2001 DODGE RAM ECU
[x] Cancel search: ECUPage 1 of 2889

GROUP TAB LOCATOR
Introduction
0Lubrication & Maintenance
2Suspension
3Differential & Driveline
5Brakes
7Cooling
8AAudio
8BChime/Buzzer
8EElectronic Control Modules
8FEngine Systems
8GHeated Systems
8HHorn
8IIgnition Control
8JInstrument Cluster
8LLamps
8MMessage Systems
8NPower Systems
8ORestraints
8PSpeed Control
8QVehicle Theft Security
8RWipers/Washers
8WWiring
9Engine
11Exhaust System
13Frame & Bumpers
14Fuel System
19Steering
21Transmission/Transaxle
22Tires/Wheels
23Body
24Heating & Air Conditioning
25Emissions Control Systems
30New Vehicle Preparation
Component and System Index
Service Manual Comment Forms (Rear of Manual)
Page 41 of 2889

DISCONNECT CABLE CLAMPS AS FOLLOWS:
²Disconnect BLACK cable clamp from engine
ground on disabled vehicle.
²When using a Booster vehicle, disconnect
BLACK cable clamp from battery negative terminal.
Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery positive
terminal.
²Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery posi-
tive terminal on disabled vehicle.
HOISTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE
Refer to the Owner's Manual for emergency vehicle
lifting procedures.
WARNING: THE HOISTING AND JACK LIFTING
POINTS PROVIDED ARE FOR A COMPLETE VEHI-
CLE. WHEN A CHASSIS OR DRIVETRAIN COMPO-
NENT IS REMOVED FROM A VEHICLE, THE
CENTER OF GRAVITY IS ALTERED MAKING SOME
HOISTING CONDITIONS UNSTABLE. PROPERLY
SUPPORT (Fig. 9) OR SECURE VEHICLE TO HOIST-
ING DEVICE WHEN THESE CONDITIONS EXIST.
FLOOR JACK
When properly positioned, a floor jack can be used
to lift a vehicle (Fig. 10). Support the vehicle in the
raised position with jack stands at the front and rear
ends of the frame rails (Fig. 9).CAUTION: Do not lift vehicle with a floor jack posi-
tioned under:
²An axle tube.
²A body side sill.
²A steering linkage component.
²A drive shaft.
²The engine or transmission oil pan.
²The fuel tank.
²A front suspension arm.
NOTE: Use the correct frame rail lifting locations
only (Fig. 11).
HOIST
A vehicle can be lifted with:
²A single-post, frame-contact hoist.
