1993 DODGE TRUCK wiring diagram
[x] Cancel search: wiring diagramPage 322 of 1502
•
ELECTRICAL
ELECTRICAL
8A - 1
Group
AUDIO
SYSTEMS
8F
BATTERY/STARTER/GENERATOR
SERVICE
.. 8B
BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING
SYSTEMS
DIAGNOSTICS
8A
HORNS
8G
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
8D
INSTRUMENT PANEL AND
GAUGES
8E
LAMPS
8L
POWER
LOCKS
8P
INDEX
Group
POWER
MIRRORS
8T
POWER
WINDOWS 8S
REAR
WINDOW DEFOGGER 8N
TURN
SIGNALS
AND HAZARD WARNING
FLASHERS
8J
VEHICLE
SPEED
CONTROL SYSTEM 8H WARNING BUZZER SYSTEM 8U
WINDSHIELD WIPERS AND
WASHERS
8K
WIRING DIAGRAMS 8W
BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS
CONTENTS
page
page
BATTERY TEST
PROCEDURES
2 GENERATOR TEST
PROCEDURES
ON VEHICLE . 13
ENGINE
STARTER MOTOR TEST
PROCEDURES
..9 SPECIFICATIONS 18
GENERAL
INFORMATION 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
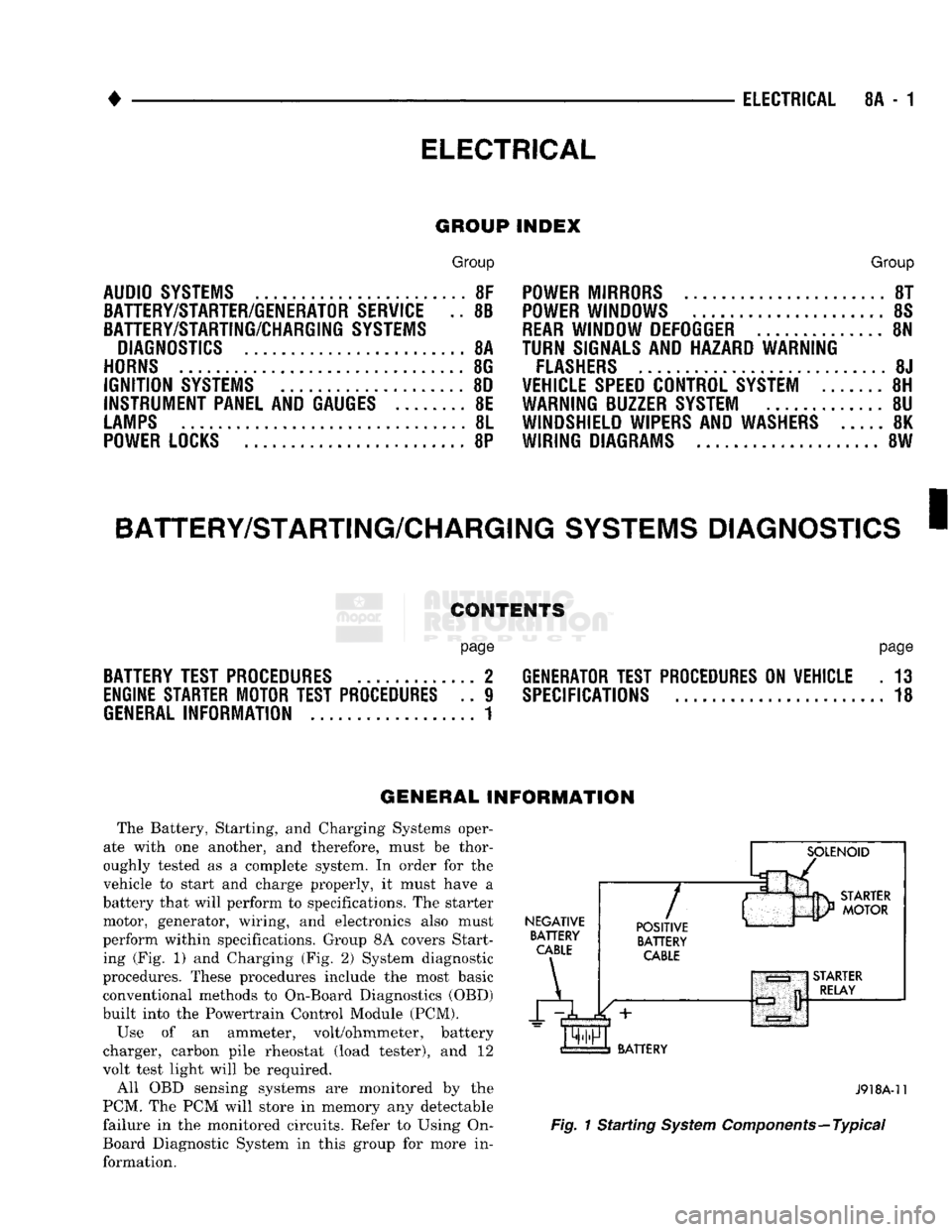
The Battery, Starting, and Charging Systems oper
ate with one another, and therefore, must be thor
oughly tested as a complete system. In order for the
vehicle to start and charge properly, it must have a
battery that will perform to specifications. The starter
motor, generator, wiring, and electronics also must
perform within specifications. Group 8A covers Start ing (Fig. 1) and Charging (Fig. 2) System diagnostic
procedures. These procedures include the most basic
conventional methods to On-Board Diagnostics (OBD)
built into the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
Use of an ammeter, volt/ohmmeter, battery
charger, carbon pile rheostat (load tester), and 12
volt test light will be required.
