1989 MITSUBISHI GALANT oil temperature
[x] Cancel search: oil temperaturePage 35 of 1273

GENERAL - Master Troubleshootinn
00-33
BOTTOMING Symptom Probable cause
1 Reference page or remedy
Bottoming
Malfunctioning shock absorber
WHEEL BEARING TROUBLESHOOTING TroublePitting
Flaking
Cracking
Sympton Probable cause
Pitting occurs because of uneven rotation of race Excessive bearing preload
and bearing surfaces Excessrve
load
The surface peels because of uneven rotation of
End of bearing life ,
the race and bearing surfaces Improper bearing assembly
Chipping or cracking of cage or roller edges Impact when
beanng was installed
(such as being hit with a hammer)
Flat spotting When large load is applied, race and roller
contact surfaces compress, formingindentations Excessive bearing preload
Excessive load
Vibration when bearings are not used, such as during shipment on
freight cars, transport trucks, etc.
NicksInstead of roiling along race surface, rollers slide, insufficient grease
thus damaging surface Excessive bearing preload
Excessive load
Faulty oil seal
Smearing Damage or wear caused by minute particles Excessive variation of loads on
adhering to surfaces results in
rolugh movement bearings
and such high temperatures that parts of surface Use of grease other than that
melt specified
Insufficient grease
Rust, corrosion Appears on various areas of the bearing Use of grease other than that
specified Faulty oil seal
Presence of water or moisture
WearWear of surface areas caused by friction Insufficient grease
Foreign matter
Rust or corrosion due to moisture
Use of grease other than that
specified
Faulty oil seal Irscoloration
Grease discoloration results from grease
deterioration which causes partic:les
of
pigment contained in grease to adhere
to surfaces Heat discoloration will appear
as a deep brown on purple Use of grease other than that
specified
Faulty oil seal Excessive bearing preload
Excessive load
TSB Revision
Page 36 of 1273

00-34GENERAL- Lubrication and Maintenance
LUBRICATION AND
MAINTE-
NANCEMOOPA-
Maintenance and lubrication service recommenda-
tions have been compiled to provide maximum protection for the vehicle owner’s investment
against all reasonable types of driving conditions. Since these conditions vary with the individual
vehicle owner’s driving habits, the area in which the
vehicle is operated and the type of driving to which
the vehicle is subjected, it is necessary to prescribe lubrication and maintenance service on a time
frequency as well as mileage interval basis.
Oils, lubricants and greases are classified and
graded according to standards recommended by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the Amer-
ican Petroleum Institute (API) and the National
Lubricating Grease Institute (NLGI).
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES Information for service maintenance is provided
under “SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE TABLE”.
Three schedules are provided; one for “Required Maintenance”, one for “General Maintenance” and
one for “Severe Usage Service”.
The item numbers used in the “SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE TABLE” correspond to th
e
“MAINTENANCE SERVICE” section numbers.
SEVERE SERVICE
Vehicles operating under severe service conditions
will require more frequent service. Component service information
isIncluded i
n
appropriate units for vehicles operating under one or
more of the following conditrons:
1.Trailer towing or police, taxi, or
commerciai
type
operation
2. Operation of Vehicle (1) Short-trip operation at freezing temperature(engine not thoroughly warmed up)
(2) More than 50% operation in heavy city traffic during hot weather above
32°C (90°F)
(3) Extensive idling
(4) Driving in sandy areas
(5) Driving in salty areas
(6) Driving in dusty conditions
ENGINE OIL
The SAE grade number indicates the viscosity of engine oils, for example, SAE 30, which is a single
grade oil. Engine oils are also identified by a dual number, for example, SAE 1
OW-30, which Indicates
a multigrade oil.
The API classification system defines oil perform- ance in terms of engine usage. Only engine oil
designed “For Service SG” or “For Service
SGKD”,
when available, should be used. These oils contain
sufficient chemical additives to provide maximum
engine protection. Both the SAE grade and the API
designation can be found on the container.
Caution
Test results submitted to EPA have shown that
laboratory animals develop skin cancer after
prolonged contact with used engine oil. Accor-
dingly, the potential exists for humans to de-
velop a number of skin disorders, including
cancer, from such exposure to used engine oil.
Care should be taken, therefore, when changing engine oil, to minimize the amount and length of
exposure time to used engine oil on your skin.
