1988 PONTIAC FIERO wiring
[x] Cancel search: wiringPage 833 of 1825
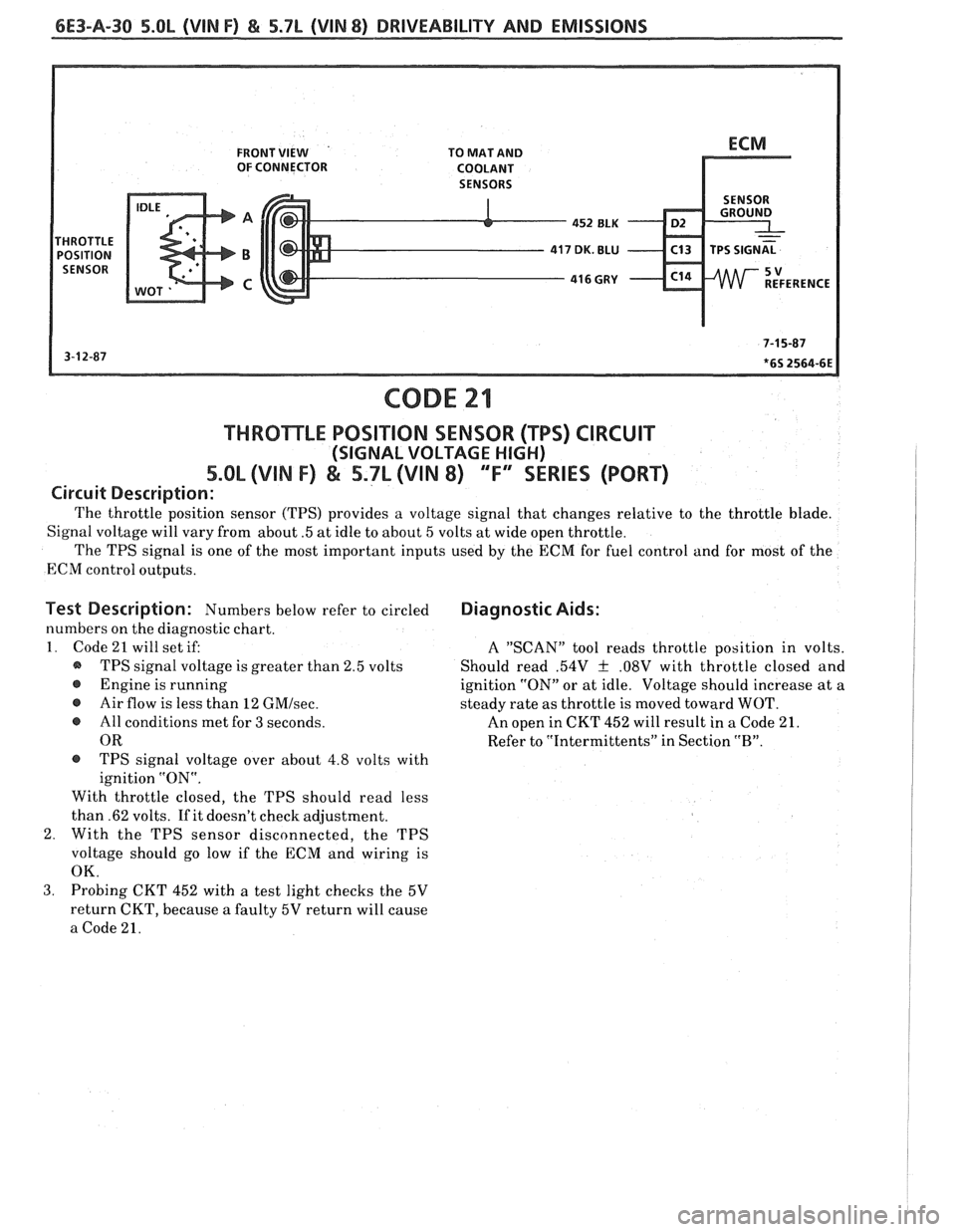
6E3-A-30 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
FRONT VIEW TO MAT AND
OF CONNECTOR
COOLANT
452
ELK D2
416 GRY - C14
CODE 21
THROmLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS) CIRCUIT
(SIGNAL VOLTAGE HIGH)
5.OL (VIN I") & 5.7L (VIN 8) 'T" SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The throttle position sensor (TPS) provides a voltage signal that changes relative to the throttle blade.
Signal voltage will vary from about
.5 at idle to about 5 volts at wide open throttle.
The TPS signal is one of the most important inputs used by the ECM for fuel control and for most of the
ECM control outputs.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Code 21 will set if:
@ TPS signal voltage is greater than 2.5 volts
@ Engine is running
@ Air flow is less than 12 GMIsec.
e All conditions met for 3 seconds.
OR
@ TPS signal voltage over about 4.8 volts with
ignition "ON".
With throttle closed, the TPS should read less
than .62 volts. If it doesn't check adjustment.
2. With the TPS sensor disconnected, the TPS
voltage should go low if the ECM and wiring is
OK.
Diagnostic Aids:
A "SCAN" tool reads throttle position in volts.