All OBD sensing systems are monitored by the
PCM. The PCM will store in memory any detectable
failure in the monitored circuits. Refer to Using On-
Board Diagnostic System in this group for more in formation.
NEGATIVE
BATTERY
CABLE
A
7
POSITIVE
BATTERY
CABLE
BATTERY
J918A-11
Fig.
1 Starting
System
Components—Typical
Page 325 of 1502

8A
- 4
ELECTRICAL
•
IGNITION
OFF
DRAW
(IOD)
Ignition off draw refers to power being drained
from the battery with the ignition turned off. A nor
mal vehicle electrical system will draw from 5 to 20
milliamps. A vehicle that has not been operated for
an extended period of time (approximately 20 days)
may discharge the battery to an inadequate level.
Battery drain should not exceed approximately 20
MA (20 milliamps = 0.020 amps). The 20 MA are needed to supply PCM memory,
digital clock memory, and ETR (electronically tuned
radio) memory. Excessive battery drain is caused by items left
turned on, internally shorted generator, or intermit
tent short in wiring.
If the IOD is excessive (over 20 milliamperes), the
defect must be found and corrected before replacing a
battery. In most cases the battery can be charged and returned to service.
TEST PROCEDURE Testing for higher amperage IOD must be per
formed first to prevent damage to most milliamp
meters.
Verify that all electrical accessories are OFF. Turn
off all lights, remove ignition key, and close all
doors.
If the vehicle is equipped with electronic acces
sories (illuminated entry, high line radio), allow the
systems to automatically shut off (time out), up to 3
minutes.
(1) After determining that the underhood lamp is
operating properly then disconnect bulb. (2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Connect a typical 12 volt test light (low watt
age bulb) between the negative cable clamp and the
battery negative terminal. The test light may light brightly for up to 3 min
utes or may not light at all (depending on the elec
trical equipment). The term brightly being used
throughout the following tests, implies the bright ness of the test light will be the same as if it were
connected across the battery.
The test light must be securely clamped to the neg
ative cable and battery terminal. If the test light be
comes disconnected during any of the IOD test, the electronic timer function will be activated and all
tests must be repeated.
(4) After 3 minutes, the test light should turn OFF
or be DIMLY lit (depending on the electrical equip
ment).
If the test light remains brightly lit do not
disconnect it. Remove each fuse or circuit breaker (refer to Group 8 - Wiring Diagrams) until test light
is either OFF or DIMLY lit. This will eliminate the
higher amperage draw.
If test light is still bright after disconnecting each
fuse and circuit breaker, disconnect the wiring har ness from the generator. Refer to Generator Testing
in this group. Do not disconnect the test light. After higher amperage IOD has been corrected, low
amperage IOD may be checked.
It is now safe to install milliamp meter to check for
low amperage IOD.
(5) With test light still connected, securely clamp
an ammeter between battery negative terminal and
negative battery cable.
If the test light or the milliamp meter circuit is
broken the various timer circuits will start. Do
not open any doors or turn on any electrical ac cessories with the test light disconnected or the
meter may be damaged.
(6) Disconnect test light. The current draw should
not exceed 0.020 amp. If it exceeds 20 milliamps iso
late each circuit by removing circuit breakers and
fuses.
The meter reading drops once the high current
problem is found. Repair this section of the circuit,
whether it is a wiring short or component failure.
BATTERY
OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST
A battery voltage (no load) test will indicate the
state of charge of a battery that will pass the Battery
Load Test described in this section. Before proceed
ing with this test or the Battery Load Test the
battery must be completely charged as de scribed in Battery Charging in this section. If a battery has a no load voltage reading of 12.4
volts or greater but will not endure a load test, it is
defective and should be replaced. Refer to Group 8B,
Battery/Starter Service for instructions. To test bat
tery no load voltage, perform the following operation: (1) Before measuring open circuit voltage, the sur
face charge must be removed from plates. Turn head lights on for 15 seconds then allow up to 5 minutes
for voltage to stabilize. (2) Remove both battery cables, negative first.
(3) Using a voltmeter connected to the battery
posts,
see instructions provided with voltmeter, mea sure open circuit voltage (Fig. 6). This voltage reading will indicate state of charge,
but will not reveal cranking capacity. Refer to Bat
tery Open Circuit Voltage chart.
