1993 DODGE TRUCK check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 886 of 1502
•
FUEL SYSTEM 14-67
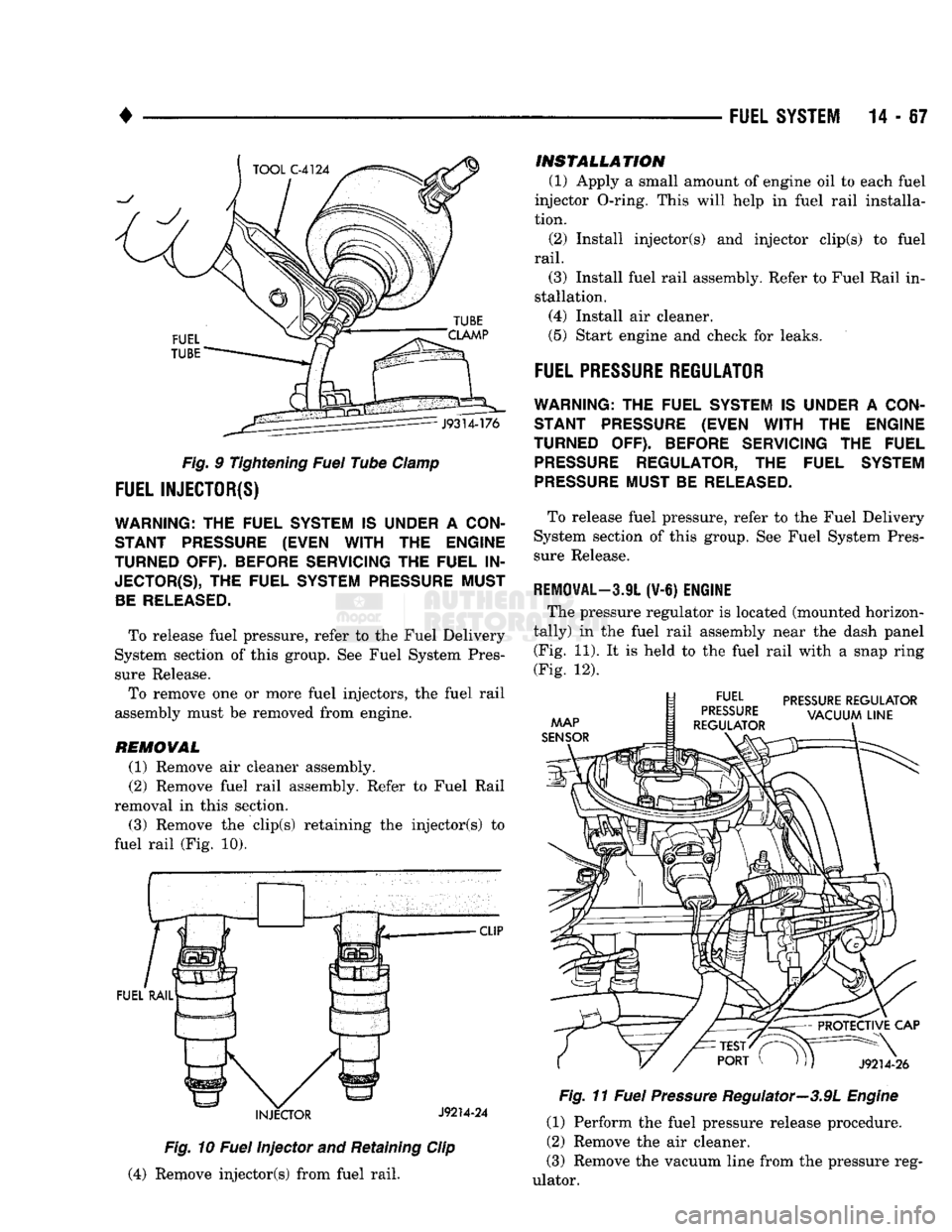
Fig. 9 Tightening Fuel Tube Clamp
FUEL INJECTOR(S)
WARNING;
THE
FUEL
SYSTEM IS
UNDER
A
CON
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN
WITH THE
ENGINE
TURNED
OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING
THE
FUEL
IN
JECTOR^),
THE
FUEL
SYSTEM
PRESSURE MUST
BE
RELEASED.
To release fuel pressure, refer to the Fuel Delivery
System section of this group. See Fuel System Pres sure Release.
To remove one or more fuel injectors, the fuel rail
assembly must be removed from engine.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air cleaner assembly. (2) Remove fuel rail assembly. Refer to Fuel Rail
removal in this section.
(3) Remove the clip(s) retaining the injector(s) to
fuel rail (Fig. 10).
CUP
Fig. 10 Fuel Injector and Retaining Clip
(4) Remove injector(s) from fuel rail.
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a small amount of engine oil to each fuel
injector O-ring. This will help in fuel rail installa
tion.
(2) Install injector(s) and injector clip(s) to fuel
rail.
(3) Install fuel rail assembly. Refer to Fuel Rail in
stallation.
(4) Install air cleaner.
(5) Start engine and check for leaks.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
WARNING:
THE
FUEL SYSTEM
IS
UNDER
A
CON STANT PRESSURE (EVEN
WITH
THE
ENGINE
TURNED
OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING
THE
FUEL
PRESSURE
REGULATOR,
THE
FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE
MUST
BE
RELEASED.
To release fuel pressure, refer to the Fuel Delivery
System section of this group. See Fuel System Pres
sure Release.
