2004 SUBARU FORESTER height
[x] Cancel search: heightPage 4 of 2870
AC-2
HVAC SYSTEM (HEATER, VENTILATOR AND A/C)
General Description
1. General Description
A: SPECIFICATION
1. HEATER SYSTEM
2. A/C SYSTEM
AUTO A/C MODEL
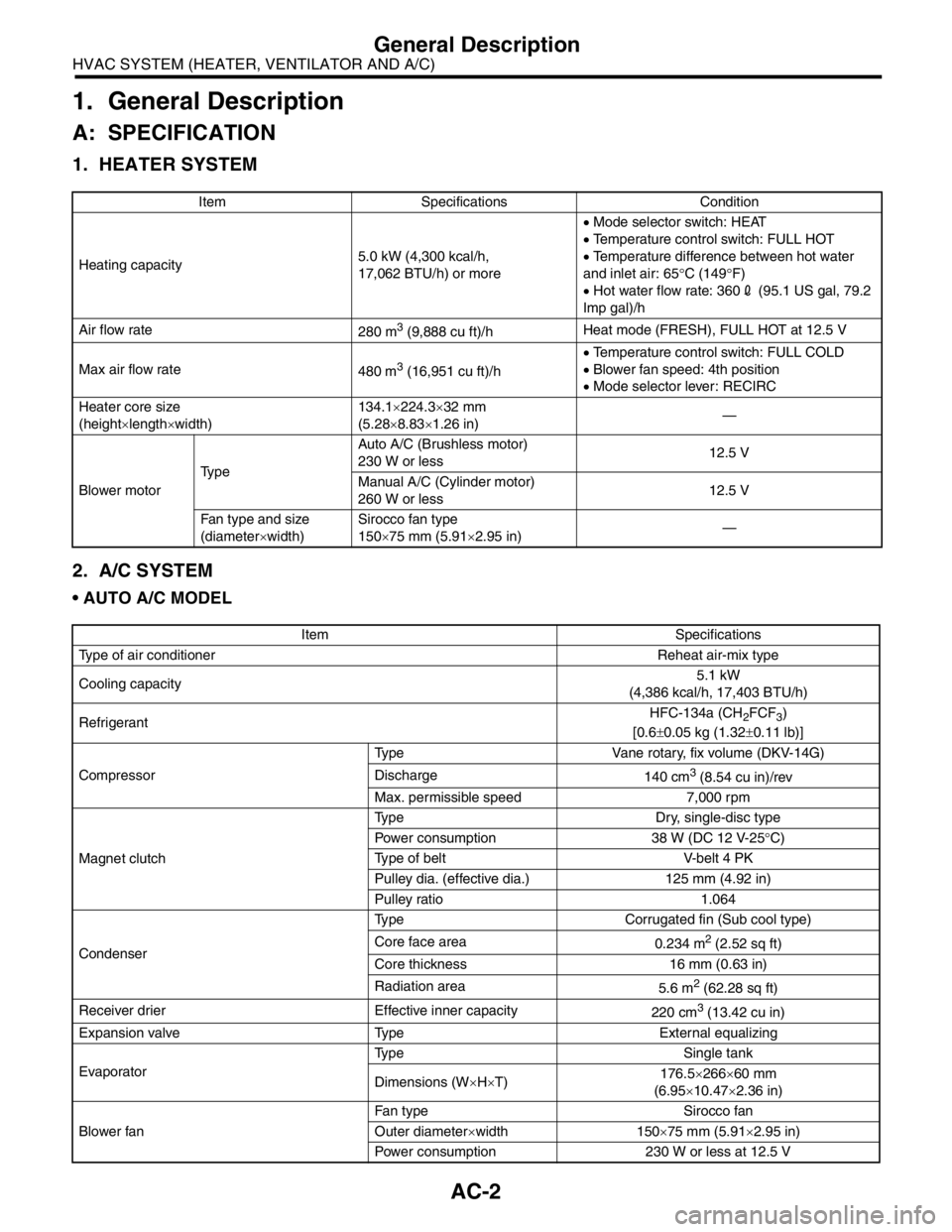
Item Specifications Condition
Heating capacity5.0 kW (4,300 kcal/h,
17,062 BTU/h) or more• Mode selector switch: HEAT
• Temperature control switch: FULL HOT
• Temperature difference between hot water
and inlet air: 65°C (149°F)
• Hot water flow rate: 3602 (95.1 US gal, 79.2
Imp gal)/h
Air flow rate
280 m
3 (9,888 cu ft)/hHeat mode (FRESH), FULL HOT at 12.5 V
Max air flow rate
480 m
3 (16,951 cu ft)/h• Temperature control switch: FULL COLD
• Blower fan speed: 4th position
• Mode selector lever: RECIRC
Heater core size
(height×length×width)134.1×224.3×32 mm
(5.28×8.83×1.26 in)—
Blower motorTy p eAuto A/C (Brushless motor)
230 W or less12.5 V
Manual A/C (Cylinder motor)
260 W or less12.5 V
Fan type and size
(diameter×width)Sirocco fan type
150×75 mm (5.91×2.95 in)—
Item Specifications
Type of air conditioner Reheat air-mix type
Cooling capacity5.1 kW
(4,386 kcal/h, 17,403 BTU/h)
RefrigerantHFC-134a (CH
2FCF3)
[0.6±0.05 kg (1.32±0.11 lb)]
CompressorType Vane rotary, fix volume (DKV-14G)
Discharge
140 cm
3 (8.54 cu in)/rev
Max. permissible speed 7,000 rpm
Magnet clutchType Dry, single-disc type
Power consumption 38 W (DC 12 V-25°C)
Type of belt V-belt 4 PK
Pulley dia. (effective dia.) 125 mm (4.92 in)
Pulley ratio 1.064
CondenserType Corrugated fin (Sub cool type)
Core face area
0.234 m
2 (2.52 sq ft)
Core thickness 16 mm (0.63 in)
Radiation area
5.6 m
2 (62.28 sq ft)
Receiver drier Effective inner capacity
220 cm
3 (13.42 cu in)
Expansion valve Type External equalizing
EvaporatorType Single tank
Dimensions (W×H×T)176.5×266×60 mm
(6.95×10.47×2.36 in)
Blower fanFan type Sirocco fan
Outer diameter×width 150×75 mm (5.91×2.95 in)
Power consumption 230 W or less at 12.5 V
Page 112 of 2870

AB-12
AIRBAG SYSTEM
Inspection Locations After a Collision
3. Inspection Locations After a
Collision
A: REPLACEMENT
When airbag system is deployed, replace the fol-
lowing parts.
1. FRONT COLLISION
1) Driver’s airbag module
2) Passenger’s airbag module
3) Driver’s seat belt (pretensioner, lap seat belt pre-
tensioner)
4) Passenger’s seat belt (pretensioner)
5) Airbag control module
6) Front sub-sensor
7) Roll connector
