1993 DODGE TRUCK remove seats
[x] Cancel search: remove seatsPage 612 of 1502
•
ENGINES
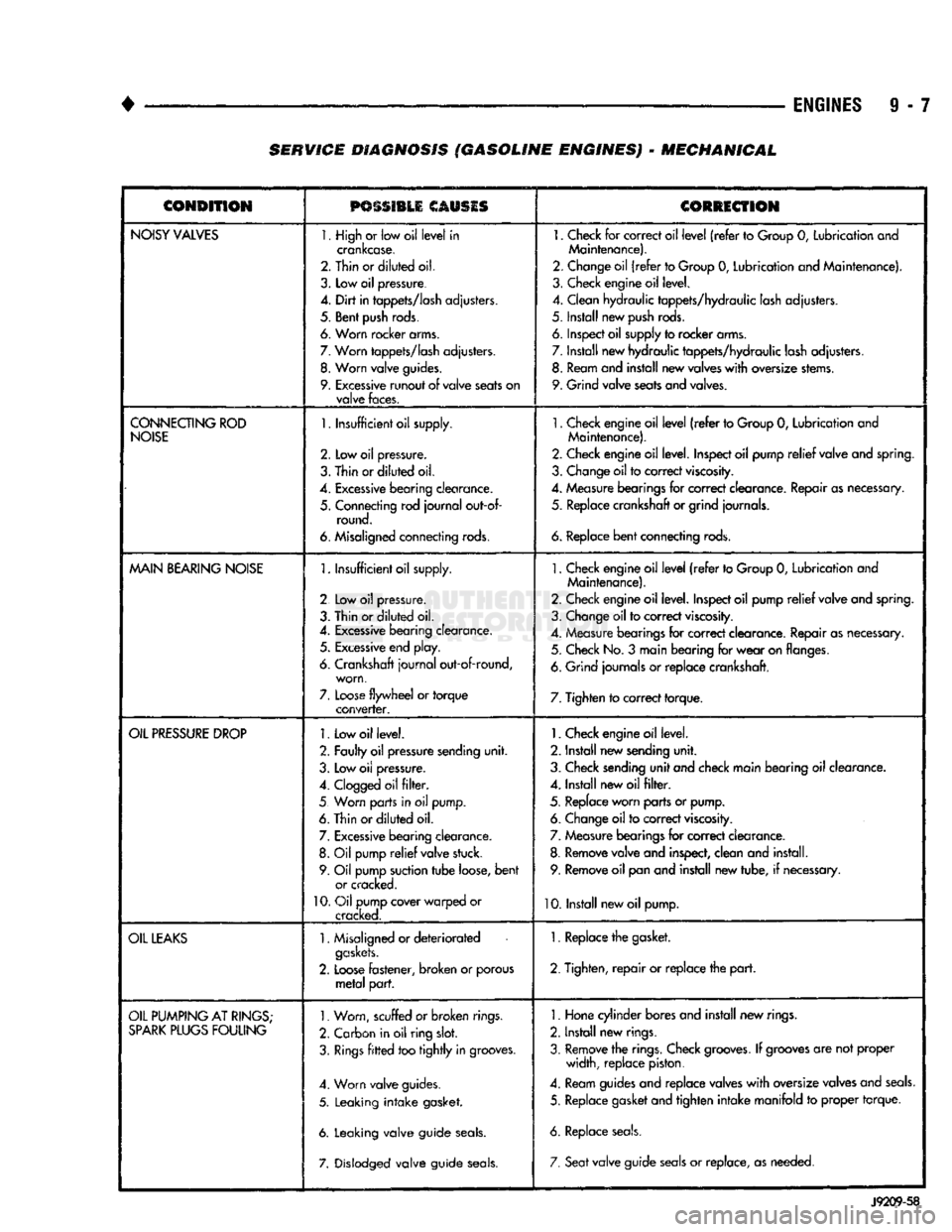
9 - 7 SERVICE DIAGNOSIS (GASOLINE ENGINES) - MECHANICAL
CONDITION
PSSSI1LI
CAUSIS
CORRECTION
NOISY
VALVES
1. High
or
low oil
level
in
crankcase.
2. Thin or
diluted
oil.
3.
Low
oil
pressure.
4.
Dirt
in
tappets/lash
adjusters.
5. Bent
push
rods.
6. Worn rocker arms.
7.
Worn
tappets/lash
adjusters.
8.
Worn
valve
guides.
9.
Excessive
runout
of
valve
seats
on
valve
faces.
1.