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE
Open
Circuit
Volts
Percent
Chang©
11.7
volts
or
less
0%
12.0 25%
12.2 50%
12.4 75%
12.6
or more 100%
918A-3
Page 334 of 1502

•
ELECTRICAL
8A - 13 GENERATOR TEST PROCEDURES ON
VEHICLE
INDEX
page
Current
Output
Test
......................
14
Diagnostic Procedures
13
General
Information
13
Generator
Output
Wire Resistance Test
.......
13
page
How
to
Use
Malfunction
Indicator
(Check Engine) Lamp
for
Fault
Codes
17
Operational Check
with
Voltmeter
............
13
Using
On-Board Diagnostic System
15
GENERAL
INFORMATION
The generator
is
belt-driven
by the
engine.
All en
gines
use
serpentine drive. The amount
of DC
current produced
by the
gener
ator
is
controlled
by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
All vehicles
are
equipped with
On
Board Diagnos
tics (OBD).
All OBD
sensing systems
are
monitored
by
the PCM. The PCM
will store
in
electronic mem ory
any
detectable failure within
the
monitored cir
cuits.
Refer
to
USING ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
in
this group
for
more information.
OPERATIONAL CHECK
WITH
VOLTMETER
When
the
ignition switch
is
turned
to the RUN po
sition, battery potential will register
on the
voltme
ter. During engine cranking
a
lower voltage will appear
on the
meter. With
the
engine running,
a
voltage reading higher than
the
first reading (igni
tion
in RUN)
should register.
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
If
the
indicator does
not
operate properly,
or if an
undercharged
or
overcharged battery condition
oc
curs,
the
following procedures
may be
used
to
diag
nose
the
charging system. Remember that
an
undercharged battery
is
often
caused
by:
• accessories being left
on
overnight
•
or by a
defective switch which allows
a
bulb, such
as a
trunk
or
glove
box
light,
to
stay
on
(refer
to
Ignition
Off
Draw).
WISUAL
INSPECTION
• Inspect condition
of
battery cable terminals, bat
tery posts, connections
at
engine block, starter motor solenoid
and
relay. They should
be
clean
and
tight.
Repair
as
required.
• Inspect
all
fuses
in the
fuse block
for
tightness
in
receptacles. They should
be
properly installed
and
tight. Repair
or
replace
as
required.
• Inspect generator mounting bolts
for
tightness.
Re
place
or
torque bolt
as
required (refer
to
Torque Specifications).
• Inspect generator drive belt condition
and
tension.
Tension
or
replace belt
as
required. Refer
to
Belt
Tension Specifications. • Inspect connection
at
generator
B+
output.
It
should
be
clean
and
tight. Repair
as
required.
GENERATOR
OUTPUT
WIRE RESISTANCE TEST
(FIG.
1)
Generator output wire resistance test will show
amount
of
voltage drop across generator output wire
between generator
BAT
terminal
and
battery posi tive post.
PREPARATION
(1) Before starting test make sure vehicle
has a
fully charged battery. Test
and
procedures
on how to
check
for a
fully charged battery
are
shown
in
Bat
tery section
of
this Group.
(2) Turn
OFF
ignition switch.
(3)
Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(4)
Disconnect generator output wire from genera
tor output Battery terminal. (5) Connect
a 0-150
ampere scale
D.C.
ammeter
in
series between generator
BAT
terminal
and
discon
nected generator output wire. Connect Positive lead
to generator
BAT
terminal
and
Negative lead
to
dis connected generator output wire. (6) Connect Positive lead
of a
test voltmeter
(Range
0-18
volts minimum)
to
disconnected genera
tor output wire. Connect negative lead
of
test voltme
ter
to
battery positive cable
at
positive post. (7) Connect
one end of a
Jumper Wire
to
ground
and with other
end
probe green
K20
lead wire
at
back
of
generator
(Fig. 1).
(This will generate
a
fault
code).
CAUTION:
Do not
connect blue
A142
lead
of
wiring
to ground. Refer
to
Group
8W
-
Wiring Diagrams
for
more information.
(8) Connect
an
engine tachometer
and
connect neg
ative cable
to
battery.
(9) Connect
a
variable carbon pile rheostat
be
tween battery terminals.
Be
sure carbon pile
is in
"Open"
or "Off
position before connecting leads.
See
Battery Section, Load Testing
for
instructions.
TEST
(1) Start engine. Immediately after starting,
re
duce engine speed
to
idle.
