2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 3732 of 4284

(4) Remove the screw that secures the back of the
rear heater-A/C unit housing to the right D-pillar.
(5) Remove the screw that secures the front of the
rear heater-A/C unit housing to the right quarter
inner panel.
(6) Take the proper precautions to protect the car-
peting below the rear heater core from spilled engine
coolant and have absorbent toweling readily avail-
able to mop up any spills.
(7) Disconnect the heater hoses at the rear heater
core. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - REAR/HEATER HOSE - REMOV-
AL).
(8) Install plugs in, or tape over the opened heater
core fittings and both heater hoses (Fig. 6).
(9) Use absorbent toweling to clean up any engine
coolant spills from the preceding operation.
(10) Release the four latch tabs that secure the
heater core in the rear heater-A/C unit housing.
(11) Carefully pull the heater core straight out of
the rear heater-A/C unit housing.
(12) Use absorbent toweling to clean up any
engine coolant spills from the preceding operation.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If the rear heater core or the rear heater-A/C
housing have been removed from the vehicle for
service, the rear heater core may be pre-filled with
the proper engine coolant mixture prior to recon-
necting the heater hoses to the heater core hose fit-
tings. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - REAR/HEATER CORE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE - HEATER CORE FILLING).
(1) Carefully slide the heater core into the rear
heater-A/C unit housing.
(2) Using hand pressure, press firmly and evenly
on the heater core end plate until the four latch tabs
that secure the heater core in the rear heater-A/C
unit housing are fully engaged (Fig. 6).
(3) Remove the plugs or tape from the heater core
fittings and both heater hoses.
(4) Reconnect the heater hoses to the rear heater
core. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - REAR/HEATER HOSE - INSTAL-
LATION).
(5) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
front of the rear heater-A/C unit housing to the right
quarter inner panel. Tighten the screw to 11 N´m (97
in. lbs.).
(6) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
back of the rear heater-A/C unit housing to the right
D-pillar. Tighten the screw to 11 N´m (97 in. lbs.).
(7) Reinstall the rear heater distribution duct onto
the right quarter inner panel. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION -
REAR/REAR HEATER DISTRIBUTION DUCT -
INSTALLATION).
(8) Remove the right quarter trim panel and right
D-pillar trim panel from the quarter inner panel.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/QUARTER TRIM
PANEL - INSTALLATION).
(9) Drain the engine cooling system. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM REFILL).
HEATER HOSE
REMOVAL
REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARNINGS AND
CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE PER-
FORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION. (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING FRONT - WARNING - HEATER PLUMBING).
(1) Partially drain engine cooling system. Refer to
Group 7, Engine Cooling.
(2) Loosen clamp at the front end of the hose
located at the right, outboard side of the underbody,
rearward of the front crossmember. (Fig. 10)
(3) Carefully rotate hose back and forth while tug-
ging slightly away from connector nipple. If the hose
will not come off, slice the hose at the connector nip-
ple and peel off heater hose. This method will require
heater hose replacement.
