1985 FORD GRANADA spark plugs
[x] Cancel search: spark plugsPage 97 of 255

The exhaust system fitted in production is
made of aluminised steel, with stainless steel
used in the endplates and baffles of the rear
silencer. Individual sections of the system are
easily renewed in service.
Emission control for the UK market is
achieved largely by the inherent efficiency of
the fuel, ignition and engine management
systems. A welcome spin-off from such
efficiency is remarkably good fuel economy for
a vehicle of such size and weight.
Precautions
Fuel
Many of the procedures in this Chapter
require the removal of fuel lines and
connections which may result in some fuel
spillage. Residual pressure in fuel-injection
systems will remain in the fuel lines long after
the vehicle was last used, therefore extra care
must be taken when disconnecting a fuel line
hose. Loosen any fuel hose slowly to avoid a
sudden release of pressure which may cause
fuel spray. As an added precaution place a rag
over each union as it is disconnected to catch
any fuel which is forcibly expelled. Before
carrying out any operation on the fuel system
refer to the precautions given in “Safety first!”
at the beginning of this Manual and follow
them implicitly. Petrol is a highly dangerous
and volatile liquid and the precautions
necessary when handling it cannot be
overstressed
Tamperproof adjustment screws
Certain adjustment points in the fuel system
(and elsewhere) are protected by tamperproof
caps, plugs or seals. The purpose of such
tamperproofing is to discourage, and to deter,
adjustment by unqualified operators.
In some EU countries (though not yet in the
UK) it is an offence to drive a vehicle with
missing or broken tamperproof seals. Before
disturbing a tamperproof seal, satisfy yourself
that you will not be breaking local or national
anti-pollution regulations by doing so. Fit a
new seal when adjustment is complete when
this is required by law.
Do not break tamperproof seals on a vehicle
which is still under warranty.
Catalytic converter
The catalytic converter is a reliable and
simple device which needs no maintenance in
itself, but there are some facts of which an
owner should be aware if the converter is to
function properly for the full service life.
a)DO NOT use leaded petrol in a car
equipped with a catalytic converter the
lead will coat the precious metals,
reducing their converting efficiency and
will eventually destroy the converter.
b)Always keep the ignition and fuel systems
well-maintained in accordance with the
manufacturer’s schedule - particularly,
ensure that the air cleaner filter element,
the fuel filter and the spark plugs are
renewed at the correct interval - if the inletair/fuel mixture is allowed to become too
rich due to neglect, the unburned surplus
will enter and burn in the catalytic
converter, overheating the element and
eventually destroying the converter.
c)If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the car at all (or at least as little as
possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in
overheating, as noted above.
d)DO NOT push- or tow-start the car - this
will soak the catalytic converter in
unburned fuel, causing it to overheat when
the engine does start - see b) above.
e)DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds - if the ignition is switched
off at anything above idle speed,
unburnedfuel will enter the (very hot)
catalytic converter, with the possible risk
of igniting on the element and damaging
the converter.
f)DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter.
g)DO NOT continue to use the car if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke - the unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages and reduce the efficiency; in
severe cases the element will overheat.
h)Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures -
hence the heat shields on the car’s
underbody and the casing will become hot
enough to ignite combustible materials
which brush against it - DO NOT,
therefore, park the car in dry undergrowth,
over long grass or piles of dead leaves.
i)Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGILE, do not strike it with tools during
servicing work, take great care when
working on the exhaust system, ensure
that the converter is well clear of any jacks
or other lifting gear used to raise the car
and do not drive the car over rough
ground, road humps, etc, in such a way as
to “ground” the exhaust system.
j)In some cases, particularly when the car is
new and/or is used for stop/start driving, a
sulphurous smell (like that of rotten eggs)may be noticed from the exhaust. This is
common to many catalytic converter-
equipped cars and seems to be due to the
small amount of sulphur found in some
petrols reacting with hydrogen in the
exhaust to produce hydrogen sulphide
(H
2S) gas; while this gas is toxic, it is not
produced in sufficient amounts to be a
problem. Once the car has covered a few
thousand miles the problem should
disappear - in the meanwhile a change of
driving style or of the brand of petrol used
may effect a solution.
k)The catalytic converter, used on a well-
maintained and well-driven car, should
last for between 50 000 and 100 000 miles
- from this point on, careful checks should
be made at all specified service intervals
of the CO level to ensure that the
converter is still operating efficiently - if
the converter is no longer effective it must
be renewed.
See Chapter 1, Section 38.
1On carburettor models only, the air cleaner
can take in both hot and cold air. Hot air is
obtained from a shroud bolted to the exhaust
manifold.
2A flap valve in the air cleaner spout
determines the mix of hot and cold air. The
valve is operated by a vacuum diaphragm.