REMOVAL—3JL
(V-6)
ENGINE
The pressure regulator is located (mounted horizon
tally) in the fuel rail assembly near the dash panel (Fig. 11). It is held to the fuel rail with a snap ring
(Fig. 12). Fig. 11 Fuel Pressure Regulator—3.9L Engine
(1) Perform the fuel pressure release procedure.
(2) Remove the air cleaner.
(3)
Remove the vacuum line from the pressure reg
ulator.
Page 887 of 1502
14
- 68
FUEL
SYSTEM
•
SNAP
RING
SNAP
RING
PLIERS
VACUUM
LINE
PROTECTIVE CAP
FUEL
PRESSURE
REGULATOR,
FUEL RAIL
J9214-47
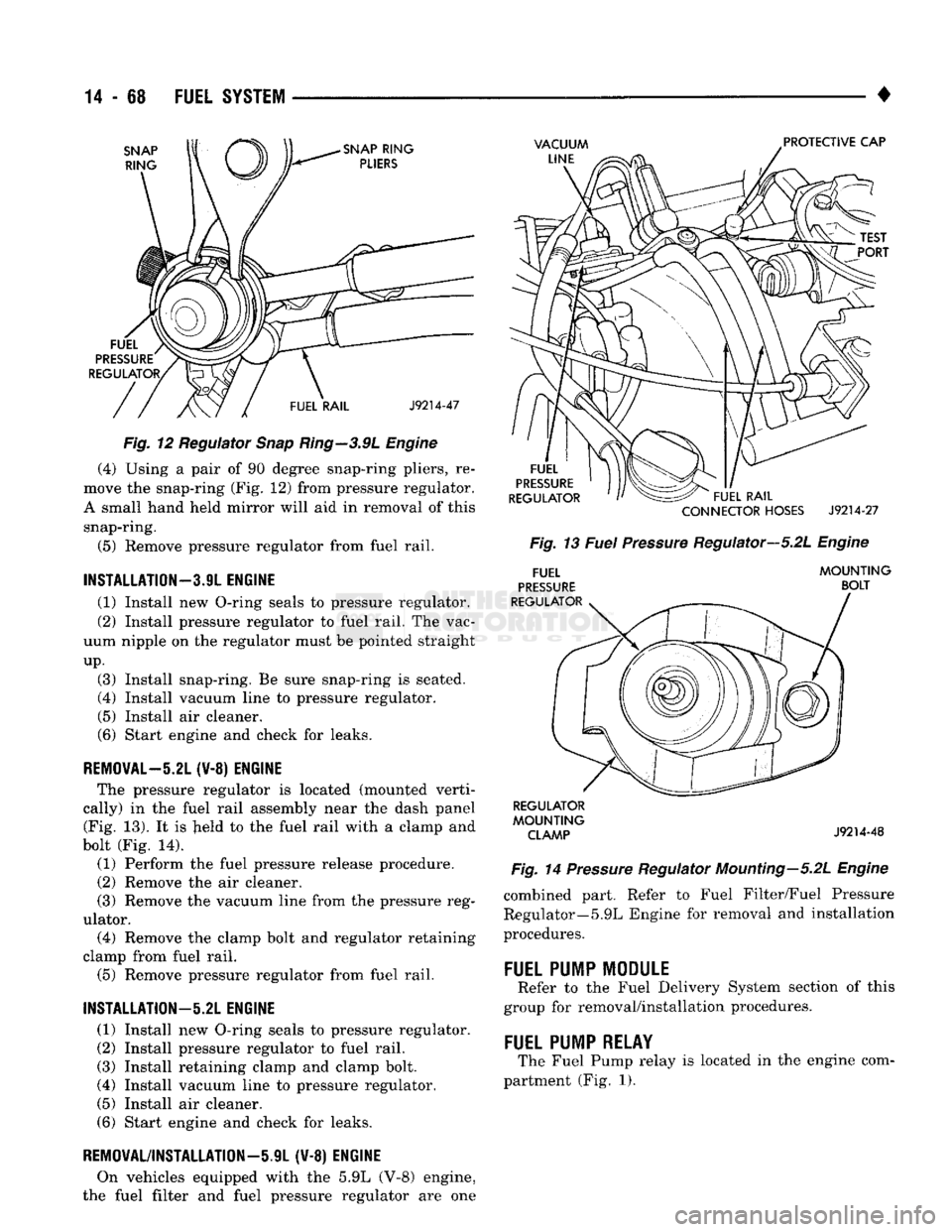
Fig. 12 Regulator Snap Ring—3.9L Engine (4) Using a pair of 90 degree snap-ring pliers, re
move the snap-ring (Fig. 12) from pressure regulator.
A small hand held mirror will aid in removal of this snap-ring.
(5) Remove pressure regulator from fuel rail.
INSTALLATION—3.9L
ENGINE
(1) Install new O-ring seals to pressure regulator.
(2) Install pressure regulator to fuel rail. The vac
uum nipple on the regulator must be pointed straight
up.
(3) Install snap-ring. Be sure snap-ring is seated.
(4) Install vacuum line to pressure regulator.
(5) Install air cleaner.
(6) Start engine and check for leaks.
REMOVAL-5.21
(¥-8) ENGINE The pressure regulator is located (mounted verti
cally) in the fuel rail assembly near the dash panel (Fig. 13). It is Jield to the fuel rail with a clamp and
bolt (Fig. 14).
(1) Perform the fuel pressure release procedure.
(2) Remove the air cleaner.
(3) Remove the vacuum line from the pressure reg
ulator. (4) Remove the clamp bolt and regulator retaining
clamp from fuel rail.
