1988 PONTIAC FIERO engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 553 of 1825

6E2-8-6 5.OL (VIN E) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
- MAP Sensor - Ignition "ON", engine stopped.
Compare MAP voltage with known good vehicle.
-
Voltage should be the same + 400 mV (.4 volts).
OR
Start and idle engine. Disconnect
sensor
electrical connector. If idle improves, substitute
a known good sensor and recheck.
- A/C refrigerant pressure too high. Check for
overcharge or faulty pressure switch.
- PCV valve for proper operation by placing finger
over inlet hole in valve end several times. Valve
should snap back. If not, replace valve.
Run a cylinder compression check See Section
" 6".
Inspect oxygen sensor for silicon contamination
from fuel, or use of improper RTV sealant. The
sensor will have a white, powdery coating, and
will result in a high but false signal voltage (rich
exhaust indication). The ECM will then reduce
the amount of fuel delivered to the engine,
causing a severe driveability problem.
EXCESSIVE EXHAUST EMISSIONS OR ODORS
Definition: Vehicle fails an emission test. Vehicle has excessive "rotten egg"
smell. Excessive odors do not necessarily indicate excessive emissions.
@ Perform "Diagnostic Circuit Check".
@ IF TEST SHOWS EXCESSIVE CO AND HC, (or
also has excessive odors)
@ Check items that will cause engine to run
RICH.
e Make sure engine is at normal operating
temperature.
o CHECK:
- Fuel pressure. See CHART A-7.
- Incorrect timing. See Vehicle Emission
Control Information label.
- Canister for fuel loading. See CHART C-3.
- PCV valve for being plugged, stuck or blocked
PCV hose or fuel in the crankcase.
- Spark plugs, plug wires, and ignition
components. See Section
"6D".
- Check for lead contamination of catalytic
converter (look for removal of fuel filler neck
restrictor).
- Check for properly installed fuel cap.
@ If the system is running rich, (block learn less
than
1181, refer to "Diagnostic Aids" on facing
page of Code
45.
o IF TEST SHOWS EXCESSIVE NOx:
@ Check items which cause car to run LEAN, or
to run too hot.
- EGR valve for not opening. See CHART C-7.
- Vacuum leaks. - Coolant system and coolant fan for proper
operation. See
CHART C-12.
- Remove carbon with top engine cleaner.
Follow instructions on can.
- Check ignition timing for excessive base
advance. See Emission Control Information
label.
@ If the system is running lean, (block learn greater
than
138) refer to "Diagnostic Aids" on facing
page of Code
44.
DIESELING, RUN-ON
Definition: Engine continues to run after key is turned "OFF", but runs very roughly.
Ifengine runs smoothly, check ignition switch and adjustment.
@ Check injector for leaking. Apply 12 volts to fuel Visually check injector and TBI assembly for fuel
pump test terminal to turn "ON" fuel pump and leakage.
pressurize fuel system.
BACKFIRE
Definition: Fuel ignites in intake manifold, making a loud popping noise.
@ CHECK: - For faulty spark plugs and/or plug wires or
- EGR operation for being open all the time. See
hoots.
CHART C-7. - Faulty A.I.R. check valve.
- Output voltage of ignition coil. @ Perform a compression check - look for sticking or
- For crossfire between spark plugs (distributor leaking valves.
cap, spark plug wires, and proper routing' of plug
- For proper valve timing.
wires).
- Broken or worn valve train parts.
- Engine timing - See Emission Control
Information label.
Page 560 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN E) 6EZ-C1-5
DIAGNOSIS
Since the ECM can have a failure which may
effect only one circuit, following the diagnostic
procedures in this section can reliably tell when a
failure has occurred in the ECM. Also,
a Code
55 in
dicates a failure of the ECM.
If a diagnostic chart indicates that the ECM
connections or ECM is the cause of a
problem,and the
ECM is replaced, but does not correct the problem, one
of the following may be the reason:
e
connections. - The diagnostic chart will say "ECM
Connections or ECM". The terminals mav have to be
removed from the connector in order to check them
properly.
@ The ECM or PROM is not correct for the
. - The incorrect ECM or PROM may cause
a malfunction and may or may not set a code.
. - This means that
time the system is
being checked. In this case, refer to the "Symptoms"
portion of the manual and make a careful physical
Solenoids and relays are turned "ON" and "OFF" by
the ECM, using internal electronic switches called
"Drivers".
A shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness in a
GMP4 computer will not damage the ECM,
but will cause the circuit and controlled
component to be inoperative. When the
circuit fault is not present or has been
repaired, the "Quad-Driver" will again
operate in a normal manner due to it's fault
protected design. If a fault has been repaired
in a circuit controlled
by a "Quad-Driver", the
original
ECM should be reinstalled and the
circuit checked for proper operation.
ECM
replacement will not be necessary if the
repaired circuit or component now operates
correctly.
534636 or BT8405 testers or equivalent provide a
fast, accurate means of checking for a shorted coil or a
short to battery voltage.
e , - Although the
PROM rarely
fails,it operates as part of the ECM.
Therefore, it could be the cause of the problem.