2. SIDE COLLISION
1) Airbag control module
2) Side airbag module (operating side seat bag)
3) Side airbag sensor (operating side)
3. INSPECTION OF OTHER PARTS
Check for the following parts, replace the damaged
parts with new ones.
1) Steering wheel and steering shaft
Check the steering wheel and steering shaft for
mounting condition and deflection of axial and radi-
al direction. Check the steering shaft for deflection
of axial direction with tilt lever released. (After a col-
lision, absorbing part of steering shaft may inflate.)
2) Check the direct type connector of driver’s air-
bag module, pretensioner, etc. for damage, and
also check each harness for pinch and connector
damage. If damage is found, replace the harness
as a unit.
B: INSPECTION
If the vehicle is involved in a collision on any side,
even if it is a slight collision, be sure to check the
following system parts.
1. DRIVER’S AIRBAG MODULE
1) Check for the following, and replace damaged
parts with new ones.
Airbag module is cracked or deformed.
Harness and/or connector is cracked, deformed
or open. Lead wire is exposed.
The module surface is fouled with grease, oil,
water or cleaning solvent.
2) When installing a new driver’s airbag module,
check the following. If necessary, install a new air-
bag module and steering wheel.
The steering wheel is in the way, making it diffi-
cult to install the airbag module. The clearance between the driver’s airbag mod-
ule and steering wheel is not constant.
The steering wheel deformation in axial and radi-
al directions exceed limits.
Specifications:
Height deflection A
Less than 6 mm (0.24 in)
O.D. deflection L
Less than 17 mm (0.67 in)
2. PASSENGER’S AIRBAG MODULE
Check for the following, and replace damaged
parts with new ones.
Airbag module is cracked or deformed.
Harness and/or connector is cracked, deformed
or open. Lead wire is exposed.
Mounting bracket is cracked or deformed.
3. SIDE AIRBAG MODULE
Check for the following, and replace damaged
parts with new ones.
Front seat is damaged or deformed.
Harness and/or connector is cracked, deformed
or open.
Lead wire is exposed.
4. AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE
Check for the following, and replace damaged
parts with new ones.
Control module is cracked or deformed.
Mounting bracket is cracked or deformed.
Connector is scratched or deformed.
Airbag is deployed.
Side airbag is deployed.
