1900 MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE air filter
[x] Cancel search: air filterPage 60 of 408
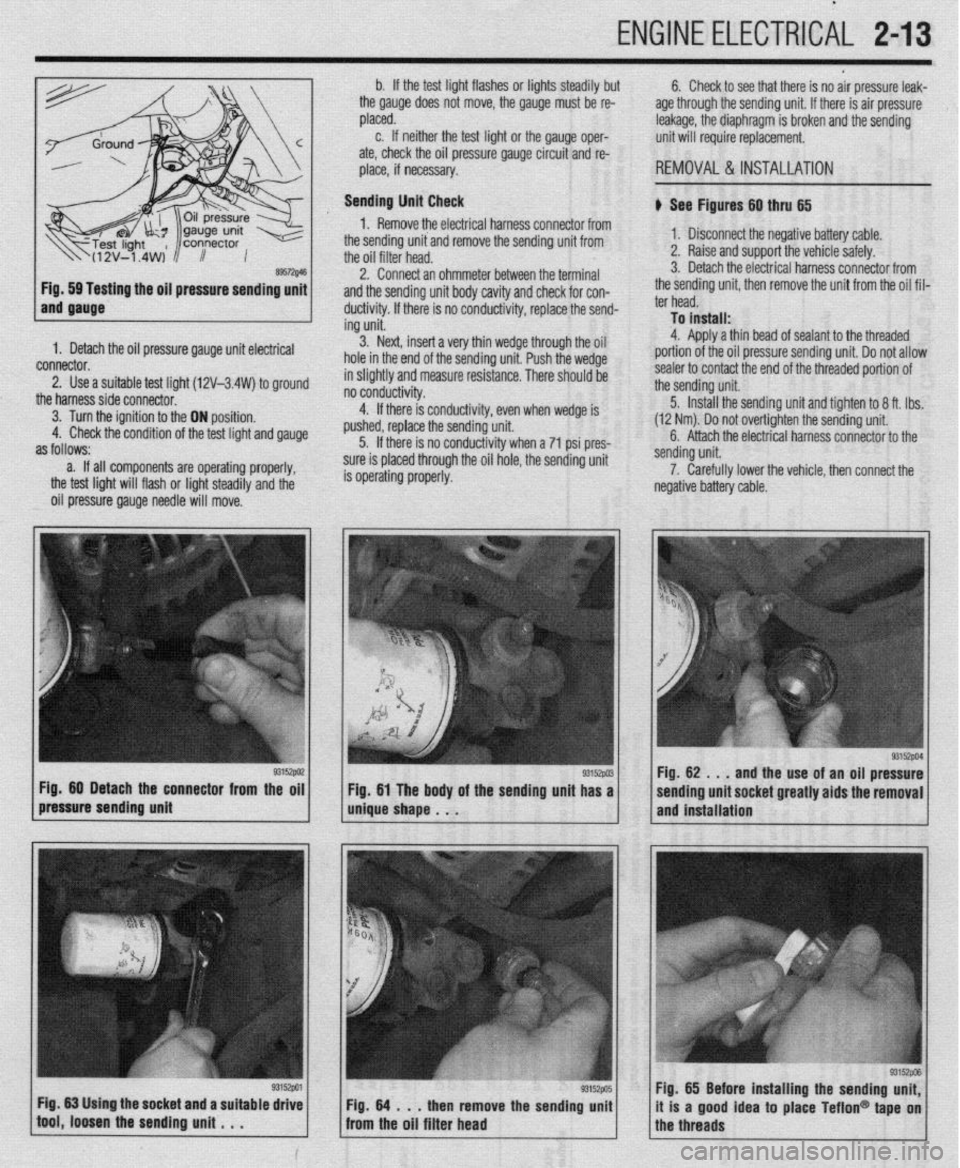
ENGINE ELECTRlCiL 2-13
ing the oil pressure sending unit
1. Detach the oil pressure gauge unit electrical
connector.
2. Use a suitable test lioht (12V-3.4W) to around
the harnesssideconnecto~ ’ ’ -
3. Turn the ignition to the ON position.
4. Check the condition of the test light and gauge
as follows:
a. If all components are operating properly,
the test light will flash or light steadily and the
oil pressure gauge needle will move. b. If the test light flashes or lights steadily but
the gauge does not move, the gauge must be re-
placed.
c. If neither the test light or the gauge oper-
ate, check the oil pressure gauge circuit and re-
place, if necessary.
Sending Unit Check
1. Remove the electrical harness connector from
the sending unit and remove the sending unit from
the oil filter head.
2. Connect an ohmmeter between the terminal
and the sending unit body cavity and check for con-
ductivity. If there is no conductivity, replace the send-
ing unit.
3. Next, insert a very thin wedge through the oil
hole in the end of the sending unit. Push the wedge
in slightly and measure resistance. There should be
- - -- d . . . .
no conoucovey.
4. If there is conductivity, even when wedge is
pushed, replace the sending unit.
5. If there is no conductivity when a 71 psi pres-
sure is placed through the oil hole, the sending unit
is operating properly. 6. Check to see that there is no air pressure leak-
age through the sending unit. If there is air pressure
leakage, the diaphragm is broken and the sending
unit will require replacement.
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
b See Figures 60 thru 65
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Raise and support the vehicle safely.
3. Detach the electrical harness connector from
the sending unit, then remove the unit from the oil fil-
ter head.
To install:
4. Aoolv a thin bead of sealant to the threaded
portion of the oil pressure sending unit. Do not allow
sealer to contact the end of the threaded portion of
the sending unit.
5. Install the sending unit and tighten to 8 ft. tbs.
(12 Nm). Do not over-tighten the sending unit.
6. Attach the electrical harness connector to the
/pressure sending unit g3’9wi / m&e shape . . . Fig 60 Detach the connector from the oil
g3152w Fig 61 The body of the sending unit has a sending unit.
7. Carefully lower the vehicle, then connect the
negative battery cable.
93152PM Fig. 62 . , .
and the use of an oil pressure
sending unit socket greatly aids the removal
and installation
Fig. 65 Before installing the sending unit,
it is a good idea to place Teflon@ tape on
the threads
Page 87 of 408

3-26 ENGINEANDENGINEOVERHAUL
18. Remove the self-locking nuts and the small
retaining bolt holding the exhaust pipe to the bottom
of the exhaust manifold. Separate the pipe from the
manifold and remove the gasket.
19. Remove the bolts holding the support brace
to the bottom of the intake manifold.
20. Use the special hex wrench (MB 998051-01)
and loosen the head bolts in the order shown in 2 or
3 passes. When all are finger loose, remove the bolts.