Vacuum is obtained from the inlet manifold
and is applied via a heat-sensing valve, which
cuts off the vacuum as the temperature of the
incoming air rises. Thus the air cleaner takes in
only hot air on starting from cold, changing
progressively to cold air as the engine warms
up (see illustrations).
3If the system fails, either the engine will take
a long time to warm up (flap stuck in “cold”
position), or it may run roughly and not
develop full power when warm (flap stuck in
“hot” position). Check it as follows.
3Air cleaner temperature control
- description and testing
2Air cleaner and element -
removal and refitting
4•4Fuel and exhaust systems
3.2b Air cleaner heat sensor3.2a Air cleaner vacuum diaphragm unit
procarmanuals.com
Page 110 of 255

12Extract the retaining clips and pull the
injectors out of the fuel rail(see illustration).
13The sealing rings and retaining clips on all
injectors must be renewed, even if only one
injector has been removed from the rail. The
lower seal fits between the thick and thin
washers at the tip of the injector (see
illustration).
14Commence refitting by coating the injector
sealing rings with silicone grease to Ford spec
ESEM 1C171A.
15Press the injectors into the fuel rail and
secure them with the new retaining clips.
Press the clips home.
16Reconnect the multi-plugs to the injectors.
17Place the assembled fuel rail on the inlet
manifold and press the injectors into their
holes.
18On V6 models, fit and tighten the fuel rail
bolts. Refit the plenum chamber, using new
gaskets, and tighten the bolts to the specified
torque. Reconnect the throttle cable(s).
19On OHCmodels, fit the fuel rail bolts but
do not tighten them yet.
20On all models, reconnect the fuel and
vacuum pipes. Tighten the fuel pipe unions.
21On OHCmodels, tighten the fuel rail bolts
to the specified torque.
22Reconnect the multi-plugs which were
displaced during removal. On V6 models,
secure the HT leads to the pressure regulator
bracket.
23On OHCmodels, refit the distributor cap.
24Refit the air inlet trunking.
25On V6 models, refit the throttle linkage
cover.
26Reconnect the battery. Run the engine
and check that there are no fuel leaks.
27Check the exhaust CO level.
DOHC engine
28Disconnect the battery negative lead.
29If desired, to improve access, disconnect
the wiring from the inlet air temperature sensor
in the inlet manifold. Similarly, the throttle
cable can be moved to one side by
disconnecting the cable from the throttle
linkage and the spark plug HT leads can be
disconnected and moved to one side, noting
their locations and routing to aid refitting.
30Slowly loosen the fuel rail fuel feed unionto relieve the pressure in the system. Be
prepared for fuel spillage, and take adequate
fire precautions.
31Disconnect the fuel feed hose from the
fuel rail (see illustration).
32Disconnect the fuel return hose from the
fuel pressure regulator. Again, be prepared for
fuel spillage.
33Disconnect the vacuum pipe from the top
of the fuel pressure regulator.
34Disconnect the wiring plugs from the fuel
temperature sensor and the fuel-injectors,
noting their locations to assist with refitting.
35Unscrew the two securing bolts, and
withdraw the fuel rail.
36Lift the fuel-injectors from their locations in
the cylinder head (see illustration).
37Overhaul of the fuel-injectors is not
possible, as no spares are available. If faulty,
an injector must be renewed.
38Commence refitting by fitting new seals to
both ends of each fuel-injector. It is advisable
to fit new seals to all the injectors, even if only
one has been removed. Lubricate the seals
with clean engine oil.
39Further refitting is a reversal of removal,
ensuring that all hoses, pipes and wiring plugs
are correctly connected.
40On completion, where applicable, check
and if necessary adjust the idle mixture.
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines
41Disconnect the battery.
42Remove the air inlet pipes from the throttle
housing.43Disconnect the link arm from the throttle
housing and unscrew the two bolts which
retain the throttle cable bracket.
44Disconnect the vacuum pipes from the
throttle housing, crankcase vent valve and the
fuel pressure regulator.
45Disconnect the wiring connectors from the
throttle position sensor, engine and coolant
temperature sensors and the idle speed
control valve.
46Extract the six Torx bolts which hold the
air inlet chamber in position.
47Carefully disconnect the fuel-injector
wiring connectors (see illustration).
48Depressurise the fuel system.
49Disconnect the fuel rail feed pipe and the
fuel return pipe. This is best done at the wing
valance and will require cutting the crimped
hose clips.
50The crimped-type clips must then be
replaced with standard worm drive hose clips
on refitting.
51Unscrew the fuel rail retaining bolts and
remove the fuel rail.
52Extract the retaining clips and remove the
injectors from the fuel rail.
53Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure bearing in mind the following.
54Renew all the upper and lower injector
seals, even if only one injector has been
disturbed. Lubricate all new seals with clean
engine oil.
55On models fitted with an early level fuel
pressure regulator, it is necessary to fit a new
fuel inlet pipe to the fuel rail, the new
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•17
4
36.12 Removing a fuel injector from the rail
A Retaining clip36.13 Injector with seals removed36.31 Disconnecting the fuel feed hose
from the fuel rail
36.36 Lifting a fuel injector from the
cylinder head36.47 Disconnecting a fuel injector wiring
connector
procarmanuals.com
Page 112 of 255

24Unbolt and remove the regulator from the
fuel rail. Remove the sealing O-ring and
discard it; a new one must be used on
refitting.
25Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure applying a smear of clean engine oil
to the new regulator O-ring. On models
equipped with a late level regulator, ensure
that the return pipe is securely held in position
by the retaining collar.
26On completion, switch the ignition on and
off five times without cranking the engine to
pressurise the fuel system.
27With the system pressurised check all
disturbed fuel unions for signs of leakage.
1The potentiometer is located on the right-
hand side of the engine compartment, behind
the MAP sensor.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Remove the securing screw, then withdraw
the potentiometer and disconnect the wiring
plug.
4Refitting is a reversal of removal. On
completion adjust the idle mixture.1On 2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines, disconnect the
battery.
2Disconnect the switch wiring connector.
3Slacken and remove the switch from the
fuel rail (see illustration).
4Refitting is a reverse of removal, tightening
the switch to the specified torque setting.
Carburettor models
All engines except DOHC
1Remove the carburettor or, if preferred, the
final removal of the carburettor from the
manifold can be left until the manifold has
been removed).
2Drain the cooling system.
3Disconnect the coolant and vacuum pipes
from the manifold, noting their positions if
there is any possibility of confusion.
4Disconnect the wires from the manifold
heater and the coolant temperature sender
unit.
5Disconnect the crankcase ventilation hose
from the manifold.
6Unscrew the six nuts and bolts which
secure the manifold and withdraw it. Recover
the gasket.
7Before refitting the manifold, make sure that
the mating surfaces are perfectly clean.
8Apply a bead of sealant at least 5 mm (0.2 in)
wide around the central coolant aperture on
both sides of a new gasket.
9Place the gasket over the studs, then fit the
manifold and secure it with the six nuts and
bolts. Tighten the nuts and bolts evenly to the
specified torque.
10The remainder of refitting is a reversal of
the removal procedure. Refill the cooling
system on completion.
DOHC engine
11Disconnect the battery negative lead.
12Drain the cooling system.13Remove the air cleaner.
14Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
thermostat housing and the inlet manifold,
noting the locations to assist with refitting.
15Disconnect the fuel supply and return
hoses from the carburettor. Plug their ends to
minimise petrol spillage.
16Release the coolant hose from the bracket
under the automatic choke housing.
17Disconnect the HT leads from the spark
plugs, and move them to one side.
18Disconnect all relevant wiring and vacuum
pipes from the carburettor, thermostat
housing and inlet manifold, noting the
locations as an aid to refitting.
19Disconnect the crankcase breather hose
from the inlet manifold.
20Disconnect the throttle cable from the
throttle linkage.
21Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant wires, pipes and hoses have been
disconnected to facilitate removal of the
manifold.
22Unscrew the ten bolts and two nuts
securing the manifold to the cylinder head.
23Lift the manifold clear of the cylinder head
and recover the gasket.
24Recover the two plastic spark plug spacers
from the recesses in the cylinder head.
25If desired, the carburettor can be removed
from the manifold by unscrewing the securing
screws.
26Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.
a)Ensure that all mating faces are clean and
renew all gaskets.
b)Ensure that the spark plug spacers are in
position in the cylinder head recesses
before refitting the manifold.
c)Tighten all manifold securing nuts and
bolts progressively to the specified torque.
d)Make sure that all hoses, pipes and wires
are securely reconnected in their original
positions. Replace all crimp-type hose
clips (where fitted) with standard worm
drive hose clips.
e)On completion, refill the cooling system,
check the adjustment of the throttle cable,
then check, and if necessary adjust the
idle speed and mixture.
Fuel-injection models
SOHC engine
27Disconnect the battery negative lead.
28Drain the cooling system.
29Disconnect the vacuum pipe(s) from the
manifold. The number of pipes varies
according to equipment. Label the pipes if
necessary (see illustration).
30Disconnect the fuel-injection harness
multi-plugs at the bulkhead end of the
manifold (see illustration).
31Disconnect the oil pressure warning light
sender wire from below the manifold.
32Release the hose clips and move the
airflow meter-to-manifold trunking clear of the
manifold.
