1988 PONTIAC FIERO check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 301 of 1825
5-8 BRAKES
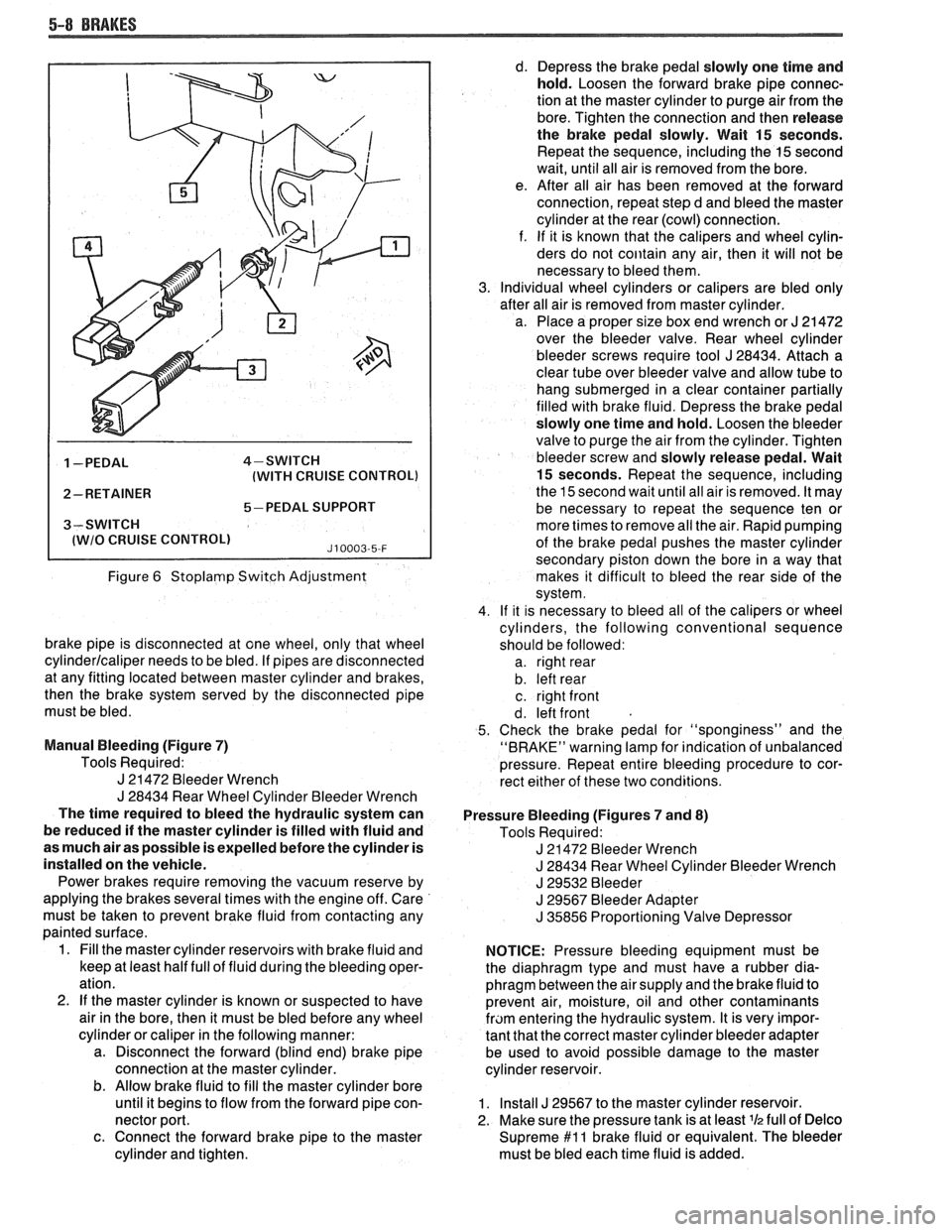
1 -PEDAL 4-SWITCH
(WITH CRUISE CONTROL)
2- RETAINER
5-PEDAL SUPPORT
3-SWITCH
I lWlO CRUISE CONTROLl J10003-5-F
Figure 6 Stoplamp Switch Adjustment
brake pipe is disconnected at one wheel, only that wheel
cylinderlcaliper needs to be bled. If pipes are disconnected
at any fitting located between master cylinder and brakes,
then the brake system served by the disconnected pipe
must be bled.
