1988 PONTIAC FIERO oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 752 of 1825
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 2.8L (VIN 5) 6E3-C2-17
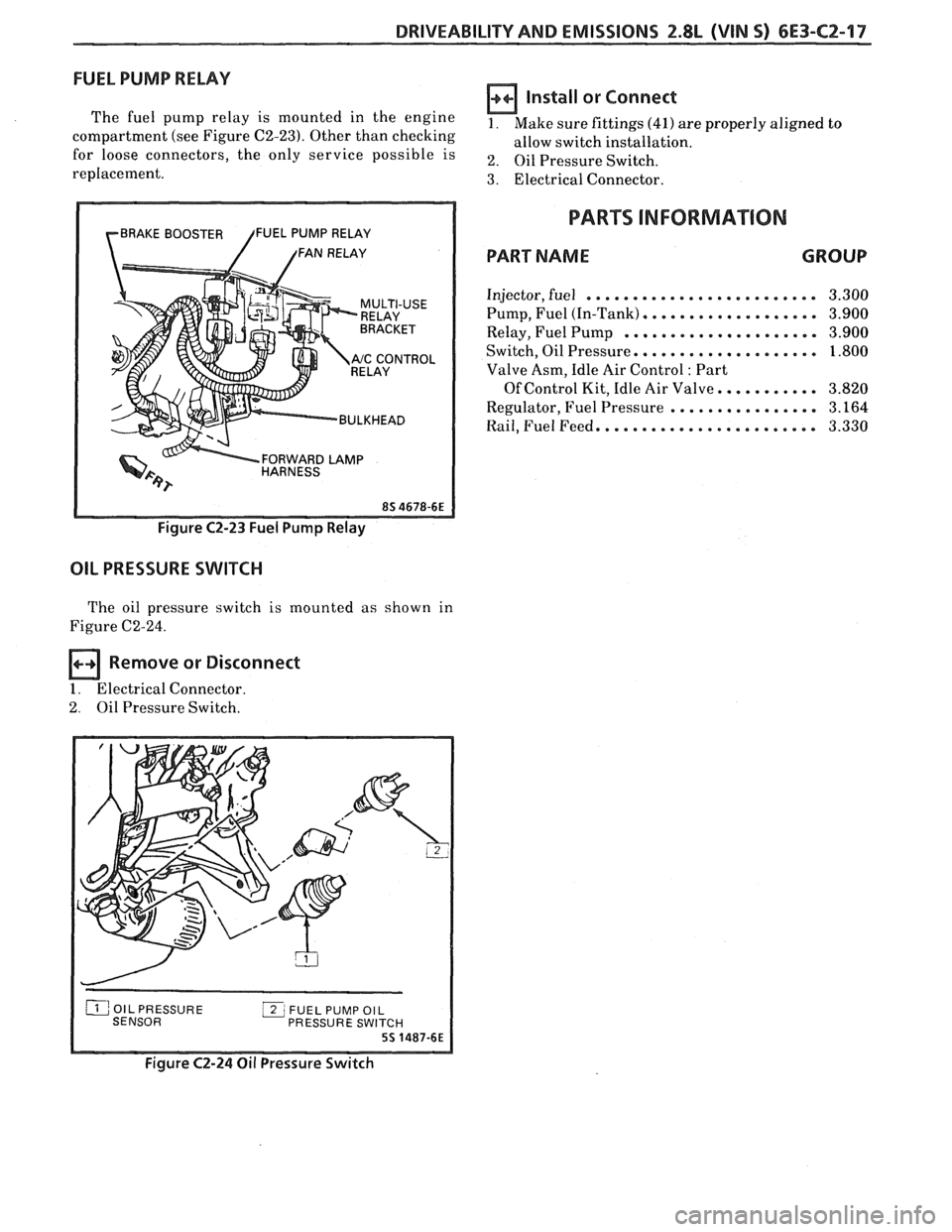
FUEL PUMP RELAY
The fuel pump relay is mounted in the engine
compartment (see Figure C2-23). Other than checking
for loose connectors, the only service possible is
replacement.
rBRAKE BOOSTER /FUEL PUMP RELAY
/ /FAN RELAY
RELAY
Y '"ccONT"L
BULKHEAD
FORWARD
LAMP HARNESS
Figure C2-23 Fuel Pump Relay
OIL PRESSURE SWITCH
The oil pressure switch is mounted as shown in
Figure C2-24.
Remove or Disconnect
1. Electrical Connector.
2. Oil Pressure Switch.
Install or Connect
1. Make sure fittings (41) are properly aligned to
allow switch installation.
2. Oil Pressure Switch.
3. Electrical Connector.
PARTS INFORMATION
PART NAME GROUP
Injector, fuel ......................... 3.300
Pump, Fuel (In-Tank)
................... 3.900
Relay, Fuel Pump
..................... 3.900
Switch, Oil Pressure.
................... 1.800
Valve Asm, Idle Air Control
: Part
Of Control Kit, Idle Air Valve.