AB-00028
L
A
Page 469 of 2870
SR-5
SUNROOF/T-TOP/CONVERTIBLE TOP (SUNROOF)
Sunroof Lid
3. Sunroof Lid
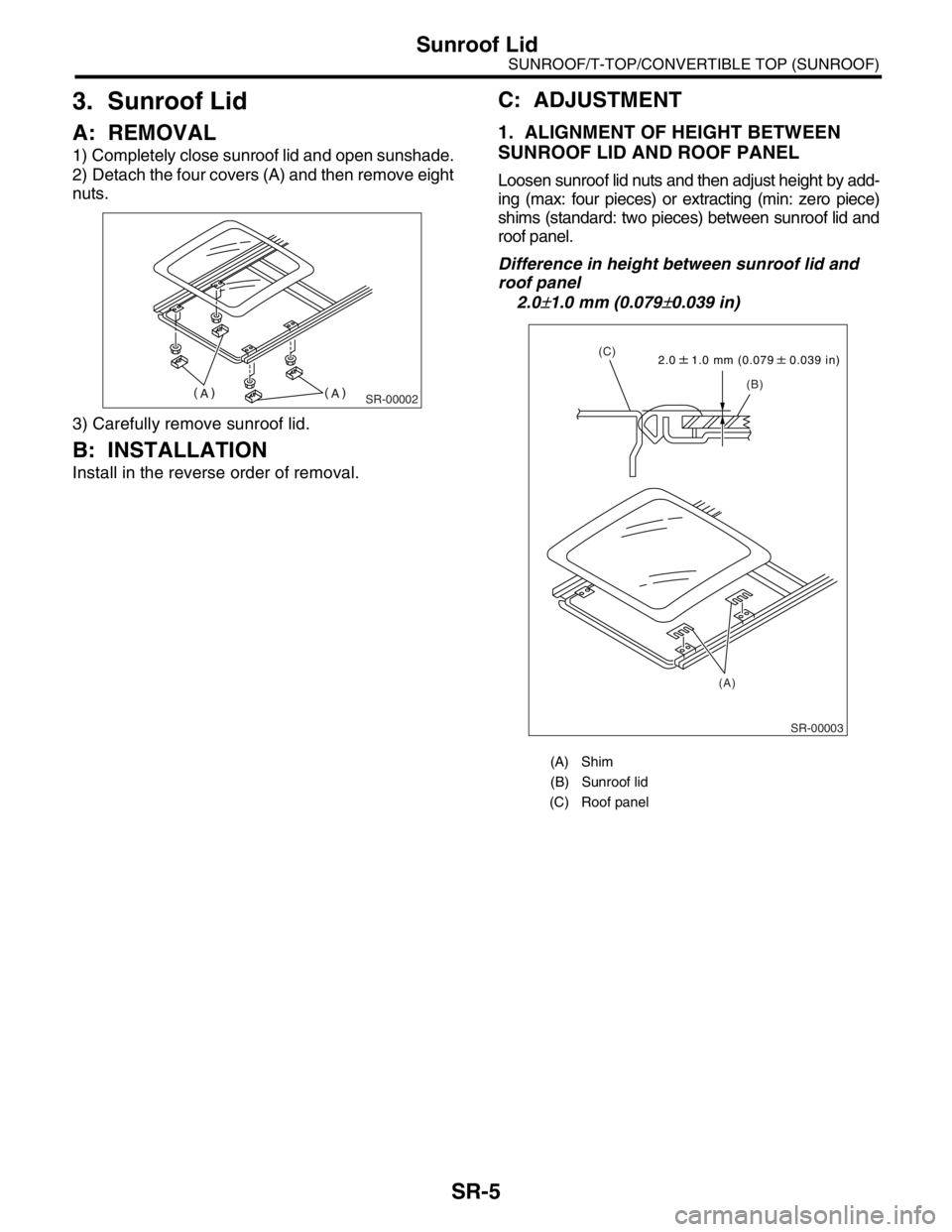
A: REMOVAL
1) Completely close sunroof lid and open sunshade.
2) Detach the four covers (A) and then remove eight
nuts.
3) Carefully remove sunroof lid.
B: INSTALLATION
Install in the reverse order of removal.
C: ADJUSTMENT
1. ALIGNMENT OF HEIGHT BETWEEN
SUNROOF LID AND ROOF PANEL
Loosen sunroof lid nuts and then adjust height by add-
ing (max: four pieces) or extracting (min: zero piece)
shims (standard: two pieces) between sunroof lid and
roof panel.