Fig. 6 Heater Core
1 - REAR HEATER-A/C HOUSING OUTLET
2 - REAR HEATER-A/C UNIT HOUSING
3 - LATCH (4)
4 - HEATER CORE
5 - RIGHT REAR WHEEL HOUSE
6 - HEATER HOSES
24 - 102 PLUMBING - REARRS
HEATER CORE (Continued)
Page 3736 of 4284
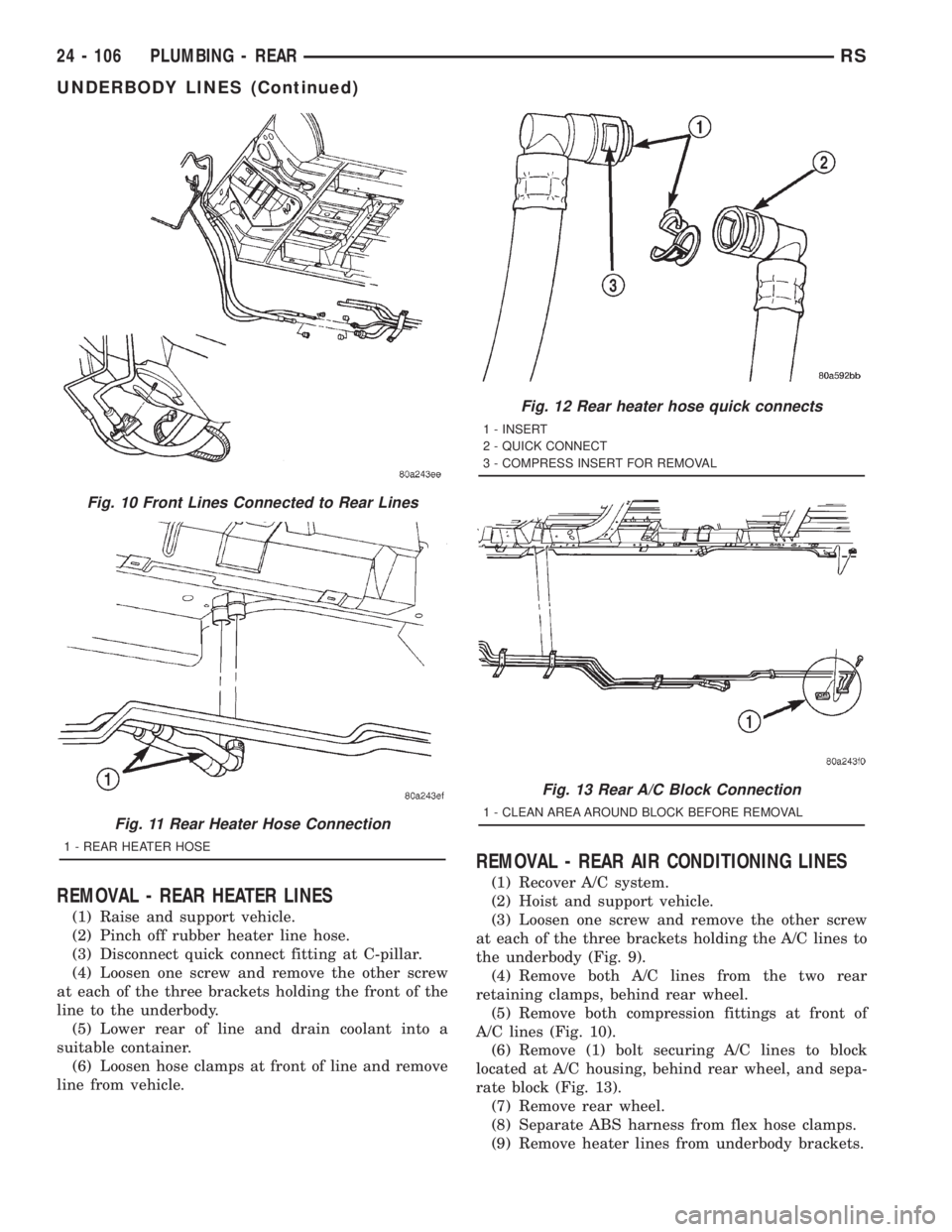
REMOVAL - REAR HEATER LINES
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Pinch off rubber heater line hose.
(3) Disconnect quick connect fitting at C-pillar.
(4) Loosen one screw and remove the other screw
at each of the three brackets holding the front of the
line to the underbody.
(5) Lower rear of line and drain coolant into a
suitable container.
(6) Loosen hose clamps at front of line and remove
line from vehicle.
REMOVAL - REAR AIR CONDITIONING LINES
(1) Recover A/C system.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle.
(3) Loosen one screw and remove the other screw
at each of the three brackets holding the A/C lines to
the underbody (Fig. 9).
(4) Remove both A/C lines from the two rear
retaining clamps, behind rear wheel.
(5) Remove both compression fittings at front of
A/C lines (Fig. 10).