40Inlet manifold - removal and
refitting
39Fuel rail temperature switch -
removal and refitting
38Mixture adjustment
potentiometer - removal and
refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•19
4
39.3 Fuel rail components
A Fuel pressure regulator
B Fuel temperature switch
C Fuel rail
D Fuel injectors
40.29 Manifold vacuum pipe T-piece
(arrowed)40.30 Fuel-injection wiring harness plugs
procarmanuals.com
Page 113 of 255
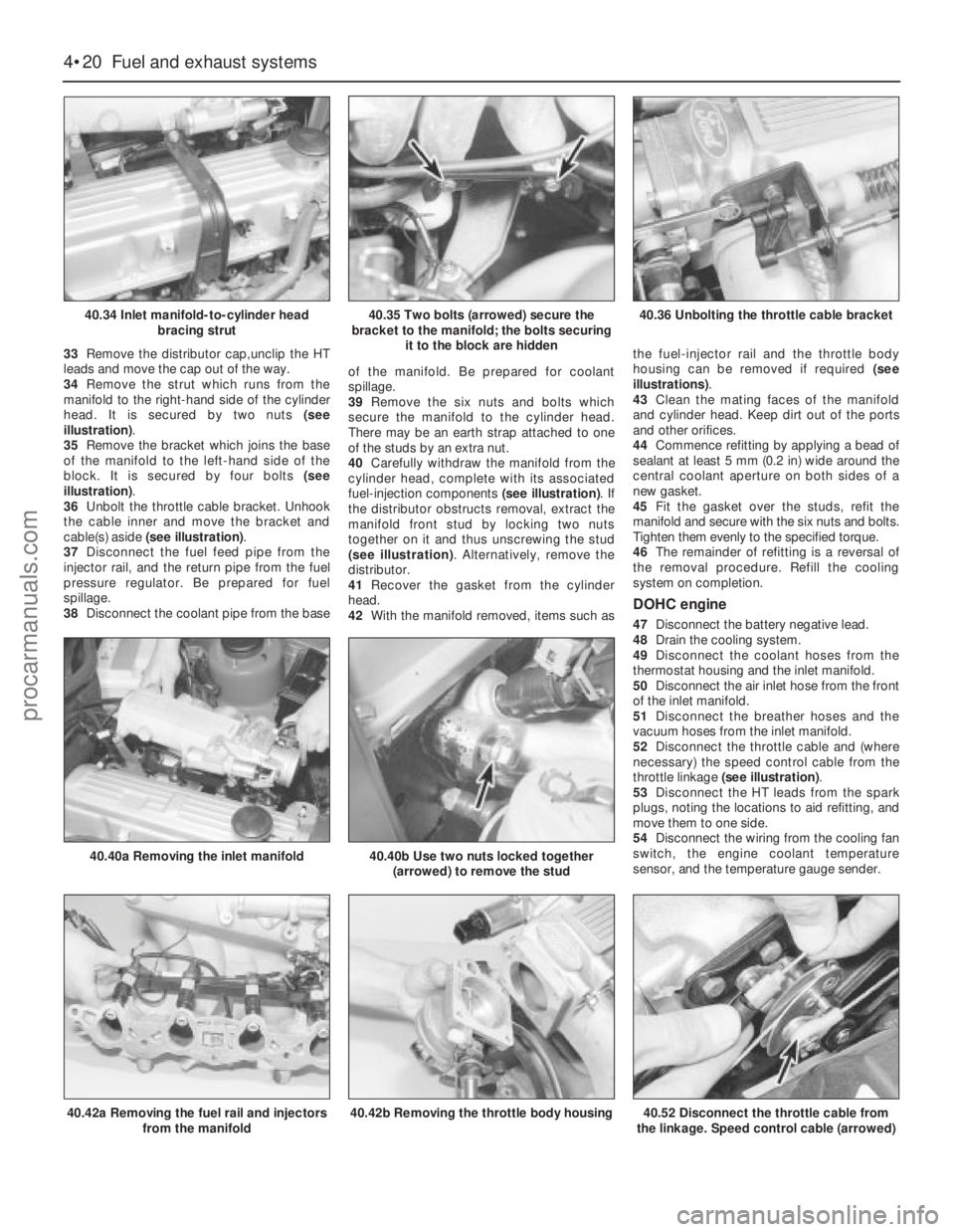
33Remove the distributor cap,unclip the HT
leads and move the cap out of the way.
34Remove the strut which runs from the
manifold to the right-hand side of the cylinder
head. It is secured by two nuts (see
illustration).
35Remove the bracket which joins the base
of the manifold to the left-hand side of the
block. It is secured by four bolts (see
illustration).