Page 336 of 1502
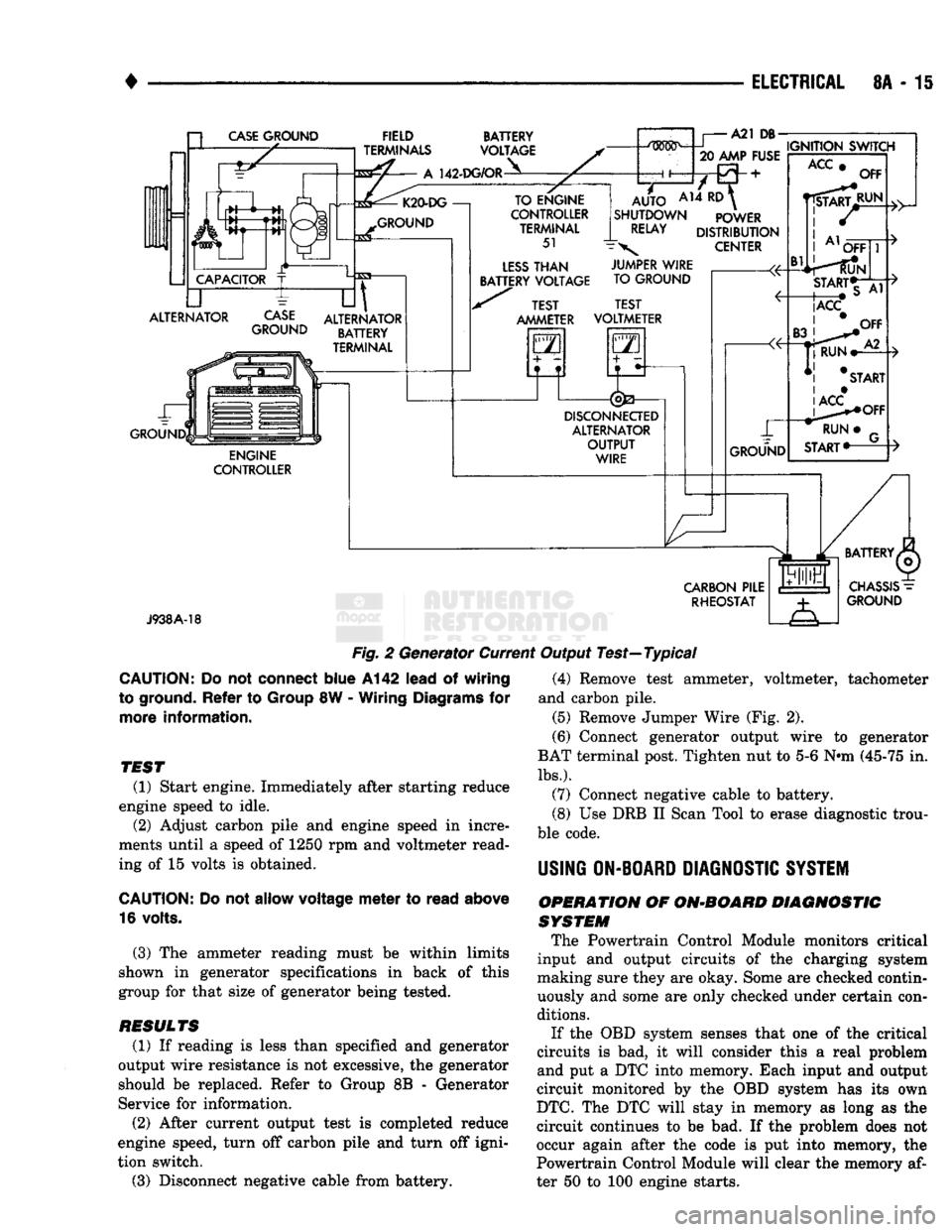
•
ELECTRICAL
8A - 15 a
CASE
GROUND
CAPACITOR
ALTERNATOR ~L FIELD
TERMINALS
A
142-DG/OR BATTERY
VOLTAGE K20-DG
—!
GROUND
CASE
GROUND
til
ALTERNATOR BATTERY
TERMINAL ENGINE
CONTROLLER TO ENGINE
CONTROLLER TERMINAL
51
LESS
THAN
BATTERY VOLTAGE A21
DB-
.....
IGNITION SWITCH
20 AMP FUSE
AUTO
AH ^
SHUTDOWN POWER
RELAY
DISTRIBUTION
\
CENTER TEST
AMMETER JUMPER WIRE
TO GROUND
TEST
VOLTMETER
GO
5—n
DISCONNECTED
ALTERNATOR OUTPUT WIRE GROUND
ACC
Bl
OFF
RUN OFF
START*T
|ACC
CARBON
PILE RHEOSTAT
J938A-18
Fig.
2 Generator Current Output Test—Typical
CAUTION:
Do not
connect
blue
A142
lead
of
wiring
to ground.
Refer
to
Group
8W -
Wiring
Diagrams
for
more
information.
TEST
(1) Start engine. Immediately after starting reduce
engine speed to idle. (2) Adjust carbon pile and engine speed in incre
ments until a speed of 1250 rpm and voltmeter read
ing of 15 volts is obtained.
CAUTION:
Do not
allow
voltage
meter
to
read
above
16 volts.
(3) The ammeter reading must be within limits
shown in generator specifications in back of this
group for that size of generator being tested.
RESULTS
(1) If reading is less than specified and generator
output wire resistance is not excessive, the generator
should be replaced. Refer to Group 8B - Generator
Service for information.
(2) After current output test is completed reduce
engine speed, turn off carbon pile and turn off igni
tion switch.
(3) Disconnect negative cable from battery. (4) Remove test ammeter, voltmeter, tachometer
and carbon pile. (5) Remove Jumper Wire (Fig. 2).