Check
for
correct oil
level
(refer
to
Group
0,
Lubrication and
Maintenance).
2. Change oil
(refer
to Group
0,
Lubrication and Maintenance).
3. Check engine oil level.
4. Clean hydraulic tappets/hydraulic lash adjusters.
5. Install new
push
rods.
6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms.
7. Install new hydraulic tappets/hydraulic lash adjusters. 8. Ream and install new valves
with
oversize stems.
9. Grind valve seats and valves.
CONNECTING
ROD
NOISE
1.
Insufficient oil supply.
2.
Low oil
pressure.
3.
Thin
or
diluted
oil.
4.
Excessive
bearing
clearance.
5. Connecting rod
journal
out-of- round.
6. Misaligned connecting rods.
1.
Check engine oil
level
(refer
to Group
0,
Lubrication and
Maintenance).
2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil pump
relief
valve and spring.
3. Change oil to correct
viscosity.
4. Measure bearings for correct clearance. Repair as necessary, 5. Replace crankshaft or grind journals.
6.
Replace
bent
connecting rods.
MAIN
BEARING
NOISE
1.
Insufficient oil supply.
2 Low
oil
pressure.
3. Thin or
diluted
oil.
4.
Excessive
bearing clearance. 5.
Excessive
end play.
6. Crankshaft
journal
out-of-round, worn,
7.
Loose
flywheel
or
torque
converter.
1.
Check engine oil
level
(refer
to Group
0,
Lubrication and
Maintenance).
2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil pump
relief
valve and spring.
3. Change oil to correct
viscosity.
4. Measure bearings for correct clearance. Repair as necessary. 5. Check No.
3
main bearing for
wear
on flanges.
6. Grind journals
or
replace crankshaft.
7. Tighten to correct torque.
OIL
PRESSURE
DROP
1.
Low oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending
unit.
3. Low
oil
pressure.
4.
Clogged
oil
filter.
5 Worn parts in
oil
pump.
6. Thin or
diluted
oil.
7.
Excessive
bearing clearance. 8.
Oil
pump
relief
valve stuck.
9. Oil pump suction
tube
loose,
bent
or cracked.
10.
Oil pump cover warped
or
cracked.
1.
Check engine oil level.
2. Install new sending
unit.
3. Check sending
unit
and check main bearing oil clearance.
4. Install new oil
filter.
5. Replace worn parts or pump. 6. Change oil to correct
viscosity.
7. Measure bearings for correct clearance.
8. Remove valve and inspect, clean and install. 9. Remove oil pan and install new tube,
if
necessary.
10. Install new oil pump.
OIL
LEAKS
1.
Misaligned or
deteriorated
gaskets.
2.
Loose
fastener, broken
or
porous
metal
part.
1. Replace the gasket.
2. Tighten,
repair
or replace the
part.
OIL
PUMPING
AT
RINGS;
SPARK
PLUGS
FOULING
1.
Worn, scuffed
or broken
rings.
2. Carbon in oil ring
slot.
3.
Rings
fitted
too
tightly
in grooves.
4. Worn valve guides.
5. Leaking
intake
gasket.
6. Leaking valve guide
seals.
7. Dislodged valve guide
seals.
1.
Hone cylinder bores and install new rings.
2. Install new rings.
3. Remove the rings. Check
grooves.
If
grooves
are not proper width, replace piston.
4. Ream guides and replace valves
with
oversize valves and
seals.
5. Replace gasket and tighten
intake
manifold
to
proper torque.
6. Replace
seals.
7. Seat
valve guide
seals
or
replace, as needed.
J9209-58
Page 630 of 1502

•
3.9L
ENGINE
9 - 25
VALVES
/
VALVE
SPRINGS
The valves are arranged in-line and inclined 18°.
The rocker pivot support and the valve guides are cast integral with the heads. This procedure requires the removal of the cylinder
head.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head.
(2) Compress valve springs using Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD-998772A.
(3) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring re
tainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(4) Before removing valves, remove any burrs from
valve stem lock grooves to prevent damage to the
valve guides. Identify valves to ensure installation in
original location.
VALVE
CLEANING
Clean valves thoroughly. Discard burned, warped
and cracked valves.
Remove carbon and varnish deposits from inside of
valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
VALVE
INSPECTION
Measure valve stems for wear. If wear exceeds
0.051 mm (0.002 inch), replace the valve. Measure valve stem guide clearance as follows:
(a) Install Valve Guide Sleeve Tool C-3973 over
valve stem and install valve (Fig. 10). The special sleeve places the valve at the correct height for
checking with a dial indicator.