.......... 3.820
Regulator, Fuel Pressure
................ 3.164
Rail, Fuel Feed. ....................... 3.330
PRESSURE SWI
Figure C2-24 Oil Pressure Switch
Page 753 of 1825

6E3-C2-18 2.8L (VIN S) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CHART C-2A
INJECTOR BALANCE TEST
The injector balance tester is a tool used to turn the injector on for a precise
amount of time, thus spraying a measured amount of fuel into the manifold.
This causes a drop in fuel rail pressure that we can record and compare between
each injector. All injectors should have the same amount of pressure drop
( k 10
kpa). Any injector with a pressure drop that is 10 kpa (or more) greater or less
than the average drop of the other injectors should be considered faulty and
replaced.
Engine "cool down" period
(10 minutes) is necessary to avoid irregular
readings due to "Hot Soak" fuel boiling. With ignition
"OFF" connect fuel gauge
5347301 or equivalent to fuel pressure tap. Wrap a shop towel around fitting
while connecting gage to avoid fuel spillage.
Disconnect harness connectors at all injectors, and connect injector tester
J-
34730-3, or equivalent, to one injector. On Turbo equipped engines, use adaptor
harness furnished with injector tester to energize injectors that are not
accessible. Follow manufacturers instructions for use of adaptor harness.
Ignition must be
"OFF" at least 10 seconds to complete ECM shutdown cycle.
Fuel pump should run about
2 seconds after ignition is turned "ON". At this
point, insert clear tubing attached to vent valve into a suitable container and
bleed air from gauge and hose to insure accurate gauge operation. Repeat this
step until all air is bled from gauge.
STEP 2
Turn ignition "OFF" for 10 seconds and then "ON" again to get fuel pressure
to its maximum. Record this initial pressure reading. Energize tester one time
and note pressure drop at its lowest point (Disregard any slight pressure
increase after drop hits low point.). By subtracting this second pressure reading
from the initial pressure, we have the actual amount of injector pressure drop.
STEP 3
Repeat step 2 on each injector and compare the amount of drop. Usually, good
injectors will have virtually the same drop. Retest any injector that has
a
pressure difference of lOkPa, either more or less than the average of the other
injectors on the engine. Replace any injector that also fails the retest. If the
pressure drop of all injectors is within
lOkPa of this average, the injectors
appear to be flowing properly. Reconnect
them and review "Symptoms," Section
"B".
NOTE: The entire test should not be repeated more than once without
running the engine to prevent flooding. (This includes any retest on
fa ulty injectors).
Page 755 of 1825
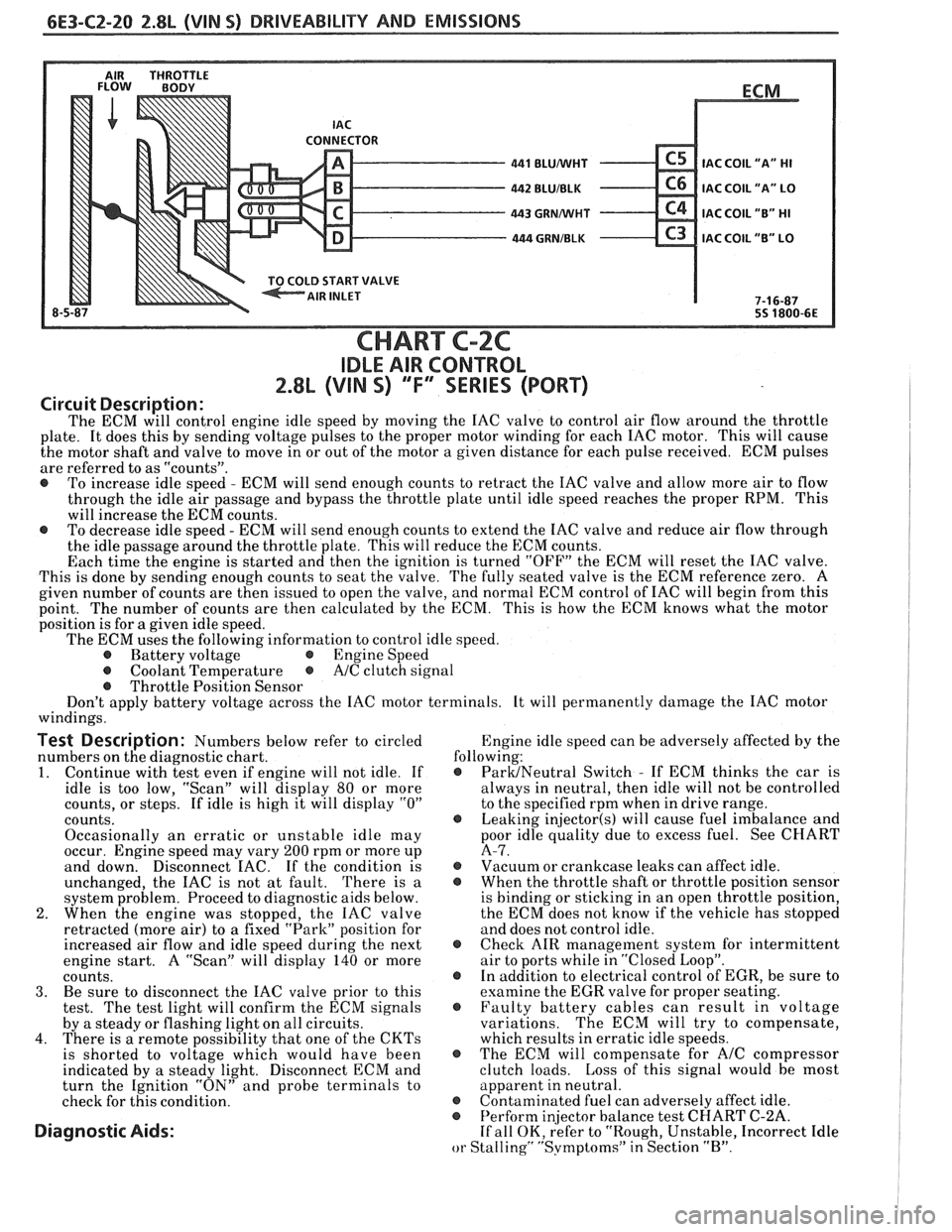
6E3-C2-20 2.8L (VIN S) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
AIR THROTTLE FLOW BODY
LD START VALVE
8-5 BLUNVHT
BLUIBLK
GRMNVHT
. GRNIBLK
ECM
.