Should read
.54V f .08V with throttle closed and
ignition "ON" or at idle. Voltage should increase at a
steady rate as throttle is moved toward WOT.
An open in CKT 452 will result in
a Code 21.
Refer to "Intermittents" in Section
"B".
3. Probing CKT 452 with a test light checks the 5V
return CKT, because
a faulty 5V return will cause
a Code 21.
Page 835 of 1825
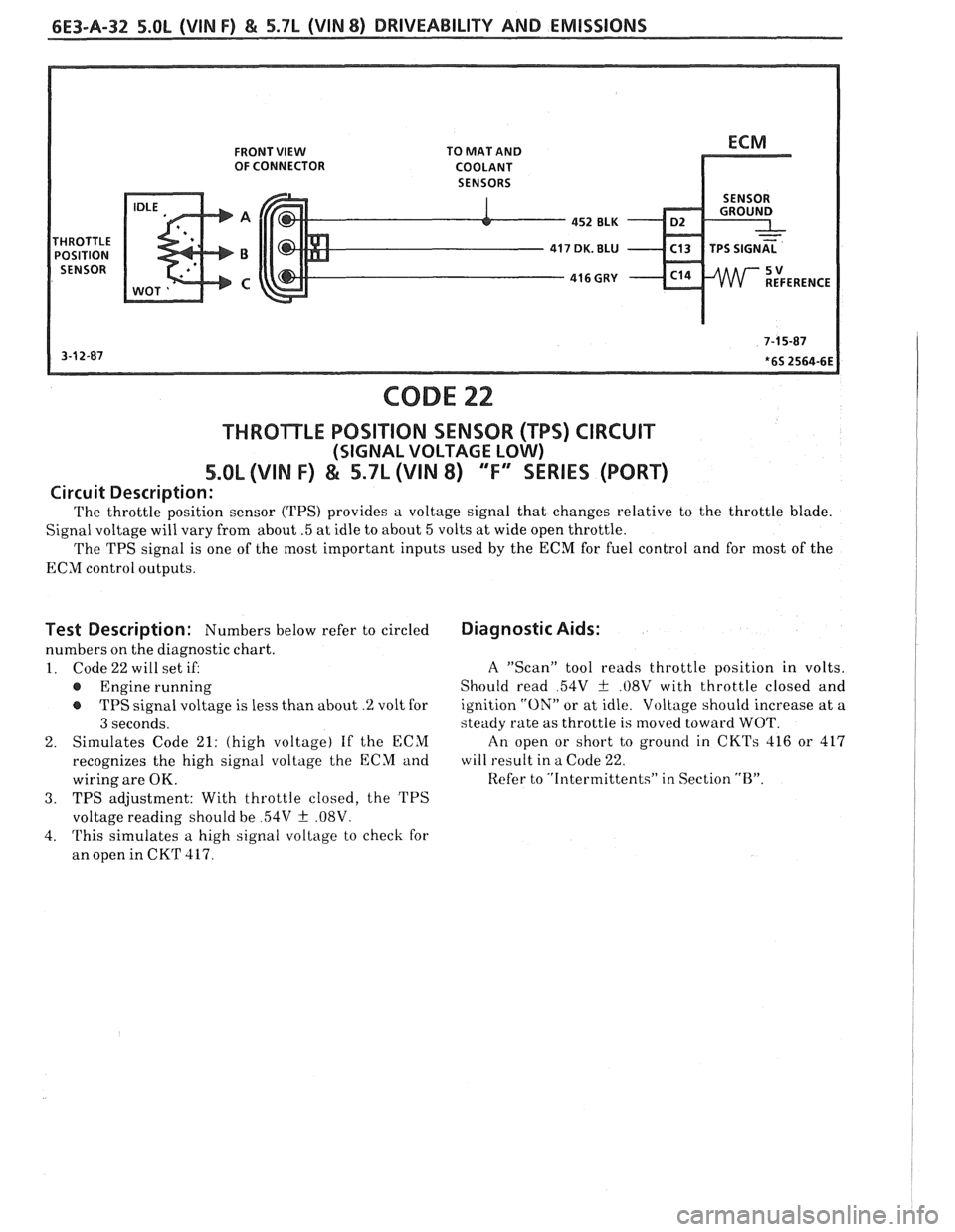
6E3-A-32 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
FRONT VIEW TO MAT AND OF CONNECTOR COOLANT
SENSORS
452 BLK - D2 .
416 GUY - C14
CODE 22
THROTLE POSITION SENSOR (WS) CIRCUIT
(SIGNAL VOLTAGE LOW)
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) "F'YSERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The throttle position sensor (TPS) provides a voltage signal that changes relative to the throttle blade.
Signal voltage will vary from about
.5 at idle to about 5 volts at wide open throttle.
The TPS signal is one of the most important inputs used by the
ECM for fuel control and for most of the
ECM control outputs.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Code22willsetiE
@ Engine running
TPS signal voltage is less than about
.% volt for
3 seconds.
2. Simulates
Code
21: (high voltage) If the ECM
recognizes the high signal voltage the ECM and
wiring are
OK.
3. TPS adjustment: With throttle closed, the TPS
voltage reading should be
54V f .08V.
4. This simulates a high signal voltage to check for
an open in CKT
417.