Difference in height between sunroof lid and
roof panel
2.0
±1.0 mm (0.079±0.039 in)
SR-00002
(A) Shim
(B) Sunroof lid
(C) Roof panel
SR-00003
2.0 1.0 mm (0.079 0.039 in)
(B) (C)
(A)
Page 539 of 2870
EB-9
EXTERIOR BODY PANEL
Front Hood Panel
2. Front Hood Panel
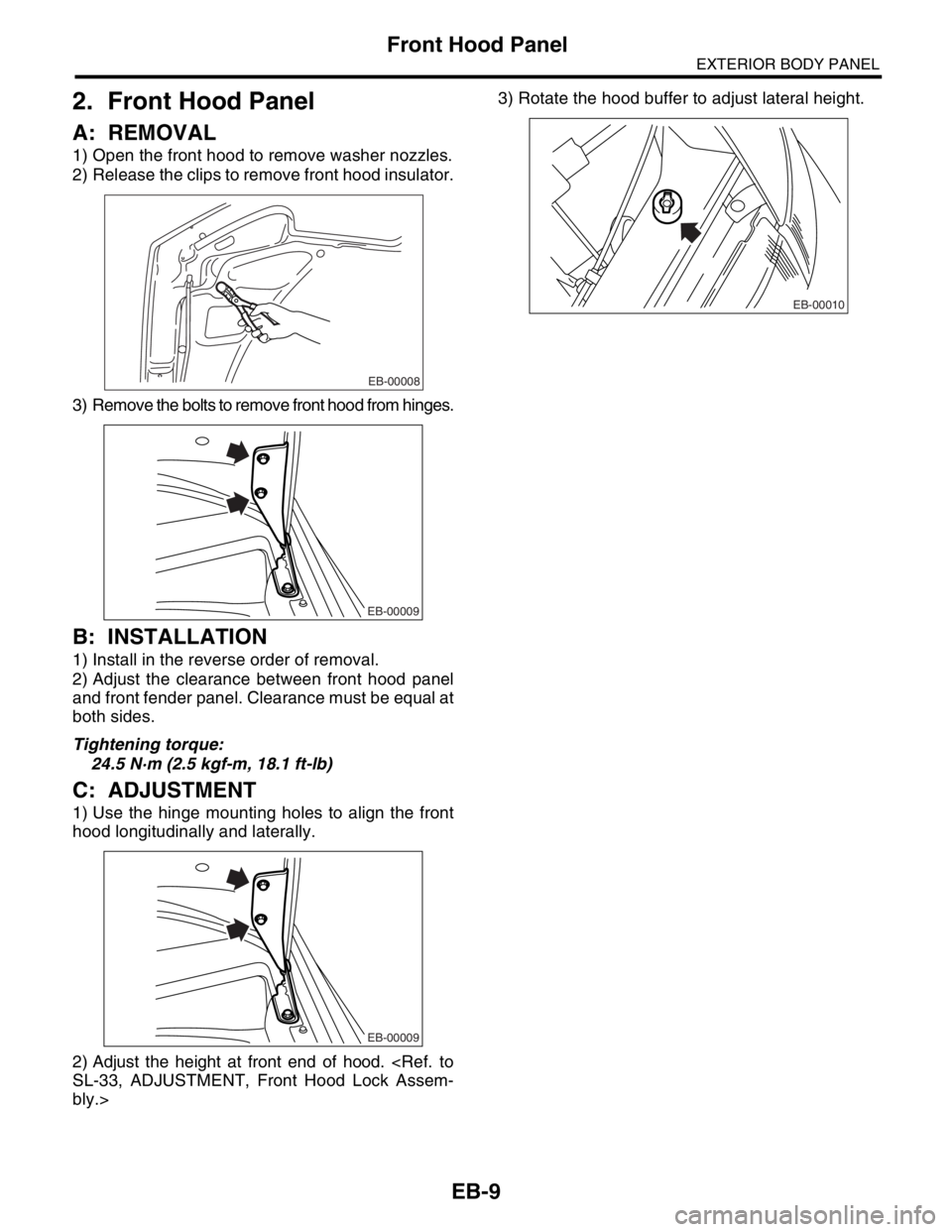
A: REMOVAL
1) Open the front hood to remove washer nozzles.
2) Release the clips to remove front hood insulator.
3) Remove the bolts to remove front hood from hinges.
B: INSTALLATION
1) Install in the reverse order of removal.
2) Adjust the clearance between front hood panel
and front fender panel. Clearance must be equal at
both sides.
Tightening torque:
24.5 N·m (2.5 kgf-m, 18.1 ft-lb)
C: ADJUSTMENT
1) Use the hinge mounting holes to align the front
hood longitudinally and laterally.
2) Adjust the height at front end of hood.
bly.>3) Rotate the hood buffer to adjust lateral height.