Manual Bleeding (Figure
7)
Tools Required:
J 21472 Bleeder Wrench
J 28434 Rear Wheel Cylinder Bleeder Wrench
The time required to bleed the hydraulic system can
be reduced if the master cylinder is filled with fluid and
as much air as possible is expelled before the cylinder is
installed on the vehicle.
Power brakes require removing the vacuum reserve by
applying the brakes several times with the engine off. Care
must be taken to prevent brake fluid from contacting any
painted surface.
1. Fill the master cylinder reservoirs with brake fluid and
keep at least half full of fluid during the bleeding oper-
ation.
2.
If the master cylinder is known or suspected to have
air in the bore, then it must be bled before any wheel
cylinder or caliper in the following manner:
a. Disconnect the forward (blind end) brake pipe
connection at the master cylinder.
b. Allow brake fluid to fill the master cylinder bore
until it begins to flow from the forward pipe con-
nector port.
c. Connect the forward brake pipe to the master
cylinder and tighten. d.
Depress the brake pedal slowly one time and
hold. Loosen the forward brake pipe connec-
tion at the master cylinder to purge air from the
bore. Tighten the connection and then release
the brake pedal slowly. Wait
15 seconds.
Repeat the sequence, including the
15 second
wait, until all air is removed from the bore.
e. After all air has been removed at the forward
connection, repeat step d and bleed the master
cylinder at the rear (cowl) connection.
f. If it is known that the calipers and wheel cylin-
ders do not
coiitain any air, then it will not be
necessary to bleed them.
Individual wheel cylinders or calipers are bled only
after all air is removed from master cylinder.
a. Place a proper size box end wrench or
J 21 472
over the bleeder valve. Rear wheel cylinder
bleeder screws require tool
J 28434. Attach a
clear tube over bleeder valve and allow tube to
hang submerged in a clear container partially
filled with brake fluid. Depress the brake pedal
slowly one time and hold. Loosen the bleeder
valve to purge the air from the cylinder. Tighten
bleeder screw and slowly release pedal. Wait
15 seconds. Repeat the sequence, including
the 15 second wait until all air is removed. It may
be necessary to repeat the sequence ten or
more times to remove all the air. Rapid pumping
of the brake pedal pushes the master cylinder
secondary piston down the bore in a way that
makes it difficult to bleed the rear side of the
system.
If it is necessary to bleed all of the calipers or wheel
cylinders, the following conventional sequence
should be followed: a. right rear
b. left rear
c. right front
d. left front
Check the brake pedal for "sponginess" and the
"BRAKE" warning lamp for indication of unbalanced
pressure. Repeat entire bleeding procedure to cor-
rect either of these two conditions.
Pressure Bleeding (Figures
7 and 8)
Tools Required:
J 21472 Bleeder Wrench
J 28434 Rear Wheel Cylinder Bleeder Wrench
J 29532 Bleeder
J 29567 Bleeder Adapter
J 35856 Proportioning Valve Depressor
NOTICE: Pressure bleeding equipment must be
the diaphragm type and must have a rubber dia-
phragm between the air supply and the brake fluid to
prevent air, moisture, oil and other contaminants
fram entering the hydraulic system. It is very impor-
tant that the correct master cylinder bleeder adapter
be used to avoid possible damage to the master
cylinder reservoir.
1. Install J 29567 to the master cylinder reservoir.
2. Make sure the pressure tank is at least
lh full of Delco
Supreme $1 1 brake fluid or equivalent. The bleeder
must be bled each time fluid is added.
