1973 DATSUN B110 battery
[x] Cancel search: batteryPage 432 of 513

ENGINE
Arma
ture
shaft
Outer
diameter
Pinion
side
mm
in
12
950
to
12
968
0
5082
to
0
5105
11
450
to
II
468
0
4507
to
0
4515
0
1
0
0039
0
08
0
0031
Rear
end
mm
in
Wear
limit
Bend
limit
mm
in
mm
in
Gap
1
between
the
pinion
front
edge
and
the
pinion
stopper
mm
in
0
3
to
1
5
0
0118
to
0
0591
Magnetic
switch
Coil
resistance
Series
cuil
Q
Shunt
coil
n
Plunger
L
dimension
mm
in
0
3
at
20De
68UF
0
9
at
ooe
680F
317t032
3
l
248
to
1
272
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
12
950
to
12
968
0
5082
to
0
5105
11
450
to
II
468
0
4507
to
0
4515
l
0
1
0
0039
0
08
0
0031
0
3
to
1
5
0
0118
to
0
0591
0
3
at
20De
680Fl
0
9
at
200e
680F
317
to
32
3
l
248
to
I
272
Troubles
Trouble
location
Causes
Remedies
Starting
motor
will
not
operate
No
magnetic
switch
Battery
Defective
battery
Replace
battery
operating
sound
Over
discharging
Measure
specific
gravity
of
e
Ie
ctrolyte
and
ch
lrge
or
replace
the
battery
Ignition
switch
Defective
contact
Correct
or
replace
ig
nition
switch
Wiring
Faulty
starting
motor
grounding
Correct
Faulty
battery
grounding
Correct
Broken
or
disconnected
cable
Correct
or
replace
EE
12
Page 433 of 513
Magnetic
switch
operating
sound
is
heard
The
starting
motor
rotates
Pinion
gear
does
not
intermesh
with
ring
gear
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
Starter
Magnetic
switch
Battery
Wiring
Starting
motor
Magnetic
switch
Ring
gear
Starting
motor
Broken
armature
or
field
coil
cable
Broken
brush
pig
tail
Defective
mica
Broken
or