²A twin-post, chassis hoist.
²A ramp-type, drive-on hoist.
Fig. 8 Jumper Cable Clamp ConnectionsÐDiesel
Engine
1 - POSITIVE CABLE CONNECTION
2 - BATTERY
3 - NEGATIVE OR GROUND CABLE CONNECTION
Fig. 9 Safety Stands
1 - SAFETY STANDS
0 - 28 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEBR/BE
JUMP STARTING (Continued)
Page 42 of 2889
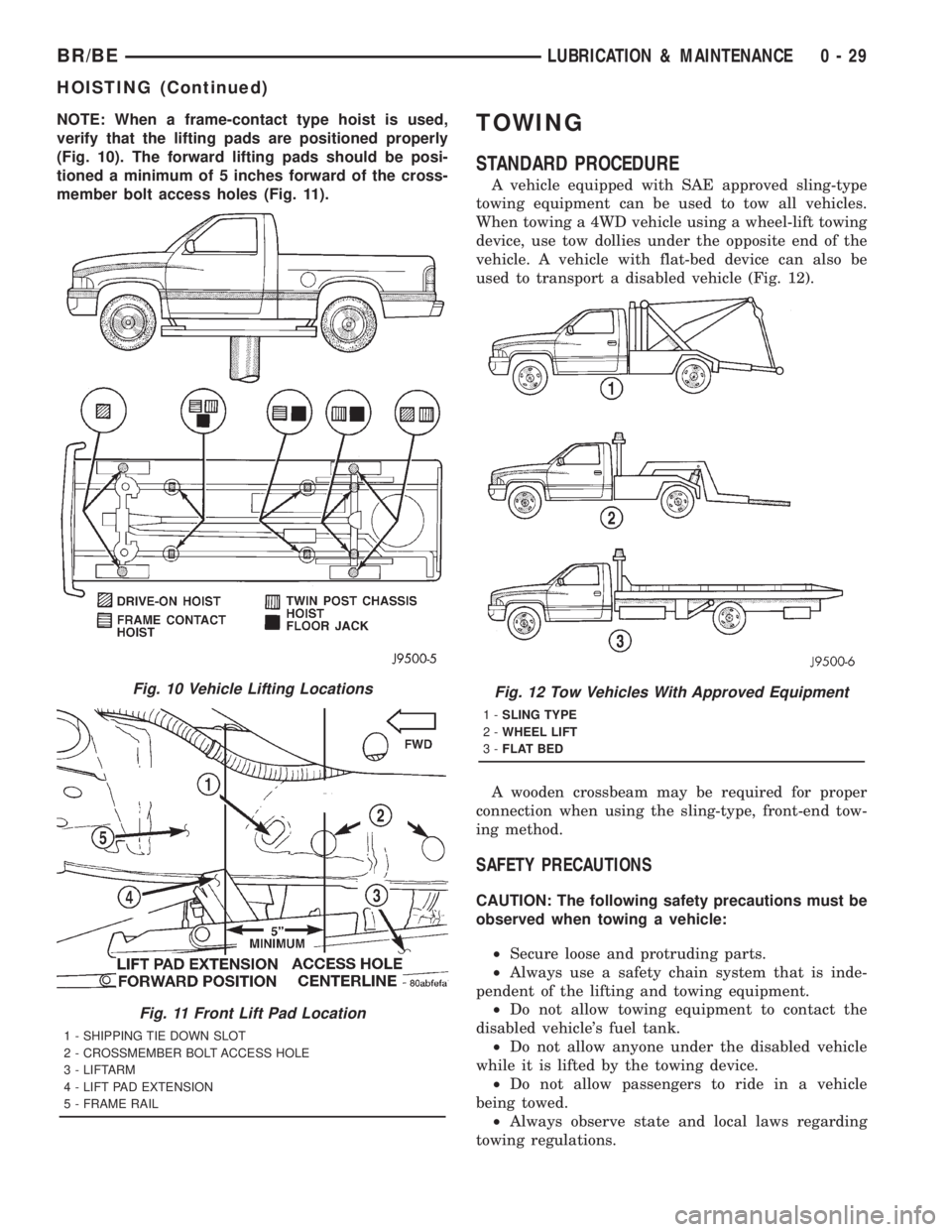
NOTE: When a frame-contact type hoist is used,
verify that the lifting pads are positioned properly
(Fig. 10). The forward lifting pads should be posi-
tioned a minimum of 5 inches forward of the cross-
member bolt access holes (Fig. 11).TOWING
STANDARD PROCEDURE
A vehicle equipped with SAE approved sling-type
towing equipment can be used to tow all vehicles.
When towing a 4WD vehicle using a wheel-lift towing
device, use tow dollies under the opposite end of the
vehicle. A vehicle with flat-bed device can also be
used to transport a disabled vehicle (Fig. 12).
A wooden crossbeam may be required for proper
connection when using the sling-type, front-end tow-
ing method.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
CAUTION: The following safety precautions must be
observed when towing a vehicle:
²Secure loose and protruding parts.
²Always use a safety chain system that is inde-
pendent of the lifting and towing equipment.
²Do not allow towing equipment to contact the
disabled vehicle's fuel tank.
²Do not allow anyone under the disabled vehicle
while it is lifted by the towing device.
²Do not allow passengers to ride in a vehicle
being towed.
²Always observe state and local laws regarding
towing regulations.
Fig. 10 Vehicle Lifting Locations
Fig. 11 Front Lift Pad Location
1 - SHIPPING TIE DOWN SLOT
2 - CROSSMEMBER BOLT ACCESS HOLE
3 - LIFTARM
4 - LIFT PAD EXTENSION
5 - FRAME RAIL
Fig. 12 Tow Vehicles With Approved Equipment
1-SLING TYPE
2-WHEEL LIFT
3-FLAT BED
BR/BELUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 29
HOISTING (Continued)
Page 43 of 2889

²Do not tow a vehicle in a manner that could
jeopardize the safety of the operator, pedestrians or
other motorists.