(5) Remove pressure regulator from fuel rail.
INSTALLATION—5.2L
ENGINE
(1) Install new O-ring seals to pressure regulator.
(2) Install pressure regulator to fuel rail. (3) Install retaining clamp and clamp bolt.
(4) Install vacuum line to pressure regulator.
(5) Install air cleaner.
(6) Start engine and check for leaks.
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION—iJL (V-8) ENGINE
On vehicles equipped with the 5.9L (V-8) engine,
the fuel filter and fuel pressure regulator are one
FUEL
PRESSURE
REGULATOR FUEL RAIL
CONNECTOR
HOSES
J9214-27
Fig. 13 Fuel Pressure Regulator—5.2L Engine
FUEL
PRESSURE
REGULATOR MOUNTING
BOLT REGULATOR
MOUNTING CLAMP
J9214-48
Fig. 14 Pressure Regulator Mounting—5.2L Engine combined part. Refer to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure
Regulator—5.9L Engine for removal and installation
procedures.
FUEL
PUMP
MODULE
Refer to the Fuel Delivery System section of this
group for removal/installation procedures.
FUEL
PUMP
RELAY
The Fuel Pump relay is located in the engine com
partment (Fig. 1).
Page 889 of 1502
14
- 70
FUEL
SYSTEM
•
CANISTER PURGE
SOLENOID/BRACKET VACUUM
CONNECTOR
J9214-50
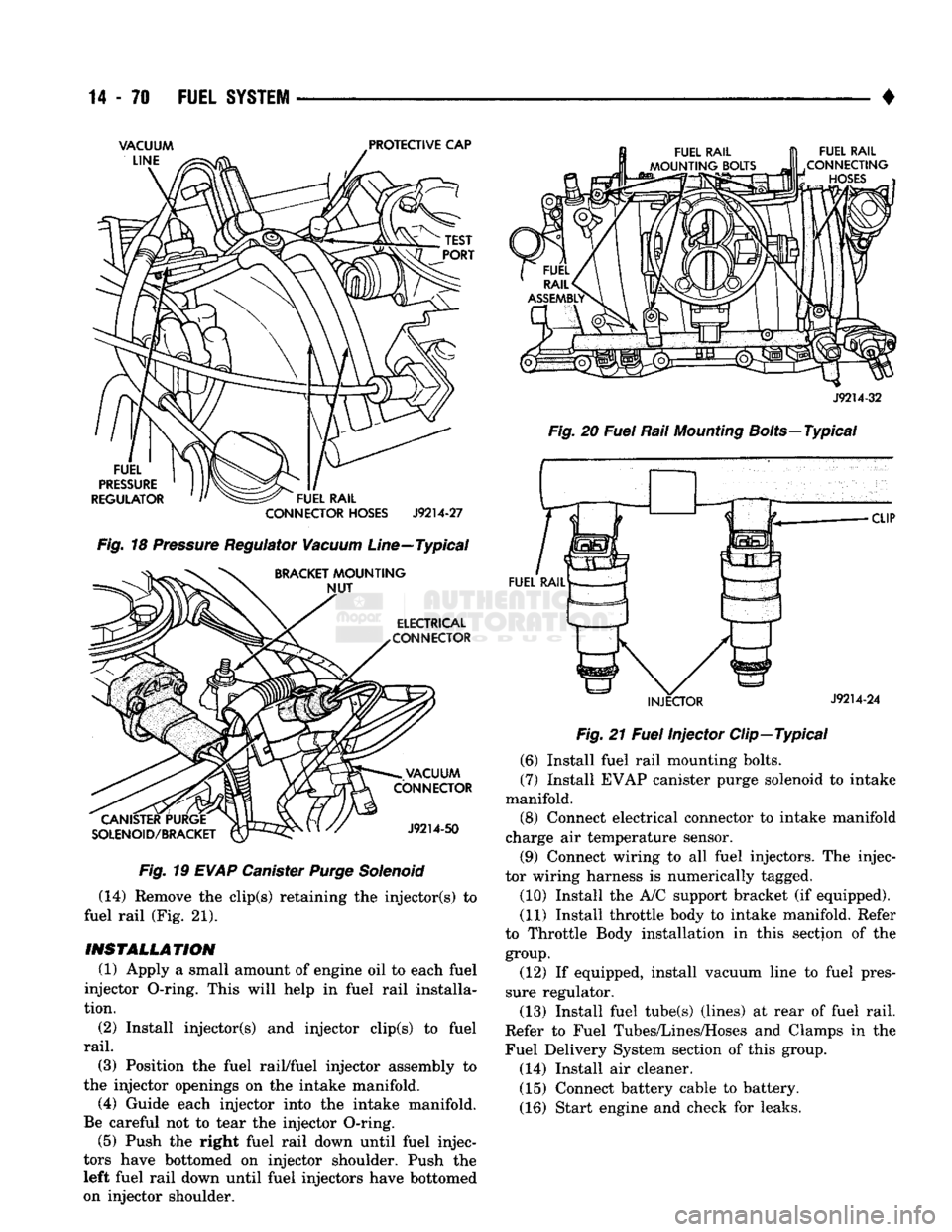
Fig.
19
EVAP
Canister
Purge
Solenoid
(14) Remove the clip(s) retaining the injector(s) to
fuel rail (Fig. 21).
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a small amount of engine oil to each fuel
injector O-ring. This will help in fuel rail installa
tion.
(2) Install injector(s) and injector clip(s) to fuel
rail.