36Unbolt the throttle cable bracket. Unhook
the cable inner and move the bracket and
cable(s) aside (see illustration).
37Disconnect the fuel feed pipe from the
injector rail, and the return pipe from the fuel
pressure regulator. Be prepared for fuel
spillage.
38Disconnect the coolant pipe from the baseof the manifold. Be prepared for coolant
spillage.
39Remove the six nuts and bolts which
secure the manifold to the cylinder head.
There may be an earth strap attached to one
of the studs by an extra nut.
40Carefully withdraw the manifold from the
cylinder head, complete with its associated
fuel-injection components (see illustration). If
the distributor obstructs removal, extract the
manifold front stud by locking two nuts
together on it and thus unscrewing the stud
(see illustration). Alternatively, remove the
distributor.
41Recover the gasket from the cylinder
head.
42With the manifold removed, items such asthe fuel-injector rail and the throttle body
housing can be removed if required (see
illustrations).
43Clean the mating faces of the manifold
and cylinder head. Keep dirt out of the ports
and other orifices.
44Commence refitting by applying a bead of
sealant at least 5 mm (0.2 in) wide around the
central coolant aperture on both sides of a
new gasket.
45Fit the gasket over the studs, refit the
manifold and secure with the six nuts and bolts.
Tighten them evenly to the specified torque.
46The remainder of refitting is a reversal of
the removal procedure. Refill the cooling
system on completion.
DOHC engine
47Disconnect the battery negative lead.
48Drain the cooling system.
49Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
thermostat housing and the inlet manifold.
50Disconnect the air inlet hose from the front
of the inlet manifold.
51Disconnect the breather hoses and the
vacuum hoses from the inlet manifold.
52Disconnect the throttle cable and (where
necessary) the speed control cable from the
throttle linkage (see illustration).
53Disconnect the HT leads from the spark
plugs, noting the locations to aid refitting, and
move them to one side.
54Disconnect the wiring from the cooling fan
switch, the engine coolant temperature
sensor, and the temperature gauge sender.
4•20Fuel and exhaust systems
40.34 Inlet manifold-to-cylinder head
bracing strut
40.42a Removing the fuel rail and injectors
from the manifold
40.40a Removing the inlet manifold40.40b Use two nuts locked together
(arrowed) to remove the stud
40.42b Removing the throttle body housing40.52 Disconnect the throttle cable from
the linkage. Speed control cable (arrowed)
40.35 Two bolts (arrowed) secure the
bracket to the manifold; the bolts securing
it to the block are hidden40.36 Unbolting the throttle cable bracket
procarmanuals.com
Page 114 of 255

55Release the throttle position sensor wiring
connector from the clip under the throttle
body, and separate the two halves of the
connector.
56Remove the fuel-injectors.
57Check that all relevant wiring, hoses and
pipes have been disconnected to facilitate
removal of the manifold.
58Unscrew the ten bolts and two nuts
securing the inlet manifold to the cylinder
head, and carefully withdraw the manifold.
Recover the gasket.
59Recover the two plastic spark plug
spacers from the recesses in the cylinder head
(see illustration).
60If desired, the manifold can be dismantled
with reference to the relevant paragraphs of
this Chapter.
61Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.
a)Ensure that the spark plug spacers are in
position in the cylinder head recesses
before refitting the manifold.
b)Ensure manifold and cylinder head mating
surfaces are clean and dry and fit a new
gasket.
c)Tighten the manifold retaining nuts and
bolts evenly and progressively to the
specified torque.
d)Refit the fuel-injectors.
e)Make sure that all hoses, pipes and wires
are securely reconnected in their original
positions.
f)On completion, refill the cooling system.
g)Check the adjustment of the throttle cable
and where necessary, adjust the speed
control cable so that only a small amount
of slack is present in the cable.
h)Where applicable, check and if necessary
adjust the idle speed and mixture.
V6 engines
62Disconnect the battery negative lead.
63Drain the cooling system.
64Remove the throttle linkage cover.
65Release the hose clips and move the
airflow meter-to-manifold trunking aside.
Unclip or remove the crankcase ventilation
hose.
66Disconnect the radiator top hose and the
heater hose from the outlet at the front of the
manifold. Be prepared for some coolant spillage.67Disconnect the multi-plugs from the idle
speed control valve, the temperature gauge
sender unit; the coolant temperature sensor
and the throttle position sensor. Also
disconnect the injector wiring harness.
68Disconnect the throttle cable from the
linkage, unclip it and move it aside. On
automatic transmission models, also
disconnect the downshift cable or multi-plug,
as applicable.
69Disconnect the fuel feed and return pipes.
Be prepared for fuel spillage.
70Remove the HT leads and the distributor.