IAC COIL
"A" HI
IAC COIL "A" LO
IAC COIL "B" HI
C3 IAC COIL "B" LO
7-1 6-87
55 1800-6E
CHART C-2C
IDLE AIR CONTROL
2.8L (VIN S) ""F-SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The ECM will control engine idle speed by moving the IAC valve to control air flow around the throttle
plate. It does this by sending voltage pulses to the proper motor winding for each IAC motor. This will cause
the motor shaft and valve to move in or out of the motor a given distance for each pulse received. ECM pulses
are referred to as "counts".
@ To increase idle speed - ECM will send enough counts to retract the IAC valve and allow more air to flow
through the idle air passage and bypass the throttle plate until idle speed reaches the proper RPM. This
will increase the ECM counts.
@ To decrease idle speed - ECM will send enough counts to extend the IAC valve and reduce air flow through
the idle passage around the throttle plate. This will reduce the ECM counts.
Each time the engine is started and then the ignition is turned "OFF" the ECM will reset the IAC valve.
This is done by sending enough counts to seat the valve. The fully seated valve is the ECM reference zero. A
given number of counts are then issued to open the valve, and normal ECM control of IAC will begin from this
point. The
number of counts are then calculated by the ECM. This is how the ECM knows what the motor
position is for
a given idle speed.
The ECM uses the following information to control idle speed.
@ Battery voltage @ Engine Speed
@ Coolant Temperature @ A/C clutch signal
@ Throttle Position Sensor
Don't apply battery voltage across the IAC motor terminals. It will permanently damage the IAC motor
windings.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled Engine
idle speed can be adversely affected by the
numbers on the diagnostic chart. following:
1. Continue
with test even if engine will not idle. If @ ParUNeutral Switch - If ECM thinks the car is
idle is too low, "Scan" will display
80 or more always
in neutral, then idle will not be controlled
counts, or steps. If idle is high it will display
"0" to the specified rpm when in drive range.
counts.
@ Leaking injector(s) will cause fuel imbalance and
Occasionally an erratic or unstable idle may poor
idle quality due to excess fuel. See CHART
occur. Engine speed may vary
200 rpm or more up A-7.
and down. Disconnect
EAC. If the condition is @ Vacuum or crankcase leaks can affect idle.
unchanged, the IAC is not at fault. There is
a @ When the throttle shaft or throttle position sensor
system problem. Proceed to diagnostic aids below. is
binding or sticking in an open throttle position,
2. When the engine was stopped, the IAC valve the
ECM does not know if the vehicle has stopped
retracted (more air) to a fixed "Park" position for and does not control idle.
increased air flow and idle speed during the next
@ Check AIR management system for intermittent
engine start. A "Scan" will display
140 or more air
to ports while in "Closed Loop".
counts. @ In addition to electrical control of EGR, be sure to
3. Be sure to disconnect the IAC valve prior to this examine the
EGR valve for proper seating.
test. The test light will confirm the ECM signals @ Faulty battery cables can result in voltage
by a steady or flashing light on all circuits. variations. The
ECM will try to compensate,
4. There is a remote possibility that one of the CKTs which results in erratic idle speeds.
is shorted to voltage which would have been @ The ECM will compensate for A/C compressor
indicated by a steady light. Disconnect ECM and clutch
loads. Loss of this signal would be most
turn the Ignition "ON" and probe terminals to apparent
in neutral.
check for this condition.
@ Contaminated fuel can adversely affect idle. @ Perform in
or Stalling" "Svmptoms" in Section "B".
