2001 DODGE RAM torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 63 of 2889

(8) Install a new cotter pin in hub nut. Tighten the
nut as needed to align cotter pin hole in shaft with
the opening in the nut.
(9) Install the rotor, brake caliper with adapter,
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION).
(10) Install the ABS wheel speed sensor if
equipped, (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/ELECTRICAL/
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR - INSTALLA-
TION).
(11) Install the wheel and tire assemblies, (Refer
to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(12) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
(13) Apply the brakes several times to seat the
brake shoes and the caliper piston. Do not move the
vehicle until a firm brake pedal is obtained.
KNUCKLE
DESCRIPTION
The knuckles are a single casting with legs
machined for the upper and lower ball joints. The
knuckles also has machined mounting locations for
the front brake calipers adapters and hub bearing
assembly.
OPERATION
The steering knuckles pivots between the upper
and lower ball joints. The steering linkage is
attached to the knuckles controls vehicle steering.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove hub bearing and axle shaft.
(2) Remove tie-rod or drag link end from the steer-
ing knuckle arm.
(3) Remove the ABS sensor wire and bracket from
knuckle.
(4) Remove the cotter pin from the upper ball stud
nut. Remove the upper and lower ball stud nuts.
(5) Strike the steering knuckle with a brass ham-
mer to loosen. Remove knuckle from axle tube yokes.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove hub bearing and axle shaft.
(2) Remove tie-rod or drag link end from the steer-
ing knuckle arm.
(3) Remove the ABS sensor wire and bracket from
knuckle. Refer to Brakes, for proper procedures.
(4) Remove the cotter pin from the upper ball stud
nut. Remove the upper and lower ball stud nuts.
(5) Strike the steering knuckle with a brass ham-
mer to loosen.
(6) Remove knuckle from axle tube yokes.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the steering knuckle on the ball studs.
(2) Install and tighten lower ball stud nut to 108
N´m (80 ft. lbs.) torque. Advance nut to next slot to
line up hole and install new cotter pin.
(3) Install and tighten upper ball stud nut to 101
N´m (75 ft. lbs.) torque. Advance nut to next slot to
line up hole and install new cotter pin.
(4) Install the hub bearing and axle shaft.
(5) Install tie-rod or drag link end onto the steer-
ing knuckle arm.
(6) Install the ABS sensor wire and bracket to the
knuckle. Refer to Brakes, for proper procedures.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the steering knuckle on the ball studs.
(2) Install and tighten lower ball stud nut to 47
N´m (35 ft. lbs.) torque. Do not install cotter pin at
this time.
(3) Install and tighten upper ball stud nut to 94
N´m (70 ft. lbs.) torque. Advance nut to next slot to
line up hole and install new cotter pin.
(4) Retorque lower ball stud nut to 190±217 N´m
(140±160 ft. lbs.) torque. Advance nut to next slot to
line up hole and install new cotter pin.
(5) Install the hub bearing and axle shaft.
(6) Install tie-rod or drag link end onto the steer-
ing knuckle arm.
(7) Install the ABS sensor wire and bracket to the
knuckle. Refer to Brakes, for proper procedure.
LOWER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Paint or scribe alignment marks on the cam
adjusters and suspension arm for installation refer-
ence (Fig. 15).
(3) Remove the lower suspension arm nut, cam
and cam bolt from the axle.
(4) Remove the nut and bolt from the frame rail
bracket and remove the lower suspension arm (Fig.
22).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the lower suspension arm at the axle
bracket and frame rail bracket.
(2) Install the rear bolt and finger tighten the nut.
(3) Install the cam bolt, cam and nut in the axle
and align the reference marks.
(4) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
(5) Tighten cam nut at the axle bracket to 190
N´m (140 ft. lbs.). Tighten rear nut at the frame
bracket to 190 N´m (140 ft. lbs.).
