1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO STARTING
[x] Cancel search: STARTINGPage 468 of 2053

1F2 -- 50 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
PURGE CONTROL VALVE
YAA1F440
The fuel vaporization control system is installed to inhibit the fuel vaporized gas from discharging into the atmosphere.
The fuel vaporized gas that is accumulated in the canister abstracts through the purge control valve purification during
the engine combustion (except the decreasing mode) and coolant temperature of over 80°C. For this reason, the En-
gine Control Module (ECM) transacts the engine speed, air inflow quantity, coolant temperature, and intake tempera-
ture.
The purge control valve is activated by the ECM frequency according with the engine rotating speed to adjust the
purification rate. The purification rate is determined by the continuous valve opening interval.
The purge control valve is activated by the ECM for the following conditions:
DCoolant temperature of over 80°C
DEngine speed of over 1,000 rpm
D2 minutes after starting
DWhen the fuel cut -- off mode is not activated
Page 512 of 2053

1F2 -- 94 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
IMMOBILIZER
KAB1F360
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
25Communication with
transponder missingWhen missing the
transponder signal
DInspection the Engine Control Module
(ECM) pin 13, 14 about short circuit or
open with bad contact
DInspection the power source or ground
short circuit or open of immobilizer unit
DInspection the transponder condition
(broken etc.)
DInspection the ECM
141Unprogramed ECM with
immobilizer
When malfunction of
immobilizer
Required immobilizer
encoding, no paired condition
of immobilizer even through
start trial
DFulfill the immobilizer pairing
Circuit Description
Immobilizer is a device disabling vehicle ignition unless a specific key is used and designed to help prevent vehicle
theft.
Immobilizer is comprised of two devices, a key with encoded transponder and ECM with the same encoding of the
transponder. When a key is inserted into the hole to start vehicle and turned to ON, the ECM reads and decodes the
transponder code and, if the same, starts the engine, it is called immobilizer. It means immobilizersystem disables
starting by stopping fuel supply if the code in the transponder does not match the code stored in ECM each other.
Page 651 of 2053

1B3 -- 102 OM600 ENGINE MECHANICAL
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Checking
Notice
The noise which continues short time during short
travel (frequent starting of the engine) or engine
starting after a long time storage is normal operating
conditions. So, it does not need to be repaired. De-
termine the malfunctions in valve clearance com-
pensation device with noise through following tests.
If defective, replace as respectively.
1. Run the engine at more than 3000rpm for approx. 4
minutes.
2. Stop the engine. After 5minutes, check the engine
oil level and adjust if necessary.
3. Remove the cylinder head cover.
4. Check the valve tappets at TDC position of each cyl-
inders.
5. Using a drift, lightly press the valve tappet and mea-
sure clearance between the cam and valve tappet.
Notice
If the clearance exceeds 0.4mm, replace the valve
tappet.
6. If a valve tappet moves down too far in comparison
to the others, replace the valve tappet.
7. Rotate the engine and check the remaining valve
tappets.
Notice
DUnnecessary rotation of the engine will damage
the valve tappets.
DDo not rotate the engine by using the camshaft
sprocket bolt or to the opposite direction of the
engine rotation.
Page 774 of 2053

OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F3 -- 17
D AEW OO M Y_2000
FUEL PUMP TEST
Notice
Before test, replace the fuel filter cartridge and fuel pre-
filter.
Fuel Feed Test
1. Disconnect the fuel return line (1) and seal up it with
plug.
2. Insert the plastic hose (5) and put the end into the
measuring beaker (6).
3. Disconnect the vacuum line (4) from vacuum unit
(engine stop) (5) and connect the vacuum pump (7)
to the vacuum unit.
4. To avoid the engine starting, build up vacuum
(approx. 500 mbar).
5. Operate the starter motor for exactly 30 seconds
and measure fuel volume in the beaker.
Min. volume150cm3for 30 seconds
Page 890 of 2053

PROPELLER SHAFT 3C-3
SSANGYONG MY2002
PROPELLER SHAFT
Inspection Procedure
1. Visually check the propeller shaft.
2. Using a dial indicator, measure propeller shaft
runout by turning the shaft. If runout exceeds limit,
replace the propeller shaft or correct it.
Adjustment Notice
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURES
KAA3C020
Specification 0.4 mm (0.016 inch)
3. Measure the universal joint starting torque.
Adjustment Notice
Specification 0.54 N•m (4.78 lb-in)
KAA3C030
4. Measure the spider outer diameter.
Adjustment Notice
Specification 16.668 mm (0.656 inch)
KAA3C040
4. Measure the spider outer diameter.
Adjustment Notice
Specification 0.064 mm (0.0025 inch)
KAA3C050
Page 998 of 2053

ABS AND TCS 4F-15
SSANGYONG MY2002
DIAGNOSIS
KAA4F110
DIAGNOSTIC CIRCUIT CHECK
The Diagnostic Circuit Check is an organized approach
to identifying a problem created by an antilock brake
system (ABS) malfunction. If must be the starting point
for any ABS complaint diagnosis because it directs
the service technician to the next logical step in
diagnosing the complaint.