21. Rock the head gently to break it loose; if tap-
ping is necessary, do so with a rubber or wooden
mallet at the corners of the head. DO NOT pry the
head up by wedging tools between the head and the
block.
22. Lift the head free of the engine. It is coming
off with both manifolds and the intake plenum at-
tached; the help of an assistant is recommended for
lifting. Support the head assembly on wooden blocks
on a suitable workbench. Refer to Cleaning and In-
spection in this section for work to be done before in-
stalling the head. If the head has been removed for
work other than gasket replacement, the rocker as-
sembly and camshaft or other components may be
removed.
Before reinstallation, the head should be com-
pletely assembled on the bench. This allows proper
location and tightening of all the external items.
To install: 23. Place a new gasket on the engine so that the
identifying mark faces up (towards the head) and is at
the timing belt end of the block. Install a new gasket
on the exhaust pipe.
Do not apply sealant to the head gasket or
mating surfaces.
24. Install the head straight down onto the block.
Try to eliminate most of the side-to-side adjust-
ments as this may move the gasket out of position.
Install the bolts by hand and just start each bolt 1 or
2 turns on the threads.
25. The head bolt torque specification is 68 ft.
Ibs. (92 Nm) for a cold engine. The bolts must be
tightened in the order shown in 3 steps. On the first
pass, tighten all the bolts to about 22 ft. Ibs. (30 Nm),
then proceed through the order tightening each bolt
to about 45 ft. Ibs. (61 Nm). The final torque is
achieved on the third pass.
26. Install the intake manifold support brace to
the manifold and tighten the bolts to 16 ft. Ibs. (22
Nm). 27. Making sure the gasket is still in place, con-
nect the exhaust pipe to the base of the exhaust man-
ifold. Use new self-locking nuts; tighten the nuts and
the small bracket bolt to 26 ft. Ibs. (35 Nm).
28. Make sure the camshaft has not changed po-
sition during repalrs. Carefully install the camshaft
sprocket and belt onto the camshaft. Tighten the re-
taining bolt to 66 ft. Ibs. (91 Nm).
29. Install the upper timing belt cover, then
tighten the bolts to 8 ft. Ibs. (11 Nm).
30. Apply sealant to the contact surfaces of the
half-circle plug and install the plug in the head In-
stall the valve cover and gasket.
31. Install the engine mount bracket to the en-
gine. Tighten the mounting nuts and bolts to 42 ft.
Ibs. (57 Nm).
32. Adjust the jack (if necessary) so that the en-
gine mount bushing aligns with the bodywork
bracket. Install the through-bolt and tighten the nuts
snug.
33. Slowly release tension on the floor jack so
that the weight of the engine bears fully on the
mount. Tighten the through-bolt to 52 ft. Ibs. (71
Nm) and the small safety nut to 26 ft. tbs. (36 Nm).
34. Install the bracket holding the power steering
hose and air conditioning hose to the top of the en-
gine mount.
35. Position the control wiring harness and in-
stall the retaining bolts. Attach each electrical con-
nector to its proper location, making sure the wires
are properly routed and firmly connected.
36. Install the spark plug wires in the distributor
cap.
37. Connect the PCV hose and the vacuum
hose(s).
38. Connect the fuel return line. Connect the
brake booster vacuum hose.
39. Install the heater hose, the coolant by-pass
hose and.the upper radiator hose. Pay close attention
to the position and routing of these hoses and insure
that they are not crimped or constricted. Install the
clamps in the same location as before removal.
40. Install a new O-ring on the high pressure fuel
line and lubricate it with a coating of gasoline. Care-
fully connect the high pressure fuel line to the fuel
rail, taking care not to damage the O-ring. Tighten the
bolts only to 4 ft. Ibs. (6 Nm).
41. Connect the accelerator cable and adjust it as
necessary.
42. Install the air intake hose.
43. Fill the cooling system with coolant.
44. Changing the oil and filter is recommended
to eliminate pollutants in the oil.
Intake side
I Front of
engine
Exhaust side
Fig. 116 Cylinder head bolt removal se-
quence-l .6L and 2.OL DDHC engines intake
side
Front of
entine
Exhaust side 7923PG18
Fig. 117 Cylinder head bolt torque se-
quence-l .6L and 2.OL DDHC engines Operating the engine without the proper
amount and type of engine oil will result in
severe engine damage.
45. Connect the negative battery cable.
46. Start the engine and check for leaks of fuel,
vacuum or oil.
47. Check the operation of all engine electrical
systems as well as dashboard gauges and lights.
48. Perform necessary adjustments to the accel-
erator cable, drive belts and engine specifications.
Adjust the coolant level after the engine has cooled
Off.
1.6L and 2.OL DDHC Engines
ti See Figures 116,117, and 116
1. Relieve fuel system pressure.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Drain the cooling system.
Never open, service or drain the radiator or
cooling system when hot; serious burns can
occur from the steam and hot coolant. Also,
when draining engine coolant, keep in mind
that cats and dogs are attracted to ethylene
glycol antifreeze and could drink any that is
left in an uncovered container or in puddles
on the ground. This will prove fatal in suffi-
cient quantities. Always drain coolant into a
sealable container. Coolant should be reused
unless it is contaminated or is several years
old.
4. Disconnect the accelerator cable. There will
be 2 cables if equipped with cruise-control.
5. Remove the air cleaner with the air intake
hose.
6. Detach the electrical connectors from the the
oxygen sensor, engine coolant temperature sensor,
the engine coolant temperature gauge unit and the
engine coolant temperature switch on vehicles with
air conditioning.
7. Disconnect the wiring from the ISC motor,
throttle position sensor, crankshaft angle sensor, fuel
injectors, ignition coil, power transistor, noise filter,
knock sensor on turbocharged engines, EGR temper-
ature sensor (California vehicles), ground cable and
engine control wiring harness.
Painted mark Painted mark
Fig. 116 To ensure that the bolts are tight-
ened exactly 160 total degrees, mark the
11.6L and 2.OL DDHC engines head bolt and cylinder head as shown-
Page 88 of 408

ENGlNEANDENGlNEOVERHALiL 3-27
8. Remove the upper radiator hose and the
sages thoroughly. Check the head for flatness. End to 31. Install the air cleaner and intake hose. Con-
overflow tube. end, the head should be within 0.002 in. (0.05mm) nect the breather hose.
9. Remove the spark plug cable center cover,
normally, with 0.008 in. (0.2mm) the maximum al- 32. Change the engine oil and oil filter,
then remove the spark plug cables.
lowed out of true. The total thickness allowed to be 33. Fill the system with coolant.