EB-00008
EB-00009
EB-00009
EB-00010
Page 691 of 2870
SPC-2
SPECIFICATION
Forester
1. Forester
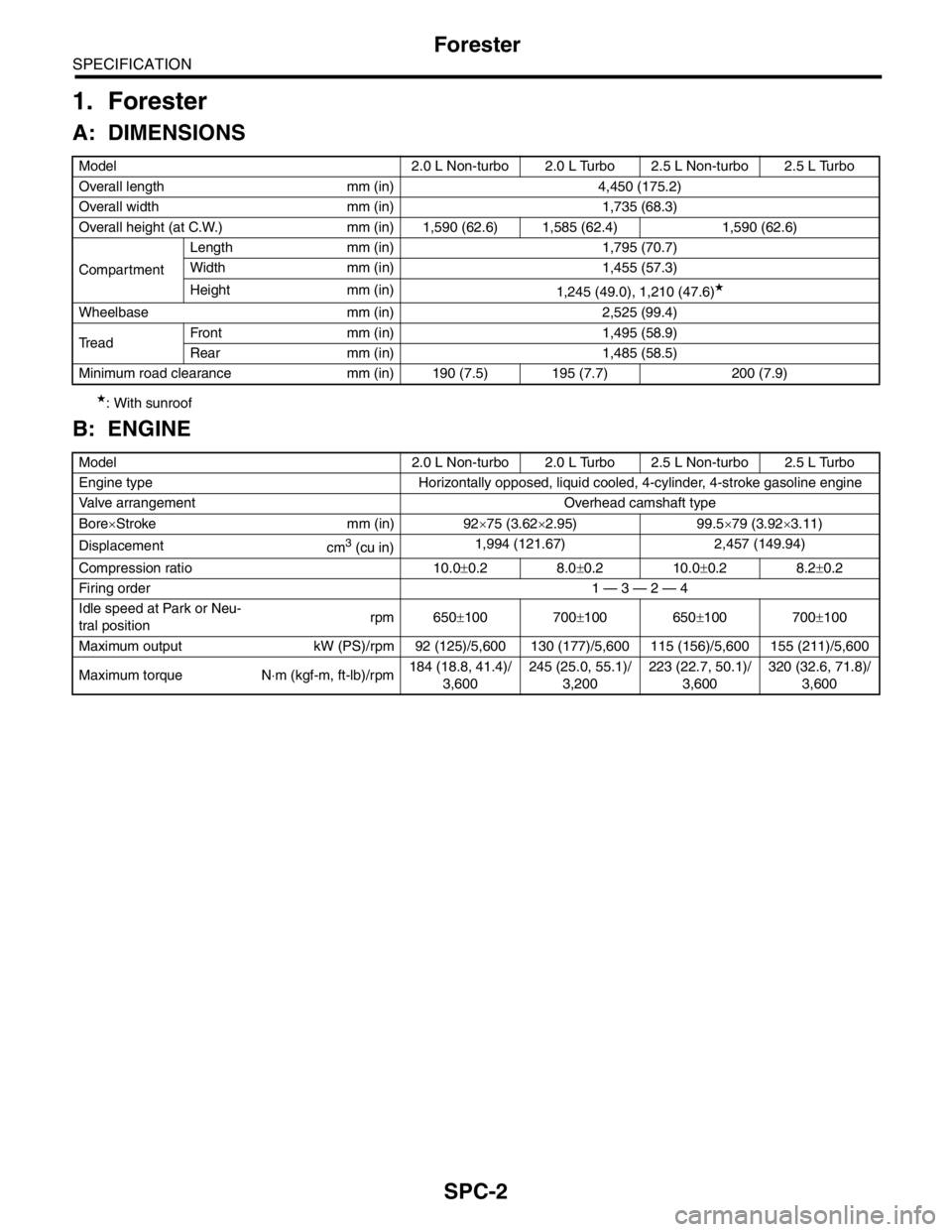
A: DIMENSIONS
★: With sunroof
B: ENGINE
Model 2.0 L Non-turbo 2.0 L Turbo 2.5 L Non-turbo 2.5 L Turbo
Overall length mm (in) 4,450 (175.2)
Overall width mm (in) 1,735 (68.3)
Overall height (at C.W.) mm (in) 1,590 (62.6) 1,585 (62.4) 1,590 (62.6)
CompartmentLength mm (in) 1,795 (70.7)
Width mm (in) 1,455 (57.3)
Height mm (in)
1,245 (49.0), 1,210 (47.6)
★
Wheelbase mm (in) 2,525 (99.4)
Tread Front mm (in) 1,495 (58.9)
Rear mm (in) 1,485 (58.5)
Minimum road clearance mm (in) 190 (7.5) 195 (7.7) 200 (7.9)
Model 2.0 L Non-turbo 2.0 L Turbo 2.5 L Non-turbo 2.5 L Turbo
Engine type Horizontally opposed, liquid cooled, 4-cylinder, 4-stroke gasoline engine
Valve arrangement Overhead camshaft type
Bore×Stroke mm (in) 92×75 (3.62×2.95) 99.5×79 (3.92×3.11)