Fig.
10 Positioning Valve with Tool C-3973
(b) Attach dial indicator Tool C-3339 to cylinder
head and set it at right angle of valve stem being
measured (Fig. 11).
(c) Move valve to and from the indicator. The to
tal dial indicator reading should not exceed 0.432
mm (0.017 inch). Ream the guides for valves with
oversize stems if dial indicator reading is excessive
or if the stems are scuffed or scored.
Service valves with oversize stems are available
(Fig. 12).
Slowly turn reamer by hand and clean guide thor
oughly before installing new valve. Ream the valve
guides from standard to 0.381 mm (0,015 inch).
Fig.
11 Measuring Valve Guide Wear
Reamer
O/S
Valve
Guide
Size
0.076
mm
8.026
-
8.052
mm
(0.003 in.) (0.316 -0.317 in.)
0.381
mm 8.331 -8.357 mm
(0.015 in.)
(0.328-0.329
in.)
J9309-30
Fig.
12
Reamer
Sizes
Use a 2 step procedure so the valve guides are
reamed true in relation to the valve seat:
•
Step 1-Ream to 0.0763 mm (0.003 inch).
•
Step 2-Ream to 0.381 mm (0.015 inch).
REFACING
VALVES
/
VALVE
SEATS
The intake and exhaust valves have a 43-1/4° to
43-3/4° face angle and a 44-1/4° to 44-3/4° seat angle
(Fig. 13).
VAL¥ES
Inspect the remaining margin after the valves are
refaced (Fig. 14). Valves with less than 1.190 mm (0.047 inch) margin should be discarded.
VALVE
SEATS
CAUTION:
DO NOT
un-shroud
valves
during
valve
seat
refacing (Fig. 15).
(1) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat ing stones. A true and complete surface must be ob
tained.
(2) Measure the concentricity of valve seat using a
dial indicator. Total runout should not exceed 0.051
mm (0.002 inch) total indicator reading.
Page 631 of 1502

A
-
SEAT
WIDTH
-
INTAKE
1.016
-
1.524
mm
(0.040
-
0.060
in.)
EXHAUST
1.524
-
2.032
mm
(0.060
-
0.080
in.)
B
-
FACE
ANGLE
(INTAKE
& EXHAUST)
4374°
-
433A°
C
-
SEAT
ANGLE
(INTAKE
& EXHAUST)
4474°
-
44%°
D
-
CONTACT SURFACE
J9309-95
Fig.
13
Valve
Face and
Seat
Angles
i
INTAKE
VALVE
\
MARGIN
/ "
>FACE'
•STEM"
VALVE SPRING
RETAINER LOCK GROOVE EXHAUST
VALVE
J9209-127
Fig.
14 Intake and
Exhaust
Valves
(3) Inspect
the
valve seat with Prussian blue
to de
termine where
the
valve contacts
the
seat.
To do
this,
coat valve seat LIGHTLY with Prussian blue
then
set
valve
in
place. Rotate
the
valve with light
pressure.
If the
blue
is
transferred
to the
center
of
valve face, contact
is
satisfactory.
If
the blue
is
trans
ferred
to the top
edge
of
valve face, lower valve seat
with
a 15°
stone.
If
the blue
is
transferred
to
bottom edge
of
valve face raise valve seat with
a 60°
stone.
(4)
When seat
is
properly positioned
the
width
of
intake seats should
be 1.016-1.524 mm (0.040-0.060
inch).
The
width
of the
exhaust seats should
be 1.524-2.032 mm (0.060-0.080
inch).
Fig.
15 Refacing
Valve
Seats
VALVE
SPRING
INSPECTION
Whenever valves have been removed
for
inspection,
reconditioning
or
replacement, valve springs should
be tested.
As an
example
the
compression length
of
the spring
to be
tested
is 1-5/16
inch. Turn table
of
Valve Spring Tester Tool
C-647
until surface
is in
line with
the 1-5/16
inch mark
on the
threaded stud.
Be sure
the
zero mark
is to the
front (Fig.
16).
Place spring over stud
on the
table
and
lift compressing
le
ver
to set
tone device. Pull
on
torque wrench until
ping
is
heard. Take reading
on
torque wrench
at
this instant. Multiply this reading
by 2.
This will give
the spring load
at
test length. Fractional measure ments
are
indicated
on the
table
for
finer adjustments. Refer
to
specifications
to
obtain specified
height
and
allowable tensions. Discard
the
springs
that
do not
meet specifications.
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-647
9209-37
Fig.