Substitute a known good PROM.
o . - After the
ECM is replaced, the system should be rechecked for
proper operation. If the diagnostic chart again
indicates the ECM is the problem, substitute a known
good ECM. Although this is a rare condition, it could
happen. The
components or circuits and the codes or
charts, related to them are:
@ Code 55 indicates a failure of the ECM.
@ PROM - Code 51.
@ Coolant Temperature Sensor - CHARTS 14 -
15.
@ MAP sensor - CHART 33 or 34. To check the
sensor with no code set, use CHART
C-1D.
e TPS - CHARTS 21 or 22.
e PIN switch - CHART C-1A
@ Crank Signal - CHART C-1B
@ O2 Sensor - CHARTS 13,44,45.
@ VSS - CHART 24 and in TCC System.
e Distributor - CHART 42 and in EST system.
@ Distributor - Chart and in the EST system.
ECM
A faulty ECM will be determined in the diagnostic
charts, or by a Code 55.
PROM
An incorrect or faulty PROM, which is part of the
ECM, may set a Code 51.
ECM INPUTS
All of the sensors and input switches can be
diagnosed by the use of a "Scan" tool. Following is
a
short description of how the sensors and switches can
be diagnosed by the use of "a Scan" tool. The
"Scan"
tool can also by used to compare the values for a
normal running engine with the engine you're
diagnosing.
Coolant Temperature Sensor
A "Scan" tool displays engine temp. in degrees
centigrade. After the engine is started, the
temperature should rise steadily to about
90°C, then
stabilize when thermostat opens.
A fault in the
coolant sensor circuit should set a Code 14 or 15. The
code charts also contain a chart to check for sensor
resistance values relative to temperature.
MAT Sensor
A "Scan" tool displays temperature of the air
entering the engine and should read close ambient air
temperature, when engine is cold, and rise
as
underhood temperature increases. If the engine has
not been run for several hours (overnight), the MAT
sensor temperature and coolant temperature should
read close to each other.
Page 573 of 1825
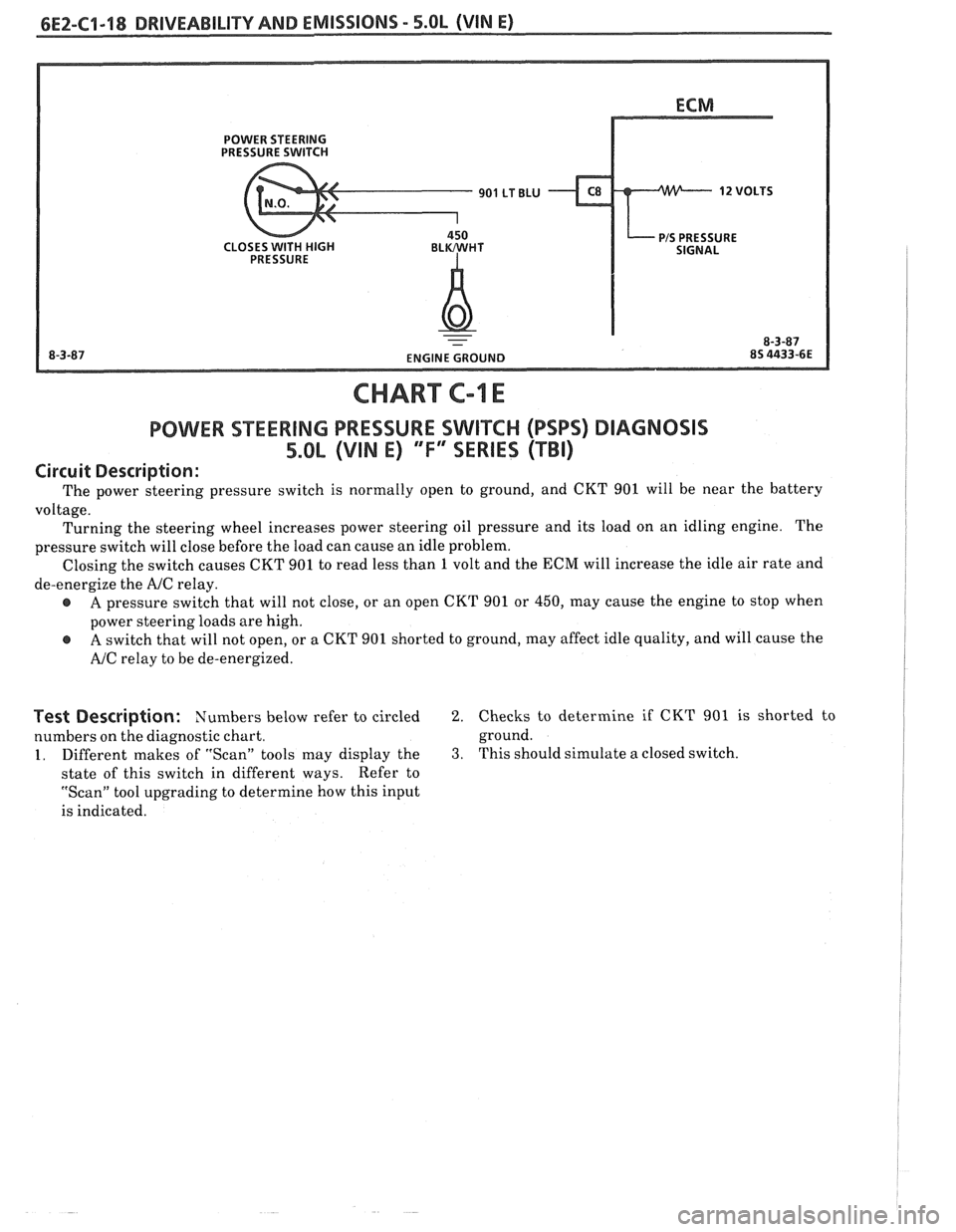
6E2-C1-18 DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - 5.OL (VIN E)
CHART C-1 E
POWER SEERING PRESSURE SWIKCH (PSPS) DIAGNOSIS
5.0L (VIN E) "F" SERIES (TBI)
Circuit Description:
The power steering pressure switch is normally open to ground, and CKT 901 will be near the battery
voltage. Turning the steering wheel increases power steering oil pressure and its load on an idling engine. The
pressure switch will close before the load can cause an idle problem.