Diagnostic Process
Perform the following steps in order when servicing
the ABS/TCS system. Failure to do so may result in
the loss of important diagnostic data and may lead to
difficulties and time-consuming diagnosis procedures.
1. Perform the tests of the table below.2. Perform a road test if directed by the table.
Test drive the vehicle while using the snapshot
feature of the scan tool.
Perform normal acceleration, stopping, and
turning maneuvers.
If this does not reproduce the malfunction,
perform an ABS stop or TCS maneuver on a low
friction surface such as gravel.
3. Clear the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) after
all system malfunctions have been corrected.
Page 1096 of 2053
5A-2 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
SSANGYONG MY2002
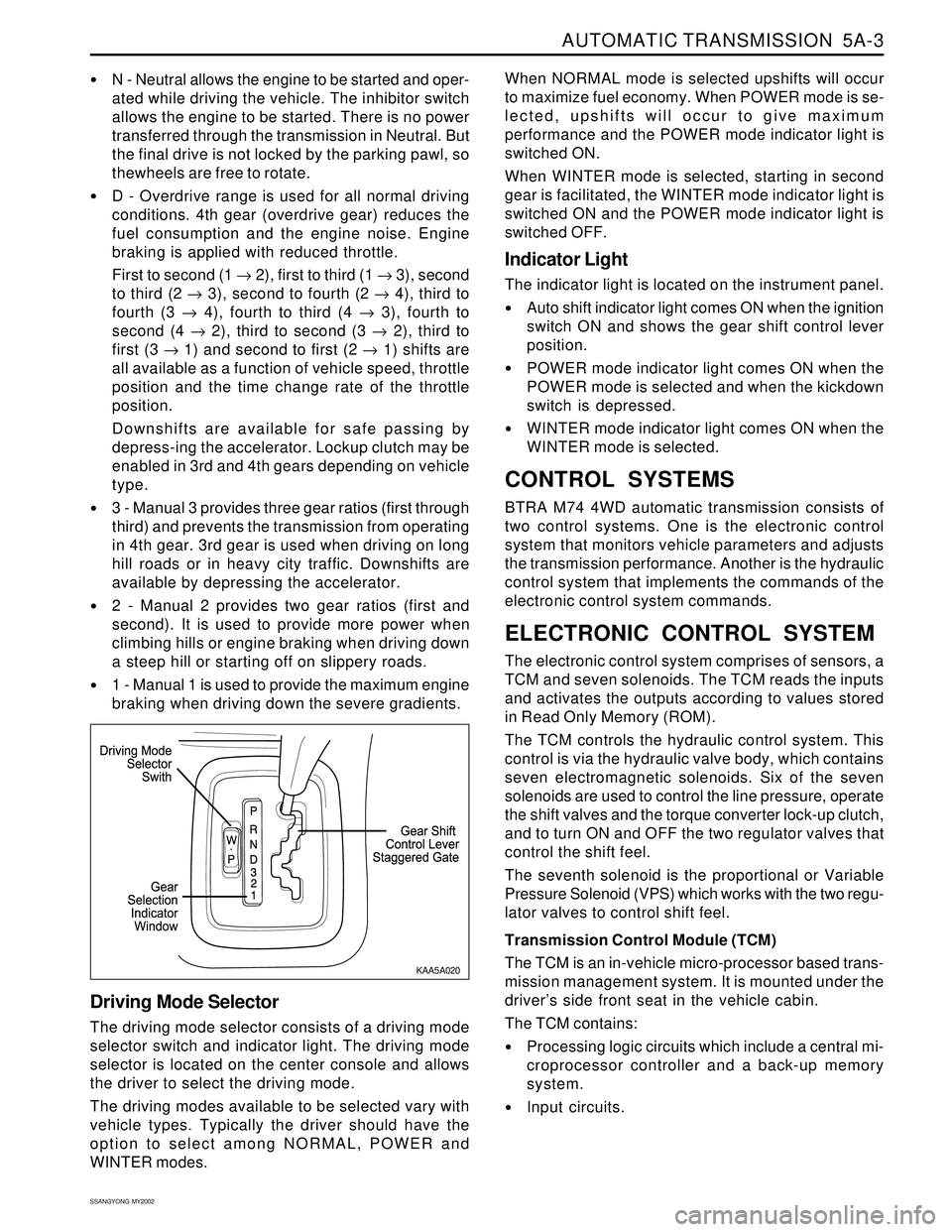
OPERATORS INTERFACES
There are three operator interfaces as the following;
•Gear Shift Control Lever
Driving Mode Selector
Indicator Light
Gear Shift Control lever
The transmission uses a conventional shift control lever.