Diagnostic Aids:
A "Scan" tool reads throttle position in volts.
Should read
54V + .08V with throttle closed and
ignition
"ON" or at idle. Voltage should increase at a
steady rate as throttle is moved toward WOT.
An open or short to ground in
CKTs 416 or 417
will result in a Code 22.
Refer to "Intermittents" in Section
"B".
Page 837 of 1825
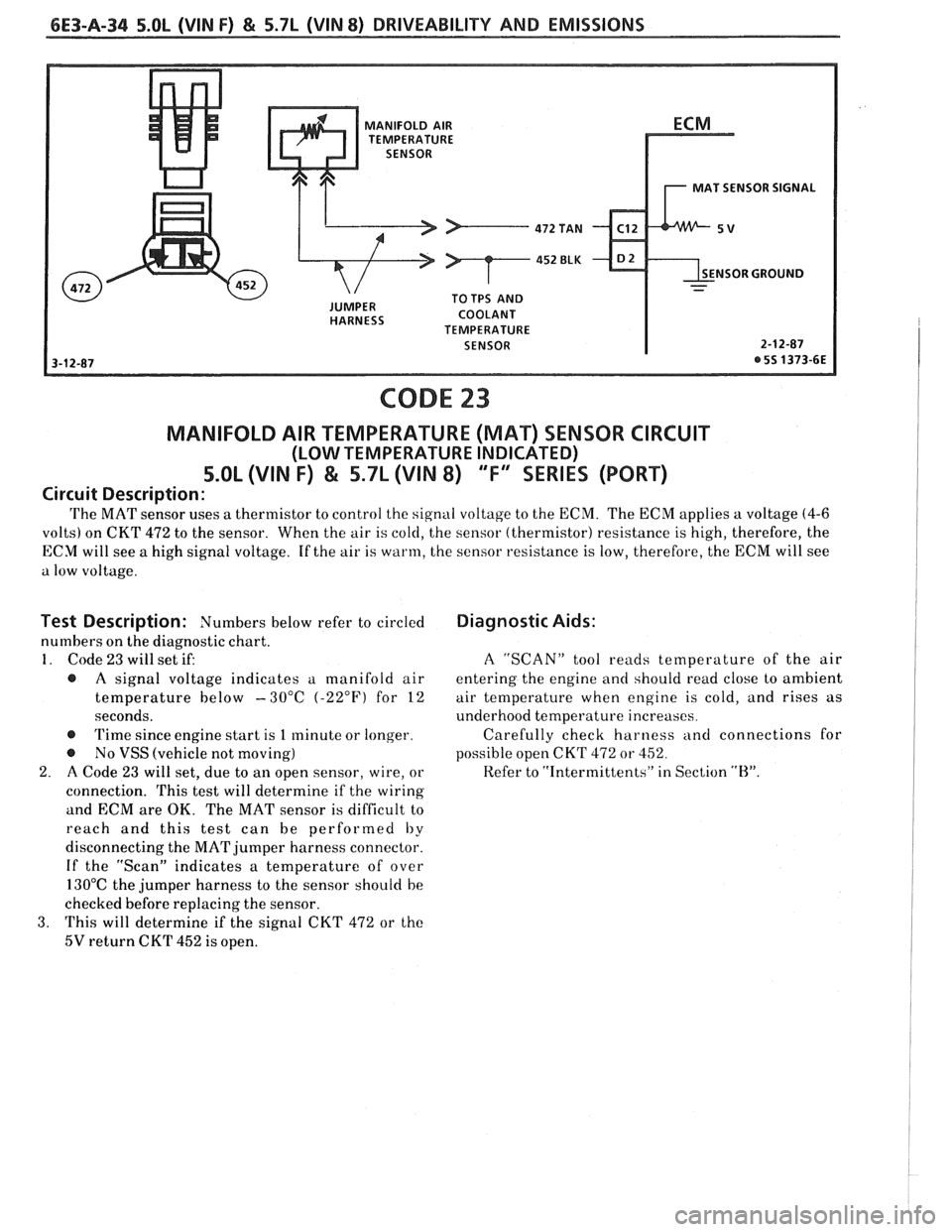
6E3-A-34 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
MANIFOLD AIR
TEMPERATURE
MAT SENSOR SIGNAL
NSOR GROUND
COOLANT
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
CODE 23
MANIFOLD AIR TEMPERATURE (MAT) SENSOR CIRCUIT
(LOW TEMPERATURE INDICATED)
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) "F" SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
'I'he MAT sensor uses a thermistor to control the signal voltage to the ECM. The ECM applies a voltage (4-6
volts) on CKT 472 to the sensor. When the air is cold, the sensor (thermistor) resistance is high, therefore, the
ECY will see a high signal voltage. If the air is warm, the sensor resistance is low, therefore, the ECM will see
a low voltage.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Code 23 will set if:
@ A signal voltage indicates u manifold air
temperature below -30°C (-22°F) for
12
seconds.
@ Time since engine start is 1 minute or longer.
@ No VSS (vehicle not moving)
2. A Code 23 will set, due to an open sensor, wire, or
connection. This test will determine if the wiring
and ECM are OK. The MAT sensor is difficult to
reach and this test can be performed
by
disconnecting the MAT jumper harness connector.
