1973 DATSUN B110 check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 58 of 513

Judgement
in
measurmg
line
pressure
I
Low
idling
line
pressures
in
the
ranges
D
2
loR
and
P
It
can
be
artributed
to
trouble
in
the
pressure
supply
system
or
too
low
output
of
power
caused
by
1
A
worn
oil
pump
2
An
oil
pressure
leakage
in
the
oil
pump
valve
body
or
case
3
A
sticking
regulator
valve
2
Low
idling
line
pressures
in
cer
tain
ranges
only
It
is
caused
pressumabIy
by
an
oil
leakage
in
the
devices
or
circuits
con
nected
to
the
relevant
ranges
1
When
there
is
an
oil
leakage
in
the
rear
clutch
and
governor
the
line
pressures
in
D
2
and
I
are
low
but
the
pressure
is
normal
in
R
2
When
an
oil
leakage
occurs
in
the
low
and
reverse
brake
circuit
the
line
pressures
in
R
and
p
are
low
but
the
pressure
is
normal
in
0
2
and
I
3
High
idling
line
pressures
It
is
presumed
to
be
caused
by
an
increased
vacuum
throttle
pressure
owing
to
a
leakage
in
the
vacuum
tube
or
diaphragm
or
by
an
increased
line
pressure
due
to
a
sticking
regulator
CHASSIS
valve
Vacuum
leakage
is
checked
by
di
reetly
measuring
the
negative
pressure
after
removing
the
vacuum
pipe
A
puncture
of
the
vacuum
dia
phragm
can
be
easily
ascertained
because
the
torque
converter
oil
is
absorbed
into
the
engine
and
the
exhaust
pipe
blows
up
the
white
smoke
4
Checking
items
when
the
line
pressure
is
increasing
In
trJs
checking
the
line
pressure
should
be
measured
with
vacuums
of
450
mmHg
and
0
mmHg
in
accordance
with
the
stall
test
procedure
test
procedure
1
If
the
line
pressures
do
not
increase
despite
the
vacuum
decrease
check
whether
the
vacuum
rod
is
incorporated
2
If
the
line
pressures
do
not
meet
the
standard
it
is
caused
mostly
by
a
sticking
pressure
regulating
valve
pres
sure
regulating
valve
plug
or
amptifier
TROUBLE
SHOOTING
CHART
Inspecting
items
1
Inspection
with
automatic
trans
mission
on
vehicle
J
AT
54
A