2 - 20 FRONT - 4WDBR/BE
HUB / BEARING (Continued)
Page 69 of 2889

REAR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR
DESCRIPTION...........................26
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................26
SPRING AND SHOCK....................26
SPECIFICATIONS........................27
SPECIAL TOOLS.........................28
BUSHINGS
REMOVAL..............................28
INSTALLATION...........................28
JOUNCE BUMPER
DESCRIPTION...........................28
OPERATION.............................28
SHOCK
DESCRIPTION...........................28OPERATION.............................28
REMOVAL..............................28
INSTALLATION...........................28
SPRING
DESCRIPTION...........................28
OPERATION.............................28
REMOVAL..............................28
INSTALLATION...........................29
STABILIZER BAR
DESCRIPTION...........................30
OPERATION.............................30
REMOVAL..............................30
INSTALLATION...........................30
REAR
DESCRIPTION
The rear suspension is comprised of:
²Shock Absorbers
²Jounce Bumpers
²Stabilizer Bar (optional)
²Leaf Springs
²Drive Axle
CAUTION: A vehicle should always be loaded so
the vehicle weight center-line is located immedi-
ately forward of the rear axle. Correct vehicle load-
ing provides proper front tire-to-road contact. This
results in maximum vehicle handling stability and
safety. Incorrect vehicle weight distribution can
cause excessive tire tread wear, spring fatigue or
failure, and erratic steering.
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber/ure-
thane bushings (except stabilizer bar) should be
tightened with the vehicle at normal ride height. It is
important to have the springs supporting the weight
of the vehicle when the fasteners are torqued. If
springs are not at their normal ride position, vehicle
ride comfort could be affected and premature bush-