(3) Position the fuel rail/fuel injector assembly to
the injector openings on the intake manifold.
(4) Guide each injector into the intake manifold.
Be careful not to tear the injector O-ring. (5) Push the right fuel rail down until fuel injec
tors have bottomed on injector shoulder. Push the
left fuel rail down until fuel injectors have bottomed
on injector shoulder.
INJECTOR
J9214-24
Fig.
21
Fuel
Injector Clip—Typical
(6) Install fuel rail mounting bolts.
(7) Install EVAP canister purge solenoid to intake
manifold. (8) Connect electrical connector to intake manifold
charge air temperature sensor.
(9) Connect wiring to all fuel injectors. The injec
tor wiring harness is numerically tagged.
(10) Install the A/C support bracket (if equipped).
(11) Install throttle body to intake manifold. Refer
to Throttle Body installation in this section of the
group.
(12) If equipped, install vacuum line to fuel pres
sure regulator.
(13) Install fuel tube(s) (lines) at rear of fuel rail.
Refer to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps in the
Fuel Delivery System section of this group.
(14) Install air cleaner. (15) Connect battery cable to battery.
(16) Start engine and check for leaks.
Page 892 of 1502
•
FUEL SYSTEM
14-73 (1) Install the 02 sensor into the exhaust manifold.
Tighten to 30 N*m (22 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect the 02 sensor wire connector.
(3) Lower the vehicle.
PARK/NEUTRAL
SWITCH
Refer to Group 21, Transmission and Transfer Case
for removal/installation procedures.
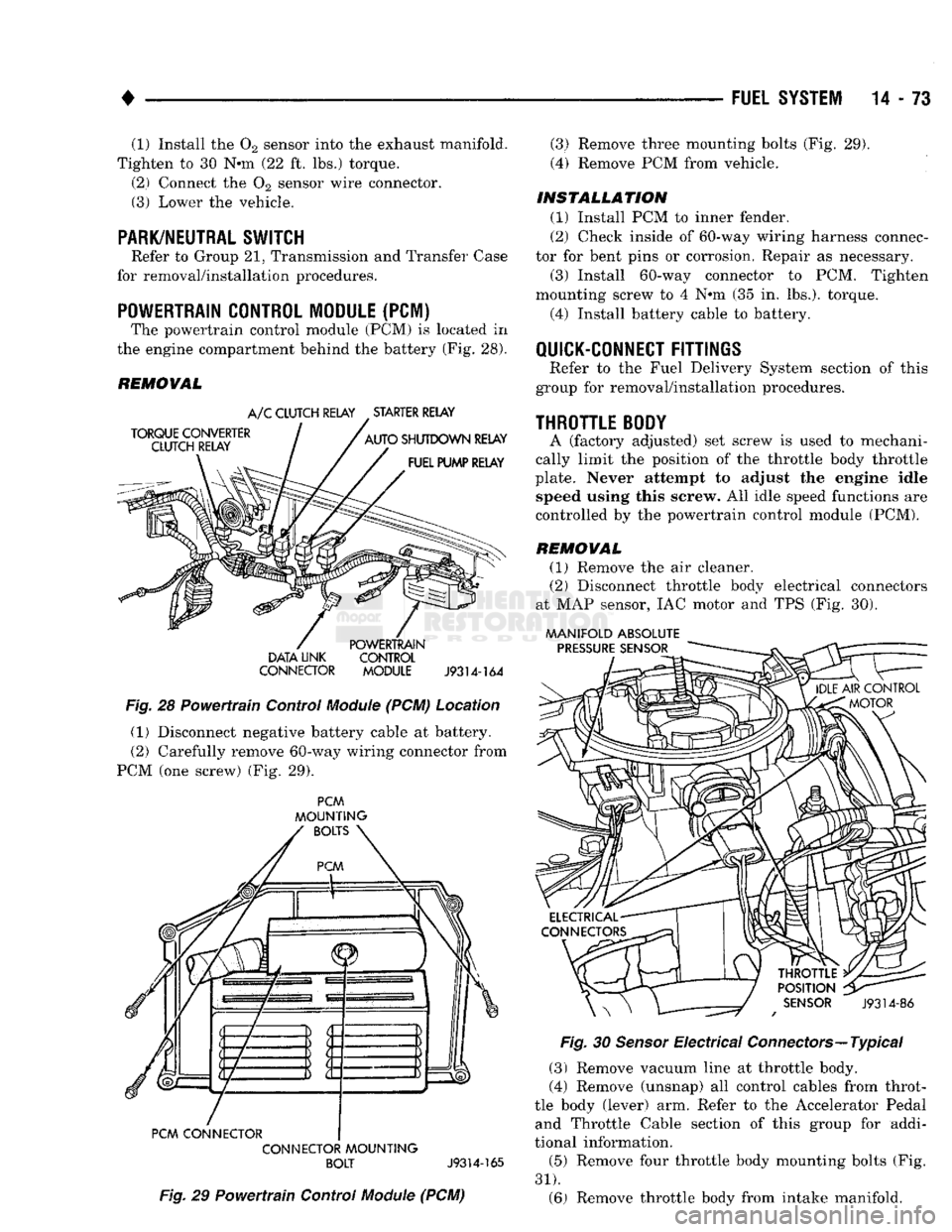
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
(PCM) The powertrain control module (PCM) is located in
the engine compartment behind the battery (Fig. 28).
REMOVAL
DATA LINK CONTROL
CONNECTOR MODULE
J9314-164
Fig.