Page 765 of 1825

6E3-C4-2 2.8L (WIN S) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION
An open or ground in the EST circuit will set a
Code 42 and cause the engine to run on the HE1
module timing. This will cause reduced performance
and poor fuel economy.
The ECM uses information from the
MAF and
coolant sensors in addition to rpm to calculate spark
~tdvance as follows:
@ Cold engine = more spark advance.
@ Engine under minimum load based on rpm
and low amount of air flow- more spark
advance. Hot engine
= less spark advance.
@ Engine under heavy load based on rprn and
high amount of air flow- less spark advance.
The description, operation, and diagnosis of the
HE1 system are found in Section "GD" of this manual.
CODE 12
Code 12 is used during the Diagnostic Circuit
Check procedure to test the code display ability of the
ECM. This code indicates that the ECM is not
receiving the engine
rpnl (REFERENCE) signal. This
occurs with the ignition key "ON" and the engine not
running.
The "Reference" signal also triggers the fuel
injection system. Without the "Reference" signal the
engine cannot run.
OM-CAR SERVICE
SETTING TIMING
The initial base timing is set by disconnecting the
timing connector, located near the blower motor.
Refer to Emission Control Information Label for
procedure.
This will cause Code 42 to store in the code
memory of the ECM.
The memory must be cleared
after setting timing.
How Code 42 Is Determined
When the system is running on the HE1 module,
that is no voltage on the bypass line, the
HE1 module
grounds the EST signal.
The ECk1 expects to see no
voltage
on the EST line during this condition. If it sees
a voltage, it sets code 42 and will not go into the EST
mode.
When the rpm for EST
is reachecl bout 300 rprn)
the ECM applies 5 volts to the bypass line and the E:SrI'
should no longer be grounded in the tIEI nodule so
the EST voltage should be varying.
If the bypass line is open or grounclecl, the IIEI
tnod~lle will not switch to EST mode so the EST
voltage will be low
and Code 42 will be set. Refer to
Section
"611" for on vehicle service.
PARTS INFORMATION
PART NAME GROUP
Controller, ECM
(Remanufi~ctured) ................ 3.670
.......................... Distributor 2.36 1
Module, Distr ........................ 3.380
........................... Coil, Distr 2.170
Page 767 of 1825
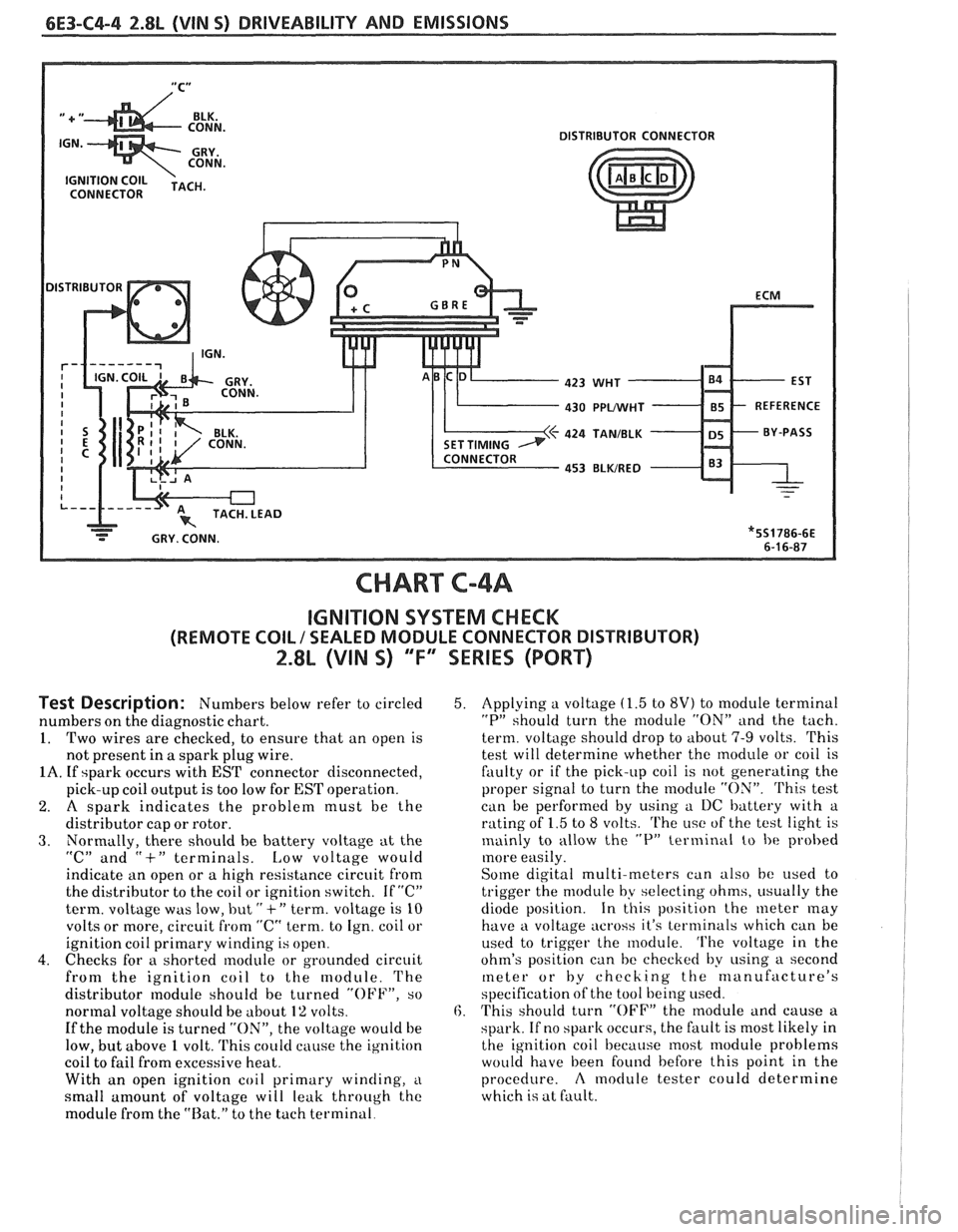
6E3-C4-4 2.8L (VIN S) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
430 PPLMlHT - 85 - REFERENCE
424
TANIBLK
453 BLWRED
CHART C-4A
IGNITION SYSTEM CHECK
(REMOTE COIL / SEALED MODULE CONNECTOR DISTRIBUTOR)
2.8L (VIN 5) "F" SERIES (PORT)
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Two wires are checked, to ensure that an open is
not present in
a spark plug wire.