10. Disconnect and plug the high pressure fuel
removed from the head and block is 0.008 in.
line. 34. Connect the negative battery cable.
(0.2mm) maximum. 35. Run the vehicle until the thermostat opens,
11. Disconnect the small vacuum hoses.
23. Place a new head gasket on the cylinder and fill the radiator completely.
12. Remove the heater hose and water bypass
block with the identification marks at the front top 36. Check and adjust the idle speed and ignition
hose.
(upward) position. Make sure the gasket has the timing.
13. Remove the PCV hose.
proper identification mark for the engine. Do not use 37. Once the vehicle has cooled, recheck the
14. If turbocharged, remove the vacuum hoses,
sealer on the gasket. Replace the turbo gasket and coolant level.
water line and eyebolt connection for the oil line for
ring, if equipped.
the turbo.
24. Carefully install the cylinder head on the 2.41 Engine
15. Disconnect and plug the fuel return hose. block. Using 3 even steps, torque the head bolts, in
16. Disconnect the brake booster vacuum hose.
sequence, to 65-72 ft. Ibs. (90-100 Nm). This torque b See Figures 119 thru 131
17. Remove the timing belt. applies to a cold engine. If checking cylinder head
18. Remove the valve cover and the half-round
bolt torque on hot engine, the desired specification is 1. Relieve the fuel system pressure.
seal.
7240 ft. Ibs. (100-110 Nm). 2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
19. On non-turbocharged engines, remove the 3. Remove the air cleaner with all air intake
25. On turbocharged engine, install the heat
hoses.
exhaust pipe self-locking nuts and separate the ex-
shield. On non-turbocharged engines, install a new
haust pipe from the exhaust manifold. Discard the
exhaust pipe gasket and connect the exhaust pipe to 4. Drain the cooling system.
gasket.
the manifold.
20. On turbocharged engines, remove the sheet
26. Apply sealer to the perimeter of the half-
metal heat protector and remove the bolts that attach
round seal and to the lower edges of the half-round Never open, service or drain the radiator or
the turbocharger to the exhaust manifold.
portions of the belt-side of the new gasket. Install the cooling system when hot; serious burns can
21. Loosen the cylinder head mounting bolts in 3
valve cover. occur from the steam and hot coolant. Also,
steps, starting from the outside and working inward,
27. Install the timing belt and all related items. when draining engine coolant, keep in mind
Lift off the cylinder head assembly and remove the
28. Connect or install all previously disconnected that cats and dogs are attracted to ethylene
n head gasket.
hoses, cables and electrical connections. Adjust the glycol antifreeze and could drink any that is
To install:
throttle cable(s). left in an uncovered container or in puddles
22. Thoroughly clean and dry the mating surfaces
29. Install the spark plug cable center cover. on the ground. This will prove fatal in suffi-
of the head and block. Check the cylinder head for
30. Replace the O-rings and connect the fuel eient quantities. Always drain coolant into a
cracks, damage or engine coolant leakage. Remove
lines. sealable container. Coolant should be reused
scale, sealing compound and carbon. Clean oil pas- unless it is contaminated or is several years
old.
g3153p44 Fig. 119 Remove the upper radiator hose
* . . 1 Fig. 129 . . . and also the lower rad:gzi / cyl.der head g3153W
Fig 121 Remove the heater hose from the
hoses from the thermostat housing
Fig. 122 Remove the three thermostat hous-
Fig. 123 . . . then remove the thermostat
ing retaining bolts . . .
housing from the cylinder head
93153p50 Fig. 124 Using a suitable device, such as a
breaker bar and the appropriate socket,
loosen the cylinder head bolts in the proper
sequence
Page 90 of 408
ENGINEANDENGINEOVERHAUL 3-29
l HOzS sensor l ECT gauge sender l ECT sensor l MAP sensor l IAT sensor l TP sensor l IAC motor l injector harness l ignition coil l CMP sensor l EGR solenoid valve
33. Install the spark plug wires and cover,
34. Replace the O-rings and connect the fuel
lines.
35. Install the air cleaner and intake hose. Con-
nect the breather hose.
36. Fill the cooling system.
37. Connect the negative battery cable
3.01 DDHC Engine
ti See Figures 132 and 133
1. Relieve fuel system pressure. Disconnect the
negative battery cable.
2. Drain the cooling system.
Never open, service or drain the radiator or
cooling system when hot; serious burns can
occur from the steam and hot coolant. Also,
when draining engine coolant, keep in mind
that cats and dogs are attracted to ethylene
glycol antifreeze and could drink any that is
left in an uncovered container or in puddles
on the ground. This will prove fatal in suffi-
cient quantltles. Always drain coolant into a
sealable container. Coolant should be reused
unless it is contaminated or is several years
old.
3. Remove the air intake hoses.
4. Remove air intake plenum and intake mani-
fold.
5. Remove the exhaust manifold.
6. Remove the timing belt. Refer to the timing
belt procedure in this section.
7. Remove the breather hose.
8. Remove the spark plug wire center cover and
remove the spark plug wires.
9. Remove the rocker covers.
10. Remove the intake camshaft sprockets.
11. Remove the rear timing belt cover.
12. Remove the ignition coil assembly.
13. Disconnect all water hoses from the thermo-
stat housing and remove the housing.
14. Disconnect the water inlet from the front
head.
15. Loosen the cylinder head mounting bolts in
the reverse of the torque sequence and loosen the
bolts in three steps. Lift off the cylinder head assem-
bly and remove the head gasket.
To install: 16. Thoroughly clean the sealing surfaces of the
head and block.
17. Place a new head gasket on the cylinder
block with the identification marks in the front top
(upward) position. Do not use sealer on the gasket,
18. Carefully install the cylinder head on the
block. Be sure the head bolt washers are installed
with the chamfered edge upward. Using three even
steps, torque the head bolts in sequence, to 76-83 ft.
Ibs. (105-115 Nm).
@ Timing belt side
7923PG26 :ig. 132 Tighten the cylinder head bolts ac-
:ording to the sequence shown-3.01
SDHC and DDHC) engines
Rear bank
[::od
04
~8 01
Front bank
'1 "8
509 010 011 6
1.03 07 02 7923ffi25 Fig. 133 Rocker cover bolt torque se-
quence-Diamante 3.OL DDHC engine
19. Install new O-ring and connect the water inlet
to the head. Tighten the mounting bolt to 9-11 ft. Ibs
(12-15 Nm).
20. Replace the gaskets and install the thermostat
housing. Tighten the mounting bolts to 12-14 ft. Ibs.
(17-20 Nm).
21. Using new hose clamps, connect the hoses to
the thermostat housing.
22. Install the Ignition coil and torque the mount-
ing bolts to 7 ft. Ibs. (10 Nm).