71Remove the plenum chamber, which is
secured by eight bolts.
72Remove the rocker covers, which are each
secured by seven bolts.
73Disconnect the water pump bypass hose
from the inlet manifold.
74Remove the eight bolts which secure the
inlet manifold to the cylinder heads.
75Lift off the manifold complete with fuel
pressure regulator, fuel rail, throttle body
housing etc. If it is stuck, carefully lever it free.
Do not apply leverage at the mating faces.
Recover the gasket.
76Clean all mating faces, being careful to
keep dirt out of ports and other orifices.
Obtain new gaskets for both the cylinder head
and plenum chamber sides of the manifold,
and for the rocker covers.
77Commence refitting by applying sealant
(Ford part No A70X-19554-BA, or equivalent)
around the ports and coolant passages on the
cylinder head.
78Apply sealant around the apertures on
both sides of the gasket. then fit the gasket to
the cylinder heads.
79Refit the manifold and insert the securing
bolts. Tighten the bolts, in the order shown
(see illustration),through the first four stages
given in the Specifications.
80Refit the water pump bypass hose.
81Refit the rocker covers, using new
gaskets. The adhesive sides of the gaskets
must face the covers.
82Reverse the remaining removal
operations, but do not refit the throttle linkage
cover yet.
83When the cooling system has beenrefilled, reconnect the battery and start the
engine. Check for fuel and other leaks.
84Bring the engine to operating temperature,
then stop it and carry out the final tightening of
the inlet manifold bolts as follows.
85Release the air inlet trunking. Unplug the
idle speed control valve and the throttle
position sensor. Unbolt the plenum chamber
and move it aside, disconnecting vacuum and
breather hoses as necessary.
86Slacken, but do not remove, the two bolts
which secure the fuel rail to the manifold.
87Tighten the inlet manifold bolts to the
Stage 5 specified torque, again following the
sequence shown. A special cranked spanner
(Ford tool No 21-079, or equivalent)(see
illustration)will be needed to tighten No 4
bolt when the distributor is fitted. In the
absence of such a spanner, remove the
distributor again.
88Tighten the fuel rail securing bolts.
89Refit the disturbed components. Run the
engine again and check the ignition timing and
the exhaust CO level .
90Refit the throttle linkage cover.
SOHC and all V6 engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Apply copious quantities of penetrating oil
to the manifold and exhaust pipe flange nuts
and bolts.
3On carburettor models, remove the air
cleaner and the hot air pick-up pipe.
4Unbolt any heat shields or shrouds from the
manifold.
5Unbolt the exhaust pipe(s) from the manifold
flange. Support the exhaust system if
necessary.
6Unbolt the manifold from the cylinder head
and remove it. Recover the gasket.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Use a new gasket, and apply anti-seize
compound to the various nuts and bolts.
Tighten the manifold fastenings to the
specified torque.
41Exhaust manifold(s) - removal
and refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•21
4
40.59 Removing a spark plug spacer from
the cylinder head recess40.79 Inlet manifold bolt tightening
sequence
Arrow points to front of engine40.87 Cranked spanner needed for
tightening V6 inlet manifold bolt with
distributor fitted
procarmanuals.com
Page 118 of 255

Chapter 5
Engine electrical systems
Air charge temperature sensor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .25
Alternator - brush renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Alternator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Alternator - testing on the vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Battery - charging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Battery - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Carburettor stepper motor (2.0 litre models) - removal, refitting and
adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Coolant temperature sensor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Crankshaft speed/position sensor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . .24
Distributor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Electrical fault-finding - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Engine management control module - removal and refitting . . . . . .18
Engine management system relays - testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Fuel temperature sensor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26Fuel trap (carburettor models) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . .17
General information and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
HT leads, distributor cap and rotor arm - removal, inspection and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Ignition coil - testing, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Ignition module (fuel-injection models) - removal and refitting . . . .15
Ignition timing - checking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Ignition timing and idle speed adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor - removal and refitting . .28
Manifold heater (carburettor models) - removal and refitting . . . . . .21
Spark plugs - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Starter motor - brush renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Starter motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Starter motor - testing on the vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Vehicle speed sensor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
General
Electrical system type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 volt, negative earth
Ignition system type: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Breakerless, Hall effect, with electronic control of advance
Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ESC II system
Fuel-injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . EEC IV system
Firing order:
OHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3-4-2 (No 1 at pulley end)
V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4-2-5-3-6 (No 1 at front of right-hand bank)
Alternator
Make and type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bosch KI-55A, NI-70A or NI-90A
Rated output at 13.5 volts and 6000 engine rpm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55, 70 or 90 amps
Rotor winding resistance at 20°C (68°F):
KI-55A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.4 to 3.7 ohms
NI-70A and NI-90A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.8 to 3.1 ohms
Brush wear limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 mm (0.2 in)
Regulated voltage at 4000 engine rpm and 3 to 7 amp load . . . . . . . . . 13.7 to 14.6 volts
Voltage regulator type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Solid state, integral
Starter motor
Make and type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bosch short frame, long frame or reduction gear
Rating:
Short frame . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.85 or 0.95 kW
Long frame . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.1 kW
Reduction gear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.4 kW
Brush wear limit:
Short frame and reduction gear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 mm (0.32 in)
Long frame . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 mm (0.39 in)
Commutator minimum diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32.8 mm (1.29 in)
Armature endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.3 mm (0.012 in)
5•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
5
procarmanuals.com
Page 119 of 255

The ignition system is responsible for
igniting the fuel/air charge in each cylinder at
the correct moment. The components of the
system are the spark plugs, ignition coil,
distributor and connecting leads. Overall
control of the system is one of the functions of
the engine management module. Fuel-
injection models have a subsidiary ignition
module mounted on the distributor.
