1990 MITSUBISHI SPYDER sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 8 of 2103
G E N E R A L How to Use Troubleshooting/Inspection Service Points
Troubleshooting of electronic control systems for which the scan tool the basic outline
described below. Furthermore, even in systems for w hich the scan tool cannot be used, part of these
systems still follow this outline.
TROUBLESHOOTING CONTENTS
1. STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING
The main procedures for diagnostic troubleshooting are shown.
2. SYSTEM OPERATION AND SYMPTOM VERIFICATION TESTS If verification of the trouble symptoms is difficul t, procedures for checking operation and verifying
trouble symptoms are shown.
3. DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION The following diagnostic functions are shown.
l ,Method of reading diagnostic trouble codes
Method of erasing diagnostic trouble codes
lInput inspection service points
4. INSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
5. INSPECTION PROCEDURE FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE S
Indicates the inspection procedures corresponding t o each diagnostic trouble code. (Refer to the
next page on how to use the inspection procedures.)
6. INSPECTION CHART FOR TROUBLE SYMPTOMS
If there are trouble symptoms, even though the scan tool displays no diagnostic inspection
procedures for each trouble symptom will be found b y means of this chart.
7. INSPECTION PROCEDURE FOR TROUBLE SYMPTOMS
Indicates the inspection procedures corresponding t o each trouble symptoms the Inspection
Chart for Trouble Symptoms. (Refer to the next page on how to use the inspection procedures.)
8. DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE
Inspection items and normal judgement values have b een provided in this chart as reference
9. CHECK AT ECU TERMINALS
Terminal numbers for the ECU connectors, inspection items and standard values have been provided
in this chart as reference information.
Terminal Voltage Checks
1. Connect a needle-nosed wire probe or paper clip to a voltmeter probe.
2.Insert the needle-nosed wire probe into each of the ECU connector from the wire side,
and measure the voltage while referring to the chec k chart.
NOTE
1. Measure voltage with the ECU connectors connecte d.
2. You may find it convenient to pull out the ECU t o make it easier to reach the connector
terminals.
3. Checks don’t have to be carried out in the order given in the chart.
Short-circuiting the positive probe between a connector damage
the vehicle wiring, the sensor, the ECU, or all thr ee.
Use care to prevent this
3. If voltage readings differ from Normal Condition values, related actuators, and
wiring, then replace or repair.
TSB Revision
Page 9 of 2103

GENERAL How to Use Troubleshooting/Inspection Service Points
4.After repair or replacement, recheck the voltmeter to confirm the repair
the problem.
Terminal Resistance and Continuity Checks
1. Turn the ignition switch to off.
2. Disconnect the ECU connector.
3.Measure the resistance and check for continuity bet ween the terminals of the ECU
connector while referring to the check chart.
NOTE
Checks don’t have to be carried out in the order gi ven in the chart.
Cautlon
If resistance and continuity checks are performed the wrong terminals, damage
vehicle wiring, sensors, ECU, and/or ohmmeter may o ccur.
Use care to prevent this!
4.If the ohmmeter shows any deviation from the Normal Condition value, check the corresponding
5.
sensor, actuator and related electrical wiring, then repair or replace.
After repair or replacement, recheck with the ohmme ter to confirm that the repair
the problem.
10. INSPECTION PROCEDURES USING AN OSCILLOSCOPE
When there are inspection procedures using an oscil loscope, these are listed here.
,
TSB Revision
Page 13 of 2103
G E N E R A L How to Use __
HOW TO COPE WITH INTERMITTENT
Most intermittent malfunctions occur under certain conditions. If those conditions can be identified, the
cause will be easier to find.
TO COPE WITH INTERMITTENT MALFUNCTION;1. Ask the customer about the malfunction
Ask what it feels
it sounds like, etc.
Then ask about
conditions; weather,
frequency of occurrence, and so on.
2.Determine the from the custom-
er’s responses
Typically, almost all intermittent malfunctions
occur from conditions like vibration, tempera-
ture and/or moisture change, poor connections.
From the customer’s replies, it should be rea-
soned which condition is influenced.
3. Use simulation test In the cases of vibration or poor connections,
use the simulation tests below to attempt to
duplicate the customer’s complaint. Determine
the most likely circuit(s) and perform
tion tests on the connectors and parts of that
circuit(s). Be sure to use the inspection proce-
dures provided for trouble codes
a n d t r o u b l e s y m p t o m s .