(6) Remove (1) bolt securing A/C lines to block
located at A/C housing, behind rear wheel, and sepa-
rate block (Fig. 13).
(7) Remove rear wheel.
(8) Separate ABS harness from flex hose clamps.
(9) Remove heater lines from underbody brackets.
Fig. 10 Front Lines Connected to Rear Lines
Fig. 11 Rear Heater Hose Connection
1 - REAR HEATER HOSE
Fig. 12 Rear heater hose quick connects
1 - INSERT
2 - QUICK CONNECT
3 - COMPRESS INSERT FOR REMOVAL
Fig. 13 Rear A/C Block Connection
1 - CLEAN AREA AROUND BLOCK BEFORE REMOVAL
24 - 106 PLUMBING - REARRS
UNDERBODY LINES (Continued)
Page 3737 of 4284

(10) Pinch off rubber heater line hoses at front of
vehicle.
(11) Loosen hose clamps at front of heater lines
and allow them to hang from vehicle.
(12) Remove rear A/C lines from vehicle.
(13) Remove nylon wedge holding lines into rear
block (Fig. 14).INSTALLATION - REAR HEATER LINES
(1) Install line into underbody straps.
(2) Install line into front hose and install hose
clamp.
(3) Connect quick fitting at rear of line.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
INSTALLATION - REAR AIR CONDITIONING
LINES
(1) Before installation, replace all O-rings and gas-
kets. Coat all sealing surfaces with approved wax-
free refrigerant oil.
(2) Install A/C line into rear block with nylon
wedge.
(3) Install A/C lines into five underbody brackets.
(4) Connect forward compression fittings.
(5) Install bolt at sealing block to rear A/C hous-
ing.
(6) Install ABS harness into clips.
(7) Install heater hoses into underbody brackets.
(8) Install lines into front hoses and install hose
clamps.
(9) Lower vehicle.
(10) Evacuate and recharge system.
(11) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 14 UNDERBODY LINE WEDGES
1 - O-RING
2 - DISCHARGE LINE
3 - NYLON WEDGE
4 - SEALING BLOCK
5 - VISE
6 - SUCTION LINE
RSPLUMBING - REAR24 - 107
UNDERBODY LINES (Continued)
Page 3751 of 4284

EMISSIONS CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................8EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS.................10
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION............20
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS.................23
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION - MONITORED COMPONENT
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (Check Engine) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum
and 1600 rpm.Any component that has an associated
limp in will set a fault after 1 trip with the malfunc-
tion present.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
The following is a list of the monitored compo-
nents:
²Comprehensive Components
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS
Along with the major monitors, OBD II requires
that the diagnostic system monitor any component
that could affect emissions levels. In many cases,
these components were being tested under OBD I.
The OBD I requirements focused mainly on testing
emissions-related components for electrical opens and
shorts.However, OBD II also requires that inputs from
powertrain components to the PCM be tested for
rationality, and that outputs to powertrain compo-
nents from the PCM be tested forfunctionality.
Methods for monitoring the various Comprehensive
Component monitoring include:
(1) Circuit Continuity
²Open
²Shorted high
²Shorted to ground
(2) Rationality or Proper Functioning
²Inputs tested for rationality
²Outputs tested for functionality
NOTE: Comprehensive component monitors are
continuous. Therefore, enabling conditions do not
apply.
Input RationalityÐWhile input signals to the
PCM are constantly being monitored for electrical
opens and shorts, they are also tested for rationality.
This means that the input signal is compared against
other inputs and information to see if it makes sense
under the current conditions.
PCM sensor inputs that are checked for rationality
include:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Oxygen Sensor (O2S)
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensors
²Power Steering Switch
²Oxygen Sensor Heater
²Engine Controller
²Brake Switch
²Leak Detection Pump Switch
²P/N Switch
²Trans Controls
Output FunctionalityÐPCM outputs are tested
for functionality in addition to testing for opens and
shorts. When the PCM provides a voltage to an out-
RSEMISSIONS CONTROL25-1
Page 3754 of 4284

PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the output of
the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxygen content
(lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a low content
of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL (check
engine lamp) will be illuminated.