28 Powertrain Control
Module
(PCM) Location (1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Carefully remove 60-way wiring connector from
PCM (one screw) (Fig. 29).
PCM
MOUNTING
PCM CONNECTOR CONNECTOR
MOUNTING
BOLT
J9314-165
Fig.
29 Powertrain Control
Module
(PCM) (3) Remove three mounting bolts (Fig. 29).
(4) Remove PCM from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install PCM to inner fender.
(2) Check inside of 60-way wiring harness connec
tor for bent pins or corrosion. Repair as necessary.
(3) Install 60-way connector to PCM. Tighten
mounting screw to 4 Nem (35 in. lbs.), torque.
(4) Install battery cable to battery.
QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS
Refer to the Fuel Delivery System section of this
group for removal/installation procedures.
THROTTLE
BODY
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate. Never attempt to adjust the engine idle speed using this screw. All idle speed functions are
controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM).
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the air cleaner.
(2) Disconnect throttle body electrical connectors
at MAP sensor, IAC motor and TPS (Fig. 30).
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
Fig.
30
Sensor
Electrical Connectors—Typical
(3) Remove vacuum line at throttle body.
(4) Remove (unsnap) all control cables from throt
tle body (lever) arm. Refer to the Accelerator Pedal and Throttle Cable section of this group for addi
tional information.
(5) Remove four throttle body mounting bolts (Fig.
31).
(6) Remove throttle body from intake manifold.
Page 901 of 1502

14 - 82
FUEL 'SYSTEM
—. — ~—— — «
INTAKE HEATER CYCLE CHART
Intake
featperafwre
Preheat
Cycle
Time
Ignition
l£ey ON
Engine
Not
Running
Pestheat
Cycle
Ignition
Key ON
Snglne Running
Above
15
°C
(59
°F)
0 Seconds
No
-8°C(18°F)to
15°C (59
°F)
10
Seconds
Yes
-17°C(1
°F)
-9
°C(]6°F)
15
Seconds
Yes
«2d°C(-15°F)
to-18°C(0
°F) 17.5
Seconds
Yes
Below-26
°C (-15
*F)
20 Seconds
Yes
J9114-239
AUTO SHUT DOWN (ASD) RELAY-PCM OUTPUT
The ASD relay is located in the engine compart
ment (Fig. 14).
TORQUE CONVERTER
CLUTCH RELAY A/C CLUTCH RELAY STARTER RELAY
AUTO SHUTDOWN RELAY FUEL PUMP RELAY DATA LINK
CONNECTOR
POWERTRAIN
CONTROL MODULE
J9314-164
Fig.
14 Relay Location—Typical The ASD relay supplies battery voltage to the gen
erator field winding to provide regulation of the
charging system. The ground circuit for the ASD re
lay is controlled by the PCM. The PCM operates the
relay by switching the ground circuit on and off.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP-PCM OUTPUT
The malfunction indicator lamp (formerly referred
to as the check engine lamp) illuminates at the bot
tom of the instrument panel each time the ignition
key is turned on. It will stay on for three seconds as
a bulb test. If the powertrain control module (PCM) receives an
incorrect signal, or no signal from certain sensors or emission related systems, the lamp is turned on. This
is a warning that the PCM has recorded a system or
sensor malfunction. In some cases, when a problem is
declared, the PCM will go into a limp-in mode. This is an attempt to keep the system operating. It signals
an immediate need for service.
The lamp can also be used to display a diagnostic
trouble code (DTC). Cycle the ignition switch
On-Off-
On-Off-On within three seconds and any codes stored
in the PCM memory will be displayed. This is done
in a series of flashes representing digits. Refer to On-
Board Diagnostics in the General Diagnosis section
of this group for more information.
OVERDRIVE
INDICATOR LAMP-PCM OUTPUT
Indicates the state of the overdrive defeat switch
on the instrument panel.
OVERDRIVE
S0LEN0ID-PCM OUTPUT
The overdrive solenoid is used on vehicles that
have an automatic transmission. The solenoid is op erated by the PCM. It controls shifting in and out of
overdrive through the overdrive solenoid. Refer to Group 21 for overdrive solenoid service.
SCI
TRANSMIT—PCM OUTPUT
SCI Transmit is the serial data communication
transmit circuit for the DRB II scan tool. The PCM
transmits data to the DRB II through the SCI Trans
mit circuit.
SPEED
C0NTR0L-PCM OUTPUT
The speed control vacuum and vent solenoids are
operated by the PCM. The vacuum solenoid main
tains vacuum at a required pressure to resume, set or accelerate the speed control system. The vent so
lenoid allows vacuum to bleed off during decelera
tion, when the brakes are applied, or the
transmission is shifted into park or neutral.
TACHOMETER-PCM
OUTPUT
This output generates the necessary signal needed
to operate a dealer installed tachometer (if equipped).
The input for this signal is from the engine speed sensor.
WAIT-TO-START LAMP-PCM OUTPUT
The wait-to-start lamp is turned on and off by the
PCM based on the charge air temperature sensor in
put. The light is turned on when the ignition is first ac
tivated. It will remain on for two seconds as a bulb
test. If the PCM reads intake manifold air tempera
ture below 15°C (59°F), it will turn the wait-to-start light on for the intake heater preheat cycle. The
light stays on until the preheat cycle is over. The wait-to-start light will flash on and off if the
charge air temperature sensor input to the PCM is
Page 905 of 1502

14-86
FUEL
SYSTEM
WARNING:
USE
EXTREME CAUTION WHEN
IN
SPECTING
FOR
HIGH
PRESSURE
FUEL
LEAKS.