23. Install the rear timing belt cover and torque
the mounting bolts to 17 ft. Ibs. (24 Nm).
24. Install the intake camshaft sprockets. Tighten
the retaining bolt to 65 ft. Ibs. (90 Nm).
25. Apply sealer to the lower edges of the valve
cover. Tighten the bolts in the proper sequence to
44-51 inch Ibs. (5-6 Nm).
26. Connect the spark plug wires and install the
center cover. Tighten the bolts that secure the center
cover to 27 inch Ibs. (3 Nm)
27. Install the breather hose.
28. Install the timing belt. Refer to the timing belt
procedure in this section,
29. Install the exhaust manifold assembly.
30. Using all new gaskets, install the intake man-
ifold and air intake plenum.
31. Install the air intake hoses.
32. Change the engine oil and oil filter. 33. Fill the system wrth coolant.
34. Connect the negabve battery cable.
35. Adjust the accelerator cable.
36. Start the engine.
37. Check and adjust the idle speed and ignition
timing.
38. Once the vehicle has cooled, recheck the
coolant level.
3.OL SDHC Engine
# See Figure 132
1. Relieve the fuel system pressure.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Drain the cooling system.
Never open, service or drain the radiator or
cooling system when hot; serious burns can
occur from the steam and hot coolant. Also,
when draining engine coolant, keep in mind
that cats and dogs are attracted to ethylene
alvcol antifreeze and could drink any that is
Left in an uncovered container or in puddles
on the ground. This will Drove fatal in suff i-
cient quantities. Always drain coolant into a
sealable container. Coolant should be reused
Unless it is Contaminated or is several years
old.
4. Remove the air intake hose.
5. Remove the exhaust manifold.
6. Remove the air intake plenum and intake
manifold.
7. Remove the timing belt. Refer to the timing
belt procedure in this section.
8. Remove the camshaft sprockets and the rear
timing belt cover.
9. Remove the power steering pump bracket. If
removing the rear head, remove the alternator brace.
10. Disconnect the water inlet pipe.
11. Remove the purge pipe assembly.
12. Remove the valve cover,
13. Using the reverse sequence of the installation
sequence, loosen the cylinder head mounting bolts in
three steps. Lift off the cylmder head assembly and
remove the head gasket.
To install: 14. Thoroughly clean the sealing surfaces of the
head and block.
15. Place a new head gasket on the cylinder
block making sure the identification mark on the
cylrnder head gasket is in the front top (upward) loca-
tion. Do not use sealer on the gasket,
16. Carefully install the cylinder head on the
block. Be sure the head bolt washers are installed
with the chamfered edge upward. Using three even
steps, torque the head bolts in sequence, to 7683 ft.
Ibs. (105-115 Nm).
17. Apply sealer to the lower edges of the half-
round portions and install the valve cover. Tighten
valve cover bolts to 7 ft. Ibs. (9 Nm).
18. Install the purge pipe assembly.
19. Connect the water inlet pipe.
20. Install the power steering pump bracket and
alternator brace.
21. Install the rear timing belt cover and camshaft
sprockets. Torque the retaining bolt to 65 ft. Ibs. (90
Nm).
22. Install the timing belt. Refer to the timing belt
procedure in this section.
Page 118 of 408

ENGINEANDENGINEOVERHAUL 3-57
Anything that generates heat and/or friction WIII
eventually burn or wear out (for example, a light bulb
generates heat, therefore its life span is limited). With
this in mind, a running engine generates tremendous
amounts of both; friction is encountered by the mov-
ing and rotating parts inside the engine and heat is
created by friction and combustion of the fuel How-
ever, the engine has systems designed to help reduce
the effects of heat and friction and provide added
longevrty. The oiling system reduces the amount of
friction encountered by the moving parts inside the
engine, while the cooling system reduces heat cre-
ated by friction and combustion If either system is
not maintained, a break-down will be inevitable.
Therefore, you can see how regular maintenance can
affect the service life of your vehicle, If you do not
drain, flush and refill your cooling system at the
proper intervals, deposits WIII begin to accumulate in
the radiator, thereby reducing the amount of heat it
can extract from the coolant The same applies to
your oil and filter; If it is not changed often enough it
becomes laden with contaminates and is unable to
properly lubricate the engine. This increases friction
and wear.
There are a number of methods for evaluating the
condition of your engine. A compression test can re-
veal the condition of your pistons, piston rings,
cylinder bores, head gasket(s), valves and valve
seats. An oil pressure test can warn you of possible
engine bearing, or oil pump failures. Excessrve oil
consumption, evidence of oil in the engine air intake
area and/or bluish smoke from the tailpipe may indi-
cate worn piston rings, worn valve guides and/or
valve seals. As a general rule, an engine that uses no
more than one quart of oil every 1000 miles is in
good condition. Engines that use one quart of oil or
more in less than 1000 miles should first be checked
for oil leaks. If any oil leaks are present, have them
fixed before determining how much oil is consumed
by the engine, especrally if blue smoke is not visible
at the tailpipe
COMPRESSION TEST
# See Figure 226
tccs3801 Fig. 226 A screw-in type compression gauge
is more accurate and easier to use without
an assistant
A noticeable lack of engine power, excessive oil
consumption and/or poor fuel mileage measured
over an extended period are all indicators of internal
engine wear. Worn piston rings, scored or worn
cylinder bores, blown head gaskets, sticking or burnt
valves, and worn valve seats are all possible culprits.
A check of each cylinders compression WIII help lo-
cate the problem.
*A screw-in type compression gauge is
more accurate than the type you simply hold
against the spark plug hole. Although it takes
slightly longer to use, it’s worth the effort to
obtain a more accurate reading.
1 Make sure that the proper amount and vis-
cosity of engine oil is in the crankcase, then ensure
the battery is fully charged.
2. Warm-up the engine to normal operating
temperature, then shut the engine
OFF. 3. Disable the ignition system.
4. Label and disconnect all of the spark plug
wires from the plugs,
5. Thoroughly clean the cylinder head area
around the spark plug ports, then remove the spark
plugs.
6. Set the throttle plate to the fully open (wide-
open throttle) position You can block the accelerator
linkage open for this, or you can have an assistant
fully depress the accelerator pedal.
7. Install a screw-in type compression gauge
into the No. 1 spark plug hole until the fitting is snug.
Be careful not to crossthread the spark plug
hole.
8. According to the tool manufacturers instruc-
tions, connect a remote starting switch to the starting
circuit.