Monitor OperationÐTo monitor catalyst effi-
ciency, the PCM expands the rich and lean switch
points of the heated oxygen sensor. With extended
switch points, the air/fuel mixture runs richer and
leaner to overburden the catalytic converter. Once
the test is started, the air/fuel mixture runs rich and
lean and the O2 switches are counted. A switch is
counted when an oxygen sensor signal goes from
below the lean threshold to above the rich threshold.
The number of Rear O2 sensor switches is divided by
the number of Front O2 sensor switches to determine
the switching ratio.
The test runs for 20 seconds. As catalyst efficiency
deteriorated over the life of the vehicle, the switch
rate at the downstream sensor approaches that of the
upstream sensor. If at any point during the test
period the switch ratio reaches a predetermined
value, a counter is incremented by one. The monitor
is enabled to run another test during that trip. When
the test fails three times, the counter increments to
three, a malfunction is entered, and a Freeze Frame
is stored. When the counter increments to three dur-ing the next trip, the code is matured and the MIL is
illuminated. If the test passes the first, no further
testing is conducted during that trip.
The MIL is extinguished after three consecutive
good trips. The good trip criteria for the catalyst
monitor is more stringent than the failure criteria. In
order to pass the test and increment one good trip,
the downstream sensor switch rate must be less than
80% of the upstream rate (60% for manual transmis-
sions). The failure percentages are 90% and 70%
respectively.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must typically be met before the PCM runs the cat-
alyst monitor. Specific times for each parameter may
be different from engine to engine.
²Accumulated drive time
²Enable time
²Ambient air temperature
²Barometric pressure
²Catalyst warm-up counter
²Engine coolant temperature
²Accumulated throttle position sensor
²Vehicle speed
²MAP
²RPM
²Engine in closed loop
²Fuel level
Pending ConditionsÐ
²Misfire DTC
²Front Oxygen Sensor Response
²Front Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Front Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Rationality (middle check)
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Fuel System Monitor
²All TPS faults
²All MAP faults
²All ECT sensor faults
²Purge flow solenoid functionality
²Purge flow solenoid electrical
²All PCM self test faults
²All CMP and CKP sensor faults
²All injector and ignition electrical faults
²Idle Air Control (IAC) motor functionality
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Brake switch
²Intake air temperature
ConflictÐThe catalyst monitor does not run if any
of the following are conditions are present:
²EGR Monitor in progress
²Fuel system rich intrusive test in progress
²EVAP Monitor in progress
²Time since start is less than 60 seconds
²Low fuel level
²Low ambient air temperature
25 - 4 EMISSIONS CONTROLRS
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 3757 of 4284

the O2S must be tested to ensure that it is heating
the sensor properly.
The O2S circuit is monitored for a drop in voltage.
The sensor output is used to test the heater by iso-
lating the effect of the heater element on the O2S
output voltage from the other effects.
EGR MONITOR
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) performs
an on-board diagnostic check of the EGR system.
The EGR monitor is used to test whether the EGR
system is operating within specifications. The diag-
nostic check activates only during selected engine/
driving conditions. When the conditions are met, the
EGR is turned off (solenoid energized) and the O2S
compensation control is monitored. Turning off the
EGR shifts the air fuel (A/F) ratio in the lean direc-
tion. The O2S data should indicate an increase in the
O2 concentration in the combustion chamber when
the exhaust gases are no longer recirculated. While
this test does not directly measure the operation of
the EGR system, it can be inferred from the shift in
the O2S data whether the EGR system is operating
correctly. Because the O2S is being used, the O2S
test must pass its test before the EGR test.
MISFIRE MONITOR
Excessive engine misfire results in increased cata-
lyst temperature and causes an increase in HC emis-
sions. Severe misfires could cause catalyst damage.
To prevent catalytic convertor damage, the PCM
monitors engine misfire.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
for misfire during most engine operating conditions
(positive torque) by looking at changes in the crank-
shaft speed. If a misfire occurs the speed of the
crankshaft will vary more than normal.