shorted
series
coil
Faulty
plunger
sliding
Over
discharging
Faulty
terminal
contact
or
loose
connection
Faulty
B
or
M
terminal
connections
Shorted
armature
or
field
coil
Worn
brush
or
improper
spring
pressure
Contaminated
commutator
or
de
fective
mica
Faulty
brush
connection
Seized
metal
Armature
contacted
with
pole
core
Insufficient
plunger
L
dimension
Faulty
contact
Broken
or
shorted
shunt
coil
wire
Worn
teeth
Weakened
pinion
sleeve
spring
Worn
pinion
teeth
EE
13
Replace
Replace
Correct
or
replace
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Measure
specific
gravity
of
electrolyte
arid
charge
if
necessary
Clean
and
retighten
Retighten
Repair
or
replace
Repair
or
replace
Clean
or
repair
Repair
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Adjust
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Page 434 of 513

Pinion
intermeshes
with
ring
gear
Starting
motor
rotates
and
pinion
intermeshes
with
ring
gear
but
ro
tation
is
too
slow
When
starting
switch
is
set
to
OFF
the
start
ing
motor
does
not
stop
Starting
motor
Battery
Wiring
Ignition
switch
Starting
motor
Ignition
switch
Magnetic
switch
Starting
motor
ENGINE
Faulty
pinion
sliding
Dropped
off
lever
pin
Excessive
plunger
L
dimension
Defective
over
running
clutch
Over
discharging
Improper
or
loose
terminal
contact
Improperly
tightened
connection
Rough
contact
surface
Shorted
armature
coil
or
field
coil
Worn
brush
or
insufficient
spring
pressure
Contaminated
commutator
or
im
proper
brush
contact
Defective
mica
Lack
of
metal
lubrication
Armature
contacted
with