The gear shift control lever can be moved from one
position to another within the staggered configuration
of the shift control lever gate to positively indicate the
gear selection.
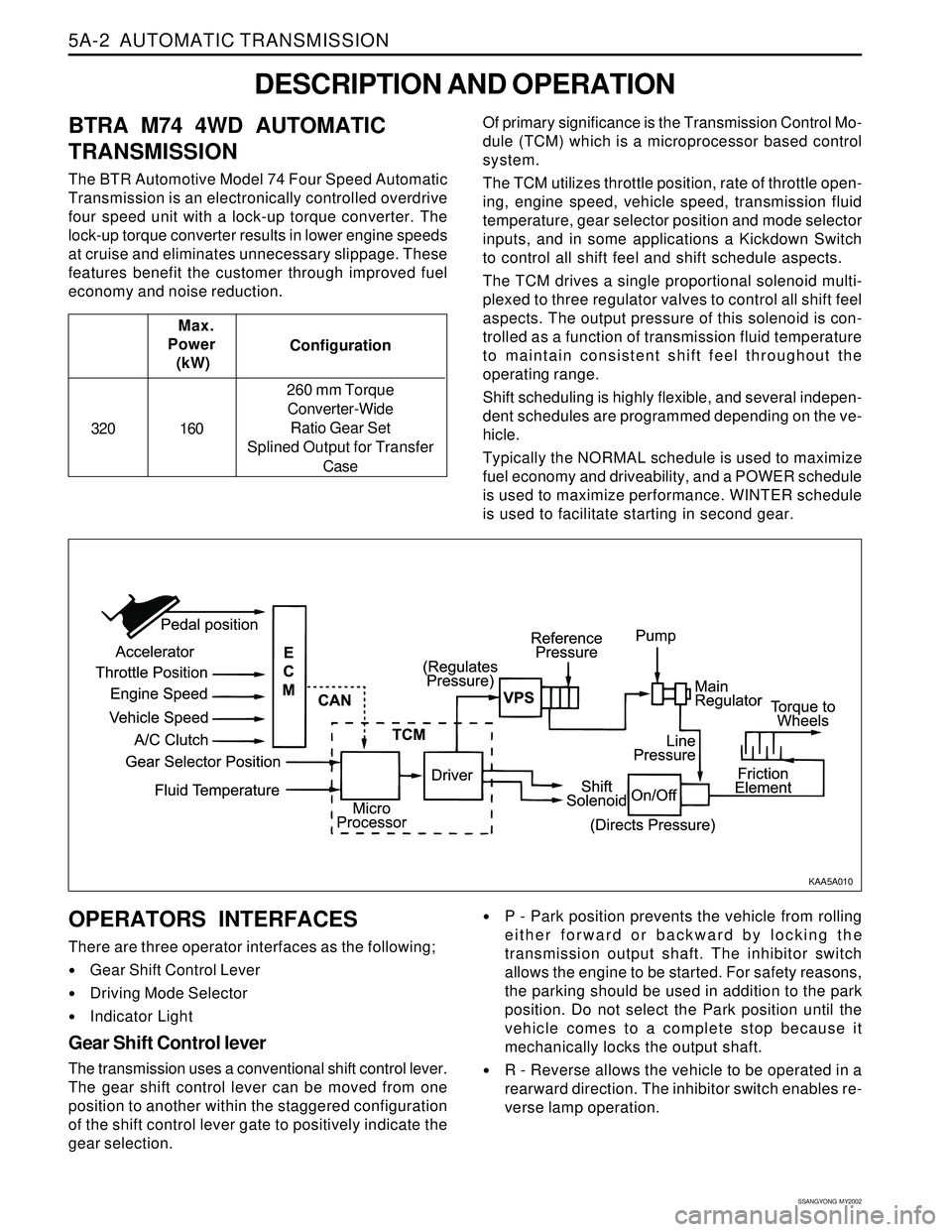
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BTRA M74 4WD AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
The BTR Automotive Model 74 Four Speed Automatic
Transmission is an electronically controlled overdrive
four speed unit with a lock-up torque converter. The
lock-up torque converter results in lower engine speeds
at cruise and eliminates unnecessary slippage. These
features benefit the customer through improved fuel
economy and noise reduction.Of primary significance is the Transmission Control Mo-
dule (TCM) which is a microprocessor based control
system.
The TCM utilizes throttle position, rate of throttle open-
ing, engine speed, vehicle speed, transmission fluid
temperature, gear selector position and mode selector
inputs, and in some applications a Kickdown Switch
to control all shift feel and shift schedule aspects.