Page 347 of 1825

6-2 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION
6E3 - Fuel Injection (Ported) This section has information
on all exhaust
system parts, such as tailpipes, mufflers, and the
SECTION 6F - EXHAUST SYSTEM catalytic converter.
GENERAL INFORMAflION
CLEANLINESS AND CARE
An automobile engine is a combination of many
machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with
tolerances that are measured in the ten-thousandths of
an inch. When any internal engine parts are serviced,
care and cleanliness are important. A liberal coating of
engine oil should be applied to friction areas during
assembly, to protect and lubricate the surfaces on
initial operation. Throughout this section, it should be
understood that proper cleaning and protection of
machined surfaces and friction areas is part of the
repair procedure. This is considered standard shop
practice, even if not specifically stated. PREVENTING
DAMAGE AND IN
CONTRIBUTING TO RELIABLE ENGINE
PERFORMANCE.
When raising or supporting the engine for any
reason, do not use a jack under the oil pan. Due to the
small clearance between the oil pan and the oil pump
screen, jacking against the oil pan may cause it to be
bent against the pump screen resulting in a damaged
oil pick-up unit.
When working on the engine, remember that the
12-volt electrical system is capable of causing short
circuits. When performing any work where electrical terminals could possibly be grounded, the ground cable
of the battery should be disconnected at the battery.
Any time the carburetor or air cleaner is
train components are removed removed, the intake opening should be covered. This for service, they should be in order' will protect against entrance of foreign be installed in the same locations, and with the same material, which could follow the intake passage into mating surfaces, as when removed
the cylinder and cause extensive damage when the -
Battery cables should be disconnected before any engin; is started.
major work is performed on the engine. Failure to IN THE MECHANICAL PROCEDURES
disconnect cables may result in damage to wire harness DESCRIBED IN THIS SECTION, GENERALLY
or other electrical parts. NO
REFERENCES WILL BE MADE TO THE
REMOVAL OF OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT SUCH
ENGINE SERVICE AS POWER STEERING PUMP, AIR
CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR, ETC.
THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION ON SHOULD IT BECOME NECESSARY TO
ENGINE SERVICE SHOULD BE NOTED REMOVE ANY SUCH ITEM TO
PERFORM
CAREFULLY, AS IT IS IMPORTANT IN OTHER SERVICE, REFER TO THE
APPROPRIATE SECTION OF THIS SERVICE
MANUAL FOR SPECIFIC INFORMATION.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION interchangeably for so long, it was necessary to decide
on the most common usage and then define them. If the
Engine Performance procedures are definition is not understood, and the exact Symptom is
guides that will lead to the most probable causes of not used, the Diagnostic procedure will not work. engine performance complaints. They cover the
components of the fuel, ignition, and mechanical It
is important to keep two facts in mind:
systems that could cause a particular
complaint, and 1. The procedures are written to diagnose problems
then outline repairs in a logical sequence. on cars
that have
"run well at one time" and
that time and wear have created the condition.
It is important to determine if the
"Service ~~~i~~ soon- light is "ON,~' or has come for 2. All possible causes cannot be covered,
a short interval while driving. If the
"Service Engine particularly with regard to emission controls. If
Soon" light has come "ON," the Computer doing the work prescribed does not correct the
Command Control System or DECS should be complaint, then either the wrong Symptom was
checked for stored
"Trouble Codes" (See Diagnostic used, or a more detailed analysis will have to be
Circuit Check, Section 6E, for the engine you are made.
working on) which may indicate the cause for the All of the Symptoms can be caused by worn out
performance
complaint.Each Symptom is defined, and or defective parts such as Spark Plugs, Ignition
it is important that the correct one be selected, based Wiring, etc. If time and/or mileage indicate that
on the complaints reported or found. The definition of parts should be replaced, it is recommended that
each symptom is included with the symptom. it
be done.