Oil
level
B
Range
selecr
linkage
C
Inhibitor
switch
and
wiring
D
Vacuum
diaphragm
and
piping
E
Downshift
solenoid
kick
down
switch
and
wiring
F
Engine
idling
rpm
G
Oil
pressure
throttle
H
Engine
stall
rpm
I
Rear
lubrication
J
Control
valve
manual
K
Governor
valve
L
Band
servo
M
Transmission
air
check
N
Oil
quantity
o
Ignition
switch
and
starter
motor
P
Engine
adjustment
and
brake
in
spection
2
Inspection
after
inspecting
auto
matic
transmission
on
vehicle
m
Rear
clutch
n
Front
clutch
q
Band
brake
r
Low
and
reverse
brake
s
Oil
pump
Leakage
of
oil
passage
u
One
way
clutch
of
torque
converter
v
One
way
clutch
of
transmission
w
Front
clutch
check
ball
x
Parking
linkage
y
Planetary
gear
Page 59 of 513
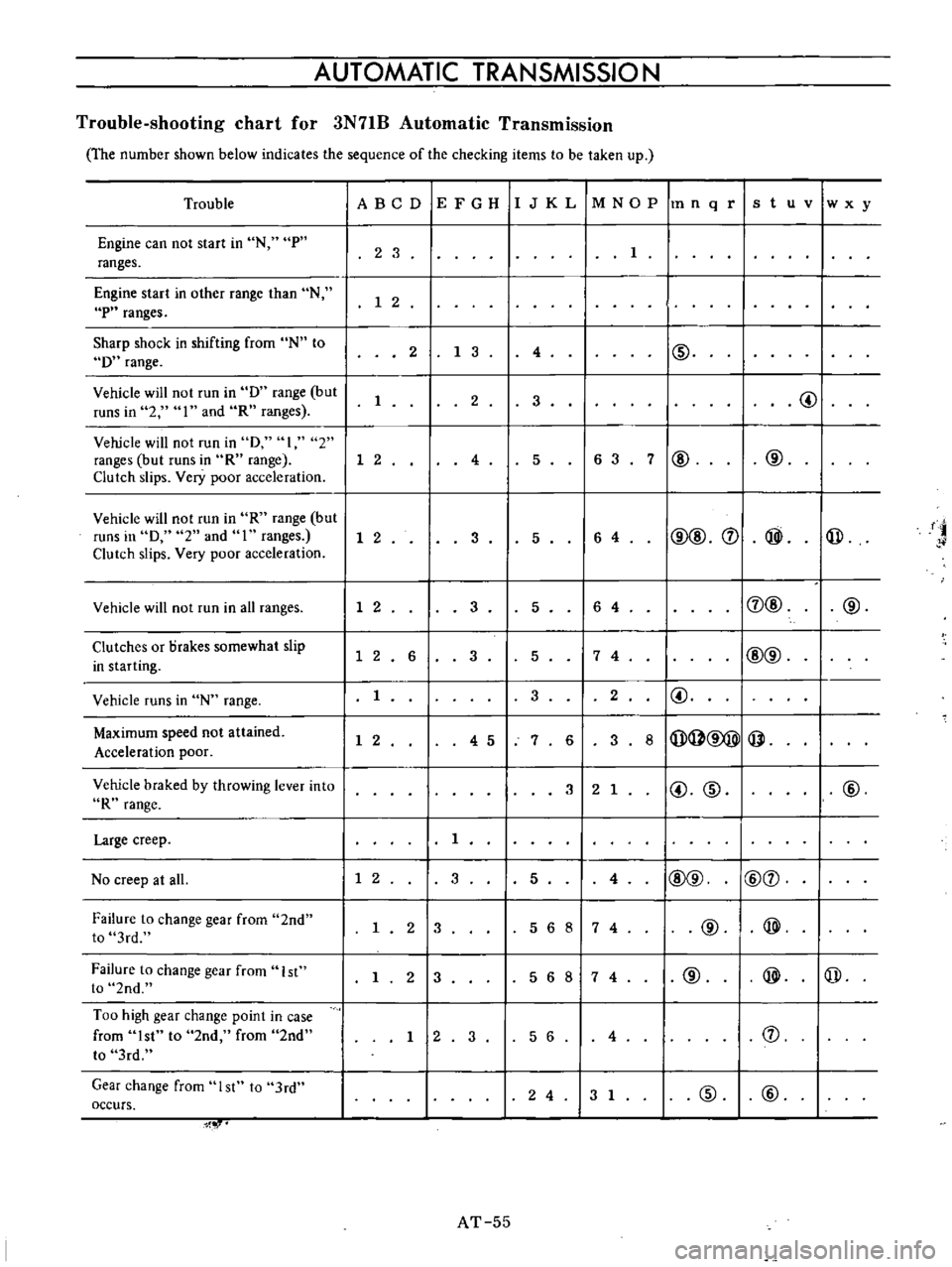
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSIO
N
Trouble
shooting
chart
for
3N71B
Automatic
Transmission
The
number
shown
below
indicates
the
sequence
of
the
checking
items
to
be
taken
up
Trouble
Engine
can
not
start
in
N
P
ranges
Engine
start
in
other
range
than
N
P
ranges
Sharp
shock
in
shifting
from
N
to
D
range
Vehicle
will
not
run
in
D
range
but
runs
in
2
I
and
R
ranges
Vehicle
will
not
run
in
D
I
2
ranges
but
runs
in
R
range
1
2
Clutch
slips
Very
poor
acceleration
Vehicle
will
not
run
in
R
range
but
runs
in
0
2
and
I
ranges
1
2
Clutch
slips
Very
poor
acceleration
Vehicle
will
not
run
in
all
ranges
Clutches
or
Drakes
somewhat
slip
in
starting
Vehicle
runs
in
N
range
Maximum
speed
not
attained
Acceleration
poor
Vehicle
braked
by
throwing
lever
into
R
range
Large
creep
No
creep
at
all
Failure
to
change
gear
from
2nd
to
3rd
Failure
to
change
gear
from
1st
to
2nd
Too
high
gear
change
point
in
case
from
1st
to
2nd
from
2nd
to
3rd
Gear
change
from
st
to
3rd
occurs
W
IABCDIEFGH
IJKL
MNOP
mnqrlstuv
wxy
2
3
I
1
2
2
I
1
3
4
@
1
2
3
4
63
7
@
5
@
@
3
6
4
@@
j
@
@
t
5
1
2
3
5
6
4
1
2
6
3
5
7
4
I
2
@
3
8
@@@
@
@
3
I
2
4
5
7
6