pole
core
Faulty
returning
Seized
contact
Shorted
coil
Faulty
plunger
sliding
Pinion
does
not
disengage
from
the
ring
gear
smoothly
Pinion
spline
does
not
disengage
smoothly
Seized
pinion
metal
EE
14
Repair
Repair
Adjust
Replace
Charge
battery
Repair
and
retighten
Retighten
Repair
or
replace
Repair
or
replace
Repair
or
replace
Repair
Repair
Repair
or
replace
Repair
or
replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Repair
or
replace
Replace
Page 435 of 513
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
CHARGING
CIRCUIT
IGNITION
1
i
n
ITCH
r
B
i
i
vel
oU
ARMATURE
lip
J
l
t
lJ
FIEL
Df
e
I
I
3
2
I
u
P
5
0
IL
U
p
P
f
H
i
I
I
L
J
L
J
ALTERNATOR
VOL
TAGE
REGULATOR
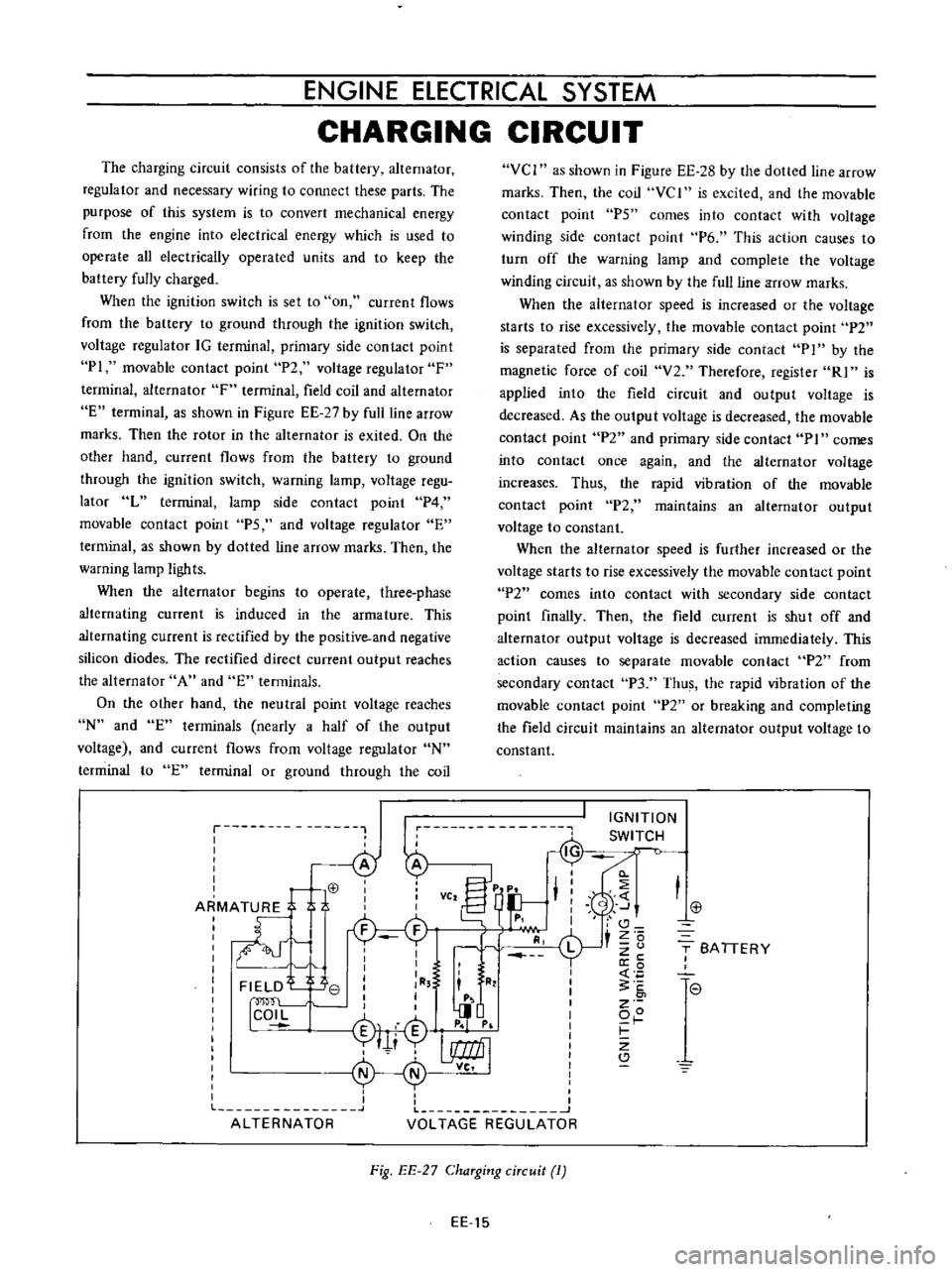
The
charging
circuit
consists
of
the
battery
alternator
regulator
and
necessary
wiring
to
connect
these
parts
The
purpose
of
this
system
is
to
convert
mechanical
energy
from
the
engine
into
electrical
energy
which
is
used
to
operate
all
electrically
operated
units
and
to
keep
the
battery
fully
charged
When
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
on
current
flows
from
the
battery
to
ground
through
the
ignition
switch
voltage
regulator
IG
terminal
primary
side
contact
point
PI
movable
contact
point
P2
voltage
regulator
F
terminal
alternator
F
terminal
field
coil
and
alternator
E
terminal
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
27
by
full
line
arrow
marks
Then
the
rotor
in
the
alternator
is
exited
On
the
other
hand
current
flows
from
the
battery
to
ground
through
the
ignition
switch
warning