The TCM drives a single proportional solenoid multi-
plexed to three regulator valves to control all shift feel
aspects. The output pressure of this solenoid is con-
trolled as a function of transmission fluid temperature
to maintain consistent shift feel throughout the
operating range.
Shift scheduling is highly flexible, and several indepen-
dent schedules are programmed depending on the ve-
hicle.
Typically the NORMAL schedule is used to maximize
fuel economy and driveability, and a POWER schedule
is used to maximize performance. WINTER schedule
is used to facilitate starting in second gear. Configuration Max.
Power
(kW)
320 160260 mm Torque
Converter-Wide
Ratio Gear Set
Splined Output for Transfer
Case
P - Park position prevents the vehicle from rolling
either forward or backward by locking the
transmission output shaft. The inhibitor switch
allows the engine to be started. For safety reasons,
the parking should be used in addition to the park
position. Do not select the Park position until the
vehicle comes to a complete stop because it
mechanically locks the output shaft.
R - Reverse allows the vehicle to be operated in a
rearward direction. The inhibitor switch enables re-
verse lamp operation.
KAA5A010
Page 1097 of 2053
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-3
SSANGYONG MY2002
N - Neutral allows the engine to be started and oper-
ated while driving the vehicle. The inhibitor switch
allows the engine to be started. There is no power
transferred through the transmission in Neutral. But
the final drive is not locked by the parking pawl, so
thewheels are free to rotate.
D - Overdrive range is used for all normal driving
conditions. 4th gear (overdrive gear) reduces the
fuel consumption and the engine noise. Engine
braking is applied with reduced throttle.
First to second (1 → 2), first to third (1 → 3), second
to third (2 → 3), second to fourth (2 → 4), third to
fourth (3 → 4), fourth to third (4 → 3), fourth to
second (4 → 2), third to second (3 → 2), third to
first (3 → 1) and second to first (2 → 1) shifts are
all available as a function of vehicle speed, throttle
position and the time change rate of the throttle
position.
Downshifts are available for safe passing by
depress-ing the accelerator. Lockup clutch may be
enabled in 3rd and 4th gears depending on vehicle
type.
3 - Manual 3 provides three gear ratios (first through
third) and prevents the transmission from operating
in 4th gear. 3rd gear is used when driving on long
hill roads or in heavy city traffic. Downshifts are
available by depressing the accelerator.
2 - Manual 2 provides two gear ratios (first and
second). It is used to provide more power when
climbing hills or engine braking when driving down
a steep hill or starting off on slippery roads.
1 - Manual 1 is used to provide the maximum engine
braking when driving down the severe gradients.When NORMAL mode is selected upshifts will occur
to maximize fuel economy. When POWER mode is se-
lected, upshifts will occur to give maximum
performance and the POWER mode indicator light is
switched ON.
When WINTER mode is selected, starting in second
gear is facilitated, the WINTER mode indicator light is
switched ON and the POWER mode indicator light is
switched OFF.
Indicator Light
The indicator light is located on the instrument panel.
Auto shift indicator light comes ON when the ignition
switch ON and shows the gear shift control lever
position.
POWER mode indicator light comes ON when the
POWER mode is selected and when the kickdown
switch is depressed.
WINTER mode indicator light comes ON when the
WINTER mode is selected.
CONTROL SYSTEMS
BTRA M74 4WD automatic transmission consists of
two control systems. One is the electronic control
system that monitors vehicle parameters and adjusts
the transmission performance. Another is the hydraulic
control system that implements the commands of the
electronic control system commands.
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The electronic control system comprises of sensors, a
TCM and seven solenoids. The TCM reads the inputs
and activates the outputs according to values stored
in Read Only Memory (ROM).
The TCM controls the hydraulic control system. This
control is via the hydraulic valve body, which contains
seven electromagnetic solenoids. Six of the seven
solenoids are used to control the line pressure, operate
the shift valves and the torque converter lock-up clutch,
and to turn ON and OFF the two regulator valves that
control the shift feel.
The seventh solenoid is the proportional or Variable
Pressure Solenoid (VPS) which works with the two regu-
lator valves to control shift feel.
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
The TCM is an in-vehicle micro-processor based trans-
mission management system. It is mounted under the
driver’s side front seat in the vehicle cabin.
The TCM contains:
Processing logic circuits which include a central mi-
croprocessor controller and a back-up memory
system.
Input circuits.
Driving Mode Selector
The driving mode selector consists of a driving mode
selector switch and indicator light. The driving mode
selector is located on the center console and allows
the driver to select the driving mode.
The driving modes available to be selected vary with
vehicle types. Typically the driver should have the
option to select among NORMAL, POWER and
WINTER modes.
KAA5A020