9. With the ignition switch in the
OFF position,
use the remote starting switch to crank the engine
through at least five compression strokes (approxi-
mately 5 seconds of cranking) and record the highest
reading on the gauge
10. Repeat the test on each cylinder, cranking the
engine approximately the same number of compres-
sion strokes and/or time as the first.
11. Compare the hrghest readings from each
cylinder to that of the others. The indicated compres-
sion pressures are considered within specifications if
the lowest reading cylinder is within 75 percent of the
pressure recorded for the highest reading cylinder
For example, if your highest reading cylinder pres-
sure was 150 psi (1034 kPa), then 75 percent of that
would be 113 psi (779 kPa). So the lowest reading
cylinder should be no less than 113 psi (779 kPa).
12. If a cylinder exhibits an unusually low com-
pression reading, pour a tablespoon of clean engine
oil into the cylinder through the spark plug hole and
repeat the compression test. If the compression rises
after adding oil, it means that the cylinder’s piston
rings and/or cylinder bore are damaged or worn, If
the pressure remains low, the valves may not be seat-
ing properly (a valve job is needed), or the head gas-
ket may be blown near that cylinder. If compression in any two adjacent cylinders is low, and if the addi-
tion of oil doesn’t help raise compression, there is
leakage past the head gasket. Oil and coolant in the
combustion chamber, combined with blue or con-
stant white smoke from the tailpipe, are symptoms of
this problem. However, don’t be alarmed by the nor-
mal white smoke emitted from the tailpipe during en-
gine warm-up or from cold weather driving. There
may be evidence of water droplets on the engine dip-
stick and/or oil droplets in the cooling system if a
head gasket is blown.
OIL PRESSURETEST
Check for proper oil pressure at the sending unit
passage with an externally mounted mechanical oil
pressure gauge (as opposed to relying on a factory
Installed dash-mounted gauge). A tachometer may
also be needed, as some specifications may require
running the engine at a specific rpm.
1. With the engine cold, locate and remove the oil
pressure sending unit.
2. Followrng the manufacturers instructions,
connect a mechanical oil pressure gauge and, if nec-
essary, a tachometer to the engine.
3 Start the engine and allow it to idle.
4 Check the oil pressure reading when cold and
record the number. You may need to run the engine
at a specified rpm, so check the specifications,
5. Run the engine until normal operating temper-
ature is reached (upper radiator hose will feel warm)
6. Check the oil pressure reading again with the
engine hot and record the number. Turn the engine
OFF. 7. Compare your hot oil pressure reading to that
given in the chart If the reading is low, check the
cold pressure reading against the chart. If the cold
pressure IS well above the specification, and the hot
reading was lower than the specification, you may
have the wrong viscosity oil in the engine. Change
the oil, making sure to use the proper grade and
quantity, then repeat the test.
Low oil pressure readings could be attributed to
internal component wear, pump related problems, a
low oil level, or oil viscosity that is too low. High oil
pressure readings could be caused by an overfilled
crankcase, too htgh of an oil viscosity or a faulty
pressure relief valve.
Now that you have determined that your engine is
worn out, you must make some decisions. The ques-
tion of whether or not an engine IS worth rebuilding
is largely a subjective matter and one of personal
worth. Is the engine a popular one, or IS it an obso-
lete model? Are parts available? Will it get acceptable
gas mileage once It is rebuilt? Is the car its being put
into worth keeping? Would it be less expensive to
buy a new engine, have your engine rebuilt by a pro,
rebuild it yourself or buy a used engine from a sal-
vage yard? Or would It be simpler and less expensive
to buy another car? If you have considered all these
matters and more, and have still decided to rebuild
the engine, then it is time to decide how you will re-
build it.
Page 289 of 408

7-10 DRIVETRAIN
The automatic transaxle allows engine torque and
power to be transmitted to the front wheels within a
narrow range of engine operating speeds. It will allow
the engine to turn fast enough to produce plenty of
power and torque at very low speeds, while keeping it
at a sensible rpm at high vehicle speeds (and it does
this job without driver assistance). The transaxle uses
a light fluid as the medium for the transmission of
power. This fluid also works in ths operation of vari-
ous hydraulic control circuits and as a lubricant. Be-
cause the transaxle fluid performs all of these func-
tions, trouble within the unit can easily travel from one
part to another For this reason, and because of the
complexity and unusual operating principles of the
transaxle, a very sound understanding of the basic
principles of operation will simplify troubleshooting
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
Pan removal, fluid and filter
in Section 1 of this manual changes are covered
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
1990-97 Mirage and 1990-93 Galant
# See Figure 44
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the selector cable from the lever
3. Remove the two retaining screws and lift off
the switch.
To install: 4. Mount and position new switch. Do not tighten
the bolts until the switch is adjusted.
5. Connect selector cable and adjust switch.
6. After installation and adjustment make sure the
engine only starts in the
P and N selections. Also check
that the reverse lights operate only in the R selectlon.
1994-00 Galant and 1998-00 Mirage
e See Figure 44
93157pm Fig. 44 Typically, the park/neutral position
switch is located on the top of the transaxle
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the nut attaching the shift control ca-
ble from the transaxle manual shaft lever. Position
the control cable out of the way.
3. Place the manual shaft lever in the Neutral
position, remove the nut and the manual shaft lever.
4. Detach the park/neutral switch electrical con-
nector.
5. Remove the park/neutral switch mounting
bolts and remove the switch from the transaxle man-
ual shaft.
To install: 6. Install the park/neutral switch to the transaxle
manual shaft and install the switch mounting bolts
Do not tighten the mounting bolts unh the switch is
adjusted.
7. Install the manual shaft lever to the park/neu-
tral switch with the nut. Make sure that the shaft lever
is in the Neutral position.
8. Adjust the switch in the following manner:
turn the switch body until the hole in the body of the
switch aligns with the hole in the manual shaft lever.
Insert a drill bit or equivalent into the holes. Tighten
the switch mounting bolts to 8 ft. Ibs. (11 Nm).
9. Attach the electrical connector.
10. Install the control cable to the manual shaft
lever with the nut. Adjust the cable so that there is no
slack in the cable and that the selector lever moves
smoothly
11. Reconnect the negative battery cable Check
for proper starting and proper reverse light operatron.
Diamante
ti See Figure 44
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
Wait at least 90 seconds after the negative
battery cable is disconnected to prevent pos-
sible deployment of the air bag.
2. Disconnect the selector cable from the lever.
3. Remove the two retaining screws and lift off
the switch.
To install: 4. Install the lever, tighten the bolts only hand
tight.
5. Rotate switch body so the manual control lever
0.20 inch (5mm) hole and the switch body 0.20 inch
(5mm) holes are aligned.
6. Tighten the mounting bolts to 7-8 ft. Ibs.
(10-12 Nm).