FUEL SYSTEM MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide. The catalyst works best
when the air fuel (A/F) ratio is at or near the opti-
mum of 14.7 to 1.
The PCM is programmed to maintain the optimum
air/fuel ratio. This is done by making short term cor-
rections in the fuel injector pulse width based on the
O2S output. The programmed memory acts as a self
calibration tool that the engine controller uses to
compensate for variations in engine specifications,
sensor tolerances and engine fatigue over the life
span of the engine. By monitoring the actual air-fuel
ratio with the O2S (short term) and multiplying that
with the program long-term (adaptive) memory and
comparing that to the limit, it can be determined
whether it will pass an emissions test. If a malfunc-tion occurs such that the PCM cannot maintain the
optimum A/F ratio, then the MIL will be illuminated.
CATALYST MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide.
Normal vehicle miles or engine misfire can cause a
catalyst to decay. A meltdown of the ceramic core can
cause a reduction of the exhaust passage. This can
increase vehicle emissions and deteriorate engine
performance, driveability and fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2S's strategy is based on the fact that as a cat-
alyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity and its
efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring the oxy-
gen storage capacity of a catalyst, its efficiency can
be indirectly calculated. The upstream O2S is used to
detect the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas
before the gas enters the catalytic converter. The
PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the output of
the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxygen content
(lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a low content
of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL (Check
Engine lamp) will be illuminated.
RSEMISSIONS CONTROL25-7
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 3765 of 4284
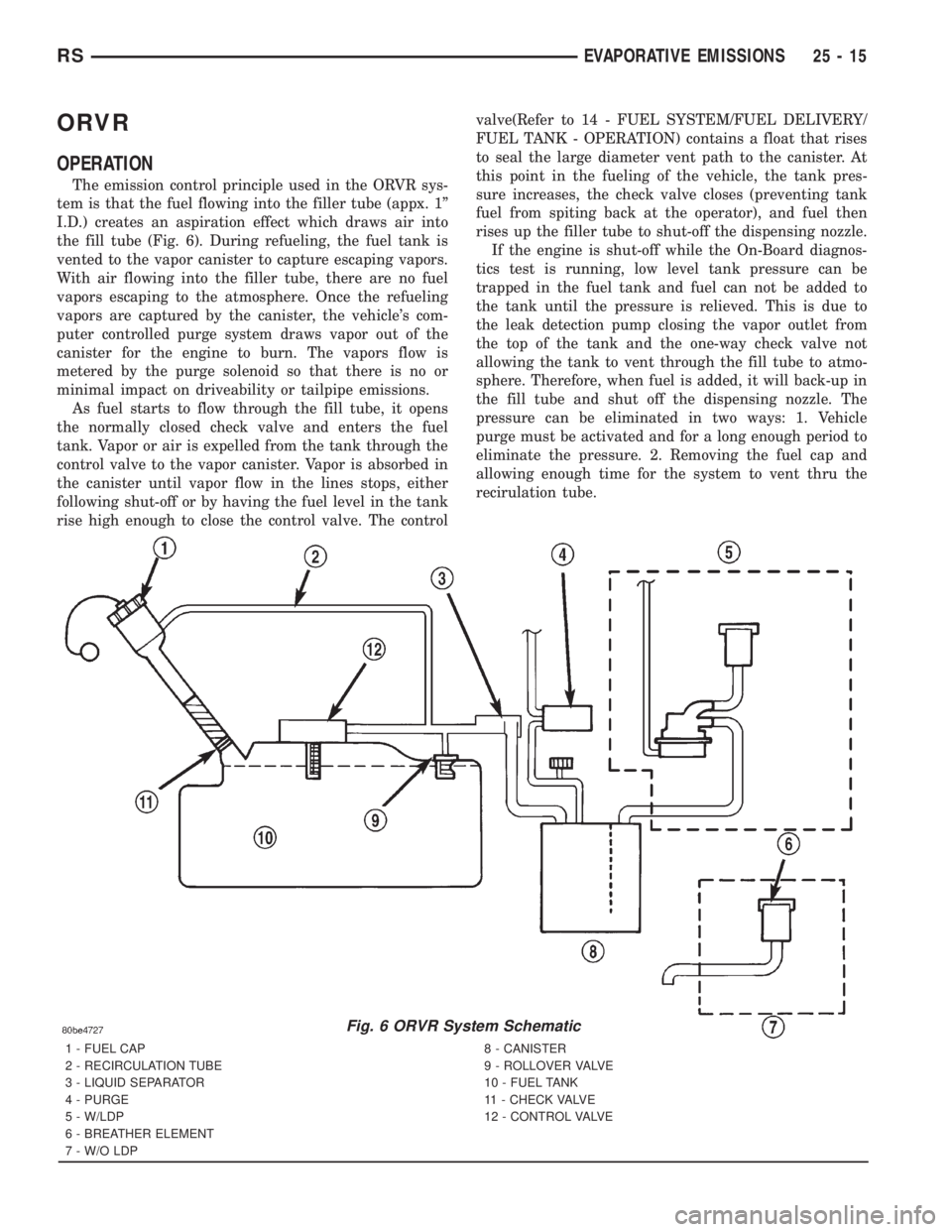
ORVR
OPERATION
The emission control principle used in the ORVR sys-
tem is that the fuel flowing into the filler tube (appx. 1º
I.D.) creates an aspiration effect which draws air into
the fill tube (Fig. 6). During refueling, the fuel tank is
vented to the vapor canister to capture escaping vapors.
