1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO STARTING
[x] Cancel search: STARTINGPage 257 of 2053
1F1 -- 94 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
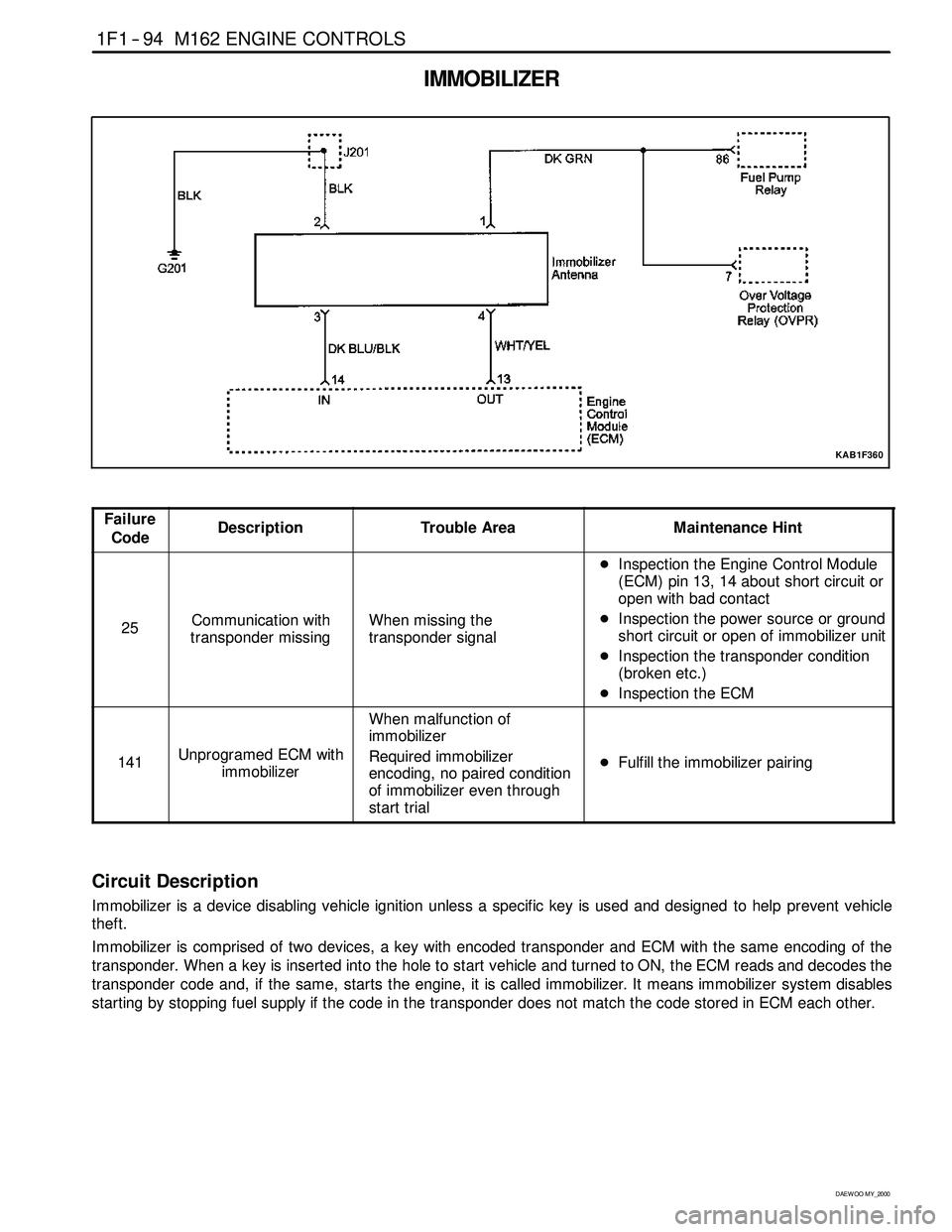
IMMOBILIZER
KAB1F360
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
25Communication with
transponder missingWhen missing the
transponder signal
DInspection the Engine Control Module
(ECM) pin 13, 14 about short circuit or
open with bad contact
DInspection the power source or ground
short circuit or open of immobilizer unit
DInspection the transponder condition
(broken etc.)
DInspection the ECM
141Unprogramed ECM with
immobilizer
When malfunction of
immobilizer
Required immobilizer
encoding, no paired condition
of immobilizer even through
start trial
DFulfill the immobilizer pairing
Circuit Description
Immobilizer is a device disabling vehicle ignition unless a specific key is used and designed to help prevent vehicle
theft.
