1990 MITSUBISHI SPYDER fuel pump
[x] Cancel search: fuel pumpPage 503 of 2103

ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> On-vehicle
FUEL PUMP
(HOW TO REDUCE FUEL LINE PRESSURE)
When removing the fuel pipe, hose., etc., since fuel
in the fuel pipe line is high, do the following operation so
as to release fuel pressure in the line and
running out.
.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5 . Remove the rear seat cushion. (Refer to
Seat.)
Remove the protector to’
the fuel pump
connector.
Start the engine and let it run until it turn
the ignition switch to OFF.
Connect the fuel pump connector to install the prot ector.
Install the rear seat cushion..
Revision
Page 504 of 2103
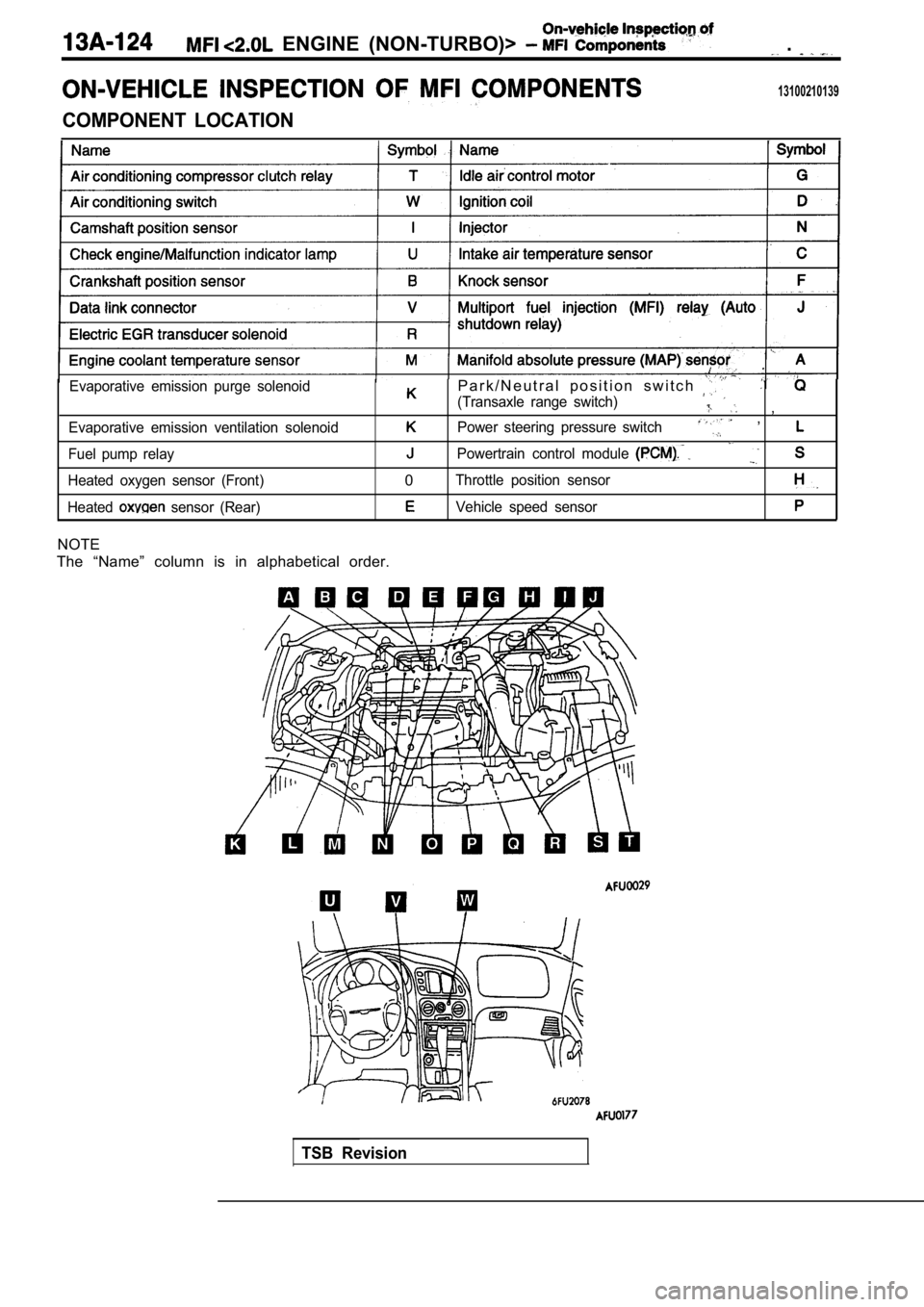
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> .