(6) Connect generator output wire to generator
BAT terminal post. Tighten nut to 5-6 Nnn (45-75 in.
lbs.).
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
(8) Use DRB II Scan Tool to erase diagnostic trou
ble code.
USING
ON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTIC
SYSTEM
OPERATION
OF
ON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTIC
SYSTEM
The Powertrain Control Module monitors critical
input and output circuits of the charging system
making sure they are okay. Some are checked contin
uously and some are only checked under certain con
ditions.
If the OBD system senses that one of the critical
circuits is bad, it will consider this a real problem
and put a DTC into memory. Each input and output
circuit monitored by the OBD system has its own
DTC.
The DTC will stay in memory as long as the
circuit continues to be bad. If the problem does not
occur again after the code is put into memory, the
Powertrain Control Module will clear the memory af
ter 50 to 100 engine starts.
Page 337 of 1502
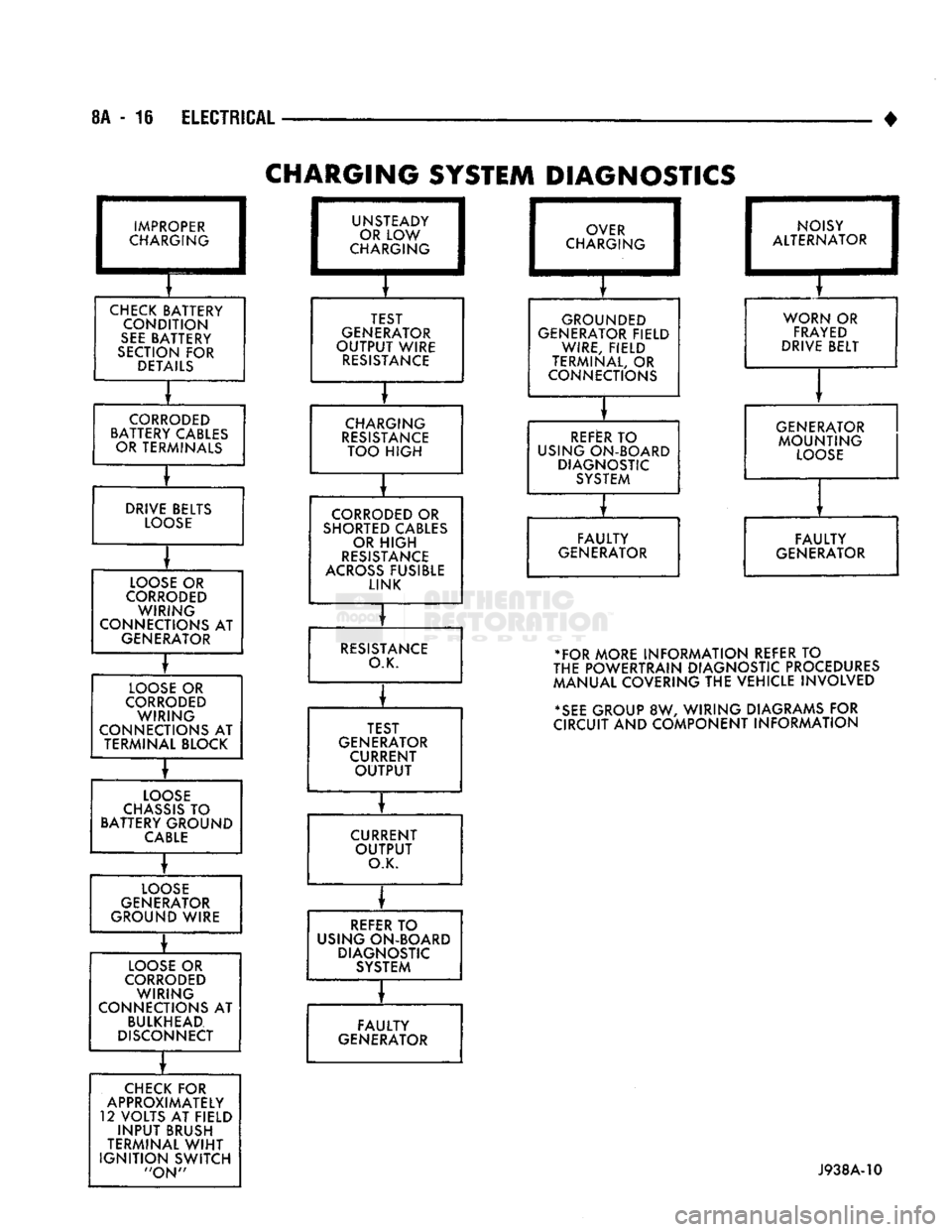
8A
- 16
ELECTRICAL
CHARGING
SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS
IMPROPER
CHARGING
CHECK
BATTERY CONDITION
SEE
BATTERY
SECTION
FOR
DETAILS
CORRODED
BATTERY CABLES OR TERMINALS
DRIVE BELTS
LOOSE
LOOSE
OR
CORRODED
WIRING
CONNECTIONS
AT
GENERATOR
LOOSE
OR
CORRODED
WIRING
CONNECTIONS
AT
TERMINAL BLOCK
LOOSE
CHASSIS
TO
BATTERY GROUND
CABLE
LOOSE
GENERATOR
GROUND WIRE
LOOSE
OR
CORRODED
WIRING
CONNECTIONS
AT
BULKHEAD
DISCONNECT
CHECK
FOR
APPROXIMATELY
12 VOLTS
AT
FIELD
INPUT
BRUSH
TERMINAL
WIHT
IGNITION
SWITCH
"ON"
UNS'
OR
CHAF rEADY
LOW
K3ING
TEST
GENERATOR
OUTPUT
WIRE
RESISTANCE
CHARGING
RESISTANCE
TOO
HIGH
CORRODED
OR
SHORTED CABLES OR
HIGH
RESISTANCE
ACROSS
FUSIBLE LINK
RESISTANCE
O.K.