Closing the switch causes CKT 901 to read less than
1 volt and the ECM will increase the idle air rate and
de-energize the
AJC relay.
A pressure switch that will not close, or an open CKT 901 or 450, may cause the engine to stop when
power steering loads are high.
A switch that will not open, or a CKT 901 shorted to ground, may affect idle quality, and will cause the
AJC relay to be de-energized.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled 2. Checks to determine if CKT 901 is shorted to
numbers on the diagnostic chart. ground.
1. Different
makes of "Scan" tools may display the 3. This should simulate a closed switch.
state of this switch in different ways. Refer
to
"Scan" tool upgrading to determine how this input
is indicated.
Page 576 of 1825
DRIVEABILIW AND EMISSIONS - 5.OL (VIN E) 6E2-62-1
SECTION C2
FUEL CONTROL SYSTEM
TBI MODEL 228
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-1
PURPOSE ......................... C2-1
MODES OF OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-1
Starting Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-1
Clear Flood Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-2
RunMode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-2
Open Loop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-2
Closed Loop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-2
Acceleration Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-2
Deceleration Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-2
Battery Correction Mode . . . . . . . . . . . C2-2
Fuel Cut Off Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-2
FUEL CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
. . . C2-2
BASIC SYSTEM OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . C2-3
THROTTLE BODY INJECTION (TBI) UNIT. . . C2-3
Fuel Injectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-3
Pressure Regulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-3
ldle Air Control (IAC) Valve . . . . . . . . . . C2-4
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) . . . . . . . . C2-4
FUEL PUMP.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-5
FUEL PUMP ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT . . . . . . . C2-5
DIAGNOSIS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . * C2-5
FUEL CONTROL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-5
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
PURPOSE
The basic function of the fuel control system is to
control fuel delivery to the engine. Fuel is delivered to
the engine by
a throttle body injection ('FBI) unit.
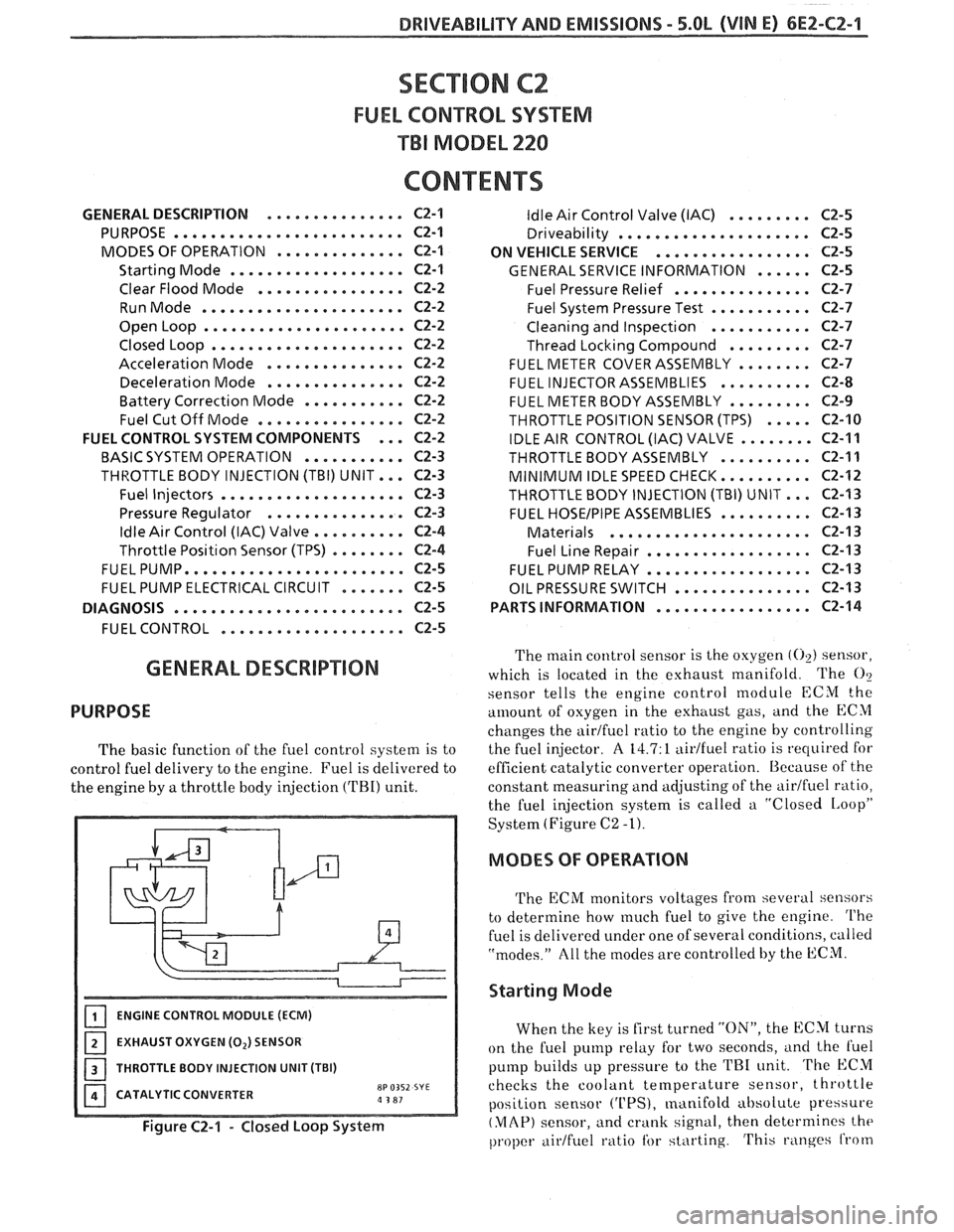
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
EXHAUST OXYGEN (0,) SENSOR
I 1 THROTTLE BODY INJECTION UNIT (TBI)
CATALYTIC CONVERTER
8P 0352 SYE a 3 81
Figure C2-1 - Closed Loop System
ldle Air Control Valve (IAC) . . . . . . . . . C2-5
Driveability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. C2-5
ON VEHICLE SERVICE
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-5
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION . . . . . . C2-5
Fuel Pressure Relief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-7