13100210139
COMPONENT LOCATION
Evaporative emission purge solenoid
Evaporative emission ventilation solenoid
Fuel pump relay
Heated oxygen sensor (Front)
Heated
sensor (Rear)
P a r k / N e u t r a l p o s i t i o n s w i t c h
(Transaxle range switch) ,
Power steering pressure switch ,
Powertrain control module
0Throttle position sensor
Vehicle speed sensor
NOTE
The “Name” column is in alphabetical order.
TSB Revision
Page 508 of 2103
28 of
( N O N - T U R B O ) >
Bottom view
of relay
I
Intake air temperature
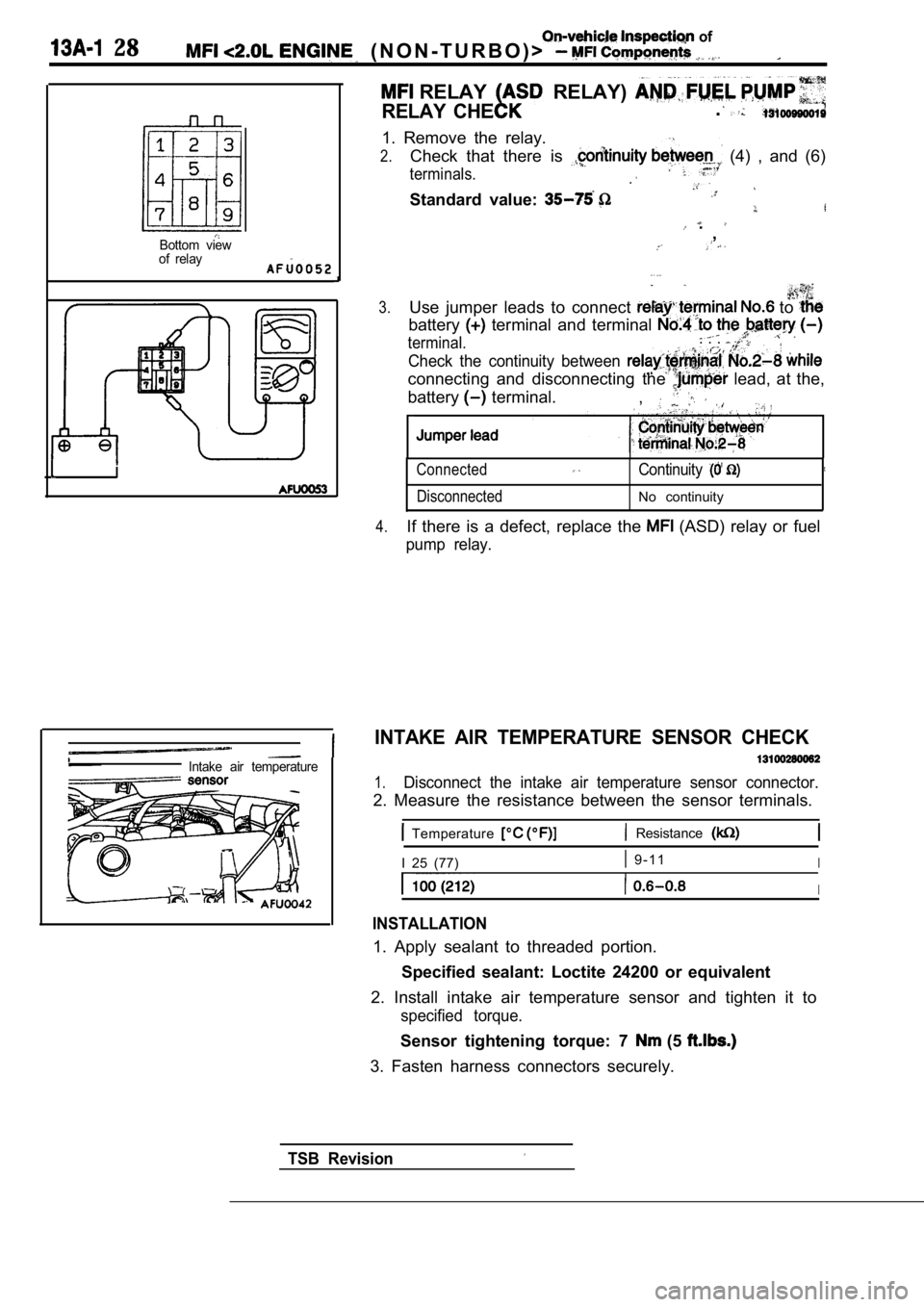
RELAY RELAY)
RELAY CHE.