For temperature and/or moisture conditions re-
lated intermittent malfunctions, using common
sense, try to change the of
circuit components, then use
tion tests below,
4. Verify the intermittent malfunction is elimi-
nated
Repair the malfunctioning part and try to
the condition(s) again to verify the intermit-
tent malfunction has been eliminated.
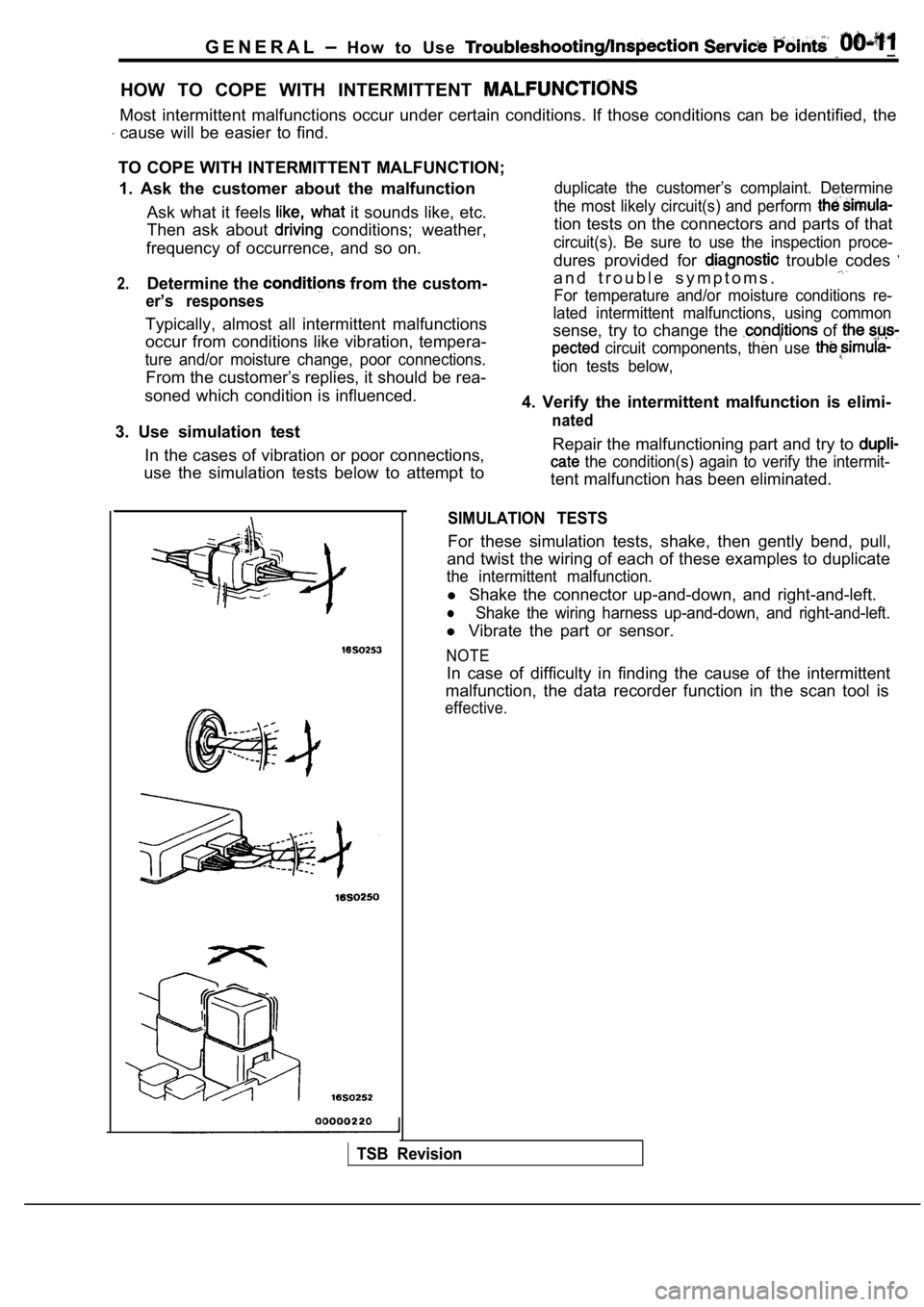
SIMULATION TESTS
For these simulation tests, shake, then gently bend , pull,
and twist the wiring of each of these examples to d uplicate
the intermittent malfunction.
l Shake the connector up-and-down, and right-and-left .
lShake the wiring harness up-and-down, and right-and -left.
l Vibrate the part or sensor.