If the "Scan" indicates a temperature of over
130°C the jumper harness to the sensor should be
checked before replacing the sensor.
3. This will determine if the signal CKT 472 or the
5V return CKT 452 is open.
Diagnostic Aids:
A "SCAN" tool reads temperature of the air
entering the engine and should read close to ambient
air temperature when engine is cold, and rises as
underhood temperature increases.
Carefully check harness
ancl connections for
possible open CKT
472 or 452.
Refer to "Intermittents" in Section
"H".
Page 839 of 1825
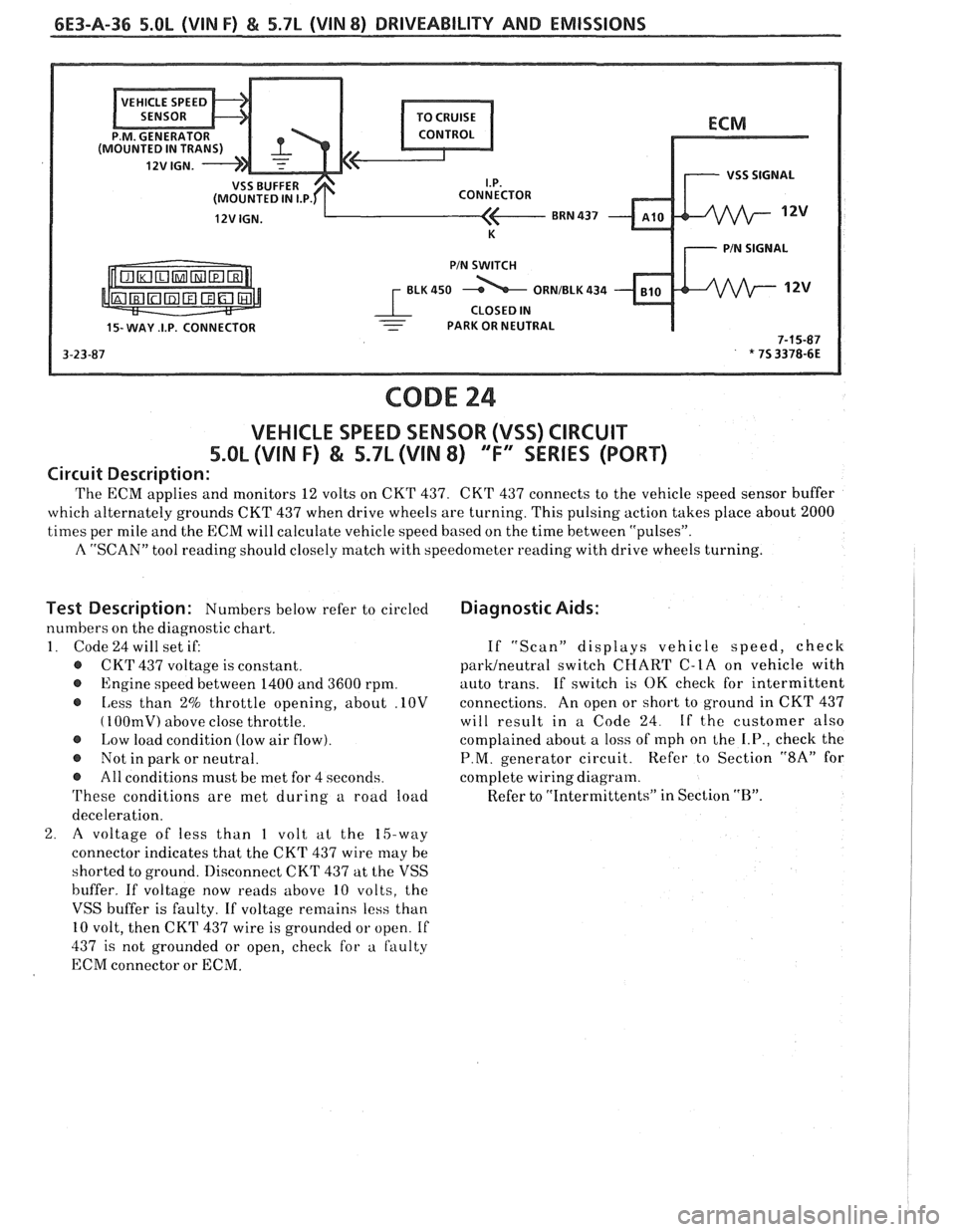
6E3-A-36 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CONNECTOR
15- WAY .I.P. CONNECTOR - - PARK OR NEUTRAL
CODE 24
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (VSS) CIRCUIT
5.0L (VIN F) & S.SL (VIN 8) "F" SERIES (PORT)
rcuit Description:
'I'he ECM applies and monitors 12 volts on CKT 437. CK'I' 437 connects to the vehicle speed sensor buffer
which alternately grounds CKT 437 when drive wheels are turning. This pulsing action takes place about 2000
times per mile and the ECM will calculate vehicle speed based on the time between "pulses".
A "SCAN" tool reading should closely match with speedometer reading with drive wheels turning.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Code
24 will set it
@ CKT 437 voltage is constant.