16 Testing
Valve
Spring
for
Compressed
Length
with
Tool
C-647
INSTALLATION
(1)
Coat valve stems with lubrication
oil and
insert
them
in
cylinder head.
Page 632 of 1502

•
3.9L
ENGINE
9 - 27 (2) If valves or seats are reground, check valve
stem height. If valve is too long, replace cylinder
head.
(3) Install new seals on all valve guides. Install
valve springs and valve retainers.
(4) Compress valve springs with Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD-998772A, install locks and re
lease tool. If valves and/or seats are ground, measure
the installed height of springs. Make sure the mea surement is taken from bottom of spring seat in cyl
inder head to the bottom surface of spring retainer. If
spacers are installed, measure from the top of spacer.
If height is greater than 42.86 mm (1-11/16 inches), install a 1.587 mm (1/16 inch) spacer in head coun-
terbore. This should bring spring height back to nor
mal 41.27 to 42.86 mm (1-5/8 to
1-11/16
inch).
VALVE STEM SEAL
/
SPRING REPLACEMENT
This procedure is done with the cylinder head in
stalled. (1) Set engine basic timing to TDC and remove air
cleaner. (2) Remove cylinder head covers and spark plugs.
(3) Remove coil wire from distributor and secure to
good ground to prevent engine from starting. (4) Using suitable socket and flex handle at crank
shaft retaining bolt, turn engine so the No.l piston is
at Top Dead Center on the compression stroke. (5) Remove rocker arms.
(6) With air hose attached to an adapter installed
in No.l spark plug hole, apply 620-689 kPa (90-100
psi) air pressure. (7) Using Valve Spring Compressor Tool
MD-998772A, compress valve spring and remove re
tainer valve locks and valve spring. (8) Install seals on the exhaust valve stem and po
sition down against valve guides. (9) The intake valve stem seals should be pushed
firmly and squarely over the valve guide using the valve stem as a guide. DO NOT force seal against
top of guide. When installing the valve retainer
locks,
compress the spring only enough to install the
locks.
(10) Follow the same procedure on the remaining 5
cylinders using the firing sequence
1-6-5-4-3-2.
Make sure piston in cylinder is at TDC on the valve spring
that is being removed. (11) Remove adapter from the No.l spark plug
hole.
(12) Install rocker arms.
(13) Install covers and coil wire to distributor.
(14) Install air cleaner.
(15) Road test vehicle.
HYDRAULIC
TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor
rect tappet noise, check the oil pressure. If vehicle
has no oil pressure gauge, install a reliable gauge at the pressure sending unit. The pressure should be be
tween 207-552 kPa (30-80 psi) at 3,000 RPM.
Check the oil level after the engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize
oil level, check dipstick.
The oil level in the pan should never be above the
FULL mark or below the ADD OIL mark on dipstick.
Either of these 2 conditions could be responsible for
noisy tappets.
OIL
LEWEL
HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark, it is possible
for the connecting rods to dip into the oil. With the engine running, this condition could create foam in
the oil pan. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the hy draulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to lose
length and allow valves to seat noisily.
LOW
Low oil level may allow oil pump to take in air.
When air is fed to the tappets, they lose length
which allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on in
take side of oil pump through which air can be drawn will create the same tappet action. Check the
lubrication system from the intake strainer to the
pump cover, including the relief valve retainer cap.
When tappet noise is due to aeration, it may be in
termittent or constant, and usually more than 1 tap
pet will be noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected, operate the engine at fast idle. Run engine
for a sufficient time to allow all of the air inside the
tappets to be bled out.
TAPPET
NOISE DIAGNOSIS
(1) To determine source of tappet noise, operate en
gine at idle with cylinder head covers removed. (2) Feel each valve spring or rocker arm to detect
noisy tappet. The noisy tappet will cause the affected
spring and/or rocker arm to vibrate or feel rough in
operation.
Worn valve guides or cocked springs are some
times mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is the
case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not appre ciably reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in
the tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets and push rod ends for wear.
(3) Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces sive leak down around the unit plunger or by the
plunger partially sticking in the tappet body cylin der. The tappet should be replaced. A heavy click is
caused by a tappet check valve not seating or by for
eign particles becoming wedged between the plunger
and the tappet body. This will cause the plunger to
stick in the down position. This heavy click will be
Page 661 of 1502
9
- 56 5.2L
ENGINE
•
VALVE
SPRING
RETAINER LOCK GROOVE
EXHAUST
VALVE
J9209-127 the spring load at test length. Fractional measure
ments are indicated on the table for finer adjust
ments. Refer to specifications to obtain specified
height and allowable tensions. Discard the springs
that do not meet specifications.