IN
SPECT
FOR
HIGH
PRESSURE
FUEL
LEAKS
WITH
A
SHEET
OF
CARDBOARD. HIGH FUEL INJECTION
PRESSURE
CAN
CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY
IF
CONTACT
IS
MADE
WITH
THE
SKIN.
MECHANICAL
LIFT
PUMP
The mechanical lift pump
is
located
on the
left side
of
the engine cylinder block.
The
lift pump
is
driven
by an
eccentric
on the
camshaft that actuates
a
spring loaded lever
in the
pump
(Fig. 25). The
lever
is
connected
to
the pump diaphragm. When
the
eccentric
on the
cam shaft pushes
the
lever upward,
the
lever
in
turn pulls
the diaphragm
to its
extended position. With
the
lever in
the
extended position, fuel
is
drawn into
the
pump
chamber through
the
inlet check valve. When
the
pump
gathers more fuel
in the
fuel chamber than
the
engine
can consume,
the
outlet check valve
is
held closed. Fuel
gathered
in
lift pump chamber prevents
the
diaphragm
from relaxing.
The
lever will continue
to
move
up and
down
on the
shaft connecting
it to the
diaphragm. How ever,
it is
prevented from operating
the
diaphragm until
the check valve again opens
and the
fuel
in the
pump chamber
is
expelled. This process continues
as
long
as
the engine
is
running. Minimum lift pump output pressure
is 21 Kpa (3
psi).
Lift pump output volume
is 0.75
liters
(0.70 U.S.
quarts)
per 30
seconds
of
engine cranking.
Fig.
25 Lift
Pump
The lift pump housing
has a
weep hole
at the
bot
tom
of the
casing
(Fig. 25). If the
diaphragm rup
tures,
fuel will exit
out of the
weep hole
and the
pump must
be
replaced.
The
lift pump
is not
service able
and
must
be
replaced
as a
complete assembly.
CAUTION:
Do not
operate
the
engine
if the
fuel
sup
ply
line
has a
restriction
of
more than
95 MM Hg
(3.75
in Hg).
The lift pump
has a
manual lever
(Fig. 26). The le
ver
is
located
on the
lower right side
of the
pump
housing.
The
purpose
of the
lever
is to
prime
the
fuel system
and
bleed
air
from
the
system
if the
vehicle
has
run out of
fuel. Raise
and
lower
the
lever until
resistance
is
felt
to
prime
the
system
up to the
injec
tor pump. During vehicle operation
the
pump
le
ver must
be in the up
position.
FUEL
PUMP
MANUAL
JKT /
LEVER
——-—•
.
LJ*y^"^^
J9114-3
Fig.
26 Lift
Pump
Manual
Lever
SYSTEM
OPERATION
IGNITION
SWITCH
ON
When
the
ignition switch
is put in the ON (run)
position,
the
following occurs: •
The PCM
receives
an
ignition sense input.
It
then
powers
up.
Battery voltage
is
supplied through
the
battery voltage input. •
The
wait-to-start lamp
and the
water-in-fuel lamp are turned
on by the PCM for 2.8
seconds
as a
bulb test.
•
The PCM
monitors
the
charge
air
temperature
sensor input.
If
manifold
air
temperature
is at or be
low
15°C
(59°F),
the PCM
will start
the air
intake
heater preheat cycle.
It
will energize
the
intake heat
ers
by
grounding
the air
intake heater relays.
The
PCM will turn
the
wait-to-start light
on
until
the
preheat cycle
is
over.
If PCM
receives
a
crank signal
from engine speed sensor before preheat cycle
is
over, it will abort preheat cycle.
•
The PCM
monitors engine speed. When
the
engine speed
is
above
384 rpm, the PCM
determines that
the engine
is
running.
•
The PCM
will turn
on the
water-in-fuel lamp
if a
signal
is
received from
the
water-in-fuel sensor.
ENGINE
START-UP
When
the
ignition
key is put in the
start position,
the following occurs: •
The PCM
receives
a
crank signal input from
the
engine speed sensor.
•
The air
intake heaters
are not
energized during cranking.
Page 907 of 1502
DIESEL FUEL INJECTION—GENERAL DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page
Air
in
Fuel System
90
Air Intake Heater
. 90
Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC)
. 95
DRB
II
Scan
Tool
95
Engine
Speed
Sensor
91
Fuel Heater
91
Fuel
Injection
Pump
91
Fuel Injectors
92
Fuel Supply Restrictions
92
page
Fuel/Water Separator
Filter 92
High
Pressure Fuel Line Restrictions
93
KSB
Solenoid
. 93
Mechanical
Lift
Pump
93
On-Board
Diagnostics (OBD)
94
System
Schematics—5.9L Diesel Engine
....... 95
Throttle
Position
Sensor
Test
94
Visual
Inspection
88
VISUAL
INSPECTION
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected, or incor
rectly routed wires and hoses should be made before attempting to diagnose or service the fuel injection
system. A visual check will help find these condi
tions.
It also saves unnecessary test and diagnostic
time.