NOTE
In case of difficulty in finding the cause of the i ntermittent
malfunction, the data recorder function in the scan tool is
effective.
TSB Revision
Page 23 of 2103
GENERAL Precautions before Service . .
Caution
1.Before connecting or disconnecting the negative
be sure to turn off the ignition and
the lighting switch.
(if this is not done, the possibility semi-
conductor parts being damaged.)
2.After completion of the work steps [when the bat-
tery’s negative terminal is connected], warm
up the engine and allow it for approximately
five minutes under the conditions be-
low, in order to stabilize the engine condi-
tions, and then check to be sure that idling’ is
satisfactory.
Engine temperature:
Lights, electric fans, accessories: OFF
Transaxle: Neutral position
(A/T models: “N” or “P”)
Steering
neutral (center) position
mm (in.)
Scan tool
ROM pack
VEHICLE WASHING
If high-pressure car-washing equipment or steam car -washing
equipment is used to wash the vehicle, be maintain
the spray nozzle at a distance of at ‘least 300 mm (12 in.)
from any plastic parts and all opening parts (doors , luggage
compartment, etc.).
APPLYING ANTI-CORROSION
OTHER UNDERCOAT AGENTS.,
Be careful not to adhere oil or grease to the heate d oxygen
sensor. If adhered, the sensor may malfunction.
Protect the heated oxygen sensor with a cover befor e applying
anti-corrosion agent, etc.
SCAN TOOL
To operate the scan tool, refer to the “MUT-II OPER ATING
INSTRUCTIONS”.
Caution
Turn the ignition switch off befoie connecting and discon-
necting the scan tool.
Page 35 of 2103

GENERAL Lubrication arid Maintenance,
00100120067
Maintenance and lubrication service recommenda-
tions have been compiled to provide maximum
protection for the vehicle owner’s investment
against all reasonable types of driving conditions.
Since these conditions vary with the individual ve-
hicle owner’s driving habits, the area in which the
vehicle is operated and the type of to which
the vehicle is subjected, it is necessary to prescr ibe
lubrication and maintenance service on a time fre-
quency as well as mileage interval basis.
Oils, lubricants and greases are classified and
graded according to standards recommended by
the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the
American Petroleum Institute (API) and the National
Lubricating Grease Institute (NLGI).
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
Information for service maintenance is provided
under “SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE TABLE”.
Three schedules are provided; one for “Required
Maintenance”, one for “General Maintenance” and
one for “Severe Usage Service”. Item numbers in the “SCHEDULED MAINTE-
NANCE TABLE” correspond to the item
in the “MAINTENANCE SERVICE” section.
SEVERE SERVICE
Vehicles operating under severe service conditions
will require more frequent service. Component service information is included in ap-
propriate units for vehicles operating under one
or more of the following conditions:
1. Police, taxi, or commercial type operation
2. Operation of Vehicle
(1) Short-trip operation at freezing temperature
(engine not thoroughly warmed up)
(2) More than 50% operation in heavy city traf-
fic during hot weather above
(3) Extensive idling
(4) Driving in sandy areas
(5) Driving in salty areas
(6) Driving in dusty conditions
ENGINE OIL
Either of the following engine oils should be used:
(1) Engine oil displaying EOLCS certification mark
(2) Engine oil conforming to the API classification SH
or ECII.
For further details, refer to “LUBRICANTS SELEC-
TION” section.
Caution
Test to EPA have shown
laboratory animals develop skin after
prolonged contact with used engine oil. Accord-
ingly, the potential exists for
to
a number:, of skin disorders, including
from such exposure to used
Care should be taken, when changing
engine oil, to minimize the
of exposure time to used your
skin. Protective clothing and that
be penetrated by worn.
should be thoroughly with soap
use waterless hand remove,
any used engine oil. Do not use gasoline, thin- ners, or solvents.
GEAR LUBRICANTS
The SAE grade number indicates
of Multi-purpose Gear Lubricants.
The API classification system
cants in terms of gear lubricants
conforming to API
or ‘with a
of SAE are recommended for
transaxle.
LUBRICANTS GREASES
Semi-solid lubricants bear the
designation
and are further classified as grades 0, 1, 2; 3 etc .
Whenever “Chassis Lubricant” is specified, Multi-
purpose Grease,
grade 2, should be used.
