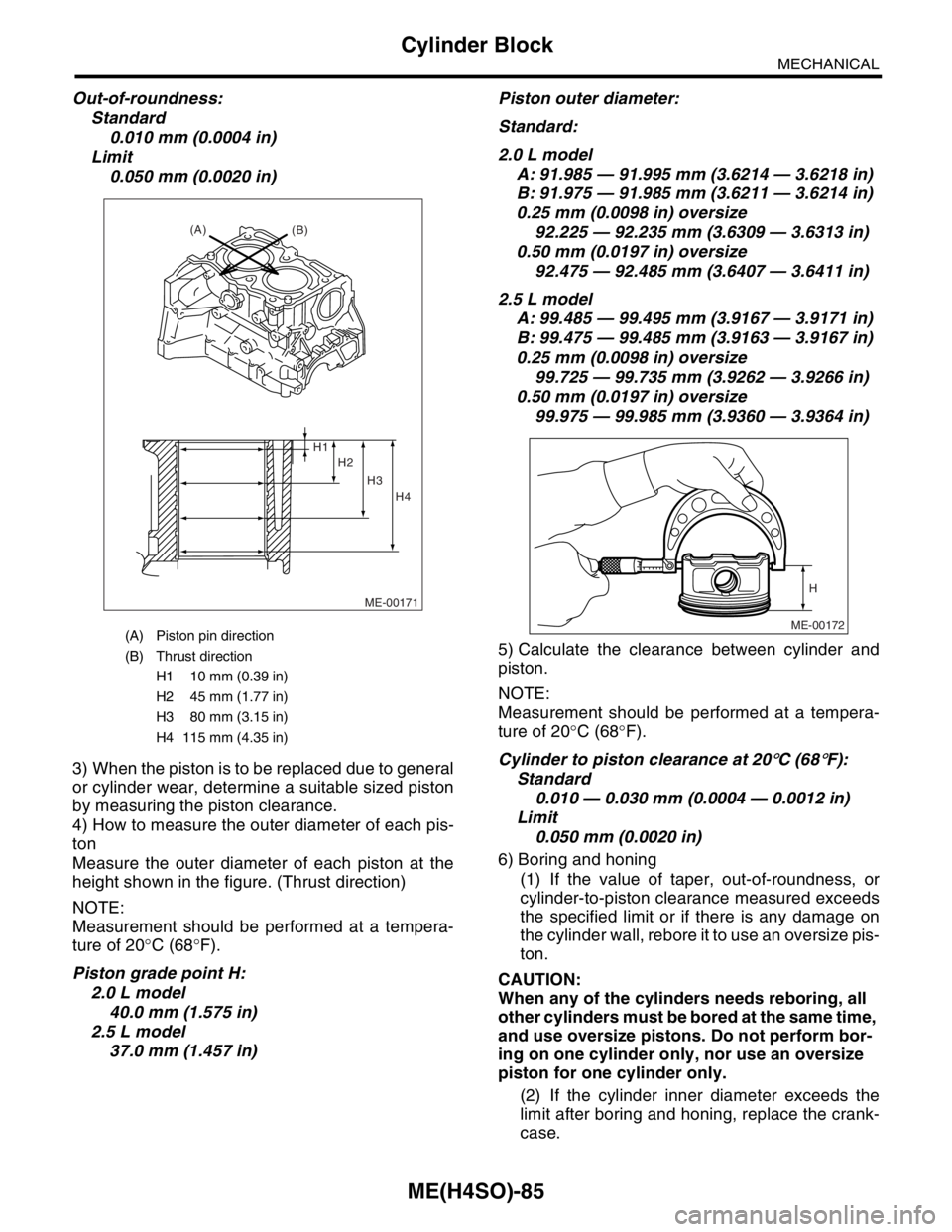
Out-of-roundness:
Standard
0.010 mm (0.0004 in)
Limit
0.050 mm (0.0020 in)
3) When the piston is to be replaced due to general
or cylinder wear, determine a suitable sized piston
by measuring the piston clearance.
4) How to measure the outer diameter of each pis-
ton
Measure the outer diameter of each piston at the
height shown in the figure. (Thrust direction)
NOTE:
Measurement should be performed at a tempera-
ture of 20°C (68°F).
Piston grade point H:
2.0 L model
40.0 mm (1.575 in)
2.5 L model
37.0 mm (1.457 in)Piston outer diameter:
Standard:
2.0 L model
A: 91.985 — 91.995 mm (3.6214 — 3.6218 in)
B: 91.975 — 91.985 mm (3.6211 — 3.6214 in)
0.25 mm (0.0098 in) oversize
92.225 — 92.235 mm (3.6309 — 3.6313 in)
0.50 mm (0.0197 in) oversize
92.475 — 92.485 mm (3.6407 — 3.6411 in)
2.5 L model
A: 99.485 — 99.495 mm (3.9167 — 3.9171 in)
B: 99.475 — 99.485 mm (3.9163 — 3.9167 in)
0.25 mm (0.0098 in) oversize
99.725 — 99.735 mm (3.9262 — 3.9266 in)
0.50 mm (0.0197 in) oversize
99.975 — 99.985 mm (3.9360 — 3.9364 in)
5) Calculate the clearance between cylinder and
piston.
NOTE:
Measurement should be performed at a tempera-
ture of 20°C (68°F).