The words used may not be what you are used to Refer to:
in all cases, but because these terms have been used
@ Section 6E - Driveability and Emissions
Page 348 of 1825

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION 6-3
B, Section 6E2 - Fuel Injection (TBI)
B, Section 6E3 - Fuel Injection (Ported)
ENGINE MECHANICAL DIAGNOSIS
The following diagnostic information covers common problems and possible causes. When
the proper diagnosis is made, the problem should be corrected by adjustment, repair or part
replacement as required. Refer to the appropriate section of the manual for these procedures.
EXCESSIVE OIL LOSS
B, External oil leaks. Tighten bolts and/or replace o Continuous high speed driving, and/or severe
gaskets and seals as necessary. usage
such as trailer hauling, will normally cause
decreased oil mileage.
e Improper reading of dipstick. Check oil with car PCV system malfunctioning. on a level surface and allow adequate drain-down Valve guides and/or valve stem seals worn, or time.
seals omitted. Ream guides and install oversize
service valves and/or new valve stem seals.
Improper Use S.A'E' Piston rings broken, worn, or not seateded. Allow viscosity for prevailing temperatures. See
adequate time for rings to seat. Replace broken
Owner's Manual for proper specifications.
or worn rings, as necessary.
Piston improperly installed or misfitted.
LOW OIL PRESSURE
Slow idle speed. Set idle speed to correct
specification, if not ECM controlled.
Incorrect, or malfunctioning, oil pressure switch.
Incorrect, or malfunctioning, oil pressure gage.
Replace with proper gage.
.*
Improper oil viscosity, or diluted oil. install oil of
proper viscosity for expected temperature, or
install new oil if diluted with moisture or
unburned fuel mixtures.
o Oil pump worn or dirty.
e Plugged oil filter.
e Oil pickup screen loose or plugged.
B, Hole in oil pickup tube.
e Excessive bearing clearance. Replace if necessary.
o Cracked, porous or plugged oil galleys. Repair or
replace block.
o Galley plugs missing or misinstalled. Install
plugs, or repair as necessary.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE
e Low oil pressure. Repair as necessary. (See o Broken valve spring.
preceding diagnosis for low oil pressure.)
o Sticking valves.
o Loose rocker arm attachments. Inspect and B, Lifters worn, dirty, or defective. Clean, inspect,
test and replace as necessary.
repair as necessary.
o Camshaft worn, or poor machining. Replace
o Worn rocker arm and/or pushrod. camshaft.
B, Worn valve guides.
ENGINE KNOCK DIAGNOSIS
KNOCKS COLD AND CONTINUES FOR TWO TO THREE MINUTES
INCREASES
WITH TORQUE
o Vacuum operated EFE engines may have valve o Excessive piston to bore clearance. Replace
knock. Replace EFE valve. piston.
e Flywheel contacting splash shield. Reposition
splash shield.
e Loose or broken balancer or drive pulleys.
Tighten, or replace as necessary. Cold engine piston knock usually
disappears when the cylinder is grounded
out. Cold engine piston knock which
disappears in 1.5 minutes should be
considered acceptable.
Page 349 of 1825

6-4 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION
Bent connecting rod.
HEAVY KNOCK H0"FVVI"F TORQUE APPLIED
Broken balancer, or pulley hub. Replace parts as e Exhaust system grounded. Reposition as
necessary. necessary.
Loose torque converter bolts. Flywheel
cracked.
e Excessive main bearing clearance. Replace as
Accessory belts too tight or nicked. Replace
necessary.
and/or tension to specs as necessary.
e Excessive rod bearing clearance. Replace as
necessary.
LIGHT KNOCK HOT
Detonation or spark knock. Check operation of e Loose torque converter bolts.
EST or ESC (See Section
6D or 6E). Check e Exhaust leak at manifold. Tighten bolts and/or
engine timing and fuel quality.
replace gasket.