There are no contact breaker points in the
distributor. A square wave signal is generated
by the distributor electro-magnetically; this
signal is used by the engine management
module as a basis for switching the coil LT
current. Speed-related (centrifugal) advance is
also handled by the module. On carburettor
models, ignition timing is also advanced under
conditions of high inlet manifold vacuum.The engine management models are “black
boxes” which regulate both the fuel and the
ignition systems to obtain the best power,
economy and emission levels. The module
fitted to carburettor models is known as the
ESC II (Electronic Spark Control Mk II) module.
On fuel-injection models the more powerful
EEC IV (Electronic Engine Control Mk IV)
module is used.
Both types of module receive inputs from
sensors monitoring coolant temperature,
distributor rotor position and (on some
models) manifold vacuum. Outputs from the
module control ignition timing, inlet manifold
heating and (except on 1.8 litre models) idle
speed. The EEC IV module also has overall
control of the fuel-injection system, from
which it receives information.
Provision is made for the ignition timing to
be retarded to allow the use of low octane fuel
if necessary. On all except 1.8 litre models
there is also a facility for raising the idle speed.The EEC IV module contains self-test
circuitry which enables a technician with the
appropriate test equipment to diagnose faults
in a very short time. A Limited Operation
Strategy (LOS) means that the car is still
driveable, albeit at reduced power and
efficiency, in the event of a failure in the
module or its sensors.
Due to the complexity and expense of the
test equipment dedicated to the engine
management system, suspected faults should
be investigated by a Ford dealer, or other
competent specialist. This Chapter deals with
component removal and refitting, and with
some simple checks and adjustments.
On DOHC carburettor engines, the basic
operating principles of the ignition system are
as described above. A development of the
ESC II (Electronic Spark Control ll) system is
used to control the operation of the engine.
The ESC II module receives information from a
crankshaft speed/position sensor and an
1General information and
precautions
5•2Engine electrical systems
Ignition coil
Make . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Bosch, Femsa or Polmot
Primary resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.72 to 0.86 ohm
Secondary resistance:
All except DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.5 to 7.0 k ohms
DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.5 to 8.6 k ohms
Output voltage (open-circuit):
All except DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25 kV minimum
DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 kV minimum
HT leads
Maximum resistance per lead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 k ohms
Distributor
Make . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Bosch or Motorcraft
Rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Clockwise (viewed from above)
Automatic advance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Controlled by module
Dwell angle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Controlled by module
Ignition timing (see text)
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines:
Leaded fuel (97 octane):
Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10°BTDC
Fuel-injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12°BTDC
Unleaded fuel (95 octane):
Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6°BTDC
Fuel-injection models:
2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8°BTDC
2.8 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12°BTDC (no change)
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines:
Models with catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15°BTDC
Models without catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12°BTDC*
* Standard setting for 97 octane leaded fuel.
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Alternator adjusting strap:
To steering pump bracket (OHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2616 to 19
To front cover (V6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Spark plugs:
All models except 2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2815 to 21
2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 to 4022 to 30
Air charge temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Engine coolant temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Fuel rail temperature sensor (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Crankshaft speed/position sensor screw (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 to 52 to 4
procarmanuals.com
Page 122 of 255

Solenoid check
3Disconnect the battery negative lead, and all
leads from the solenoid.
4Connect a battery and a 3 watt test lamp
between the solenoid body and the solenoid
motor terminal (see illustration).The test
lamp should light: if not, the solenoid windings
are open-circuit.
5Connect a battery and an 18 to 21 watt test
lamp across the solenoid motor and battery
terminals. Connect a further lead from the
battery positive terminal to the solenoid spade
terminal(see illustration).The solenoid
should be heard to operate and the test lamp
should light: if not, the solenoid contacts are
defective.