Protective clothing and gloves, that cannot be
penetrated by oil, should be worn. The skin
should be thoroughly washed with soap and
water, or use waterless hand cleaner, to remove
any used engine oil. Do not use gasoline,
thinners, or solvents.
GEAR LUBRICANTS
The SAE grade number also indicates the viscosity of Multi-Purpose Gear Lubricants.
The API classfication
system defines gear lubricants
in terms of usage. Typically gear lubricants conform-
ing to API
GL-4 or GL-5 with a viscosity of SAE 75W-85W
are recommended for manual transaxle.
LUBRICANTS
- GREASES
Semi-solid lubricants, bear the
NLGI designation and
are further classified as grades 0, 1, 2, 3 etc.
Whenever “Chassis Lubricant” is specified,
Multi-
Purpose Grease, NLGI grade 2 should be used.
FUEL USAGE STATEMENT
Your vehicle must use unleaded gasoline only.
This vehicle has a fuel filler tube especially designed
to accept only the smaller-diameter unleaded gaso- line
dispensrng nozzle.
Caution
Using leaded gasoline in your vehicle will damage
the catalytic converter, and affect the warranty
coverage validity.
All vehicles except those with DOHC engines
Your vehicle is designed to operate on unleaded
gasoline having a minimum octane rating of 87 or
91 RON (Research Octane Number).
Vehicles equipped with DOHC engines
Your vehicle is designed to operate on premiumunleaded gasoline having a minimum
octane rating
of 91 or 95 RON (Research Octane Number).
TSB Revision
Page 38 of 1273

00-36
GENERAL -Recommended Lubricants and Lubricant Capacities Table
LUBRICANT CAPACITIES TABLE
Descrrptron
Engrne 011
Crankcase
Models built up to April 1992
Models built from May 1992
Oil filter
Oil cooler
(rncludrng heater and coolant reserve system)
Manual Transaxle
F5M3
1
Transfer
qear Axle
4utomatrc Transaxle
‘ower Steering %el
Tank
Metric measure
3.5 dm3
4.0 dm3
4.0 dm3
0.3 dm3
0.3 dm3
7.2 dm3
1.8 dm31.9 qts.
2.3
dm32.4 qts.
2.3 dm32.4 qts.
3.6 dm363 qt.
3.7
dm374 qt.
6.1 dm3
6.5 dms
3.9 dm3 60
dm3
62 dm3
U.S. measure
3.7qts.
4.2qts.
4.2qts.
1 I2qt.
1 I2qt.
7.6qts.
5.4 qts.
6.9 qts.
95 qt.
15.9 gals.
16.4 gals.
Temperature range anticipated before next oil chanae
SAE SW-30 SW-40IRecommendedviscosity (SAE) M03BOOl
SELECTION OF LUBRICANTS
ENGINE OIL
Engine oil should be used which conform to the requirements
of the API classification “For Service SG” or “For Service
SGKD”, and have the proper SAE grade number for the
expected temperature range.
Caution
Nondetergent or straight mineral oil must never be used.
Energy Conserving Oil
In order to improve fuel economy and conserve energy new,
lower friction engine oils have been developed. These oils are readily available and can be identified by such labels as “Energy
Conserving”, “Energy Saving”,
“Improved Fuel Economy”,
etc.