With air flowing into the filler tube, there are no fuel
vapors escaping to the atmosphere. Once the refueling
vapors are captured by the canister, the vehicle's com-
puter controlled purge system draws vapor out of the
canister for the engine to burn. The vapors flow is
metered by the purge solenoid so that there is no or
minimal impact on driveability or tailpipe emissions.
As fuel starts to flow through the fill tube, it opens
the normally closed check valve and enters the fuel
tank. Vapor or air is expelled from the tank through the
control valve to the vapor canister. Vapor is absorbed in
the canister until vapor flow in the lines stops, either
following shut-off or by having the fuel level in the tank
rise high enough to close the control valve. The controlvalve(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/
FUEL TANK - OPERATION) contains a float that rises
to seal the large diameter vent path to the canister. At
this point in the fueling of the vehicle, the tank pres-
sure increases, the check valve closes (preventing tank
fuel from spiting back at the operator), and fuel then
rises up the filler tube to shut-off the dispensing nozzle.
If the engine is shut-off while the On-Board diagnos-
tics test is running, low level tank pressure can be
trapped in the fuel tank and fuel can not be added to
the tank until the pressure is relieved. This is due to
the leak detection pump closing the vapor outlet from
the top of the tank and the one-way check valve not
allowing the tank to vent through the fill tube to atmo-
sphere. Therefore, when fuel is added, it will back-up in
the fill tube and shut off the dispensing nozzle. The
pressure can be eliminated in two ways: 1. Vehicle
purge must be activated and for a long enough period to
eliminate the pressure. 2. Removing the fuel cap and
allowing enough time for the system to vent thru the
recirulation tube.
Fig. 6 ORVR System Schematic
1 - FUEL CAP
2 - RECIRCULATION TUBE
3 - LIQUID SEPARATOR
4 - PURGE
5 - W/LDP
6 - BREATHER ELEMENT
7 - W/O LDP8 - CANISTER
9 - ROLLOVER VALVE
10 - FUEL TANK
11 - CHECK VALVE
12 - CONTROL VALVE
RSEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS25-15
Page 3775 of 4284

Major Monitors. If the Task Manager cannot run a
Global Good Trip because a component fault is stop-
ping the monitor from running, it will attempt to
count an Alternate Good Trip.