On load voltage check
6Remake the original connections to the
solenoid and reconnect the battery negative
lead. Connect a voltmeter across the battery
terminals, then disconnect the low tension
lead from the coil positive terminal and
operate the starter by turning the ignition
switch. Note the reading on the voltmeter
which should not be less than 10.5 volts.
7Now connect the voltmeter between the
starter motor terminal on the solenoid and the
starter motor body. With the coil low tension
lead still disconnected, operate the starter and
check that the recorded voltage is not more
than 1 volt lower than thatpreviously noted. If
the voltage drop is more than 1 volt a fault
exists in the wiring from the battery to the
starter.
8Connect the voltmeter between the battery
positive terminal and the terminal on the
starter motor. With the coil low tension lead
disconnected operate the starter for two or
three seconds. Battery voltage should be
indicated initially, then dropping to less than 1
volt. If the reading is more than 1 volt there is a
high resistance in the wiring from the battery
to the starter and the check in paragraph 9
should be made. If the reading is less than 1
volt proceed to paragraph 10.
9Connect the voltmeter between the two
main solenoid terminals and operate the
starter for two or three seconds. Batteryvoltage should be indicated initially then
dropping to less than 0.5 volt. If the reading is
more than 0.5 volt, the solenoid and
connections may be faulty.
10Connect the voltmeter between the
battery negative terminal and the starter motor
body, and operate the starter for two or three
seconds. A reading of less than 0.5 volt should
be recorded; however, if the reading is more,
the earth circuit is faulty and the earth
connections to the battery and body should be
checked.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead. Raise
and support the front of the vehicle.
2From underneath the vehicle, disconnect
the feed (heavy) cable from the solenoid.
3Disconnect the command lead from the
solenoid spade terminal.
4Undo the starter motor securing bolts and
(where fitted) the support bracket fastenings.
Withdraw the starter motor from the vehicle.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Check for correct operation on completion.
1Disconnect the motor lead from the
solenoid terminal.
2Remove the two screws which secure the
armature end cap. Remove the cap, the C-
washer and the plain washer(s).
3Remove the two through-bolts or studs.
4Remove the commutator end cover to
expose the brushgear. Carefully withdraw the
brushplate from the commutator. Be careful to
avoid damage to the brushes as they are
released.
5Examine the brushes: they should not beexcessively worn (see Specifications) and
must slide freely in their holders. Brush
renewal varies according to motor type as
follows:
Short frame - the brush lead must be
removed from the stand-off connector on the
brushplate, and the clip on the new brush lead
soldered to the connector.
Long frame - the old brush leads must be
cut and the new leads attached by soldering
Reduction gear - the brushplate must be
renewed complete with brushes, holders and
springs
6Reassembly is the reverse of dismantling
whilst noting the following:
7Clean the commutator with a rag moistened
with methylated spirit, then refit the
brushplate.
8Either clip the brushes in place after fitting
the plate, or use a tube of suitable diameter to
keep the brushes retracted during fitting.
9Make sure that the brushplate is correctly
positioned to allow the passage of through-
bolts or studs.
See Chapter 1, Section 20.
See Chapter 1, Section 39.
All engines except 2.4 & 2.9 litre V6
Note: The distributor should not be removed
without good cause, since the accuracy of
ignition timing achieved in production is
unlikely to be regained
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the distributor cap as described in
the previous Section. Depending on model, it
may be possible to move the cap aside
without disconnecting the HT leads.
3Using a spanner on the crankshaft pulley
bolt, turn the engine to bring No 1 cylinder to
firing point. (If the distributor cap is secured by
clips, make sure the clips stay clear of the
distributor moving parts.) No 1 cylinder is at
firing point when:
a)The timing marks are in alignment.
b)The tip of the rotor arm is pointing to the
place occupied by the No 1 HT lead
connector in the distributor cap (see
illustration).
4With No 1 cylinder at firing point, the tip of
the rotor arm should also be aligned with a
notch in the distributor body. Mark the notch
for reference when refitting.
5Depress the locking tab on the distributor
13Distributor - removal and
refitting
12HT leads, distributor cap and
rotor arm - removal, inspection
and refitting
11Spark plugs - removal,
inspection and refitting
10Starter motor - brush renewal
9Starter motor - removal and
refitting
Engine electrical systems 5•5
5
8.4 Solenoid winding check
A Battery terminal
B Motor terminalC Spade terminal
8.5 Solenoid contact check
A Battery terminal
B Motor terminalC Spade terminal
If the stud nuts are
inaccessible, lock two nuts
together on the stud and turn
them to unscrew it .
procarmanuals.com