TEST
GENERATOR CURRENT
OUTPUT
CURRENT
OUTPUT
O.K.
REFER
TO
USING ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
o
CHAR
/ER
.GING
GROUNDED
GENERATOR FIELD WIRE, FIELD
TERMINAL,
OR
CONNECTIONS
1 NO
1
ALTERf
ISY
MATOR
WORN
OR
FRAYED
DRIVE BELT
REFER
TO
USING ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM GENERATOR
MOUNTING
LOOSE
FAULTY
GENERATOR
FAULTY
GENERATOR •FOR MORE INFORMATION REFER
TO
THE POWERTRAIN DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
MANUAL COVERING
THE
VEHICLE INVOLVED
*SEE
GROUP
8W,
WIRING DIAGRAMS
FOR
CIRCUIT
AND
COMPONENT INFORMATION
FAULTY
GENERATOR
J938A-V0
Page 358 of 1502

•
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
80 - 7
DIAGNOSTICS/SERW1CE
PROCEDURES
INDEX
page
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) Relay
7
Camshaft Position
Sensor
Test
...............
7
Crankshaft Position
Sensor
Test
8
Distributor
Cap
8
Distributor
Rotor
8
Engine
Coolant Temperature
Sensor
Test
10
General
Information
7
Ignition
Coil
8
Ignition
Secondary
Circuit
Diagnosis
10
GENERAL
INFORMATION
This section
of the
group, Diagnostics/Service Pro
cedures, will discuss basic ignition system diagnos
tics
and
service adjustments. For system operation
and
component identification,
refer
to the
Component Identification/System Opera
tion section
of
this group. For removal
or
installation
of
ignition system com
ponents, refer
to the
Component Removal/Installa
tion section
of
this group. For other useful information, refer
to
On-Board
Di
agnostics
in the
General Diagnosis sections
of
Group
14,
Fuel System
in
this manual. For operation
of the DRB II
Diagnostic Scan Tool,
refer
to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce
dures service manual.
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN
(ASD)
RELAY
Refer
to
Relays—Operation/Testing
in the
Group
14,
Fuel System section
of
this service manual.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR TEST
The camshaft position sensor
is
located
in the
dis
tributor
on all
engines. To perform
a
complete test
of
this sensor
and its
circuitry, refer
to the DRB II
diagnostic scan tool.
Also refer
to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics
Procedures manual.
To
test
the
sensor only, refer
to
the following: For this test,
an
analog (non-digital) voltmeter
is needed.
Do not
remove
the
distributor connector from
the
distributor. Using small paper clips, insert
them into
the
backside
of the
distributor wire har ness connector
to
make contact with
the
terminals.
Be sure that
the
connector
is not
damaged when
in
serting
the
paper clips. Attach voltmeter leads
to
these paper clips. (1) Connect
the
positive (
+
)
voltmeter lead into
the sensor output wire. This
is at
done
the
distribu tor wire harness connector.
For
wire identification,
refer
to
Group
8W,
Wiring Diagrams.
page
Ignition
Timing
12
Intake Manifold Charge
Air
Temperature
Sensor
Test
12
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
Sensor
Test
. 12
Oxygen
Sensor
Tests
17
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
............
14
Spark
Plug Secondary Cables
16
Spark
Plugs
............................
14
Throttle
Position
Sensor
Test
17
(2) Connect
the
negative
(-)
voltmeter lead into
the
ground wire.
For
wire identification, refer
to
Group
8W, Wiring Diagrams.
(3)
Set the
voltmeter
to the 15
Volt
DC
scale. (4) Remove distributor
cap
from distributor
(two
screws). Rotate (crank)
the
engine until
the
distribu
tor rotor
is
pointed towards
the
rear
of
vehicle.
The
movable pulse ring should
now be
within
the
sensor
pickup.
(5) Turn ignition
key to ON
position. Voltmeter
should read approximately
5.0
volts.
(6)
If
voltage
is not
present, check
the
voltmeter
leads
for a
good connection.
(7)
If
voltage
is
still
not
present, check
for
voltage
at
the
supply wire.
For
wire identification, refer
to
Group
8W,
Wiring Diagrams.