The Task Manager counts an Alternate Good Trip
for Comprehensive components when the following
conditions are met:
²Two minutes of engine run time
²No other faults occur
The Task Manager counts an Alternate Good Trip
for a Major Monitor when the monitor runs and
passes. Only the Major Monitor that failed needs to
pass to count an Alternate Good Trip.
Warm-Up Cycles
Once the MIL has been extinguished by the Good
Trip Counter, the PCM automatically switches to a
Warm-Up Cycle Counter that can be viewed on the
DRBIIIt. Warm-Up Cycles are used to erase DTCs
and Freeze Frames. Forty Warm-Up cycles must
occur in order for the PCM to self-erase a DTC and
Freeze Frame. A Warm-Up Cycle is defined as fol-
lows:
²Engine coolant temperature must start below
and rise above 160É F
²Engine coolant temperature must rise by 40É F
²No further faults occur
Freeze Frame Data Storage
Once a failure occurs, the Task Manager records
several engine operating conditions and stores it in a
Freeze Frame. The Freeze Frame is considered one
frame of information taken by an on-board data
recorder. When a fault occurs, the PCM stores the
input data from various sensors so that technicians
can determine under what vehicle operating condi-
tions the failure occurred.
The data stored in Freeze Frame is usually
recorded when a system fails the first time for two
trip faults. Freeze Frame data will only be overwrit-
ten by a different fault with a higher priority.
CAUTION: Erasing DTCs, either with the DRBIIIT;or
by disconnecting the battery, also clears all Freeze
Frame data.
Similar Conditions Window
The Similar Conditions Window displays informa-
tion about engine operation during a monitor. Abso-
lute MAP (engine load) and Engine RPM are stored
in this window when a failure occurs. There are two
different Similar conditions Windows: Fuel System
and Misfire.
FUEL SYSTEM
²Fuel System Similar Conditions WindowÐ
An indicator that 'Absolute MAP When Fuel Sys Fail'
and 'RPM When Fuel Sys Failed' are all in the samerange when the failure occurred. Indicated by switch-
ing from 'NO' to 'YES'.
²Absolute MAP When Fuel Sys FailÐ The
stored MAP reading at the time of failure. Informs
the user at what engine load the failure occurred.
²Absolute MAPÐ A live reading of engine load
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²RPM When Fuel Sys FailÐ The stored RPM
reading at the time of failure. Informs the user at
what engine RPM the failure occurred.
²Engine RPMÐ A live reading of engine RPM
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²Adaptive Memory FactorÐ The PCM utilizes
both Short Term Compensation and Long Term Adap-
tive to calculate the Adaptive Memory Factor for
total fuel correction.
²Upstream O2S VoltsÐ A live reading of the
Oxygen Sensor to indicate its performance. For
example, stuck lean, stuck rich, etc.
²SCW Time in Window (Similar Conditions
Window Time in Window)Ð A timer used by the
PCM that indicates that, after all Similar Conditions
have been met, if there has been enough good engine
running time in the SCW without failure detected.
This timer is used to increment a Good Trip.
²Fuel System Good Trip CounterÐATrip
Counter used to turn OFF the MIL for Fuel System
DTCs. To increment a Fuel System Good Trip, the
engine must be in the Similar Conditions Window,
Adaptive Memory Factor must be less than cali-
brated threshold and the Adaptive Memory Factor
must stay below that threshold for a calibrated
amount of time.
²Test Done This TripÐ Indicates that the
monitor has already been run and completed during
the current trip.
MISFIRE
²Same Misfire Warm-Up StateÐ Indicates if
the misfire occurred when the engine was warmed up
(above 160É F).
²In Similar Misfire WindowÐ An indicator
that 'Absolute MAP When Misfire Occurred' and
'RPM When Misfire Occurred' are all in the same
range when the failure occurred. Indicated by switch-
ing from 'NO' to 'YES'.
²Absolute MAP When Misfire OccurredÐ
The stored MAP reading at the time of failure.
Informs the user at what engine load the failure
occurred.
²Absolute MAPÐ A live reading of engine load
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
RSON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS25-25
TASK MANAGER (Continued)