A thorough visual inspection of the fuel injec
tion system includes the following checks: (1) Be sure that the battery connections are tight
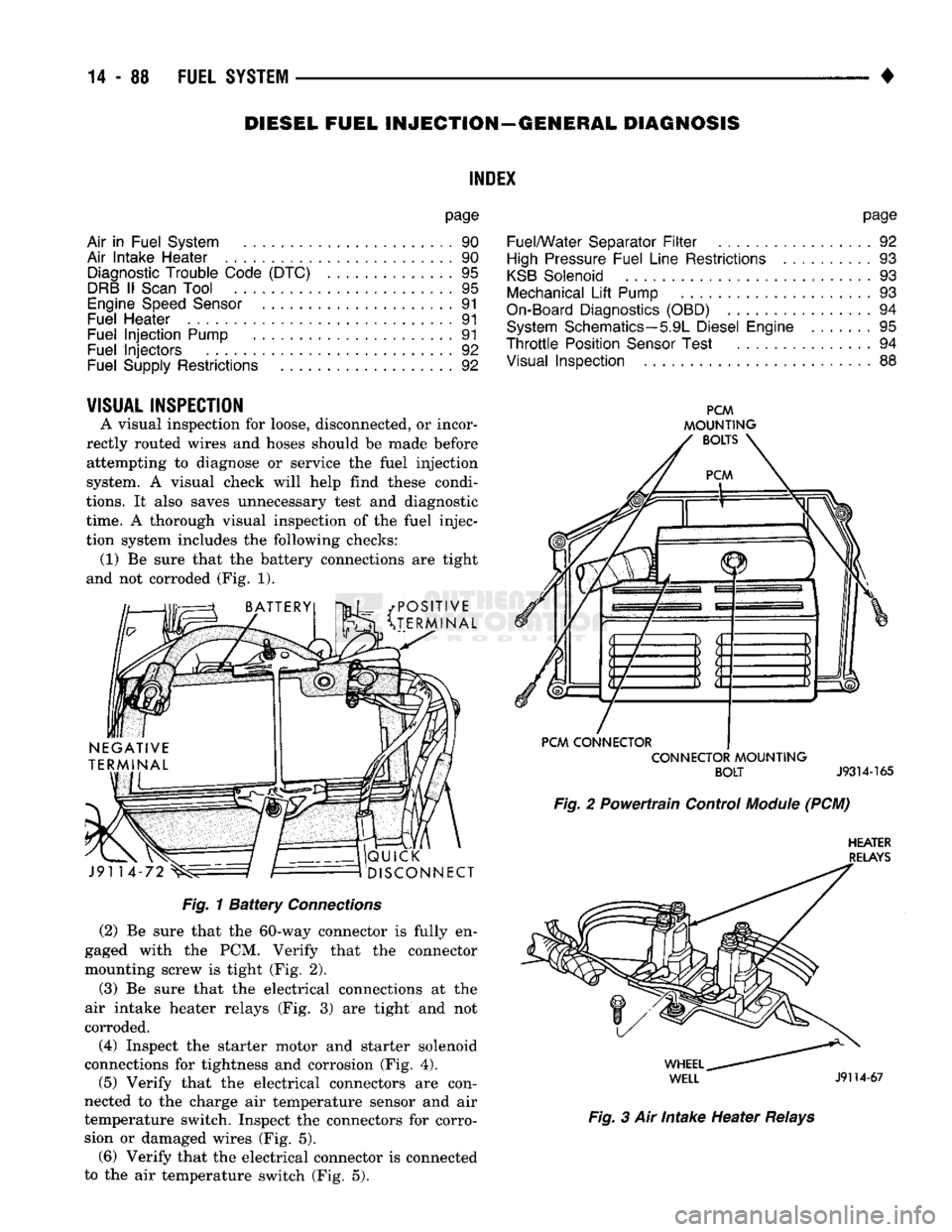
and not corroded (Fig. 1).
• POSITIVE
v^3t
^TERMINAL J91 14
QUICK
DISCONNECT
PCM
MOUNTING
BOLTS
PCM
CONNECTOR CONNECTOR
MOUNTING
BOLT
J9314-165
Fig.
2 Powertrain Control
Module
(PCM)
HEATER
RELAYS
Fig.
1
Battery
Connections
(2)
Be sure that the 60-way connector is fully en
gaged with the PCM. Verify that the connector
mounting screw is tight (Fig. 2).
(3)
Be sure that the electrical connections at the
air intake heater relays (Fig. 3) are tight and not
corroded.
(4)
Inspect the starter motor and starter solenoid
connections for tightness and corrosion (Fig. 4).
(5)
Verify that the electrical connectors are con
nected to the charge air temperature sensor and air
temperature switch. Inspect the connectors for corro sion or damaged wires (Fig. 5). (6) Verify that the electrical connector is connected
to the air temperature switch (Fig. 5).
WHEEL
^
WELL
J9114-67
Fig.