@ Engine speed between 1400 and 3600 rpm.
@ Less than 2% throttle opening, about .10V
( 100mV) above close throttle.
@ Low load condition (low air flow).
@ Not in park or neutral.
@ All conditions must be met for 4 seconds.
'I'hese conditions are met during a road load
deceleration.
2. A voltage of less than 1 volt at the 15-way
connector indicates that the CKT 437 wire may be
shorted to ground. Disconnect CKT 437 at the VSS
buffer. If voltage now reads above 10 volts, the
VSS buffer is faulty. If voltage remains less than
10 volt, then CKT 437 wire is grounded
or open. If
437 is not grounded or open, check for a faulty
ECM connector or ECM.
Diagnostic Aids:
If "Scan" displays vehicle speed, check
parWneutra1 switch CHART C-1A on vehicle with
auto trans. If switch is
OK check for intermittent
connections. An open or short to ground in CKT 437
will result in a Code 24
If the customer also
complained about a loss of mph on the
I.P., check the
P.M. generator circuit. Refer to Section "8A" for
complete wiring diagram.
Refer to "Intermittents" in Section
"B".
Page 845 of 1825
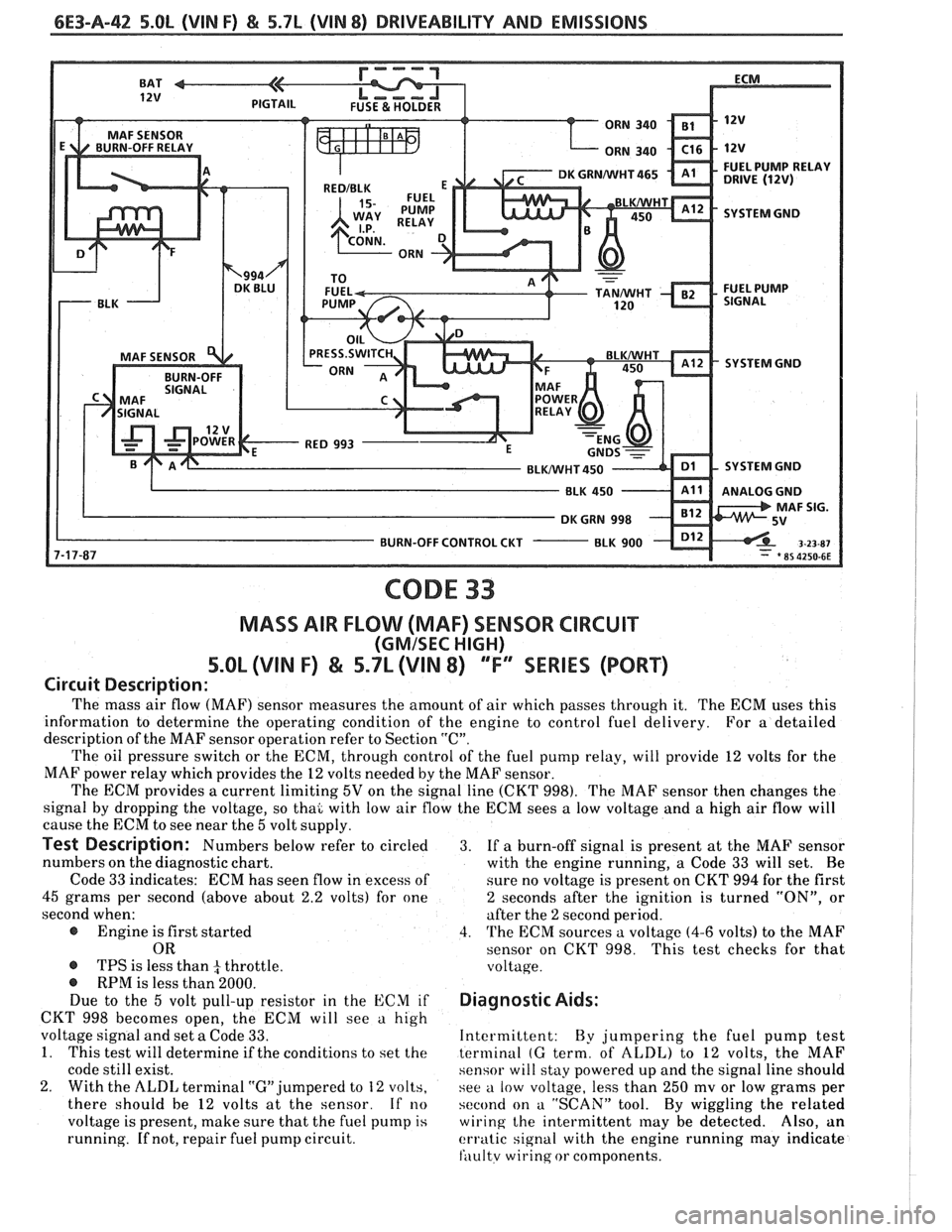
6E3-A-42 S.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
SYSTEM GND
SYSTEM GND
SYSTEM GND
ANALOG GND
BURN-OFF CONTROL CKT
-
CODE 33
MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR CIRCUIT
(GMISEC HIGH)
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) ""FY"IES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of air which passes through it. The ECM uses this
information to determine the operating condition of the engine to control fuel delivery.