8 Excessive rod bearing clearance. Replace
bearings as necessary.
KNOCKS ON INITIAL START-UP BUT ONLY LASTS A FEW SECONDS
Noisy mechanical fuel pump. Replace pump.
When the engine is stopped, some valves
will be open. Spring pressure against lifters
Improper oil viscosity. Install proper oil viscosity will
tend to bleed lifter down. Attempts to
for expected temperatures. See Owner's Manual. repair
should be made only if the problem
is consistent.
Hydraulic lifter bleed down. Clean, test and @ Excessive crankshaft end clearance. Replace
replace as necessary. crankshaft
thrust bearing.
@ Excessive front main bearing clearance. Replace
worn parts.
KNOCKS AT IDLE HOT
Loose or worn drive belts. Tension and/or @ Excessive piston pin clearance. Ream and install
replace as necessary. oversize pins. (VIN R and 2) or replace piston
A/C Compressor or generator bearing. Replace and
pin.
as necessary.
e Connecting rod alignment. Check and replace
rods as necessary.
Noisy mechanical fuel pump. Replace pump.
8 Insufficient piston to bore clearance. Hone bore
Valve train. Replace parts as necessary. and
fit new piston.
@ Loose crankshaft balancer. Torque and/or
Improper oil viscosity. Install proper viscosity oil
replace worn parts.
for expected temperature4 See Owner" e Piston pin offset to wrong side. Install correct
ENGINE OVERHEATS
Coolant system leak, oil cooler system leak, or
2. Belt slipping or damaged. Replace tensioner, or
coolant recovery system not operating. Check for belt, as required.
leaks and correct as required. Check coolant
3. Thermostat stuck closed. Check and replace if
recovery tank, hose and radiator cap.
required.
4. Electrical cooling fan operation. See the
ELECTRICAL TROUBLESHOOTING
MANUAL.
5. Head gasket leaking. Check and repair as
required.
Page 350 of 1825

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION 6-5
INSTRUMENT PANEL OIL WARNING LAMP "ON" AT IDLE
1. Oil cooler, or oil or cooler line restricted. Remove 2. Oil pump pressure low. See oil pump repair
restrictions in cooler or cooler line. procedures
in Section
6A.
ENGINE COMPRESSION EST
COMPRESSION TEST
Important
e Disconnect the "BAT." terminal from the - HE1 distributor or ignition module.
To determine if the valves or pistons are at fault,
a test should be made to determine the cylinder
compression pressure. When checking cylinder
compression, the throttle and choke should be open, all
spark plugs removed, and the battery at or near full
charge. The lowest reading cylinder should not be less
than
70% of the highest and no cylinder reading
should be less than
689 kPa (100 PSI). This
should be done with four
"puffs" per
cylinder.
Normal - Compression builds up quickly and
evenly to specified compression on each cylinder.
Piston Rings - Compression low on first
stroke, tends to build up on following strokes, but does
not reach normal. Improves considerably with addition
of oil.
Valves - Low on first stroke, does not tend to
build up on following strokes. Does not improve much
with addition of oil.
Use approximately three squirts from a plunger
type oiler.