3 Air Intake Heater
Relays
Page 910 of 1502
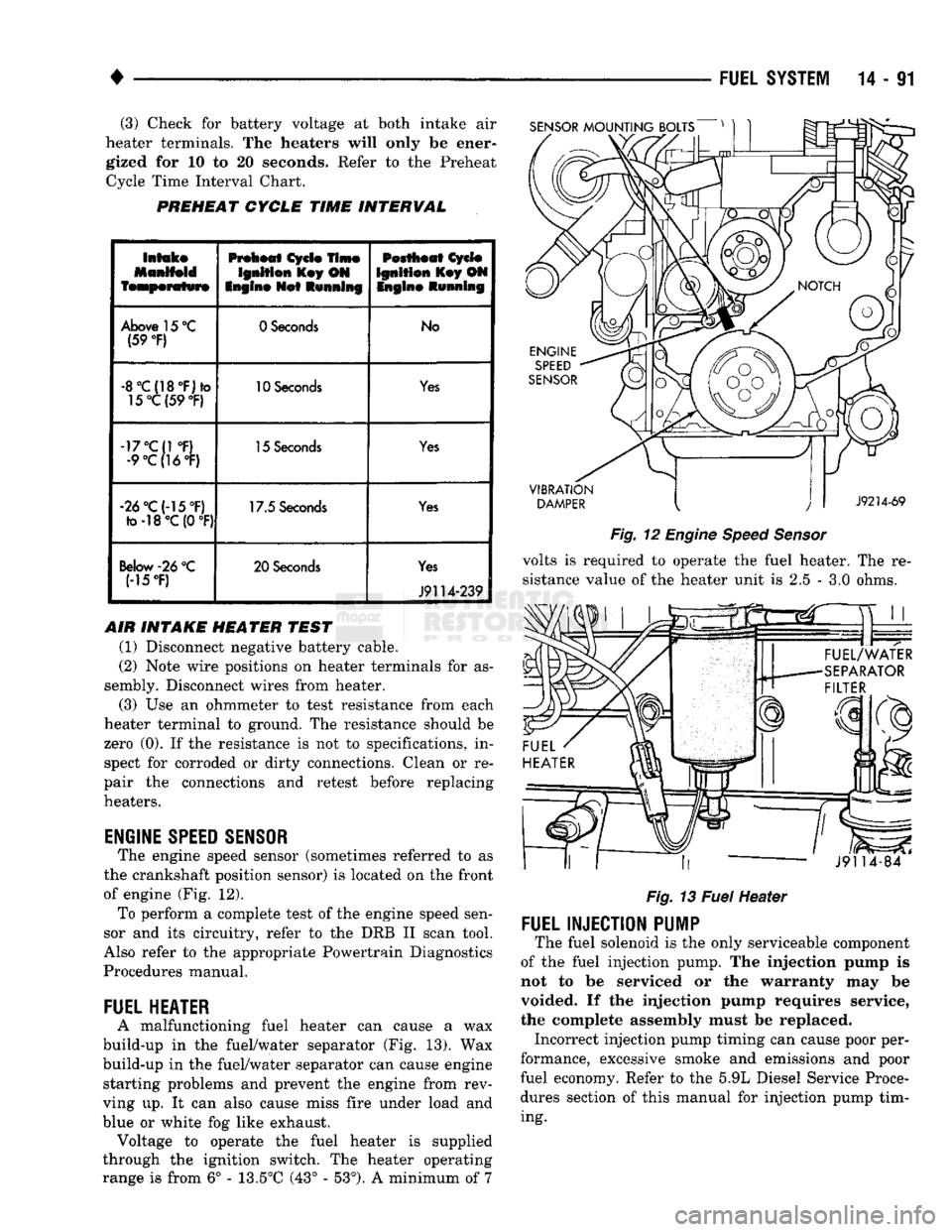
(3) Check for battery voltage at both intake air
heater terminals. The heaters will only be ener gized for 10 to 20 seconds. Refer to the Preheat Cycle Time Interval Chart.
PREHEAT
CYCLE
TIME
INTERVAL
SENSOR
MOUNTING
BOLTS
Intake
Manifold
temperature
Preheat
Cycle
Time
Ignition
Key ON
Engine
Net
Running
Pestheat
Cycle
Ignition
Key ON Ingin©
Running
Above 15 °C (59
°F)
0 Seconds
No
-8°C{18°F)*o 15°C(59
°F)
10 Seconds
Yes
-17°C{1 °F) •9°C(16°F) 15 Seconds
Yes
-26°C(-15°F) fo-18°C (0
°F)
17.5 Seconds
Yes
Below
-26
°C
(15T) 20 Seconds
Yes
J9114-239
AIR INTAKE HEATER TEST (1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Note wire positions on heater terminals for as
sembly. Disconnect wires from heater.
(3) Use an ohmmeter to test resistance from each
heater terminal to ground. The resistance should be
zero (0). If the resistance is not to specifications, in spect for corroded or dirty connections. Clean or re
pair the connections and retest before replacing
heaters.
ENGINE
SPEED
SENSOR
The engine speed sensor (sometimes referred to as
the crankshaft position sensor) is located on the front
of engine (Fig. 12). To perform a complete test of the engine speed sen
sor and its circuitry, refer to the DRB II scan tool.
Also refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics
Procedures manual.
FUEL
HEATER
A malfunctioning fuel heater can cause a wax
build-up in the fuel/water separator (Fig. 13). Wax
build-up in the fuel/water separator can cause engine starting problems and prevent the engine from rev
ving up. It can also cause miss fire under load and
blue or white fog like exhaust. Voltage to operate the fuel heater is supplied
through the ignition switch. The heater operating
range is from 6° - 13.5°C (43° - 53°). A minimum of 7
VIBRATION
DAMPER
J9214-69
Fig.
12
Engine
Speed
Sensor
volts is required to operate the fuel heater. The re
sistance value of the heater unit is 2.5 - 3.0 ohms.
««.
* rr ,,
J9114-84
Fig.
13
Fuel
Heater
FUEL
INJECTION
PUMP
The fuel solenoid is the only serviceable component
of the fuel injection pump. The injection pump is
not to be serviced or the warranty may be
voided. If the injection pump requires service,
the complete assembly must be replaced. Incorrect injection pump timing can cause poor per
formance, excessive smoke and emissions and poor
fuel economy. Refer to the 5.9L Diesel Service Proce
dures section of this manual for injection pump tim
ing.