Displacement
cm
3 (cu in)1,994 (121.67) 2,457 (149.94)
Compression ratio 10.0±0.2 8.0±0.2 10.0±0.2 8.2±0.2
Firing order 1 — 3 — 2 — 4
Idle speed at Park or Neu-
tral positionrpm 650±100 700±100 650±100 700±100
Maximum output kW (PS)/rpm 92 (125)/5,600 130 (177)/5,600 115 (156)/5,600 155 (211)/5,600
Maximum torque N⋅m (kgf-m, ft-lb)/rpm184 (18.8, 41.4)/
3,600245 (25.0, 55.1)/
3,200223 (22.7, 50.1)/
3,600320 (32.6, 71.8)/
3,600
Page 708 of 2870
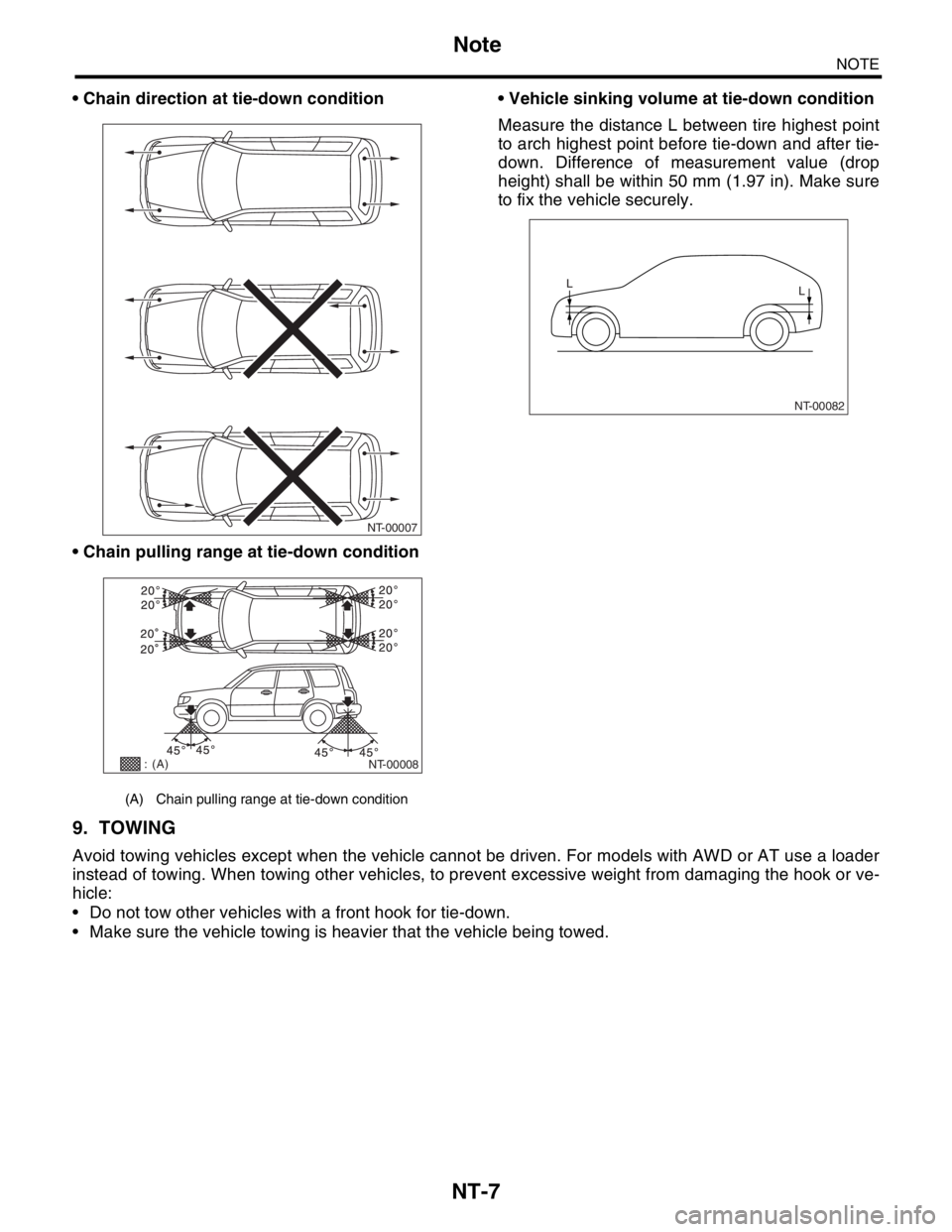
NT-7
NOTE
Note
Chain direction at tie-down condition
Chain pulling range at tie-down condition Vehicle sinking volume at tie-down condition
Measure the distance L between tire highest point
to arch highest point before tie-down and after tie-
down. Difference of measurement value (drop
height) shall be within 50 mm (1.97 in). Make sure
to fix the vehicle securely.