For
a detailed
description of the MAF sensor operation refer to Section
"C".
The oil pressure switch or the ECM, through control of the fuel pump relay, will provide 12 volts for the
MAF power relay which provides the
12 volts needed by the MAF sensor.
The ECM provides
a current limiting 5V on the signal line (CKT 998). The MAF sensor then changes the
signal by dropping the voltage, so thai with low air flow the ECM sees
a low voltage and a high air flow will
cause the ECM to see near the
5 volt supply.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled 3. If a burn-off signal is present at the MAF sensor
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
with the engine running, a Code
33 will set. Be
Code
33 indicates: ECM has seen flow in excess of
sure no voltage is present on CKT 994 for the first
45 grams per second (above about 2.2 volts) for one 2 seconds after the ignition is turned "ON", or
second when: after the
2 second period.
@ Engine is first started 4. The ECM sources a voltage (4-6 volts) to the MAF
OR sensor on CKT 998. This test checks for that
@ TPS is less than 4 throttle. voltage. @ RPM is less than 2000.
Due to the 5 volt pull-up resistor in the ECM if Diagnostic Aids:
CKT 998 becomes open, the ECM will see a high
voltage signal and set
a Code 33. Intermittent:
By jumpering the fuel pump test
1. This test will determine if the conditions to set the terminal (G term, of ALDL) to 12 volts, the MAF
code still exist. sensor will stay powered up and the signal line should
2. With the ALDL terminal "G" jumpered to 12 volts,
see a low voltage, less than 250 mv or low grams per
there should be
12 volts at the sensor. If no second on a "SCAN" tool. By wiggling the related
voltage is present, make sure that the fuel pump
is wiring the intermittent may be detected. Also, an
running.
If not, repair fuel pump circuit. erratic signal with the engine running may indicate
fili~ltv wirinq or components.
Page 847 of 1825
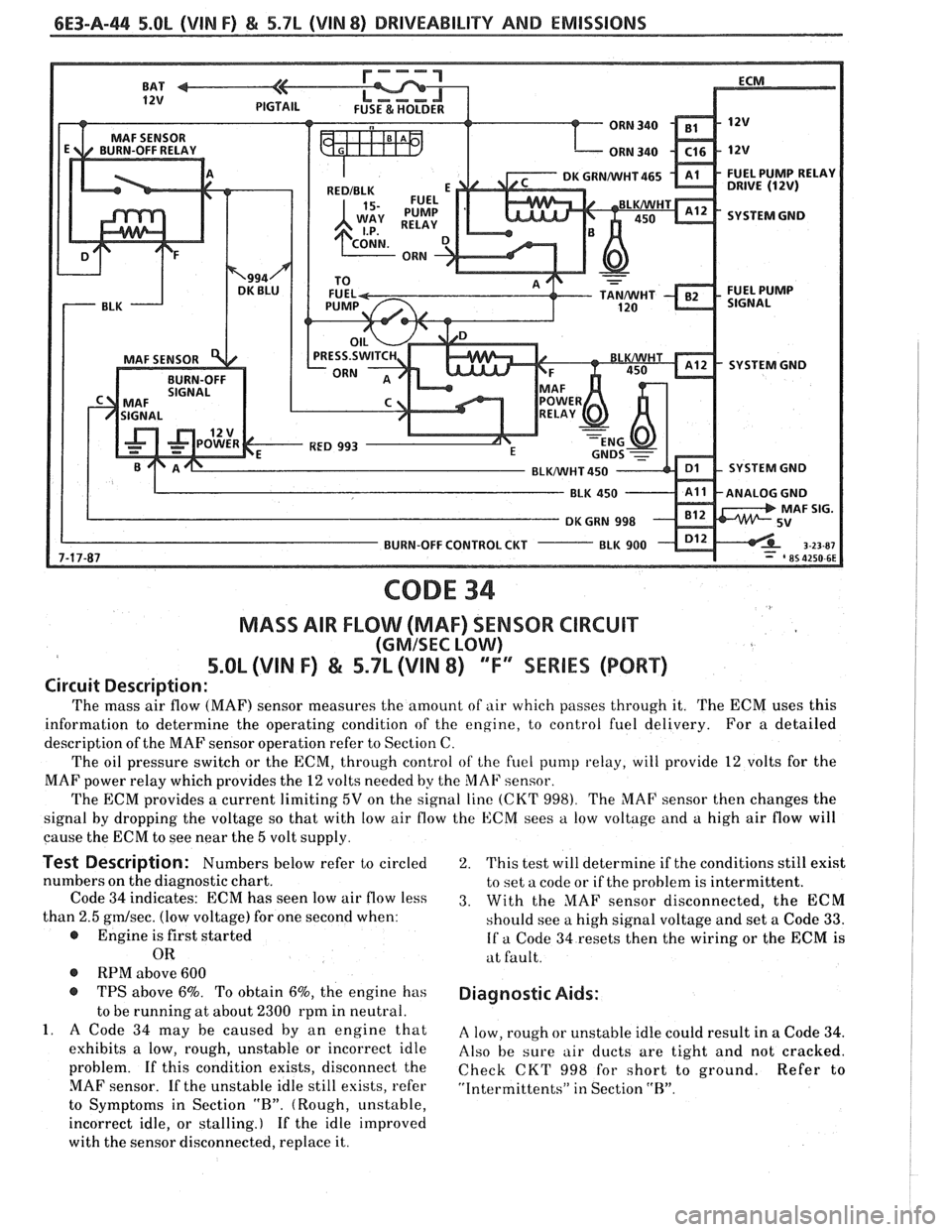
6E3-A-44 5.0b (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
SYSTEM GND
SYSTEM GND
BLUNVHT 450 SYSTEM GND
BURN-OFF CONTROL CUT
CODE 34
MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR CIRCUIT
(GMISEC LOW)
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (\/IN 8) "F"" SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of air which passes through it. The ECM uses this
information to determine the operating condition of the engine, to control fuel delivery. For a detailed
description of the MAF sensor operation refer to Section C.