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-647
Fig.
14 Intake and
Exhaust
Valves
Fig.
15 Refacing
Valve
Seats
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans
ferred to the top edge of valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15° stone. If the blue is transferred to bottom edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 60° stone.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake seats should be
1.016-1.524
mm (0.040-0.060
inch).
The width of the exhaust seats should be
1.524-2.032
mm (0.060-0.080 inch).
WALVE SPRING INSPECTION Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested. As an example the compression length of
the spring to be tested is
1-5/16
inch. Turn table of Valve Spring Tester Tool C-647 until surface is in line with the
1-5/16
inch mark on the threaded stud.
Be sure the zero mark is to the front (Fig. 16). Place spring over stud on the table and lift compressing le
ver to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this instant. Multiply this reading by 2. This will give ^
9209-37
Fig.
16 Testing
Valve
Spring
for
Compressed
Length
with
Tool
C-647
INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with lubrication oil and insert
them in cylinder head.
(2) If valves or seats are reground, check valve
stem height. If valve is too long, replace cylinder
head.
(3) Install new seals on all valve guides. Install
valve springs and valve retainers.
(4) Compress valve springs with Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD-998772A, install locks and re
lease tool. If valves and/or seats are ground, measure
the installed height of springs. Make sure the mea surement is taken from bottom of spring seat in cyl
inder head to the bottom surface of spring retainer. If spacers are installed, measure from the top of spacer.
If height is greater than 42.86 mm (1-11/16 inches),
install a 1.587 mm (1/16 inch) spacer in head coun-
terbore. This should bring spring height back to nor mal 41.27 to 42.86 mm (1-5/8 to
1-11/16
inch).
VALVE STEM SHIELD
/
SPRING REPLACEMENT
# This procedure is done with the cylinder head in
stalled. (1) Set engine basic timing to Top Dead Center
(TDC) and remove air cleaner. (2) Remove cylinder head covers and spark plugs.
(3) Remove coil wire from distributor and secure to
good ground to prevent engine from starting. (4) Using suitable socket and flex handle at crank
shaft retaining bolt, turn engine so the No.l piston is
at TDC on the compression stroke. (5) Remove rocker arms.
Page 691 of 1502
9
• 86 5.9L
ENGINE
•
INTAKE
VALVE
\
MARGIN
/ >
\ACE^
*
STEM
*
VALVE
SPRING
RETAINER
LOCK
GROOVE EXHAUST
VALVE
J9209-127
Fig.
14
intake
and
Exhaust
Waives
REFACING STONE MUST
NOT CUT
VALVE SHROUD Fig.
15 Refacing
Waive
Seats
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans ferred to the top edge of valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15° stone. If the blue is transferred to bottom edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 60° stone.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake seats should be
1.016-1.524
mm (0.040-0.060
inch).
The width of the exhaust seats should be
1.524-2.032
mm (0.060-0.080 inch).
VALVE
SPRING
INSPECTION
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should be tested. As an example the compression length of
the spring to be tested is
1-5/16
inch. Turn table of
Valve Spring Tester Tool C-647 until surface is in
line with the
1-5/16
inch mark on the threaded stud. Be sure the zero mark is to the front (Fig. 16). Place spring over stud on the table and lift compressing le
ver to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this instant. Multiply this reading by 2. This will give the spring load at test length. Fractional measure
ments are indicated on the table for finer adjust
ments. Refer to specifications to obtain specified
height and allowable tensions. Discard the springs that do not meet specifications.
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-647
9209-37
Fig.
16 Testing
Waive
Spring
for
Compressed
Length
with
Tool
C-647
INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with lubrication oil and insert
them in cylinder head.
(2) If valves or seats are reground, check valve
stem height. If valve is too long, replace cylinder
head.
(3) Install new seals on all valve guides. Install
valve springs and valve retainers.
(4) Compress valve springs with Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD-998772A, install locks and re
lease tool. If valves and/or seats are ground, measure
the installed height of springs. Make sure the mea surement is taken from bottom of spring seat in cyl
inder head to the bottom surface of spring retainer. If
spacers are installed, measure from the top of spacer.
If height is greater than 42.86 mm (1-11/16 inches),
install a 1.587 mm (1/16 inch) spacer in head coun-
terbore. This should bring spring height back to nor mal 41.27 to 42.86 mm (1-5/8 to
1-11/16
inch).