1A. If spark occurs with EST connector disconnected,
pick-up coil output is too low for
EST operation.
2. A spark indicates the problem must be the
distributor cap or rotor.
3. Normally, there should he battery voltage at the
"C" and "+" terminals. Low voltage would
indicktte an open or a high resistance circuit from
the distributor to the coil or ignition switch. If
"C"
term. voltage was low, but " +" term. voltage is 10
volts or more, circuit from "C" term. to Ign. coil or
ignition coil primary winding is open.
4. Checks for a shorted module or grounded circuit
from the ignition coil to the module. The
distributor
nodule should be turned "OFF", so
normal voltage should be about
1% volts.
If the module is turned "ON", the voltage would be
low, but above
1 volt. 'I'his could cause the ig~lition
coil to fail from excessive heat.
With an open ignition coil primary
winding, i~
small amount of voltage will leak through the
module from the "Rat." to the tach terminal.
5. Applying a voltage (1.5 to 8V) to module terminal
"P" should turn the nlodule "ON" and the tach.
term. voltage should drop to about
7-9 volts. This
test will determine whether the module or coil is
faulty or if the pick-up coil is not generating the
proper signal to turn the
rnodule "ON". 'Phis test
can be performed by using a I)C battery with a
rating of
1.5 to 8 volts. The i~sc of the test light is
mainly to allow the
"P" terminal to be probed
more easily.
Some digital multi-meters can also be used t,o
trigger the module by selecting ohms, i~sually the
diode position. In this position the meter
may
have a voltage across it's terminals which can be
used to trigger the module.
'I'he voltage in the
ohm's position can be checked by