The oil pressure switch or the ECM, through control
of the fuel pump relay, will provide 12 volts for the
MAF power relay which provides the
12 volts needed by the MAF sensor.
The ECM provides a current limiting
5V on the signal line (CKT 998). The MAF sensor then changes the
signal by dropping the voltage so that with low air flow the ECM sees
a low voltage and a high air flow will
cause the ECM to see near the
5 volt supply.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
Code
34 indicates: ECM has seen low air flow less
than
2.5 gmlsec. (low voltage) for one second when:
@ Engine is first started
OR
@ RPM above 600
@ TPS above 6%. To obtain 6%, the engine has
to be running at about
2300 rpm in neutral.
1. A Code 34 may be caused by an engine that
exhibits a low, rough, unstable or incorrect idle
problem. If this condition exists, disconnect the
MAF sensor. If the unstable idle still esists, refer
to Symptoms in Section
"R". (Rough, unstable,
incorrect idle, or stalling.) If the idle improved
with the sensor disconnected, replace it.
2. This test will determine if the conditions still exist
to set a code or if the problem is intermittent.
3. With the MAF sensor disconnected, the ECM
should see a high signal voltage and set a Code
33.
If a Code 34 resets then the wiring or the ECM is
at fault.
Diagnostic Aids:
A low, rough or unstable idle could result in a Code 34.
Also be sure air ducts are tight and not cracked.
Check CKT
998 for short to ground. Refer to
"Intermittents" in Section "R".
Page 855 of 1825
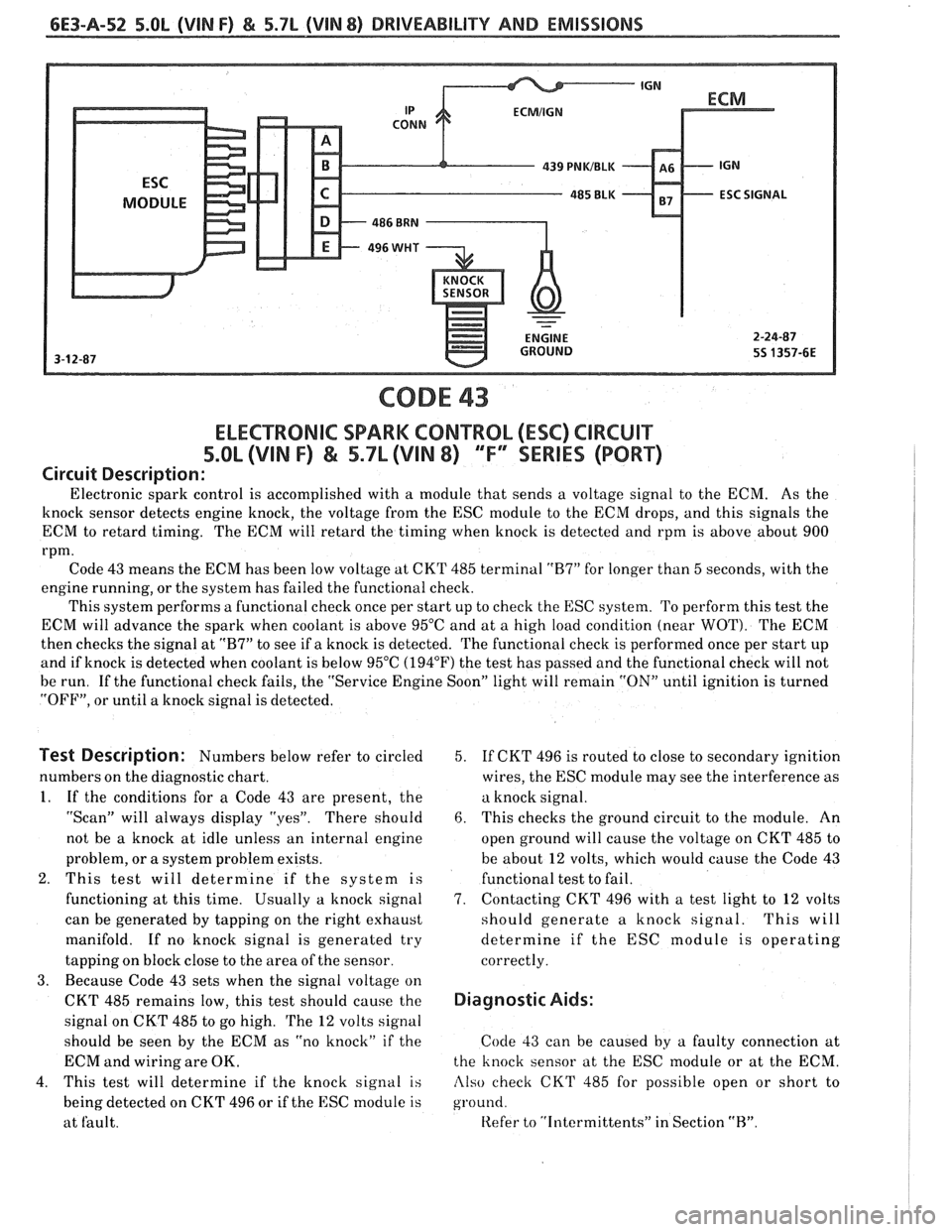
6E3-A-52 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CODE 43
ELECTRONIC SPARK CONTROL (ESC) ClRCUlT
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) 'TF" SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
Electronic spark control is accomplished with a module that sends a voltage signal to the ECM. As the
knock sensor detects engine knock, the voltage from the ESC module to the ECM drops, and this signals the
ECM to retard timing. The ECM will retard the timing when knock is detected and rpm is above about 900
rpm.