TSB Revision
Page 39 of 1273
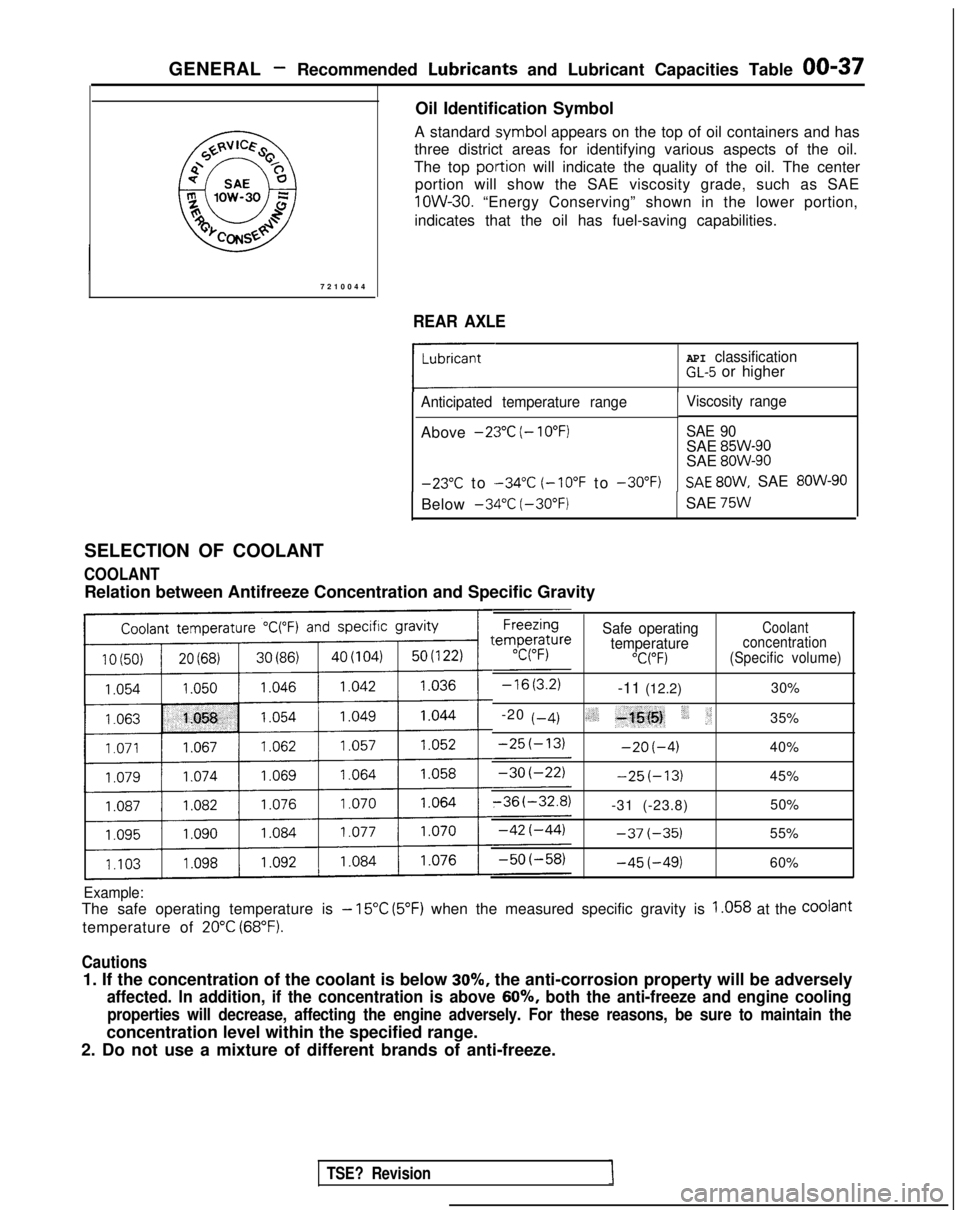
GENERAL - Recommended LubricaMs and Lubricant Capacities Table 00-37
721004
4
Oil Identification Symbol
A standard
.symbol appears on the top of oil containers and has
three district areas for identifying various aspects of the oil.
The top
polqion will indicate the quality of the oil. The center
portion will show the SAE viscosity grade, such as SAE lOW-30.
“Energy Conserving” shown in the lower portion,
indicates that the oil has fuel-saving capabilities.
REAR AXLE
API classificationGL-5 or higher
Anticipated temperature range
Above -23°C
(- 10°F)
-23°C to --34°C (-10°F
to -30°F)
Viscosity range
SAE 90
SAE 85W-90SAE 8OW-90
SAE 8OW. SAE 8OW-90
Below
-34°C
(-30°F)SAE 75W
SELECTION OF COOLANT
COOLANT
Relation between Antifreeze Concentration and Specific Gravity
Safe operatingCoolant
temperatureconcentration
“C(“F)(Specific volume)
-11 (12.2) 30%
-20
t-4)(,.‘_ -+j{@, ‘, :;35%
-2O(-4)40%
-25(-13)45%
-31 (-23.8) 50%
-37(-35)55%
-45(-49)60%
Example:
The safe operating temperature is - 15°C (5°F) when the measured specific gravity is 1.058 at the Coolant
temperature of 20°C (68°F).
Cautions
1. If the concentration of the coolant is below 30%, the anti-corrosion property will be adversely
affected. In addition, if the concentration is above 60%, both the anti-freeze and engine cooling
properties will decrease, affecting the engine adversely. For these reas\
ons, be sure to maintain the
concentration level within the specified range.