3
2
1
@@
I
I
I@@
I
2
3
5
4
1
2
3
56874
123
56874
@
1
2
3
5
6
4
2
4
13
1
AT
55
j
@
@
I@@
I
@
@
I
I
@
j
@
@
@
j
@
@
Page 62 of 513
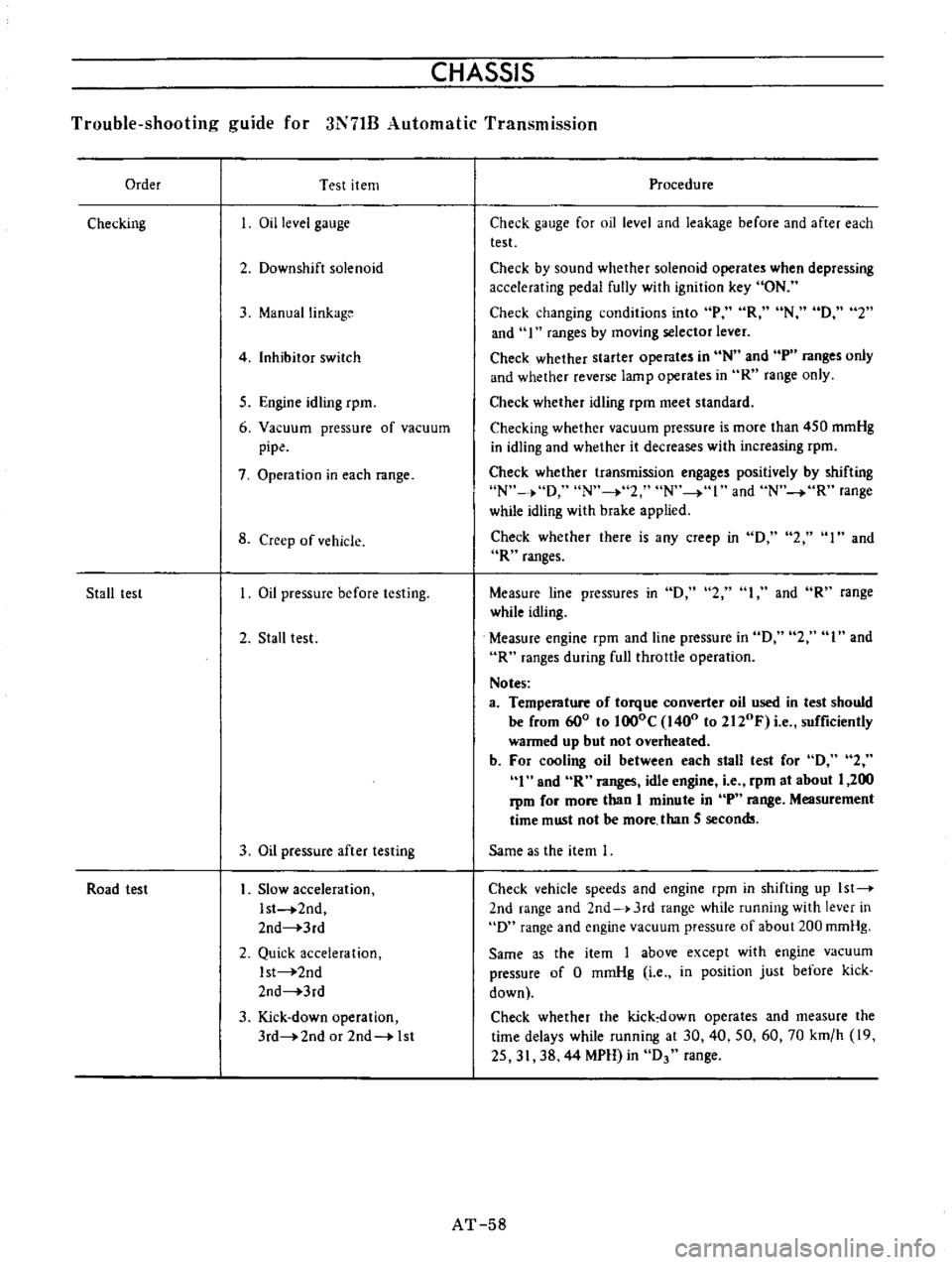
CHASSIS
Trouble
shooting
guide
for
3N71B
Automatic
Transmission
Order
Test
item
Checking
Oil
level
gauge
2
Downshift
solenoid
3
ManuaIlinkage
4
Inhibitor
switch
5
Engine
idling
rpm
6
Vacuum
pressure
of
vacuum
pipe
7
Operation
in
each
range
8
Creep
of
vehicle
Stall
lest
Oil
pressure
before
testing
2
Stall
test
3
Oil
pressure
after
testing
Road
test
Slow
acceleration
Ist
2nd
2nd
3rd
2
Quick
acceleration
Ist
2nd
2nd
3rd
3
Kick
down
operation
3rd
2nd
or
2nd
1st
Procedure
Check
gauge
for
oil
level
and
leakage
before
and
after
each
test
Check
by
sound
whether
solenoid
operates
when
depressing
accelerating
pedal
fully
with
ignition
key
ON
Check
changing
conditions
into
P
R
N
D
2
and
I
ranges
by
moving
selector
lever
Check
whether
starter
operates
in
N
and
tp
ranges
only
and
whether
reverse
lamp
operates
in
R
range
only
Check
whether
idling
rpm
meet
standard
Checking
whether
vacuum
pressure
is
more
than
450
mmHg
in
idling
and
whether
it
decreases
with
increasing
rpm
Check
whether
transmission
engages
positively
by
shifting
N
o
D
N
2
N
I
and
N
R
range
while
idling
with
brake
applied
Check
whether
there
is
any
creep
in
D
2
I
and
R
ranges
2
1
and
R
range
Measure
line
pressures
in
D
while
idling
Measure
engine
rpm
and
line
pressure
in
D
2
I
and
R
ranges
during
fullthrallIe
operation
Notes
a
Temperature
of
torque
converter
oil
used
in
test
should
be
from
600
to
lOOoC
1400
to
2120F
i
e
sufficiently
warmed
up
but
not
overheated
b
For
cooling
oil
between
each
stall
test
for
D
2
1
and
R
ranges
idle
engine
i
e
rpm
at
about
1
200
rpm
for
more
than
1
minute
in
P
range
Measurement
time
must
not
be
more
than
5
secon
Same
as
the
item
I
Check
vehicle
speeds
and
engine
rpm
in
shifting
up
1st
2nd
range
and
2nd
J
3rd