Code 43 means the ECM has been low voltage at CKT 485 terminal
"R7" for longer than 5 seconds, with the
engine running, or the system has failed the functional check.
This system performs a functional check once per start up to check the
ESC system. To perform this test the
ECM will advance the spark when coolant is above 95°C and at a high load condition (near
WOT). The ECM
then checks the signal at
"B7" to see if a knock is detected. The functional check is performed once per start up
and if knock is detected when coolant is below 95°C
(194°F') the test has passed and the functional check will not
be run. If the functional check fails, the "Service Engine Soon" light will remain
"ON" until ignition is turned
"OFF", or until a knock signal is detected.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. If the conditions for a Code 43 are present, the
"Scan" will always display "yes". There should
not be a knock at idle unless an internal engine
problem, or
a system problem exists.
2. This test will determine if the system is
functioning at this time. Usually
a knock signal
can be generated by tapping on the right exhaust
manifold. If no knock signal is generated try
tapping on block close to the area of the sensor.
3. Because Code 43 sets when the signal voltage on
CKT 485 remains low, this test should cause the
signal on CKT 485 to go high. The
12 volts signal
should be seen by the ECM as "no knock" if the
ECM and wiring are OK.
4. This test will determine if the knock signal
is
being detected on CKT 496 or if the ESC module is
at fault. 5.
If CKT
496 is routed to close to secondary ignition
wires, the ESC module may see the interference as
a knock signal.
6. This checks the ground circuit to the module. An
open ground will cause the voltage on CKT 485 to
be about
12 volts, which would cause the Code 43
functional test to fail.
7. Contacting CKT 496 with a test light to 12 volts
should generate a knock signal. This will
determine if the ESC module is operating
correctly.
Diagnostic Aids:
Code 33 can be caused by a faulty connection at
the knock sensor at the ESC module or at the ECM.
Also check CKT 485 for possible open or short to
ground.
Refer to "Intermittents" in Section "R".
Page 866 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) 6E3-B-1
SYMPTOMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
............................................................. Before Starting Page B-I
lntermittents............................................................... PageB-2
...................................................... Hesitation, Sag, Stumble Page 8-3
....................................................... Surges and/or Chuggle Page B-3
.............................................. Lack of Power, Sluggish, or Spongy Page 8-4
Detonation/SparkKnock ...................................................... PageB-4
Cuts Out, Misses
............................................................ Page B-5
Backfire................................................................... PageB-5
.......................................................... Poor Fuel Economy Page 8-6
.......................................................... Dieseling, Run-on,. Page B-6
........................................ Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling Page B-6
............................................. Excessive
Exhaust Emissions or Odors Page B-7
Restricted Exhaust System Check (Chart
B-1) ....................................... Page 8-8
BEFORE STARTING
Before using this section you should have
performed the DIAGNOSTIC CIRCUIT CHECK
and found out that:
1. The ECM and "Service Engine Soon" light are
operating.
2. There are no trouble codes stored, or there is a
trouble code but no "Service Engine Soon" light.
Verify the customer complaint, and locate the
correct SYMPTOM below. Check the items
indicated under that symptom.
If the ENGINE CRANKS BUT WILL NOT
RUN, see CHART A-3.
Several of the symptom procedures below call
for a Careful Visual Check. This check should
include:
@ ECM grounds for being clean and tight
@ Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections, as shown on Emission Control
Information label.
@ Air leaks at throttle body mounting and intake
manifold.
@ Air leaks between MAF sensor and throttle
body.
@ Ignition wires for cracking, hardness, proper
routing, and carbon tracking.
@ Wiring for proper connections, pinches, and cuts.
The importance of this step cannot be stressed
too strongly
- it can lead to correcting a problem
without further checks and can save valuable time.