Page 358 of 1825
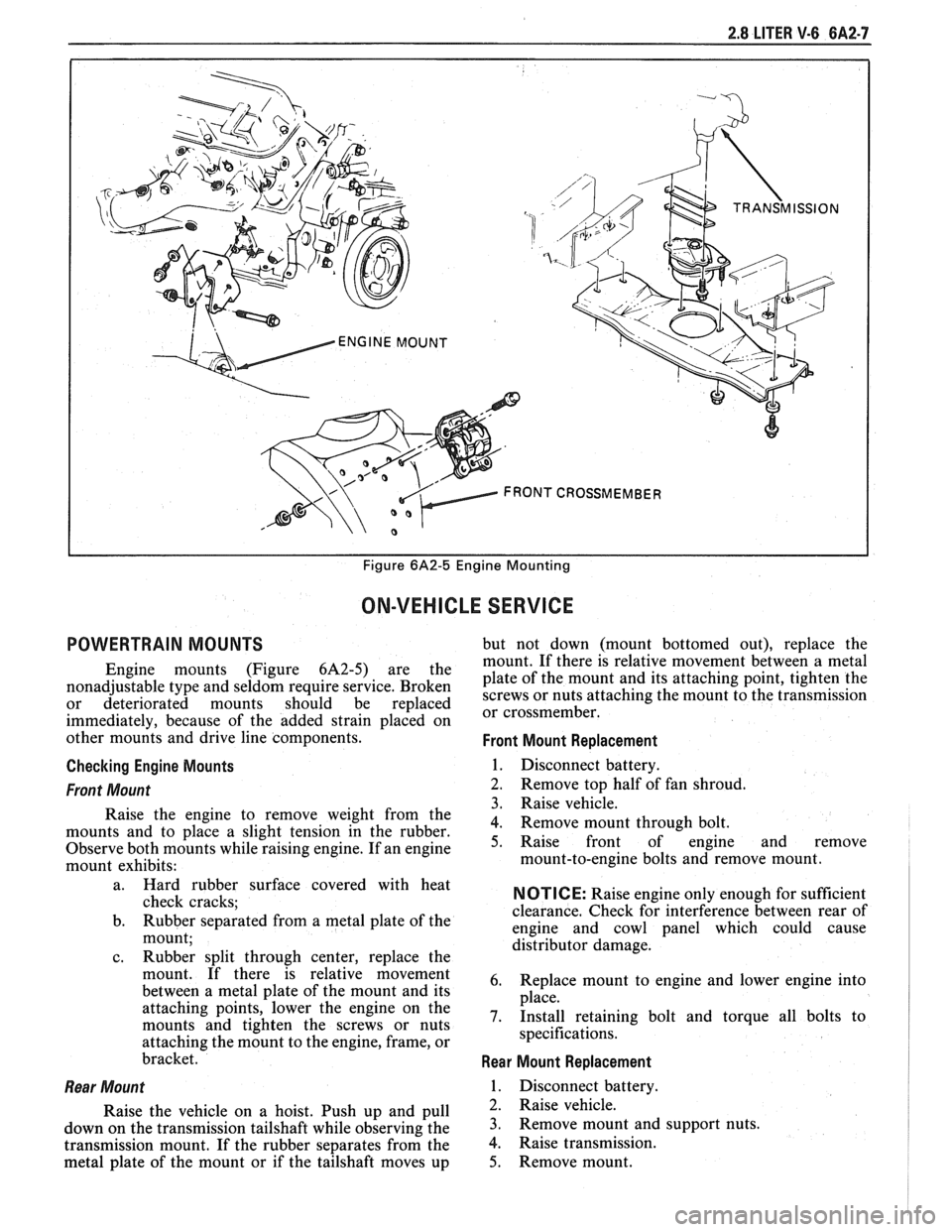
2.8 LITER V-6 6A2-7
I I Figure 6A2-5 Engine Mounting
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
POWERTRAIN MOUNTS but not down (mount bottomed out), replace the
mount. If there is relative movement between a metal
Engine mounts (Figure 6A2-5) are the plate of the mount and its attaching point, tighten the nonadjustable type and seldom require service. Broken screws or nuts attaching the mount to the transmission or deteriorated mounts should be replaced or cross member^
immediately, because of the added strain placed on
other mounts and drive line components.
Front Mount Replacement
Checking Engine Mounts
1. Disconnect battery.
Front Mount 2. Remove top half of fan shroud.