¥AL¥E
STEM SHIELD
/
SPRING REPLACEMENT
This procedure is done with the cylinder head in
stalled. (1) Set engine basic timing to Top Dead Center
(TDC) and remove air cleaner. (2) Remove cylinder head covers and spark plugs. (3) Remove coil wire from distributor and secure to
good ground to prevent engine from starting. (4) Using suitable socket and flex handle at crank
shaft retaining bolt, turn engine so the No.l piston is
at TDC on the compression stroke. (5) Remove rocker arms.
Page 723 of 1502
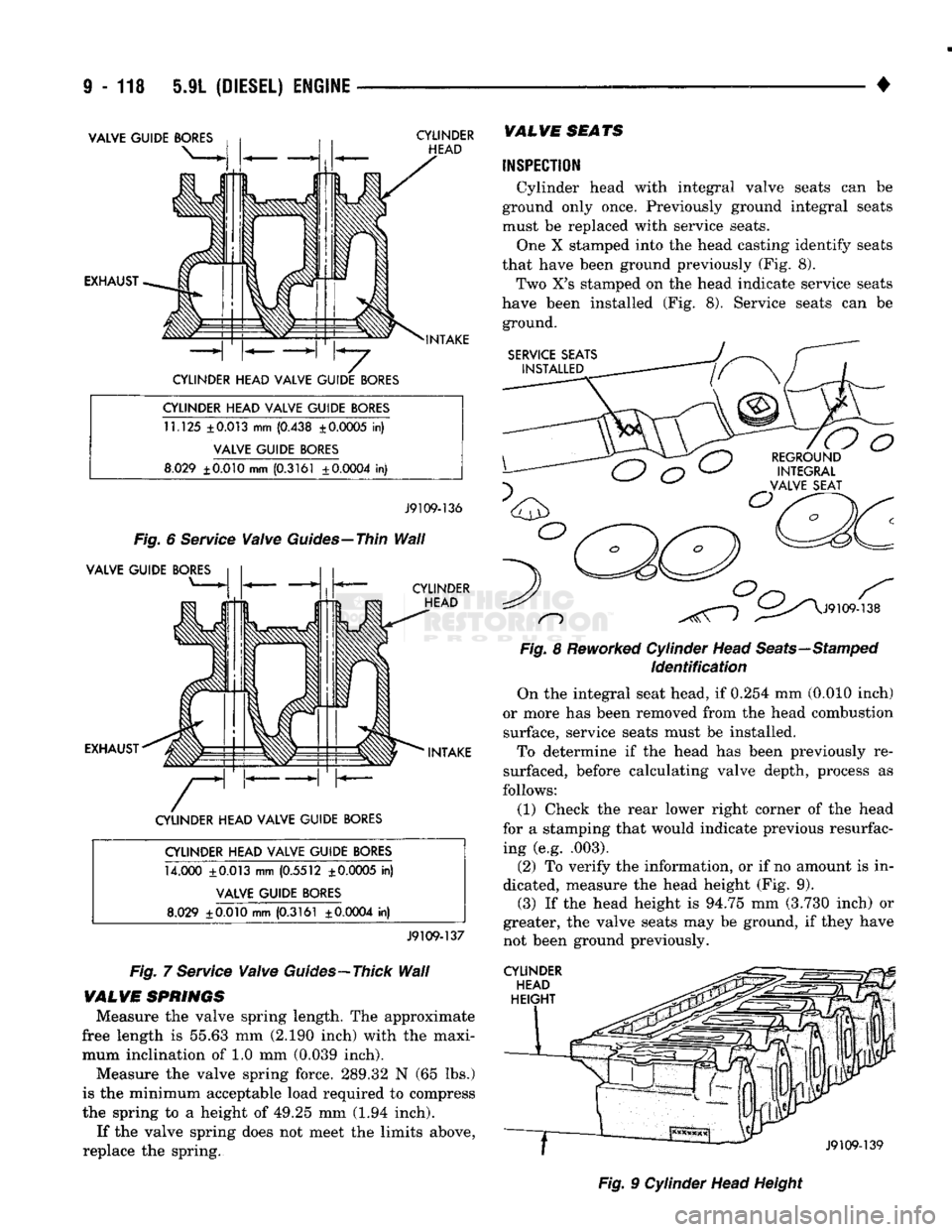
i - 118 5.9L
(DIESEL) ENGINE
VALVE GUIDE
BORES
EXHAUST CYLINDER
HEAD
INTAKE
CYLINDER HEAD VALVE GUIDE
BORES
CYLINDER HEAD VALVE GUIDE
BORES
11.125
±0.013 mm (0.438 ± 0.0005 in)
VALVE GUIDE
BORES
8.029
±0.010
mm
(0.3161 ±0.0004 in)
J9109-136
Fig.