using a second
meter or by checking the manufacture's
specification of the tool being used.
6. This should turn "OFF" the nlodule and cause a
spark. If no
spark occurs, the fault is most likely in
the ignition coil because most module problems
would have been found before this point in the
procedure.
A moclule tester could determine
which is at fault.
Page 768 of 1825
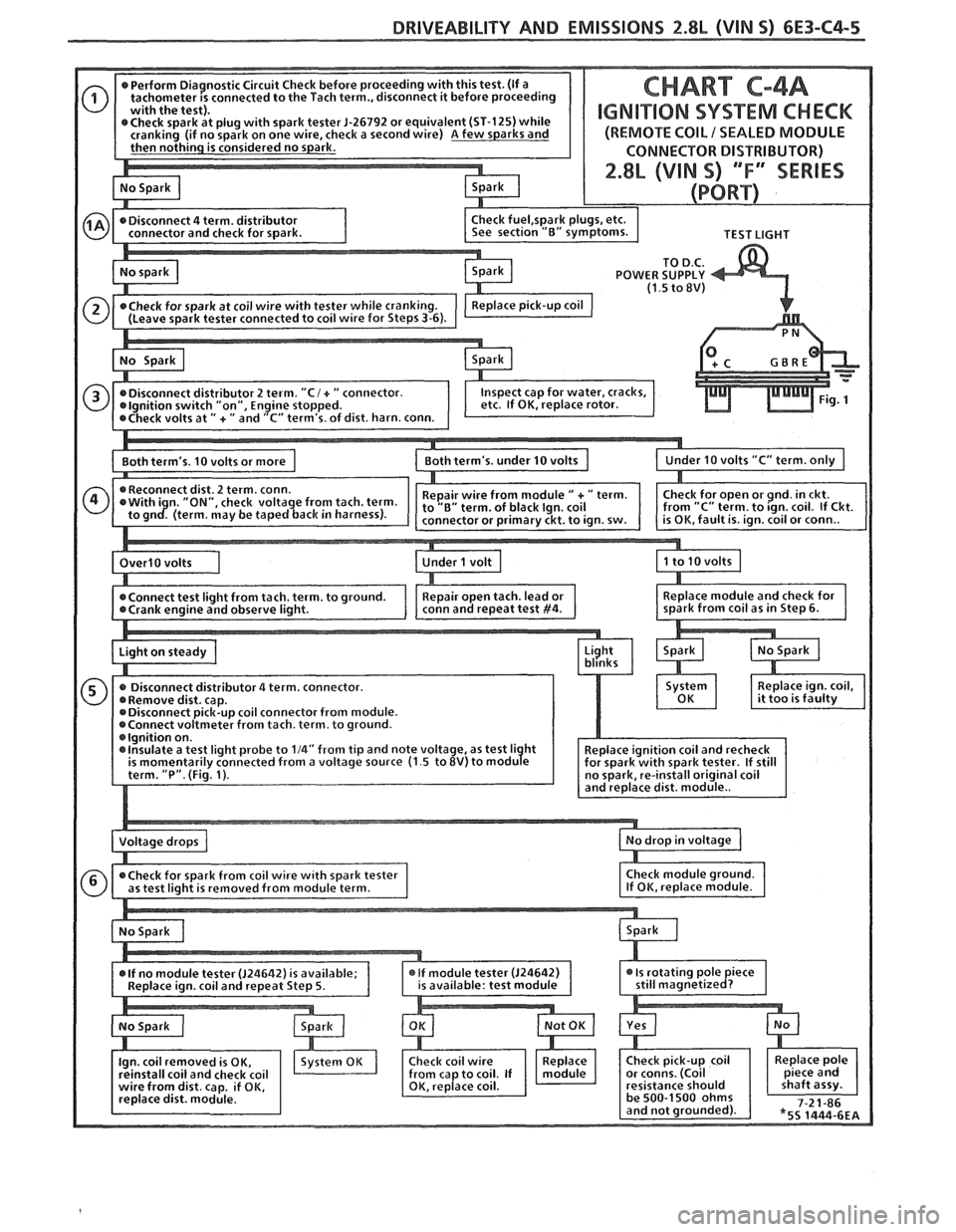
DRlVEABlLlTY AND EMISSIONS 2.8L (VIN S) 6E3-C4-5
r J-26792 or equivalent (ST-125) while IGNI"PION SYSTEM CHECK
eck a second wire) A few sparks and
POWER SUPPLY
coil connector from module.
from tach. term. to ground.
Page 771 of 1825
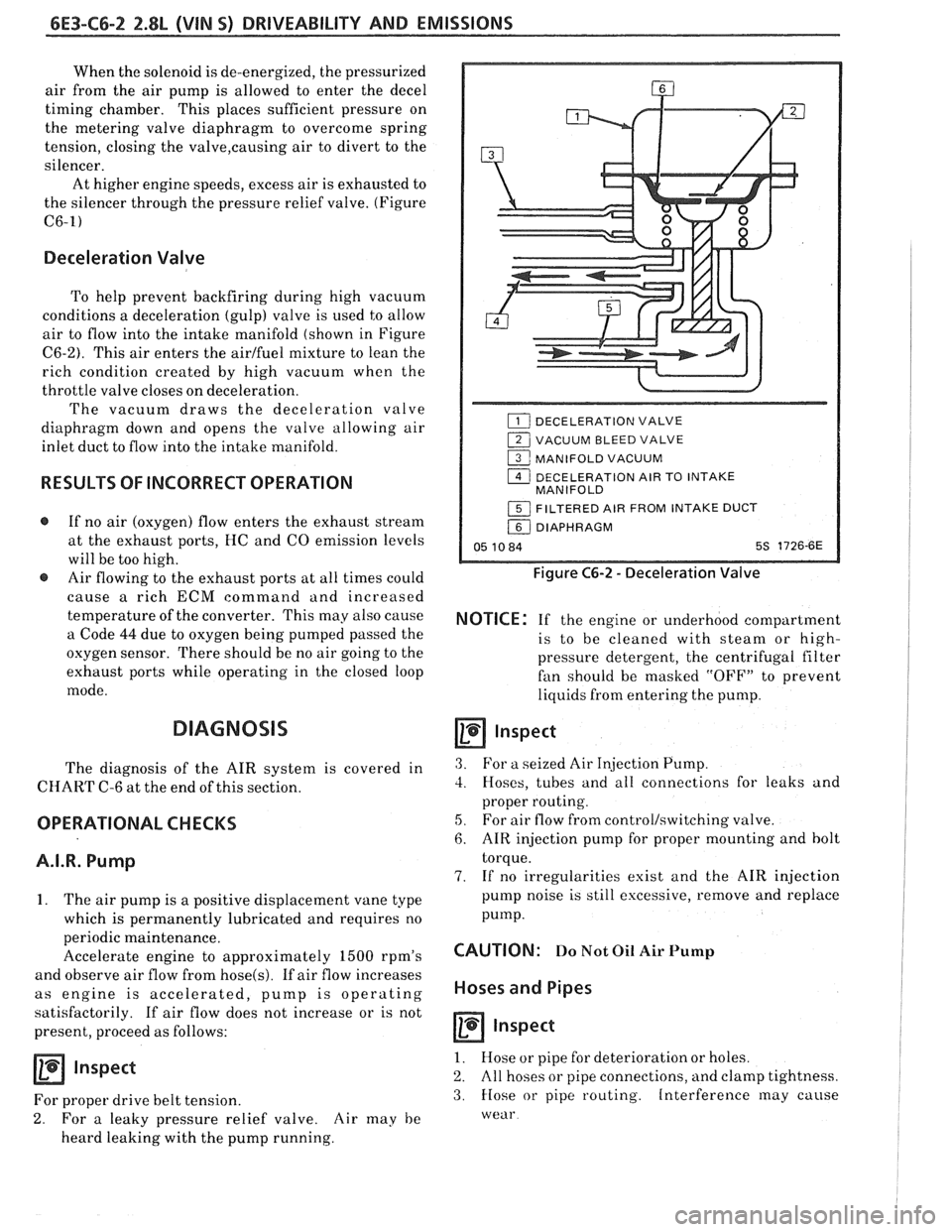
6E3-C6-2 2.8L (WIN 5) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
When the solenoid is de-energized, the pressurized
air from the air pump is allowed to enter the decel
timing chamber. This places sufficient pressure on
the metering valve diaphragm to overcome spring
tension, closing the
valve,causing air to divert to the
silencer.
At higher engine speeds, excess air is exhausted to
the silencer through the pressure relief valve. (Figure
C6-1)
Deceleration Valve
To help prevent backfiring during high vacuum
conditions a deceleration (gulp) valve is used to allow
air to flow into the intake manifold (shown in Figure
C6-2). This air enters the airlfuel mixture to lean the
rich condition created by high vacuum when the
throttle valve closes on deceleration.
The vacuum draws the deceleration valve
diaphragm down and opens the valve allowing air
inlet duct to flow into the intake manifold.
RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION
@ If no air (oxygen) flow enters the exhaust stream