3. Raise vehicle.
Raise the engine to remove weight from the
4. Remove mount through bolt. mounts and to place a slight tension in the rubber.
Observe both mounts while raising engine. If an engine 5. Raise front of engine and remove
mount exhibits: mount-to-engine
bolts and remove mount.
l
a. Hard rubber surface covered with heat
check cracks;
b. Rubber separated from a metal plate
of the
mount;
c. Rubber split through center, replace the
mount. If there is relative movement
between a metal plate of the mount and its
attaching points, lower the engine on the
mounts and tighten the screws or nuts
attaching the mount to the engine, frame, or
bracket.
Rear Mount
Raise the vehicle on a hoist. Push up and pull
down on the transmission tailshaft while observing the
transmission mount. If the rubber separates from the
metal plate of the mount or if the tailshaft moves up
NOTICE: Raise engine only enough for sufficient
clearance. Check for interference between rear of
engine and cowl panel which could cause
distributor damage.
6. Replace mount to engine and lower engine into
place.
7. Install retaining bolt and torque all bolts to
specifications.
Rear Mount Replacement
1. Disconnect battery.
2. Raise vehicle.
3. Remove mount and support nuts.
4. Raise transmission.
5. Remove mount.
Page 360 of 1825

2.8 LITER V-6 6A2-9
INTAKE MANIFOLD (FIGURE 6A2-7)
Removal
Disconnect battery.
Remove air cleaner.
Drain coolant.
Refer to Section 6E3 for removal of the following
PFI sub-assemblies.
e Plenum
e Fuel Rail
e Runner
Disconnect spark plug wires at spark plugs.
Disconnect wires at coil.
Remove distributor cap and spark plug wires.
Mark distributor position and remove hold down
bracket.
Remove distributor.
Remove air management hose, manual
transmission only.
Disconnect emission canister hoses. Remove pipe
bracket (front left valve cover).
Remove left valve cover.
Remove air management bracket, manual
transmission only.
Remove right valve cover.
Remove upper radiator hose.
Disconnect heater hose.
Disconnect coolant switches.
Remove manifold bolts.
Remove manifold. Discard manifold gaskets and
remove loose RTV from front and rear ridges of
cylinder case.
Installation
When installing intake gaskets, notice that the
gaskets are marked Right Side and Left Side
(carbureted only). Use them only as indicated to
maintain designed efficiency of this engine.
1. Make
sure that no oil or water is present on
surface when new RTV is applied. Place a 5mm
diameter
(3/16") bead of RTV, # 1052917 or
equivalent, on each ridge.
2. Install
new intake gaskets on cylinder heads.
Hold in place by extending ridge RTV bead up
6mm onto the gasket ends. The new intake
gaskets will have to be cut, where indicated, to
install behind push rods. Cut only those areas
that are necessary.
3. Install intake
manifold on engine. Make sure
areas between case ridges and intake are
completely sealed.
4. Install manifold retaining bolts and nuts and
torque in the sequence shown in Figure 6A2-7.
5. Install heater and radiator hose to manifold.
6. Install rocker covers as previously outlined.
7. Connect coolant switches.
8. Install air management bracket.
9. Install pipe bracket (front left rocker cover).
10. Install distributor, distributor cap and retaining
nut. Do not tighten.
11. Refer to Section 6E3 for installation of PFI
sub-assemblies removed. 12.
Connect
necessary wires and hoses.
13. Fill cooling system with
the proper mixture of
ethylene glycol anti-freeze and water. Do not
install radiator cap.
14. Start
engine, set intitial timing. After set, torque
distibutor hold down clamp bolt to 34
N-m (25
lb. ft.). Recheck timing after torquing bolt.
15. Let engine
run until radiator upper hose becomes
hot (thermostat open).
16. With
engine idling, add coolant to radiator, if
necessary, until level reaches bottom of filler
neck.
17. Install
radiator cap, making sure arrows on cap
line up with overflow tube.
Figure 6A2-8 Exhaust Manifold
EXHAUST MANIFOLD (FIGURE 6A2-8)
Removal (Left)
1. Disconnect battery.
2. Raise vehicle.
3. Disconnect exhaust pipe.
4. Remove
(4) rear manifold bolts and (1) nut.