range
while
running
with
lever
in
D
range
and
engine
vacuum
pressure
of
about
200
mmHg
Same
as
the
item
1
above
except
with
engine
vacuum
pressure
of
0
mmHg
i
e
in
position
just
before
kick
down
Check
whether
the
kick
down
operates
and
measure
the
time
delays
while
running
at
30
40
50
60
70
km
h
19
25
31
38
44
MPH
in
D
range
AT
58
Page 63 of 513
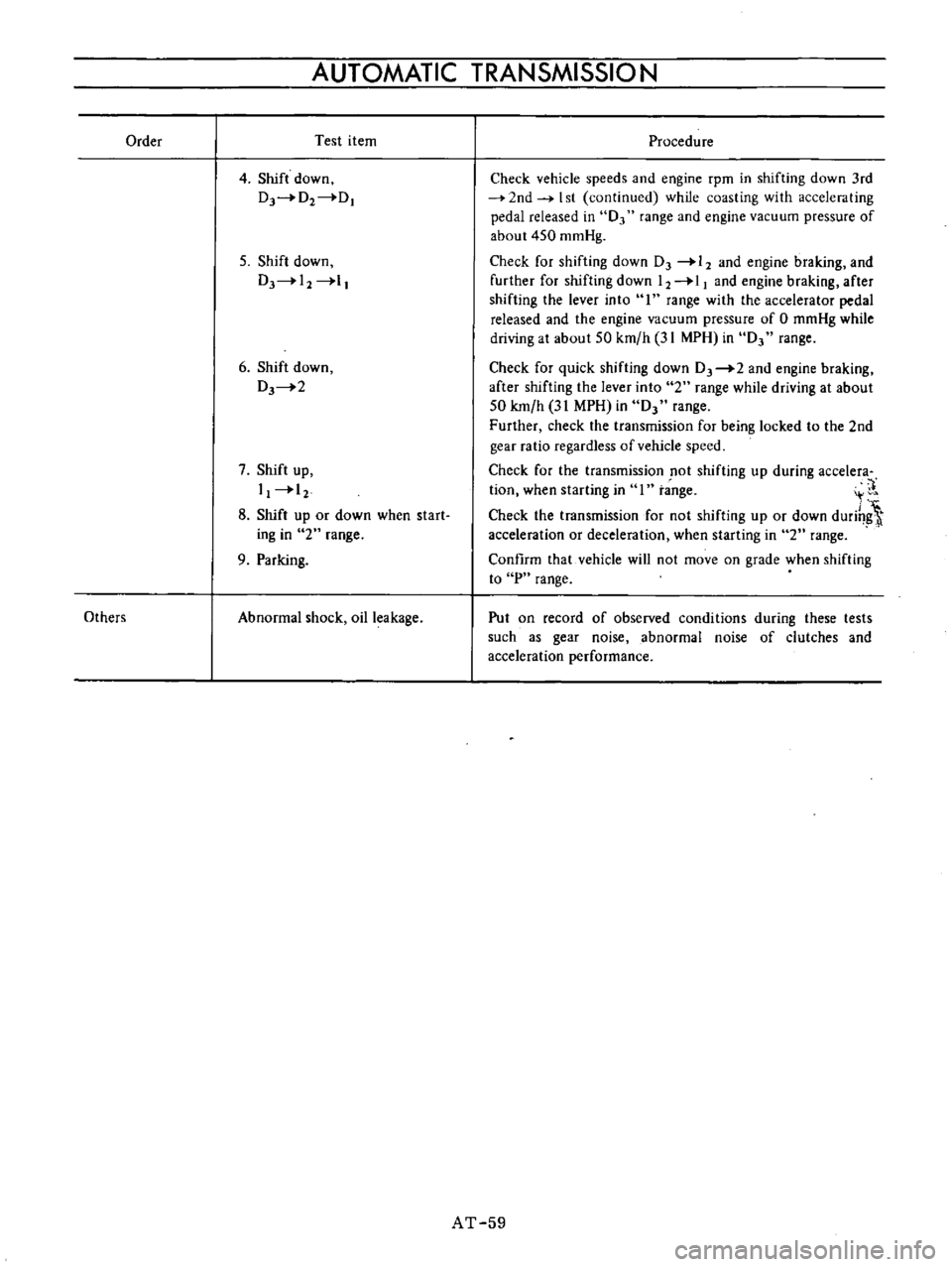
Order
Others
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
Test
item
4
Shift
down
Dr4D2
DI
5
Shift
down
DJ
I2
l
6
Shift
down
DJ
2
7
Shift
up
I
12
8
Shift
up
or
down
when
start
ing
in
2
range
9
Parking
Abnormal
shock
oil
leakage
Procedure
Check
vehicle
speeds
and
engine
rpm
in
shifting
down
3rd
2nd
I
st
continued
while
coasting
with
acceleraling
pedal
released
in
0
range
and
engine
vacuum
pressure
of
about
450
mmHg
Check
for
shifting
down
DJ
12
and
engine
braking
and
further
for
shifting
down
12
11
and
engine
braking
after
shifting
the
lever
into
I
range
with
the
accelerator
pedal
released
and
the
engine
vacuum
pressure
of
0
mmHg
while
driving
at
about
SO
km
h
31
MPH
in
DJ
range
Check
for
quick
shifting
down
DJ
2
and
engine
braking
after
shifting
the
lever
into
2
range
while
driving
at
about
50
km
h
31
MPH
in
DJ
range
Further
check
the
transmission
for
being
locked
to
the
2nd
gear
ratio
regardless
of
vehicle
speed
Check
for
the
transmission
not
shifting
up
during
acceIera
tion
when
starting
in
1
t
nge
It
Check
the
transmission
for
not
shifting
up
or
down
durih
t
acceleration
or
deceleration
when
starting
in
2
range
Confirm
that
vehicle
will
not
move
on
grade
when
shifting
to
P
range
Put
on
record
of
observed
conditions
during
these
tests
such
as
gear
noise
abnormal
noise
of
clutches
and
acceleration
performance
AT
59
Page 131 of 513

Tightening
torque
3
way
connector
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
10
8
to
13
0
ft
lh
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