lamp
voltage
regu
lator
L
terminal
lamp
side
contact
point
P4
movable
contact
point
PS
and
voltage
regulator
E
terminal
as
shown
by
dotted
line
arrow
marks
Then
the
warning
lamp
ligh
ts
When
the
alternator
begins
to
operate
three
phase
alternating
current
is
induced
in
the
armature
This
alternating
current
is
rectified
by
the
positive
and
negative
silicon
diodes
The
rectified
direct
current
output
reaches
the
alternator
A
and
E
terminals
On
the
other
hand
the
neutral
point
voltage
reaches
N
and
E
terminals
nearly
a
half
of
the
output
voltage
and
current
flows
from
voltage
regulator
N
terminal
to
E
terminal
or
ground
through
the
coil
VCI
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
28
by
the
dolled
line
arrow
marks
Then
the
coil
vc
I
is
excited
and
the
movable
contact
point
P5
comes
into
contact
with
voltage
winding
side
contact
point
P6
This
action
causes
to
turn
off
the
warning
lamp
and
complete
the
voltage
winding
circuit
as
shown
by
the
ullline
arrow
marks
When
the
alternator
speed
is
increased
or
the
voltage
starts
to
rise
excessively
the
movable
contact
point
P2
is
separated
from
the
primary
side
contact
P
1
by
the
magnetic
force
of
coil
V2
Therefore
register
RI
is
applied
into
the
field
circuit
and
output
voltage
is
decreased
As
the
outpu
t
voltage
is
decreased
the
movable
contact
point
P2
and
primary
side
contact
PI
comes
into
contact
once
again
and
the
alternator
voltage
increases
Thus
the
rapid
vibration
of
the
movable
contact
point
P2
maintains
an
alternator
output
voltage
to
constant
When
the
alternator