²Do not attach tow chains, T-hooks, J-hooks, or a
tow sling to a bumper, steering linkage, drive shafts
or a non-reinforced frame hole.
²Do not tow a heavily loaded vehicle. Damage to
the cab, cargo box or frame may result. Use a flatbed
device to transport a loaded vehicle.
GROUND CLEARANCE
CAUTION: If vehicle is towed with wheels removed,
install lug nuts to retain brake drums or rotors.
A towed vehicle should be raised until lifted wheels
are a minimum 100 mm (4 in) from the ground. Be
sure there is adequate ground clearance at the oppo-
site end of the vehicle, especially when towing over
rough terrain or steep rises in the road. If necessary,
remove the wheels from the lifted end of the vehicle
and lower the vehicle closer to the ground, to
increase the ground clearance at the opposite end of
the vehicle. Install lug nuts on wheel attaching studs
to retain brake drums or rotors.
RAMP ANGLE
If a vehicle with flat-bed towing equipment is used,
the approach ramp angle should not exceed 15
degrees.
TOWING WHEN KEYS ARE NOT AVAILABLE
When the vehicle is locked and keys are not avail-
able, use a flat bed hauler. A Wheel-lift or Sling-type
device can be used on 4WD vehicles providedall the
wheels are lifted off the ground using tow dol-
lies.
FOUR-WHEEL-DRIVE VEHICLE TOWING
Chrysler Corporation recommends that a vehicle be
transported on a flat-bed device. A Wheel-lift or
Sling-type device can be used providedall the
wheels are lifted off the ground using tow dol-
lies.
WARNING: WHEN TOWING A DISABLED VEHICLE
AND THE DRIVE WHEELS ARE SECURED IN A
WHEEL LIFT OR TOW DOLLIES, ENSURE THE
TRANSMISSION IS IN THE PARK POSITION (AUTO-
MATIC TRANSMISSION) OR A FORWARD DRIVE
GEAR (MANUAL TRANSMISSION).
CAUTION: Many vehicles are equipped with air
dams, spoilers, and/or ground effect panels. To
avoid component damage, a wheel-lift towing vehi-
cle or a flat-bed hauling vehicle is recommended.
0 - 30 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEBR/BE
TOWING (Continued)
Page 46 of 2889

down several times. Always release the bumper in
the down position.Set the front end alignment to
specifications while the vehicle is in its NOR-
MALLY LOADED CONDITION.
Camber and caster angle adjustments involve
changing the position of the upper suspension arm
pivot bar (Fig. 3). Refer to the Alignment Specifica-
tion Chart for the correct setting.
CASTER:Move the rear position of the pivot bar
in or out. This will change the caster angle signifi-
cantly and camber angle only slightly. To retain cam-
ber move the forward pivot very slightly in the
opposite direction.
NOTE: For example, to increase a positive caster
angle, move the rear position of the pivot bar
inward (toward the engine). Move the front of pivot
bar outward (away from the engine) slightly until
the original camber angle is obtained.CAMBER:Move the forward position of the pivot
bar in or out. This will change the camber angle sig-
nificantly and caster angle only slightly. The camber
angle should be adjusted as close as possible to the
preferred service specification. After adjustment
is made tighten pivot bar nuts to specifications.
TOE POSITION:The wheel toe position adjust-
ment should be the final adjustment.
(1) Start the engine and turn wheels both ways
before straightening the wheels. Center and secure
the steering wheel and turn off engine.
(2) Loosen the tie rod adjustment sleeve clamp
bolts/nuts.
NOTE: Each front wheel should be adjusted for
one-half of the total toe position specification. This
will ensure the steering wheel will be centered
when the wheels are positioned straight-ahead.
(3) Adjust the wheel toe position by turning the tie
rod adjustment sleeves as necessary.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - CASTER
CORRECTION MEASUREMENT
NOTE: To determine the correct caster alignment
angle for Cab-Chassis vehicles the following proce-
dure must be performed.
NOTE: 4x2 11000 GVW has a solid front axle and
uses a 4x4 frame.