5. Lower vehicle.
6. Disconnect air management, hoses and wires.
7. Remove power steering and fuel line bracket.
8. Remove manifold.
Installation (Left)
1. Clean mating surfaces on manifold and head,
then install manifold in position and install bolts.
2. Torque
manifold bolts to 34
N.m (25 ft. lbs.).
3. Install power steering bracket.
4. Raise vehicle.
5. Install exhaust pipe.
6. Lower vehicle.
7. Connect battery.
Removal (Right)
1. Disconnect battery.
2. Raise vehicle.
3. Disconnect exhaust pipe.
4. Lower vehicle.
Page 361 of 1825

6A2-10 2.8 LITER V-6
5. Remove air management valve from A.I.R.
pump. 6. Remove alternator bracket.
7. Remove exhaust manifold bolts.
8. Disconnect air management hose.
9. Remove manifold.
Installation (Right)
1. Clean
mating surfaces on manifold and head,
then install manifold in position and install bolts.
2. Torque
manifold bolts to 34
N-m (25 ft. lbs.).
3. Attach air management hose.
4. Raise vehicle.
5. Install exhaust pipes.
6. Lower vehicle.
7. Install alternator bracket.
8. Install air management valve.
7. Connect battery.
Figure 6A2-9 Rocker Arm and Push Rods
ROCKER ARM AND PUSH ROD (FIGURE 6A2-9)
Removal
1. Remove
rocker arm cover as previously outlined.
2. Remove rocker arm nuts, rocker arm balls,
rocker arms and push rods. Place components in
a rack so they can be reinstalled in the same
location.
lnstallation and Adiustment
Whenever new rocker arms and/or rocker arm
balls are being installed, coat bearing surfaces of rocker
arms and rocker balls with a thin even coating of
"Molykote" or its equivalent.
1. Install push rods. Be sure push rods seat in lifter.
2. Install rocker arms, rocker arm balls and rocker
arm nuts. Tighten rocker arm nuts until all lash
is eliminated.
3. Adjust valves when lifter is on base circle of
camshaft lobe as follows:
a. Crank engine until mark on torsional
damper lines up with
"0" mark on the
timing tab. The engine should also be in the
# 1 firing position. This may be determined
Figure 6A2-10 Adjusting Valve Lash
by placing fingers on the # 1 rocker arms as
the mark on the damper comes near the
"0"
mark. If the valves are not moving, the
engine is in the
# 1 firing position. If the
valves move as the mark comes up to the
timing tab, the engine is in the
#4 firing
position and should be rotated one
revolution to reach the
# 1 position.
b. With the
engine in the
# 1 firing position,
the following valves may be adjusted.
Exhaust 1, 2, 3
Intake 1, 5,
6
c. Back
out adjusting nut until lash is felt at
the push rod, then turn in adjusting nut
until all lash is removed (Figure
6A2-10).
(This can be determined by rotating push
rod while turning adjusting nut). When lash
has been removed, turn adjusting nut in
1-1/2 additional turns (to center lifter
plunger).
d. Crank the
engine one revolution until the
timing tab
"0" mark and torsional damper
mark are again in alignment. This is the
#4
firing position. With the engine in this
position, the following valves may be
adjusted:
Exhaust 4, 5,
6
Intake 2, 3, 4
4.
Install rocker arm covers as previously outlined.
5. Start
engine and check timing and idle speed.
VALVE MECHANISM
Valve Stern Oil Seal and/or Valve Spring (Figure
6A2-12)
Removal
1. Remove rocker
arm cover as previously outlined.
2. Remove spark plug, rocker arm and push rod on
the
cylinder(s) to be serviced.
3. Install
air line adapter Tool J-23590 to spark plug
port and apply compressed air to hold the valves
in place.