Fuel System Pressure Test . . . . . . . . . . . C2-7
Cleaning and Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . C2-7
Thread Locking Compound . . . . . . . . . C2-7
FUEL METER COVER ASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . C2-7
FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLIES . . . . . . . . . . C2-8
FUEL METER BODY ASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . C2-9
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS) . . . . . C2-10
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) VALVE . . . . . . . . C2-11
THROTTLEBODYASSEMBLY .......... C2-11
MINIMUM IDLE SPEED CHECK.. . . . . . . . . C2-12
THROTTLE BODY INJECTION (TBI) UNIT.. . C2-I3
FUEL HOSEIPIPE ASSEMBLIES . . . . . . . . . . C2-13
Materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-13
Fuel Line Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-13
FUEL PUMP RELAY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-13
OIL PRESSURE SWITCH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-13
PARTS INFORMATION
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C2-14
The main control sensor is the oxygen (02) sensor,
which is located in the exhaust manifold. The
O?
sensor tells
the engine control module ECM the
amount of osygen in the exhttust gas, and the ECM
changes the airtfuel ratio to the engine by controlling
the fuel injector.
A 14.7: 1 aidfuel ratio is required for
efficient catalytic converter operation. Because of the
constant measuring and adjusting of the
airlfuel ratio,
the fuel injection system is called a "Closed
IAoopP
System (Figure C2 -1).
MODES OF OPERATION
The ECM monitors voltages from several sensors
to determine how
much fuel to give the engine. The
fuel is delivered under one of several conditions, called
"modes." All the modes are controlled by the ECM.
Starting Mode
When the key is first turned "ON", the ECM turns
on the fuel pump relay for two seconds,
i~nd the l'uel
pump builds up pressure to the TRI unit. The ECM
checks the coolant
temperature sensor, throttle
position sensor
('UPS), manifold absolute pressure
(MAP) sensor, and crank signal, then determines the
proper airtfuel ratio tbr starting. This ranges from
Page 578 of 1825
DRIVEABILITY AND EMlSSlONS - 5.0L (VIN E) 6E2-C2-3
BASIC SYSTEM OPERATION
The fuel control system (Figure C2-2) has an
electric fuel pump, located in the fuel tank with the
gage sending unit, which pumps fuel to the TBI
through the fuel supply line, then through an in-line
fuel filter. The pump is designed to provide
pressurized fuel at about 125
kPa (18 psi). A pressure
regulator in the TBI keeps fuel available to the
injectors at a constant pressure between 62 and 90
kPa (9 and 13 psi). Fuel in excess of injector need is
returned to the fuel tank by
a separate line.
The ECM controls the injectors that are located in
the fuel meter body assembly of the TBI. The injectors
deliver fuel in one of several modes, described above.
In order to properly control the fuel supply, the
fuel pump is operated by the ECM through the fuel
pump relay and oil pressure switch (see "Fuel Pump
Electrical Circuit").