9. TOWING
Avoid towing vehicles except when the vehicle cannot be driven. For models with AWD or AT use a loader
instead of towing. When towing other vehicles, to prevent excessive weight from damaging the hook or ve-
hicle:
Do not tow other vehicles with a front hook for tie-down.
Make sure the vehicle towing is heavier that the vehicle being towed.
(A) Chain pulling range at tie-down condition
NT-00007
NT-00008
: (A)
NT-00082
L
L
Page 759 of 2870
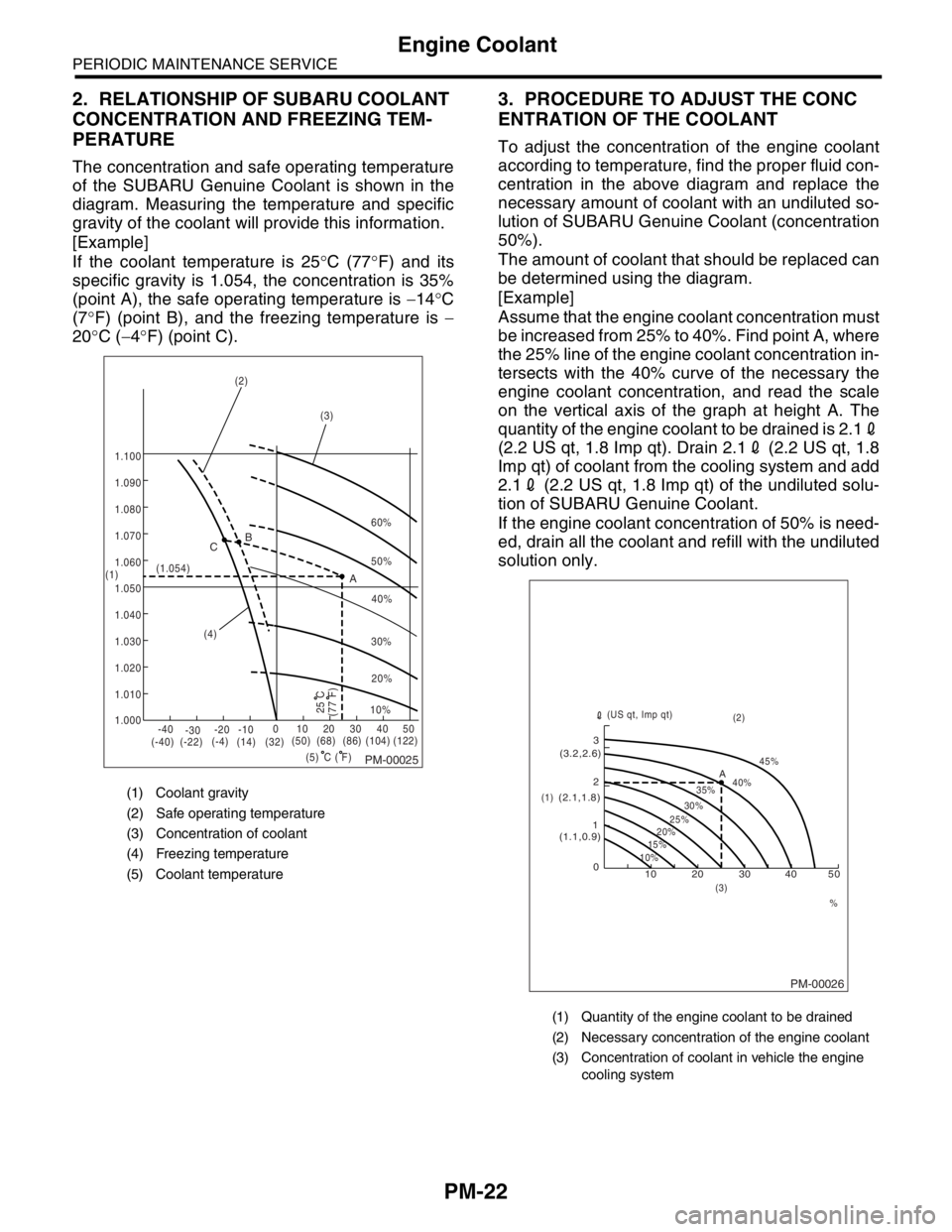
PM-22
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE SERVICE
Engine Coolant
2. RELATIONSHIP OF SUBARU COOLANT
CONCENTRATION AND FREEZING TEM-
PERATURE
The concentration and safe operating temperature
of the SUBARU Genuine Coolant is shown in the
diagram. Measuring the temperature and specific
gravity of the coolant will provide this information.
[Example]
If the coolant temperature is 25°C (77°F) and its
specific gravity is 1.054, the concentration is 35%
(point A), the safe operating temperature is −14°C
(7°F) (point B), and the freezing temperature is −
20°C (−4°F) (point C).