speed
is
further
increased
or
the
voltage
starts
to
rise
excessively
the
movable
contact
point
P2
comes
into
contact
with
secondary
side
contact
point
finally
Then
the
field
current
is
shut
off
and
alternator
output
voltage
is
decreased
immediately
This
action
causes
to
separate
movable
contact
P2
from
secondary
contact
P3
Thus
the
rapid
vibration
of
the
movable
contact
point
P2
or
breaking
and
completing
the
field
circuit
maintains
an
alternator
output
voltage
to
constant
j
T
SA
TIERY
I
l
e
7
Fig
EE
27
ChaTging
ciTcuit
1
EE
15
Page 436 of 513
ENGINE
r
Ignition
switJ
c
o
iArm
ture
j
i
i
VC2
P
tP2
d
I
I
I
PI
I
ll
Rl
L
I
I
lRJ
t
R
I
Field
e
I
I
I
I
Ps
I
1
I
I
n
I
coil
M
4
i
f
I
L
1
J
Alternator
Voltage
regulator
Fig
EE
2B
ChaTging
ciTcuit
II
ALTERNATOR
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION
REMOVAL
DISASSEMBL
Y
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
Rotor
inspection
Inspection
of
stator
I
nspection
of
diode
EE
16
EE
17
EE
17
EE
19
EE
19
EE
19
EE
20
DESCRIPTION
In
the
alternator
a
magnetic
field
is
produced
by
the
rotor
which
consists
of
alternator
shaft
field
coil
pole
pieces
and
slip
rings
The
slip
rings
pressed
in
the
shaft
conduct
only
a
small
field
current
Output
current
is
generated
in
the
armature
coils
located
in
the
stator
The
stator
has
three
windings
and
generates
three
phase
alternating
currenl
Silicon
diudes
act
like
a
one
way
valve
for
electricity
so
that
charging
currcnt
passes
easily
but
reverse
current
is
shut
out
In
this
alternator
six
diodes
0
E
0
c
co
0
E
c
o
0
c
Cl
Battery