THROTTLE BODY INJECTION (TBI) UNIT
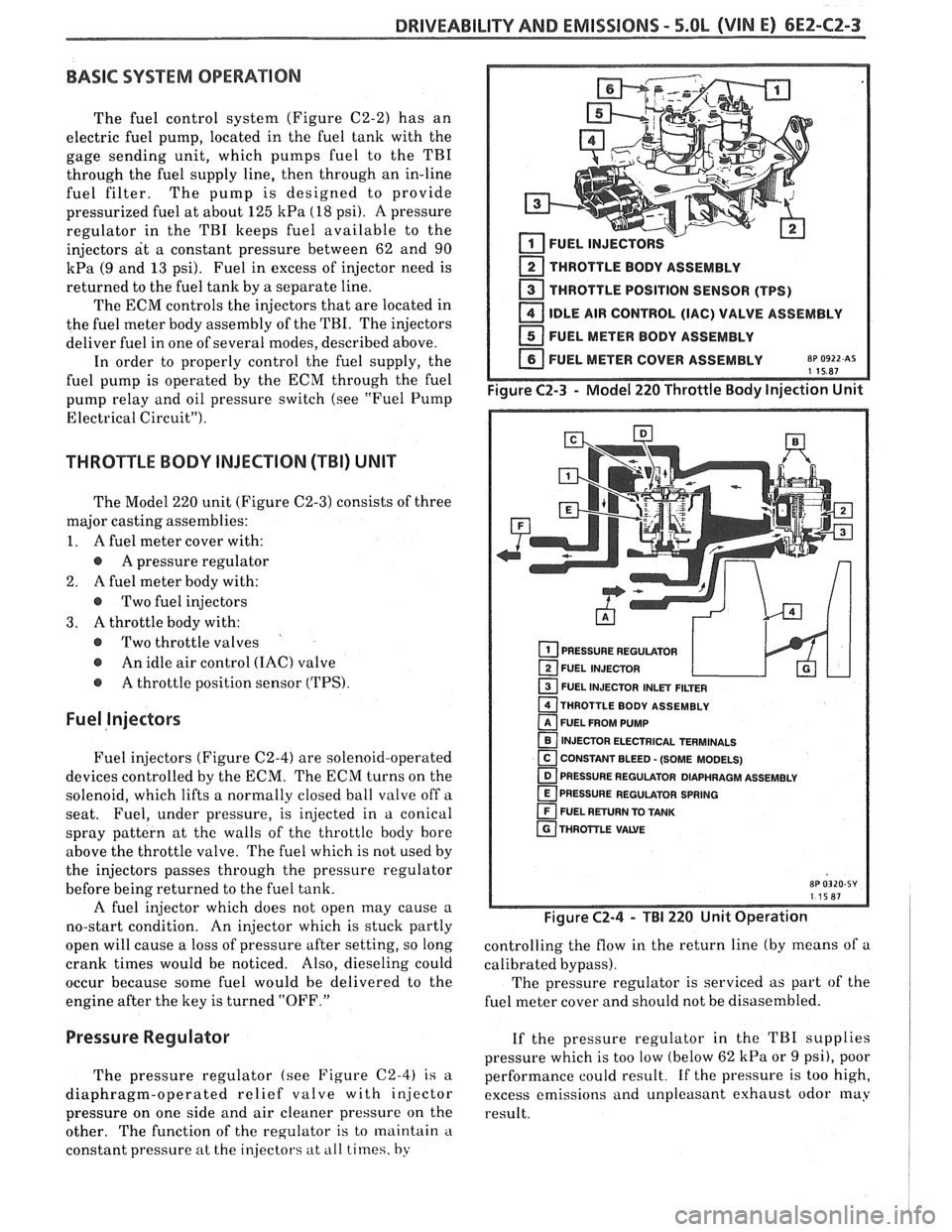
The Model 220 unit (Figure C2-3) consists of three
major casting assemblies:
1. A fuel meter cover with:
A pressure regulator
2.
A fuel meter body with:
@ Two fuel injectors
3. A throttle body with:
@ Two throttle valves
@ An idle air control (IAC) valve
@ A throttle position sensor (TPS).
Fuel Injectors
Fuel injectors (Figure C2-4) are solenoid-operated
devices controlled by the ECM. The ECM turns on the
solenoid, which lifts a normally closed ball valve off a
seat. Fuel, under pressure, is injected in a conical
spray pattern at the walls of
the throttle body bore
above the throttle valve. The fuel which is not used by
the injectors passes through the pressure regulator
before being returned to the fuel tank.
A fuel injector which does not open may cause a
no-start condition. An injector which is stuck partly
open will cause a loss of pressure after setting, so long
crank times would be noticed. Also, dieseling could
occur because some fuel would be delivered to the
engine after the key is turned "OFF."
2 THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) VALVE ASSEMBLY
FUEL METER BODY ASSEMBLY
FUEL METER COVER ASSEMBLY
8~ 0922 AS 115R7
PRESSURE REGULATOR
FUEL INJECTOR
1 FUEL INJECTOR INLET FILTER
THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY
FUEL FROM PUMP
INJECTOR ELECTRICAL TERMINALS
[ CONSTANT BLEED - (SOME MODELS) - PRESSURE REGULATOR DIAPHRAGM ASSEMBLY
PRESSURE REGULATOR SPRING
FUEL RETURN TO TANK
THROTTLE
VAWE
Figure C2-4 - TBI 220 Unit Operation
controlling the flow in the return line (by means of a
calibrated bypass).