2. Do not use a mixture of different brands of anti-freeze.
TSE? Revision
Page 41 of 1273
GENERAL - Scheduled Maintenance Table/Maintenance Service00-39
SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE UNDER SEVEiRE USAGE CONDITIONS
The maintenance items should be performed according to the following tab\
le:
Maintenance Item Service to be
Performed
IEngine Oil Change Every or
3 Months
(:z:.:a::I
Rear Drum Brake
Linings and Rear
Wheel Cylinders Inspect for Wear
and Leaks
1
Mileage Intervals Kilometers in Thousands (Miles in Thousands) Severe Usage
Conditions
More Frequently
Every 4,800 km
(3,000 miles)/xlxlx/xI I I1 Every
9,600 km (6,000 miles)
IxIxlxIxI I I>(
More Frequently1x1 I I I 1x1I I I I I I I
More Frequently
Ix1 I I I lx/
Severe usage conditions A-Driving in dusty conditions
- -B- I railer
towing or police.
taxi,
or commercial
type
operation
C-Extensive idling
D-Short trip operation at freezing temperatures (engine not thoroughly warmed up) E-Driving in sandy areas- -..F-Dnvlng In salty areas
G-More than 50% operation in heavy city trafic during
hot weather above 32°C (90°F)
MAINTENANCE SERVICE
1. FUEL SYSTEM (Tank, Lines, Connections and
Fuel Tank Filler Tube Cap) (Check for leaks)/2.
FUEL HOSES (Check for leaks or
damagekOOSnOB.
1.Check for damage or leakage in the fuel lines and con-
nections and looseness of the fuel tank filler tube cap.
2. Inspect the surface of fuel hoses for heat and mecha-
nicall damage. Hard and brittle rubber, cracking, check-
ing, tears, cuts, abrasions and excessive swelling
indicate deterioration of the rubber.
3. If the fabric casing of the rubber hose is exposed by cracks and abrasions in the fuel system, the hoses
should be changed.
3. AIR CLEANER ELEMENT (Replace)
MMlSAKH
The air cleaner element will become dirty and loaded with dust during use, and the filtering effect will be substantiallyreduced. Replace it with a new one.
(1) Loosen the clamp coupling the air intake hose and the air cleaner cover, and separate the hose.
(2) Disconnect the volume air flow sensor connectors.
(3) Unclamp the air cleaner cover clip.
(4) Lifting the air intake hose, remove the air cleaner cover.
TSB Revision1
Page 43 of 1273