ing wear may occur.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPRING AND
SHOCK
A knocking or rattling noise from a shock absorber
may be caused by movement between mounting
bushings and metal brackets or attaching compo-
nents. These noises can usually be stopped by tight-
ening the attaching nuts. If the noise persists,
inspect for damaged and worn bushings, and attach-
ing components. Repair as necessary if any of these
conditions exist.
A squeaking noise from the shock absorber may be
caused by the hydraulic valving and may be intermit-
tent. This condition is not repairable and the shock
absorber must be replaced.
The shock absorbers are not refillable or adjust-
able. If a malfunction occurs, the shock absorber
must be replaced. To test a shock absorber, hold it in
an upright position and force the piston in and out of
the cylinder four or five times. The action throughout
each stroke should be smooth and even.
The spring eye and shock absorber bushings do not
require any type of lubrication. Do not attempt to
stop spring bushing noise by lubricating them.
Grease and mineral oil-base lubricants will deterio-
rate the bushing rubber.
If the vehicle is used for severe, off-road operation,
the springs should be examined periodically. Check
for broken and shifted leafs, loose and missing clips,
and broken center bolts. Refer to Spring and Shock
Absorber Diagnosis chart for additional information.
2 - 26 REARBR/BE
Page 70 of 2889
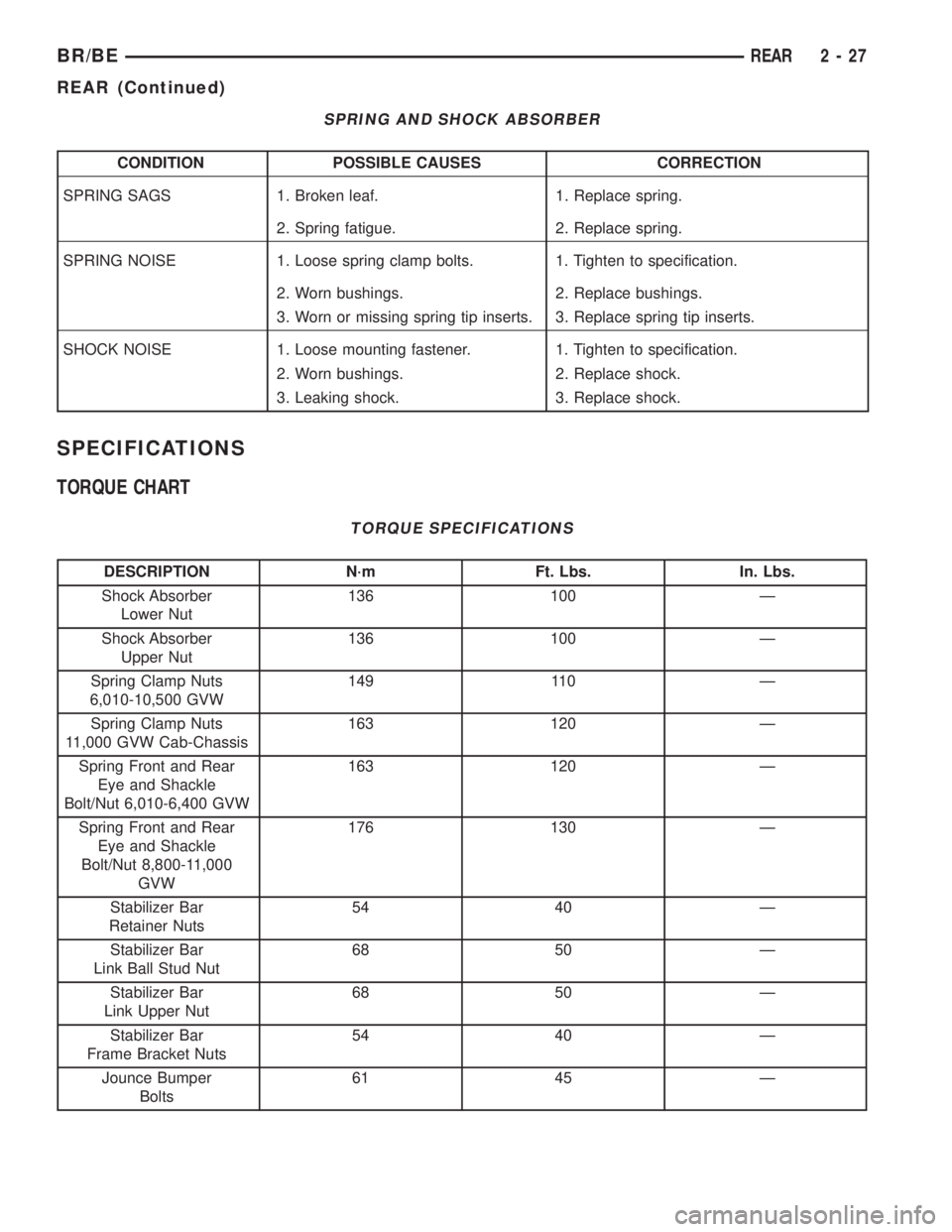
SPRING AND SHOCK ABSORBER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SPRING SAGS 1. Broken leaf. 1. Replace spring.
2. Spring fatigue. 2. Replace spring.
SPRING NOISE 1. Loose spring clamp bolts. 1. Tighten to specification.
2. Worn bushings. 2. Replace bushings.
3. Worn or missing spring tip inserts. 3. Replace spring tip inserts.
SHOCK NOISE 1. Loose mounting fastener. 1. Tighten to specification.
2. Worn bushings. 2. Replace shock.
3. Leaking shock. 3. Replace shock.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Shock Absorber