7. Connect the selector cable to the lever.
8. Connect the negative battery cable.
9. After installahon and adjustment make sure the
engine only starts in the
P and N selections. Also
check that the reverse lights operate only in the R se- lection.
ADJUSTMENT
1990-97 Mirage and 1990-93 Galant
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable and lo-
cate the neutral safety switch on the top of the
transaxle.
*Apply parking brake and chock wheels be-
fore placing transaxle into the N position
2. At the transmission, loosen the shift cable ad-
justment nut. Inside the vehicle place the gearshift
selector lever in N
3. Place the manual shift control lever in N.
4. Loosen neutral safety switch mounhng screws
and rotate switch body so the manual control lever
0.20 in. (5mm) hole and the switch body 0.20 in.
(5mm) holes are aligned.
5. Tighten switch body mounting bolts to 7-8 ft.
Ibs. (lo-12 Nm).
6. At the shift cable adjusting nut, gently pull ca-
ble to remove any slack. Tighten locknut to 8 ft. Ibs.
(12 Nm)
7. Verify that the switch lever moves to positions
corresponding to each position of the selector lever.
Connect the negative battery terminal.
8. Make sure the engine only starts in the
P and
N positions. Also make sure the reverse lights oper-
ate only in
R selection.
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
Diamante
) See Figures 45, 46, 47, and 48
1. Properly disarm the SRS system (air bag).
Refer to Section 6.
2. Raise and safely support the vehicle.
3. Remove the front wheels.
4. Remove the engine side cover and undercov-
ers.
5. Drain the transaxle assembly into a suitable
container.
6. If equipped, remove the front catalytic con-
verter.
7. Remove the exhaust pipe, main muffler and
catalytic converter.
8. Disconnect the tie rod end and ball joint from
the steering knuckle.
9. Unbolt the support bearing for the left side
halfshaft.
10. Remove the halfshafts by inserting a prybar
between the transaxle case and the driveshaft and
prying the shaft from the transaxle.
11. Remove the air cleaner assembly and adjoin-
ing duct work.
12. Detach the engine harness connection.
13. If the vehicle is equipped with Active Elec-
tronlc Controlled Suspension (Active-ECS), remove
the compressor assembly from the transaxle and sus-
pend with wire. Do not allow the compressor to hang
from the air hose.
14. If equipped, remove the roll stopper stay
bracket.
15. Disconnect the speedometer cable from the
transaxle.
16. Remove the clip that secures the shifter and
disconnect the shifter control cable from the
transaxle.
17. Disconnect and plug the oil cooler hoses
from the transaxle.
18. Detach the following:
Page 334 of 408
- 8-38 SUSPENSION AND STEERING
11. Adjust the power steering belt for proper ten-
sion and tighten the adjusting bolts.
12. Reconnect the negative battery cable.
13. Refill the reservoir and bleed the system.
3. Of EIJGINE
1. Disconnect the battery negative cable. 2. Disconnect the return fluid line. Remove the
reservoir cap and allow the return line to drain the
fluid from the reservoir. If the fluid is contaminated,
disconnect the ignition high tension cable and crank
the engine several times to drain the fluid from the
gear box.
3. Remove the power steering pump drive belt.
4. Remove the pressure switch connector from
the side of the pump.
5. If the alternator is located under the oil pump,
cover it with a shop towel to protect it from oil.
6. Disconnect the high pressure hose and the
return hose from the pump.
7. Remove the pump drive belt and unbolt the
pump from its bracket and remove the pump.
To install: 8. Install the pump, *rap the belt around the
pulley and tighten the bolts that secure the pump to
17 ft. Ibs. (24 Nm).
9. Replace the O-rings and connect the high
pressure hose. Connect the pressure line so the
notch in the fitting aligns and contacts the pump’s
guide bracket. Tighten the mounting nut with lock-
washer to 17 ft. Ibs. (24 Nm).
IO. Using a new hose clamp, connect the return
line.
11. Attach the pressure switch connector.
12. Adjust the belt tension and tighten the
adjust- ing bolts.
13. Refill the reservoir and bleed the system.
Diamante *
FRONT
. 1. Disconnect the battery negative cable. 2. Disconnect the return fluid line. Remove the
reservoir cap and allow the return line to drain the
fluid from the reservoir. If the fluid is contaminated,
disconnect the ignition high tension cable and crank
the engine several times to drain the fluid from the
gearbox.
3. Remove the power steering pump drive belt.
4. Remove the pressure switch connector from
the side of the pump.
5. If the alternator is located under the oil pump,
cover it with a shop towel to protect it from oil.
6. Disconnect the high pressure hose and the
return hose from the pump.
7. Remove the pump drive belt and unbolt the
pump from its bracket and remove the pump.
To install: 8. Install the pump, wrap the belt around the
pulley and tighten the bolts that secure the pump to
17 ft. Ibs. (24 Nm).
9. Replace the O-rings and connect the high
pressure hose. Connect the pressure line so the
notch in the fitting aligns and contacts the pump’s
guide bracket. Tighten the mounting nut with lock-
washer to 17 ft. Ibs. (24 Nm).
10. Using a new hose clamp, connect the return
line.
Il. Attach the pressure switch connector.
12. Adjust the belt tension and tighten the adjust-
ing bolts.
13. Refill the reservoir and bleed the system.
REAR
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Drain the power steering fluid.
3. Remove the rear power steering pump heat
protector, located on the engine side of the differen-
tial on the transaxle.
4. Disconnect the pressure line from the pump.
5. Disconnect the suction hose from the pump.
6. Remove the mounting bolts and remove the
pump from the transaxle.