Immobilizer is comprised of two devices, a key with encoded transponder and ECM with the same encoding of the
transponder. When a key is inserted into the hole to start vehicle and turned to ON, the ECM reads and decodes the
transponder code and, if the same, starts the engine, it is called immobilizer. It means immobilizersystem disables
starting by stopping fuel supply if the code in the transponder does not match the code stored in ECM each other.
Page 387 of 2053
M161 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B2 -- 99
D AEW OO M Y_2000
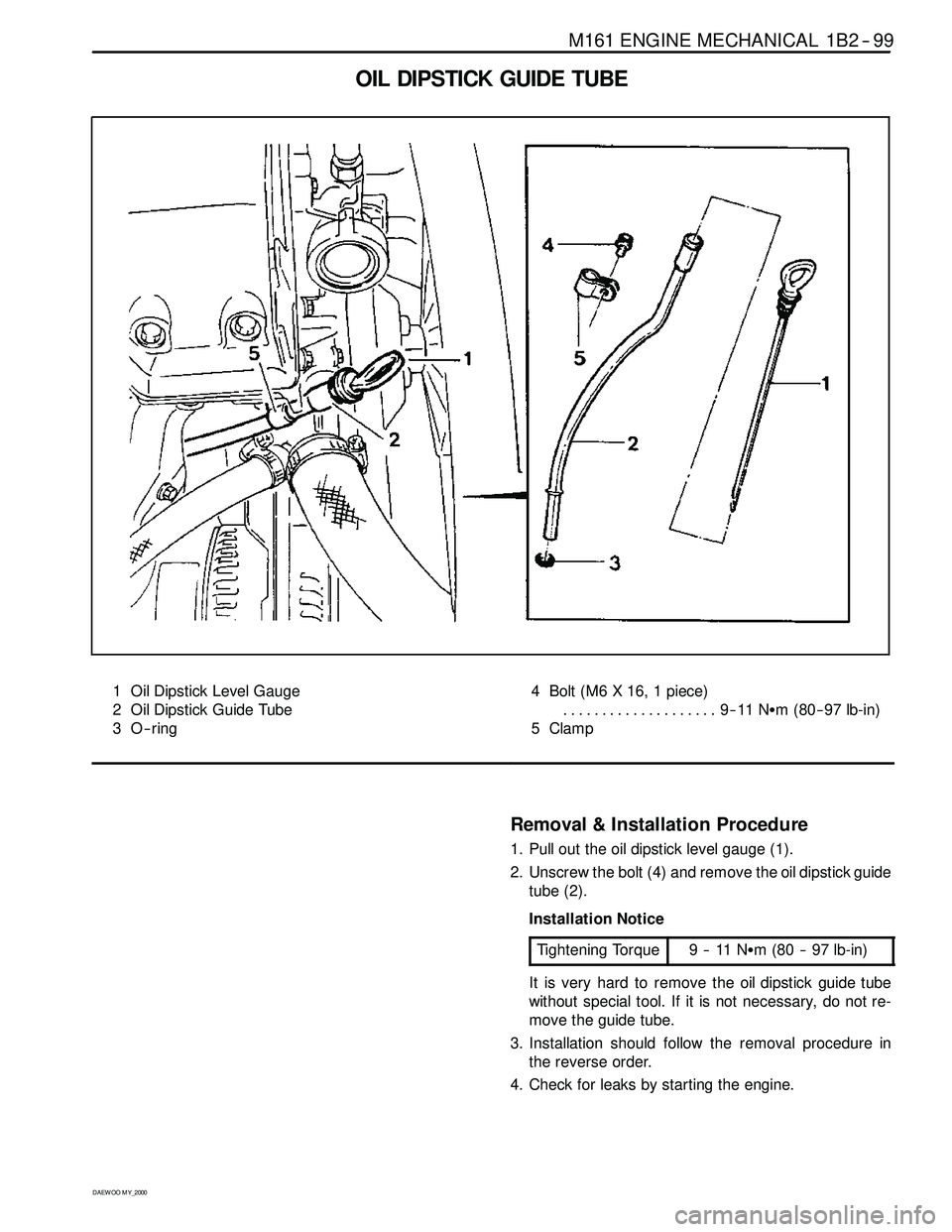
OIL DIPSTICK GUIDE TUBE
1 Oil Dipstick Level Gauge
2 Oil Dipstick Guide Tube
3O--ring4 Bolt (M6 X 16, 1 piece)
9--11 NSm (80-- 97 lb-in) ....................