Lower Nut136 100 Ð
Shock Absorber
Upper Nut136 100 Ð
Spring Clamp Nuts
6,010-10,500 GVW149 110 Ð
Spring Clamp Nuts
11,000 GVW Cab-Chassis163 120 Ð
Spring Front and Rear
Eye and Shackle
Bolt/Nut 6,010-6,400 GVW163 120 Ð
Spring Front and Rear
Eye and Shackle
Bolt/Nut 8,800-11,000
GVW176 130 Ð
Stabilizer Bar
Retainer Nuts54 40 Ð
Stabilizer Bar
Link Ball Stud Nut68 50 Ð
Stabilizer Bar
Link Upper Nut68 50 Ð
Stabilizer Bar
Frame Bracket Nuts54 40 Ð
Jounce Bumper
Bolts61 45 Ð
BR/BEREAR 2 - 27
REAR (Continued)
Page 72 of 2889
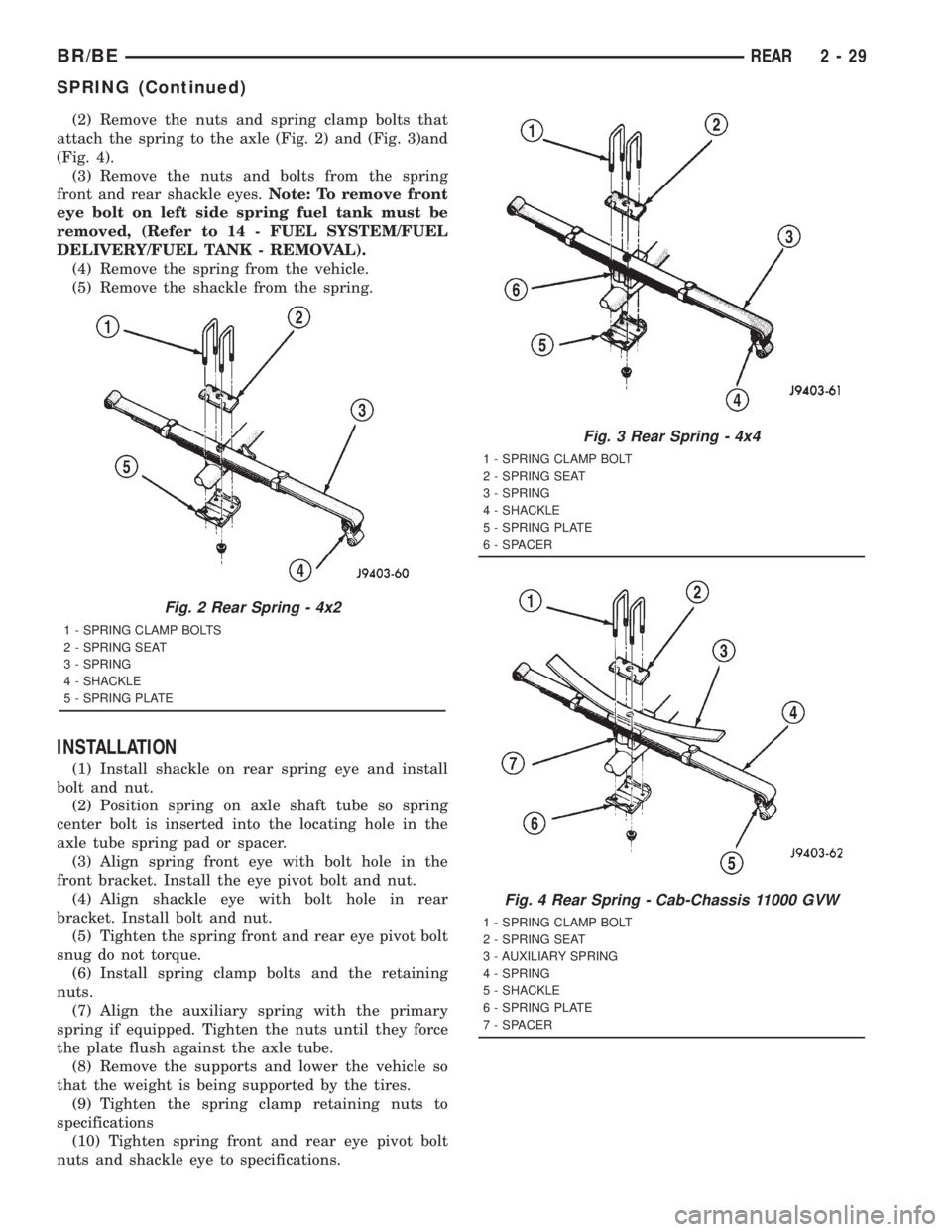
(2) Remove the nuts and spring clamp bolts that
attach the spring to the axle (Fig. 2) and (Fig. 3)and
(Fig. 4).
(3) Remove the nuts and bolts from the spring
front and rear shackle eyes.Note: To remove front
eye bolt on left side spring fuel tank must be
removed, (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY/FUEL TANK - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the spring from the vehicle.
(5) Remove the shackle from the spring.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install shackle on rear spring eye and install
bolt and nut.
(2) Position spring on axle shaft tube so spring
center bolt is inserted into the locating hole in the
axle tube spring pad or spacer.
(3) Align spring front eye with bolt hole in the
front bracket. Install the eye pivot bolt and nut.
(4) Align shackle eye with bolt hole in rear
bracket. Install bolt and nut.
(5) Tighten the spring front and rear eye pivot bolt
snug do not torque.
(6) Install spring clamp bolts and the retaining
nuts.
(7) Align the auxiliary spring with the primary
spring if equipped. Tighten the nuts until they force
the plate flush against the axle tube.
(8) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle so
that the weight is being supported by the tires.
(9) Tighten the spring clamp retaining nuts to
specifications
(10) Tighten spring front and rear eye pivot bolt
nuts and shackle eye to specifications.