1. Remove the relay.
2.Check that there is (4) , and (6)
terminals..
Standard value:
.,
3.Use jumper leads to connect to
battery terminal and terminal
terminal.. . .
Check the continuity between
connecting and disconnecting the lead, at the,
battery
terminal. ,
Connected
DisconnectedContinuity
No continuity
4.If there is a defect, replace the (ASD) relay or fuel
pump relay.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR CHECK
1.Disconnect the intake air temperature sensor connec tor.
2. Measure the resistance between the sensor terminals.
Temperature Resistance
I 25 (77) 9 - 1 1I
I
INSTALLATION
1. Apply sealant to threaded portion.
Specified sealant: Loctite 24200 or equivalent
2. Install intake air temperature sensor and tighte n it to
specified torque.
Sensor tightening torque: 7 (5
3. Fasten harness connectors securely.
TSB Revision
Page 518 of 2103

ENGINE
AND ENGINE> G e n e r a l
ENGINE (TURBO) AND ENGINE>13199910319
GENERAL INFORMATIONThe
Fuel Injection System consists
of sensors which detect the engine conditions,
the ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) which
controls the system based on signals from these
sensors, and actuators which operate under
the control of the ECM.
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
The injector drive times and injector timing are
controlled so that the optimum air/fuel mixture
is supplied to the engine to correspond to the
continually-changing engine operation condi-
tions.
A single injector is mounted at the intake port
of each cylinder. Fuel is sent under pressure
from the fuel tank by the fuel pump, with the
pressure regulated by the fuel pressure regula-
tor. The regulated fuel is distributed to each
of the injectors.
Fuel injection is normally carried out once for
each cylinder for every two rotations of the
IDLE AIR CONTROL The idle speed is kept at the optimum speed
by controlling the amount of air that bypasses
the throttle valve in accordance with changes
in idling conditions and engine load during id-
ling.
The ECM drives the idle air control (IAC) motor
to keep the engine running at the pre-set idle
target speed in accordance with the engine
IGNITION TIMING CONTROL
The ignition power transistor located in the igni-
tion primary circuit turns ON and OFF to control
the primary current flow to the ignition coil.
This controls the ignition timing in order to pro-
vide the optimum ignition timing with respect The ECM carries out activities such as fuel
injection control, idle air control and ignition
timing control.
In addition, the ECM is equipped with several
diagnostic test modes which simplify trouble-
shooting when a problem develops.
. .
crankshaft. The firing is This
is called
The provides a richer
air/fuel mixture by carrying out “open-loop” con-
trol when the engine is cold or operating under high load
in order to maintain engine
performance. In addition, when the engine is warm or operat-
ing under normal conditions, the ECM controls
the air/fuel mixture by using the heated oxygen
sensor signal to carry out “closed-loop” control
in order to obtain the theoretical air/fuel mixture
ratio that provides the maximum cleaning per-
formance from the three way catalyst.
coolant temperature and air conditioning load.
In addition, when the air’ conditioning switch
is turned off and on while the
is
the motor operates to adjust the throttle
valve bypass air amount in accordance with
the engine load conditions in order to avoid
fluctuations in the engine speed.
to the engine operating conditions. The ignition
timing is determined by the ECM from the en-
gine speed, intake air volume, engine coolant
temperature and atmospheric pressure.
TSB Revision
Page 519 of 2103

ENGINE (TURBO)
ENGINE>
DIAGNOSTIC TEST MODEl When an abnormality is detected in one
of the sensors or actuators related to emis-
sion control, the CHECK
FUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP illuminates
as a warning to the driver.
l When an abnormality is detected in one
of the’ sensors or actuators, a
OTHER CONTROL FUNCTIONS
1. Fuel Pump Control
Turns the fuel pump relay ON current
is supplied to the fuel pump while the engine
is cranking or running.
2. A/C Compressor Clutch Relay Control Turns the A/C compressor clutch ON and
OFF.
3. Fan Relay Control
The radiator fan and condenser fan speeds
are controlled in response to the engine
coolant temperature and vehicle speed.