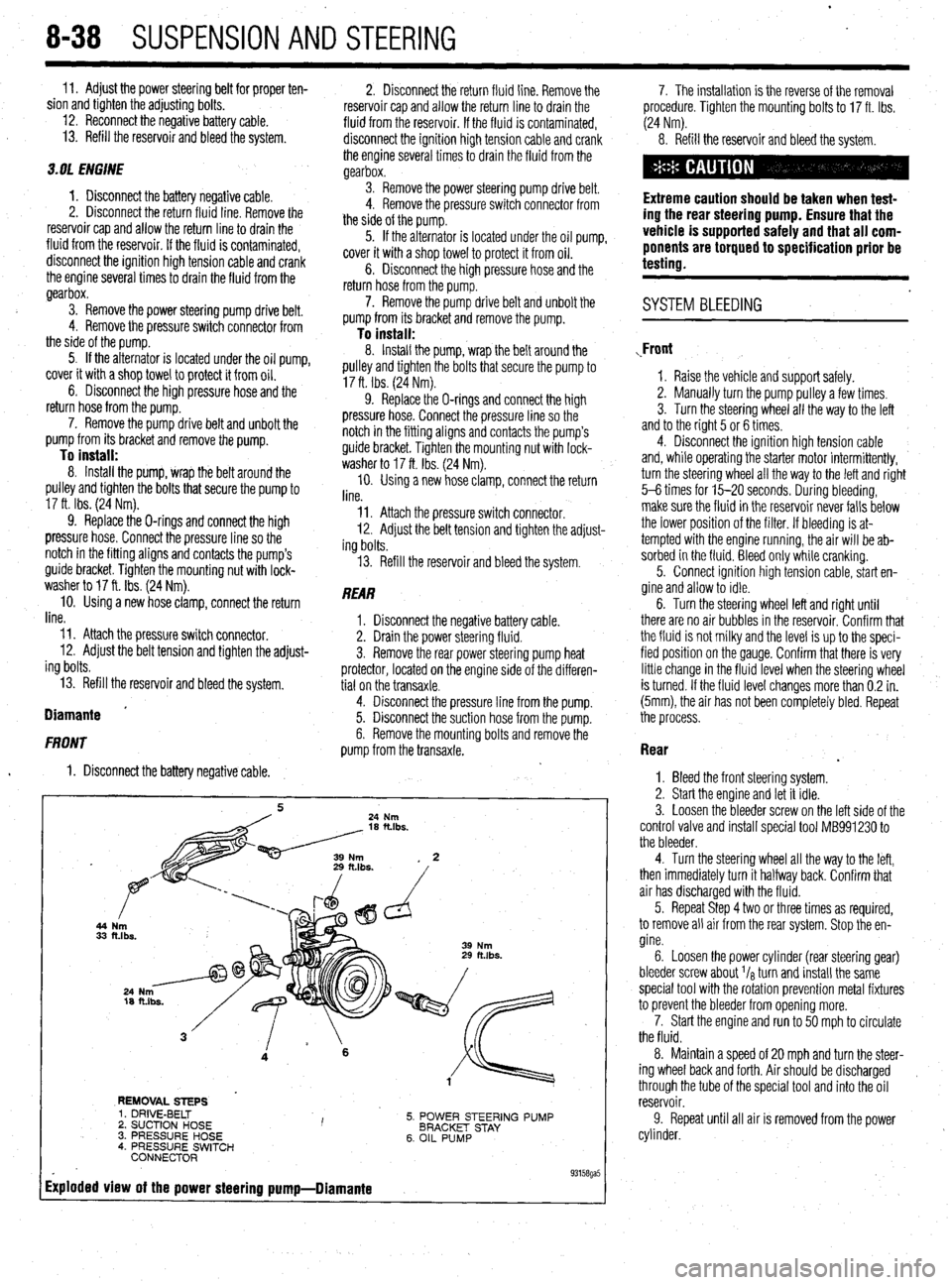
44
33
REMOVAL STEPS
5. POWER STEERING PUMP
BRACKET STAY
6. OIL PUMP 1. DRIVE-BELT
2. SUCTION HOSE I ’ 3. PRESSURE HOSE
4. PRESSURE SWITCH
CONNECTOR
Exploded view of the power steering pump-Diamante
. 93158ga5
7. The installation is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Tighten the mounting bolts to 17 ft. Ibs.
(24 Nm).
8. Refill the reservoir and bleed the system.
Extreme caution should be taken when test-
ing the rear steering pump. Ensure that the
vehicle is supported safely and that all com-
ponents are torqued to specification prior be
testing.
. SYSTEM BLEEDING
,Front
1. Raise the vehicle and support safely.
2. Manually turn the pump pulley a few times.
3. Turn the steering wheel all the way to the left
and to the right 5 or 6 times.
4. Disconnect the ignition high tension cable
and, while operating the starter motor intermittently,
turn the steering wheel all the way to the letI and right
5-6 times for 15-20 seconds. During bleeding,
make sure the fluid in the reservoir never falls below
the lower position of the filter. If bleeding is at-
tempted with the engine running, the air will be ab-
sorbed in the fluid. Bleed only while cranking.
5. Connect ignition high tension cable, start en-
gine and allow to idle.
6. Turn the steering wheel left and right until
there are no air bubbles in the reservoir. Confirm that
the fluid is not milky and the level is up to the speci-
fied position on the gauge. Confirm that there is very
little change in the fluid level when the steering wheel
is turned. If the fluid level changes more than 0.2 in.
(5mm), the air has not been completely bled. Repeat
the process.
Rear
.
1. Bleed the front steering system.
2. Start the engine and let it idle.
3. Loosen the bleeder screw on the left side of the
control valve and install special tool MB991230 to
the bleeder.
4. Turn the steering wheel all the way to the left,
then immediately turn it halfway back. Confirm that
air has discharged with the fluid.
5. Repeat Step 4 two or three times as required,
to remove all air from the rear system. Stop the en-
gine.
6. Loosen the power cylinder (rear steering gear)
bleeder screw about I/* turn and install the same
special tool with the rotation prevention metal fixtures
to prevent the bleeder from opening more.
7. Start the engine and run to 50 mph to circulate
the fluid.
8. Maintain a speed of 20 mph and turn the steer-
ing wheel back and forth. Air should be discharged ,
through the tube of the special tool and into the oil
reservoir.
9. Repeat until all air is removed from the power
cylinder.
Page 388 of 408

II-6 TROUBLESHOOTING
DIAGhUSTIC PROCEDURES
Gasoline Engines
1. Engine turns over, but wilt not start
a. Check fuel level in fuel tank, add fuel if empty.
b. Check battery condition and state of charge. If voltage and load test below specifica-
tion, charge or replace battery.
c. Check battery terminal and cable condition and tightness. Clean terminals and replace
damaged, worn or corroded cables.
d. Check fuel delivery system. If fuel is not reaching the fuel injectors, check for a loose
electrical connector or defective fuse, relay or fuel pump and replace as necessary.
e. Engine may have excessive wear or mechanical damage such as low cylinder cranking
pressure, a broken camshaft drive system, insufficient valve clearance or bent valves.
f. Check for fuel contamination such as water in the fuel. During winter months, the wa-
ter may freeze and cause a fuel restriction. Adding a fuel additive may help, however
the fuel system may require draining and purging with fresh fuel.
g. Check for ignition system failure. Check for loose or shorted wires or damaged igni-
tion system components. Check the spark plugs for excessive wear or incorrect elec-
trode gap. If the problem is worse in wet weather, check for shorts between the spark
plugs and the ignition coils.
h. Check the engine management system for a failed sensor or control module.