Fig. 2 Rear Spring - 4x2
1 - SPRING CLAMP BOLTS
2 - SPRING SEAT
3 - SPRING
4 - SHACKLE
5 - SPRING PLATE
Fig. 3 Rear Spring - 4x4
1 - SPRING CLAMP BOLT
2 - SPRING SEAT
3 - SPRING
4 - SHACKLE
5 - SPRING PLATE
6 - SPACER
Fig. 4 Rear Spring - Cab-Chassis 11000 GVW
1 - SPRING CLAMP BOLT
2 - SPRING SEAT
3 - AUXILIARY SPRING
4 - SPRING
5 - SHACKLE
6 - SPRING PLATE
7 - SPACER
BR/BEREAR 2 - 29
SPRING (Continued)
Page 74 of 2889

DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PROPELLER SHAFT.......................1
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI....................12
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI....................45
REAR AXLE-91/4.......................77REAR AXLE - 248RBI....................109
REAR AXLE - 267RBI....................140
REAR AXLE - 286RBI....................169
PROPELLER SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PROPELLER SHAFT
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................3
PROPELLER SHAFT.....................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................5
SPECIFICATIONS.........................8
SPECIAL TOOLS..........................8
PROPELLER SHAFT - FRONT
REMOVAL...............................8
INSTALLATION............................8PROPELLER SHAFT - REAR
REMOVAL...............................9
INSTALLATION............................9
CENTER BEARING
DESCRIPTION...........................10
OPERATION.............................10
REMOVAL..............................10
INSTALLATION...........................10
ADJUSTMENTS..........................10
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS
DISASSEMBLY...........................11
PROPELLER SHAFT
DESCRIPTION
A propeller shaft (Fig. 1), (Fig. 2), (Fig. 3), and
(Fig. 4) is a shaft which connects the transmission/
transfer case to the axle differential. This is the link
through which the engine power is transmitted to the
axle.
The propeller shaft is designed and built with the
yoke lugs in line with each other which is called zero
phasing. This design produces the smoothest running
condition, an out-of-phase shaft can cause a vibra-
tion.
Tubular propeller shafts are balanced by the man-
ufacturer with weights spot welded to the tube.
Use the exact replacement parts when installing
the propeller shafts. The use of the correct replace-
ment parts helps to ensure safe operation. All fasten-
ers must be torqued to the specified values for safe
operation.Also make alignment reference marks (Fig. 5)on
the propeller shaft yoke and axle, or transmission,
yoke prior to servicing. This helps to eliminate possi-
ble vibration.
CAUTION: Do not allow the propeller shaft to drop
or hang from any propeller shaft joint during
removal. Attach the propeller shaft to the vehicle
underside with wire to prevent damage to the joints.
OPERATION
The propeller shaft must operate through con-
stantly changing relative angles between the trans-
mission and axle. It must also be capable of changing
length while transmitting torque. The axle rides sus-
pended by springs in a floating motion. The propeller
shaft must be able to change operating angles when
going over various road surfaces. This is accom-
plished through universal joints, which permit the
propeller shaft to operate at different angles. The slip
joints (or yokes) permit contraction or expansion.
BR/BEDIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE 3 - 1
Page 76 of 2889

Before undercoating a vehicle, the propeller
shaft and the U-joints should be covered to pre-
vent an out-of-balance condition and driveline
vibration.
CAUTION: Use original equipment replacement
parts for attaching the propeller shafts. The speci-
fied torque must always be applied when tightening
the fasteners.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PROPELLER
SHAFT
VIBRATION
Tires that are out-of-round, or wheels that are
unbalanced, will cause a low frequency vibration.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
Brake drums that are unbalanced will cause a
harsh, low frequency vibration. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
Driveline vibration can also result from loose or
damaged engine mounts.
Propeller shaft vibration increases as the vehicle
speed is increased. A vibration that occurs within a
specific speed range is not usually caused by a pro-
peller shaft being unbalanced. Defective universal
joints, or an incorrect propeller shaft angle, are usu-
ally the cause of such a vibration.
Fig. 3 Rear Propeller Shaft - Dana Axles
1 - SLIDING YOKE
2 - PROPELLER SHAFT
3 - PINION YOKE
4 - CLAMP
5 - SCREW
6 - OUTPUT SHAFT
Fig. 4 Rear Propeller Shaft - Corporate Axles
1 - COMPANION FLANGE
2 - COMPANION YOKE
3 - REAR PROPELLER SHAFT
Fig. 5 Propeller Shaft And Yoke
1 - REFERENCE MARKS
BR/BEPROPELLER SHAFT 3 - 3
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 77 of 2889

DRIVELINE VIBRATION
Drive Condition Possible Cause Correction
Propeller Shaft Noise 1) Undercoating or other foreign
material on shaft.1) Clean exterior of shaft and wash
with solvent.
2) Loose U-joint clamp screws. 2) Install new clamps and screws
and tighten to proper torque.
3) Loose or bent U-joint yoke or
excessive runout.3) Install new yoke.
4) Incorrect driveline angularity. 4) Measure and correct driveline
angles.