The pressure regulator is serviced as part
of the
fuel meter cover and should not be disasembled.
Pressure Regulator If the pressure regulator in the TBI supplies
pressure which
is too low (below 62 kPa or 9 psi), poor
The pressure regulator (see Figure
C2-4) is a performance could result. if the pressure is too high,
diaphragm-operated relief valve with injector excess emissions and unpleasant exhaust odor
may
pressure on one side and air cleaner pressure on the
result.
other. The function of the regulator is to maintain
'1
constant pressure at the in.jecto1.s at ill1 times, by
Page 580 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - 5.OL (\/IN El 6EZ-CZ-5
sent to the ECM. The ECM then increases the injector
base pulse width, permitting increased fuel flow.
As the throttle valve rotates in response to
movement of the accelerator pedal, the throttle shaft
transfers this rotational movement to the
'I'PS. A
potentiometer (variable resistor) within the TPS
assembly changes its resistance (and voltage drop) in
proportion to throttle movement.
By applying a reference voltage (5.0 volts) to the
TPS input, a varying voltage (reflecting throttle
position) is available at the TPS output. For example,
approximately 2.5 volts results from a 50% throttle
valve opening (depending on TPS calibration). The
voltage output from the TPS assembly is routed to the
ECM for use in determining throttle position.
FUEL PUMP
The fuel pump is a turbine type, low pressure
electric pump, mounted in the fuel tank. Fuel
is
pumped at a positive pressure (above 62
kPa or 9 psi)
from the fuel pump through the in-line filter to the
pressure regulator in the TBI assembly Excess
fuel is
returned to the fuel tank through the fuel return line.
The fuel pump is attached to the fuel gage sender
assembly. A fuel strainer is attached to the fuel pump
inlet line and prevents dirt particles from entering the
fuel line and tends to separate
water from the fuel
Vapor lock problems are reduced when using an
electric
pump because the fuel is pushed from the tank
under pressure rather than being pulled
under
vacuum, a condition that produces vapor.
An inoperative fuel pump would cause
a. no start
condition. A fuel pump which does not provide enough
pressure can result in poor performance. (See "Fuel
System Pressure Test" procedure).
FUEL PUMP ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT
When the key is first turned "ON" without the
engine running, the ECM turns the
Fuel pump relay
"ON" for two seconds. This builds
up the fuel pressure
quickly. If the engine is not started within two
seconds, the
ECM shuts the fuel pump "OFF" and
waits until the engine starts. As soon as the engine is
cranked, the ECM turns the relay
"ON" and runs the
fuel pump.
As a backup system to the fuel pump relay, the
fuel pump can also be turned on
by the oil pressure
switch. The oil pressure sender has two circuits
internally. One operates the oil pressure indicator or
gage in the instrument cluster,
itnd the other is
anormally open switch which closes when oil pressure
reaches about 28
kPa (4 psi). If the fuel pump relay
fails, the oil pressure switch will run the fuel pump. An
inoperative fuel pump relay can result in long
cranking times, particularly if the engine is cold. The
oil pressure switch will turn on the fuel pump as soon
as oil pressure
reaches about 28 kPa (4 psi).
FUEL CONTROL
Always start with the "Diagnostic Circuit Check"
in Section
"6E2-A". This will reduce diagnosis time
and prevents unnecessary replacement of parts. The
information in this check will direct diagnosis
concerning "Engine
Crunlis But Won't Run" and the
"Fuel Control System," Section
"6E2-C2", including
diagnosis of an injector, pressure regulator,
fuel pump,
fuel
pump relay, and oil pressure switch.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
A "Scan" tool reads IAC position in steps, calletl
"Counts." "0" steps indicates the ECM is commanding
the
IAC to be driven in, to a fully seiltetl position
(minimum idle air).
The higher the number steps, the
more idle air being allowed to pass
by the IAC valve.
cnose Refer to CHART C-2C for information to cliil,
the function of the IAC valve.
Driva bility
Refer to Section "B" for driveability symptoms
related to the fuel control.
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
GENERAL SEWVICE INFORMATION
CAUTION:
e To prevent personal injury or damage to the
vehicle
as the result sf an accidental start,
disconnect and reconnect the negative
battery cable before and after service is
performed.
@ Also, catch any fuel that leaks out when
disconnecting the fuel lines, by covering the
fittings with
a shop cloth. Place the cloth in
an approved container when work is
complete.
The 'FBI unit repair procedures cover component
replacement with the unit on the vehicle,
tIowever,
throttle body replacement requires that the complete
unit
be removed from the enginc.
Page 588 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - S.0L (VIN E) 6EZ-C2-13
"THROTTLE BODY INJECTION (TBI) UNIT
Replacement (Figure C2-18)
a Remove or Disconnect
1. THERMAC hose from engine fitting.
2. Electrical connectors to IAC valve, TPS and fuel
injectors.
3. Grommet with wires from throttle body.
4. Throttle linkage, return
spring(s) transmission
control cable and cruise control (wherever
applicable).
5. Vacuum hoses (noting position of hoses) and
bracket.