T
e
I
nspection
of
brush
Spring
pressure
test
REASSEMBL
Y
ALTERNATOR
TEST
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
Specifications
Service
data
EE
20
EE
21
EE
21
EE
21
EE
22
EE
22
EE
22
are
used
three
negatives
and
three
positives
Positive
plate
has
three
positive
diodes
and
negative
plate
has
three
negative
diodes
and
are
installed
in
positive
and
negative
plates
as
an
assembly
Pack
type
silicone
diodes
are
used
in
this
alternator
These
diodes
are
direct
soldered
at
their
tips
and
con
structed
with
positive
and
negative
conjunction
They
are
mounted
on
the
two
plates
which
combine
the
function
of
heat
dissipating
plate
and
positive
negative
terminals
and
are
light
in
weight
and
easy
to
service
EE
16
Page 437 of 513
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
CD
@
@
@
y
@
1
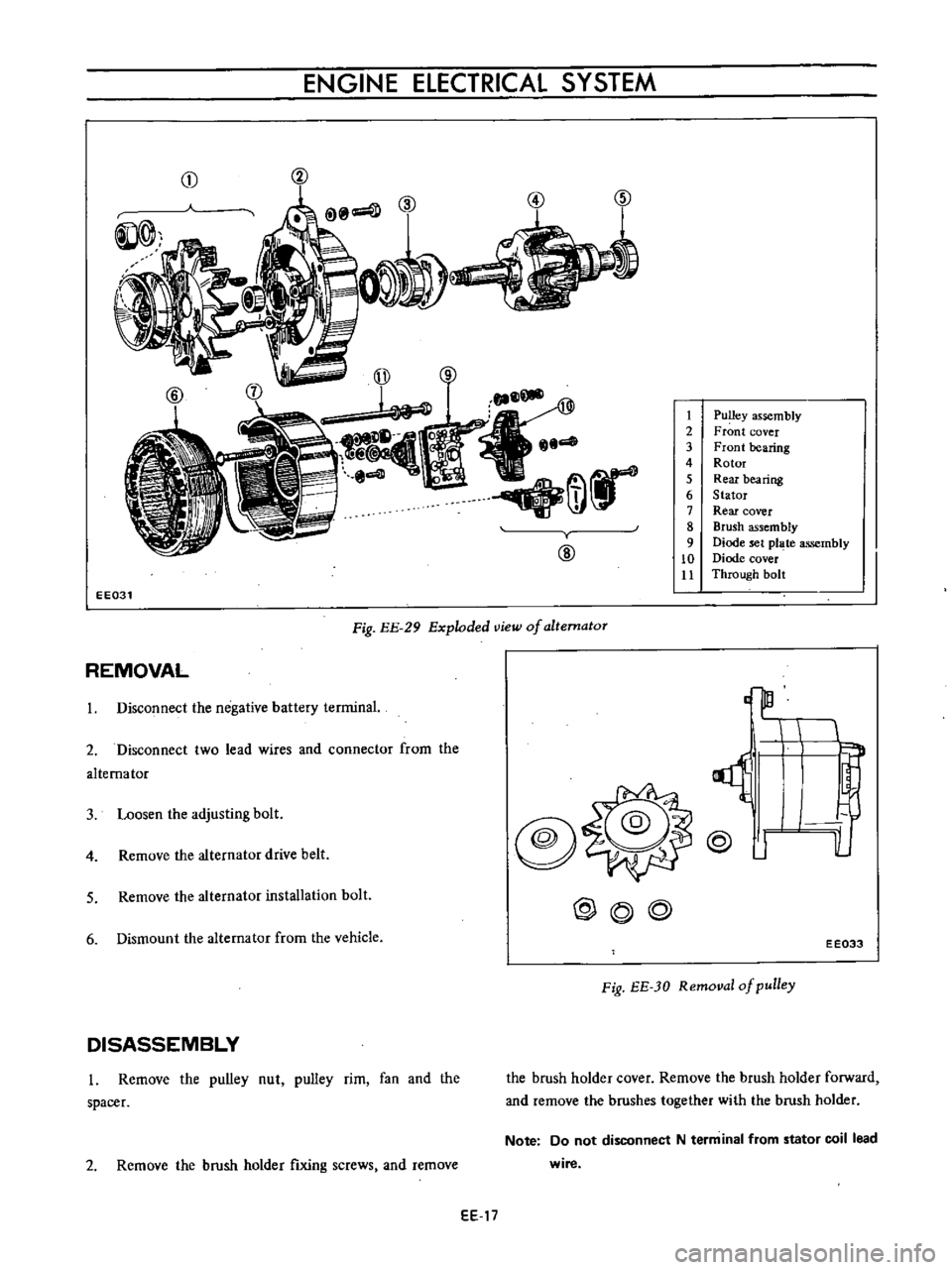
Pulley
assembly
2
Front
cover
3
Front
bearing
4
Rotor
5
Rear
bearing
6
Stator
7
Rear
cover
8
Brush
assembly
9
Diode
set
pl
te
assembly
10
Diode
cover
Jl
Through
bolt
EE031
Fig
EE
29
Exploded
view
of
altematoT
REMOVAL
3
Loosen
the
adjusting
bolt
@
o
lL
1
Disconnect
the
negative
battery
terminal
2
Disconnect
two
lead
wires
and
connector
from
the
alternator
4
Remove
the
alternator
drive
belt
@
J
5
Remove
the
alternator
installation
bolt
@@@
6
Dismount
the
alternator
from
the
vehicle
EE033
Fig
EE
JO
Removal
of
pulley
DISASSEMBLY
l
Remove
the
pulley
nut
pulley
rim
fan
and
the
spacer
the
brush
holder
cover
Remove
the
brush
holder
forward
and
remove
the
brushes
together
with
the
brush
holder
2