6
Service
Valve
Guides—Thin
Wall
VALVE GUIDE
BORES
CYLINDER HEAD
EXHAUST INTAKE
CYLINDER HEAD VALVE GUIDE
BORES
CYLINDER HEAD VALVE GUIDE
BORES
14.000 ±0.013
mm
(0.5512 ± 0.0005 in)
VALVE GUIDE
BORES
8.029
±0.010
mm
(0.3161 ±0.0004 in)
J9109-137
Fig.
7
Service
Valve
Guides—Thick
Wall
VALVE
SPRINGS
Measure
the
valve spring length.
The
approximate
free length
is
55.63
mm
(2.190 inch) with
the
maxi mum inclination
of 1.0 mm
(0.039 inch).
Measure
the
valve spring force. 289.32
N (65 lbs.)
is
the
minimum acceptable load required
to
compress
the spring
to a
height
of
49.25
mm (1.94
inch). If
the
valve spring does
not
meet
the
limits above,
replace
the
spring.
VALVE
SEATS
INSPECTION
Cylinder head with integral valve seats
can be
ground only once. Previously ground integral seats
must
be
replaced with service seats. One
X
stamped into
the
head casting identify seats
that have been ground previously
(Fig. 8).
Two
X's
stamped
on the
head indicate service seats
have been installed
(Fig. 8).
Service seats
can be
ground.
SERVICE SEATS
INSTALLED
n
o
REGROUND INTEGRAL
VALVE SEAT
J9109-138
Fig.
8
Reworked
Cylinder Head
Seats—Stamped
Identification
On
the
integral seat head,
if
0.254
mm
(0.010 inch)
or more
has
been removed from
the
head combustion surface, service seats must
be
installed. To determine
if the
head
has
been previously
re
surfaced, before calculating valve depth, process
as
follows:
(1) Check
the
rear lower right corner
of the
head
for
a
stamping that would indicate previous resurfac ing
(e.g.
.003).
(2)
To
verify
the
information,
or if no
amount
is in
dicated, measure
the
head height
(Fig. 9).
(3)
If the
head height
is
94.75
mm
(3.730 inch)
or
greater,
the
valve seats
may be
ground,
if
they have
not been ground previously.
CYLINDER
HEAD
HEIGHT
J9109-139
Fig.
9
Cylinder Head Height
Page 724 of 1502
•
5.9L (DIESEL) ENGINE
9 - 119
INTEGRAL VALWE SEAT GRINDING
After resurfacing the valves and determining that
all valves meet specifications, install the valves in
their designated locations and measure valve depth (Fig. 10). The valve depth is the distance from the
valve face to the head deck. Record the depth of each valve.
CYLINDER
HEAD DECK GRIND
TO 15°
VALVE
DEPTH
J9109-140
Fig.
10
Valve
Depth
Grind the valve seats to remove scores, scratches
and burns. The seat angle should be—Intake 30° and
Exhaust 45°. Install the valves in their respective bores and
measure the depth again (Fig. 10). Record the depth
of each valve.
The grinding depth is the difference between the
measurement before grinding and the measurement after grinding. The grinding depth maximum limit (integral seats only) is 0.254 mm (0.010 inch). Ser
vice valve seats are available for over limit integral
valve seats.
Identify ground valve seats by stamping the cylin
der head.
Install the valves in their designated locations and
measure the depth of each. The valve depth limit (In
tegral and Inserted Seats) is 0.99 mm to 1.52 mm (0.039 inch to 0.060 inch). Replace the valve if the
depth is over this limit.
Apply a light coat of valve lapping compound to
each valve and lap each valve to its mating seat.
Remove the valves and clean lapping compound
from the valves and seats.
Measure the valve seat width indicated by the lap
ping surface. The valve seat width limit is
1.50-2.00
mm (0.060-0.080 inch).
If required, grind the areas with a 60° stone and a
15° stone to center the seat on the valve face. Main
tain the valve seat width limits (Fig. 11).
SERVICE
VALVE
SEAT
INSTALLATION
Inspect the valve guide bores as described in the
valve guide section of this manual. If it is necessary
to install valve guides, install the guides before in stalling the service seats.
J9109-141
Fig.
11
Grind
Valve
Seat
Replacement valve seat inserts must be installed if
the valve seats have been ground previously. The il lustrated marks indicate valve seats have been
ground previously.