10
8
to
13
0
ft
lh
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
10
8
to
13
0
ft
lb
0
7
to
0
9
kg
m
5
1
to
6
5
ft
1b
Master
cylinder
Brake
hose
Air
bleeder
5
Fill
the
master
cylinder
brake
fluid
reservoir
with
brake
fluid
and
perform
air
bleeding
complele1y
Note
a
Do
not
use
brake
fluid
other
than
specified
b
The
specified
brake
fluid
is
used
for
both
single
and
tandem
type
master
cylinders
6
Upon
completion
of
air
bleeding
make
sure
that
the
brake
operates
correctly
and
check
the
brake
tube
and
hose
connectors
for
fluid
leaking
Fully
depress
the
brake
pedal
continue
to
depress
the
brake
pedal
for
several
seconds
and
make
sure
that
no
brake
fluid
leaks
from
any
part
of
the
brake
line
Replace
defective
part
if
required
Brake
line
pressure
differential
warning
light
switch
A
warning
light
is
located
on
the
instrument
panel
to
warn
the
driver
when
a
pressure
difference
of
13
to
17
kg
cm2
185
to
2421bJsq
in
exists
between
the
front
and
rear
b
rake
systems
A
hydraulically
actuated
warning
light
switch
is
located
in
the
engine
compartment
Both
front
and
rear
brake
systems
are
connected
to
this
switch
assembly
When
a
pressure
difference
of
13
to
17
kgJcm2
185
to
242
lbJsq
in
occurs
between
the
front
and
rear
brake
systems
the
valves
will
shuttle
toward
the
side
with
the
low
pressure
The
valve
contacts
with
the
switch
terminal
BRAKE
the
ground
circuit
for
the
warning
light
is
completed
and
thus
the
warning
light
lights
In
this
case
correct
the
hydraulic
brake
problem
and
bleed
the
brakes
Check
the
warning
light
switch
assembly
for
a
proper
operation
Check
the
switch
assembly
for
fluid
leakage
Note
Do
not
attempt
to
repair
switch
for
any
reason
replace
switch
assembly
completely
1
To
front
brake
L
H
2
From
master
cylinder
F
3
From
master
cylinder
R
4
To
rear
brake
L
B
R
M
5
To
front
brake
R
H
Fig
BR
12
Warning
light
switch
r
I
@
I
I
3
I