Remove
the
brush
holder
fixing
screws
and
remove
Note
Do
not
disconnect
N
term
inal
from
stator
coil
lead
wire
EE
17
Page 441 of 513
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
EE127
Fig
EE
45
Brush
wear
limit
Spring
pressure
test
With
the
brush
projected
approximately
2
mm
0
0787
in
from
the
brush
holder
measure
brush
spring
pressure
using
a
spring
balance
Normally
the
rated
pressure
of
a
new
brush
spring
is
255
to
345
grams
9
0
to
12
2
oz
Moreover
when
the
brush
is
worn
pressure
decreases
approximately
20
grams
per
I
mm
0
0394
in
wear
2
rnm
0
0787
in
r
II
EEQ49
Fig
EE
46
Measuring
spring
pressure
REASSEMBLY
Reassemble
the
alternator
in
reverse
sequence
of
disassembly
noting
the
following
matters
I
When
soldering
each
stator
coil
lead
wire
to
the
diode
assembly
terminal
carry
out
the
operatic
as
fast
as
possible
2
When
install
the
diode
A
terminal
install
the
insulating
bushing
and
insulating
tube
correctly
EE
21
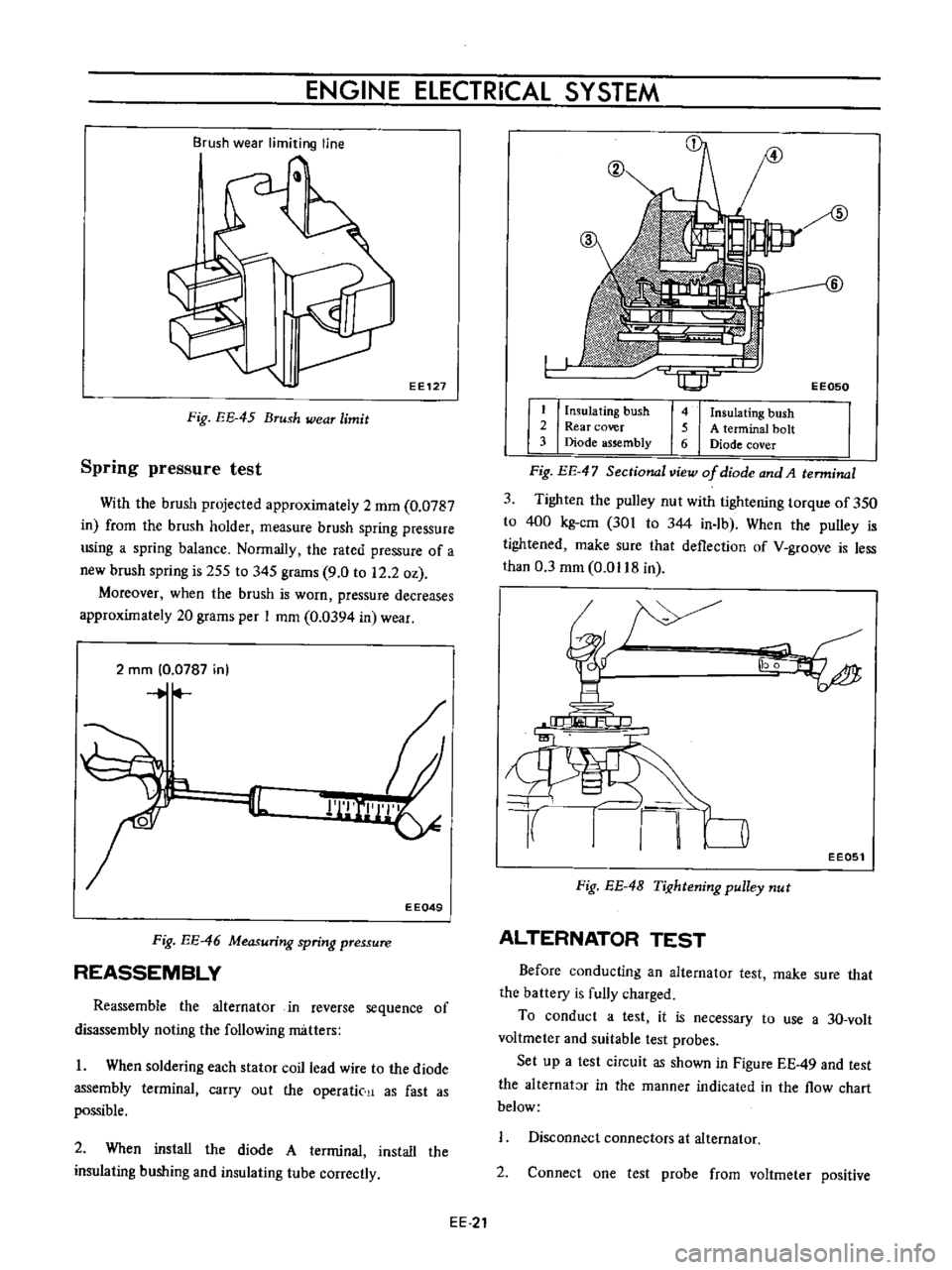
EE050
I
Insulating
bush
2
Rear
cover
3
Diode
assembly
4
Insulating
bush
5
A
terminal
bolt
6
Diode
cover
Fig
EE
47
Sectional
view
of
diode
and
A
terminal
3
Tighten
the
pulley
nut
with
tightening
torque
of
350
to
400
kg
cm
301
to
344
in
Ib
When
the
pulley
is
tightened
make
sure
that
deflection
of
V
groove
is
less
than
0
3
mm
0
0118
in
EE051
Fig
EE
4B
TiJ
htening
pulley
nut
ALTERNATOR
TEST
Before
conducting
an
alternator
test
make
sure
that
the
battery
is
fully
charged
To
conduct
a
test
it
is
necessary
to
use
a
3D
volt
voltmeter
and
suitable
test
probes
Set
up
a
test