GENERAL - Maintenance Service00-41
-1
6COOO9
L!6COO39
OlR0344
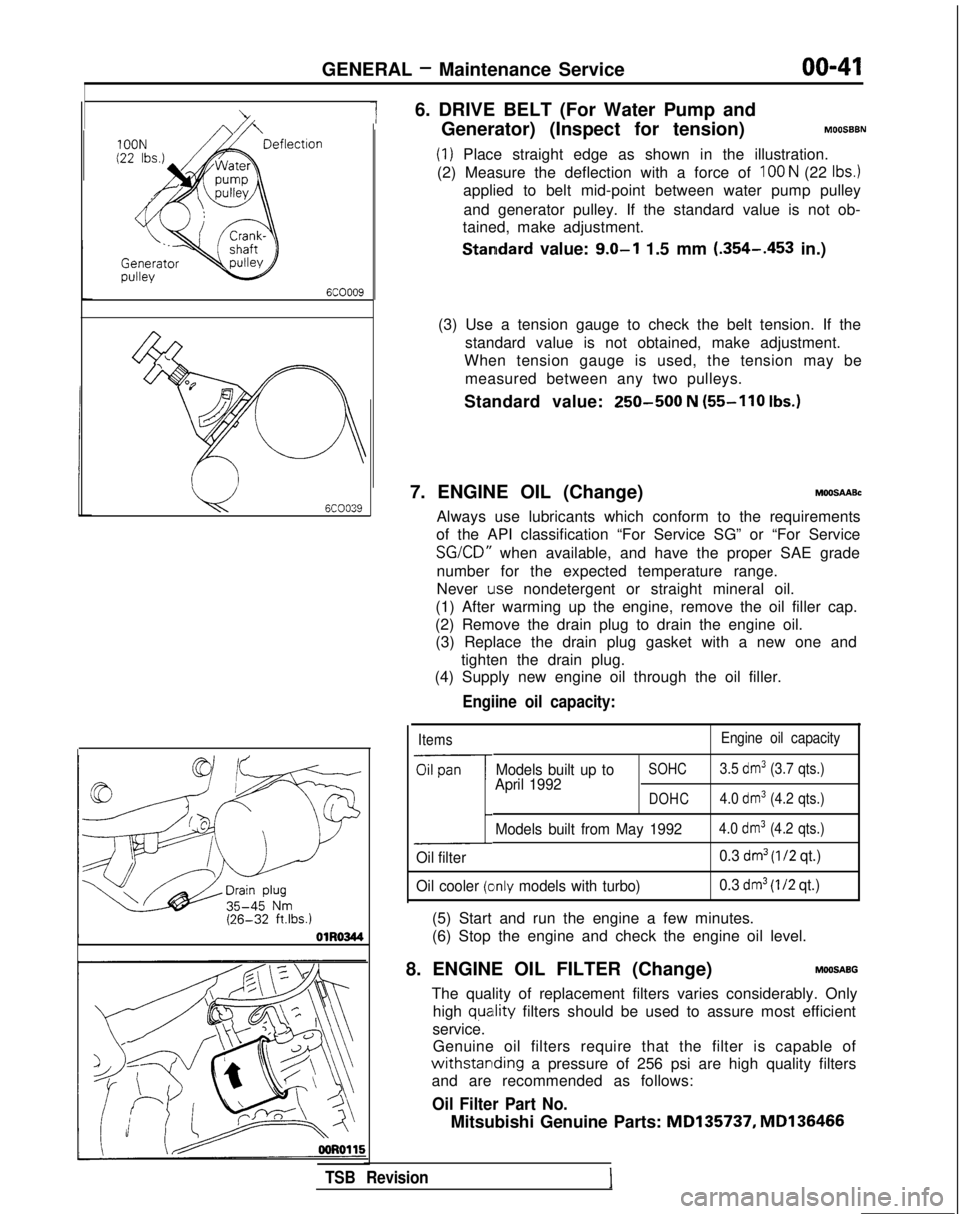
6. DRIVE BELT (For Water Pump and
Generator) (Inspect for tension)
MOOSBBN
(1) Place straight edge as shown in the illustration.
(2) Measure the deflection with a force of
100 N (22 Ibs.)
applied to belt mid-point between water pump pulley
and generator pulley. If the standard value is not ob-
tained, make adjustment.
Standard value: 9.0-l 1.5 mm (.354-.453
in.)
(3) Use a tension gauge to check the belt tension. If the standard value is not obtained, make adjustment.
When tension gauge is used, the tension may be
measured between any two pulleys.
Standard value:
250-500 N (55-110
Ibs.)
7. ENGINE OIL (Change)MOOSAABc
Always use lubricants which conform to the requirements
of the API classification “For Service SG” or “For Service SG/CD”
when available, and have the proper SAE grade
number for the expected temperature range.
Never
Lose nondetergent or straight mineral oil.
(1) After warming up the engine, remove the oil filler cap.
(2) Remove the drain plug to drain the engine oil. (3) Replace the drain plug gasket with a new one and
tighten the drain plug.
(4) Supply new engine oil through the oil filler.
Engiine oil capacity:
Items Engine oil capacity
Oil pan
1
Models built up toSOHC3.5 dm3 (3.7 qts.)
April 1992DOHC4.0 dm3 (4.2 qts.)
Models built from May 19924.0 dm3 (4.2 qts.)
Oil filter 0.3 dm3 (l/2 qt.)
Oil cooler
(clnly models with turbo) 0.3 dm3 (I/2 qt.)
(5) Start and run the engine a few minutes.
(6) Stop the engine and check the engine oil level.
8. ENGINE OIL FILTER (Change)
MOOSABG
The quality of replacement filters varies considerably. Only high
quatlity filters should be used to assure most efficient
service. Genuine oil filters require that the filter is capable of
withstarlding a pressure of 256 psi are high quality filters
and are recommended as follows:
Oil Filter Part No.
Mitsubishi Genuine Parts: MD135737,
MD136466
TSB Revision
Page 45 of 1273
GENERAL - Maintenance Service00-43
1
O.AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE
Inspect fluid levelMOOSSDA
1. Drive until the fluid temperature reaches the usual ternperature
[70-80°C (160- 18O”F)I.