Valve
assembly
4
Piston
load
spring
Wire
terminal
Brake
tube
Fig
BR
13
Sectional
view
of
warning
light
switch
BR
7
Page 225 of 513
BODY
b
Method
2
Start
the
engine
and
turn
on
the
window
defogger
system
With
a
d
c
voltmeter
setup
shown
in
Figure
BF
70
check
each
heat
wire
for
discontinuity
If
the
meter
indicates
12
volts
or
0
on
a
specific
wire
that
line
is
broken
Normal
indication
6
volts
A
break
in
that
line
can
then
be
detected
by
moving
the
positive
lead
of
meter
along
the
line
until
an
abrupt
variation
in
the
meter
indication
is
encountered
Fig
BF
70
Checking
for
broken
heat
wire
with
d
c
voltmeter
c
Method
3
With
an
ohmmeter
setup
shown
in
Figure
BF
7l
locate
one
lead
on
each
end
of
a
heat
wire
and
the
other
in
the
rniddle
section
of
that
wire
If
the
meter
registers
on
a
specific
grid
line
a
value
twice
as
much
on
any
other
line
that
line
is
broken
A
break
in
that
line
can
then
be
located
by
an
abrupt
variation
in
the
meter
indication
as
the
test
lead
moves
along
the
broken
heat
wire
r
I
I
I
J
I
I
v
Ejl
Fig
BF
71
Checking
for
broken
heat
wire
with
ohmmeter
2
Repair
a
Repair
equipment
1
Conductive
silver
composition
Dupont
No
4817
2
Ruler
30
em
11
81
in
long
3
Drawing
pen
4
Heat
gun
5
Alcohol
6
Cloth
b
Repair
procedure
1
Wipe
clean
broken
heat
wire
and
its
surrounding
area
with
a
cloth
dampened
in
alcohol
2
Apply
a
small
amount
of
conductive
silver
composi
tion
to
the
tip
of
drawing
pen
Note
Shake
silver
composition
container
sufficiently
before
use
3
Place
ruler
on
glass
along
broken
line
to
be
repaired
as
shown
in
Figure
BF
72
Deposite
conductive
silver
composition
to
break
line
with
drawing
pen
Slightly
overlap
existing
heat
wire
either
side
5
mm
0
1969
in
preferable
of
the
break
Heat
wire
0
en
0
0
d
ci
1
I
Break
I
1
I
kr
I
I
Ruler
Drawing
pen
Unit
mm
in
Fig
BF
72
Locating
ruler
in
position
8F
35
Page 241 of 513

INSPECTION
Referring
to
the
wiring