(1) Take a height measurement to the center of the
front gauge hole in the frame. Take another measure-
ment to the center of the rear spring hanger bolt
(Fig. 4). Take these measurements on both sides of
the vehicle.
(2) Subtract the front measurement from the rear
measurement and use the average between the right
and left side. Use this number (caster correlation
valve) with the Corrected Caster Chart to obtain the
preferred caster angle.
Fig. 3 Caster Camber Adjustment Location
1 - PIVOT BAR
2 - UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
3 - SUSPENSION ARM FRAME MOUNT
4 - ADJUSTMENT SLOTS
BR/BEWHEEL ALIGNMENT 2 - 3
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 48 of 2889

CORRECTED CASTER CHART-CAB CHASSIS
Caster
Correlation
Value
(inches)4x2 8800
lb. GVW
134.7 in.
wheel
base4x4 8800
lb. GVW
4x2 & 4x4
11000 lb.
GVW
134.7 &
138.7 in.
wheel
base4x2 & 4x4
11000 lb.
GVW 162.7
in. wheel
base
Caster61
deg.Caster61
deg.Caster61
deg.
þ5.00 4.27É 3.77É 3.81É
þ4.75 4.39É 3.89É 3.91É
þ4.50 4.51É 4.01É 4.01É
þ4.25 4.64É 4.14É 4.11É
þ4.00 4.76É 4.26É 4.21É
þ3.75 4.88É 4.38É 4.31É
þ3.50 5.00É 4.50É 4.41É
þ3.25 5.12É 4.62É 4.51É
þ3.00 5.25É 4.75É 4.61É
þ2.75 5.37É 4.87É 4.71É
þ2.50 5.49É 4.99É 4.81É
þ2.25 5.61É 5.11É 4.91É
þ2.00 5.74É 5.24É 5.01É
þ1.75 5.86É 5.36É 5.11É
þ1.50 5.98É 5.48É 5.21É
þ1.25 6.10É 5.60É 5.31É
þ1.00 6.23É 5.73É 5.41É
þ0.75 6.33É 5.83É 5.51É
þ0.50 6.47É 5.97É 5.61É
þ0.25 6.59É 6.09É 5.71É
0.00 6.71É 6.21É 5.81É
STANDARD PROCEDURES - ALIGNMENT
LINK/COIL SUSPENSION
Before each alignment reading the vehicle should
be jounced (rear first, then front). Grasp each
bumper at the center and jounce the vehicle up and
down several times. Always release the bumper in
the down position.Set the front end alignment to
specifications while the vehicle is in its NOR-
MALLY LOADED CONDITION.
CAMBER:The wheel camber angle is preset and
is not adjustable.
CASTER:Check the caster of the front axle for
correct angle. Be sure the axle is not bent or twisted.Road test the vehicle and make left and right turn.
Observe the steering wheel return-to-center position.
Low caster will cause poor steering wheel returnabil-
ity.
Caster can be adjusted by rotating the cams on the
lower suspension arm (Fig. 5). (Refer to 2 - SUSPEN-
SION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
TOE POSITION:The wheel toe position adjust-
ment should be the final adjustment.
(1) Start the engine and turn wheels both ways
before straightening the wheels. Center and Secure
the steering wheel and turn off engine.
(2) Loosen the adjustment sleeve clamp bolts.
(3) Adjust the right wheel toe position with the
drag link. Turn the sleeve until the right wheel is at
the correct TOE-IN position. Position clamp bolts to
their original position and tighten to specifications.
Make sure the toe setting does not change dur-
ing clamp tightening.
(4) Adjust left wheel toe position with tie rod at
left knuckle. Turn the sleeve until the left wheel is at
the correct TOE-IN position. Position clamp bolts to
their original position and tighten to specifications.
Make sure the toe setting does not change dur-
ing clamp tightening.
(5) Verify the right toe setting.
Fig. 5 Adjustment Cam
1 - ADJUSTMENT CAM
2 - AXLE BRACKET
3 - BRACKET REINFORCEMENT
4 - LOWER SUSPENSION ARM
BR/BEWHEEL ALIGNMENT 2 - 5
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 90 of 2889

(8) Disconnect the stabilizer bar links at the axle
brackets.