5 Clamp
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Pull out the oil dipstick level gauge (1).
2. Unscrew the bolt (4) and remove the oil dipstick guide
tube (2).
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque
9--11NSm (80 -- 97 lb-in)
It is very hard to remove the oil dipstick guide tube
without special tool. If it is not necessary, do not re-
move the guide tube.
3. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
4. Check for leaks by starting the engine.
Page 405 of 2053
1D2 -- 10 M161 ENGINE COOLING
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Tools Required
124589152100 Tester
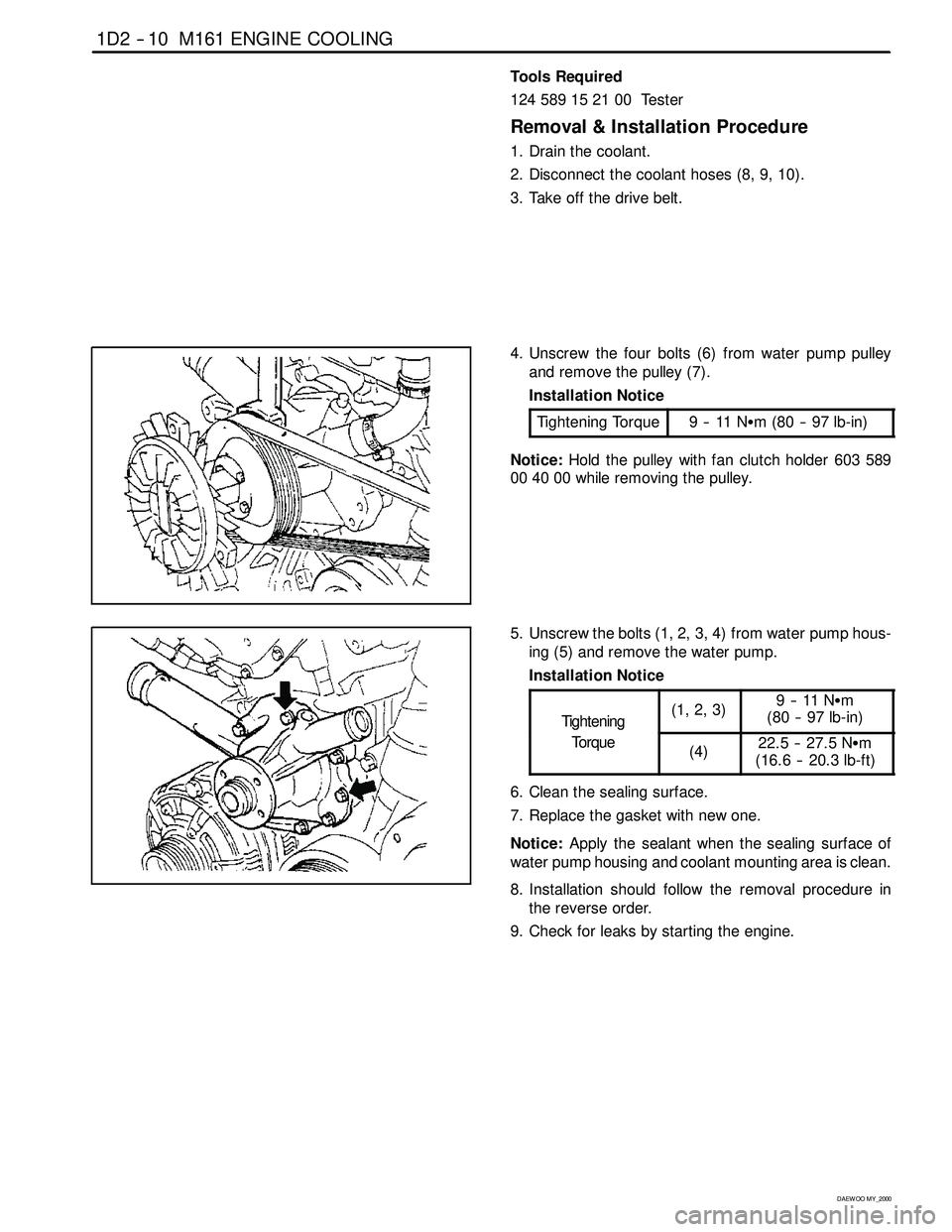
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Drain the coolant.
2. Disconnect the coolant hoses (8, 9, 10).
3. Take off the drive belt.
4. Unscrew the four bolts (6) from water pump pulley
and remove the pulley (7).