FUEL USAGE
Your car must use unleaded
This car has a fuel filler tube especially
to accept only the smaller-diameter unleaded gaso- line dispensing nozzle.
Caution
Using leaded gasoline in your car will damage
the catalytic converter and oxygen sensor, and
affect the warranty coverage validity.
Your car is designed to operate on premium
leaded gasoline having a minimum octane rating
of 91 or 95 RON (Research Octane
If premium unleaded gasoline is not
leaded gasoline having a octane rating of 87,
91 RON (Research Octane Number) may be used. In this case, the performance and fuel consumption
will suffer a little degradation.
Gasolines Containing Alcohol
Some gasolines sold at service stations contain
alcohol, although they may not be so identified.
TSB Revision
Page 54 of 2103
GENERAL Maintenance Service
0 0 0 0 0 1 6 7
Inflator case
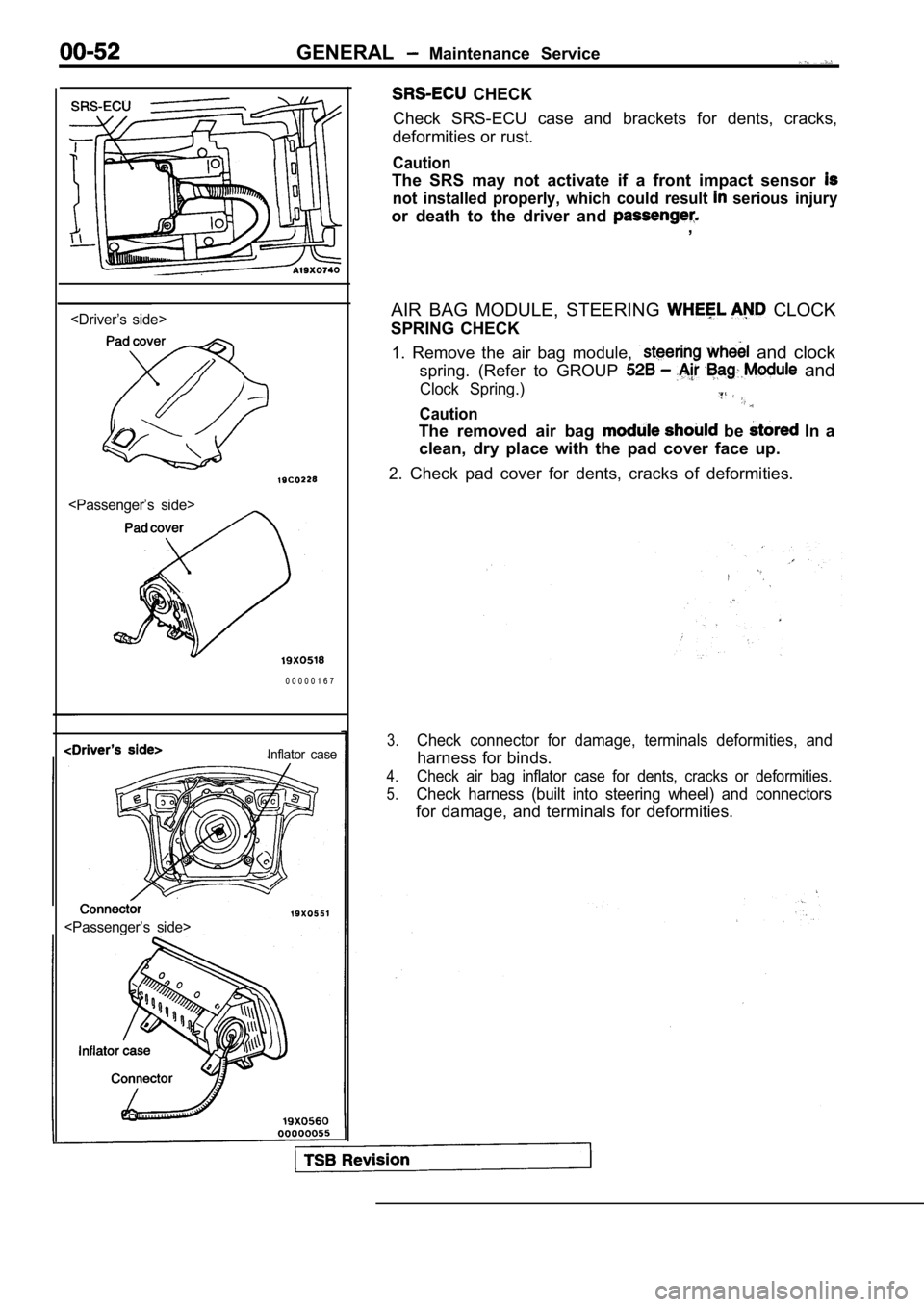
CHECK
Check SRS-ECU case and brackets for dents, cracks,
deformities or rust.