(9) Disconnect the shock absorbers from axle
brackets.
(10) Disconnect the track bar from the axle
bracket.
(11) Disconnect the tie rod and drag link from the
steering knuckles.
(12) Position the axle with a suitable lifting device
under the axle assembly.
(13) Secure axle to lifting device.
(14) Mark suspension alignment cams for installa-
tion reference.
(15) Disconnect the upper and lower suspension
arms from the axle bracket.
(16) Lower the axle. The coil springs will drop
with the axle.
(17) Remove the coil springs from the axle bracket.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings should be tightened with the weight of the
vehicle on the suspension, at normal height. If
springs are not at their normal ride position, vehicle
ride comfort could be affected and premature bush-
ing wear may occur. Rubber bushings must never
be lubricated.
(1) Support the axle on a suitable lifting device.
(2) Secure axle to lifting device.
(3) Position the axle under the vehicle.
(4) Install the springs, retainer clip and bolts.
(5) Raise the axle and align it with the spring
pads.
(6) Position the upper and lower suspension arms
in the axle brackets. Install bolts, nuts and align the
suspension alignment cams to the reference marks.
Do not tighten at this time.
(7) Connect the track bar to the axle bracket and
install the bolt. Do not tighten at this time.
(8) Install the shock absorber and tighten bolts to
121 N´m (89 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install the stabilizer bar link to the axle
bracket. Tighten the nut to 37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(10) Install the drag link and tie rod to the steer-
ing knuckles and tighten the nuts to 88 N´m (65 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(11) Install the ABS wheel speed sensors, if
equipped. Refer to group 5, Brakes, for proper proce-
dures.
(12) Install the brake calipers and rotors. Refer to
Group 5, Brakes, for proper procedures.
(13) Connect the vent hose to the tube fitting.
(14) Connect vacuum hose and electrical connector
to disconnect housing.(15) Install front propeller shaft.
(16) Check and add differential lubricant, if neces-
sary. Refer to Lubricant Specifications in this section
for lubricant requirements.
(17) Install the wheel and tire assemblies.
(18) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(19) Tighten the upper suspension arm nuts at
axle to 121 N´m (89 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the
upper suspension arm nuts at frame to 84 N´m (62 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(20) Tighten the lower suspension arm nuts at
axle to 84 N´m (62 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the lower
suspension arm nuts at frame to 119 N´m (88 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(21) Tighten the track bar bolt at the axle bracket
to 176 N´m (130 ft. lbs.) torque.
(22) Check the front wheel alignment.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. The identifying numbers for the ring and
pinion gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig.
4). A plus (+) number, minus (±) number or zero (0) is
etched into the face of the pinion gear. This number
is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth
varies from the standard depth setting of a pinion
etched with a (0). The standard setting from the cen-
ter line of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion
is 109.5 mm (4.312 in.). The standard depth provides
the best gear tooth contact pattern. Refer to Back-
lash and Contact Pattern in this section for addi-
tional information.
Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim/oil baffle. The shims are
placed between the rear pinion bearing and the pin-
ion gear head (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 Pinion Gear ID Numbers
1 - PRODUCTION NUMBERS
2 - PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
3 - GEAR MATCHING NUMBER
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 216FBI 3 - 17
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI (Continued)
Page 92 of 2889
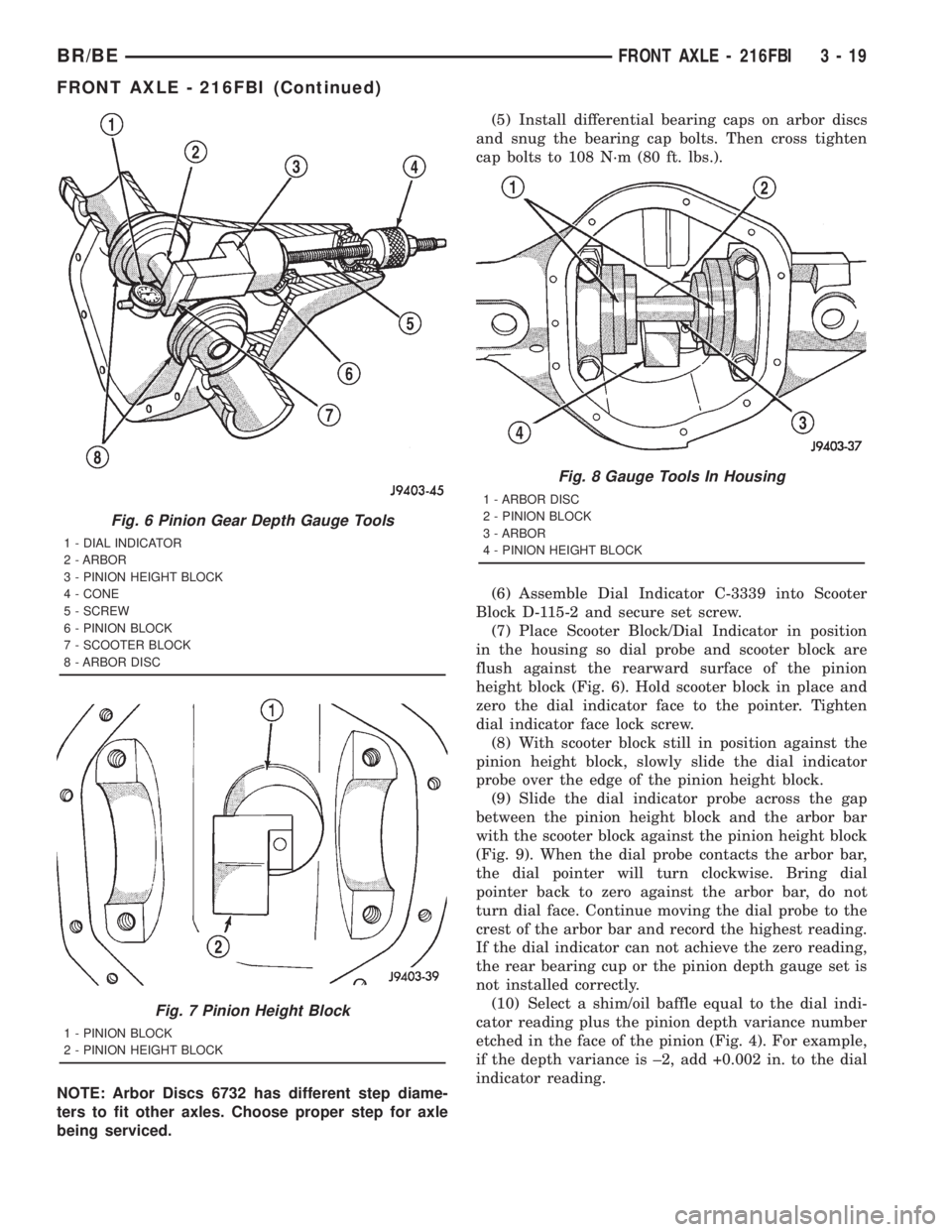
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.(5) Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs
and snug the bearing cap bolts. Then cross tighten
cap bolts to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
(6) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(7) Place Scooter Block/Dial Indicator in position
in the housing so dial probe and scooter block are
flush against the rearward surface of the pinion
height block (Fig. 6). Hold scooter block in place and
zero the dial indicator face to the pointer. Tighten
dial indicator face lock screw.
(8) With scooter block still in position against the
pinion height block, slowly slide the dial indicator
probe over the edge of the pinion height block.
(9) Slide the dial indicator probe across the gap
between the pinion height block and the arbor bar
with the scooter block against the pinion height block
(Fig. 9). When the dial probe contacts the arbor bar,
the dial pointer will turn clockwise. Bring dial
pointer back to zero against the arbor bar, do not
turn dial face. Continue moving the dial probe to the
crest of the arbor bar and record the highest reading.
If the dial indicator can not achieve the zero reading,
the rear bearing cup or the pinion depth gauge set is
not installed correctly.
(10) Select a shim/oil baffle equal to the dial indi-
cator reading plus the pinion depth variance number
etched in the face of the pinion (Fig. 4). For example,
if the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
Fig. 6 Pinion Gear Depth Gauge Tools
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 7 Pinion Height Block
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 8 Gauge Tools In Housing
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 216FBI 3 - 19
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI (Continued)