6. Fuel inlet and return lines (use back-up wrench
J-29698-A or BT-8251-A). Discard o-
rings from
nuts.
7. TBI mounting hardware.
8. TBI flange (manifold mounting) gasket and
discard.
NOTICE: Stuff manifold opening with a rag to
prevent material from entering
engine, and remove old gasket
material from surface of intake
manifold.
Inspect
@ Intake manifold bore for loose parts and foreign
material, etc.
@ Intake manifold sealing surface for cleanliness.
Install or Connect
1. New TBI flange (manifold mounting) gasket.
2.
TI31 with mounting hardware.
Tighten
@ Hardwareto, 16.5N-m( 12Ib. ft.).
3. New o-rings on fuel line nuts
4. Fuel inlet and outlet lines.
Tighten - @ To 23 N.m (17 lb. ft.). (Use back-up wrench
J-29698-A or BT-8251-A to keep TBI nuts
from turning.)
5. Vacuum hoses and bracket.
6. Throttle linkage, return
spring(s) transmission
control cable and cruise control (wherever
applicable).
7. Grommet with wire harness to throttle body.
8. Electrical connectors, making sure connectors are
fully seated and latched.
9. Check to see if accelerator pedal is free by
depressing pedal to the floor
and releasing while
engine is "OFF".
10. With engine "OFF," and ignition "ON," check for
leaks around fuel line nuts.
11. Start engine and check for fuel leaks.
FUEL HOSEIPIPE ASSEMBLIES
Materials
Fuel Lines. These are welded steel tubes, meeting GM
Specification 124-M, or its equivalent. The fuel feed
line is
318" diameter, and the fuel return line is 5/16"
diameter. Do not use copper or aluminum tubing to
replace steel tubing. Those materials do not have
satisfactory durability to withstand normal vehicle
vibr, ii t' lon.
Clamps. These are stainless steel, screw band type
clamps,
#249472, or equivalent.
Coupled Hose. These are not to be repaired and are
replaced
&as an assembly.
Uncoupled Hose. Use only reinforced fuel resistant
hose, made of "fluroelastomer" material.
[lo not use w
hose within 4 inches (100 mm) of any part of the
exhaust system, or within 10 inches
(254 mm) of the
catalytic converter. The hose's inside diameter nus st
match the outside diameter of the steel tubing.
Fuel Line Repair
1. Cut
a piece of fuel hose 4 inches (100 mm) longer
than the section of line to be removed. If
more
than 6 inches (152 tnm) is to be removed, use a .
combination of steel pipe and hose. The
hose
length should not be more than 10 inches total.
2. Cut a section of pipe to be replacccl, with a tube
cutter. C'se the first step of a double flaring tool to
form a bead on the ends
of the pipe and also, on the
new section of pipe, if used.
3. Slide
the hose
clanlps onto the pip2 and push the
hose
2 inches (51 mm) onto each portion of the fuel
pipe. Tighten a
clamp on each side of the repair.
4. Secure
fuel line to the frame.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
(Figure
CZ-19)
The fuel pump relay is mounted in the engine
compartment. Other than checking for loose
connectors, the only service possible is replacement.
OIL PRESSURE SWITCH
(Figure C2-20)
The oil pressure switch is li~ounted on the engine.
This switch is a parallel power supply, with the fuel
pump relay, and will provide battery voltage to the
fuel
pump, after approximately 28 kPa (4 psi) oil
pressure is reached.
Page 600 of 1825
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.QL (VIN E) 6Ef-C4-1
SECTION C4
IGNITION SYSTEM 1 (EST)
CQN"FEB\BTO
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ............... C4-1
PURPOSE ........................ C4-1
OPERATION
............*......... C4-1
DIAGNOSIS
........................ C4-1
..... RESULTS OF INCORRECT EST OPER. C4-1
HOW CODE 42 IS DETERMINED ....... C4-2
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
PURPOSE
The High Energy Ignition (HE11 system controls
fuel combustion by providing a spark to ignite the
compressed
aidfuel mixture at the correct time. To
provide improved engine performance, fuel economy,
and control of exhaust emissions, the ECM controls
distributor spark advance (timing) with the Electronic
Spark Timing (EST) system.
Only the Electronic Spark 'Timing (EST) system
will be described here. Additional information on the
HE1 system is found in Section 6D.