Cylinder to piston clearance at 20
°C (68°F):
Standard
0.010 — 0.030 mm (0.0004 — 0.0012 in)
Limit
0.050 mm (0.0020 in)
6) Boring and honing
(1) If the value of taper, out-of-roundness, or
cylinder-to-piston clearance measured exceeds
the specified limit or if there is any damage on
the cylinder wall, rebore it to use an oversize pis-
ton.
CAUTION:
When any of the cylinders needs reboring, all
other cylinders must be bored at the same time,
and use oversize pistons. Do not perform bor-
ing on one cylinder only, nor use an oversize
piston for one cylinder only.
(2) If the cylinder inner diameter exceeds the
limit after boring and honing, replace the crank-
case.
(A) Piston pin direction
(B) Thrust direction
H1 10 mm (0.39 in)
H2 45 mm (1.77 in)
H3 80 mm (3.15 in)
H4 115 mm (4.35 in)
ME-00171
(A)
(B)
H2 H1
H3
H4
ME-00172
H
Page 986 of 2870
CO(H4SO)-3
COOLING
General Description
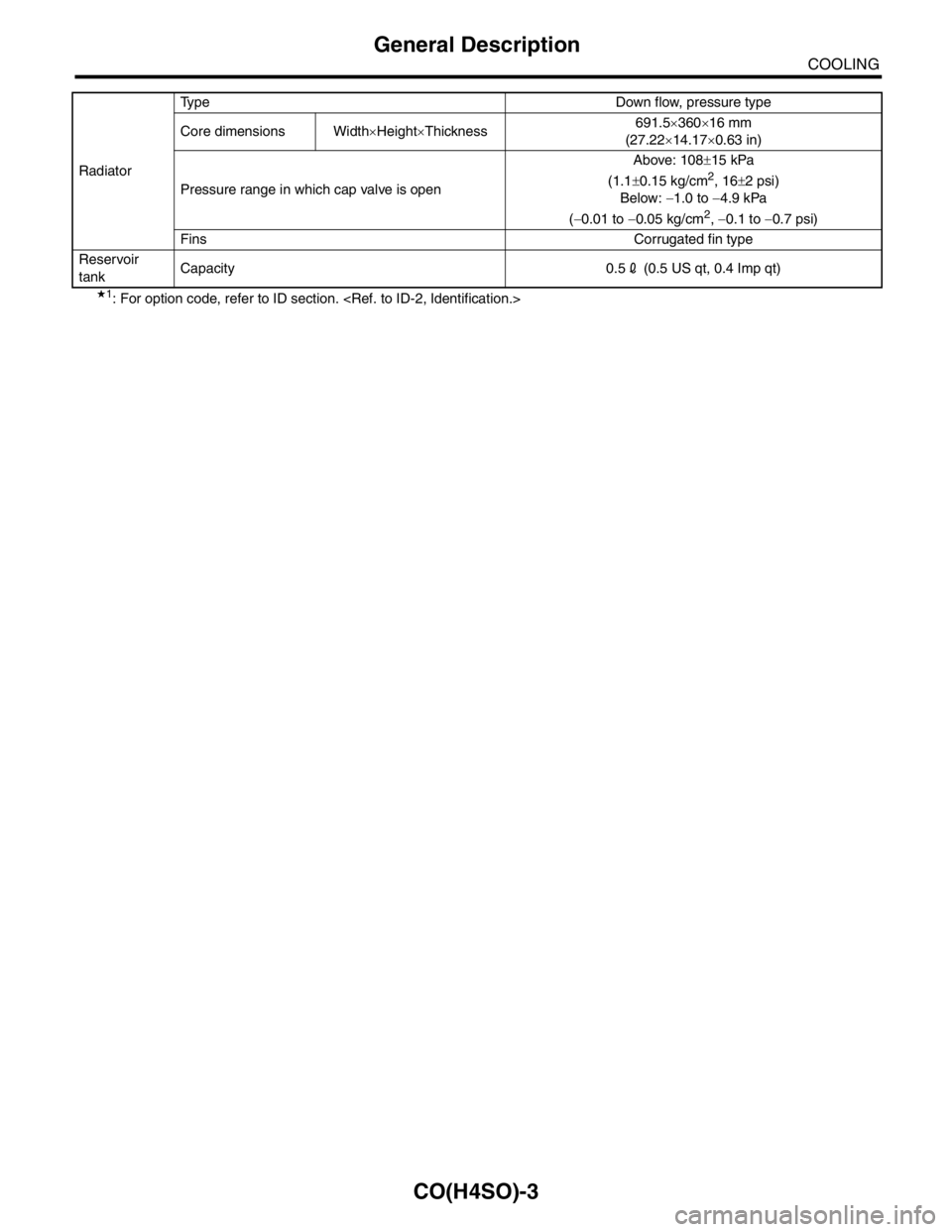
★1: For option code, refer to ID section.
Core dimensions Width×Height×Thickness691.5×360×16 mm
(27.22×14.17×0.63 in)
Pressure range in which cap valve is openAbove: 108±15 kPa
(1.1±0.15 kg/cm
2, 16±2 psi)
Below: −1.0 to −4.9 kPa
(−0.01 to −0.05 kg/cm
2, −0.1 to −0.7 psi)
Fins Corrugated fin type
Reservoir
tankCapacity 0.52 (0.5 US qt, 0.4 Imp qt)