(8)
If
voltage
is not
present
at
supply wire, check
for voltage
at
pin-7
of
powertrain control module (PCM) 60-way connector. Leave
the PCM
connector
connected
for
this test. (9)
If
voltage
is
still
not
present, perform vehicle
test using
the DRB II
diagnostic scan tool. (10)
If
voltage
is
present
at
pin-7,
but not at the
supply wire: (a) Check continuity between
the
supply wire.
This
is
checked between
the
distributor connector and pin-7
at the PCM. If
continuity
is not
present,
repair
the
harness
as
necessary. (b) Check
for
continuity between
the
camshaft
position sensor output wire
and
pin-44
at the PCM.
If continuity
is not
present, repair
the
harness
as
necessary. (c) Check
for
continuity between
the
ground cir
cuit wire
at the
distributor connector
and
ground.
If continuity
is not
present, repair
the
harness
as
necessary. (11) While observing
the
voltmeter, crank
the en
gine with ignition switch.
The
voltmeter needle should fluctuate between
0 and 5
volts while
the en
gine
is
cranking. This verifies that
the
camshaft
po
sition sensor
in the
distributor
is
operating properly
and
a
sync pulse signal
is
being generated.
Page 405 of 1502
![DODGE TRUCK 1993 Service Repair Manual
8F
- 2
AUDIO
SYSTEMS
• RADIO CONNECTOR PINS
BLACK
CHRYSLER
AM/FM STEREO
RADIOS
4 SPEAKERS
GRAY
BLACK
XL
GRAY
0@[3]S[3]@[D
X52 X54 VIEWED
FROM
X58
WIRE
END X56
E2 DODGE TRUCK 1993 Service Repair Manual
8F
- 2
AUDIO
SYSTEMS
• RADIO CONNECTOR PINS
BLACK
CHRYSLER
AM/FM STEREO
RADIOS
4 SPEAKERS
GRAY
BLACK
XL
GRAY
0@[3]S[3]@[D
X52 X54 VIEWED
FROM
X58
WIRE
END X56
E2](/manual-img/12/56922/w960_56922-404.png)
8F
- 2
AUDIO
SYSTEMS
• RADIO CONNECTOR PINS
BLACK
CHRYSLER
AM/FM STEREO
RADIOS
4 SPEAKERS
GRAY
BLACK
XL
GRAY
0@[3]S[3]@[D
X52 X54 VIEWED
FROM
X58
WIRE
END X56
E2 Ml
X51
X53 X57
X55
L7 XI2
AM/FM STEREO
RADIOS
2 SPEAKERS
BLACK
GRAY
4
BLACK
GRAY
[ZlSmEIULIlLT]
X54 X54 VIEWED
FROM