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque
9--11NSm (80 -- 97 lb-in)
Notice:Hold the pulley with fan clutch holder 603 589
00 40 00 while removing the pulley.
5. Unscrew the bolts (1, 2, 3, 4) from water pump hous-
ing (5) and remove the water pump.
Installation Notice
Tightening
(1,2,3)9--11NSm
(80 -- 97 lb-in)
Tightening
Torque(4)22.5 -- 27.5 NSm
(16.6 -- 20.3 lb-ft)
6. Clean the sealing surface.
7. Replace the gasket with new one.
Notice:Apply the sealant when the sealing surface of
water pump housing and coolant mounting area is clean.
8. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
9. Check for leaks by starting the engine.
Page 412 of 2053

D AEW OO M Y_2000
SECTION 1E2
M161 ENGINE ELECTRICAL
CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a
tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable
will help prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless other -
wise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications 1E2 -- 2............................
Generator Specifications 1E2-- 2..................
Starting Motor Specifications 1E2-- 2...............
Battery Specifications 1E2-- 2.....................
Fastener Tightening Specifications 1E2 -- 2..........
Maintenance and Repair 1E2 -- 3...................
On-- Vehicle Service 1E2-- 3.........................Generator 1E2-- 3...............................
Starting Motor 1E2--4...........................
Battery 1E2--5.................................
Spark Plug 1E2 -- 6..............................
Ignition Cable 1E2-- 8............................
Unit Repair 1E2 -- 11..............................
Battery 1E2--11................................
Page 413 of 2053

1E 2 -- 2 M161 ENGINE ELECTRICAL
D AEW OO M Y_2000
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationDescription
Current11 5 A
Output Voltage12 -- 14 v
Resistance Between Rotor Core and Slip Ring∞Ω
STARTER SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationDescription
Output Power1.2 kw
Voltage12 v
BATTERY SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationDescription
Capacity90 AH
Max. Tolerance Between Cells≥0.04
Specific Gravity≥1.24
FASTER TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationNSmLb-FtLb-In
Generator Terminal B+Nut14 -- 1810 -- 13--
Generator Terminal D+Nut4--5--35 -- 44
Generator Mounting Bolt2518--
Battery Cable Nut on Starting Motor12 -- 159--11--
Electric Wire Nut on Starting Motor6--7--53 -- 62
Starting Motor Mounting Bolt35 -- 4826 -- 35--
Battery Mounting Bracket Nut12 -- 189--13--
Battery Negative Cable12 -- 189--13--
Battery Positive Cable12 -- 189--13--
Spark plug Cover Bolt9--11--80 -- 97
Ignition Cable Bolt9--11--80 -- 97
Spark plug20 -- 3015 -- 22--
Page 415 of 2053

1E 2 -- 4 M161 ENGINE ELECTRICAL
D AEW OO M Y_2000
STARTING MOTOR
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Disconnect the ground cable.
2. Unscrew the nut and disconnect the battery cable (1).
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque
12 -- 15 NSm (9 -- 11 lb-ft)
3. Unscrew the nut and disconnect the engine electric
wire (2).
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque
6--7NSm (53 -- 62 lb-in)
1 Battery Cable
2 Engine Electric Wire
4. Unscrew the mounting bolts (3) of starting motor.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque
35 -- 48 NSm (26 -- 35 lb-ft)