at the exhaust ports, HC and
CO emission levels
will be too high.
@ Air flowing to the exhaust ports at all times could
cause
a rich ECM command and increased
temperature of the converter. This may also cause
a Code
44 due to oxygen being pumped passed the
oxygen sensor. There should be no air going to the
exhaust ports while operating in the closed loop
mode.
DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis of the AIR system is covered in
CHART C-6 at the end of this section.
OPERATIONAL CHECKS
A.I.R. Pump
1. The air pump is a positive displacement vane type
which is permanently lubricated and requires no
periodic maintenance.
Accelerate engine to approximately
1500 rpm's
and observe air flow from
hose(s). If air flow increases
as engine is accelerated, pump is operating
satisfactorily. If air flow does not increase or is not
present, proceed as follows:
Inspect
For proper drive belt tension.
2. For a leaky pressure relief valve. Air may he
heard leaking with the pump running.
DECELERATION VALVE
1 VACUUM BLEED VALVE
1 MANIFOLD VACUUM
1 DECELERATION AIR TO INTAKE
MANIFOLD
1 FILTERED AIR FROM INTAKE DUCT
/ DIAPHRAGM
05 10 84 5s 1726-6E
Figure C6-2 - Deceleration Valve
NOTICE: If the engine or underhood compartment
is to he cleaned with
steam or high-
pressure detergent, the centrifugal filter
fan should be masked "OFF7' to prevent
liquids from entering the pump.
Inspect
3. For a seized Air Injection Pump.
3. Hoses, tubes and all connections for leaks and
proper routing.
5, For air flow from controllswitching valve.
6. AIR injection pump for proper mounting and bolt
torque.
7. If no irregularities exist and the AIR injection
pump noise is still excessive, remove and replace
pump.