Caution
The SRS may not activate if a front impact sensor
not installed properly, which could result serious injury
or death to the driver and ,
AIR BAG MODULE, STEERING
CLOCK
SPRING CHECK
1. Remove the air bag module,
and clock
spring. (Refer to GROUP
and
Clock Spring.)
Caution
The removed air bag be In a
clean, dry place with the pad cover face up.
2. Check pad cover for dents, cracks of deformities .
3.Check connector for damage, terminals deformities, and
harness for binds.
4.Check air bag inflator case for dents, cracks or deformities.
5.Check harness (built into steering wheel) and conne ctors
for damage, and terminals for deformities.
Page 57 of 2103

GENERAL Main and Adhesive Table
MAIN SEALANT AND ADHESIVE TABLE
SEALANTS FOR ENGINE ACCESSORIES
Application Recommended brand
Sealing between rocker cover and camshaft bearing c ap
DOHC ATD Part No. 8680 or equivalent
and
engines only)
1Sealing between semi-circular packing and rocker co ver and between
semi-circular packing and cylinder head
Oil pressure switch (except
and engines). . .
Engine coolant temperature switch, Engine coolant t emperature sensor, Nut Locking Part No. 4171 or
valve, switch, Joints, Engine coolant temperature lent
gauge unit (large size)
Engine coolant temperature gauge unit (small size, only) ATD Part No. 8660 or equivalent
Oil pan (except
engine)MITSUBISHI GENUINE ‘Part
0 or equivalent
SEALING BETWEEN GLASS AND WEATHERSTRIP
Application
Sealing between tempered glass and weatherstrip
Sealing between body flange and weatherstrip
Sealing between laminated glass and weatherstripRecommended brand
ATD Part No. 8513 or equivalent
ATD Part No. 8509 or equivalent
ADHESION WITH RIBBON SEALER
Application Recommended brand
Waterproof film for door, Fender panel, Splash shie ld, Mud guard, Rear
ATD Part No. 8625 or equivalent
combination light
ADHESIVES FOR INTERIOR TRIM
Application Recommended brandI
Adhesion of polyvinyl chloride sheetI Part No. 368 or equivalentI
Adhesion of door weatherstrip to body ATD No. 8001 or ATD Part No.
8011 or equivalent
Sealing between grommet or packing, and metal seal
Adhesion of headlining and other interior trim mate rials
Adhesion of fuel tank to pad
ATD Part No. 8513 or equivalent
Part No. or ATD Part No.
8080 or equivalent
BODY SEALANT
ApplicationRecommended brandI
Sealing of sheet metal, drip rail, floor, body side panel, trunk, front panel ATD No. 8531 or ATD Part No.
and the like joints8848or equivalent
Sealing of
hinges
TSB Revision
Page 71 of 2103

ENGINE On-vehicle
8. If the standard value is exceeded, check the following
items:
l Diagnostic output
l Closed-loop control (When the closed-loop control
is carried out normally, the output signal of the h eated
oxygen sensor repeats between and
,000 at idle.)
l Fuel pressure
I n j e c t o r
lIgnition coil, spark plug cable, spark plug
lEGR system and the EGR valve leak
l Evaporative emission control system
Compression pressure
NOTE
Replace the catalyst whenever the
HC contents do not remain inside the standard value .
(even though the result of the inspection is
all items.).
C O M P R E S S I O N
CHECK
1.Before inspection, check that the engine-oil, start er
battery are normal. Also, set the to the
condition:
lEngine coolant temperature:
lLights, electric cooling fan and all accessories: O FF
lTransaxle: Neutral (P range on vehicles with
2. Disconnect the spark plug cables.
3. Remove all of the spark plugs.
4.
5.
Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor connector .
NOTE
Doing this will prevent the engine control unit fro m carrying
out ignition and fuel injection.
Cover the spark plug hole with a shop towel etc., a nd
after the engine has been cranked, check that no fo reign
material is adhering to the shop towel.
TSB Revision