2. Engine does not turn over when attempting to start
a. Check the battery state of charge and condition. If the dash lights are not visible or
very dim when turning the ignition key on, the battery has either failed internally or
discharged, the battery cables are loose, excessively corroded or damaged, or the al-
ternator has failed or internally shorted, discharging the battery. Charge or replacethe
battery, clean or replace the battery cables, and check the alternator output.
b. Check the operation of the neutral safety switch. On automatic transmission vehicles,
try starting the vehicle in both Park and Neutral. On manual transmission vehicles, de-
press the clutch pedal and attempt to start. On some vehicles, these switches can be
adjusted. Make sure the switches or wire connectors are not loose or damaged. Re-
place or adjust the switches as necessary.
c. Check the starter motor, starter solenoid or relay, and starter motor cables and wires.
Check the ground from the engine to the chassis. Make sure the wires are not loose,
damaged, or corroded. If battery voltage is present at the starter relay, try using a re-
mote starter to start the vehicle for test purposes only. Replace any damaged or cor-
roded cables, in addition to replacing any failed components.
d. Check the engine for seizure. If the engine has not been started for a long period of
time, internal parts such as the rings may have rusted to the cylinder walls. The engine
may have suffered internal damage, or could be hydro-locked from ingesting water.
Remove the spark plugs and carefully attempt to rotate the engine using a suitable
breaker bar and socket on the crankshaft pulley. If the engine is resistant to moving, or
moves slightly and then binds, do not force the engine any further before determining
the problem.
3. Enpine stalls immediately when started
a. Check the ignition switch condition and operation. The electrical contacts in the run
position may be worn or damaged. Try restarting the engine with all electrical acces-
sories in the off position. Sometimes turning the key on an off will help in emergency
situations, however once the switch has shown signs of failure, it should be replaced
as soon as possible.
b. Check for loose, corroded, damaged or shorted wires for the ignition system and re-
pair or replace.
c. Check for manifold vacuum leaks or vacuum hose leakage and repair or replace parts
as necessary.
d. Measure the fuel pump delivery volume and pressure. Low fuel pump pressure can
also be noticed as a lack of power when accelerating. Make sure the fuel pump lines
are not restricted. The fuel pump output is not adjustable and requires fuel pump re-
placement to repair.
e. Check the engine fuel and ignition management system. Inspect the sensor wiring and
electrical connectors. A dirty, loose or damaged sensor or control module wire can
simulate a failed component.
f. Check the exhaust system for internal restrictions.
4. Starter motor spins, but does not engage
a. Check the starter motor for a seized or binding pinion gear.
b. Remove the flywheel inspection plate and check for a damaged ring gear.
5. Engine is difficult to start when Gold
a. Check the battery condition, battery state of charge and starter motor current draw. Re-
place the battery if marginal and the starter motor if the current draw is beyond specifi-
cation. b. Check the battery cable condition. Clean the battery terminals and replace corroded or
damaged cables.
c. Check the fuel system for proper operation. A fuel pump with insufficient fuel pressure
or clogged injectors should be replaced.
d. Check the engine’s tune-up status. Note the tune-up specifications and check for items
such as severely worn spark plugs; adjust or replace as needed. On vehicles with
manually adjusted valve clearances, check for tight valves and adjust to specification.
e. Check for a failed coolant temperature sensor, and replace if out of specification.
f. Check the operation of the engine management systems for fuel and ignition; repair or
replace failed components as necessary.
6. En#ine is ditticutt to start when hot
a. Check the air filter and air intake system. Replace the air filter if it is dirty or contami-
nated. Check the fresh air intake system for restrictions or blockage.
b. Check for loose or deteriorated engine grounds and clean, tighten or replace as
needed.
c. Check for needed maintenance. Inspect tune-up and service related items such as
spark plugs and engine oil condition, and check the operation of the engine fuel and
ignition management system.
Diesel Engines
1. Engine turns over but won’t start
a. Check engine starting procedure and restart engine.
b. Check the glow plug operation and repair or replace as necessary.
c. Check for air in the fuel system or fuel filter and bleed the air as necessary.
d. Check the fuel delivery system and repair or replace as necessary.
e. Check fuel level and add fuel as needed.
f. Check fuel quality. If the fuel is contaminated, drain and flush the fuel tank.
g. Check engine compression. If compression is below specification, the engine may
need to be renewed or replaced.
h. Check the injection pump timing and set to specification.
i. Check the injection pump condition and replace as necessary.
j. Check the fuel nozzle operation and condition or replace as necessary.
2. Engine does
hot turn over when attempting to start
a. Check the battery state of charge and condition. If the dash lights are not visible or
very dim when turning the ignition key on, the battery has either failed internally or
discharged, the battery cables are loose, excessively corroded or damaged, or the al-
ternator has failed or internally shorted, discharging the battery. Charge or replace the
battery, clean or replace the battery cables, and check the alternator output.
b. Check the operation of the neutral safety switch. On automatic transmission vehicles,
try starting the vehicle in both Park and Neutral. On manual transmission vehicles, de-
press the clutch pedal and attempt to start. On some vehicles, these switches can be
adjusted. Make sure the switches or wire connectors are not loose or damaged. Re-
place or adjust the switches as necessary.
c. Check the starter motor, starter solenoid or relay, and starter motor cables and wires.
Check the ground from the engine to the chassis. Make sure the wires are not loose,
damaged, or corroded. If battery voltage is present at the starter relay, try using a re-
mote starter to start the vehicle for test purposes only. Replace any damaged or cor-
roded cables, in addition to replacing any failed components.
d. Check the engine for seizure. If the engine has not been started for a long period of
time, internal parts such as the rings may have rusted to the cylinder walls. The engine
may have suffered internal damage, or could be hydro-locked from ingesting water.
Remove the injectors and carefully attempt to rotate the engine using a suitable
breaker bar and socket on the crankshaft pulley. If the engine is resistant to moving, or
moves slightly and then binds, do not force the engine any further before determining
the cause of the problem.
3. Engine stalls afier starting
a. Check for a restriction in the fuel return line or the return line check valve and repair as
necessary.
b. Check the glow plug operation for turning the glow plugs off too soon and repair as
necessary.
c. Check for incorrect injection pump timing and reset to specification.
d. Test the engine fuel pump and replace if the output is below specification.
e. Check for contaminated or incorrect fuel. Completely flush the fuel system and replace
with fresh fuel.
f. Test the engine’s compression for low compression. If below specification, mechanical
repairs are necessary to repair.
g. Check for air in the fuel. Check fuel tank fuel and fill as needed.
h. Check for a failed injection pump. Replace the pump, making sure to properly set the
pump timing.