5) Rear spring center bolt not in
seat.5) Loosen spring u-bolts and seat
center bolt.
6) Worn U-joint bearings. 6) Install new U-joint.
7) Propeller shaft damaged or out
of balance.7) Installl new propeller shaft.
8) Broken rear spring. 8) Install new rear spring.
9) Excessive runout or unbalanced
condition.9) Re-index propeller shaft, test,
and evaluate.
10) Excessive drive pinion gear
shaft runout.10) Re-index propeller shaft and
evaluate.
11) Excessive axle yoke deflection. 11) Inspect and replace yoke if
necessary.
12) Excessive transfer case runout. 12) Inspect and repair as necessary.
Universal Joint Noise 1) Loose U-joint clamp screws. 1) Install new clamps and screws
and tighten to proper torque.
2) Lack of lubrication. 2) Replace as U-joints as
necessary.
BALANCE
NOTE: Removing and re-indexing the propeller
shaft 180É relative to the yoke may eliminate some
vibrations.
If propeller shaft is suspected of being unbalanced,
it can be verified with the following procedure:
(1) Raise the vehicle.
(2) Clean all the foreign material from the propel-
ler shaft and the universal joints.
(3) Inspect the propeller shaft for missing balance
weights, broken welds, and bent areas.If the pro-
peller shaft is bent, it must be replaced.
(4) Inspect the universal joints to ensure that they
are not worn, are properly installed, and are cor-
rectly aligned with the shaft.
(5) Check the universal joint clamp screws torque.
(6) Remove the wheels and tires. Install the wheel
lug nuts to retain the brake drums or rotors.
(7) Mark and number the shaft six inches from the
yoke end at four positions 90É apart.(8) Run and accelerate the vehicle until vibration
occurs. Note the intensity and speed the vibration
occurred. Stop the engine.
(9) Install a screw clamp at position 1 (Fig. 6).
(10) Start the engine and re-check for vibration. If
there is little or no change in vibration, move the
clamp to one of the other three positions. Repeat the
vibration test.
(11) If there is no difference in vibration at the
other positions, the source of the vibration may not
be propeller shaft.
(12) If the vibration decreased, install a second
clamp (Fig. 7) and repeat the test.
(13) If the additional clamp causes an additional
vibration, separate the clamps (1/2 inch above and
below the mark). Repeat the vibration test (Fig. 8).
(14) Increase distance between the clamp screws
and repeat the test until the amount of vibration is
at the lowest level. Bend the slack end of the clamps
so the screws will not loosen.
3 - 4 PROPELLER SHAFTBR/BE
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 81 of 2889

SPECIFICATIONS
PROPELLER SHAFT
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Center Bearing Bolts 68 50 -
Front Shaft Flange Yoke 88 65 -
Front Shaft Axle Yoke 19 14 -
Rear Shaft 9 1/4 Axle 108 80 -
Rear Shaft Dana Axle 29 22 -
SPECIAL TOOLS
PROPELLER SHAFTPROPELLER SHAFT - FRONT
REMOVAL
(1) Shift the transmission and transfer case to
their neutral positions. Raise and support vehicle.
Remove skid plate, if equipped.
(2) Using a suitable marker, mark a line across
the companion flange at the transfer case and propel-
ler shaft flange yoke for installation reference.
(3) Mark a line across the propeller shaft yoke and
the pinion shaft yoke for installation reference.
(4) Remove the universal joint strap bolts at the
pinion shaft yoke (Fig. 14).
(5) Remove the bolts holding the propeller shaft to
the transfer case companion flange.
(6) Remove the propeller shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position front propeller shaft under vehicle
with rear universal joint over the transfer case com-
panion flange.
(2) Place front universal joint into the axle pinion
yoke.
(3) Align the mark on the flange yoke to the mark
on the transfer case companion flange.
(4) Loosely install bolts to hold universal joint to
transfer case companion flange.
(5) Align mark on front universal joint to the mark
on the axle pinion yoke.
(6) Install bolts to hold front universal joint to axle
pinion yoke. Tighten bolts to 19 N´m (14 ft. lbs.).
(7) Tighten bolts to hold universal joint to transfer
case companion flange to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install skid plate, if equipped.
(9) Lower vehicle and road test to verify repair.
Inclinometer - 7663
Bearing Splitter - 1130
Installer, Bearing - 6052
3 - 8 PROPELLER SHAFTBR/BE
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)