5. Remove the starting motor.
6. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
3 Fixing Bolt
4StartingMotor
Page 424 of 2053

1F2 -- 2 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
ENGINE AND ECM PROBLEM CHECK REPORT
VEHICLE AND CUSTOMER INFORMATION
Date problem Occurred
Customer NameVehicle Model
Driver NameVIN
Purchase dateEngine Model
License No.MileageKm
miles
MIL INFORMATION
Condition of MILjRemains onjSometimes illuminatesjDoes not illuminate
DTC inspection
(if available)jNormaljMalfunction code(s) (code )
jFreezed frame data ( )
PROBLEM DESCRIPTION
jEngine Does Not StartjNo crankingjNo initial combustionjNo complete combustion
jHard to StartjSlow cranking
jOthers
jPoor IdlingjIncorrect first IdlejAbnormal idle rpmjHigh (rpm)jLow (rpm)
jIdling UnstablejOthers
jPoor DriveabilityjHesitationjBack firejMuffler explosion (after-burning)
jSurgingjKnockingjPoor performancejOther
jEngine StalljSoon after startingjAfter accelerator pedal depressed
jAfter accelerator pedal releasedjDuring A/C operation
jShifting from N to D or D to N
jAt full steeringjOthers
jOthers
CONDITION WHEN PROBLEM OCCURS
Problem FrequencyjConstantjIntermittent (times per day/month)jOnce onlyjOthers
WeatherjFinejCloudyjRainyjSnowyjVarious/Others
Ambient TemperaturejHotjWar mjCooljCold (approx.____°F/____°C)
PlacejHighwayjSuburbsjInner CityjUphilljDownhill
jRough RoadjOthers
Engine TemperaturejColdjWarming UpjBefore warming upjAfter warm-up
jAny temp.jOthers
Engine OperationjStartingjJust after starting (min.)jIdlingjRacingjDriving
jConstant speedjAccelerationjDeceleration
jA/C switch ON/OFFjOther
Page 458 of 2053

1F2 -- 40 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
FUEL SYSTEM
The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating condi-
tions. The fuel is delivered to the engine by the individual fuel injectors mounted into the intake manifold near each
cylinder.
The main fuel control sensors are the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor and the oxygen (O2) sensors.
The MAF sensor monitors the mass flow of the air being drawn into the engine. An electrically heated element is
mounted in the intake air stream, where it is cooled by the flow of incoming air. Engine Control Module (ECM) modu-
lates the flow of heating current to maintain the temperature differential between the heated film and the intake air at a
constant level. The amount of heating current required to maintain the temperature thus provides an index for the
mass air flow. This concept automatically compensates for variations in air density, as this is one of the factors that
determines the amount of warmth that the surrounding air absorbs from the heated element. MAF sensor is located
between the air filter and the throttle valve.
Under high fuel demands, the MAF sensor reads a high mass flow condition, such as wide open throttle. The ECM
uses this information to enrich the mixture, thus increasing the fuel injector on-- time, to provide the correct amount of
fuel. When decelerating, the mass flow decreases. This mass flow change is sensed by the MAF sensor and read by
the ECM, which then decreases the fuel injector on-- time due to the low fuel demand conditions.
The O2 sensors are located in the exhaust pipe before catalytic converter. The O2 sensors indicate to the ECM the
amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas, and the ECM changes the air/fuel ratio to the engine by controlling the fuel
injectors. The best air/fuel ratio to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7 to 1, which allows the catalytic converter to
operate most efficiently. Because of the constant measuring and adjusting of the air/fuel ratio, the fuel injection system
is called a “closed loop” system.
The ECM uses voltage inputs from several sensors to determine how much fuel to provide to the engine. The fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions, called ‘‘modes”.
Starting Mode
When the ignition is turned ON, the ECM turns the fuel pump relay on for 1 second. The fuel pump then builds fuel
pressure. The ECM also checks the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor and the Throttle Position (TP) sensor
and determines the proper air/fuel ratio for starting the engine. This ranges from 1.5 to 1 at -- 36°C(--33°F) coolant
temperature to 14.7 to 1 at 94°C (201°F) coolant temperature. The ECM controls the amount of fuel delivered in the
starting mode by changing how long the fuel injector is turned on and off. This is done by ‘‘pulsing” the fuel injectors for
very short times.
Run Mode
The run mode has two conditions called ‘‘open loop” and ‘‘closed loop”.
Open Loop
When the engine is first started and it is above 690 rpm, thesystem goes into “open loop” operation. In “open loop”, the
ECM ignores the signal from the HO2S and calculates the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the ECT sensor and the
MAF sensor. The ECM stays in “open loop” until the following conditions are met:
DThe O2 has a varying voltage output, showing that it is hot enough to operate properly.
DThe ECT sensor is above a specified temperature (22.5°C).
DA specific amount of time has elapsed after starting the engine.
Closed Loop
The specific values for the above conditions vary with different engines and are stored in the Electronically Erasable
Programmable Read -- Only Memory (EEPROM). When these conditions are met, thesystem goes into “closed loop”
operation. In “closed loop”, the ECM calculates the air/fuel ratio (fuel injector on-- time) based on the signals from the
O2 sensors. This allows the air/fuel ratio to stay very close to 14.7 to 1.
Acceleration Mode
The ECM responds to rapid changes in throttle position and airflow and provides extra fuel.
Deceleration Mode
The ECM responds to changes in throttle position and airflow and reduces the amount of fuel. When deceleration is
very fast, the ECM can cut off fuel completely for short periods of time.