diagram
check
the
wiring
harness
for
connection
with
electrical
equipment
and
connector
for
conned
ion
and
installation
When
checking
the
wiring
harness
note
the
following
matters
Connected
unit
should
not
be
loose
rusted
or
contaminated
2
Cable
insulator
cover
should
not
be
damaged
crack
ed
or
insulating
material
should
not
be
deteriorated
3
For
those
parts
which
are
grounded
through
the
installation
bolts
the
bolts
should
be
in
contact
with
the
body
completely
so
that
continuity
is
provided
in
between
the
body
and
bolts
4
Terminals
of
unit
through
which
current
flows
should
not
come
into
contact
with
other
metal
parts
5
No
erroneous
connection
should
be
present
DESCRIPTION
When
an
overcunent
exceeding
the
rated
amperage
flows
to
a
circuit
the
fuse
is
heated
and
melted
the
circuit
is
interrupted
and
thus
cables
and
electrical
equipment
are
protected
from
damaging
due
to
burning
or
damaging
is
limited
to
the
minimum
This
vehicle
is
equipped
with
six
fuses
and
one
fusible
link
The
fuses
are
located
in
the
fuse
box
and
used
to
protect
illumination
signal
and
other
systems
and
the
fusible
link
is
adopted
in
the
cable
between
the
battery
and
alternator
to
protect
the
charging
and
starting
circuits
FiJ
BE
16
Fuse
box
BODY
6
Cables
should
be
damped
so
that
they
do
not
come
into
contact
with
sharp
corner
or
part
lernperature
of
which
rises
highly
7
Cables
should
be
securely
clamped
in
posItions
sufficiently
separated
from
rotating
parts
such
as
fan
pulley
fan
belt
etc
8
Cables
should
be
provided
with
an
optimum
extra
length
at
sections
stationarity
on
the
body
or
at
sections
where
vibration
occurs
due
to
engine
operation
and
others
Note
a
When
inspecting
or
performing
other
mainte
nance
service
and
no
power
supply
is
required
particularly
or
when
it
is
anticipated
that
a
part
may
be
short
circuited
disconnect
the
battery
H
terminal
b
In
no
event
should
an
unloaded