3. PROCEDURE TO ADJUST THE CONC
ENTRATION OF THE COOLANT
To adjust the concentration of the engine coolant
according to temperature, find the proper fluid con-
centration in the above diagram and replace the
necessary amount of coolant with an undiluted so-
lution of SUBARU Genuine Coolant (concentration
50%).
The amount of coolant that should be replaced can
be determined using the diagram.
[Example]
Assume that the engine coolant concentration must
be increased from 25% to 40%. Find point A, where
the 25% line of the engine coolant concentration in-
tersects with the 40% curve of the necessary the
engine coolant concentration, and read the scale
on the vertical axis of the graph at height A. The
quantity of the engine coolant to be drained is 2.12
(2.2 US qt, 1.8 Imp qt). Drain 2.12 (2.2 US qt, 1.8
Imp qt) of coolant from the cooling system and add
2.12 (2.2 US qt, 1.8 Imp qt) of the undiluted solu-
tion of SUBARU Genuine Coolant.
If the engine coolant concentration of 50% is need-
ed, drain all the coolant and refill with the undiluted
solution only.
(1) Coolant gravity
(2) Safe operating temperature
(3) Concentration of coolant
(4) Freezing temperature
(5) Coolant temperature
PM-00025
60%
(1.054)
1.000 1.010 1.020
1.030
1.040
1.050
1.060
1.070 1.080 1.090
1.100
(5) (4)(3) (2)
(1)B
A C
-40
(-40) (-22)(-4)
(14)(32)(50) (68) (86)
( F)(104) (122) -30-20 -1001020304050
(77 F)
50%
40%
30%
20%
25 C10%
C
(1) Quantity of the engine coolant to be drained
(2) Necessary concentration of the engine coolant
(3) Concentration of coolant in vehicle the engine
cooling system
PM-00026
10 0 12 3
(1.1,0.9) (2.1,1.8)(3.2,2.6)
10%15%25%
20%30%35%40%45%
A
20 30 40 50
% (3)(2)
(1)(US qt, Imp qt)
Page 768 of 2870

PM-31
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE SERVICE
Brake Line
(4) If there is no free play between clevis pin
and clevis, turn the brake switch adjusting nut
until the clearance between stopper and screw
of brake switch becomes 0.3 mm (0.012 in).
3) Check the pedal stroke.
While the engine is idling, depress the brake pedal
with a 490 N (50 kgf, 110 lb) load and measure the
distance between brake pedal and steering wheel.
With the brake pedal released, measure the dis-
tance between pedal and steering wheel again.
The difference between the two measurements
must be less than specified value. If the distance is
more than specified value, there is possibility of air
inside the hydraulic unit.
Brake pedal reserve distance: A
For Australia model
105 mm (4.13 in)/ 490 N (50 kgf , 110 lb) or less
Except for Australia model
90 mm (3.54 in)/ 490 N (50 kgf , 110 lb) or less4) Check to see if air is in the hydraulic brake line
by the feel of pedal operation. If air appears to exist
in the line, bleed it from the system.
5) Check for even operation of all brakes, using a
brake tester or by driving the vehicle for a short dis-
tance on a straight road.
2. BRAKE SERVO SYSTEM
1) With the engine off, depress the brake pedal
several times applying the same pedal force: Make
sure the travel distance should not change.
2) With the brake pedal depressed, start the en-
gine: Make sure the pedal should move slightly to-
ward the floor.
3) With the brake pedal depressed, stop the engine
and keep the pedal depressed for 30 seconds:
Make sure the pedal height should not change.
4) Check valve is built into the vacuum hose. Dis-
connect the vacuum hose to inspect function of
check valve.
Blow air into the vacuum hose from its brake boost-
er side end: Air must flow out of engine side end of
hose. Next blow air into the hose from engine side:
Air should not to brake booster side.
Replace both check valve and vacuum hose if the
check valve is faulty. Engine side of vacuum hose
is indicated by marking “ENG” as shown in illustra-
tion.
5) Check the vacuum hose for cracks or other dam-
age.
CAUTION:
When installing the vacuum hose on the engine
and brake booster, do not use soapy water or
lubricating oil on their connections.
6) Check vacuum hose to make sure it is tight and
secure.
(A) Brake switch
(B) Adjusting nut
(C) 0.3 mm (0.012 in)
(D) Stopper
(E) Clevis pin
(F) Clevis
(G) Brake pedal free play
(H) Lock nut
(I) Brake booster operating rod
(J) Play at pin
(A) Steering wheel
(B) Toe board
PM-00041
(B)
(G) (H)
(I)
(J)(C)
(D)
(E)
(F)(A)
PM-00045(B)(A) = A
1
12
2
(A) Engine side
(B) Brake booster side
(C) ENG
PM-00046
(B)
(C) (A)