4. Fuel
Control
Supplies current to fuel pressure solenoid
coil to raise the fuel pressure so that the
fuel does not vaporize when the engine
is started while it is warm.
trouble code ‘the,,
normality is output.
lThe RAM data inside the that
to the sensors and actuators can be read’
by
scan’ tool.
addition, the actuators can be controlled
under certain
5. Charge Control
Controls the intake charge pressure by con-
trolling the duty of the turbocharger
gate solenoid!
6. Intake Pressure Gauge’ Control Indicates the intake charge pressure on
the
7. Generator Output Current Control
Prevents generator output current from in-
creasing idle speed from
dropping at times such as when the head-
lights are turned on.
8.Evaporative Emission Purge Solenoid Con-
trol Engine (TURBO)>
Refer to
17.
Evaporative Emission Purge Solenoid Con-
trol GROUP 17.
9. EGR Solenoid’ Control
Refer to GROUP
,,
,
TSB Revision
Page 520 of 2103

E N G I N E ( T U R B O )
AND
Engine (Turbo)>
Item
Throttle bodyThrottle bore mm (in.)5 4
Engine control
module (ECM)
Sensors
pressure
egulator
Volume air flow sensor
Barometric pressure sensorK a r m a n v o r t e x t y p e , ,
Intake air temperature sensor Thermistor type
Engine coolant temperature sensor
T h e r m i s t o r t y p e
Heated oxygen sensor Zircon type
Vehicle speed sensor Electromagnetic resistance elem ent ‘type
Park/neutral position switchContact switch type .
Camshaft position sensor
Crankshaft position sensorHall element type
Throttle position sensor
Idle air control motor Variable resistor type
Stepper motor type [Stepper. type ‘by-pass’ air
control system
the air
Closed throttle position switch
model No.
Rotary contact type,
,
Knock sensor Piezoelectric type
Power steering pressure switch
Contact switch type
Manifold differential pressure sensor Semiconductor type
fuel injection (MFI) relay
Contact switch type
Fuel pump relay
Injector type and number
Injector identification mark Contact switch type
Electromagnetic type, 4
solenoid Duty cycle type solenoid valve
Evaporative emission purge solenoid
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
Fuel pressure solenoid
Turbocharger waste gate solenoid ON/OFF type solenoid valve
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
Regulator
(psi) 294 (43)
TSB Revision
Page 521 of 2103

ENGINE (TURBO)
AND
ENGINE> General
Engine>
ItemSpecifications
Throttle body Throttle bore mm (in.)54 (2.13)
Throttle position sensorV a r i a b l e r e s i s t o r t y p e
Idle air control motor
DC motor type [DC by-pass air control system
with the fast idle air
Closed throttle position switch
Rotary contact type, within throttle position senso r
Idle air control valve position sensor
Hall element type
Engine control Identification model No.
module (ECM)
SensorsVolume air flow sensor Karman vortex type
Barometric pressure sensorSemiconductor type.
Intake air temperature sensorThermistor type
Engine coolant temperature sensor Thermistor type
Heated oxygen sensor Zircon type
Vehicle speed sensor Electromagnetic resistance element type
Park/neutral position switch Contact switch type
Camshaft position sensor Hall element type
Crankshaft position sensor Hall element type
Power steering pressure switch Contact type
fuel injection (MFI) relay Contact switch type
Fuel pump relay Contact switch type
Fuel pump relay module Electronic control module typ e
Injector type and number Electromagnetic type, 4
Injector identification mark
,
solenoid Duty cycle type solenoid valve
Evaporative emission purge solenoid
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
pressure Regulator (psi)335 (48)
egulator
TSB Revision
Page 522 of 2103
E N G I N E ( T U R B O )
AND
ENGINE> General . .