Machine the cylinder head to install the service
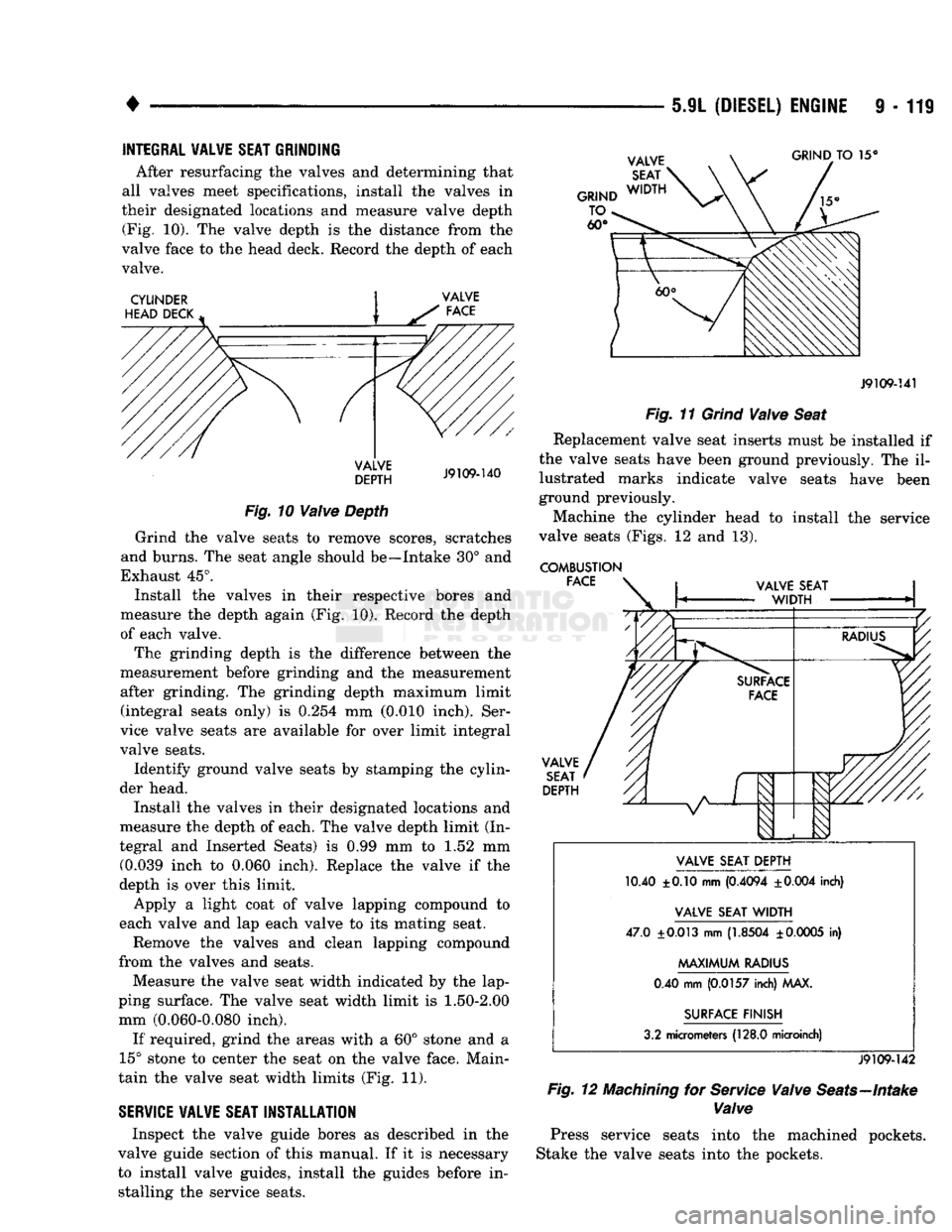
valve seats (Figs. 12 and 13).
COMBUSTION FACE VALVE
SEAT
DEPTH VALVE SEAT DEPTH
10.40 ±0.10 mm
(0.4094
±0.004
inch)
VALVE SEAT
WIDTH
47.0
±0.013
mm
(1.8504
±
0.0005
in)
MAXIMUM
RADIUS
0.40 mm
(0.0157
inch) MAX.
SURFACE FINISH
3.2 micrometers
(128.0
microinch)
J9109-142
Fig.
12
Machining
for
Service
Valve
Seats—Intake
Valve
Press service seats into the machined pockets.
Stake the valve seats into the pockets.