circuit
be
directly
connected
with
ground
Be
sure
to
use
a
test
lamp
or
circuit
tester
fUSE
Fig
BE
17
Fusible
link
INSPECTION
In
the
most
cases
fuse
can
be
checked
visually
However
when
it
is
difficult
to
check
visually
a
circuit
tester
may
be
used
The
fusible
link
can
be
inspected
visually
or
by
feeling
on
finger
tip
However
the
fusible
link
can
be
inspected
more
correctly
by
using
a
circuit
tester
BE
6
Page 248 of 513
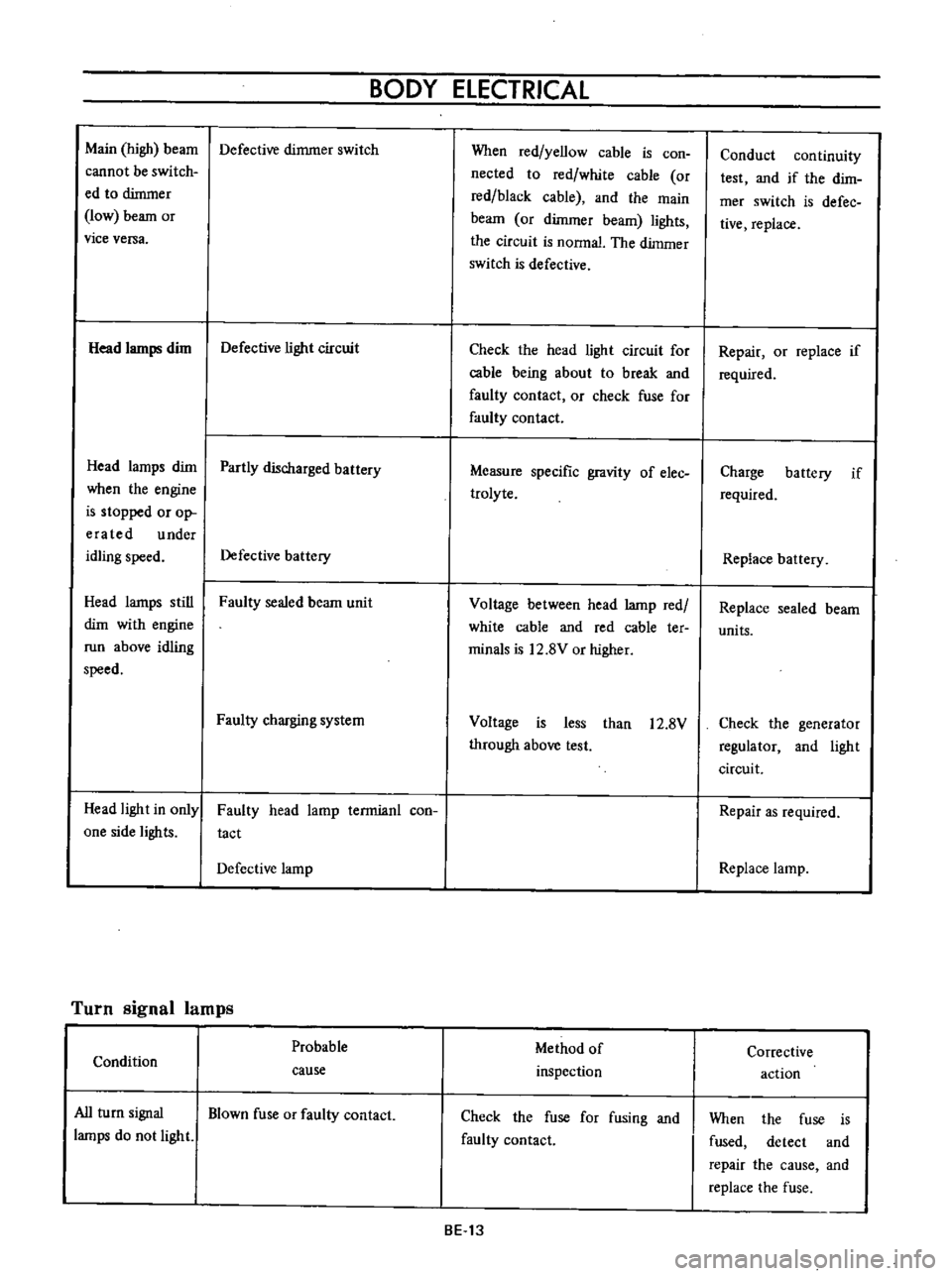
BODY
ELECTRICAL
Main
high
beam
Defective
dimmer
switch
cannot
be
switch
ed
to
dimmer
low
beam
or
vice
versa
Head
lamps
dim
Defective
light
circuit
Head
lamps
dim
Partly
discharged
battery
when
the
engine
is
stopped
or
op
era
ted
under
idling
speed
Defective
battery
Head
lamps
still
Faulty
sealed
beam
unit
dim
with
engine
run
above
idling
speed
Faulty
charging
system
Head
light
in
only
one
side
lights
Faulty
head
lamp
terrnianl
con
tact
Defective
lamp
Turn
signal
lamps
Probable
Condition
cause
All
turn
signal
Blown
fuse
or
faulty
contact
lamps
do
not
light
When
red
yellow
cable
is
con
nected
to
red
white
cable
or
red
black
cable
and
the
main
beam
or
dimmer
beam
lights
the
circuit
is
nonnal
The
dimmer
switch
is
defective
Check
the
head
light
circuit
for
cable
being
about
to
break
and
faulty
contact
or
check
fuse
for
faulty
contact
Measure
specific
gravity
of
elec
trolyte
Voltage
between
head
lamp
red
white
cable
and
red
cable
ter
minals
is
12
8V
or
higher
Voltage
is
less
than
12
8V
through
above
test
Method
of
inspection
Check
the
fuse
for
fusing
and
faulty
contact
BE
13
Conduct
continuity
test
and
if
the
dirn
mer
switch
is
defec
tive
replace
Repair
or
replace
if
required
Charge
battery
if
required
Replace
battery
Replace
sealed
beam
units
Check
the
generator
regulator
and
light
circuit
Repair
as
required
Replace
lamp
Corrective
action
When
the
fuse
is
fused
detect
and
repair
the
cause
and
replace
the
fuse