X56 WIRE END X56
E2
Ml
X53
X53 X55
X55
L7 X12
LEGEND:
E2-
ILLUMINATION
X51-LEFT
REAR FEED
X55-LEFT
DR RETURN L7-
PARK
LAMPS
X52-RIGHT
REAR FEED
X56-RIGHT
DR RETURN
Ml- BATTERY
X53-LEFT
DR FEED
X57-LEFT
REAR RETURN X12-ACC/RUN
X54-RIGHT
DR FEED
X58-RIGHT
REAR RETURN
J938F-8
TEST
PROCEDURES
RADIO DIAGNOSIS
Turn Ign. Key to
ACC.
T
Check
AM, FM and
Tape
Player
Operation
NOTE: FOR WIRE COLORS REFER TO
SECTION 8W-WIRING DIAGRAMS
Page 413 of 1502
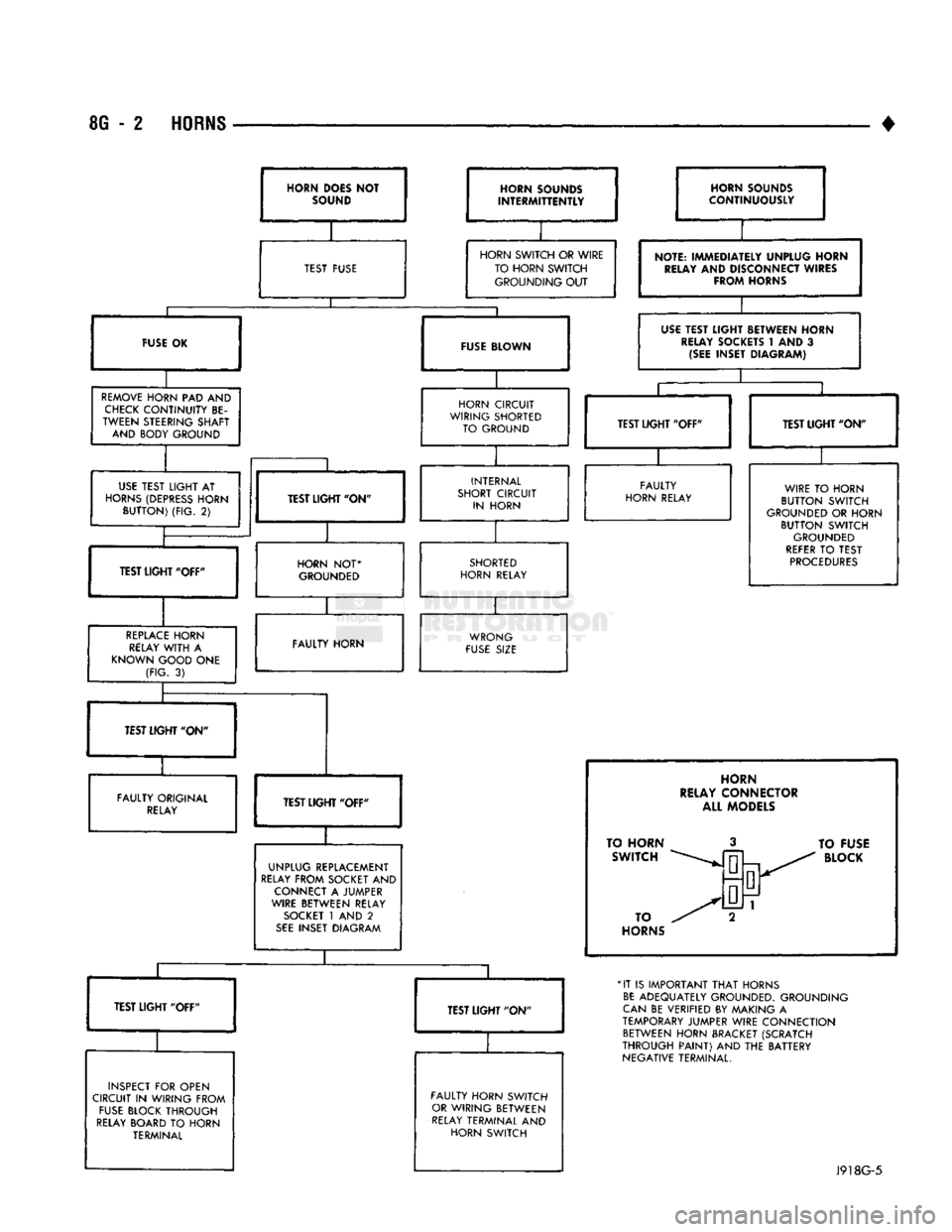
8G
- 2
HORNS
•
HORN
DOES NOT
SOUND HORN SOUNDS
INTERMITTENTLY
TEST FUSE
HORN SOUNDS
CONTINUOUSLY
HORN SWITCH
OR
WIRE TO HORN SWITCH GROUNDING
OUT
FUSE BLOWN
REMOVE
HORN
PAD AND
CHECK
CONTINUITY
BE
TWEEN STEERING SHAFT AND BODY GROUND
NOTE:
IMMEDIA1
RELAY
AND
Dl
FRO/V
rELY UNPLUG HORN
SCONNECT
WIRES
\HORNS
USE
TEST LIGHT BETWEEN HORN
RELAY
SOCKETS
t AND 3
(SEE
INSET DIAGRAM)
HORN CIRCUIT
WIRING SHORTED TO GROUND
USE
TEST
LIGHT
AT
HORNS
(DEPRESS
HORN
BUTTON)
(FIG.
2)
TEST LIGHT' ON
TEST
UGHT
"OFF" TEST LIGHT "OFF"
INTERNAL
SHORT CIRCUIT IN HORN
HORN
NOT*
GROUNDED
REPLACE
HORN
RELAY
WITH
A
KNOWN GOOD
ONE
(FIG.
3)
TEST LIGHT "ON"
FAULTY
HORN RELAY
SHORTED
HORN RELAY WIRE
TO
HORN
BUTTON SWITCH
GROUNDED
OR
HORN BUTTON SWITCH
GROUNDED
REFER
TO
TEST
PROCEDURES
FAULTY HORN WRONG
FUSE
SIZE
TEST LIGHT "ON"
FAULTY ORIGINAL
RELAY
TEST LIGI
HT
"OFF"
UNPLUG REPLACEMENT
RELAY
FROM SOCKET
AND
CONNECT
A
JUMPER
WIRE BETWEEN RELAY
SOCKET
1
AND
2
SEE
INSET DIAGRAM
INSPECT
FOR
OPEN
CIRCUIT
IN
WIRING FROM
FUSE
BLOCK THROUGH
RELAY
BOARD
TO
HORN TERMINAL FAULTY HORN SWITCH
OR
WIRING BETWEEN
RELAY
TERMINAL
AND
HORN SWITCH
HORN
RELAY CONNECTOR ALL MODELS
TO HORN SWITCH
TO
HORNS
TO
FUSE
BLOCK
*IT
IS
IMPORTANT
THAT
HORNS
BE
ADEQUATELY GROUNDED. GROUNDING
CAN
BE
VERIFIED
BY
MAKING
A
TEMPORARY
JUMPER WIRE CONNECTION BETWEEN HORN BRACKET (SCRATCH
THROUGH
PAINT)
AND THE
BATTERY
NEGATIVE TERMINAL.
J918G-5