OPERATION
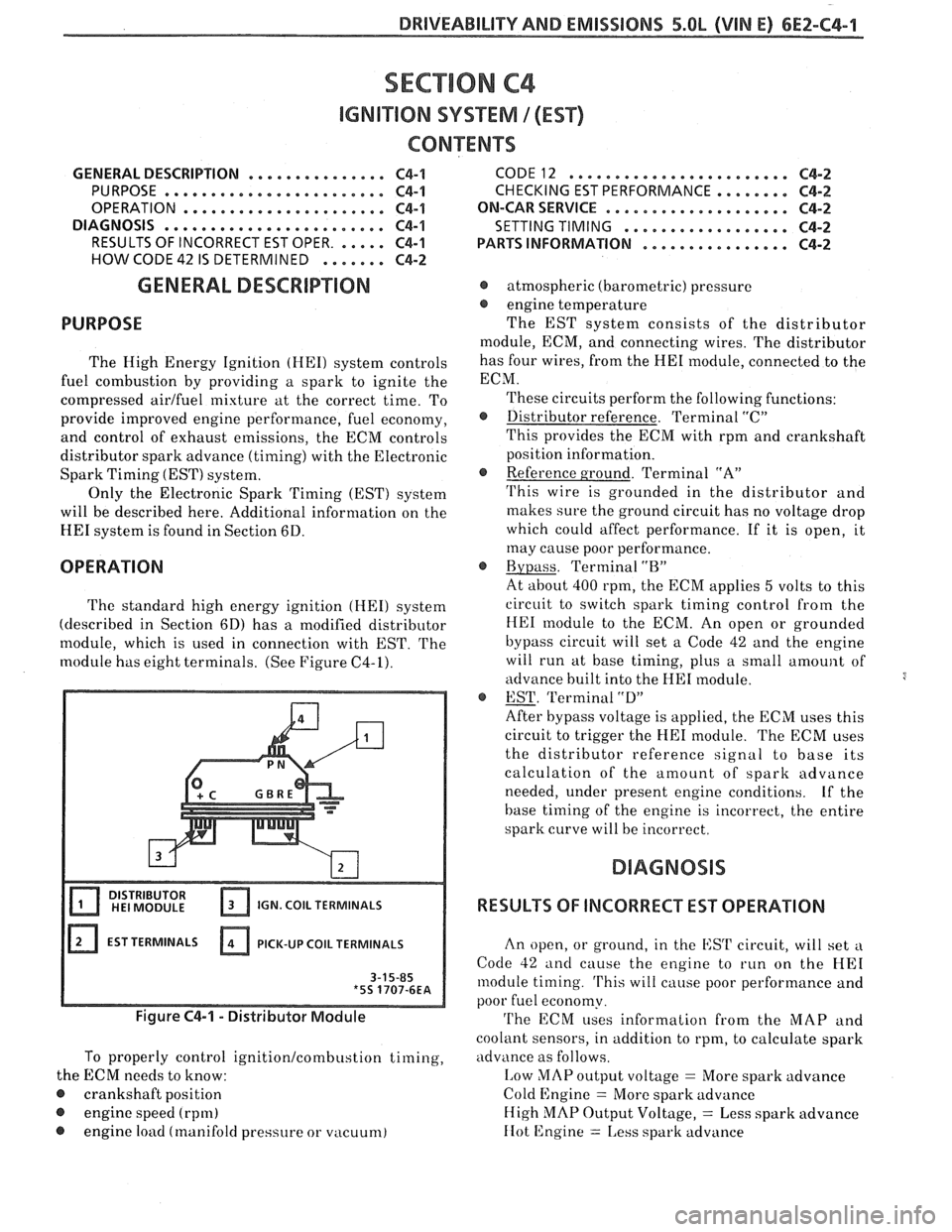
The standard high energy ignition (HEI) system
(described in Section 6D) has a modified distributor
module, which is used in connection with EST.
The
module has eight terminals. (See Figure C4-1).
IGN. COIL TERMINALS
EST TERMINALS PICK-UP
COIL TERMINALS
Figure C4-1 - Distributor Module
To properly control ignition/combustion timing,
the ECM needs to know:
@ crankshaft position
@ engine speed (rpm)
@ engine load (manifold pressure or vacuum)
CODE12 ........................ C4-2
CHECKING EST PERFORMANCE ........ C4-2
ON-CAR SERVICE ...a.e.............. C4-2
SETTING TIMING
.................. C4-2
PARTSINFORMATION ................ C4-2
@ atmospheric (barometric) pressure
@ engine temperature
The EST system consists of the distributor
module, ECM, and connecting wires. The distributor
has four wires, from the
HE1 module, connected to the
ECM.
These circuits perform the following functions:
@ Distributor reference. Terminal "C"
This provides the ECM with rpm and crankshaft
position information.
@ Reference ground. Terminal "A"
'I'his wire is grounded in the distributor and
makes sure the ground circuit has no voltage drop
which could affect performance. If it is open, it
may cause poor performance.
@ Bypass. Terminal "BJ'
At about 400 rpm, the ECM applies 5 volts to this
circuit to switch spark timing control
from the
HE1 module to the ECM. An open or grounded
bypass circuit will set a Code 42 and the engine
will run at base timing, plus a small
amount of
advance built into the
HE1 module.
@ EST. 'Terminal "D"
After bypass voltage is applied, the ECM uses this
circuit to trigger the
HE1 module. The ECM uses
the distributor reference signal to base its
calculation of the amount of spark advance
needed, under present engine conditions.
Lf the
base timing of the engine is incorrect, the entire
spark curve will be incorrect.
RESULTS OF INCORRECT EST OPERATION
An open, or ground, in the EST circuit, will set a
Code 42 and cause the engine to run on the HE1
module timing. 'I'his will cause poor performance and
poor fuel economy.
'I'he ECM uses information from the MAP and
coolant sensors, in addition to rpm, to calculate spark
advance as follows.
I,ow MAP output voltage = More spark advance
Cold Engine
= More spark advance
High
MAP Output Voltage, = Less spark advance
IIot 12ngine = 1,ess spark advance