circuit
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
49
and
test
the
alternator
in
the
manner
indicated
in
the
flow
chart
below
Disconn
ct
connectors
at
alternator
2
Connect
one
test
probe
from
voltmeter
positive
Page 442 of 513
ENGINE
terminal
to
IN
terminal
or
BAT
terminal
Connect
the
other
test
probe
to
ground
Make
sure
that
voltmeter
registers
battery
voltage
4
Start
the
engine
3
Turn
on
the
headlights
and
switch
to
main
beam
I
o
B
ttefY
E
A
J
0
il
I
5
Increase
engine
speed
gradually
until
it
is
approxi
mately
1
100
rpm
and
take
the
voltmeter
reading
6
If
the
measured
value
is
over
12
5
volts
the
alternator
is
in
good
condition
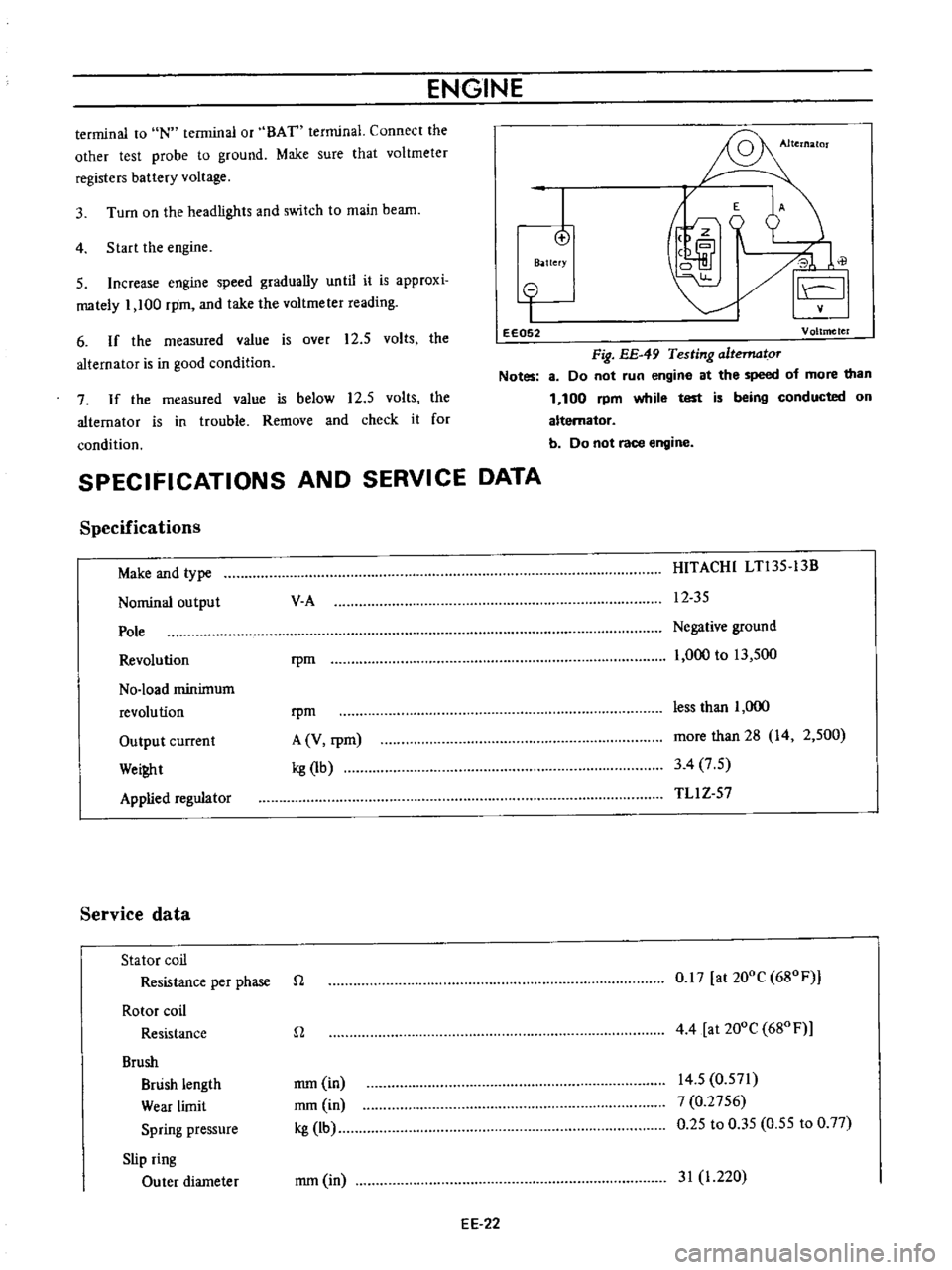
o
I
eE052
Voltmeter
Fig
EE
49
Testing
altematoT
Notes
8
Do
not
run
engine
at
the
speed
of
more
than
1
100
rpm
while
test
is
being
conducted
on
alternator
b
Do
not
race
engine
7
If
the
measured
value
is
below
12
5
volts
the
alternator
is
in
trouble
Remove
and
check
it
for
condition
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
Specifications
Make
and
type
Nominal
output
Pole
Revolution
No
load
minimum
revolution
Output
current
Wei
t
Applied
regulator
Service
data
Stator
coil
Resistance
per
phase
Rotor
coil
Resistance
Brush
Brush
length
Wear
limit
Spring
pressure
Slip
ring
Outer
diameter
V
A
HITACHI
LTl35
13B
12
35
rpm
Negative
ground
1
000
to
13
500
rpm
A
V
rpm
kg
1b
less
than
1
000
more
than
28
14
2
500
3
4
7
5
TLl
Z
57
n
0
17
at
200C
680F
n
4
4
at
200e
680
F
mm
in
mm
in
kg
lb
14
5
0
571
7
0
2756
0
25
to
0
35
0
55
to
0
77
mm
in
31
1
220
EE
22