2. Plaice vehicle on level floor.
3.Move selector lever sequentially to every position to fill
torque converter and hydraulic circuit with fluid, then place lever in “N” Neutral position. This operation is
necessary to be sure that fluid level check is accurate.
4. Before removing dipstick, wipe all dirt from area around
dipstick. Then take out the dipstick and check the
condition of the fluid.
The transaxle should be overhauled under the following
conditions.l If there is a “burning” odor.
l If the fluid color has become noticeably blacker.
l If there is a noticeably great amount of metal particles in the fluid.
5.Chleck to see if fluid level is in “HOT” range on dipstick.
If fluid level is low, add ATF until level reaches “HOT”
range.
LO\N fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows pump to take in air along with fluid. Air
trapped in hydraulic circuit forms bubbles which make
fluid spongy. Therefore, pressures will be erratic. Improper filling can also raise fluid level too high. When
transaxle has too much fluid, gears churn up foam and cause same conditions which occur with low fluid level,
resulting in accelerated deterioration of ATF.In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating, fluid
oxidation, which can interfere with normal valve, clutch,
and servo operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping from transaxle vent where it may be mistaken
for a leak.
6. Be sure to examine fluid on dipstick closely. Chaqge
fluid
Drain
tlhe fluid and check whether there is any evidence of
contamination. Replenish with new fluid after the cause of any contamina-
tion
has been corrected.
(1) Rernove drain plugs to let fluid drain.
(2) Rernove the oil pan.
(3) Check the oil filter for clogging and damage and replace
if necessary.
(4) Clean the inside of oil pan and 5 magnets.
(5) Attach the five magnets to the concave part of the oil
pan.
1 TSB Revision
(6) Clean both gasket surfaces of transaxle case and oil
pan.
(7) Install oil pan with new gasket and tighten oil pan bolts
to
IO-I 2 Nm (7.5-8.5 ftlbs.)
(8) Tighten drain plug with gasket to 30-35 Nm (22-25 ft.lbs.).
(9) Supply 4
dm3 (4.23 qts.) of specified ATF into case
through dipstick hole. [Total quantity of ATF required is 6.1
dm3 (6.45 qts.).
Actually however, approx. 4.5 dm3 (4.76 qts.) of fluid
car1 be replaced because rest of fluid remains in torque converter.]
1
Page 46 of 1273
GENERAL -Maintenance Service
(1O)Star-t engine and allow to idle for at least two minutes.
Then, with parking brake on, move selector
fever
momentarily to each position, ending in “N” Neutral
position.
(11)Add sufficient ATF to bring fluid level to lower mark.
Recheck fluid level after transaxle is at normal Operating
temperature. Fluid level should be between upper and lower marks of
“HOT” range, Insert dipstick fully to prevent dirt from
entering transaxle.
OOA0051
11 .ENGINE
COOLANT (Change)MOOSEEAC
Check the cooling system parts, such as radiator, heater,
and oil cooler hoses, thermostat and connections for
leakage and damage.
CHANGE COOLANT
1. Remove the radiator cap.
2. Loosen the drain plug to drain the coolant.
3. Drain the coolant from the reserve tank.
4. After draining the coolant, tighten the drain plug securely.
5.Supply the coolant into the radiator until it is filled up to
its filler neck.
6. Supply the coolant into the reserve tank.
7. After warming the engine until the thermostat opens, remove the radiator cap and check the coolant level.
8.Supply the coolant into the radiator until it is filled up to
its filler neck, and install the radiator cap securely.
9.Fill the reserve tank with coolant up to the “FULL” line.
14K512
1 12.DISC BRAKE PADS (Inspect for wear) MWSBFA
Check for fluid contamination and wear. Replace complete
set of pads if defective.
Caution
The pads for the right and left wheels should be
reDlaced at the same time. Never “split” or intermix
brkke pad sets.
All four pads must be replace as a complete set.
Thickness of lining (A)
Limit: 2.0 mm (.08 in.)
13.REAR DRUM BRAKE LININGS AND REAR
WHEEL CYLINDERS (Inspect for wear and
leaks)MOOSBGB
1. Remove the brake drum and check the thickness of brake shoe lining for wear. Check the automatic brake
adjusting system by hand to see if it operates smoothly.
Also see if the gears are in proper mesh with each
other. To assure smooth functioning, apply a very thin
coat of multipurpose grease to the friction surface of
adjuster and link shaft.
TSB Revision1