CAUTION: Do Not Oil Air Pump
Hoses and Pipes
Inspect
1. Hose or pipe for deterioration or holes.
2. All hoses or pipe connections, and clamp tightness.
3. Hose or pipe routing. Interference may cause
wear
Page 787 of 1825
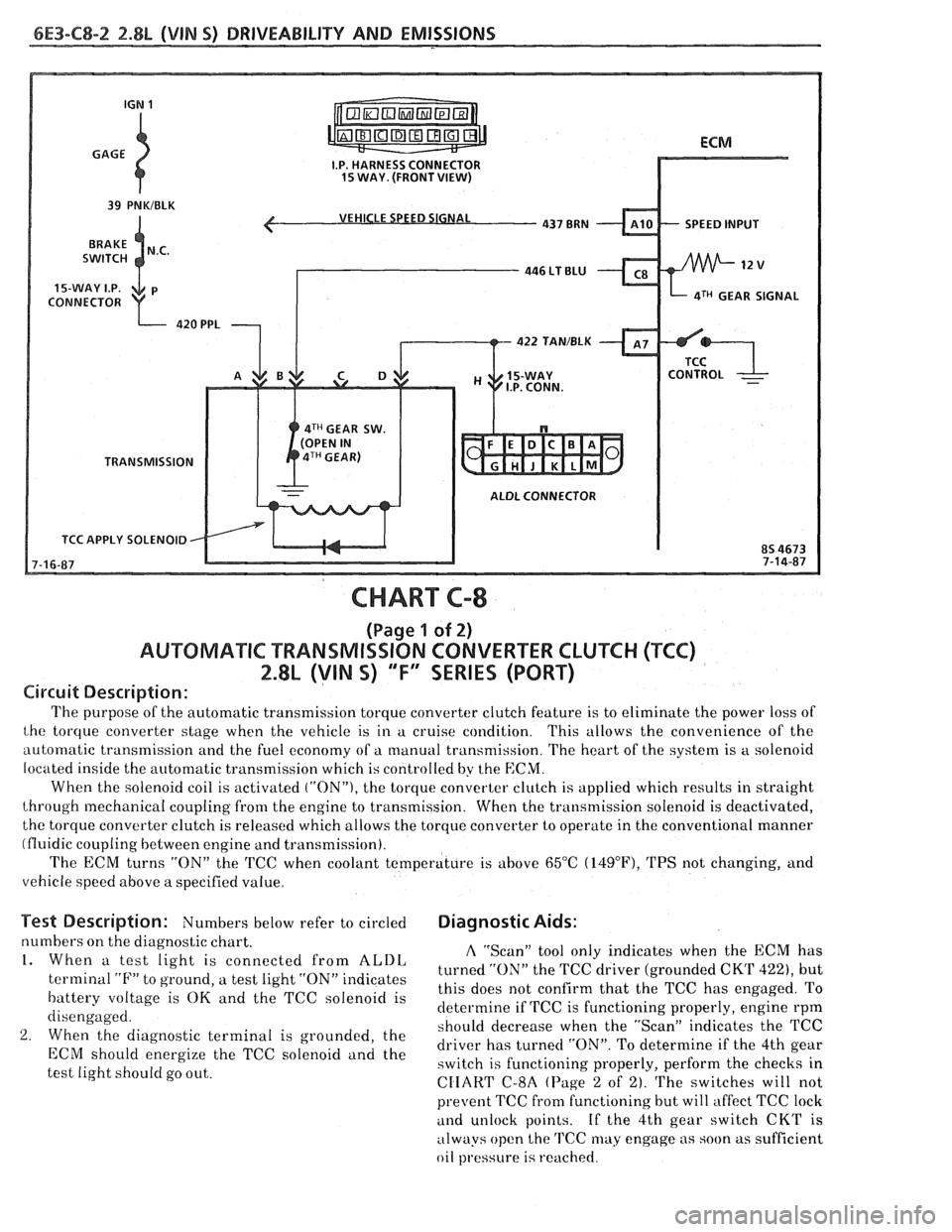
6E3-C8-2 2.8L (VIN S) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL
SPEED INPUT
CONNECTOR
aTH GEAR SIGNAL
422 TAN/BLK
4TH GEAR SW.
TRANSMISSION
ALDL CONNECTOR
TCC APPLY SOLENOID
CHART C-8
(Page 1 of 2)
AUWBMATIC TRANSMISSION CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
2.8L (VIN S) "F" SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The purpose of the automatic transmission torque converter clutch feature is to eliminate the power loss of
the torque converter stage when the vehicle is in a cruise condition. This allows the convenience of the
automatic transmission and the fuel economy of a manual transmission. The heart of the system is
a solenoid
located inside the automatic transmission which is controlled by the
ECM.
When the solenoid coil is activated ("ON"), the torque converter clutch is applied which results in straight
through mechanical coupling from the engine to transmission. When the transmission solenoid is deactivated,
the torque converter clutch is released which allows the torque converter to operate in the conventional manner
(fluidic coupling between engine and transmission).
The ECM turns
"ON" the 'KC when coolant temperature is above 65°C (14g°F), TPS not changing, and
vehicle speed above a specified value.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled Diagnostic Aids:
numbers on the diagnostic chart. A "Scan" tool only indicates when the ECM has 1. When a test light is connected from ALDL turned the TCC driver (grounded CKT 422), but terminal "F" to ground, a test light "ON" indicates
this does not confirm that the TCC has engaged. To battery voltage is OK and the TCC solenoid is
determine if TCC is functioning properly, engine rpm
disengaged.
should decrease when the "ScanJ' indicates the TCC
2. When the diagnostic terminal is grounded, the
driver has turned "ON". To determine if the 4th gear ECM energize the TCC "Ienoid and the switch is functioning properly, perform the checks in
test light should go out.
CIIART C-8A (Page 2 of 2). The switches will not
prevent TCC fi-om functioning but will affect TCC lock
and unlock points. If the 4th gear switch CKT is
always open the
TCC may engage as soon as sufficient
oil
pl.essure is reached.