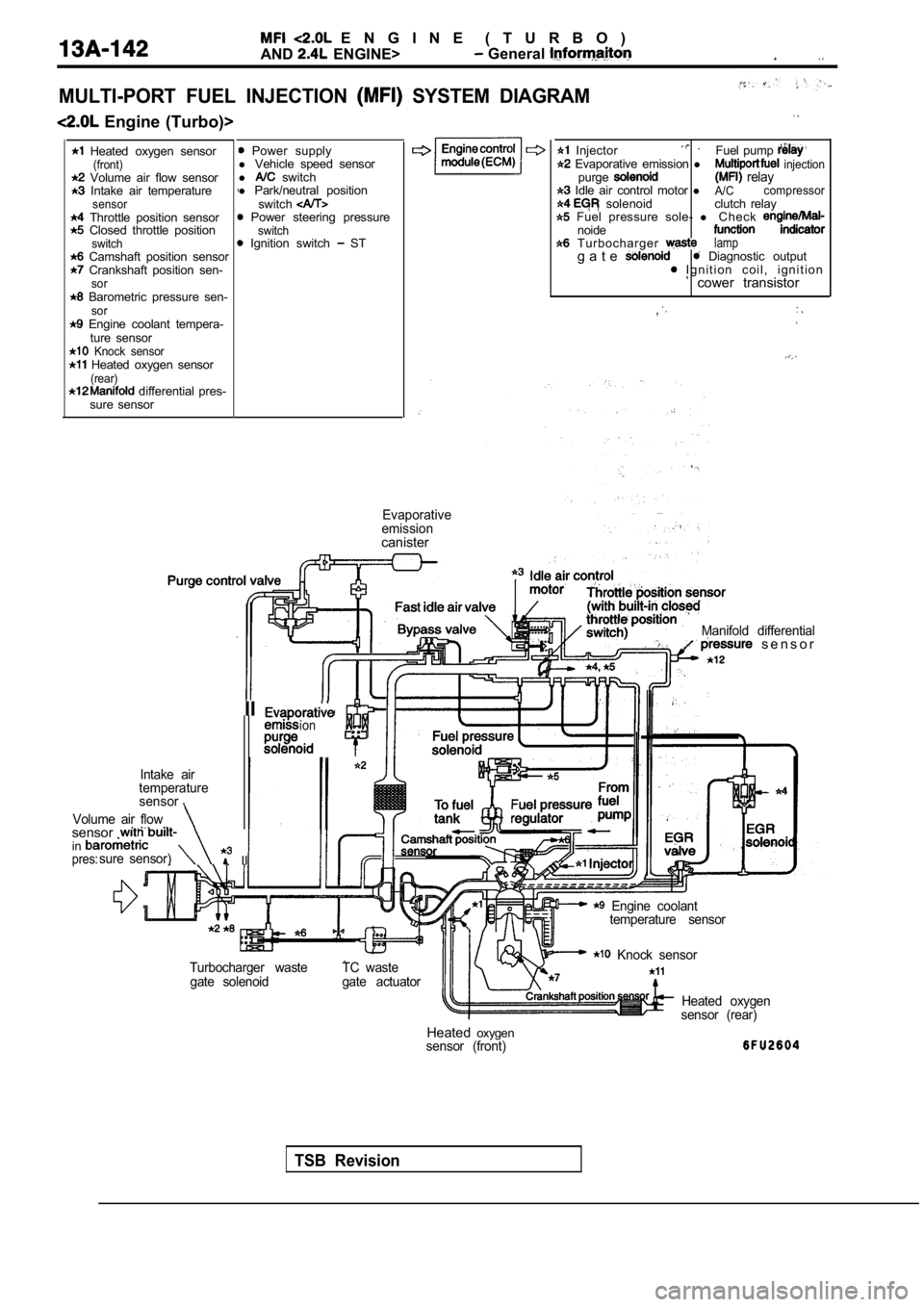
MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM DIAGRAM
Engine (Turbo)>
Heated oxygen sensor(front) Volume air flow sensor Intake air temperaturesensor Throttle position sensor Closed throttle positionswitch Camshaft position sensor Crankshaft position sen-sor Barometric pressure sen-sor Engine coolant tempera- ture sensor
Knock sensor Heated oxygen sensor(rear) differential pres-
sure sensor
Power supply
l Vehicle speed sensor
l
switch
l Park/neutral position
switch
Power steering pressureswitch Ignition switch ST
Enginecontrol Injector . Fuel pump
Evaporative emission l injectionpurge relay Idle air control motor lA/Ccompressor solenoid clutch relay Fuel pressure sole-
l C h e c knoide T u r b o c h a r g e r lampg a t e Diagnostic output I g n i t i o n c o i l , i g n i t i o n cower transistor
,
Evaporative
emission
canister
TSB Revision
Manifold differential s e n s o r
IIion. .
Intake air
temperature
sensor
Volume air flow
sensor . insure sensor) IIpres:
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Turbocharger waste gate solenoid TC waste
gate actuator
Knock sensor
Heated oxygen
sensor (rear)
Heated oxygensensor (front)